Clinical Significance of Germline Cancer Predisposing Variants in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
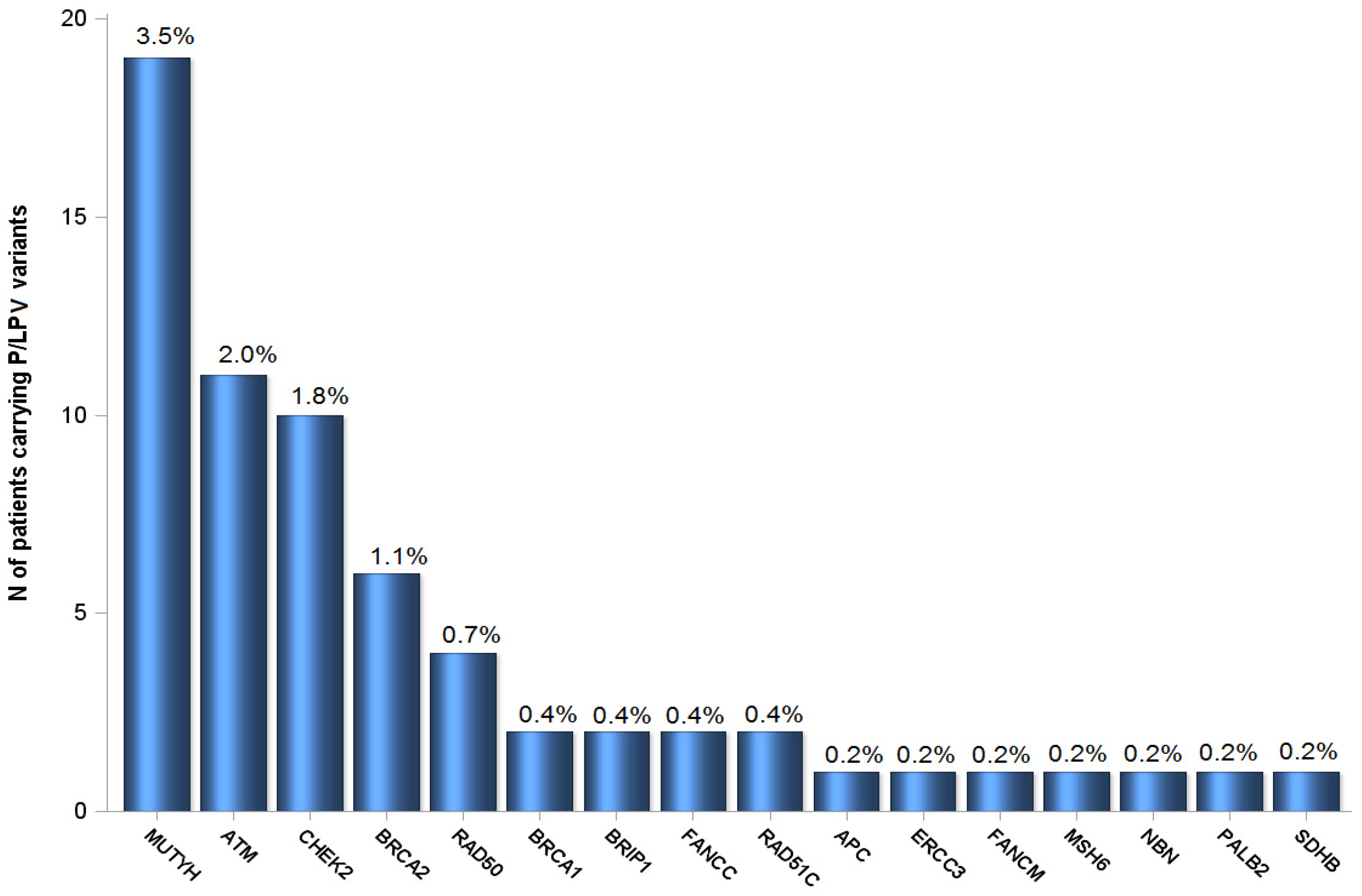
2.1. Patient Characteristics and P/LPV Prevalence
2.2. Clinical Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Multigene Panel Testing
4.3. Bioinformatics and Data Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iqbal, J.; Ragone, A.V.; Lubinski, J.; Lynch, H.T.; Moller, P.; Ghadirian, P.; Foulkes, W.D.; Armel, S.; Eisen, A.Z.; Neuhausen, S.L.; et al. The incidence of pancreatic cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, D.B.; Rabe, K.G.; Gallinger, S.; Syngal, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Goggins, M.G.; Hruban, R.H.; Cote, M.L.; McWilliams, R.R.; Roberts, N.J.; et al. BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and CDKN2A mutations in familial pancreatic cancer: A PACGENE study. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Leslie, G.; Doroszuk, A.; Schneider, S.; Allen, J.; Decker, B.; Dunning, A.M.; Redman, J.; Scarth, J.; Plaskocinska, I.; et al. Cancer Risks Associated With Germline PALB2 Pathogenic Variants: An International Study of 524 Families. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.J.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, J.; Kopelovich, L.; Petersen, G.M.; Bondy, M.L.; Gallinger, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Syngal, S.; Cote, M.L.; et al. ATM Mutations in Patients with Hereditary Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastrinos, F. Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Families with Lynch Syndrome. JAMA 2009, 302, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Polley, E.C.; Gnanaolivu, R.; Shimelis, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Lilyquist, J.; Na, J.; Moore, R.M.; Antwi, S.O.; et al. Association Between Inherited Germline Mutations in Cancer Predisposition Genes and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2018, 319, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.-O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, E.M.; Lee, J.W.; Zalupski, M.; Capanu, M.; Park, J.; Golan, T.; Tahover, E.; Lowery, M.A.; Chou, J.F.; Sahai, V.; et al. Randomized, Multicenter, Phase II Trial of Gemcitabine and Cisplatin With or Without Veliparib in Patients With Pancreas Adenocarcinoma and a Germline BRCA/PALB2 Mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattenberg, M.M.; Asch, D.; Yu, S.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Domchek, S.M.; Nathanson, K.L.; Rosen, M.A.; Beatty, G.L.; Siegelman, E.S.; Reiss, K.A. Platinum response characteristics of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and a germline BRCA1, BRCA2 or PALB2 mutation. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients With Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair–Deficient Cancer: Results From the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN. NCCN Clinical Practice Giodelines in Oncology, Pancreatic Cancer. NCCN, 2020. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Brand, R.E.; Borazanci, E.; Speare, V.; Dudley, B.; Karloski, E.; Peters, M.L.B.; Ms, L.S.; Bahary, N.; Zeh, H.; Zureikat, A.; et al. Prospective study of germline genetic testing in incident cases of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2018, 124, 3520–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffee, K.G.; Oberg, A.L.; McWilliams, R.R.; Majithia, N.; Allen, B.A.; Kidd, J.; Singh, N.; Hartman, A.-R.; Wenstrup, R.J.; Petersen, G.M. Prevalence of germ-line mutations in cancer genes among pancreatic cancer patients with a positive family history. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremin, C.; Lee, M.K.; Hong, Q.; Hoeschen, C.; MacKenzie, A.; Dixon, K.; McCullum, M.; Nuk, J.; Kalloger, S.; Karasinska, J.; et al. Burden of hereditary cancer susceptibility in unselected patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma referred for germline screening. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4004–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, T.; Kindler, H.L.; Park, J.O.; Reni, M.; Macarulla, T.; Hammel, P.; Van Cutsem, E.; Arnold, D.; Hochhauser, D.; McGuinness, D.; et al. Geographic and Ethnic Heterogeneity of Germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutation Prevalence Among Patients With Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Screened for Entry Into the POLO Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1442–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.B.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Ghelman, Y.; Overman, M.J.; Javle, M.M.; Shroff, R.T.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Wolff, R.A.; McAllister, F.; et al. Germline DNA Sequencing Reveals Novel Mutations Predictive of Overall Survival in a Cohort of Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 26, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.C.; Selander, I.; Connor, A.A.; Selvarajah, S.; Borgida, A.; Briollais, L.; Petersen, G.M.; Lerner-Ellis, J.; Holter, S.; Gallinger, S. Prevalence of Germline Mutations in Cancer Predisposition Genes in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; LaDuca, H.; Shimelis, H.; Polley, E.C.; Lilyquist, J.; Hart, S.N.; Na, J.; Thomas, A.; Lee, K.Y.; Davis, B.T.; et al. Multigene Hereditary Cancer Panels Reveal High-Risk Pancreatic Cancer Susceptibility Genes. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, A.M.; Wong, W.; Jordan, E.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kemel, Y.; Vijai, J.; Mandelker, D.; Zehir, A.; Capanu, M.; Salo-Mullen, E.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Germline Alterations in Patients With Exocrine Pancreatic Neoplasms. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo-Mullen, E.E.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Kelsen, D.P.; Ba, A.M.A.; Lowery, M.A.; Yu, K.H.; Reidy, D.L.; Epstein, A.S.; Lincoln, A.; Bs, A.S.; et al. Identification of germline genetic mutations in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer 2015, 121, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, K.; Yu, J.; Suenaga, M.; Fesharakizadeh, S.; Cho, C.; Macgregor-Das, A.; Siddiqui, A.; Witmer, P.D.; Tamura, K.; Song, T.J.; et al. Deleterious Germline Mutations in Patients With Apparently Sporadic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holter, S.; Borgida, A.; Dodd, A.; Grant, R.; Semotiuk, K.; Hedley, D.; Dhani, N.; Narod, S.; Akbari, M.; Moore, M.; et al. Germline BRCA Mutations in a Large Clinic-Based Cohort of Patients With Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3124–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurgelun, M.B.; Chittenden, A.B.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Rubinson, D.A.; Dunne, R.F.; Kozak, M.M.; Qian, Z.R.; Ba, M.W.W.; Brais, L.K.; Da Silva, A.; et al. Germline cancer susceptibility gene variants, somatic second hits, and survival outcomes in patients with resected pancreatic cancer. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, S.; Doi, M.; Ikari, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Furukawa, T. Mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2, and a panel of 50 cancer-associated genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Bamlet, W.R.; Moore, R.M.; Nandakumar, K.; Eckloff, B.W.; Lee, Y.K.; Petersen, G.M.; McWilliams, R.R.; Couch, F.J. Prevalence of Pathogenic Mutations in Cancer Predisposition Genes among Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obazee, O.; Archibugi, L.; Andriulli, A.; Soucek, P.; Małecka-Panas, E.; Ivanauskas, A.; Johnson, T.; Gazouli, M.; Pausch, T.; Lawlor, R.T.; et al. Germline BRCA2 K3326X and CHEK2 I157T mutations increase risk for sporadic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, B.; Karloski, E.; Monzon, F.A.; Singhi, A.D.; Bs, S.E.L.; Bahary, N.; Brand, R.E. Germline mutation prevalence in individuals with pancreatic cancer and a history of previous malignancy. Cancer 2018, 124, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Kasi, P.M.; Bamlet, W.R.; Ho, T.P.; Polley, E.C.; Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Rabe, K.G.; Boddicker, N.J.; Gnanaolivu, R.D.; et al. Effect of Germline Mutations in Homologous Recombination Repair Genes on Overall Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6505–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, S.; Sancho, A.; Azkona, E.; Azkuna, J.; Lopez-Vivanco, G. Hereditary pancreatic cancer: Related syndromes and clinical perspective. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2017, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.M.; Robson, M.E.; Ventz, S.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; Marcom, P.K.; Nanda, R.; Shah, P.D.; Ballinger, T.J.; Yang, E.S.-H.; Melisko, M.E.; et al. TBCRC 048: A phase II study of olaparib monotherapy in metastatic breast cancer patients with germline or somatic mutations in DNA damage response (DDR) pathway genes (Olaparib Expanded). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Blais, E.M.; Brody, J.R.; Sohal, D.; Hendifar, A.E.; Chung, V.; Mikhail, S.; Rahib, L.; Lyons, E.; Tibbetts, L.; et al. Outcomes in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDA) patients (pts) with genetic alterations in DNA damage repair (DDR) pathways: Results from the Know Your Tumor (KYT) program. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.B.; Daly, M.J.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public archive of rela-tionships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total (N = 549) | Pts with P/LPVs (N = 62) | Pts without P/LPVs (N = 487) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Median (min, max) | 65.0 (33.6, 86.0) | 65.5 (41.8, 82.3) | 65.0 (33.6, 86.0) | 0.57 b |
| Sex | 0.67 c | |||
| Female | 271 (49.4) | 29 (46.8) | 242 (49.7) | |
| Male | 278 (50.6) | 33 (53.2) | 245 (50.3) | |
| Stage | 0.25 c | |||
| Early | 192 (35.0) | 27 (43.5) | 165 (33.9) | |
| Locally advanced | 33 (6.0) | 2 (3.2) | 31 (6.4) | |
| Metastatic | 324 (59.0) | 33 (53.2) | 291 (59.8) | |
| Definitive surgery | 0.071 | |||
| Yes | 175 (31.9) | 26 (41.9) | 149 (30.6) | |
| No | 374 (68.1) | 36 (58.1) | 338 (69.4) | |
| Histological grade * | 0.32 c | |||
| G1 (Well differentiated) | 26 (6.0) | 1 (2.0) | 25 (6.5) | |
| G2 (Moderately differentiated) | 215 (49.7) | 25 (51.0) | 190 (49.5) | |
| G3 (Poorly differentiated) | 172 (39.7) | 21 (42.9) | 151 (39.3) | |
| G4 (Undifferentiated) | 2 (0.46) | 1 (2.0) | 1 (0.26) | |
| GX (Grade cannot be assessed) | 18 (4.2) | 1 (2.0) | 17 (4.4) | |
| Family history of cancer * | 0.011 c | |||
| No | 330 (70.1) | 33 (55.9) | 297 (72.1) | |
| Yes | 141 (29.9) | 26 (44.1) | 115 (27.9) | |
