Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Update in the Era of Novel Agents
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Definition, Epidemiology, and Clinical Presentation of Richter Transformation
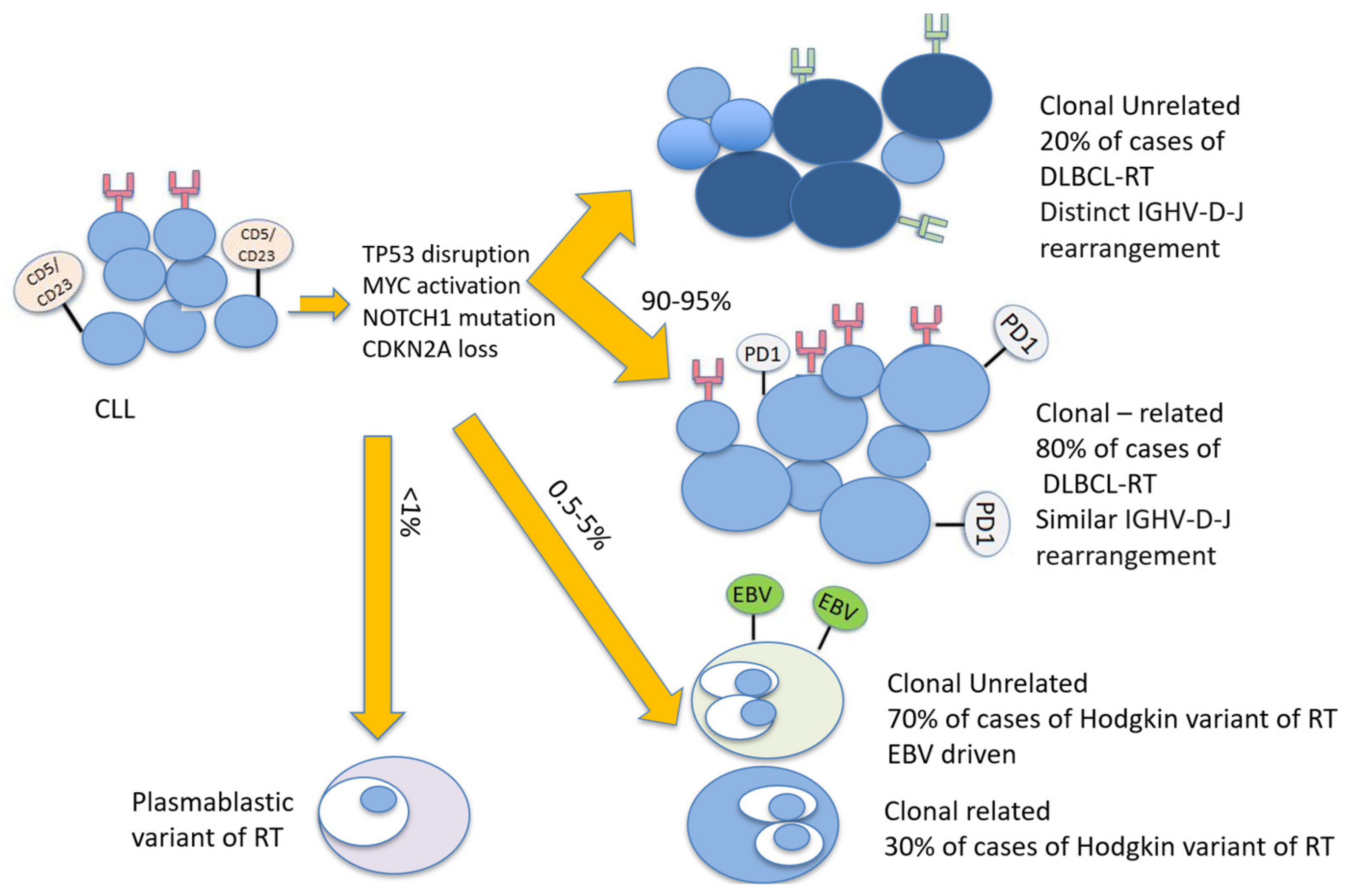
2. Pathogenesis and Risk Factors for the Development of Richter Transformation
2.1. Molecular and Genetic Changes at CLL Diagnosis Associated with Richter Transformation
2.2. Molecular and Genetic Changes Characterizing Richter Transformation
2.3. Microenvironment
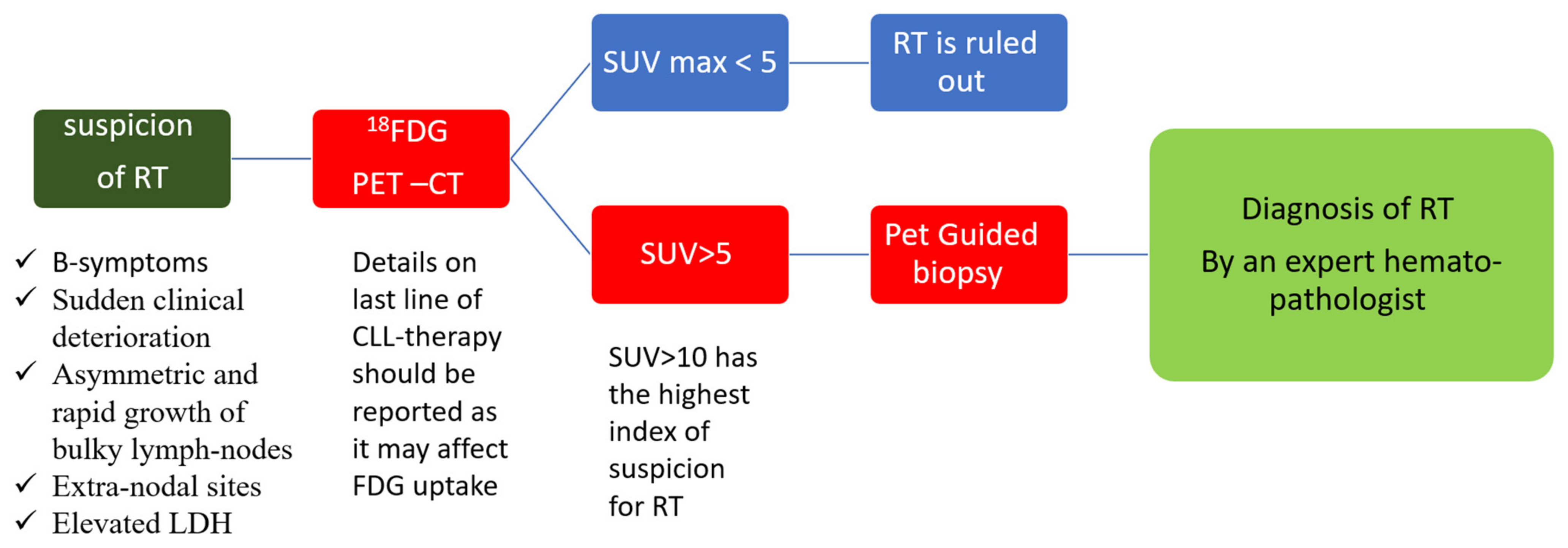
3. Diagnosis of Richter Transformation
3.1. Pathological Diagnosis
3.2. Radiological Diagnosis
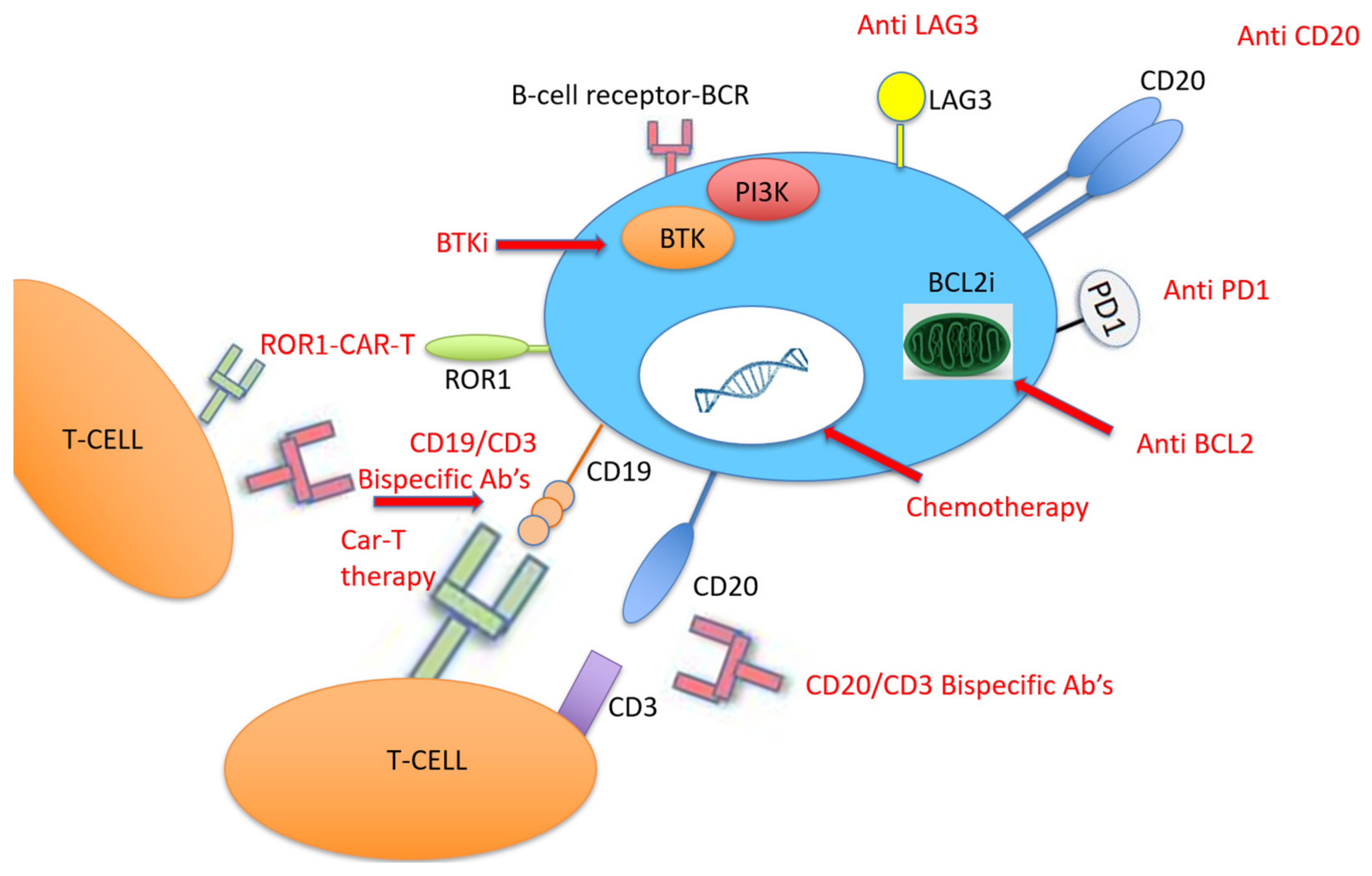
4. Current Treatment Strategies of Richter Transformation
4.1. Chemo-Immunotherapy
4.2. Stem Cell Transplantation
4.3. Novel CLL Therapies for RT
4.4. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway
4.5. Bispecific Monoclonal Antibodies
4.6. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy
4.7. Innovations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamroziak, K.; Tadmor, T.; Robak, T.; Polliack, A. Richter syndrome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Updates on biology, clinical features and therapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.N.; Furman, R.R. Current trends in the management of Richter’s syndrome. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 7, IJH09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvyin, K.; Tjønnfjord, E.B.; Breland, U.M.; Tjønnfjord, G.E. Transformation to plasmablastic lymphoma in CLL upon ibrutinib treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e235816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; O’Brien, S.; Khouri, I.; Giles, F.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Champlin, R.; Wen, S.; Do, K.A.; Smith, S.C.; Lerner, S.; et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Zent, C.S.; Habermann, T.M.; Ding, W.; Leis, J.F.; Schwager, S.M.; Hanson, C.A.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Richter syndrome) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL): A cohort study of newly diagnosed patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Cerri, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; De Paoli, L.; Laurenti, L.; Maffei, R.; Forconi, F.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Stereotyped B-cell receptor is an independent risk factor of chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to richter syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catovsky, D.; Richards, S.; Matutes, E.; Oscier, D.; Dyer, M.; Bezares, R.; Pettitt, A.; Hamblin, T.; Milligan, D.; Child, J.; et al. Assessment of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (the LRF CLL4 Trial): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solh, M.; Rai, K.R.; Peterson, B.L.; Kolitz, J.E.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Tallman, M.S.; Belch, A.; Larson, R.A.; Morrison, V.A. The impact of initial fludarabine therapy on transformation to Richter syndrome or prolymphocytic leukemia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Analysis of an intergroup trial (CALGB 9011). Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, T.; Blonski, J.Z.; Gora-Tybor, J.; Kasznicki, M.; Konopka, L.; Ceglarek, B.; Komarnicki, M.; Lewandowski, K.; Hellmann, A.; Lewandowski, K.; et al. Second malignancies and Richter’s syndrome in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with cladribine. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; Von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.; et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Coutre, S.E.; Mato, A.R.; Hillmen, P.; Tam, C.; Österborg, A.; Siddiqi, T.; Thirman, M.J.; Furman, R.R.; et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): A phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanan-Khan, A.; Cramer, P.; Demirkan, F.; Fraser, G.; Silva, R.S.; Grosicki, S.; Pristupa, A.; Janssens, A.; Mayer, J.; Bartlett, N.L.; et al. Ibrutinib combined with bendamustine and rituximab compared with placebo, bendamustine, and rituximab for previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (HELIOS): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.M.