The C-Circle Biomarker Is Secreted by Alternative-Lengthening-of-Telomeres Positive Cancer Cells inside Exosomes and Provides a Blood-Based Diagnostic for ALT Activity
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Patient Specimens
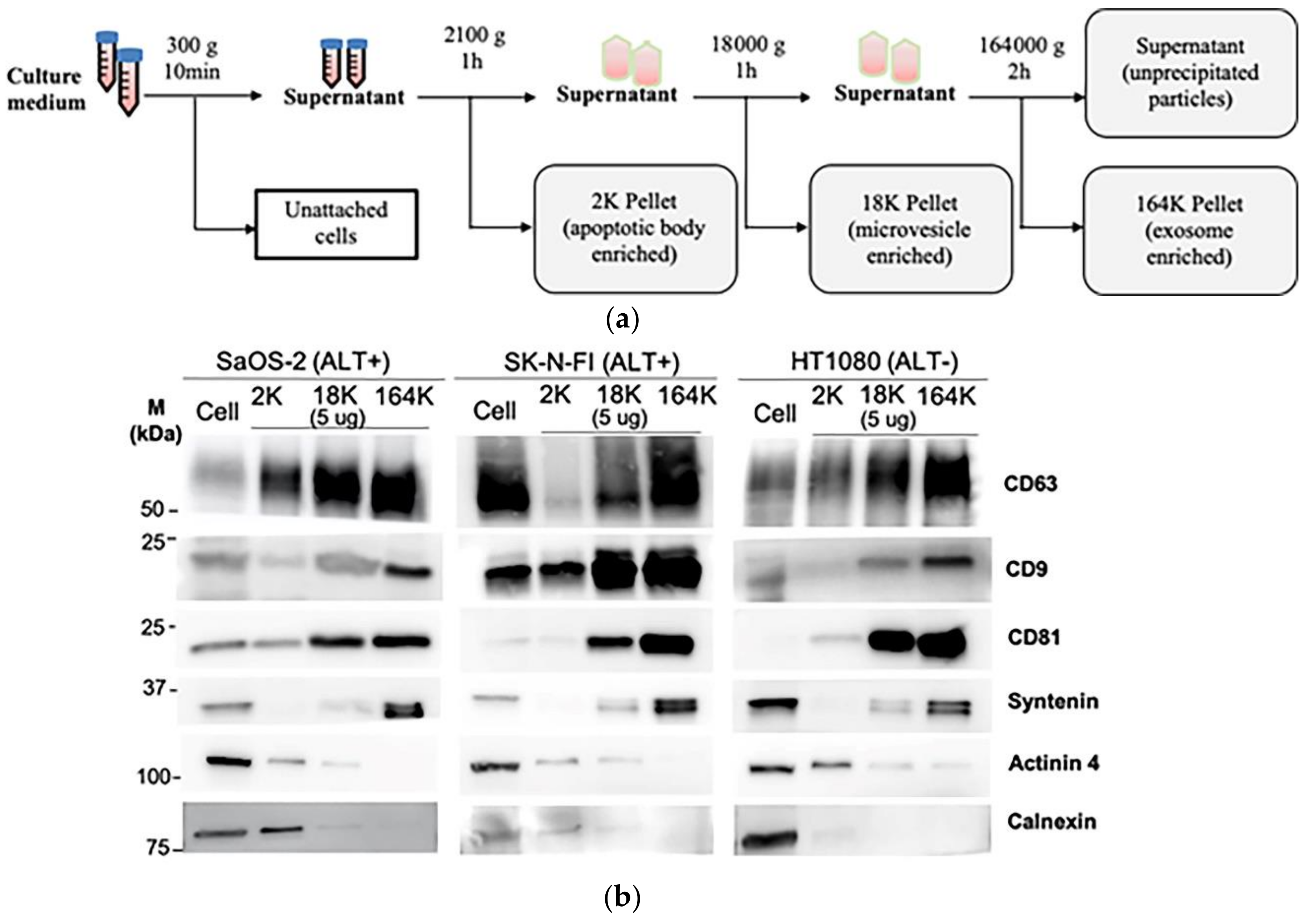
2.2. Differential Centrifugation of Extracellular Vesicles (ECV)
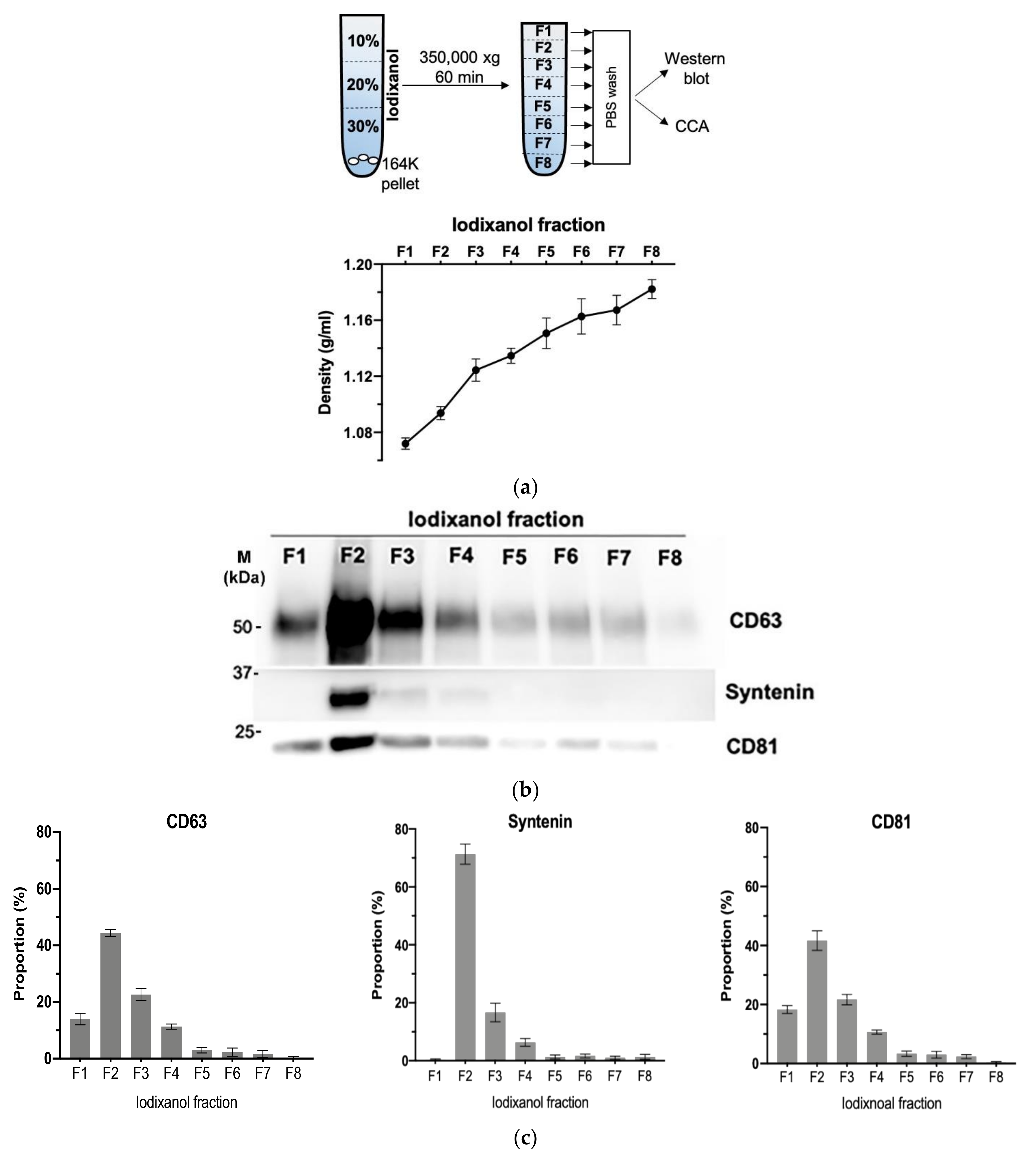
2.3. Iodixanol Gradient Separation of Evs
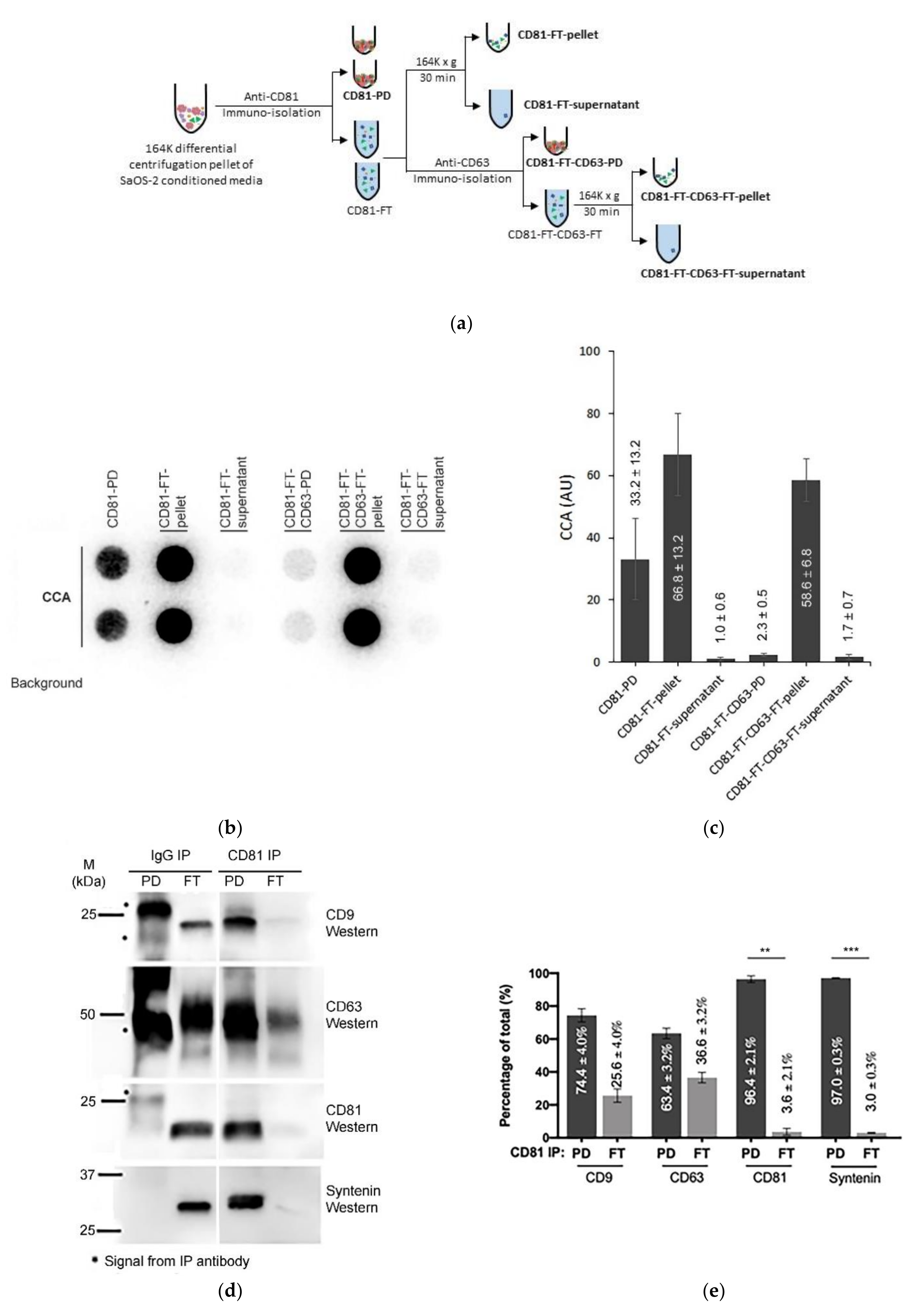
2.4. Immuno-Purification of ECV
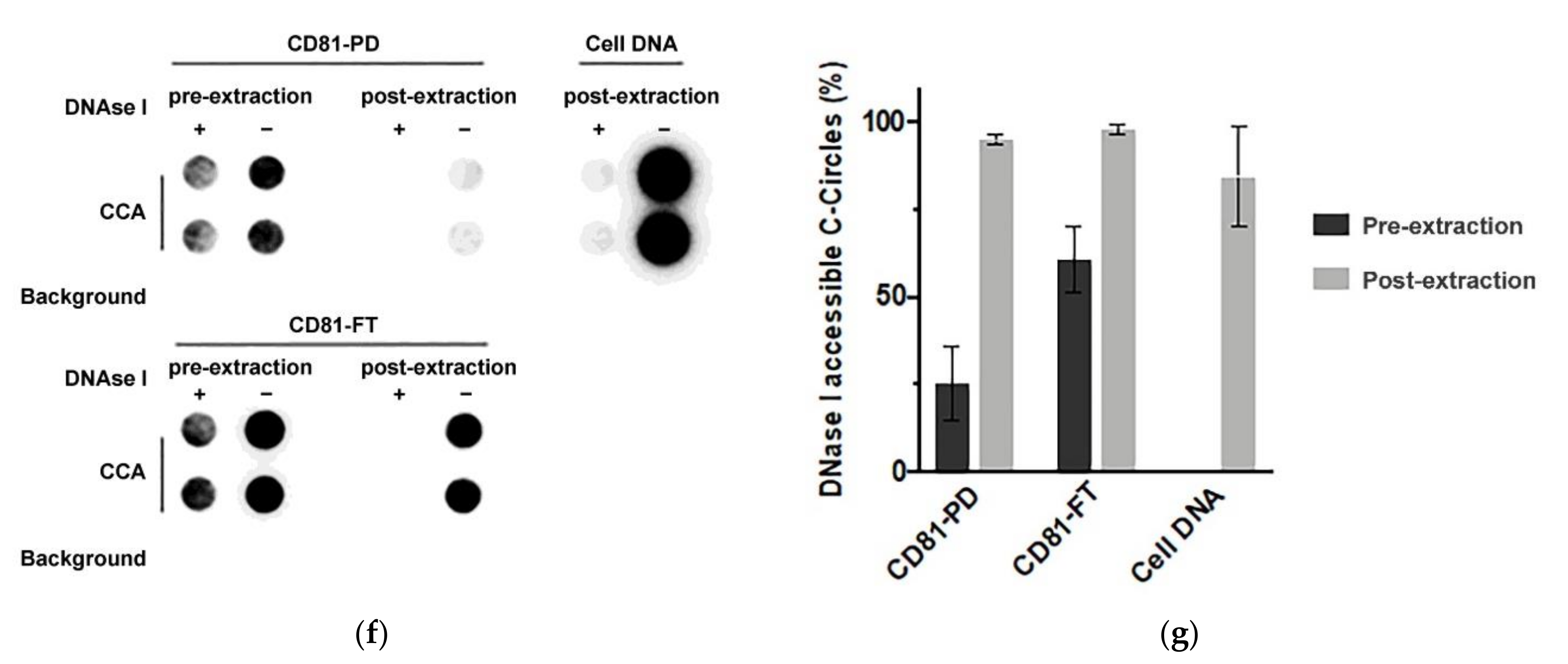
2.5. DNA Extraction/Preparation and Nuclease Protection Assay
2.6. C-Circle Assay
2.7. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of Exosomes and Microvesicles by Differential Centrifugation
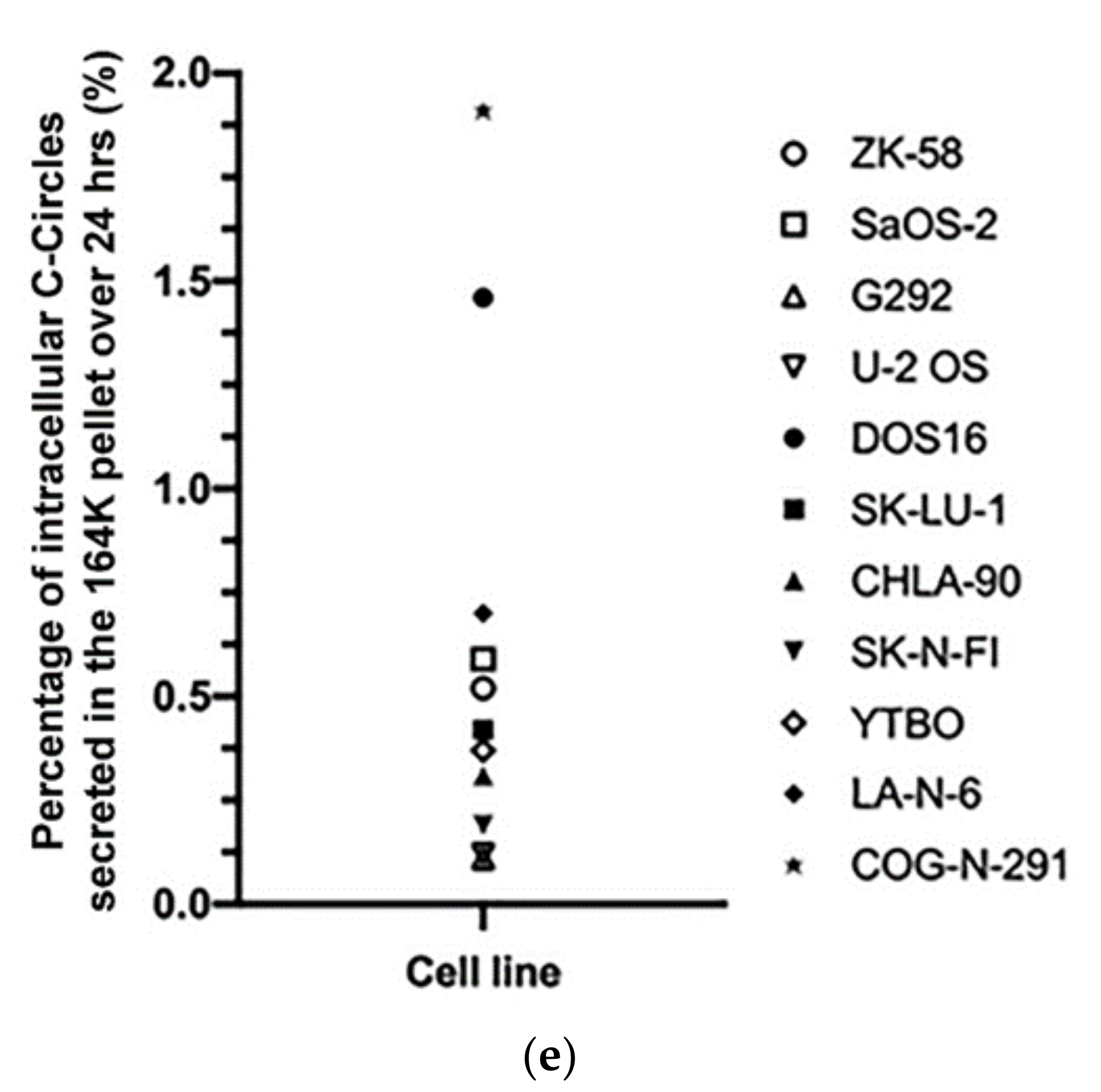
3.2. C-Circles Are Secreted inside Exosomes in ALT+ Cancer Cell Lines
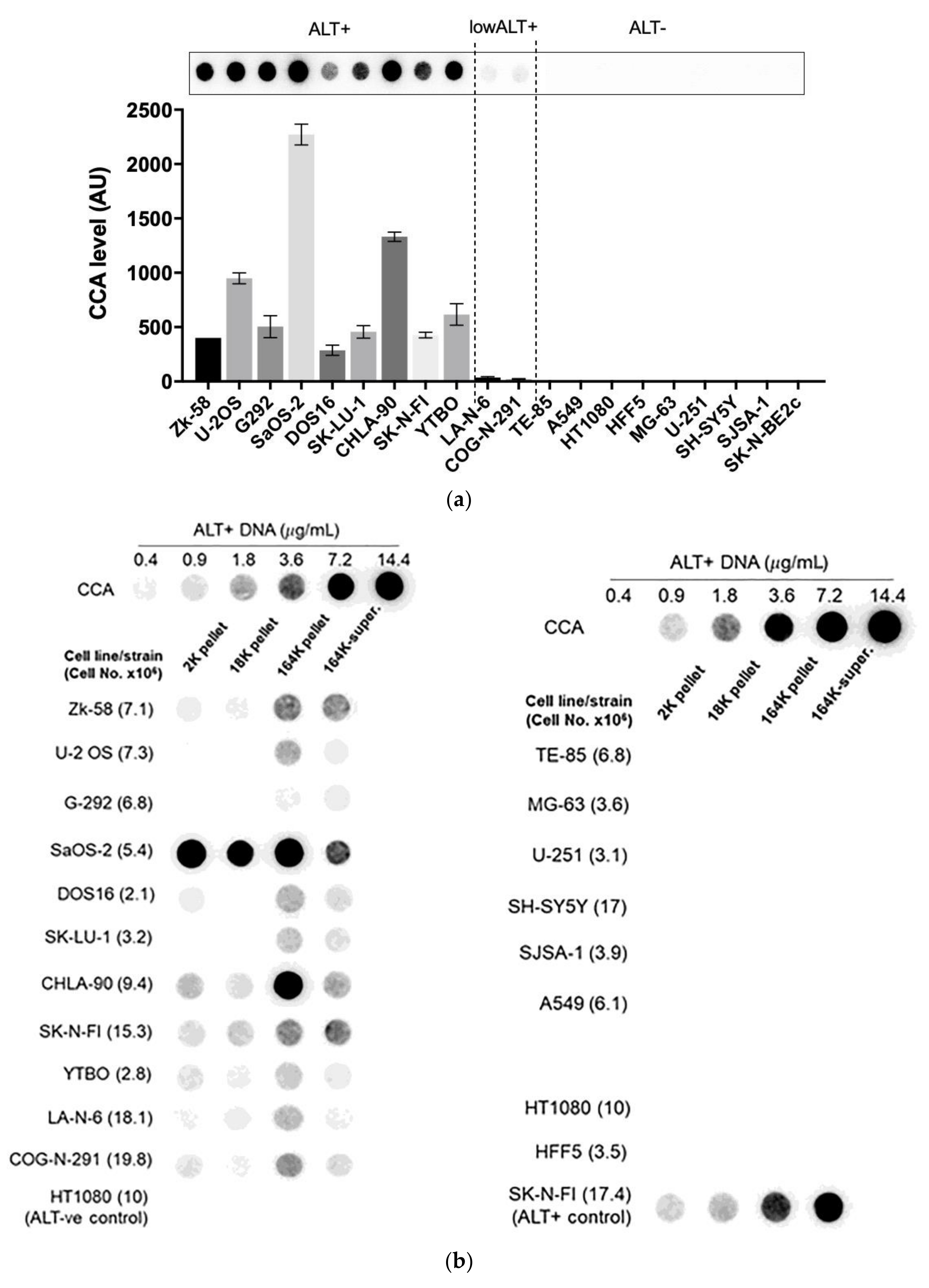
3.3. A Diverse Panel of ALT+ Cell Lines Secrete C-Circles in Exosomes
3.4. Density Gradient Purification Confirms C-Circles Are Secreted in Exosomes
3.5. Immuno-Purification Confirms That Some C-Circles Are Secreted in Exosomes
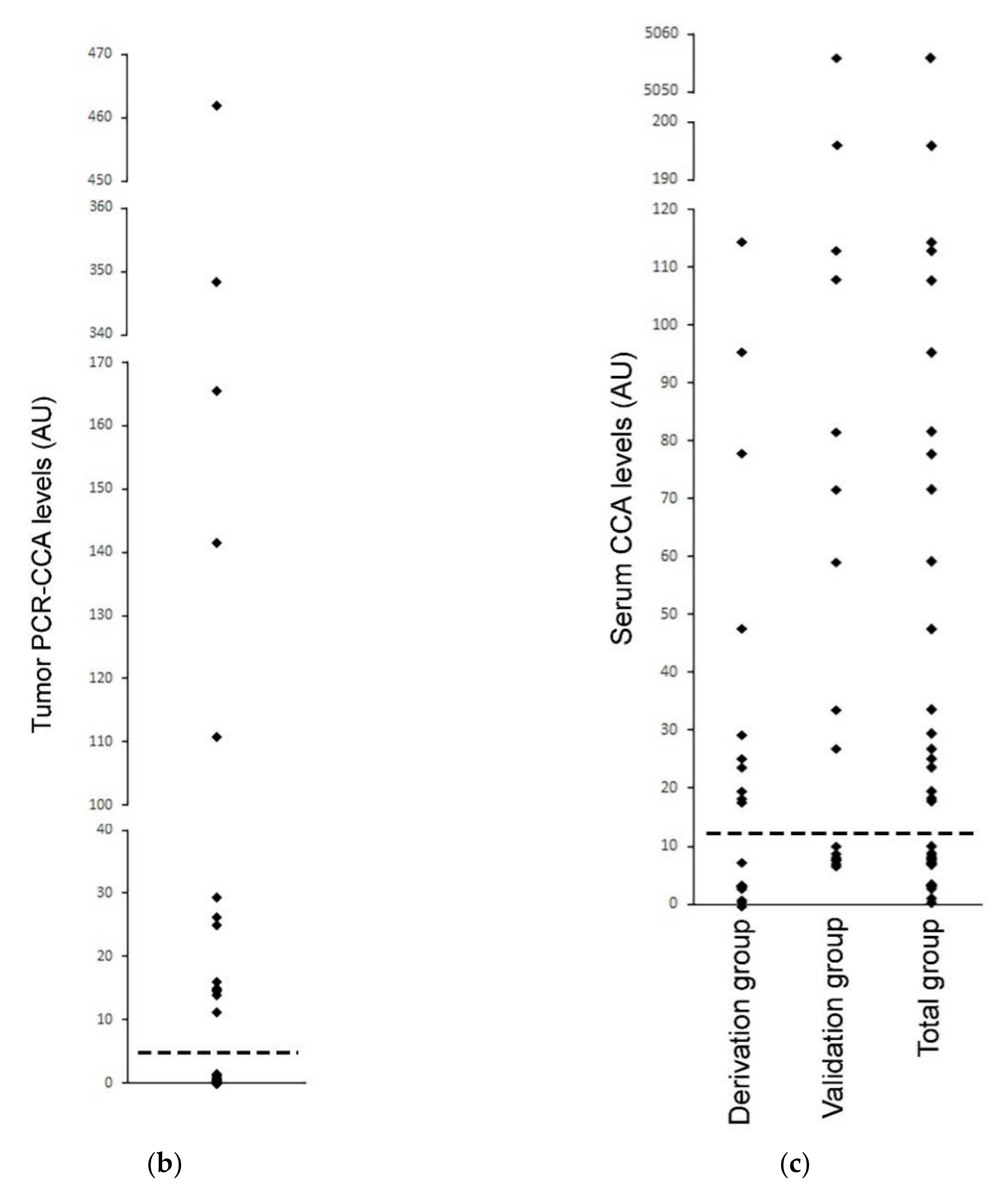
3.6. Serum-Based CCA as an ALT Diagnostic in Neuroblastoma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henson, J.D.; Reddel, R.R. Assaying and investigating Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres activity in human cells and cancers. Febs Lett. 2010, 584, 3800–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loe, T.K.; Li, J.S.