Statins Enhance the Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia when Combined with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of DMR Rates in Patients with CML Who Were Treated with IM Alone or in Combination with a Statin
2.2. Evaluation of In Vitro Cytotoxicity against CML Cell Lines
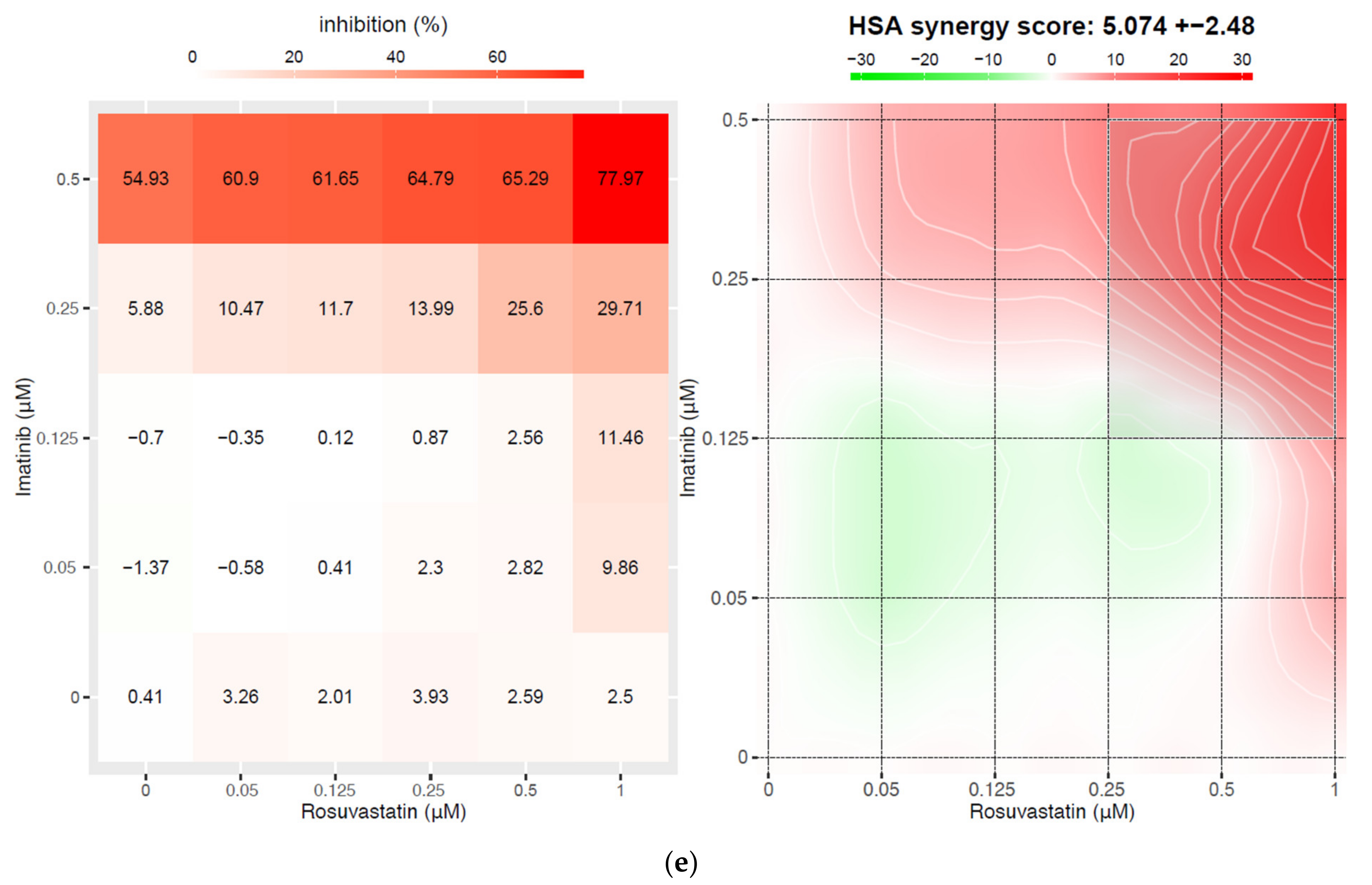
2.3. Synergy Calculations
2.4. Colony-Formation Assay
2.5. Isolation of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with CML/Healthy Individual
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis Using Whole Transcriptome and Targeted RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq)
2.7. Targeted RNA-Seq Assay
2.8. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
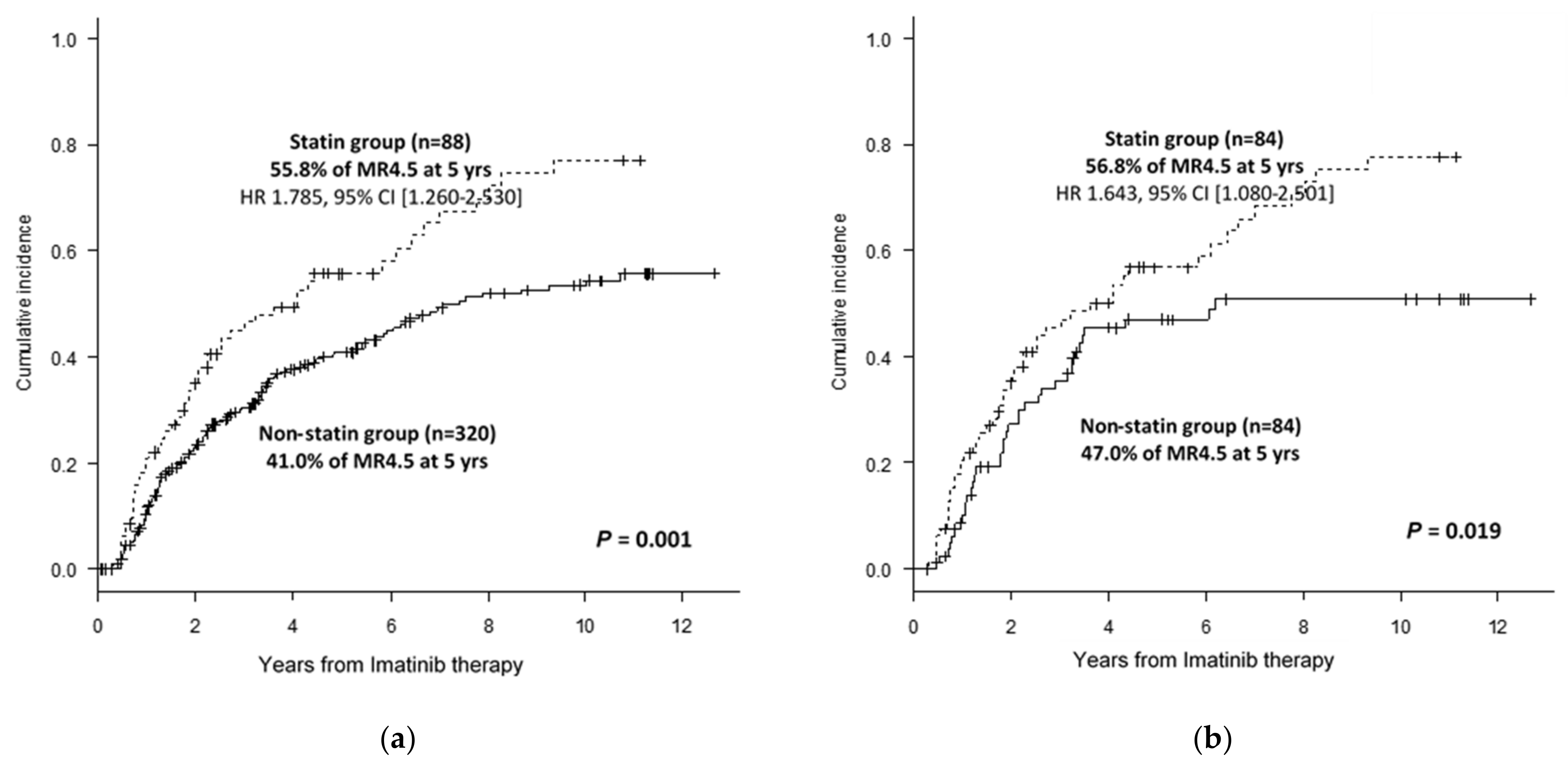
3.1. Clinical Benefits from the Use of Statins in CML Treatment with IM Therapy
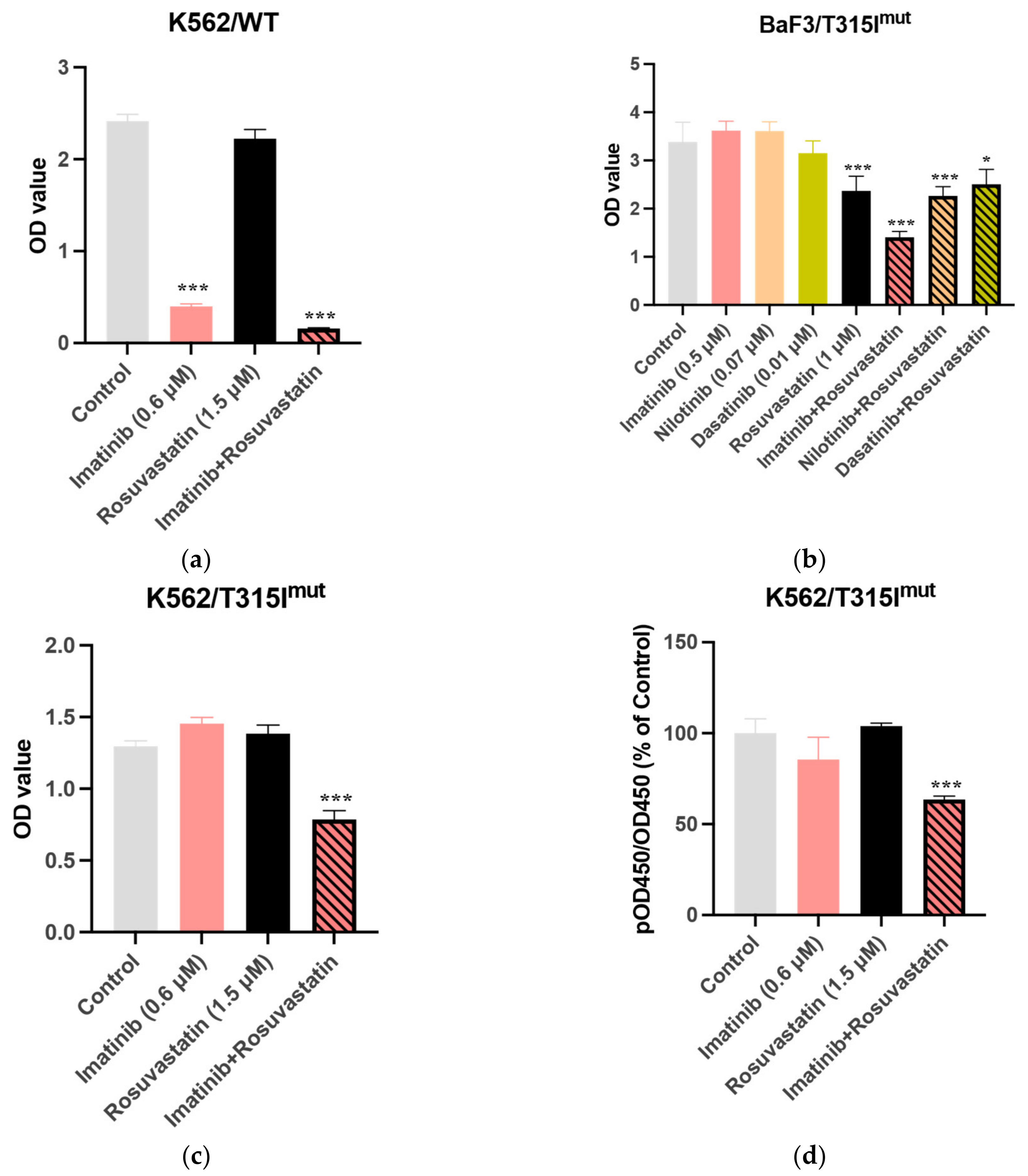
3.2. Statins Synergistically Potentiate the Cytotoxic Activity of TKIs Against the BCR-ABL1+ Cell Lines
3.3. Statins Suppress the Colony-Forming Capacity of Murine CML-KLS+ Cells In Vitro
3.4. Combination of Rosuvastatin and IM Exert Growth-Inhibitory Effects Against CML CD34+ Cells
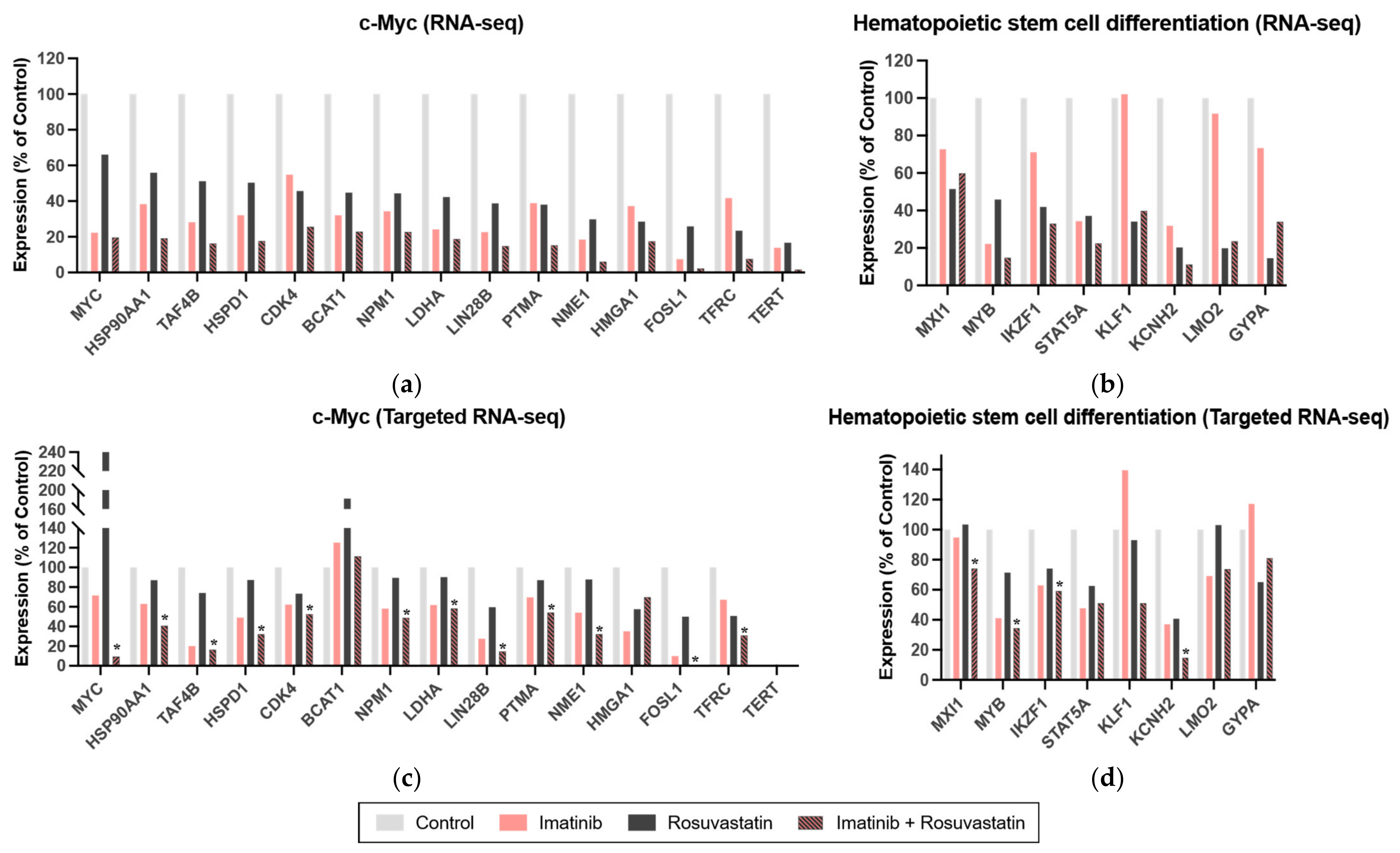
3.5. Statins Target the c-Myc and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation Pathways in CML
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, S.G.; Guilhot, F.; Larson, R.A.; Gathmann, I.; Baccarani, M.; Cervantes, F.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Fischer, T.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.; et al. Imatinib Compared with Interferon and Low-Dose Cytarabine for Newly Diagnosed Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehlmann, R.; Müller, M.C.; Lauseker, M.; Hanfstein, B.; Fabarius, A.; Schreiber, A.; Proetel, U.; Pletsch, N.; Pfirrmann, M.; Haferlach, C.; et al. Deep Molecular Response Is Reached by the Majority of Patients Treated With Imatinib, Predicts Survival, and Is Achieved More Quickly by Optimized High-Dose Imatinib: Results From the Randomized CML-Study IV. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnetti, F.; Gugliotta, G.; Breccia, M.; Stagno, F.; Iurlo, A.; Albano, F.; Abruzzese, E.; Martino, B.; Levato, L.; Intermesoli, T.; et al. Long-term outcome of chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated frontline with imatinib. