Glioblastoma Surgery Imaging–Reporting and Data System: Validation and Performance of the Automated Segmentation Task
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
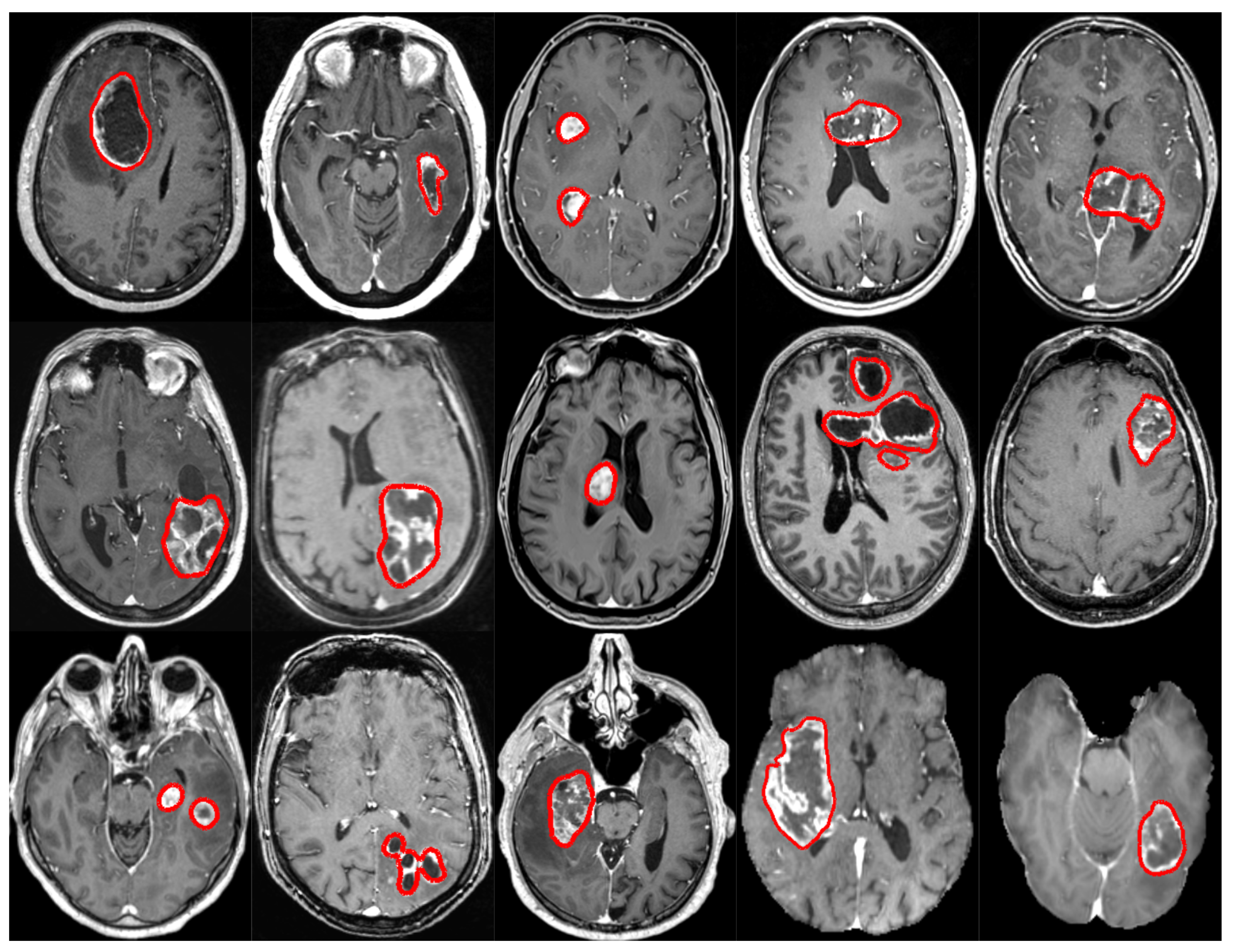
2.1. Subset 1 (GS1)
2.2. Subset 2 (GS2)
3. Methods
3.1. Segmentation
3.1.1. Specifications for nnU-Net
Preprocessing
- Light (P1): (i) cropping tightly around the patient’s head, (ii) z-score intensity normalization (zero mean, unit variance), and (iii) resampling to a spacing of using spline interpolation of order 3;
- Heavy (P2): (i) brain segmentation and brain-masking, (ii) cropping tightly around the patient’s brain, (iii) z-score intensity normalization (zero mean, unit variance), and (iv) resampling to a spacing of using spline interpolation of order 3.
