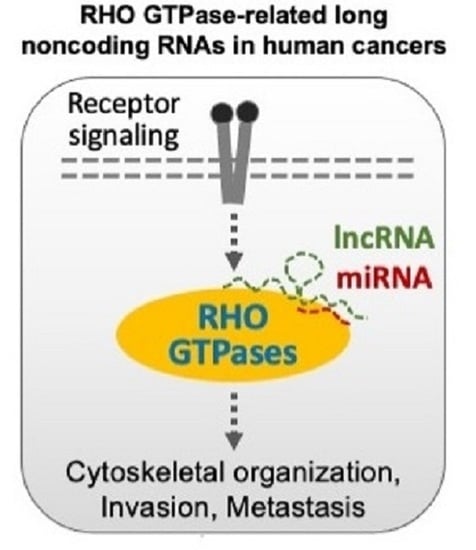
RHO GTPase-Related Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancers
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. RHOA-Related lncRNAs
1.2. RHOB-Related lncRNAs
1.3. RHOC-Related lncRNAs
1.4. RAC1-Related lncRNAs
1.5. CDC42-Related lncRNAs
2. Indirect Regulatory Effects of lncRNAs on RHO GTPases
3. Epigenetic Regulation of RHO GTPases by lncRNAs
4. lncRNAs as Novel Therapeutic Targets
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDIs | GDP dissociation inhibitors |
| GEFs | guanine nucleotide exchange factors |
| GAPs | GTPase-activating proteins |
| microRNA | miRNA |
| lncRNAs | long non-coding RNAs |
| CeRNAs | competing endogenous RNAs |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| GC | gastric cancer |
| MALAT1 | metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 |
| PDAC | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells |
| NORAD | non-coding RNA activated by DNA damage |
| RBPs | RNA-binding proteins |
| EMT | epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| ZFAS1 | zinc finger antisense 1 |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| PCAT6 | prostate cancer-associated transcript 6 |
| PCGEM1 | prostate cancer gene expression marker 1 |
| GAS5 | growth arrest specific 5 |
| TDRG1 | testis developmental-related gene 1 |
| EOC | epithelial ovarian cancer |
| PCA3 | prostate cancer gene 3 |
| CDKN2B-AS1 | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1 |
| AURKAPS1 | pseudogene of aurora kinase A |
| LCAT1 | lung cancer associated transcript 1 |
| LSINCT5 | long stress-induced noncoding transcripts |
| TP73-AS1 | P73 antisense RNA 1 |
| FTH1P3 | ferritin heavy chain 1 pseudogene 3 |
| XCI | X-chromosome inactivation |
| ESCC | esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| TUG1 | taurine upregulated 1 |
| SNHG1 | small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 |
| EC | esophageal cancer |
| SNHG15 | small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 |
| M6A | N6-Methyladenosine (m6A). |
References
- Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Always look on the bright site of Rho: Structural implications for a conserved intermolecular interface. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosaddeghzadeh, N.; Ahmadian, M.R. The RHO family GTPases: Mechanisms of regulation and signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mata, R.; Boulter, E.; Burridge, K. The’invisible hand’: Regulation of RHO GTPases by RHOGDIs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J.; Sondek, J. GEF means go: Turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-C.; Gremer, L.; Heise, H.; Janning, P.; Shymanets, A.; Cirstea, I.C.; Krause, E.; Nürnberg, B.; Ahmadian, M.R. Liposome reconstitution and modulation of recombinant prenylated human Rac1 by GEFs, GDI1 and Pak1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, M.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Deciphering the molecular and functional basis of Dbl family proteins: A novel systematic approach toward classification of selective activation of the Rho family proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 4486–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakhaei-Rad, S.; Haghighi, F.; Nouri, P.; Rezaei Adariani, S.; Lissy, J.; Kazemein Jasemi, N.S.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Structural fingerprints, interactions, and signaling networks of RAS family proteins beyond RAS isoforms. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 130–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaeizadeh, H.; Amin, E.; Nakhaei-Rad, S.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. The RAS-Effector Interface: Isoform-Specific Differences in the Effector Binding Regions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, A.E.; Visco, I.; Bieling, P.; Bement, W.M. Extraction of active RhoGTPases by RhoGDI regulates spatiotemporal patterning of RhoGTPases. Elife 2019, 8, e50471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.; Mitin, N.; Keller, P.J.; Chenette, E.J.; Madigan, J.P.; Currin, R.O.; Cox, A.D.; Wilson, O.; Kirschmeier, P.; Der, C.J. Rho Family GTPase modification and dependence on CAAX motif-signaled posttranslational modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25150–25163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitin, N.; Roberts, P.J.; Chenette, E.J.; Der, C.J. Posttranslational lipid modification of Rho family small GTPases. In Rho GTPases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Phuyal, S.; Farhan, H. Multifaceted Rho GTPase Signaling at the Endomembranes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherfils, J.; Zeghouf, M. Regulation of small gtpases by gefs, gaps, and gdis. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 269–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, M.; Communication, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Fansa, E.K.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. New insight into the molecular switch mechanism of human Rho family proteins: Shifting a paradigm. Biol. Chem 2012, 394, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, R.G.; Ridley, A.J. Regulation and functions of RhoU and RhoV. Small GTPases 2020, 11, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bustelo, X.R. RHO GTPases in cancer: Known facts, open questions, and therapeutic challenges. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, R.B.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases: Regulation and roles in cancer cell biology. Small GTPases 2016, 7, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, A.; Nobes, C.D. Rho GTPases: Molecular switches that control the organization and dynamics of the actin cytoskeleton. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, N.S.; Ridley, A.J. Targeting Rho GTPase Signaling Networks in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Manneville, S.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002, 420, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. RHO GTPASES in neuronal morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 1, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulloy, J.C.; Cancelas, J.A.; Filippi, M.-D.; Kalfa, T.A.; Guo, F.; Zheng, Y. Rho GTPases in hematopoiesis and hemopathies. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2010, 115, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Ou, J.N.; Cao, L.F.; Peng, X.Q.; Li, Y.M.; Tian, Y.Q. The Autism-Related lncRNA MSNP1AS Regulates Moesin Protein to Influence the RhoA, Rac1, and PI3K/Akt Pathways and Regulate the Structure and Survival of Neurons. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensmark, J.H.; Brakebusch, C. Rho GTPases in cancer: Friend or foe? Oncogene 2019, 38, 7447–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menacho-Marquez, M.; García-Escudero, R.; Ojeda, V.; Abad, A.; Delgado, P.; Costa, C.; Ruiz, S.; Alarcón, B.; Paramio, J.M.; Bustelo, X.R. The Rho exchange factors Vav2 and Vav3 favor skin tumor initiation and promotion by engaging extracellular signaling loops. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Justilien, V.; Ali, S.A.; Jamieson, L.; Yin, N.; Cox, A.D.; Der, C.J.; Murray, N.R.; Fields, A.P. Ect2-dependent rRNA synthesis is required for KRAS-TRP53-driven lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonyo, P.; Bergom, C.; Brandt, A.C.; Tsaih, S.-W.; Sun, Y.; Bigley, T.M.; Lorimer, E.L.; Terhune, S.S.; Rui, H.; Flister, M.J. SmgGDS is a transient nucleolar protein that protects cells from nucleolar stress and promotes the cell cycle by regulating DREAM complex gene expression. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6873–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Justilien, V.; Lewis, K.C.; Murray, N.R.; Fields, A.P. Oncogenic Ect2 signaling regulates rRNA synthesis in NSCLC. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancione, M.; Cerulo, L.; Remo, A.; Giordano, G.; Gutierrez-Uzquiza, Á.; Bragado, P.; Porras, A. Centrosome Dynamics and Its Role in Inflammatory Response and Metastatic Process. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantopoulou, Z.; White, G.; Fadlullah, M.Z.; Dreger, M.; Pickering, K.; Maltas, J.; Ashton, G.; MacLeod, R.; Baillie, G.S.; Kouskoff, V. TIAM1 antagonizes TAZ/YAP both in the destruction complex in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus to inhibit invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 621–634.e626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vu, H.L.; Rosenbaum, S.; Purwin, T.J.; Davies, M.A.; Aplin, A.E. RAC1 P29S regulates PD-L1 expression in melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspenström, P. Activated Rho GTPases in Cancer-The Beginning of a New Paradigm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Luo, W.; Yue, X.