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, H.; Björkholm, M.; Dickman, P.W.; Höglund, M.; Lambert, P.C.; Andersson, T.M.L. Life Expectancy of Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Approaches the Life Expectancy of the General Population. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahon, F.X.; Rea, D.; Guilhot, J.; Guilhot, F.; Huguet, F.; Nicolini, F.; Legros, L.; Charbonnier, A.; Guerci, A.; Varet, B.; et al. Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained complete molecular remission for at least 2 years: The prospective, multicentre Stop Imatinib (STIM) trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.M.; Branford, S.; Seymour, J.F.; Schwarer, A.P.; Arthur, C.; Yeung, D.T.; Dang, P.; Goyne, J.M.; Slader, C.; Filshie, R.J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of imatinib cessation for CML patients with stable undetectable minimal residual disease: Results from the TWISTER study. Blood 2013, 122, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imagawa, J.; Tanaka, H.; Okada, M.; Nakamae, H.; Hino, M.; Murai, K.; Ishida, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Sato, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Discontinuation of dasatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained deep molecular response for longer than 1 year (DADI trial): A multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e528–e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.R.; Gaziano, J.M.; Chan, K.S.; Hennekens, C.H. Cholesterol lowering with statin drugs, risk of stroke, and total mortality. An overview of randomized trials. JAMA 1997, 278, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Istvan, E.S.; Deisenhofer, J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 2001, 292, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, W.W.L.; Dimitroulakos, J.; Minden, M.; Penn, L. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: The statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis. Leukemia 2002, 16, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demierre, M.-F.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Gruber, S.B.; Hawk, E.; Lippman, S.M. Statins and cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Bojesen, S.E. Statin Use and Reduced Cancer-Related Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Aragaki, A.K.; Tang, J.Y.; Kurian, A.W.; Manson, J.E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Simon, M.; Desai, P.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Statin use and all-cancer survival: Prospective results from the Women’s Health Initiative. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.S.; Rao, U.S. Statins decrease the expression of c-Myc protein in cancer cell lines. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthaman, K.; Manasi, N.; Bongso, A. Statins inhibit the growth of variant human embryonic stem cells and cancer cells in vitro but not normal human embryonic stem cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manthravadi, S.; Shrestha, A.; Madhusudhana, S. Impact of statin use on cancer recurrence and mortality in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, K.M.; Keller, J.; Gage, B.F.; Luo, S.; Wang, T.F.; Moskowitz, G.; Gumbel, J.; Blue, B.; O’Brian, K.; Carson, K.R. Statins Are Associated With Reduced Mortality in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4008–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Casares, M.T.; Garcia-Alegria, E.; Lopez-Jorge, C.E.; Ferrandiz, N.; Blanco, R.; Alvarez, S.; Vaque, J.P.; Bretones, G.; Caraballo, J.M.; Sanchez-Bailon, P.; et al. MYC antagonizes the differentiation induced by imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia cells through downregulation of p27(KIP1.). Oncogene 2013, 32, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, K.; Hoshii, T.; Muraguchi, T.; Tadokoro, Y.; Ooshio, T.; Kondo, Y.; Nakao, S.; Motoyama, N.; Hirao, A. TGF-beta-FOXO signalling maintains leukaemia-initiating cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2010, 463, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Woo, Y.M.; Youm, E.M.; Hamad, N.; Won, H.H.; Naka, K.; Park, E.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; et al. HMGCLL1 is a predictive biomarker for deep molecular response to imatinib therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamburov, A.; Wierling, C.; Lehrach, H.; Herwig, R. ConsensusPathDB--a database for integrating human functional interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D623–D628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dick, J.E. Stem cell concepts renew cancer research. Blood 2008, 112, 4793–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warsch, W.; Walz, C.; Sexl, V. JAK of all trades: JAK2-STAT5 as novel therapeutic targets in BCR-ABL1+ chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallipoli, P.; Cook, A.; Rhodes, S.; Hopcroft, L.; Wheadon, H.; Whetton, A.D.