EBV-Driven Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Spectrum of Entities with a Common Denominator (Part 2)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PBL
2.1. General Features and Etiology
2.2. PBL and GIT
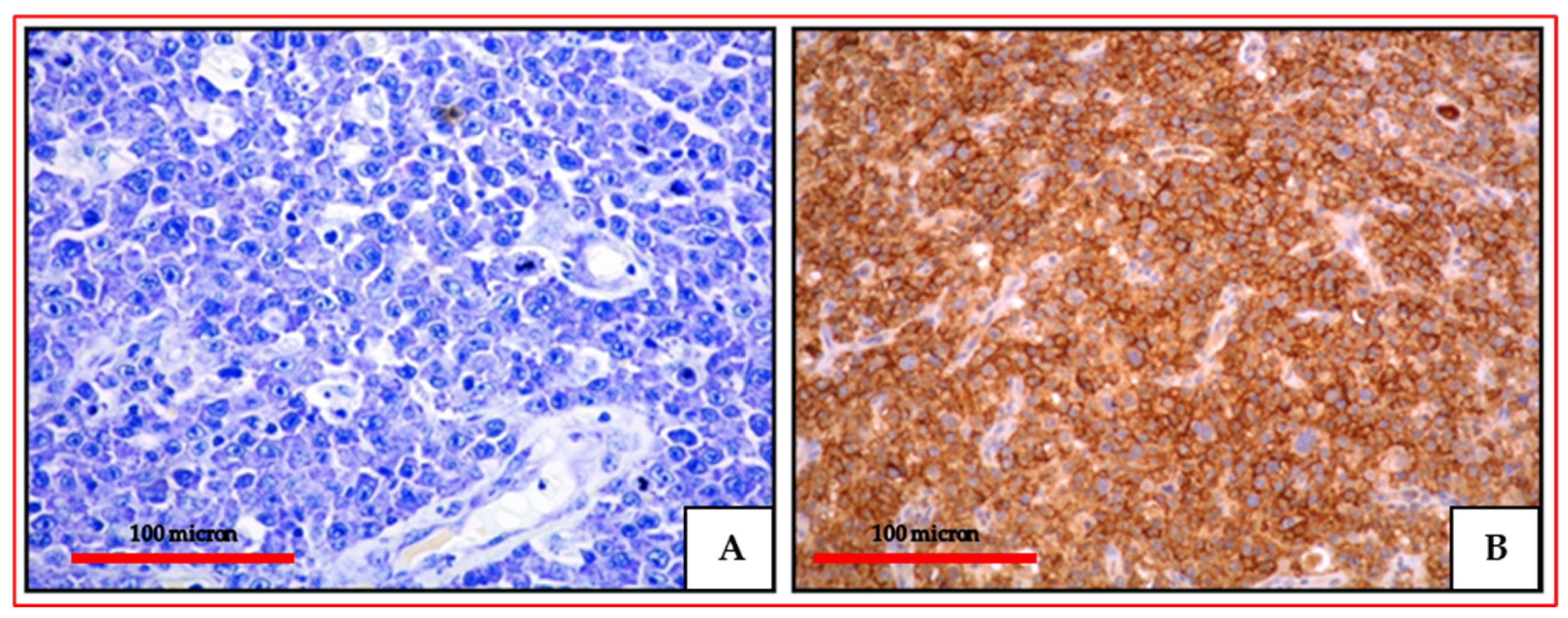
2.3. Histology, Immunophenotype and Genetic Profile
2.4. Differential Diagnosis
2.5. Treatment and Outcome
3. EC-PEL
3.1. General Features and Etiology
3.2. KSHV/HHV8
3.3. EC-PEL and GIT
3.4. Histology, Immunophenotype and Genetic Profile
3.5. Differential Diagnosis
3.6. Treatment and Outcome
4. BL
4.1. General Features and Etiology
4.2. BL and GIT
4.3. Histology, Immunophenotype and Genetic Profile
4.4. Differential Diagnosis
4.5. Treatment and Outcome
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, G.S.; Long, H.M.; Brooks, J.M.; Rickinson, A.B.; Hislop, A.D. The immunology of Epstein-Barr virus induced disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 787–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resk, S.A.; Weiss, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanner, J.E.; Alfieri, C. The Epstein-Barr virus and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease: Interplay of immunosuppression, EBV, and the immune system in disease pathogenesis. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2001, 3, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, F.T.; Gress, R.E. Immunosenescence: Deficits in adaptative immunity in the elderly. Tissue Antigens 2007, 70, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Prato, G.; Stella, S.; Scielzo, C.; Geuna, M.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. Age-dependent accumulation of monoclonal CD4+ CD8+ double positive T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of the elderly. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolcetti, R.; Dal Col, J.; Martorelli, D.; Carbone, A.; Klein, E. Interplay among viral antigens, cellular pathways and tumor microenvironment in the pathogenesis of EBV-driven lymphoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 13, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. (Eds.) WHO Classification of Tumours Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. EBV-positive lymphoproliferation of B-T- and NK-cell derivation in non-immunocompromised hosts. Pathogens 2021, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Hogquist, K.A.; Balfour, H.H. Infectious mononucleosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. 2015, 390, 151–209. [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson, A.B. Co-infections, inflammation and oncogenesis: Future directions for EBV research. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Price, A.M.; Luftig, M.A. To be or not IIb: A multi-step process for Epstein-Barr virus latency establishment and consequences for B cell tumorigenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Venkataraman, G.; Raffeld, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV positive mucocutaneous ulcer. A study of 26 cases associated with various sources of immunosuppression. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Gion, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. A review of EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcers focusing on clinical and pathological aspects. J. Clin. Exp. Hematopath. 2019, 59, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, T.; Gion, Y.; Nishimura, M.F.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. Epstein-Barr Virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer: A unique and curious disease entity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natkunam, Y.; Goodlad, J.R.; Chadburn, A.; Jong, D.; Gratzinger, D.; Chan, J.K.C.; Said, J.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV-positive B-cell proliferations of varied malignant potential. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 147, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.; Thakral, B.; Yohe, S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr.; Singh, C.; Speras, M.; McKenna, R.W. EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer in organ transplant recipients: A localized indolent posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matnani, R.; Peker, D. Azathioprine induced Epstein Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer arising in perianal fistula and abscess associated with Crohn’s disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2014, 8, 1747–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moran, N.R.; Webster, B.; Lee, K.M.; Trotman, J.; Kwan, Y.