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Azeroglu, B.; Boddy, M.N.; Denchi, E.L. Telomere length heterogeneity in ALT cells is maintained by PML-dependent localization of the BTR complex to telomeres. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, T.R.; Neumann, A.A.; Englezou, A.; Huschtscha, L.I.; Noble, J.R.; Reddel, R.R. Telomerase-negative immortalized human cells contain a novel type of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) body. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4175–4179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henson, J.D.; Hannay, J.A.; McCarthy, S.W.; Royds, J.A.; Yeager, T.R.; Robinson, R.A.; Wharton, S.B.; Jellinek, D.A.; Arbuckle, S.M.; Yoo, J.; et al. A robust assay for alternative lengthening of telomeres in tumors shows the significance of alternative lengthening of telomeres in sarcomas and astrocytomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, E.; Argani, P.; Hicks, J.L.; DeMarzo, A.M.; Meeker, A.K. Telomere lengths of translocation-associated and nontranslocation-associated sarcomas differ dramatically. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryan, T.M.; Englezou, A.; Dalla-Pozza, L.; Dunham, M.A.; Reddel, R.R. Evidence for an alternative mechanism for maintaining telomere length in human tumors and tumor-derived cell lines. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, T.M.; Englezou, A.; Gupta, J.; Bacchetti, S.; Reddel, R.R. Telomere elongation in immortal human cells without detectable telomerase activity. Embo J. 1995, 14, 4240–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesare, A.J.; Kaul, Z.; Cohen, S.B.; Napier, C.E.; Pickett, H.A.; Neumann, A.A.; Reddel, R.R. Spontaneous occurrence of telomeric DNA damage response in the absence of chromosome fusions. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovejoy, C.A.; Li, W.; Reisenweber, S.; Thongthip, S.; Bruno, J.; de Lange, T.; De, S.; Petrini, J.H.; Sung, P.A.; Jasin, M.; et al. Loss of ATRX, genome instability, and an altered DNA damage response are hallmarks of the alternative lengthening of telomeres pathway. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovejoy, C.A.; Takai, K.; Huh, M.S.; Picketts, D.J.; de Lange, T. ATRX affects the repair of telomeric DSBs by promoting cohesion and a DAXX-dependent activity. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.A.; Shen, Y.L.; Hsia, H.Y.; Tiang, Y.P.; Sung, T.L.; Chen, L.Y. Extrachromosomal telomere repeat DNA is linked to ALT development via cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, K.J.; Carroll, P.; Martin, C.A.; Murina, O.; Fluteau, A.; Simpson, D.J.; Olova, N.; Sutcliffe, H.; Rainger, J.K.; Leitch, A.; et al. cGAS surveillance of micronuclei