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Bhatia, R.; Holyoake, T.L. JAK2/STAT5 inhibition by nilotinib with ruxolitinib contributes to the elimination of CML CD34+ cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2014, 124, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madapura, H.S.; Nagy, N.; Ujvari, D.; Kallas, T.; Krohnke, M.C.L.; Amu, S.; Bjorkholm, M.; Stenke, L.; Mandal, P.K.; McMurray, J.S.; et al. Interferon gamma is a STAT1-dependent direct inducer of BCL6 expression in imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4619–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierks, C.; Beigi, R.; Guo, G.-R.; Zirlik, K.; Stegert, M.R.; Manley, P.; Trussell, C.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Landwerlin, K.; Veelken, H.; et al. Expansion of Bcr-Abl-Positive Leukemic Stem Cells Is Dependent on Hedgehog Pathway Activation. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, A.; Jamieson, C.H.; Fereshteh, M.; Abrahamsson, A.; Blum, J.; Kwon, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Chute, J.P.; Rizzieri, D.; et al. Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2009, 458, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanna, A.; Shevde, L.A. Hedgehog signaling: Modulation of cancer properies and tumor mircroenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coluccia, A.M.L.; Vacca, A.; Duñach, M.; Mologni, L.; Redaelli, S.; Bustos, V.H.; Benati, D.; Pinna, L.A.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Bcr-Abl stabilizes β-catenin in chronic myeloid leukemia through its tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Douglas, L.; Li, S. β-Catenin is essential for survival of leukemic stem cells insensitive to kinase inhibition in mice with BCR-ABL-induced chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Li, M.; McDonald, T.; Holyoake, T.L.; Moon, R.T.; Campana, D.; Shultz, L.; Bhatia, R. Microenvironmental protection of CML stem and progenitor cells from tyrosine kinase inhibitors through N-cadherin and Wnt–β-catenin signaling. Blood 2013, 121, 1824–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mak, P.Y.; Mu, H.; Mak, D.H.; Zeng, Z.; Cortes, J.; Liu, Q.; Andreeff, M.; Carter, B.Z. Combined inhibition of β-catenin and Bcr–Abl synergistically targets tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia blasts and progenitors in vitro and in vivo. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Blanco, E.; Bruns, I.; Neumann, F.; Fischer, J.C.; Graef, T.; Rosskopf, M.; Brors, B.; Pechtel, S.; Bork, S.; Koch, A.; et al. Molecular signature of CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of patients with CML in chronic phase. Leukemia 2007, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, C.; Abraham, S.A.; Shan, Y.; Guo, Z.; Desouza, N.; Cheloni, G.; Li, D.; Holyoake, T.L.; Li, S. Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase is required for chronic myeloid leukemia stem cell survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3847–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Čokić, V.P.; Mojsilović, S.; Jauković, A.; Kraguljac-Kurtović, N.; Mojsilović, S.; Šefer, D.; Mitrović Ajtić, O.; Milošević, V.; Bogdanović, A.; Đikić, D.; et al. Gene expression profile of circulating CD34+ cells and granulocytes in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2015, 55, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, S.A.; Hopcroft, L.E.M.; Carrick, E.; Drotar, M.E.; Dunn, K.; Williamson, A.J.K.; Korfi, K.; Baquero, P.; Park, L.E.; Scott, M.T.; et al. Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells. Nature 2016, 534, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takwi, A.A.L.; Li, Y.; Becker Buscaglia, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Choudhury, S.; Park, A.K.; Liu, M.; Young, K.H.; Park, W.Y.; Martin, R.C.G.; et al. A statin-regulated microRNA represses human c-Myc expression and function. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Fan-Minogue, H.; Bellovin, D.I.; Yevtodiyenko, A.; Arzeno, J.; Yang, Q.; Gambhir, S.S.; Felsher, D.W. MYC Phosphorylation, Activation, and Tumorigenic Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Are Regulated by HMG-CoA Reductase. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2286–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogu, C.C.; Maxa, J.L. Drug Interactions Due to Cytochrome P450. Bayl. Univ. Med Cent. Proc. 2000, 13, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuvonen, P.J.; Backman, J.T.; Niemi, M. Pharmacokinetic comparison of the potential over-the-counter statins simvastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin and pravastatin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 47, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glodkowska-Mrowka, E.; Mrowka, P.; Basak, G.W.; Niesiobedzka-Krezel, J.; Seferynska, I.; Wlodarski, P.K.; Jakobisiak, M.; Stoklosa, T. Statins inhibit ABCB1 and ABCG2 drug transporter activity in chronic myeloid leukemia cells and potentiate antileukemic effects of imatinib. Exp. Hematol. 