Radiomics Predicts for Distant Metastasis in Locally Advanced Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
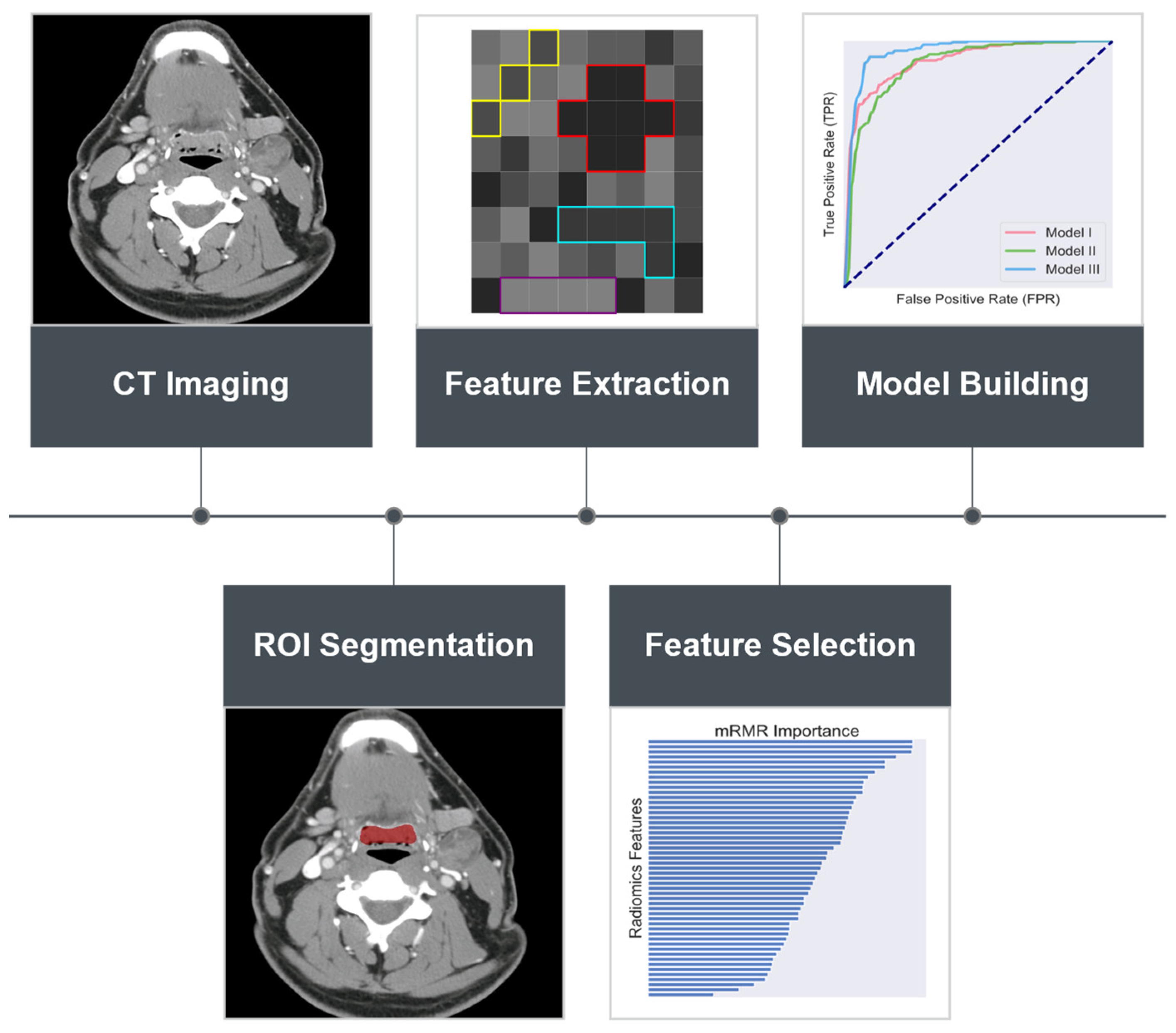
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Selection
2.2. Radiomics Feature Extraction