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Chang, J. Identification and characterization of a new isoform of small GTPase RhoE. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, D.R.; Olson, M.F. Transcriptional regulation of Rho GTPase signaling. Transcription 2011, 2, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Villarreal, O.D.; Chen, X.; Zandee, S.; Young, Y.K.; Torok, C.; Lamarche-Vane, N.; Prat, A.; Rivest, S.; Gosselin, D.; et al. QUAKING Regulates Microexon Alternative Splicing of the Rho GTPase Pathway and Controls Microglia Homeostasis. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiegen, D.; Haeusler, L.-C.; Blumenstein, L.; Herbrand, U.; Dvorsky, R.; Vetter, I.R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Alternative splicing of Rac1 generates Rac1b, a self-activating GTPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4743–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Bi, F.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y. Rho GTPase regulation by miRNAs and covalent modifications. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, M.F. Rho GTPases, their post-translational modifications, disease-associated mutations and pharmacological inhibitors. Small GTPases 2018, 9, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynds, D.L. Subcellular localization of Rho GTPases: Implications for axon regeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1032–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olayioye, M.A.; Noll, B.; Hausser, A. Spatiotemporal Control of Intracellular Membrane Trafficking by Rho GTPases. Cells 2019, 8, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiering, D.; Hodgson, L. Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, W.; Feng, W.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ke, Y.; Shi, X.; Ju, S.; Cong, H.; Wang, X.; Cui, M. LncRNA CTC-497E21. 4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via modulating miR-22/NET1 axis through RhoA signaling pathway. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Li, G.; Dou, F. Long-chain non-coding RNA LOC554202 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by binding to microRNA-31 expression and regulating RhoA expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10550–10556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, C. LncRNA ZFAS1 promotes pancreatic adenocarcinoma metastasis via the RHOA/ROCK2 pathway by sponging miR-3924. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Ying, X.; Song, J.; Chen, C.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Z. Long Non-Coding RNA PCAT6 Induces M2 Polarization of Macrophages in Cholangiocarcinoma via Modulating miR-326 and RhoA-ROCK Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 605877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.-C.; Ni, J.-J.; Cui, W.-Y.; Wang, B.-Y.; Zhuo, W. Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Carlevaro-Fita, J.; Lanzós, A.; Feuerbach, L.; Hong, C.; Mas-Ponte, D.; Pedersen, J.S.; Abascal, F.; Amin, S.B.; Bader, G.D.; Barenboim, J.; et al. Cancer LncRNA Census reveals evidence for deep functional conservation of long noncoding RNAs in tumorigenesis. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.-Z.; Luo, D.-X.; Mo, Y.-Y. Emerging roles of lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Genes Dis. 2019, 6, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, G.J.; Wickramasinghe, V.O. RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, C.A.; Chen, C.K.; Chow, A.; Surka, C.F.; Tran, C.; McDonel, P.; Pandya-Jones, A.; Blanco, M.; Burghard, C.; Moradian, A.; et al. The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature 2015, 521, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Piao, H.-L.; Kim, B.-J.; Yao, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Siverly, A.N.; Lawhon, S.E.; Ton, B.N.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Urrutia, E.; Bustamante Montes, L.P.; Ladrón de Guevara Cervantes, D.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Campos-Parra, A.D. Crosstalk Between Long Non-coding RNAs, Micro-RNAs and mRNAs: Deciphering Molecular Mechanisms of Master Regulators in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Bu, J. LncRNA GAS5 Regulates Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Regulating RHOB via Sponging miR-663a. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Ding, T.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Tian, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shen, H. LncRNA NR2F2-AS1 Upregulates Rac1 to Increase Cancer Stemness in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, L.M.; Gautier, M.; Allan, R.; Ilié, M.; Nottet, N.; Pons, N.; Paquet, A.; Lebrigand, K.; Truchi, M.; Fassy, J.; et al. Correction: The nuclear hypoxia-regulated NLUCAT1 long non-coding RNA contributes to an aggressive phenotype in lung adenocarcinoma through regulation of oxidative stress. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Noroozi, R.; Abak, A.; Taheri, M.; Salimi, A. Emerging role of lncRNAs in the regulation of Rho GTPase pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehl, T.; Backes, C.; Kern, F.; Fehlmann, T.; Ludwig, N.; Meese, E.; Lenhof, H.-P.; Keller, A. About miRNAs, miRNA seeds, target genes and target pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107167–107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humphries, B.A.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C. MicroRNA regulation of the small rho gtpase regulators—Complexities and opportunities in targeting cancer metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algaber, A.; Al-Haidari, A.; Madhi, R.; Rahman, M.; Syk, I.; Thorlacius, H. MicroRNA-340-5p inhibits colon cancer cell migration via targeting of RhoA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, J.; Chang, D.; Lv, D.; Li, H.; Feng, H. Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA. Open Med. 2020, 15, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tang, Q.; Qiu, M.; Lang, N.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Bi, F. miR-21 targets the tumor suppressor RhoB and regulates proliferation, invasion and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.S.; Wu, X.D.; Zhang, S.Q.; Li, C.F.; Yang, L.; Li, D.D.; Zhang, B.G.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.P.; Zhang, B. The tumor suppressor gene RhoBTB1 is a novel target of miR-31 in human colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, M.; Nam, J.-W.; Kim, V.N. miR-29 miRNAs activate p53 by targeting p85α and CDC42. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lang, N.; Qiu, M.; Xu, F.; Li, Q.; Tang, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. miR-137 targets Cdc42 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Yang, F.; Qi, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Yi, T.; Yin, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, X.; Bian, C. LncRNA DANCR promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in ovarian cancer through direct targeting of miR-145. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hou, J.; Shan, F.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Ren, T. Long Non-Coding RNA CRNDE Promotes Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Progression and Paclitaxel Resistance by Regulating miR-126-5p/ATAD2 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eißmann, M.; Gutschner, T.; Hämmerle, M.; Günther, S.; Caudron-Herger, M.; Groß, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Rippe, K.; Braun, T.; Zörnig, M.; et al. Loss of the abundant nuclear non-coding RNA MALAT1 is compatible with life and development. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, P.; Diederichs, S.; Wang, W.; Böing, S.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Tidow, N.; Brandt, B.; Buerger, H.; Bulk, E. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin β 4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8031–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Shen, F.; Zhao, L. The relationship between lncRNA PCGEM1 and STAT3 during the occurrence and development of endometrial carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liang, G.; Yuan, B.; Yang, C.; Gao, R.; Zhou, X. MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hamblin, M.H.; Yin, K.-J. The long noncoding RNA Malat1: Its physiological and pathophysiological functions. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, M.; Wu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, G.; Yuan, D.; Song, Y. Post-transcriptional regulation of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-B.; Ma, G.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Jing, C.; Gao, K.; Liu, Z.-H.; Yu, S.