2014, 42, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoklosa, T.; Glodkowska-Mrowka, E.; Hoser, G.; Kielak, M.; Seferynska, I.; Wlodarski, P. Diverse mechanisms of mTOR activation in chronic and blastic phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Mauro, M.J.; Cortes, J.E.; Minami, H.; Rea, D.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Breccia, M.; Goh, Y.T.; Talpaz, M.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. Asciminib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after ABL Kinase Inhibitor Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, M.; Scalzulli, E.; Colafigli, G.; Foa, R.; Breccia, M. Insights into the optimal use of ponatinib in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukaemia. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10, 2040620719826444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efficace, F.; Stagno, F.; Iurlo, A.; Breccia, M.; Cottone, F.; Bonifacio, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Castagnetti, F.; Caocci, G.; Crugnola, M.; et al. Health-related quality of life of newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with first-line dasatinib versus imatinib therapy. Leukemia 2020, 34, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, J.E.; Gotlib, J.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fleischman, A.G.; Agarwal, A.; Eide, C.A.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S.K.; Tognon, C.E.; et al. Oncogenic CSF3R mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisa, E.; Nicolosi, M.; Ferri, V.; Favini, C.; Gaidano, G.; Patriarca, A. Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Where Are We Now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, F.J.; Rea, D.; Rosti, G.; Cross, N.C.P.; Steegmann, J.L.; Griskevicius, L.; Le Coutre, P.; Coriu, D.; Petrov, L.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; et al. Impact of age on efficacy and toxicity of nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENEST1st subanalysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rea, D.; Nicolini, F.E.; Tulliez, M.; Guilhot, F.; Guilhot, J.