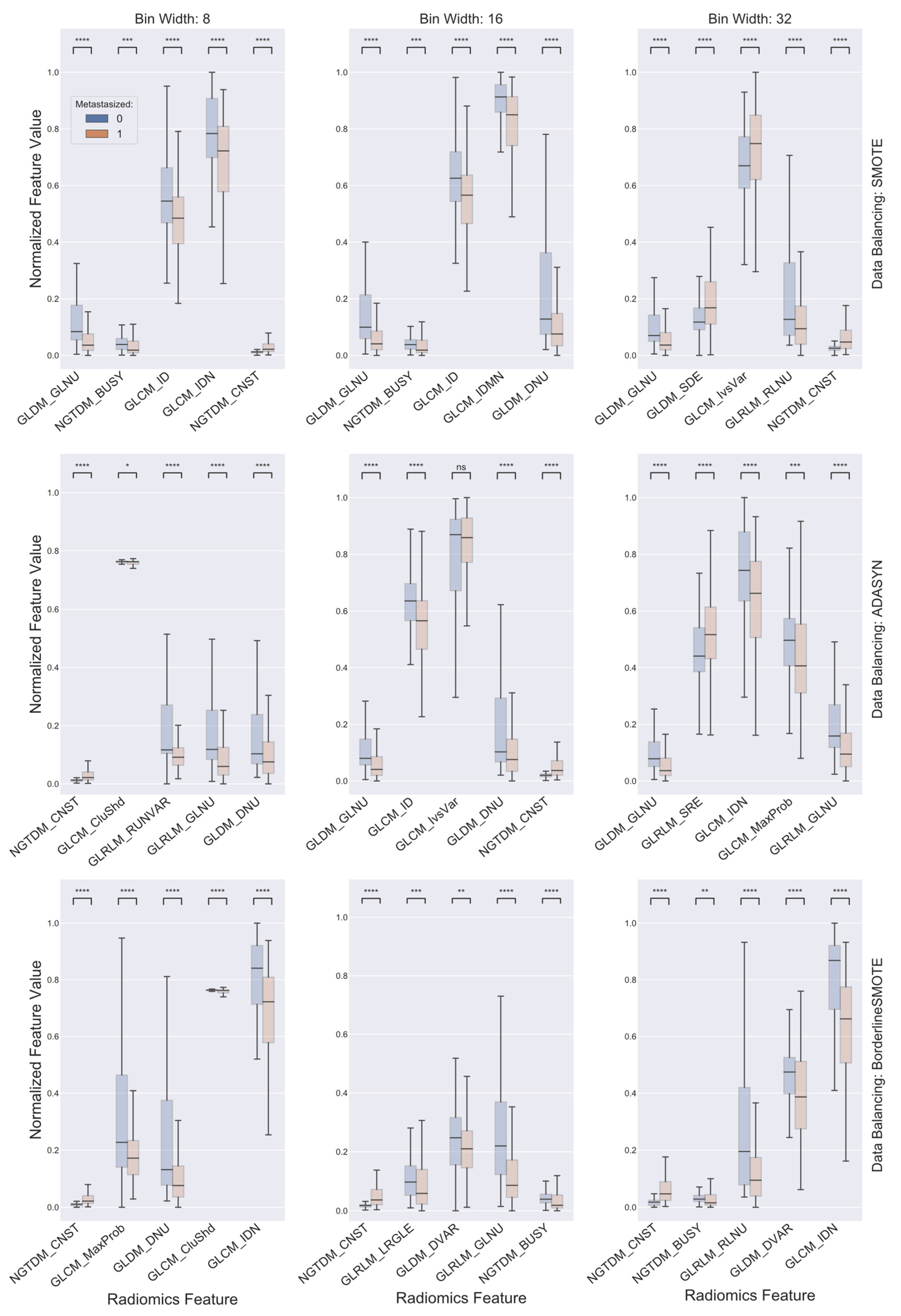
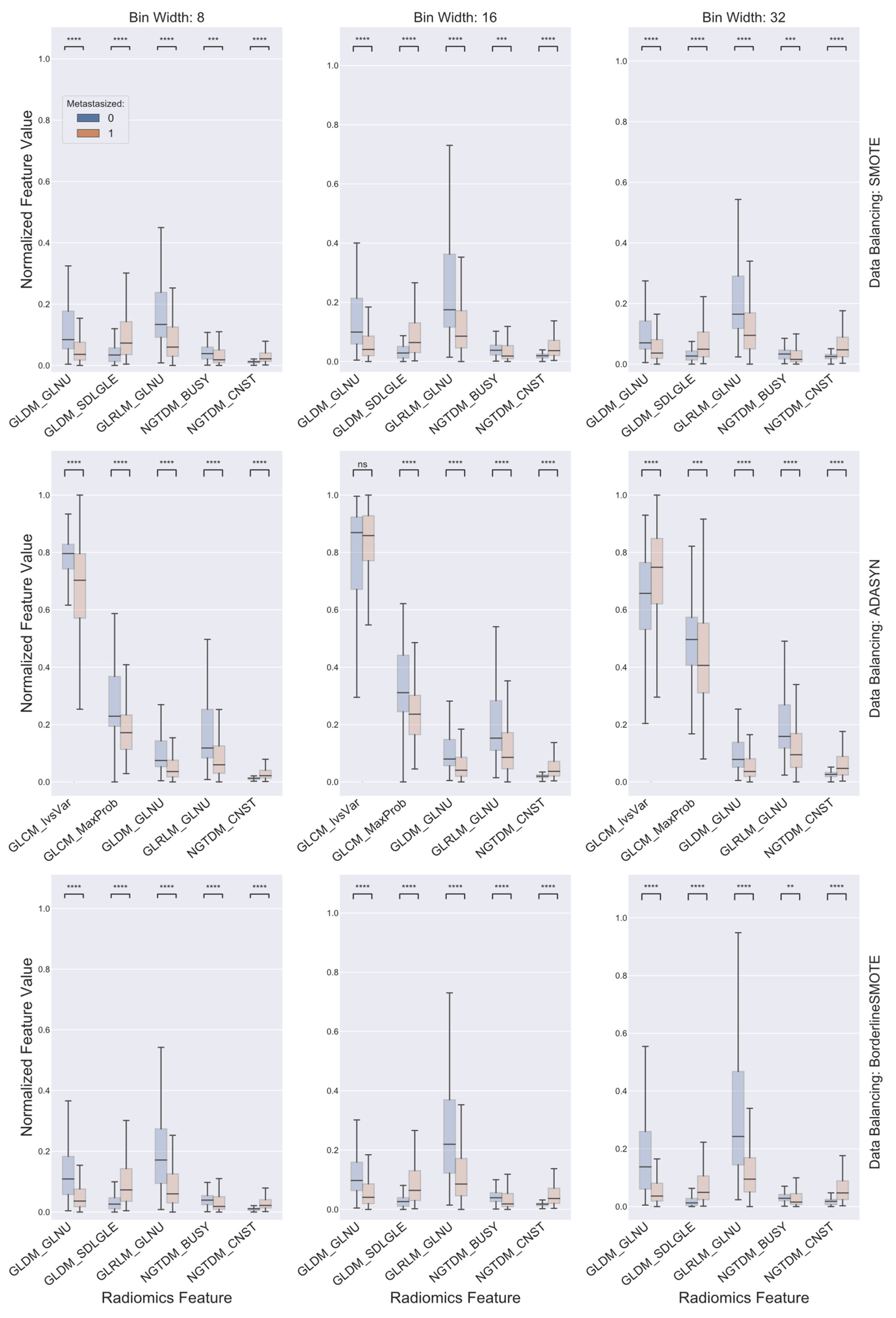
2.3. Data Balancing and Feature Selection