Architecture Design
Network Training
3.1.2. Specifications for AGU-Net
Preprocessing
- Light (P1): (i) resampling to an isotropic spacing of using spline interpolation of order 1 from NiBabel (https://github.com/nipy/nibabel, accessed on 16 September 2021), (ii) cropping tightly around the patient’s head, (iii) volume resizing to match the architecture’s input size, and (iv) normalizing intensities to the range ;
- Heavy (P2): (i) resampling to an isotropic spacing of using spline interpolation of order 1, (ii) brain segmentation and brain-masking, (iii) volume resizing to match the architecture’s input size, and (iv) zero-mean normalization of intensities.
Architecture Design
Network Training
3.2. Clinical Feature Computation
3.2.1. Volume (2 Parameters)
3.2.2. Laterality (3 Parameters)
3.2.3. Multifocality (3 Parameters)
3.2.4. Resectability (2 Parameters)
3.2.5. Cortical Structure Location Profile (87 Parameters)
3.2.6. Subcortical Structure Location Profile ( Parameters)
3.3. Proposed Software and Standardized Reporting
4. Validation Studies
4.1. Protocols
4.1.1. Leave-One-Hospital Out
4.1.2. Custom Validation
4.1.3. BraTS External Validity
4.2. Metrics and Measurements
4.2.1. Pixelwise
4.2.2. Patientwise
4.2.3. Speedwise
4.3. Experiments
5. Results
5.1. Implementation Details
5.2. Architecture Comparison
5.3. External Validity
5.4. Preprocessing Impact
5.5. Speed Performance Study
5.6. Inter-Rater Variability
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, B.K.; Hansen, S.; Laursen, R.J.; Kosteljanetz, M.; Schultz, H.; Nørgård, B.M.; Guldberg, R.; Gradel, K.O. Epidemiology of glioma: Clinical characteristics, symptoms, and predictors of glioma patients grade I–IV in the the Danish Neuro-Oncology Registry. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 135, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claes, A.; Idema, A.J.; Wesseling, P. Diffuse glioma growth: A guerilla war. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soeda, A.; Hara, A.; Kunisada, T.; Yoshimura, S.I.; Iwama, T.; Park, D.M. The evidence of glioblastoma heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binaghi, E.; Pedoia, V.; Balbi, S. Collection and fuzzy estimation of truth labels in glial tumour segmentation studies. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2016, 4, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, E.M.; Stensjøen, A.L.; Langlo, M.S.; Simonsen, S.Q.; Christensen, P.; Moholdt, V.A.; Solheim, O. Volumetric segmentation of glioblastoma progression compared to bidimensional products and clinical radiological reports. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Berger, M.S. Surgical oncology for gliomas: The state of the art. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, C.; Kosteniuk, S.E.; Lau, J.C.; Megyesi, J.F. Tumor growth dynamics in serially-imaged low-grade glioma patients. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 139, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandonnet, E.; Pallud, J.; Fontaine, D.; Taillandier, L.; Bauchet, L.; Peruzzi, P.; Guyotat, J.; Bernier, V.; Baron, M.H.; Duffau, H.; et al. Inter-and intrapatients comparison of WHO grade II glioma kinetics before and after surgical resection. Neurosurg. Rev. 2010, 33, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witt Hamer, P.C.; Hendriks, E.J.; Mandonnet, E.; Barkhof, F.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Duffau, H. Resection probability maps for quality assessment of glioma surgery without brain location bias. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73353. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging–reporting and data system: 2015, version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.R.; Choi, J.S.; Won, H.; Ko, E.Y.; Ko, E.S.; Park, K.W.; Han, B.K. Breast Cancer Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI: 3-year Outcome Analysis. Radiology 2021, 299, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Darwish, E.; Fahiem, R.; Abdelaziz, T. MRI Posttreatment Surveillance for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Proposed MR NI-RADS Criteria. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, S.C.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Koo, C.W. Implications of the updated Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS version 1.1) for lung cancer screening. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotrotsou, A.; Zinn, P.O.; Colen, R.R. Radiomics in brain tumors: An emerging technique for characterization of tumor environment. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. 2016, 24, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Krishnan, S. Radiomics in cancer diagnosis, cancer staging, and prediction of response to treatment. Transl. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Tustison, N.J.; Patel, S.H.; Meyer, C.H. Brain tumor segmentation using an ensemble of 3d u-nets and overall survival prediction using radiomic features. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isensee, F.; Petersen, J.; Klein, A.; Zimmerer, D.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.; Wasserthal, J.; Koehler, G.; Norajitra, T.; Wirkert, S.; et al. nnu-net: Self-adapting framework for u-net-based medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10486. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Cai, W.; Huang, H.; Xia, Y. H2NF-Net for Brain Tumor Segmentation using Multimodal MR Imaging: 2nd Place Solution to BraTS Challenge 2020 Segmentation Task. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15318. [Google Scholar]