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, R.R.; Sharman, J.P.; Coutre, S.E.; Cheson, B.D.; Pagel, J.M.; Hillmen, P.; Barrientos, J.C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Kipps, T.J.; Flinn, I.; et al. Idelalisib and Rituximab in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.A.; Robak, T.; Brown, J.R.; Awan, F.T.; Badoux, X.; Coutre, S.; Loscertales, J.; Taylor, K.; Vandenberghe, E.; Wach, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of idelalisib in combination with ofatumumab for previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e114–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenetz, A.D.; Barrientos, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; Coiffier, B.; Delgado, J.; Egyed, M.; Ghia, P.; Illés, Á.; Jurczak, W.; Marlton, P.; et al. Idelalisib or placebo in combination with bendamustine and rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Interim results from a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Seymour, J.F.; Huang, D.C.S. Venetoclax in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4527–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Eichhorst, B.; Schetelig, J.; Coutre, S.; Seymour, J.F.; Munir, T.; Puvvada, S.D.; Wendtner, C.M.; Roberts, A.W.; Jurczak, W.; et al. Venetoclax in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Ma, S.; Brander, D.M.; Choi, M.Y.; Barrientos, J.; Davids, M.S.; Anderson, M.A.; Beaven, A.W.; Rosen, S.T.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Venetoclax plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Tedeschi, A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Li, J.; et al. Ibrutinib as Initial Therapy for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Barr, P.M.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Regimens versus Chemoimmunotherapy in Older Patients with Untreated CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Samoilova, O.; Novak, J.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Ibrutinib–Rituximab or Chemoimmunotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Lamanna, N.; Kipps, T.J.; Flinn, I.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Burger, J.A.; Keating, M.; Mitra, S.; Holes, L.; Yu, A.S.; et al. A phase 2 study of idelalisib plus rituximab in treatment-naïve older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampson, B.L.; Kim, H.T.; Davids, M.S.; Abramson, J.S.; Freedman, A.S.; Jacobson, C.A.; Armand, P.A.; Joyce, R.M.; Arnason, J.E.; Rassenti, L.Z.; et al. Efficacy results of a phase 2 trial of first-line idelalisib plus ofatumumab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.-M.; Tandon, M.; Dixon, M.; Robrecht, S.; Warburton, S.; Humphrey, K.; Samoylova, O.; et al. Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab in Patients with CLL and Coexisting Conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnair, R.; Ellithi, M.; Kallam, A.; Shostrom, V.; Bociek, R.G. Outcomes of Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): An analysis of the SEER database. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Cramer, P.; Tresckow, J.V.; Lange, E.; Kiehl, M.; Dreyling, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)—a pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia 2021, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, M.Z.H.; Valdez, J.; Martyr, S.; Aue, G.; Saba, N.; Niemann, C.U.; Herman, S.E.M.; Tian, X.; Marti, G.; Soto, S.; et al. Ibrutinib for previously untreated and relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with TP53 aberrations: A phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Hillmen, P.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.E.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; Barr, P.M.; et al. Extended follow-up and impact of high-risk prognostic factors from the phase 3 RESONATE study in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL. Leukemia 2018, 32, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Cerri, M.; Capello, D.; Deambrogi, C.; Rossi, F.M.; Zucchetto, A.; De Paoli, L.; Cresta, S.