-L.; Napoli, J.; Leong, R.W. Epstein Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer of the colon associated Hodgkin lymphoma in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6072–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, A.; Lobaton, T.; Tapja, G.; Manosa, M.; Cabrè, E. Epstein-Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer in Crohn’s disease. A condition to consider in immunosuppressed IBD patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, M.; Mengoli, M.C.; Valli, R.; Froio, E.; Bisagni, A.; Zizzo, M.; De Marco, L.; Ascani, S. Primary classic Hodgkin lymphoma of the ileum and Epstein-Barr virus mucocutaneous ulcer of the colon: Two entities compared. Virchows Arch. 2019, 474, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, S.; Jhaveri, D.; Caimi, P.; Cameron, R.; Lemonovich, T.; Meyerson, H.; Hostoffer, R.; Tcheurekdjian, H. A rare presentation of EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer that led to the diagnosis of hypogammaglobulinemia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.; Al Salihi, M.; Abu Sitta, E.; Al Hadidi, S. A rare case of Epstein-Barr virus mucocutaneous ulcer of the colon. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Foroni, M.; De Marco, L.; Martino, G.; Ascani, S. EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer within colonic diverticulitis mimicking diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1795–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volaric, A.K.; Singh, K.; Gru, A.A. Rare EBV-associated B cell neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 38, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Gion, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Tachibana, T.; Nishikori, A.; Nishimura, M.F.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. Clinicopathological analysis of 34 Japanese patients with EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Kingma, D.; Sorbara, L.; Raffeld, M.; Banks, P.M.; Jaffe, E.S. Epstein-Barr virus-positive primary gastrointestinal Hodgkin’s disease: Association with inflammatory bowel disease and immunosuppression. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilai, M.; Polliack, A.; Avivi, I.; Herishanu, Y.; Ram, R.; Tang, C.; Perry, C.; Sarid, N. Hodgkin lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Portrait of a rare entity. Leuk. Res. 2018, 71, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, B.; Podoll, M.B.; Baumgartner, E.M.; Maley, D.H. Syncitial variant of nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lymphoma of the terminal ileum in a patient with longstanding Crohn’s disease. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 46, 219–221. [Google Scholar]
- Rezk, S.A.; Weiss, L.M. EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: Update in classification. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 12, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Donati, D.; Orem, J.; Mbidde, E.R.; Kironde, F.; Wahlgren, M.; Bejarano, M.T. Endemic Burkitt’s lymphoma as a polymicrobial disease: New insights on the interaction between Plasmodium falciparum and Epstein-Barr virus. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- Mack, A.A.; Sugden, B. EBV is necessary for proliferation of dually infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6963–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. (Eds.) WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue; IARC: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Delecleuse, H.J.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Dallenbach, F.; Hummel, M.; Marafioti, T.; Schneider, U.; Huhn, D.; Schmidt-Westhausen, A.; Reichart, P.A.; Gross, U.; et al. Plasmablastic lymphomas of the oral cavity: A new entity associated with the human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood 1997, 89, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizzo, M.; Zanelli, M.; Martiniani, R.; Sanguedolce, F.; De Marco, L.; Martino, G.; Parente, P.; Annessi, V.; Manzini, L.; Ascani, S. Oral plasmablastic lymphoma: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e22335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morscio, J.; Dierickx, D.; Nijs, J.; Verhoef, G.; Bittoun, E.; Vanoeteren, X.; Wlodarska, I.; Sagaert, X.; Tousseyn, T. Clinicopathologic comparison of plasmablastic lymphoma in HIV-positive, immunocompetent and posttransplant patients single-center series of 25 cases and meta-analysis of 277 reported cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Bibas, M.; Miranda, R.N. The biology and treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harmon, C.M.; Smith, L.B. Plasmablastic lymphoma: A review of clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Rossi, C.; Parente, P.; Ascani, S. Clinical, pathological and molecular features of plasmablastic lymphoma arising in the gastrointestinal tract: A review and reappraisal. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.D.; Sabuncyan, S.; Langmead, B.; Nagy, N.; Curley, R.; Klein, G.; Klein, E.; Salamon, D.; Feinberg, A.P. Large-scale hypomethylated blocks associated with Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell immortalization. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, A.; Abrisqueta, P. Plasmablastic lymphoma: Current perspectives. Blood Lymph. Cancer Targets Ther. 2018, 8, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foukas, P.G.; de Leval, L. Recent advances in intestinal lymphomas. Histopathology 2015, 66, 112–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luria, L.; Nguyen, J.; Zhou, J.; Jaglal, M.; Sokol, L.; Messina, J.L.; Coppola, D.; Zhang, L. Manifestations of gastrointestinal plasmablastic lymphoma: A case series with literature review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11894–11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewtra, M.; Lewis, J.D. Update on the risk of lymphoma following immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, K.; D’Rozario, J.; Pavli, P. Lymphoma and other lymphoproliferative disorders in inflammatory bowel disease: A review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Varikatt, W.; Ping, C.H. Plasmablastic lymphoma presenting as a colonic stricture in Crohn’s disease. Pathology 2014, 46, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, M.; Ragazzi, M.; Valli, R.; De Marco, L.; Cecinato, P.; Azzolini, F.; Ferrari, A.; Bacci, F.; Ascani, S. Unique presentation of a plasmablastic lymphoma superficially involving the entire large bowel. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaidano, G.; Cerri, M.; Capello, D.; Berra, E.; Deambrogi, C.; Rossi, D.; Larocca, L.M.; Campo, E.; Gloghini, A.; Tirelli, U.; et al. Molecular histogenesis of plasmablastic lymphoma of the oral cavity. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 119, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, A.; Balague, O.; Colomo, L.; Martinez, A.; Delabie, J.; Taddesse-Heath, L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Campo, E. IG/MYC rearrangements are the main cytogenetic alteration in plasmablastic lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pather, S.; Mashele, T.; Willem, P.; Patel, M.; Perner, Y.; Motaung, M.; Nagiah, N.; Waja, F.; Philip, V.; Lakha, A.; et al. MYC status in HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: Dual colour CISH, FISH and immunohistochemistry. Histopathology 2021, 79, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Moreno, S.; Martinez-Magunacelaya, N.; Zecchini-Barrese, T.; Gonzalez de Villambrosia, S.; Linares, E.; Ranchal, T.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, M.; Battle, A.; Cereceda-Company, L.; Revert-Arce, J.B.; et al. Plasmablastic lymphoma phenotype is determined by genetic alterations in MYC and PRDM1. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castillo, J.J.; Beltran, B.E.; Miranda, R.N.; Young, K.H.; Chavez, J.C.; Sotomayor, E.M. EBV-positive large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2018 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, E.; Satou, A.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamura, S.; Fujishiro, M. Epstein-Barr virus positive B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancers 2021, 13, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J. Plasmablastic lymphoma: Are more intensive regimens needed? Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretscher, D.; Kalish, A.; Wilhelm, M.; Birkmann, J. Refractory plasmablastic lymphoma. A review of treatment options beyond standard therapy. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Reagan, J.L.; Sikov, W.M.; Winer, E.S. Bortezomib in combination with infusional dose-adjusted EPOCH for the treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malki, M.M.; Castillo, J.J.; Sloan, J.M.; Re, A. Hematopoietic cell transplantation for plasmablastic lymphoma: A review. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.J.; Chuang, S.S. Lymphoid neoplasms with plasmablastic differentiation: A comprehensive review and diagnostic approaches. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2020, 27, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loghavi, S.; Alayed, K.; Aladily, T.N.; Zuo, Z.; Ng, S.B.; Tang, G.; Hu, S.; Yin, C.C.; Miranda, R.N.; Medeiros, L.J.; et al. Stage, age and EBV status impact outcomes of plasmablastic lymphoma patients: A clinicopathologic analysis of 61 patients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laurent, C.; Fabiani, B.; Do, C.; Tchernonog, E.; Cartron, G.; Gravelle, P.; Amara, N.; Malot, S.; Palisoc, M.M.; Copie-Bergman, C.; et al. Immune-checkpoint expression in Epstein-Barr virus positive and negative plasmablastic lymphoma: A clinical and pathological study in 82 patients. Haematologica 2016, 101, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanelli, M.; Valli, R.; Capodanno, I.; Ragazzi, M.; Ascani, S. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma: Description of a case with an unexpected clinical outcome. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 23, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Mengoli, M.C.; Fanni, D.; Froio, E.; De Marco, L.; Ascani, S. Multiple myeloma with multilobated plasma cells: An unusual and challenging morphological variant. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 26, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Ricci, S.; Zizzo, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; De Giorgi, F.; Palicelli, A.; Martino, G.; Ascani, S. Systemic mastocytosis associated with “smoldering” multiple myeloma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Zizzo, M.; Palicelli, A.; Bassi, M.C.; Santandrea, G.; Martino, G.; Soriano, A.; Caprera, C.; Corsi, M.; et al. Primary effusion lymphoma occurring in the setting of transplanted patients: A systematic review of a rare, life-threatening post-transplantation occurrence. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadburn, A.; Hyjek, E.; Mathew, S.; Cesarman, E.; Said, J.; Knowles, D.M. KSHV-positive solid lymphomas represent an extra-cavitary variant of primary effusion lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Leventaki, V.; Bhaijee, F.; Jackson, C.C.; Medeiros, L.J.; Vega, F. Extracavitary/solid variant of primary effusion lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 16, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.G.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Lu, Z.B.L.; Quinto, T.; Rozenvald, I.B.; Liu, L.T.; Wilson, D.; Reddy, V.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. Extracavitary KSHV-associated large B-cell lymphoma: A distinct entity or a subtype of primary effusion lymphoma? Study of 9 cases and review of an additional 43 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, V.; Faumont, N.; Cesarman, E.; Rousset, T.; Meggetto, F.; Delsol, G.; Brousset, P. Human herpes-virus-8-associated lymphoma of the bowel in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients without history of primary effusion lymphoma. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.T.; Ribera, J.M.; Juncà, J.; Millà, F. Anorectal lymphoma without effusion associated with human herpesvirus-8 and type 1 Epstein-Barr virus in an HIV infected patient. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Cai, J.; Yue, C.; Quing, X. Extracavitary/solid variant of primary effusion lymphoma presenting as a gastric mass. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanowitz, L.; Wu, Z.; Dezube, B.J.; Pihan, G. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma of the anorectum. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2005, 6, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Bertuzzi, C.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Sabattini, E.; Ascani, S. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in a post-transplantation patient. Br. J. Hematol. 2019, 187, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePond, W.; Said, J.W.; Tasaka, T.; de Vos, S.; Kahn, D.; Cesarman, E.; Knowles, D.M.; Koeffler, H.P. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and human herpesvirus 8 (KSHV/HHV8)-associated lymphoma of the bowel. Report of two cases in HIV-positive men with secondary effusion lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chang, K.L.; Gaal, K.; Aber, D.A. Primary effusion lymphoma with subsequent development of a small bowel mass in an HIV-seropositive patient: A case report and literature review. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2002, 26, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, C.; Stein, T.; Kitahara, S.; Alkan, S.; Huang, Q. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8-associated extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma presenting as multiple lymphomatous polyposis. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 79, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellet Madan, R.; Hand, J. Human herpesvirus 6, 7, and 8 in solid organ transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.A.; Brookes, L.A.; McGown, I.; Weller, I.; Crawford, D.H. HHV8 DNA in normal gastrointestinal mucosa from HIV seropositive people. Lancet 1996, 37, 1337–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Cesarman, E.; Pessin, M.; Lee, F.; Culpepper, J.; Knowels, D.M.; Moore, P.S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science 1994, 266, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soulier, J.; Grollet, L.; Oksenhendler, E.; Cacoub, P.