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Gardembas, M.; Coiteux, V.; Guillerm, G.; Legros, L.; et al. Discontinuation of dasatinib or nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: Interim analysis of the STOP 2G-TKI study. Blood 2017, 129, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baccarani, M.; Rosti, G.; De Vivo, A.; Bonifazi, F.; Russo, D.; Martinelli, G.; Testoni, N.; Amabile, M.; Fiacchini, M.; Montefusco, E.; et al. A randomized study of interferon-α versus interferon-α and low-dose arabinosyl cytosine in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preudhomme, C.; Guilhot, J.; Nicolini, F.E.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Rigal-Huguet, F.; Maloisel, F.; Coiteux, V.; Gardembas, M.; Berthou, C.; Vekhoff, A.; et al. Imatinib plus Peginterferon Alfa-2a in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselot, P.; Prost, S.; Guilhot, J.; Roy, L.; Etienne, G.; Legros, L.; Charbonnier, A.; Coiteux, V.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Huguet, F.; et al. Pioglitazone together with imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: A proof of concept study. Cancer 2017, 123, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghel, N.; Lipton, J.H.; Atenafu, E.G.; Kim, D.D.H.; Delgado, D.H. Cardiovascular Events After Exposure to Nilotinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Long-term Follow-up. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 870–878.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient Characteristics | Overall | Number of Patients (n = 408) | p-Value | Selected 84 Case-Control Pairs for PSM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statin Group | Non-Statin Group | Statin Group | Non-Statin Group | ||||
| Number of patients; n (%) | 408 | 88 (21.3) | 320 (78.7) | - | 84 (50.0) | 84 (50.0) | - |
| Age (years); median (range) | 52 (17–83) | 62 (24–83) | 49 (17–82) | <0.001 | 62 (24–77) | 62 (22–78) | 0.813 |
| Gender (female:male); n (%) | 175/231 | 39/49 | 136/182 | 0.795 | 39/45 (46.4:53.6) | 44/40 (52.4:47.6) | 0.44 |
| (43.1:56.9) | (44.3:55.7) | (42.8:57.2) | |||||
| Previous treatment; n (%) | 115 (28.2) | 29 (33.0) | 86 (26.9) | 0.262 | 28 (33.3) | 32 (38.1) | 0.52 |
| Previous history of interferon therapy; n (%) | 105 (25.7) | 26 (29.5) | 79 (24.7) | 0.356 | 26 (31.0) | 29 (34.5) | 0.622 |
| Previous history of BMT; n (%) | 16 (3.9) | 4 (4.5) | 12 (3.8) | 0.757 | 3 (3.6) | 4 (4.8) | 0.699 |
| Sokal risk group; n (%) | 170 (41.7) | 34 (38.6) | 136 (42.5) | 0.785 | 33 (39.3) | 30 (35.7) | 0.888 |
| 120 (29.4) | 28 (31.8) | 92 (28.8) | 25 (29.8) | 26 (31.0) | |||
| 118 (28.9) | 26 (29.5) | 92 (28.8) | 26 (31.0) | 28 (33.3) | |||
| Additional chromosomal abnormalities *; n (%) | 25 (6.1) | 5 (5.7) | 20 (6.3) | 0.844 | 4 (4.8) | 2 (2.4) | 0.682 |