-J. miR-429 inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristóbal, I.; Rincón, R.; Manso, R.; Caramés, C.; Aguilera, O.; Madoz-Gurpide, J.; Rojo, F.; García-Foncillas, J. Deregulation of miR-200b, miR-200c and miR-429 indicates its potential relevant role in patients with colorectal cancer liver metastasis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Peng, P. miR-429 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by downregulation of TLN1. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, J. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 interaction with miR-429 regulates the proliferation and EMT of lung adenocarcinoma cells through RhoA. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, G.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, H. Noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD): Biologic function and mechanisms in human cancers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 489, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kopp, F.; Chang, T.-C.; Sataluri, A.; Chen, B.; Sivakumar, S.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Mendell, J.T. Noncoding RNA NORAD regulates genomic stability by sequestering PUMILIO proteins. Cell 2016, 164, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munschauer, M.; Nguyen, C.T.; Sirokman, K.; Hartigan, C.R.; Hogstrom, L.; Engreitz, J.M.; Ulirsch, J.C.; Fulco, C.P.; Subramanian, V.; Chen, J. The NORAD lncRNA assembles a topoisomerase complex critical for genome stability. Nature 2018, 561, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Hu, P.; Ding, Y.-S. LncRNA NORAD contributes to colorectal cancer progression by inhibition of miR-202-5p. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Qu, C.; Wang, N. Long non-coding RNA NORAD upregulate SIP1 expression to promote cell proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Ou, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Hao, Y.; Li, W. High long non-coding RNA NORAD expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes breast cancer progression by regulating TGF-β pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, L. The long noncoding RNA NORAD promotes the growth of gastric cancer cells by sponging miR-608. Gene 2019, 687, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, N. LncRNA NORAD, sponging miR-363-3p, promotes invasion and EMT by upregulating PEAK1 and activating the ERK signaling pathway in NSCLC cells. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2021, 53, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Mao, F. LncRNA NORAD accelerates the progression and doxorubicin resistance of neuroblastoma through up-regulating HDAC8 via sponging miR-144-3p. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Lu, Z.; You, Z.; Sun, J. Long noncoding RNA NORAD regulates cancer cell proliferation and migration in human osteosarcoma by endogenously competing with miR-199a-3p. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Ji, L.; Ke, M.; Ou, Z.; Tang, N.; Li, Y. miR-125a-3p is responsible for chemosensitivity in PDAC by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Fyn. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.; Huo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhan, Q.; Cheng, D.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.; Peng, C. Long noncoding RNA NORAD, a novel competing endogenous RNA, enhances the hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian-Amiri, M.E.; Crawford, J.; French, J.D.; Smart, C.E.; Smith, M.A.; Clark, M.B.; Ru, K.; Mercer, T.R.; Thompson, E.R.; Lakhani, S.R. SNORD-host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer. Rna 2011, 17, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, S.; Fan, C.; Liu, N.; Huang, K.; Fang, X.; Wang, K. Downregulation of the long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 is associated with cell proliferation, migration and invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6405–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, G.; Cheng, B.; Jiang, R. ZFAS1 functions as an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in bladder cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Xie, J.; Shen, C.; Cheng, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Shen, B.; Peng, C. Amplification of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.; Yao, H. ZFAS1 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Metastasis Through Modulating miR-34b/SOX4 Targeting. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, G. lncRNA ZFAS1 is involved in the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells through competitively binding to miR-135a-5p. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, F.; Meng, F.; Wang, X. Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 20, 5126–5131. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Mu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Sun, M. ZFAS1: A novel tumor-related long non-coding RNA. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensner, J.R.; Iyer, M.K.; Balbin, O.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, J.C.; Laxman, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Grasso, C.S.; Kominsky, H.D. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Guo, W. Promising role of long non-coding RNA PCAT6 in malignancies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Lun, Y.; Sun, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, G.; Quan, J. Silencing of long non-coding RNA PCAT6 restrains gastric cancer cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting microRNA-15a. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2020, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, G.; Li, A.; Liu, X. LncRNA PCAT6 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes proliferation through the regulation of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Gu, G.; Pan, W.; Chen, X. LncRNA PCAT6 accelerates the progression and chemoresistance of cervical cancer through up-regulating ZEB1 by sponging miR-543. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Feng, X.; Hua, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, B.; Lu, K.; Nie, F. Long noncoding RNA PCAT6 functions as an oncogene by binding to EZH2 and suppressing LATS2 in non-small-cell lung cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, K.; Cheng, Z.-X.; Sun, Q.-C.; Wang, J.-J. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA PCAT6 inhibits proliferation and invasion in lung cancer cells. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2016, 24, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zou, Q.; He, H.; Liang, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, D.; Shen, L. Long non-coding RNA PCAT6 targets miR-204 to modulate the chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil-based treatment through HMGA2 signaling. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2484–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.-J.; Wan, J.; Wang, C.-B. MiR-326: Promising biomarker for cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 10411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jafarzadeh, M.; Soltani, B.M.; Soleimani, M.; Hosseinkhani, S. Epigenetically silenced LINC02381 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Biochimie 2020, 171, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, M.; Soltani, B.M. Long noncoding RNA LOC400043 (LINC02381) inhibits gastric cancer progression through regulating Wnt signaling pathway. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Q. Linc02381 Exacerbates rheumatoid arthritis through adsorbing miR-590-5p and activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis-fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 0963689720938023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, J.P.; Fendler, A.; Bild, M.; Jung, U.; Müller, H.; Arntzen, M.Ø.; Piso, C.; Stephan, C.; Thiede, B.; Mollenkopf, H.-J.; et al. MiR-133b targets antiapoptotic genes and enhances death receptor-induced apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Zhou, C.-X.; Zhan, M.-N.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.-L.; Ma, C.-N.; He, M.; Chen, G.-Q.; He, J.-R.; Zhao, Q. MiR-133b targets Sox9 to control pathogenesis and metastasis of breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Su, H.; Xie, P.; Ran, J. LINC02381 Promoted Cell Viability and Migration via Targeting miR-133b in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3971–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikantan, V.; Zou, Z.; Petrovics, G.; Xu, L.; Augustus, M.; Davis, L.; Livezey, J.R.; Connell, T.; Sesterhenn, I.A.; Yoshino, K.; et al. PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene, is overexpressed in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12216–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrovics, G.; Zhang, W.; Makarem, M.; Street, J.P.; Connelly, R.; Sun, L.; Sesterhenn, I.A.; Srikantan, V.; Moul, J.W.; Srivastava, S. Elevated expression of PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene with cell growth-promoting function, is associated with high-risk prostate cancer patients. Oncogene 2004, 23, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Chen, C.; Ni, H.; Sheng, N.; Hua, M.; Wu, Y. Down-regulation of lncRNA PCGEM1 inhibits cervical carcinoma by modulating the miR-642a-5p/LGMN axis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 117, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, L.; Qiu, K.; Gao, W.; Shi, C.; Shu, F. LncRNA PCGEM1 accelerates non-small cell lung cancer progression via sponging miR-433-3p to upregulate WTAP. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-L.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, X.-B.; You, R.-K.; An, X.-W.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, R.-S. LncRNA PCGEM1 contributes to malignant behaviors of glioma by regulating miR-539-5p/CDK6 axis. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, L.L.; Sun, K.X.; Liu, Y.; Guan, X.; Zong, Z.H.; Zhao, Y. LncRNA PCGEM1 Induces Ovarian Carcinoma Tumorigenesis and Progression Through RhoA Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.; Cao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, B.; Huang, J.; Xiong, S.; yu Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Li, H. A novel role for microRNA-129-5p in inhibiting ovarian cancer cell proliferation and survival via direct suppression of transcriptional co-activators YAP and TAZ. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.A.; Gilkes, D.M. RhoB: Team Oncogene or Team Tumor Suppressor? Genes 2018, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvayrac, O.; Mazières, J.; Figarol, S.; Marty-Detraves, C.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Bousquet, E.; Farella, M.; Clermont-Taranchon, E.; Milia, J.; Rouquette, I. The RAS-related GTP ase RHOB confers resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer via an AKT-dependent mechanism. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Liu, W.-R.; Tian, M.-X.; Jiang, X.-F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, P.-Y.; Ding, Z.-B.; Peng, Y.-F.; Dai, Z.; Qiu, S.-J. CCL24 contributes to HCC malignancy via RhoB-VEGFA-VEGFR2 angiogenesis pathway and indicates poor prognosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Privat, M.; Cavard, A.; Zekri, Y.; Ponelle-Chachuat, F.; Molnar, I.; Sonnier, N.; Bignon, Y.-J. A high expression ratio of RhoA/RhoB is associated with the migratory and invasive properties of basal-like Breast Tumors. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.A.; Godet, I.; DiGiacomo, J.W.; Gilkes, D.M. RhoB is regulated by hypoxia and modulates metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Rep. 2020, 3, e1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Niu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, P.; Gao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Pang, H.; Gong, H.; Shen, D.; Gu, L. RhoB acts as a tumor suppressor that inhibits malignancy of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Dai, X.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; He, X. The role of long non-coding RNA GAS5 in cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toraih, E.A.; Alghamdi, S.A.; El-Wazir, A.; Hosny, M.M.; Hussein, M.H.; Khashana, M.S.; Fawzy, M.S. Dual biomarkers long non-coding RNA GAS5 and microRNA-34a co-expression signature in common solid tumors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Ye, H.; Huang, G.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 suppresses the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via miR-21. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2691–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, J.; Ou, B.; Liu, C.; Zou, Y. GAS5 knockdown reduces the chemo-sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell to cisplatin (DDP) through regulating miR-21/PTEN axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-Q.; Wang, J.-f.; Chen, D.-H.; Ma, X.-S.; Yang, W.; Zhe, T.; Dang, X.-W. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 antagonizes the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells through down-regulation of miR-181c-5p. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Hong, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L. LncRNA GAS5 suppresses the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer by downregulating miR-196a and miR-205. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317711315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, S.-J. LncRNA Gas5 acts as a ceRNA to regulate PTEN expression by sponging miR-222-3p in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Vadamootoo, A.S.; Wang, L.; Jin, C. Identification of circulating miR-663a as a potential biomarker for diagnosing osteosarcoma. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.; Pranatharthi, A.; Ross, C.; Srivastava, S. RhoC: A fascinating journey from a cytoskeletal organizer to a Cancer stem cell therapeutic target. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, W.-F.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, X.-F.; Xiu, Y.-L.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.-M.; Zhu, Z.-T.; Sun, H.-Z.; Liu, Y.-P. The role of RhoC in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of ovarian carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleer, C.G.; Griffith, K.A.; Sabel, M.S.; Gallagher, G.; van Golen, K.L.; Wu, Z.-F.; Merajver, S.D. RhoC-GTPase is a novel tissue biomarker associated with biologically aggressive carcinomas of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 93, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Busch, H.; Boerries, M.; Brummer, T.; Timme, S.; Lassmann, S.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Specific role of RhoC in tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87364–87378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, M.; Christofori, G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; DiVito, M.M.; Merajver, S.D.; Boyanapalli, M.; Van Golen, K.L. Regulation of pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by RhoC GTPase and caveolin-1. Mol. Cancer 2005, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Wen, J.; Chen, H.; Xiao, X.; Dai, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y. Characterization of a novel human testis-specific gene: Testis developmental related gene 1 (TDRG1). Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2011, 225, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Liang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mo, K.; Su, S.; Wang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhou, R. The lncRNA TDRG1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-326 to regulate MAPK1 expression in cervical cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; He, Y.; Zou, Q.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y. Expression and localization of testis developmental related gene 1 (TDRG1) in human spermatozoa. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2015, 235, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gan, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, X.; Tang, Y. In vitro study on shRNA-mediated reduction of testis developmental related gene 1 expression and its effects on the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of NTERA-2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Wang, L.-l.; Sun, K.-x.; Liu, Y.; Guan, X.; Zong, Z.-h.; Zhao, Y. LncRNA TDRG1 enhances tumorigenicity in endometrial carcinoma by binding and targeting VEGF-A protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xia, M.; Yang, J.; Shao, J.; Liao, X.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, H. Novel insights into a treatment for aplastic anemia based on the advanced proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced by fibroblast growth factor 1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7877–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Wang, L.L.; Sun, K.X.; Xiu, Y.L.; Zong, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. The role of the long non-coding RNA TDRG1 in epithelial ovarian carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression through miR-93/RhoC pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Joosse, S.A.; Müller, V.; Trillsch, F.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Mahner, S.; Geffken, M.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of serum miR-7, miR-16, miR-25, miR-93, miR-182, miR-376a and miR-429 in ovarian cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merola, R.; Tomao, L.; Antenucci, A.; Sperduti, I.; Sentinelli, S.; Masi, S.; Mandoj, C.; Orlandi, G.; Papalia, R.; Guaglianone, S.; et al. PCA3 in prostate cancer and tumor aggressiveness detection on 407 high-risk patients: A National Cancer Institute experience. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeb, S.; Partin, A.W. Review of the literature: PCA3 for prostate cancer risk assessment and prognostication. Rev. Urol. 2011, 13, e191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Liu, S.-Y.; Wang, L.; Han, L.-Y. Long noncoding RNA PCA3 contributes to the progression of choriocarcinoma by acting as a ceRNA against miR-106b. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Dou, R.; Yin, T.; Ding, J. MiRNA-106b-5p in human cancers: Diverse functions and promising biomarker. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotelevets, L.; Chastre, E. Rac1 signaling: From intestinal homeostasis to colorectal cancer metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fritz, G.; Just, I.; Kaina, B. Rho GTPases are over-expressed in human tumors. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.T.; Asthana, S.; Gao, S.P.; Lee, B.H.; Chapman, J.S.; Kandoth, C.; Gao, J.; Socci, N.D.; Solit, D.B.; Olshen, A.B. Identifying recurrent mutations in cancer reveals widespread lineage diversity and mutational specificity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrodia, A.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, W.; Cha, E.K.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Iyer, G.; Pietzak, E.J.; Gao, S.P.; Zabor, E.C.; Ostrovnaya, I. Genetic determinants of cisplatin resistance in patients with advanced germ cell tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodis, E.; Watson, I.R.; Kryukov, G.V.; Arold, S.T.; Imielinski, M.; Theurillat, J.-P.; Nickerson, E.; Auclair, D.; Li, L.; Place, C. A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell 2012, 150, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stallings-Mann, M.L.; Waldmann, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miller, E.; Gauthier, M.L.; Visscher, D.W.; Downey, G.P.; Radisky, E.S.; Fields, A.P.; Radisky, D.C. Matrix metalloproteinase induction of Rac1b, a key effector of lung cancer progression. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 142ra95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakur, N.; Kupani, M.; Mannan, R.; Pruthi, A.; Mehrotra, S. Genetic association between CDKN2B/CDKN2B-AS1 gene polymorphisms with primary glaucoma in a North Indian cohort: An original study and an updated meta-analysis. BMC Med Genom. 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoglu, B.; Yuksel, H.; Cakmak, H.A.; Dirican, A.; Cengiz, M. Polymorphisms in the long non-coding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 may contribute to higher systolic blood pressure levels in hypertensive patients. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhai, J.; Fu, Y. LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 promotes the progression of ovarian cancer by miR-143-3p/SMAD3 axis and predicts a poor prognosis. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Xing, Y. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL is up-regulated in bladder cancer and regulates bladder cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis through the intrinsic pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Yu, T.; Shang, J.; Xiao, D.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 facilitates laryngeal squamous cell cancer through regulating miR-497/CDK6 pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Li, Y.; He, F.; Kong, J. LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 Promotes Cell Viability, Migration, and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Sponging miR-424-5p. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Wang, D.-D.; Du, C.-X.; Wang, Y. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes cervical cancer development by acting as a sponge of miR-186. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naemura, M.; Murasaki, C.; Inoue, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Kotake, Y. Long Noncoding RNA ANRIL Regulates Proliferation of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Cervical Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 5377–5382. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, S.; Cui, J.; Dang, G. Interference of the long noncoding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 upregulates miR-181a-5p/TGFβI axis to restrain the metastasis and promote apoptosis and senescence of cervical cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Xiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kan, H. LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting let-7c-5p/NAP1L1 axis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 437, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abula, A.; Saimaiti, G.; Maimaiti, X.; Wuqikun, W.; Abulaiti, A.; Ren, P.; Yusufu, A. The stimulative function of long noncoding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 in osteosarcoma by targeting the microRNA-122/CCNG1 axis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, G.; Wang, W. Long noncoding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 facilitates lung cancer development through regulating miR-378b/NR2C2. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, P.; Kulkarni, P.; Majid, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shiina, M.; Shahryari, V.; Bhat, N.S.; Tabatabai, L.; Yamamura, S.; Saini, S. LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1/miR-141/cyclin D network regulates tumor progression and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, W.; Xue, W.; Xu, P.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, S.; Qiu, X. Long noncoding RNA AURKAPS1 potentiates malignant hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating miR-142, miR-155 and miR-182. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.-Q.; You, A.B.; Zhu, X.-D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Zhang, K.-W.; Cai, H.; Shi, W.-K.; Li, X.-L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, L.Q.; Huang, Y.; Quan, J.; Hu, X.; Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Li, N.; Fan, X.G. miR-142-3p Inhibits the Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Regulating HMGB1 Gene Expression. Curr. Mol. Med. 2018, 18, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, P.; Tian, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, Q.; Luo, M.; Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, Q. LncRNA2Target v2.0: A comprehensive database for target genes of lncRNAs in human and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, Q.; Qian, X.; Yi, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Mi, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LCAT1 functions as a ceRNA to regulate RAC1 function by sponging miR-4715-5p in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cui, Z.; Lv, X.; Li, J.; Gao, M.; Yang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; et al. Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR Function as a Competing Endogenous RNA for miR-149-5p to Promote the Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 528520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Boczek, N.J.; Berres, M.W.; Ma, X.; Smith, D.I. LSINCT5 is over expressed in breast and ovarian cancer and affects cellular proliferation. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, S. LSINCT5 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by interacting with NCYM to promote bladder cancer progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Lu, M.; Xiao, D. LSINCT5 predicts unfavorable prognosis and exerts oncogenic function in osteosarcoma. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Niu, G.; Chen, S.; Yao, S. Long noncoding RNA LSINCT5 promotes endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation, cycle, and invasion by promoting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via HMGA2. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919874649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.-D.; Qi, P.; Weng, W.-W.; Shen, X.-H.; Ni, S.-J.; Dong, L.; Huang, D.; Tan, C.; Sheng, W.-Q.; Zhou, X.-Y. Long non-coding RNA LSINCT5 predicts negative prognosis and exhibits oncogenic activity in gastric cancer. Medicine 2014, 93, e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cao, W.; Ma, H. Knockdown of lncRNA LSINCT5 suppresses growth and metastasis of human glioma cells via up-regulating miR-451. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Nan, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, A.; Wang, G.; Jia, Z.; Hao, J.; Pu, P.; Zhong, Y.; Kang, C. MicroRNA miR-451 downregulates the PI3K/AKT pathway through CAB39 in human glioma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Shu, L.; Zou, W. Role of long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 in cancer. Biosci Rep 2019, 39, BSR20192274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ren, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, S. LncRNA TP73-AS1 promoted the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via PI3K/AKT pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X. Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 sponges miR-194 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via up-regulating TGFα. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 23, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, S. The long noncoding RNA TP73-AS1 interacted with miR-124 to modulate glioma growth by targeting inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Lu, J.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; Lu, Y. LncRNA TP73-AS1 enhances the malignant properties of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by increasing MMP14 expression through miRNA-200a sponging. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Huang, K.-J.; Zhou, L.-S.; Qiu, Z.-J. Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis through miRNA-128-3p/GOLM1 axis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J. LncRNA TP73-AS1 is a novel regulator in cervical cancer via miR-329-3p/ARF1 axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Song, R.; Wang, L.; Wu, X. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion through sponging miR-142. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-F.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, S.-H.; Liang, J. miR-142 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by upregulating Rb. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.-Z. Long non-coding RNA FTH1P3 facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-224-5p to modulate fizzled 5 expression. Gene 2017, 607, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Tang, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y. Long non-coding RNA FTH1P3 facilitates uveal melanoma cell growth and invasion through miR-224-5p. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y. Increased expression of lncRNA FTH1P3 predicts a poor prognosis and promotes aggressive phenotypes of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Biosci Rep 2019, 39, BSR20181644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, R.; Zhang, Q.W. The long noncoding RNA FTH1P3 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer through microRNA-145. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, W. miR-224-5p inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting PIK3R3/AKT3 in uveal melanoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 12412–12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.J.; Hendrich, B.D.; Rupert, J.L.; Lafreniere, R.G.; Xing, Y.; Lawrence, J.; Willard, H.F. The human XIST gene: Analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell 1992, 71, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockdorff, N.; Ashworth, A.; Kay, G.F.; Cooper, P.; Smith, S.; McCabe, V.M.; Norris, D.P.; Penny, G.D.; Patel, D.; Rastan, S. Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse Xist from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 1991, 351, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, D.; Guanqun, G.; Jingxin, L.; Sen, S.; Shuang, L.; Yan, S.; Minxue, Z.; Ping, Y.; Chong, L.; Zhuobo, Z. Silencing of long noncoding RNA XIST attenuated Alzheimer’s disease-related BACE1 alteration through miR-124. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Luo, Y.; Ying, Y. lncRNA XIST attenuates hypoxia-induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte injury by targeting the miR-122-5p/FOXP2 axis. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 50, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Gu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, L. The long noncoding RNA XIST regulates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting miR-101. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 13680–13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Feng, D. LncRNA XIST promotes myocardial infarction by regulating FOS through targeting miR-101a-3p. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Li, W.; Ji, T.; Li, X.; Qu, X.; Feng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Bai, S. Downregulation of XIST ameliorates acute kidney injury by sponging miR-142-5p and targeting PDCD4. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8852–8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, L.; Lu, C. Platycodin D (PD) regulates LncRNA-XIST/miR-335 axis to slow down bladder cancer progression in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Xiang, Z.; Huang, T.; Zhou, W.B. LncRNA XIST promotes chemoresistance of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by sponging miR-200c-3p to upregulate ANLN. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.g.; Cao, M.z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.y.; Sun, Q.l. LncRNA XIST modulates HIF-1A/AXL signaling pathway by inhibiting miR-93-5p in colorectal cancer. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, H.; Chen, B.; Wei, X.; Peng, J.; Ma, K.; Duan, S.; He, J. Long non-coding RNA XIST expedites lung adenocarcinoma progression through upregulating MDM2 expression via binding to miR-363-3p. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Sun, D.; Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Guo, T.; Shi, Z. Long noncoding RNA X-inactive specific transcript facilitates cellular functions in melanoma via miR-139-5p/ROCK1 pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y. The lncRNA XIST promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting miR-337. Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 21, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Du, S.; Liu, Q. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes malignant behavior of epithelial ovarian cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Wei, B.; Peng, Z.-H.; Fu, Q.-L.; Wang, C.-J.; Zheng, J.-C.; Sun, J.-C. Knockdown of lncRNA XIST suppresses osteosarcoma progression by inactivating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by sponging miR-375-3p. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 1507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Xiong, J.; Shao, X.; Cheng, H.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Di, G.; Mao, J.; Jiang, X. Knockdown of the long noncoding RNA XIST suppresses glioma progression by upregulating miR-204-5p. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Long non-coding RNA XIST exerts oncogenic functions in human glioma by targeting miR-137. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Min, L.; Qiu, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, L. Biological Function of Long Non-coding RNA (LncRNA) Xist. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 1447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhou, X.; Guo, R.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, G. miR-137: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Human Glioma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.-H.; Lv, L.-C.; Duan, J.; Wu, Y.-M.; He, S.-J.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Xiong, L.-X. Regulating Cdc42 and its signaling pathways in cancer: Small molecules and MicroRNA as new treatment candidates. Molecules 2018, 23, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maldonado, M.d.M.; Medina, J.I.; Velazquez, L.; Dharmawardhane, S. Targeting Rac and Cdc42 GEFs in metastatic cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Saini, N.; Sharma, R. miR-107 functions as a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and targets Cdc42. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3116–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, M.-G.; Li, S.; Yu, T.-T.; Qian, L.-J.; Cao, R.-S.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, B.; Jiao, C.-H.; Tang, N.-N.; Ma, J.-J. Differential expression of miR-195 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and miR-195 expression inhibits tumor cell proliferation and invasion by targeting of Cdc42. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, N.; Ye, L.; Chang, T.; Li, X.; Li, X. microRNA-195-Cdc42 axis acts as a prognostic factor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Ren, L.; Sun, C.; Yu, L.; Bian, X.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Hua, D.; Zhao, S.; Luo, W. miR-29a/b/c function as invasion suppressors for gliomas by targeting CDC42 and predict the prognosis of patients. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Craig, B.T.; Romain, C.V.; Qiao, J.; Chung, D.H. Silencing of CDC42 inhibits neuroblastoma cell proliferation and transformation. Cancer Lett. 2014, 355, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, J.; Wang, B.; Zheng, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Xi, T. MALAT1 induced migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by competitively binding miR-1 with cdc42. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 472, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Si, L.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Agula, B. Long Noncoding RNA ZFAS1 Promotes Progression of NSCLC via Regulating of miR-590-3p. Cell Transpl. 2020, 29, 963689720919435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Shang, K.; Liu, F.; Che, J.; Li, H.; Cao, B. Long non-coding RNA H19, a novel therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Yuan, J.-H.; Yuan, S.-X.; Zhou, W.-P.; Huo, X.-S.; Xu, D.; Bi, H.-S.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.-H. Epigenetic activation of the MiR-200 family contributes to H19-mediated metastasis suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zong, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Sun, L. LncRNA H19 functions as an Aquaporin 1 competitive endogenous RNA to regulate microRNA-874 expression in LPS sepsis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Zang, S.; Ma, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, C. The lncRNA H19/miR-675 axis regulates myocardial ischemic and reperfusion injury by targeting PPARα. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Mo, J.; Luo, M.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W. c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA H19 downregulates miR-107 and promotes cell cycle progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 12400. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, W.; Shan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H. LncRNA H19/miR-194/PFTK1 axis modulates the cell proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3874–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Yin, J.; Zeng, A.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, W.; You, Y. H19 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate EMT by sponging miR-130a-3p in glioma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Fu, J.; Ma, T.; Yan, B.; Gao, R.; An, Z.; Wang, D. LncRNA H19-elevated LIN28B promotes lung cancer progression through sequestering miR-196b. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiao, P.; Ning, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Yu, W.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J. Macrophages-induced long noncoding RNA H19 up-regulation triggers and activates the miR-193b/MAPK1 axis and promotes cell aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.W.S.; Xiang, X.; Garg, M.; Le, M.T.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.-C. The double-edged sword of H19 lncRNA: Insights into cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2020, 500, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Esmaeili, M.; Taheri, M. H19 lncRNA: Roles in tumorigenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, R.-G.; Qin, C.-L.; Jia, J.; Wu, X.-D.; Zha, W.-Z. LncRNA-H19 activates CDC42/PAK1 pathway to promote cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-15b in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genomics 2019, 111, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.Y.; Zeng, J.H.; Wen, D.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, P.P.; Chen, G.; Feng, Z.B. Oncogenic value of microRNA-15b-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma and a bioinformatics investigation. Oncol Lett 2019, 17, 1695–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, L.; Wan, F. Molecular mechanisms of TUG1 in the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Hu, X.; Mao, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, W. The long noncoding RNA TUG1 is required for TGF-β/TWIST1/EMT-mediated metastasis in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Liang, R.; Tang, J. Long Non-Coding RNA Taurine Upregulated Gene 1 (TUG1) Downregulation Constrains Cell Proliferation and Invasion through Regulating Cell Division Cycle 42 (CDC42) Expression Via MiR-498 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Med Sci. Monit. Int. Med J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e919714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Deng, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X.-f.; Pan, S.; Zhang, H.-b. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cell progression in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-216b-5p/DLX2 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, F. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer progression by regulating the miR-138-5p-SIRT1 axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, D.; Wei, X.; Ding, Y. TUG1 promotes prostate cancer progression by acting as a ceRNA of miR-26a. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, F.; Gopalan, V.; Law, S.; Tang, J.C.-O.; Kwok-Wah, C.; Alfred King-Yin, L. MiR-498 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological impacts and functional interactions. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 62, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.; Yu, S. Expression and gene regulatory network of SNHG1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F. Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate PDCD4 expression by sponging miR-195-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene 2019, 714, 143994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Geng, P.; Li, G.; Song, H. LncRNA SNHG1 enhances cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in cervical cancer. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, L.; Guo, C.; Jiang, T.; Zeng, L.; Li, G.; Wang, J. SNHG1 lncRNA negatively regulates miR-199a-3p to enhance CDK7 expression and promote cell proliferation in prostate cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, C.; Geng, L.; Tian, T.; Liu, H. Upregulated lncRNA SNHG1 contributes to progression of non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of miR-101-3p and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Sheng, H.G.; Deng, F.M.; Cai, L.L. Downregulation of the long noncoding RNA SNHG1 inhibits tumor cell migration and invasion by sponging miR-195 through targeting Cdc42 in oesophageal cancer. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, M.; Xu, W.; Liu, C.; Wu, J. miR-195 inhibits esophageal cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis by downregulating YAP1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Jin, H.; Wu, H.B.; Xu, J.J.; Li, B. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 promotes CDK14 expression via miR-486 to accelerate non-small cell lung cancer cells progression and metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7164–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Li, T.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Song, J.; Sun, X.; Tang, Y.; Wan, J.; Yu, Y. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 interacts with and stabilizes transcription factor Slug and promotes colon cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2018, 425, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, S.; Hou, Z.; Wang, G. Long noncoding RNA SNHG15 enhances the development of colorectal carcinoma via functioning as a ceRNA through miR-141/SIRT1/Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, Q.; Qiu, M. Long noncoding RNA SNHG15 promotes human breast cancer proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-211-3p. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Pu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, P.; Hui, B.; Ji, H.; Wang, K. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 inhibits P15 and KLF2 expression to promote pancreatic cancer proliferation through EZH2-mediated H3K27me3. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.-x.; Yin, J.-f.; Lin, B.-c.; Su, H.-f.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, C.-y.; Fei, Z.-h. Upregulated expression of long noncoding RNA SNHG15 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through regulates MMP2/MMP9 in patients with GC. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 6801–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-M.; Wang, S.; Wen, X.; Han, X.-R.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Shan, Q.; Li, M.-Q.; et al. LncRNA SNHG15 acts as a ceRNA to regulate YAP1-Hippo signaling pathway by sponging miR-200a-3p in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, C.; Cai, H.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. SNHG15 affects the growth of glioma microvascular endothelial cells by negatively regulating miR-153. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3265–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, H.; Zhao, X.; Yang, T.; Chen, W.; Yao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. MiR-153 reduces stem cell-like phenotype and tumor growth of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting Jagged1. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.L.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 348 Pt 2, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prudnikova, T.Y.; Rawat, S.J.; Chernoff, J. Molecular Pathways: Targeting the Kinase Effectors of RHO-Family GTPases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Fan, C.; Yang, L.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Nie, S.; et al. LncRNAs regulate the cytoskeleton and related Rho/ROCK signaling in cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hedman, A.C.; Smith, J.M.; Sacks, D.B. The biology of IQGAP proteins: Beyond the cytoskeleton. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-A.; Wang, M.-J.; Chi, C.-W.; Wu, C.-W.; Chen, J.-Y. Rho/Rhotekin-mediated NF-κB activation confers resistance to apoptosis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8731–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amin, E.; Dubey, B.N.; Zhang, S.C.; Gremer, L.; Dvorsky, R.; Moll, J.M.; Taha, M.S.; Nagel-Steger, L.; Piekorz, R.P.; Somlyo, A.V.; et al. Rho-kinase: Regulation, (dys)function, and inhibition. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhao, W.; Wang, N.; Li, P.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, W. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for promoting metastasis and proliferation by acting as a ceRNA of miR-144-3p in osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59417–59434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morlando, M.; Fatica, A. Alteration of Epigenetic Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.-F.; Li, W. LncRNA Functions as a New Emerging Epigenetic Factor in Determining the Fate of Stem Cells. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanly, D.J.; Esteller, M.; Berdasco, M. Interplay between long non-coding RNAs and epigenetic machinery: Emerging targets in cancer? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Pandya-Jones, A.; McDonel, P.; Shishkin, A.; Sirokman, K.; Surka, C.; Kadri, S.; Xing, J.; Goren, A.; Lander, E.S.; et al. The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science 2013, 341, 1237973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Hiju, H.; Sun, J.; Mao, Z.; Zheng, M.; Feng, B. Epigenetic modulations of noncoding RNA: A novel dimension of Cancer biology. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Weng, H.; Su, R.; Weng, X.; Zuo, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Nachtergaele, S.; Dong, L.; Hu, C.; et al. FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, W.; Yao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Zhou, A.; Liu, J.; Che, L.; Li, J. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by interacting with and triggering YAP phosphorylation and degradation and is negatively regulated by the m(6)A reader YTHDF3. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorkova, O.; Wahlestedt, C. Oligonucleotide therapies for disorders of the nervous system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Guan, X.; Yang, K.; Bai, Y. LncRNA CASC9 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through upregulating LAMC2 expression by interacting with the CREB-binding protein. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1980–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, A.M.; Sun, Z.; Ayat, N.; Schilb, A.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, D.; Scheidt, J.; Qian, V.; He, S.; et al. Systemic Delivery of Tumor-Targeting siRNA Nanoparticles against an Oncogenic LncRNA Facilitates Effective Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy. Bioconj. Chem. 2019, 30, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Zheng, X. LncRNAs linc00311 and AK141205 are identified as new regulators in STAT3-mediated neuropathic pain in bCCI rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 868, 172880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T. Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, G.; Diermeier, S.; Akerman, M.; Chang, K.-C.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Hearn, S.; Kim, Y.; MacLeod, A.R.; Krainer, A.R.; Norton, L. Differentiation of mammary tumors and reduction in metastasis upon Malat1 lncRNA loss. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özeş, A.R.; Wang, Y.; Zong, X.; Fang, F.; Pilrose, J.; Nephew, K.P. Therapeutic targeting using tumor specific peptides inhibits long non-coding RNA HOTAIR activity in ovarian and breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taiana, E.; Favasuli, V.; Ronchetti, D.; Todoerti, K.; Pelizzoni, F.; Manzoni, M.; Barbieri, M.; Fabris, S.; Silvestris, I.; Cantafio, M.E.G. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 targeting impairs the DNA repair machinery and triggers anti-tumor activity in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2020, 34, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, N.; Stamato, M.A.; Juli, G.; Morelli, E.; Fulciniti, M.; Manzoni, M.; Taiana, E.; Agnelli, L.; Cantafio, M.E.G.; Romeo, E. Drugging the lncRNA MALAT1 via LNA gapmeR ASO inhibits gene expression of proteasome subunits and triggers anti-multiple myeloma activity. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Guo, B.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; Rouskas, G.N. A large-scale nesting ring multi-chip architecture for manycore processor systems. Opt. Switch. Netw. 2019, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, G.; Rong, S.; Santillan, D.A.; Santillan, M.K.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Bao, W. National Estimates of e-Cigarette Use Among Pregnant and Nonpregnant Women of Reproductive Age in the United States, 2014–2017. JAMA Pediatrics 2019, 173, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.E.; Li, Q.C. Research progress of relationship between notch signaling pathway and asthma. J Pr. Med 2019, 35, 315–317. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Cai, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Kang, C.; Li, M.; Jiang, C. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1, regulated by the EGFR pathway, contributes to glioblastoma progression through the WNT/β-catenin pathway by scaffolding EZH2. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2018, 24, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedram Fatemi, R.; Salah-Uddin, S.; Modarresi, F.; Khoury, N.; Wahlestedt, C.; Faghihi, M.A. Screening for small-molecule modulators of long noncoding RNA-protein interactions using AlphaScreen. J. Biomol. Screen. 2015, 20, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abulwerdi, F.A.; Xu, W.; Ageeli, A.A.; Yonkunas, M.J.; Arun, G.; Nam, H.; Schneekloth, J.S.; Dayie, T.K.; Spector, D.; Baird, N.; et al. Selective Small-Molecule Targeting of a Triple Helix Encoded by the Long Noncoding RNA, MALAT1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Ji, H.; Xiong, Y. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of multiple myeloma cells via NEAT1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damase, T.R.; Sukhovershin, R.; Boada, C.; Taraballi, F.; Pettigrew, R.I.; Cooke, J.P. The Limitless Future of RNA Therapeutics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 628137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, M.S.; Aggarwal, R.R.; Boyd, E.; Comerford, K.; Zhang, J.; Méndez, B.; Valenzuela, P.; Grabowsky, J.; Thomas, S.; Munster, P.N. Phase 1 study of ANDES-1537: A novel antisense oligonucleotide against non-coding mitochondrial DNA in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.W.; Khachigian, L.M. DNAzymes and their therapeutic possibilities. Intern. Med. J. 2009, 39, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long Noncoding RNA and Cancer: A New Paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saliani, M.; Mirzaiebadizi, A.; Mosaddeghzadeh, N.; Ahmadian, M.R. RHO GTPase-Related Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215386
Saliani M, Mirzaiebadizi A, Mosaddeghzadeh N, Ahmadian MR. RHO GTPase-Related Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancers. Cancers. 2021; 13(21):5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215386
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaliani, Mahsa, Amin Mirzaiebadizi, Niloufar Mosaddeghzadeh, and Mohammad Reza Ahmadian. 2021. "RHO GTPase-Related Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancers" Cancers 13, no. 21: 5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215386
APA StyleSaliani, M., Mirzaiebadizi, A., Mosaddeghzadeh, N., & Ahmadian, M. R. (2021). RHO GTPase-Related Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancers. Cancers, 13(21), 5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215386