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Babinet, P.; d’Agay, M.F.; Clauvel, J.P.; Raphael, M.; Degos, L. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood 1995, 86, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesarman, E.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S.; Said, J.W.; Knowles, D.M. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.Q.; Diss, T.C.; Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Cabecadas, J.; Dong, H.Y.; Lee Harris, N.; Chan, J.K.C.; Rees, J.W.; et al. KSHV and EBV-associated germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder. Blood 2002, 100, 3415–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Bisagni, A.; Froio, E.; De Marco, L.; Valli, R.; Filosa, A.; Luminari, S.; Martino, G.; Massaro, F.; et al. Germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder: A systematic review. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Fraternali Orcioni, G.; Zizzo, M.; De Marco, L.; Martino, G.; Cerrone, G.; Cabra, A.D.; Ascani, S. HHV-8- and EBV-positive germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2439–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Mengoli, M.C.; Del Sordo, R.; Cagini, A.; DE Marco, L.; Simonetti, E.; Martino, G.; Zizzo, M.; Ascani, S. Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma, Epstein-Barr virus positive with multiorgan involvement; a clinical dilemma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Stingeni, L.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Sanguedolce, F.; Marra, A.; Crescenzi, B.; Pileri, S.A. HHV8-positive Castleman disease and in situ mantle cell neoplasia within dermatopathic lymphadenitis, in longstanding psoriasis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurain, K.; Polizzotto, M.N.; Aleman, K.; Bhutani, M.; Wyvill, K.M.; Goncalves, P.H.; Ramaswami, R.; Marshall, V.A.; Miley, W.; Steinberg, S.M.; et al. Viral, immunologic and clinical features of primary effusion lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, S.; Goto, H.; Yotsumoto, M. Current status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2014, 3, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burkitt, D. A sarcoma involving the jaw of African children. Br. J. Surg. 1958, 46, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Virus particle in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 1, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Thé, G.; Geser, A.; Day, N.E.; Tukei, P.M.; Williams, E.H.; Beri, D.P.; Smith, P.G.; Dean, A.G.; Bronkamm, G.W.; Feorino, P.; et al. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt’s lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature 1978, 274, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bosch, C. A role for RNA viruses in the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma: The need for reappraisal. Adv. Hematol. 2012, 2012, 494758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, F.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Mundo, L.; Laginestra, M.A.; Fulingni, F.; Rossi, M.; Zairis, S.; Gazaneo, S.; De Falco, G.; Lazzi, S.; et al. Distinct viral and mutational spectrum of endemic Burkitt lymphoma. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Thè, G. Is Burkitt’s lymphoma related to perinatal infection by Epstein-Barr virus? Lancet 1977, 309, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, A.; Asano, N.; Nakazawa, A.; Osumi, T.; Tsurusawa, M.; Ishiguro, A.; Elsayed, A.A.; Nakamura, N.; Ohshima, K.; Kinoshita, T.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive sporadic Burkitt lymphoma: And age-related lymphoproliferative disorder? Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Anderson, W.F.; Ferlay, J.; Bhatia, K.; Chang, C.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Devesa, S.S.; Parkin, D.M. Pediatric, elderly and emerging adult-onset peaks in Burkitt’s lymphoma incidence diagnosed in four continents, excluding Africa. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibson, T.M.; Morton, L.M.; Shiels, M.S.; Clarke, C.A.; Engels, E.A. Risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes in HIV-infected people during the HAART era: A population-based study. AIDS 2014, 28, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molyneux, E.M.; Rochford, R.; Griffin, B.; Newton, R.; Jackson, G.; Menon, G.; Harrison, C.J.; Israels, T.; Bailey, S. Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet 2012, 379, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- England, R.J.; Oillay, K.; Davidson, A.; Numanoglu, A.; Millar, A.J. Intussusception as a presenting feature of Burkitt lymphoma: Implications for management and outcome. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2012, 28, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.; Kelly, G.L.; Bell, A.I.; Rickinson, A.B. Burkitt’s lymphoma: The Rosetta stone deciphering Epstein-Barr virus biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allday, M.J. How does Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) complement the activation of MYC in the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duleavy, K.; Little, R.F.; Wilson, W.H. Update on Burkitt lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2016, 30, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.; Paneesha, S.; Jackson, N.; Jones, L.; Mahendra, P. Burkitt’s lymphoma: Single centre experience with modified BMF protocol. Clin. Lab. Haematol. 2002, 24, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| PEL | PBL | BL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunosuppression | Usually present | Usually present | Present in the immunodeficiency-associated variant |
| HIV status | + (− in elderly and EBV-negative cases) | + (often); in HIV negative pts other causes of IS are present. | + in the immunodeficiency-associated variant |
| Clinical presentation | Effusion in its classic form. Extra-nodal sites (mostly) and nodal sites in EC-PEL | Extra-nodal sites frequent; rarely nodal sites | Extra-nodal sites mostly; nodal sites in the Immunodeficiency associated variant |
| Histology | PBs/IBs in fluids in the classic form; sheets of PBs/IBs in EC-PEL | PBs/IBs (diffuse pattern of growth) | Medium-sized cells (diffuse monotonous pattern of growth) |
| CD45 | + (often − in EC-PEL) | − or weakly + in a minority of cells | + |
| CD20 | − (often + in EC-PEL) | − or weakly + in a minority of cells | + |
| PAX5 | − (often + in EC-PEL) | − or weakly + in a minority of cells | + |
| CD79α | − (often + in EC-PEL) | + in about 40% of cases | + |
| MUM1/IRF4 | + | + | −/+ |
| CD10 | - | − (+ in 20%) | + |
| BCL6 | - | - | + |
| BCL2 | + often | - | − (rarely weakly +) |
| CD38 | + | + | + often |
| CD138 | + | + | - |
| CD30 | + | + | - |
| EMA | Often + | + | - |
| MYC protein | May be + (due to HHV8-encoded latent proteins) | + (more often in EBV+ cases) | + |
| T cell markers | Occasionally + (more often in EC-PEL) | Occasionally + | - |
| Light chain restriction | Absent (often + in EC-PEL) | + (often IgG kappa or lambda) | + (IgM kappa or lambda) |
| HHV8 | + | - | - |
| EBV (by EBER-ISH) | + (− in elderly HIV-negative pts) | + in HIV-positive pts and post-transplant pts | >95% endemic variant; 20–30% sporadic variant; 25–40% immunodeficiency-associated variant |
| MYCrearrangements | absent | Present in 50% of cases (mainly in EBV-positive cases) | + in 90% of cases |
| Clonality (Ig genes) | Monoclonal (IgG genes hypermutated) | Monoclonal | Monoclonal |
| Outcome | Poor | Poor | Highly aggressive, but potentially curable |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanelli, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Palicelli, A.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Caprera, C.; Fragliasso, V.; Soriano, A.; Valle, L.; Ricci, S.; et al. EBV-Driven Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Spectrum of Entities with a Common Denominator (Part 2). Cancers 2021, 13, 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184527
Zanelli M, Sanguedolce F, Palicelli A, Zizzo M, Martino G, Caprera C, Fragliasso V, Soriano A, Valle L, Ricci S, et al. EBV-Driven Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Spectrum of Entities with a Common Denominator (Part 2). Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184527
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanelli, Magda, Francesca Sanguedolce, Andrea Palicelli, Maurizio Zizzo, Giovanni Martino, Cecilia Caprera, Valentina Fragliasso, Alessandra Soriano, Luca Valle, Stefano Ricci, and et al. 2021. "EBV-Driven Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Spectrum of Entities with a Common Denominator (Part 2)" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184527
APA StyleZanelli, M., Sanguedolce, F., Palicelli, A., Zizzo, M., Martino, G., Caprera, C., Fragliasso, V., Soriano, A., Valle, L., Ricci, S., Gozzi, F., Cimino, L., Cavazza, A., Merli, F., Pileri, S. A., & Ascani, S. (2021). EBV-Driven Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Spectrum of Entities with a Common Denominator (Part 2). Cancers, 13(18), 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184527