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; et al. Biological and clinical risk factors of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoti, C.E.; Omoti, A.E. Richter syndrome: A review of clinical, ocular, neurological and other manifestations. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenti, I.; Rossi, D.; Trapè, G.; Autore, F.; Larocca, L.M.; Gomes, V.; Cerri, M.; Falcucci, P.; Sica, S.; Gaidano, G.; et al. Clinical, pathological, and biological characterization of Richter syndrome developing after ibrutinib treatment for relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks-Christianson, K.; Slager, S.L.; Zent, C.S.; Reinalda, M.; Call, T.G.; Habermann, T.M.; Bowen, D.A.; Hoyer, J.D.; Schwager, S.; Jelinek, D.F.; et al. Risk factors for development of a second lymphoid malignancy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.D.; Bellas, C.; Santon, A.; Shah, G.; Pocock, C.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Matutes, E.; Catovsky, D. Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The possible role of fludarabine and the Epstein-Barr virus in its pathogenesis. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Kay, N.E.; Shanafelt, T.D. How we treat Richter syndrome. Blood 2014, 123, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Shanafelt, T.D. Risk Factors for Richter Syndrome in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2014, 9, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timár, B.; Fülöp, Z.; Csernus, B.; Angster, C.; Bognár, Á.; Szepesi, Á.; Kopper, L.; Matolcsy, A. Relationship between the mutational status of VH genes and pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Richter’s syndrome. Leukemia 2004, 18, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rezvani, S.; Tominna, M.; Al-Katib, S.; Smith, M.D.; Cousineau, C.; Al-Katib, A. Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Rapidly Progressing Peribronchovascular Pulmonary Infiltrates. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2019, 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Deambrogi, C.; Rasi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; Rocque, G.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; et al. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Bodoni, C.L.; Genuardi, E.; Monitillo, L.; Drandi, D.; Cerri, M.; Deambrogi, C.; Ricca, I.; Rocci, A.; Ferrero, S.; et al. Telomere length is an independent predictor of survival, treatment requirement and Richter’s syndrome transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Rigolin, G.M.; Mauro, F.R.; Martines, A.; Frezzato, F.; Imbergamo, S.; Pravato, S.; Gargarella, L.R.; Bardi, M.A.; Nanni, M.; et al. Complex Karyotype Subtypes at Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Diagnosis Refine the Risk of Developing a Richter Syndrome. The Richter Syndrome Scoring System. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. S1), 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Bonaldi, L.; Rigolin, G.M.; Mauro, F.R.; Martines, A.; Frezzato, F.; Pravato, S.; Gargarella, L.R.; Bardi, M.A.; Cavallari, M.; et al. The complex karyotype landscape in chronic lymphocytic leukemia allows to refine the risk of Richter syndrome transformation. Haematologica 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigrinova, E.; Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Rossi, D.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Strefford, J.C.; Oscier, D.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Papadaki, T.; Berger, F.; et al. Two main genetic pathways lead to the transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to Richter syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Monti, S.; Greco, M.; Ciardullo, C.; Famà, R.; Cresta, S.; Bruscaggin, A.; et al. Different impact of NOTCH1 and SF3B1 mutations on the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhaas, V.; Blakemore, S.J.; Al-Maarri, M.; Nickel, N.; Pal, M.; Roth, A.; Hövelmeyer, N.; Schäfer, S.C.; Knittel, G.; Lohneis, P.; et al. Active Akt signaling triggers CLL toward Richter transformation via overactivation of Notch1. Blood 2021, 137, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisitti, T.; Braggio, E.; Allan, J.N.; Arruga, F.; Serra, S.; Zamo, A.; Tam, W.; Chadburn, A.; Furman, R.R.; Deaglio, S. Novel richter syndrome xenograft models to study genetic architecture, biology, and therapy responses. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3413–3420. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, T.; Maier, J.; Martin, M.; Tasdogan, A.; Tausch, E.; Barth, T.F.E.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Bloehdorn, J.; Möller, P.; Mellert, K. U-RT1–A new model for Richter transformation. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintman, J.; Appleby, N.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Ridout, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Robbe, P.; Pascua, L.L.; Knight, S.J.L.; Dreau, H.; Cabes, M.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic correlates of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 2800–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrackova, A.; Turcsanyi, P.; Papajik, T.; Kriegova, E. Revisiting Richter transformation in the era of novel CLL agents. Blood Rev. 2021, 49, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Piazza, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; et al. B Cell Receptor signaling and genetic lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B cooperate in Richter Transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, C.; Guillemin, F.; Remen, T.; Bouclet, F.; Hergalant, S.; Quinquenel, A.; Dartigeas, C.; Tausch, E.; Lazarian, G.; Blanchet, O.; et al. Clinical, biological, and molecular genetic features of Richter syndrome and prognostic significance: A study of the French Innovative Leukemia Organization. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Augé, H.; Notarantonio, A.B.; Morizot, R.; Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.M.; Hergalant, S.; Feugier, P.; Broséus, J. Microenvironment Remodeling and Subsequent Clinical Implications in Diffuse Large B-Cell Histologic Variant of Richter Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sinha, S.; Wellik, L.E.; Secreto, C.R.; Rech, K.L.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Kenderian, S.S.; Muchtar, E.; Hayman, S.R.; et al. Distinct immune signatures in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilleux, E.J.; Wotherspoon, A.; Eyre, T.A.; Clifford, R.; Cabes, M.; Schuh, A.H. Diagnostic dilemmas of high-grade transformation (Richter’s syndrome) of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Results of the phase II National Cancer Research Institute CHOP-OR clinical trial specialist haemato-pathology central review. Histopathology 2016, 69, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Chitalia, A.; Ozdemirli, M.; Ray, G.; Gehan, E.; Cheson, B.D. Cell of Origin in Richter’s Transformation of CLL. Blood 2012, 120, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; O’Brien, S. Richter’s transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncology 2012, 26, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Federmann, B.; Mueller, M.R.; Steinhilber, J.; Horger, M.S.; Fend, F. Diagnosis of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Histology tips the scales. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, L.; Keating, M.J.; Marom, E.M.; Truong, M.T.; Schlette, E.J.; Sargent, R.L.; Trinh, L.; Wang, X.; Smith, S.C.; Jain, N.; et al. Correlation between FDG/PET, histology, characteristics, and survival in 332 patients with chronic lymphoid leukemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Siddiqi, R.; Thompson, P.A. Approach to Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of novel therapies. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Rossi, D. Treatment of Richter’s Syndrome. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Gaidano, G. Biology and treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontoizeau, C.; Girard, A.; Mesbah, H.; Haumont, L.A.; Devillers, A.; Tempescul, A.; Salaün, P.Y.; Lamy, T.; Le Jeune, F.; Palard-Novello, X. Prognostic Value of Baseline Total Metabolic Tumor Volume Measured on FDG PET in Patients with Richter Syndrome. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Camoni, L.; Rodella, C.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. 2-[18F]-FDG PET/CT Role in Detecting Richter Transformation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Predicting Overall Survival. Clin. Lymphoma, Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e277–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musanhu, E.; Sharma, R.K.; Attygalle, A.; Wotherspoon, A.; Chau, I.; Cunningham, D.; Dearden, C.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Iyengar, S.; Sharma, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and Richter’s transformation: Multimodal review and new imaging paradigms. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Plunkett, W.; Kurzrock, R.; O’Brien, S.; Wen, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Estrov, Z.; et al. Phase I-II study of oxaliplatin, fludarabine, cytarabine, and rituximab combination therapy in patients with Richter’s syndrome or fludarabine- refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Wen, S.; Plunkett, W.; O’Brien, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Jones, J.A.; Badoux, X.; Kantarjian, H.; Keating, M.J. Phase I-II clinical trial of oxaliplatin, fludarabine, cytarabine, and rituximab therapy in aggressive relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or Richter syndrome. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Busch, R.; Anheier, N.; Dürig, J.; Bergmann, M.; Goebeler, M.E.; Hurtz, H.J.; Stauch, M.B.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Döhner, H.; et al. Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Clifford, R.; Bloor, A.; Boyle, L.; Roberts, C.; Cabes, M.; Collins, G.P.; Devereux, S.; Follows, G.; Fox, C.P.; et al. NCRI phase II study of CHOP in combination with ofatumumab in induction and maintenance in newly diagnosed Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Salem, G.; Stephens, D.M.; Heerema, N.A.; Andritsos, L.A.; Awan, F.T.; Byrd, J.C.; Flynn, J.M.; et al. A single-institution retrospective cohort study of first-line R-EPOCH chemoimmunotherapy for Richter syndrome demonstrating complex chronic lymphocytic leukaemia karyotype as an adverse prognostic factor. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durot, E.; Michallet, A.S.; Leprêtre, S.; Le, Q.H.; Leblond, V.; Delmer, A. Platinum and high-dose cytarabine-based regimens are efficient in ultra high/high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s syndrome: Results of a French retrospective multicenter study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2015, 95, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaja, B.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Albitar, M.; Schlette, E.S.; Faderl, S.; Sarris, A.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin (daunoxome), and dexamethasone (hyperCVXD) regimen in Richter’s syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.; Thomas, D.A.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Wierda, W.; Alvarado, Y.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin, and dexamethasone plus rituximab and granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) alternating with methotrexate and cytarabine plus rituximab and GM-CSF in patients with Rich. Cancer 2003, 97, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadmor, T.; Shvidel, L.; Bairey, O.; Goldschmidt, N.; Ruchlemer, R.; Fineman, R.; Rahimi-Levene, N.; Herishanu, Y.; Yuklea, M.; Arad, A.; et al. Richter’s transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A retrospective study reporting clinical data, outcome, and the benefit of adding rituximab to chemotherapy, from the Israeli CLL Study Group. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E218–E222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwynarski, K.; Van Biezen, A.; De Wreede, L.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Bunjes, D.; Metzner, B.; Koza, V.; Mohty, M.; Remes, K.; Russell, N.; et al. Autologous and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for transformed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Richter’s syndrome): A retrospective analysis from the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Subcommittee of the Chronic Leukemia Working Party and Lymphoma Working P. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoud, O.B.; Devlin, S.M.; Maloy, M.A.; Roeker, L.E.; Dahi, P.B.; Ponce, D.M.; Gyurkocza, B.; Koehne, G.; Young, J.W.; Castro-Malaspina, H.R.; et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s transformation. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2879–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Stingo, F.E.; Khimani, F.; Hussaini, M.; Ayala, E.; Nishihori, T.; Shah, B.; Locke, F.L.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; et al. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Richter Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, e35–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Baker, P.O.; Parry, E.; Davids, M.; Alyea, E.P.; Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.; Koreth, J.; Gooptu, M.; Romee, R.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in patients with Richter’s transformation. Haematologica 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, S.; Reljic, T.; Yassine, F.; Ayala, E.; Chavez, J.C.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Kumar, A.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is an effective treatment for patients with Richter syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2021, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Ding, W.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Leis, J.F.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Bowen, D.; Conte, M.; Schwager, S.M.; et al. The efficacy of ibrutinib in the treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, A.; Imbergamo, S.; Scomazzon, E.; Pravato, S.; Frezzato, F.; Bonaldi, L.; Pizzi, M.; Vio, S.; Gregianin, M.; Burei, M.; et al. BCR kinase inhibitors, idelalisib and ibrutinib, are active and effective in Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaglowski, S.M.; Jones, J.A.; Nagar, V.; Flynn, J.M.; Andritsos, L.A.; Maddocks, K.J.; Woyach, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grever, M.R.; Smucker, K.; et al. Safety and activity of BTK inhibitor ibrutinib combined with ofatumumab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A phase 1b/2 study. Blood 2015, 126, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmen, P. Acalabrutinib Monotherapy Effective for Richter Transformation. ASH Annu. Meet. 2016, 19, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Appleby, N.; Eyre, T.A.; Cabes, M.; Jackson, A.; Boucher, R.; Yates, F.; Fox, S.; Rawstron, A.; Hillmen, P.; Schuh, A. The STELLAR trial protocol: A prospective multicentre trial for Richter’s syndrome consisting of a randomised trial investigation CHOP-R with or without acalabrutinib for newly diagnosed RS and a single-arm platform study for evaluation of novel agents in. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouclet, F.; Calleja, A.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Véronèse, L.; Pereira, B.; Amorim, S.; Cymbalista, F.; Herbaux, C.; de Guibert, S.; Roos-Weil, D.; et al. Real-world outcomes following venetoclax therapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or Richter syndrome: A FILO study of the French compassionate use cohort. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Pazienza, S.; Renner, S.K.; Montegaard, J.; Rocchio, M.; Ihuoma, U.; Jacobson, C.A.; Fisher, D.C.; et al. A multicenter phase II study of venetoclax plus dose- adjusted R-EPOCH (VR- EPOCH) for Richter ’ s POPULAR. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Rossi, D. Richter Syndrome. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Dotson, E.; Lundberg, J.; Andritsos, L.A.; Awan, F.T.; Woyach, J.A.; Byrd, J.C. Use of PD-1 (PDCD1) inhibitors for the treatment of Richter syndrome: Experience at a single academic centre. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, P.; Murawski, N.; Molin, D.; Zain, J.; Eichhorst, B.; Gulbas, Z.; Hawkes, E.A.; Pagel, J.M.; Phillips, T.; Ribrag, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e117–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Basu, S.; Thompson, P.A.; Burger, J.A.; Kadia, T.M.; Estrov, Z.E.; Pemmaraju, N.; Lopez, W.; Thakral, B.