links genome instability to innate immunity. Nature 2017, 548, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henson, J.D.; Cao, Y.; Huschtscha, L.I.; Chang, A.C.; Au, A.Y.; Pickett, H.A.; Reddel, R.R. DNA C-circles are specific and quantifiable markers of alternative-lengthening-of-telomeres activity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shengzhao, G.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y. Strand break-induced replication fork collapse leads to C-circles, C-overhangs and telomeric recombination. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henson, J.D.; Lau, L.M.; Koch, S.; Martin La Rotta, N.; Dagg, R.A.; Reddel, R.R. The C-Circle Assay for alternative-lengthening-of-telomeres activity. Methods 2017, 114, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniloski, Z.; Smith, S. Loss of Tumor Suppressor STAG2 Promotes Telomere Recombination and Extends the Replicative Lifespan of Normal Human Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5530–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udugama, M.M.; Chang, F.T.; Chan, F.L.; Tang, M.C.; Pickett, H.A.R.; McGhie, J.D.; Wong, L.H. Histone variant H3.3 provides the heterochromatic H3 lysine 9 tri-methylation mark at telomeres. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10227–10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilley, R.L.; Verma, P.; Cho, N.W.; Winters, H.D.; Wondisford, A.R.; Greenberg, R.A. Break-induced telomere synthesis underlies alternative telomere maintenance. Nature 2016, 539, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, R.J.; Arnoult, N.; Lackner, D.H.; Oganesian, L.; Haggblom, C.; Corpet, A.; Almouzni, G.; Karlseder, J. Rapid induction of alternative lengthening of telomeres by depletion of the histone chaperone ASF1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres Mediated by Mitotic DNA Synthesis Engages Break-Induced Replication Processes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 37, e00226–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagg, R.A.; Pickett, H.A.; Neumann, A.A.; Napier, C.E.; Henson, J.D.; Teber, E.T.; Arthur, J.W.; Reynolds, C.P.; Murray, J.; Haber, M.; et al. Extensive Proliferation of Human Cancer Cells with Ever-Shorter Telomeres. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Dahmane, N.; Tsai, K.; Wang, P.; Williams, D.R.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Showe, L.C.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Q.; et al. Telomeric repeat-containing RNA (TERRA) constitutes a nucleoprotein component of extracellular inflammatory exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6293–E6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, C.; Heuser, J.; Stahl, P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 97, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.T.; Teng, K.; Wu, C.; Adam, M.; Johnstone, R.M. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thery, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollert, T.; Hurley, J.H. Molecular mechanism of multivesicular body biogenesis by ESCRT complexes. Nature 2010, 464, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Thery, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Aleckovic, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; Garcia-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Understanding extracellular vesicle diversity-current status. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Hvam, M.L.; Primdahl-Bengtson, B.; Boysen, A.T.; Whitehead, B.; Dyrskjot, L.; Orntoft, T.F.; Howard, K.A.; Ostenfeld, M.S. Comparative analysis of discrete exosome fractions obtained by differential centrifugation. J. Extracell Vesicles 2014, 3, 25011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grootjans, J.J.; Zimmermann, P.; Reekmans, G.; Smets, A.; Degeest, G.; Durr, J.; David, G. Syntenin, a PDZ protein that binds syndecan cytoplasmic domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13683–13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latysheva, N.; Muratov, G.; Rajesh, S.; Padgett, M.; Hotchin, N.A.; Overduin, M.; Berditchevski, F. Syntenin-1 is a new component of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains: Mechanisms and consequences of the interaction of syntenin-1 with CD63. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 7707–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, L.M.; Dagg, R.A.; Henson, J.D.; Au, A.Y.; Royds, J.A.; Reddel, R.R. Detection of alternative lengthening of telomeres by telomere quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Wauben, M.H. Immune cell-derived vesicles: Modulators and mediators of inflammation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2357–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
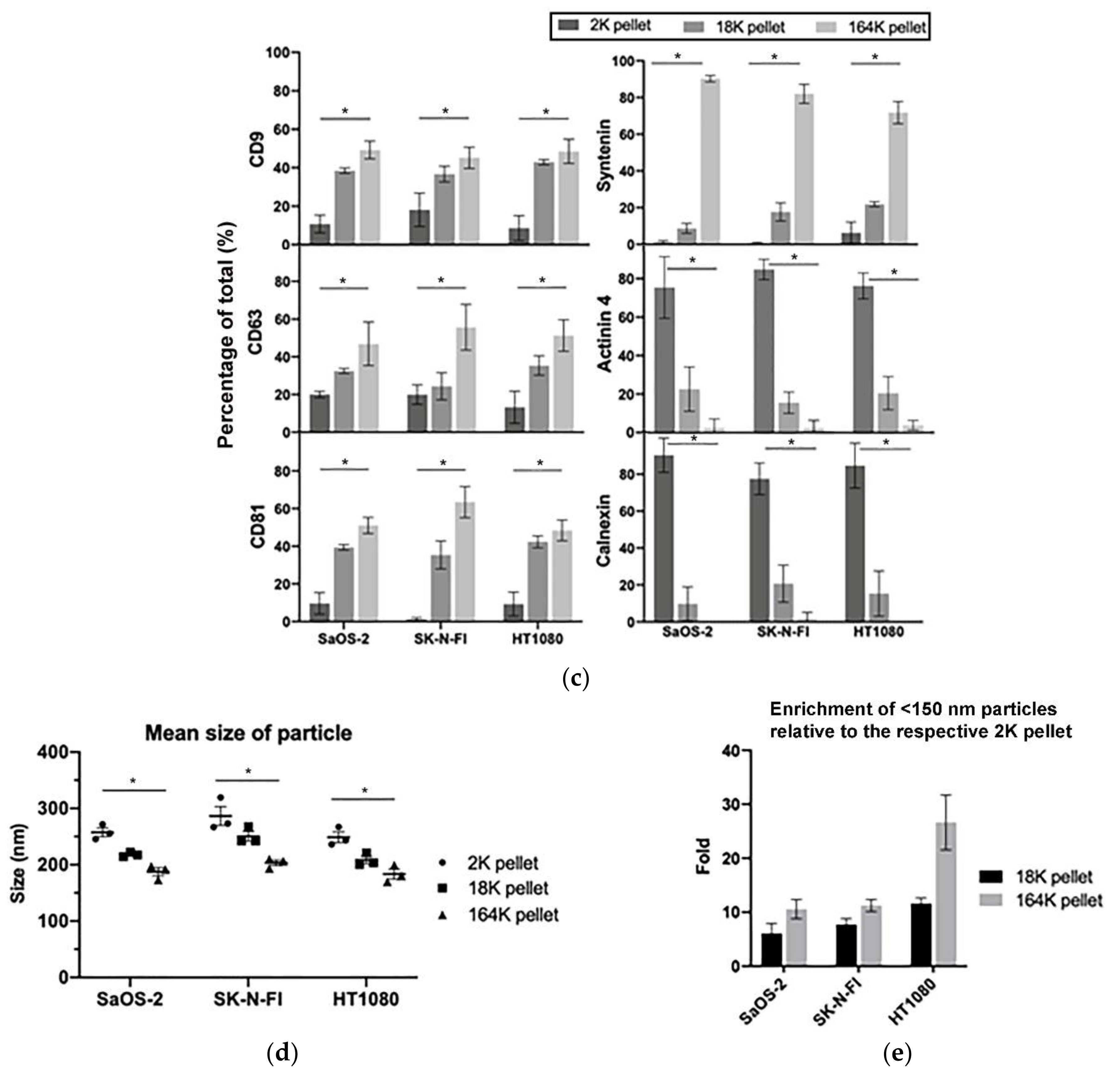




| Characteristic | Percentage of All Pellets Combined; Mean (±95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (Protein/DNA) | 2K Pellet | 18K Pellet | 164K Pellet |
| AB (Calnexin) | 84% (9%) | 15% (8%) | 1% (2%) |
| MV and AB (Actinin-4) | 80% (9%) | 19% (7%) | 1% (3%) |
| EXO (Syntenin) | 1% (1%) | 9% (2%) | 90% (1%) |
| CD9 | 14% (6%) | 38% (3%) | 47% (4%) |
| CD63 | 20% (3%) | 29% (5%) | 51% (9%) |
| CD81 | 5% (5%) | 37% (4%) | 57% (7%) |
| C-Circles | 27% (10%) | 19% (4%) | 53% (10%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-Y.; Dagg, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, J.H.Y.; Lu, R.; Martin La Rotta, N.; Sampl, S.; Korkut-Demirbaş, M.; Holzmann, K.; Lau, L.M.S.; et al. The C-Circle Biomarker Is Secreted by Alternative-Lengthening-of-Telomeres Positive Cancer Cells inside Exosomes and Provides a Blood-Based Diagnostic for ALT Activity. Cancers 2021, 13, 5369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215369