| Chemotherapy * | 0.037 c | |||
| No | 9 (1.7) | 3 (4.9) | 6 (1.3) | |
| Yes | 525 (98.3) | 58 (95.1) | 467 (98.7) | |
| Platinum-based chemotherapy | 0.47 c | |||
| No | 275 (52.4) | 33 (56.9) | 242 (51.8) | |
| Yes | 250 (47.6) | 25 (43.1) | 225 (48.2) |
| Parameter | Events/Total | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | |||
| Early | 118/181 (65.2%) | 0.37 (0.29−0.46) | <0.001 |
| Advanced | 284/344 (82.6%) | Reference | -- |
| Interaction term of platinum-based CT with P/LPVs presence | 0.60 | ||
| P/LPVs among patients treated with platinum-based CT (N = 250) | |||
| Yes | 18/25 (72%) | 0.77 (0.47−1.23) | 0.18 |
| No | 167/225 (74.2%) | Reference | -- |
| P/LPVs in non-platinum-based CT (N = 275) | |||
| Yes | 20/33 (60.6%) | 0.65 (0.43−1.05) | 0.077 |
| No | 197/242 (81.4%) | Reference | -- |
| Entire Cohort (N = 515) | Treated with Platinum-Based CT (N = 239) | No Platinum-Based CT (N = 262) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events/Total | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Events/Total | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Events/Total | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Presence of P/LPVs | |||||||||
| No | 372/479 (77.7%) | Reference | -- | 167/225 (74.2%) | Reference | -- | 197/242 (81.4%) | Reference | -- |
| Yes | 23/36 (63.9%) | 0.68 (0.44−1.03) | 0.070 | 9/14 (64.3%) | 0.58 (0.29−1.13) | 0.11 | 12/20 (60%) | 0.69 (0.39−1.24) | 0.21 |
| P/LPVs in PDAC- associated genes | |||||||||
| No | 381/494 (77.1%) | Reference | -- | 172/232 (74.1%) | Reference | -- | 201/250 (80.4%) | Reference | -- |
| Yes | 14/21 (66.7%) | 0.63 (0.37−1.08) | 0.095 | 4/7 (57.1%) | 0.34 (0.12−0.92) | 0.033 | 8/12 (66.7%) | 0.85 (0.42−1.73) | 0.65 |
| P/LPVs in HRR genes | |||||||||
| No | 374/483 (77.4%) | Reference | -- | 168/226 (74.3%) | Reference | -- | 197/244 (80.7%) | Reference | -- |
| Yes | 21/32 (65.63%) | 0.76 (0.49−1.18) | 0.22 | 8/13 (61.5%) | 0.52 (0.25−1.06) | 0.074 | 12/18 (66.7%) | 0.86 (0.48−1.55) | 0.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fountzilas, E.; Eliades, A.; Koliou, G.-A.; Achilleos, A.; Loizides, C.; Tsangaras, K.; Pectasides, D.; Sgouros, J.; Papakostas, P.; Rallis, G.; et al. Clinical Significance of Germline Cancer Predisposing Variants in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020198
Fountzilas E, Eliades A, Koliou G-A, Achilleos A, Loizides C, Tsangaras K, Pectasides D, Sgouros J, Papakostas P, Rallis G, et al. Clinical Significance of Germline Cancer Predisposing Variants in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(2):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020198
Chicago/Turabian StyleFountzilas, Elena, Alexia Eliades, Georgia-Angeliki Koliou, Achilleas Achilleos, Charalambos Loizides, Kyriakos Tsangaras, Dimitrios Pectasides, Joseph Sgouros, Pavlos Papakostas, Grigorios Rallis, and et al. 2021. "Clinical Significance of Germline Cancer Predisposing Variants in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 2: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020198
APA StyleFountzilas, E., Eliades, A., Koliou, G.-A., Achilleos, A., Loizides, C., Tsangaras, K., Pectasides, D., Sgouros, J., Papakostas, P., Rallis, G., Psyrri, A., Papadimitriou, C., Oikonomopoulos, G., Ferentinos, K., Koumarianou, A., Zarkavelis, G., Dervenis, C., Aravantinos, G., Bafaloukos, D., ... Patsalis, P. C. (2021). Clinical Significance of Germline Cancer Predisposing Variants in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 13(2), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020198