| Response | |||||||
| Median follow-up (months) | 72 | 69 | 69 | 0.376 | 74 | 75 | 0.705 |
| MCyR at 6 months (% ± SE) | 68.9 ± 4.7 | 76.2 ± 9.5 | 68.5 ± 5.4 | 0.38 | 76.2 ± 9.7 | 72.0 ± 10.1 | 0.684 |
| CCyR at 12 months (% ± SE) | 64.4 ± 4.9 | 70.1 ± 10.3 | 62.8 ± 5.6 | 0.091 | 71.1 ± 10.4 | 67.1 ± 10.5 | 0.417 |
| MMR at 18 months (% ± SE) | 53.1 ± 5.2 | 67.3 ± 10.5 | 49.2 ± 5.8 | 0.005 | 68.2 ± 10.7 | 53.1 ± 11.1 | 0.072 |
| DMR at 5 years (% ± SE) | 44.2 ± 5.5 | 55.8 ± 11.7 | 41.0 ± 6.1 | 0.001 | 56.8 ± 11.9 | 47.0 ± 11.6 | 0.019 |
| FTF at 3 years (% ± SE) | 87.6 ± 1.7 | 90.2 ± 3.3 | 86.9 ± 2.0 | 0.525 | 89.8 ± 3.4 | 91.9 ± 3.7 | 0.953 |
| PFS at 5 years (% ± SE) | 95.4 ± 1.1 | 96.5 ± 2.0 | 95.0 ± 1.4 | 0.686 | 96.4 ± 2.0 | 97.3 ± 1.9 | 0.938 |
| OS at 5 years (% ± SE) | 97.4 ± 0.1 | 98.8 ± 1.2 | 97.0 ± 0.1 | 0.542 | 98.8 ± 1.2 | 97.3 ± 1.9 | 0.734 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, H.-J.; Woo, Y.-M.; Naka, K.; Park, J.-H.; Han, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Ahn, J.-S.; Kim, T.; Kimura, S.; et al. Statins Enhance the Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia when Combined with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215543
Jang H-J, Woo Y-M, Naka K, Park J-H, Han H-J, Kim H-J, Kim S-H, Ahn J-S, Kim T, Kimura S, et al. Statins Enhance the Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia when Combined with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers. 2021; 13(21):5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215543
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Hyeok-Jae, Young-Min Woo, Kazuhito Naka, Jong-Ho Park, Ho-Jae Han, Hee-Jin Kim, Sun-Hee Kim, Jae-Sook Ahn, Taehyung Kim, Shinya Kimura, and et al. 2021. "Statins Enhance the Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia when Combined with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" Cancers 13, no. 21: 5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215543
APA StyleJang, H.-J., Woo, Y.-M., Naka, K., Park, J.-H., Han, H.-J., Kim, H.-J., Kim, S.-H., Ahn, J.-S., Kim, T., Kimura, S., Zarabi, S., Lipton, J. H., Minden, M. D., Jung, C.-W., Kim, H.-J., Kim, J.-W., & Kim, D. D. H. (2021). Statins Enhance the Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia when Combined with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers, 13(21), 5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215543