Chen Y-Y, Dagg R, Zhang Y, Lee JHY, Lu R, Martin La Rotta N, Sampl S, Korkut-Demirbaş M, Holzmann K, Lau LMS, et al. The C-Circle Biomarker Is Secreted by Alternative-Lengthening-of-Telomeres Positive Cancer Cells inside Exosomes and Provides a Blood-Based Diagnostic for ALT Activity. Cancers. 2021; 13(21):5369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215369
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuan-Yin, Rebecca Dagg, Yuchen Zhang, Joyce H. Y. Lee, Robert Lu, Nancy Martin La Rotta, Sandra Sampl, Medina Korkut-Demirbaş, Klaus Holzmann, Loretta M. S. Lau, and et al. 2021. "The C-Circle Biomarker Is Secreted by Alternative-Lengthening-of-Telomeres Positive Cancer Cells inside Exosomes and Provides a Blood-Based Diagnostic for ALT Activity" Cancers 13, no. 21: 5369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215369
APA StyleChen, Y. -Y., Dagg, R., Zhang, Y., Lee, J. H. Y., Lu, R., Martin La Rotta, N., Sampl, S., Korkut-Demirbaş, M., Holzmann, K., Lau, L. M. S., Reddel, R. R., & Henson, J. D. (2021). The C-Circle Biomarker Is Secreted by Alternative-Lengthening-of-Telomeres Positive Cancer Cells inside Exosomes and Provides a Blood-Based Diagnostic for ALT Activity. Cancers, 13(21), 5369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215369