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Nivolumab Combined with Ibrutinib for Patients with Richter Transformation. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. S1), 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Mackrides, N.; Chapman, J.R.; Vega, F.; Lossos, I.S. Rapid complete response to blinatumomab as a successful bridge to allogeneic stem cell transplantation in a case of refractory Richter syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, C.J.; Hay, K.A.; Hanafi, L.A.; Li, D.; Cherian, S.; Chen, X.; Wood, B.; Lozanski, A.; Byrd, J.C.; Heimfeld, S.; et al. Durable molecular remissions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with CD19-Specific chimeric antigen Receptor-modified T cells after failure of ibrutinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3010–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, J.; Hirayama, A.V.; Purushe, J.; Hay, K.A.; Lymp, J.; Li, D.H.; Yeung, C.C.S.; Sheih, A.; Pender, B.S.; Hawkins, R.M.; et al. Feasibility and efficacy of CD19-targeted CAR T cells with concurrent ibrutinib for CLL after ibrutinib failure. Blood 2020, 135, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, O.; Shimoni, A.; Besser, M.; Shem-tov, N.; Danylesko, I.; Yerushalmi, R.; Merkel, D.G.; Tadmor, T.; Lavie, D.; Fineman, R.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of CD19-CAR T Cells in Richter’s Transformation after Targeted Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. S1), 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittai, A.S.; Bond, D.A.; William, B.; Saad, A.; Penza, S.; Efebera, Y.; Larkin, K.; Wall, S.A.; Choe, H.K.; Bhatnagar, B.; et al. Clinical activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in adult patients with Richter syndrome. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4648–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Schuster, S.J.; Foss, F.M.; Isufi, I.; Kothari, S.K.; Ding, W.; Brander, D.M.; Sitlinger, A.; Rosenthal, A.C.; Leis, J.F.; et al. A Once Daily, Oral, Triple Combination of BTK Inhibitor, mTOR Inhibitor and IMiD for Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Richter’s Transformation and De Novo Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdad, A.; Griffin, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ma, S.; Kelemen, K.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.C. PD-1 is highly expressed by neoplastic B-cells in Richter transformation. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, M.P.; Bonifant, C.L.; Gottschalk, S. Redirecting T cells to hematological malignancies with bispecific antibodies. Blood 2018, 131, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, S.A.; Lunning, M.A. CAR T-Cell Therapy in Hematologic Malignancies: A Voyage in Progress. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisitti, T.; Arruga, F.; Vitale, N.; Lee, T.-T.T.; Ko, M.; Chadburn, A.; Braggio, E.; Di Napoli, A.; Iannello, A.; Allan, J.; et al. ROR1 targeting with the antibody drug-conjugate VLS-101 is effective in Richter syndrome patient-derived xenograft mouse models. Blood 2021, 137, 3365–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskus, W.; Mill, C.P.; Perera, D.; Birdwell, C.; Deng, Q.; Yang, H.; Lara, B.H.; Jain, N.; Burger, J.; Ferrajoli, A.; et al. BET proteolysis targeted chimera-based therapy of novel models of Richter Transformation-diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2621–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trial Reference | Treatment | Del (17p) | Incidence of Richter Transformation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemo-immunotherapy | |||
| Tsimberidou, 2006 [4] | Chemo-immunotherapy | NA | 3.7% |
| Parikh, 2013 [5] | Chemo-immunotherapy | 3.3% | 2.3% |
| Robak, 2004 [9] | Cladribine, Alkylating | NA | 0.9% |
| Rossi, 2009 [6] | Chemo-immunotherapy | NA | 8.8% |
| Catvosky, 2007 [7] | F vs. FC vs. Chl | NA | 1.7% |
| Solh, 2013 [8] | F vs. Chl vs. F and Chl | NA | 6.5% |
| Fischer, 2016 [10] | FC vs. FCR | 6.2% | 4.0% |
| Novel therapies—R/R CLL | |||