- Laukamp, K.R.; Thiele, F.; Shakirin, G.; Zopfs, D.; Faymonville, A.; Timmer, M.; Maintz, D.; Perkuhn, M.; Borggrefe, J. Fully automated detection and segmentation of meningiomas using deep learning on routine multiparametric MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laukamp, K.R.; Pennig, L.; Thiele, F.; Reimer, R.; Görtz, L.; Shakirin, G.; Zopfs, D.; Timmer, M.; Perkuhn, M.; Borggrefe, J. Automated Meningioma Segmentation in Multiparametric MRI. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 31, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouget, D.; Pedersen, A.; Hosainey, S.A.M.; Vanel, J.; Solheim, O.; Reinertsen, I. Fast meningioma segmentation in T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging volumes using a lightweight 3D deep learning architecture. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 8, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouget, D.; Pedersen, A.; Hosainey, S.A.M.; Solheim, O.; Reinertsen, I. Meningioma segmentation in t1-weighted mri leveraging global context and attention mechanisms. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.07715. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, B.D.; Gore, A.; Shu, H.K.G.; Olson, J.J.; Duszak, R.; Voloschin, A.D.; Hoch, M.J. Management-based structured reporting of posttreatment glioma response with the brain tumor reporting and data system. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommers, I.; Bouget, D.; Pedersen, A.; Eijgelaar, R.S.; Ardon, H.; Barkhof, F.; Bello, L.; Berger, M.S.; Conti Nibali, M.; Furtner, J.; et al. Glioblastoma Surgery Imaging—Reporting and Data System: Standardized Reporting of Tumor Volume, Location, and Resectability Based on Automated Segmentations. Cancers 2021, 13, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, T.; Alber, G.; Bette, S.; Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Gempt, J.; Ringel, F.; Alberts, E.; Zimmer, C.; Bauer, J. Reliability of semi-automated segmentations in glioblastoma. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2017, 27, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezhnevets, V.; Konouchine, V. GrowCut: Interactive multi-label ND image segmentation by cellular automata. In Proc. Graphicon; Citeseer: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Garcia, A.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Oprea, S.; Villena-Martinez, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J. A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.06857. [Google Scholar]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ségonne, F.; Dale, A.M.; Busa, E.; Glessner, M.; Salat, D.; Hahn, H.K.; Fischl, B. A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Schell, M.; Pflueger, I.; Brugnara, G.; Bonekamp, D.; Neuberger, U.; Wick, A.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Heiland, S.; Wick, W.; et al. Automated brain extraction of multisequence MRI using artificial neural networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 4952–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonov, V.S.; Evans, A.C.; McKinstry, R.C.; Almli, C.; Collins, D. Unbiased nonlinear average age-appropriate brain templates from birth to adulthood. Neuroimage 2009, 47, S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonov, V.; Evans, A.C.; Botteron, K.; Almli, C.R.; McKinstry, R.C.; Collins, D.L.; Brain Development Cooperative Group. Unbiased average age-appropriate atlases for pediatric studies. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, D.M.; Robe, P.A.; Ardon, H.; Barkhof, F.; Bello, L.; Berger, M.S.; Bouwknegt, W.; Van den Brink, W.A.; Nibali, M.C.; Eijgelaar, R.S.; et al. Quantifying eloquent locations for glioblastoma surgery using resection probability maps. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.L.; Zijdenbos, A.P.; Baaré, W.F.; Evans, A.C. ANIMAL+ INSECT: Improved cortical structure segmentation. In Biennial International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 210–223. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, N.; Goldstein, J.M.; Kennedy, D.; Hodge, S.M.; Caviness, V.S.; Faraone, S.V.; Tsuang, M.T.; Seidman, L.J. Decreased volume of left and total anterior insular lobule in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 83, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, J.A.; Chiu, S.; Breeze, J.L.; Makris, N.; Lange, N.; Kennedy, D.N.; Herbert, M.R.; Bent, E.K.; Koneru, V.K.; Dieterich, M.E.; et al. Structural brain magnetic resonance imaging of limbic and thalamic volumes in pediatric bipolar disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.M.; Seidman, L.J.; Makris, N.; Ahern, T.; O’Brien, L.M.; Caviness, V.S., Jr.; Kennedy, D.N.; Faraone, S.V.; Tsuang, M.T. Hypothalamic abnormalities in schizophrenia: Sex effects and genetic vulnerability. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, A.; Kong, R.; Gordon, E.M.; Laumann, T.O.; Zuo, X.N.; Holmes, A.J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Yeo, B.T. Local-global parcellation of the human cerebral cortex from intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 3095–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas Yeo, B.; Krienen, F.M.; Sepulcre, J.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Lashkari, D.; Hollinshead, M.; Roffman, J.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Zöllei, L.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1125–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojkova, K.; Volle, E.; Urbanski, M.; Humbert, F.; Dell’Acqua, F.; De Schotten, M.T. Atlasing the frontal lobe connections and their variability due to age and education: A spherical deconvolution tractography study. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killeen, P.R. An alternative to null-hypothesis significance tests. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 16, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Fold | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val. | HAG | MIL | ZWO | VIE | ALK | PAR | SLO | STO | SFR | GRO | UTR | AMS | TIL |
| Test | TIL | HAG | MIL | ZWO | VIE | ALK | PAR | SLO | STO | SFR | GRO | UTR | AMS |
| Category | Pixelwise | Patientwise (PW) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice | Dice-TP | HD95 | FPPP | F1 | Recall | Precision | |
| All | |||||||
| Unifocal | |||||||
| Multifocal | |||||||
| Small | |||||||
| Large | |||||||
| Hospital | Pixelwise | Patientwise (PW) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice | Dice-TP | HD95 | FPPP | F1 | Recall | Precision | |
| TIL | |||||||
| HAG | |||||||
| MIL | |||||||
| ZWO | |||||||
| VIE | |||||||
| ALK | |||||||
| PAR | |||||||
| SLO | |||||||
| STO | |||||||
| SFR | |||||||
| GRO | |||||||
| UTR | |||||||
| AMS | |||||||
| 0 | |||||||
| Arch. | Pixelwise | Patientwise (PW) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice | Dice-TP | HD95 | FPPP | F1 | Recall | Precision | |
| HNF-Net | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| nnU-Net | |||||||
| AGU-Net | |||||||
| Configuration | Pixelwise | Patientwise (PW) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice | Dice-TP | HD95 | FPPP | F1 | Recall | Precision | |
| nnU-Net/GS1/P1 | |||||||
| nnU-Net/GS1/P2 | |||||||
| AGU-Net/GS1/P1 | |||||||
| AGU-Net/GS1/P2 | |||||||
| nnU-Net/GS2/P1 | |||||||
| nnU-Net/GS2/P2 | |||||||
| AGU-Net/GS2/P1 | |||||||
| AGU-Net/GS2/P2 | |||||||
| Brain Segmentation (s) | Registration (s) | Tumor Segmentation (s) | Features Computation (s) | Total (s) | Total (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample1 | ||||||
| Sample2 |
| Arch. | Pre. | Ground Truth | Consensus | Novices | Experts | Total | Novices | Experts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nnU-Net | P1 | |||||||
| P2 | ||||||||
| AGU-Net | P1 | |||||||
| P2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouget, D.; Eijgelaar, R.S.; Pedersen, A.; Kommers, I.; Ardon, H.; Barkhof, F.; Bello, L.; Berger, M.S.; Nibali, M.C.; Furtner, J.; et al. Glioblastoma Surgery Imaging–Reporting and Data System: Validation and Performance of the Automated Segmentation Task. Cancers 2021, 13, 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184674
Bouget D, Eijgelaar RS, Pedersen A, Kommers I, Ardon H, Barkhof F, Bello L, Berger MS, Nibali MC, Furtner J, et al. Glioblastoma Surgery Imaging–Reporting and Data System: Validation and Performance of the Automated Segmentation Task. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184674
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouget, David, Roelant S. Eijgelaar, André Pedersen, Ivar Kommers, Hilko Ardon, Frederik Barkhof, Lorenzo Bello, Mitchel S. Berger, Marco Conti Nibali, Julia Furtner, and et al. 2021. "Glioblastoma Surgery Imaging–Reporting and Data System: Validation and Performance of the Automated Segmentation Task" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184674
APA StyleBouget, D., Eijgelaar, R. S., Pedersen, A., Kommers, I., Ardon, H., Barkhof, F., Bello, L., Berger, M. S., Nibali, M. C., Furtner, J., Fyllingen, E. H., Hervey-Jumper, S., Idema, A. J. S., Kiesel, B., Kloet, A., Mandonnet, E., Müller, D. M. J., Robe, P. A., Rossi, M., ... Solheim, O. (2021). Glioblastoma Surgery Imaging–Reporting and Data System: Validation and Performance of the Automated Segmentation Task. Cancers, 13(18), 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184674