| Munir, 2019 [11] | Ibrutinib | 32% | 10% |
| O’Brien, 2016 [12] | Ibrutinib | 100% | 12% |
| Chanan-Khan, 2016 [13] | Ibrutinib and BR | 0 | 0 |
| Ahn, 2017 [14] | Ibrutinib | 60% | 9% |
| Furman, 2014 [15] | Idelalisib and R | 42% | NA |
| Jones, 2017 [16] | Idelalisib and O | 40% | NA |
| Zelenetz, 2017 [17] | Idelalisib and BR | 33% | 2% |
| Roberts, 2017 [18] | Venetoclax | 30% | 16% |
| Stilgenbauer, 2016 [19] | Venetoclax | 100% | 10% |
| Seymour, 2017 [20] | Venetoclax and R | 31% | 10% |
| Novel therapies—Treatment naive CLL | |||
| Burger, 2015 [21] | Ibrutinib | 0 | 0 |
| Ahn, 2017 [14] | Ibrutinib | 60% | 4% |
| Woyach, 2018 [22] | Ibrutinib Ibrutinib and R | 5% 8% | 0 1% |
| Moreno, 2019 [23] | Ibrutinib and O | 12% | 0.9% |
| Shanafelt, 2019 [24] | Ibrutinib and R | 0.6% | NA |
| Sharman, 2020 [25] | Acalabrutinib Acalabrutinib and O | 8.9% 9.5% | 3% 1% |
| O’Brien, 2015 [26] | Idelalisib and R | 14% | 0 |
| Lampson, 2019 [27] | Idelalisib and O | 17% | NA |
| Fischer, 2019 [28] | Venetoclax and O | 12% | 1% |
| Regimen | Author, Year | Institution | No. of Patients | Median Age (Years) | CR (%) | ORR (%) | Median PFS (mo) | Median OS (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFAR-2 | Tsimberidou, 2013 [69] | MDACC | 35 | 63 | 6 | 39 | 3 | 7 |
| OFAR-1 | Tsimberidou, 2008 [68] | MDACC | 20 | 66 | 20 | 50 | 4 | 8 |
| R-CHOP | Langerbeins, 2014 [70] | GCLLSG | 15 | 69 | 7 | 67 | 10 | 21 |
| O-CHOP | Eyre, 2016 [71] | UK | 37 | 66 | 25 | 44 | 6 | 11 |
| R-Hyper-CVAD | Tsimberidou, 2013 [69] | MDACC | 35 | NA | NA | 46 | 6 | 9 |
| R-EPOCH | Rogers, 2018 [72] | OSU | 46 | 67 | 20 | 38 | 4 | 6 |
| DHAP, ESHAP | Durot, 2015 [73] | France | 28 | 63 | 25 | 43 | 7 | 8 |
| R-Hyper-CVXD | Tsimberidou, 2003 [75] | MDACC | 30 | 59 | 27 | 43 | 6 | 8 |
| Hyper-CVXD | Dabaja, 2001 [74] | MDACC | 29 | 61 | 38 | 41 | NA | 10 |
| Regimen | Author, Year | Institution | No. of Pts | Median Age (yrs) | CR (%) | ORR (%) | Median PFS (mo) | Median OS (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib | Tsang, 2015 [82] | Mayo | 4 | 67 | 50 | 75 | NA | NA |
| Ibrutinib | Visentin, 2019 [83] | Italy | 4 | 69 | 0 | 25 | NA | NA |
| Ibrutinib and O | Jaglowski, 2015 [84] | Ohio | 3 | 64 | 0 | 33 | NA | NA |
| Acalabrutinib | Hillmen, 2016 [85] | San Diego | 25 | NA | 9.5 | 38 | 2.1 | NA |
| Veneto | Davids, 2017 [87] | Dana-Farber | 7 | 73 | 0 | 43 | 1 | 6 |
| Veneto | Bouclet, 2021 [88] | France | 7 | 67 | 0 | 29 | NA | 1.1 |
| Veneto and R-EPOCH | Davids, 2020 [89] | Dana-Farber | 27 | 63 | 48 | 59 | 16.3 | 16.3 |
| PDCD1 | Rogers, 2019 [91] | Ohio | 10 | 69 | 10 | 10 | NA | 2 |
| Pembro | Ding, 2017 [92] | Mayo | 9 | 69 | 11 | 44 | 5.4 | 10.7 |
| Pembro | Armand, 2020 [93] | Dana-Farber | 23 | NA | 4.3 | 13 | 1.6 | 3.8 |
| Nivo and Ibru | Jain, 2016 [94] | MDACC | 23 | 65 | 35 | 43 | NA | 13.8 |
| Bispecific | Alderuccio, 2019 [95] | Italy | 1 | NA | 0 | 100 | NA | NA |
| CAR-T | Turtle, 2017 [96] | Hutchinson | 5 | 65 | NA | 71 | NA | NA |
| CAR-T and Ibru | Gauthier, 2020 [97] | Hutchinson | 4 | 65 | NA | 83 | NA | NA |
| CAR-T | Benjamini, 2020 [98] | Israel | 8 | 64 | 71 | 71 | NA | NA |
| CAR-T | Kittai, 2020 [99] | Ohio | 8 | 64 | 62 | 100 | NA | NA |
| DTRM-55 | Mato, 2020 [100] | Memorial Sloan | 13 | 71 | NA | 45 | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadmor, T.; Levy, I. Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Update in the Era of Novel Agents. Cancers 2021, 13, 5141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205141
Tadmor T, Levy I. Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Update in the Era of Novel Agents. Cancers. 2021; 13(20):5141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205141
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadmor, Tamar, and Ilana Levy. 2021. "Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Update in the Era of Novel Agents" Cancers 13, no. 20: 5141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205141
APA StyleTadmor, T., & Levy, I. (2021). Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Update in the Era of Novel Agents. Cancers, 13(20), 5141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205141