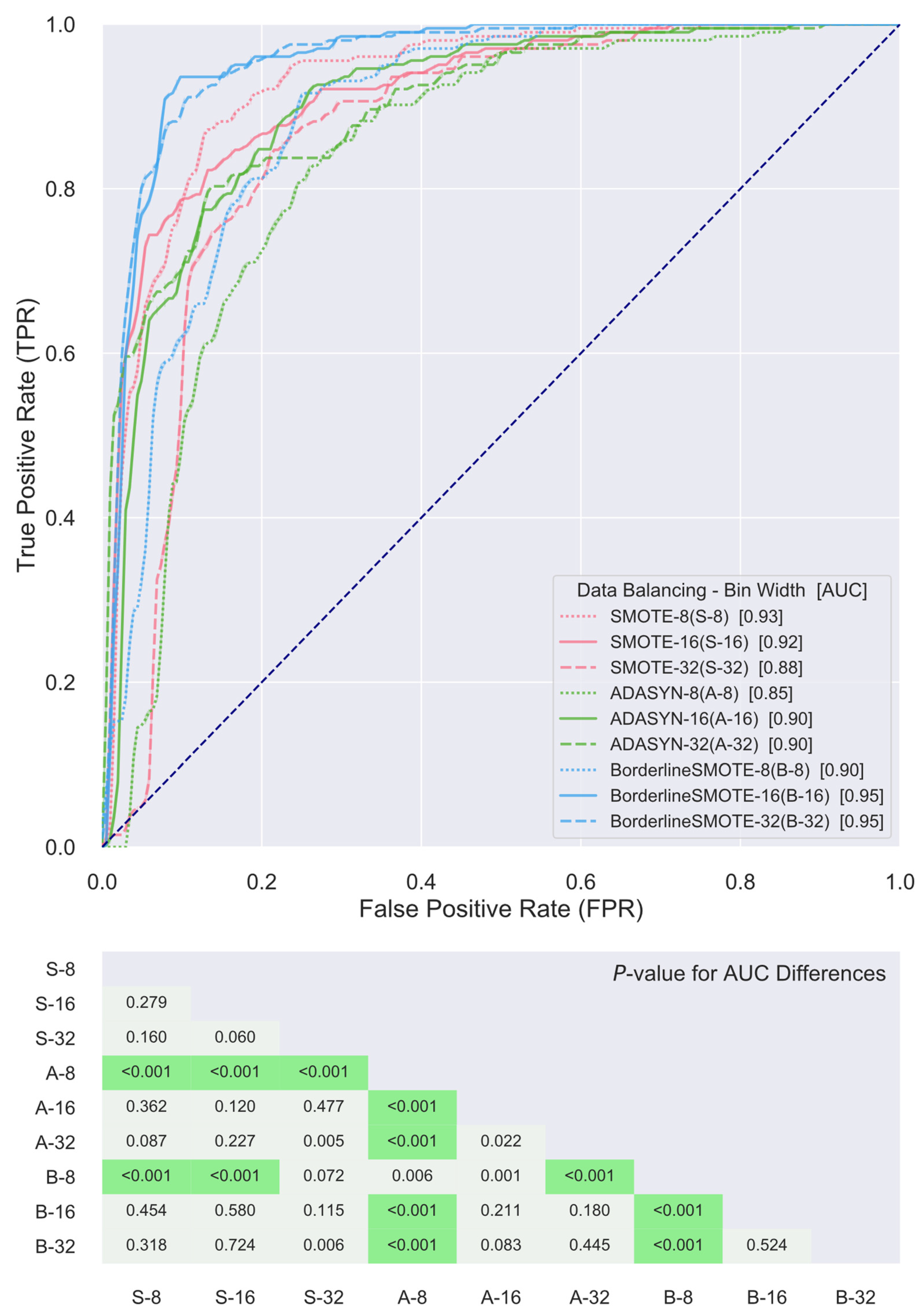
2.4. Classifier Construction and Validation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
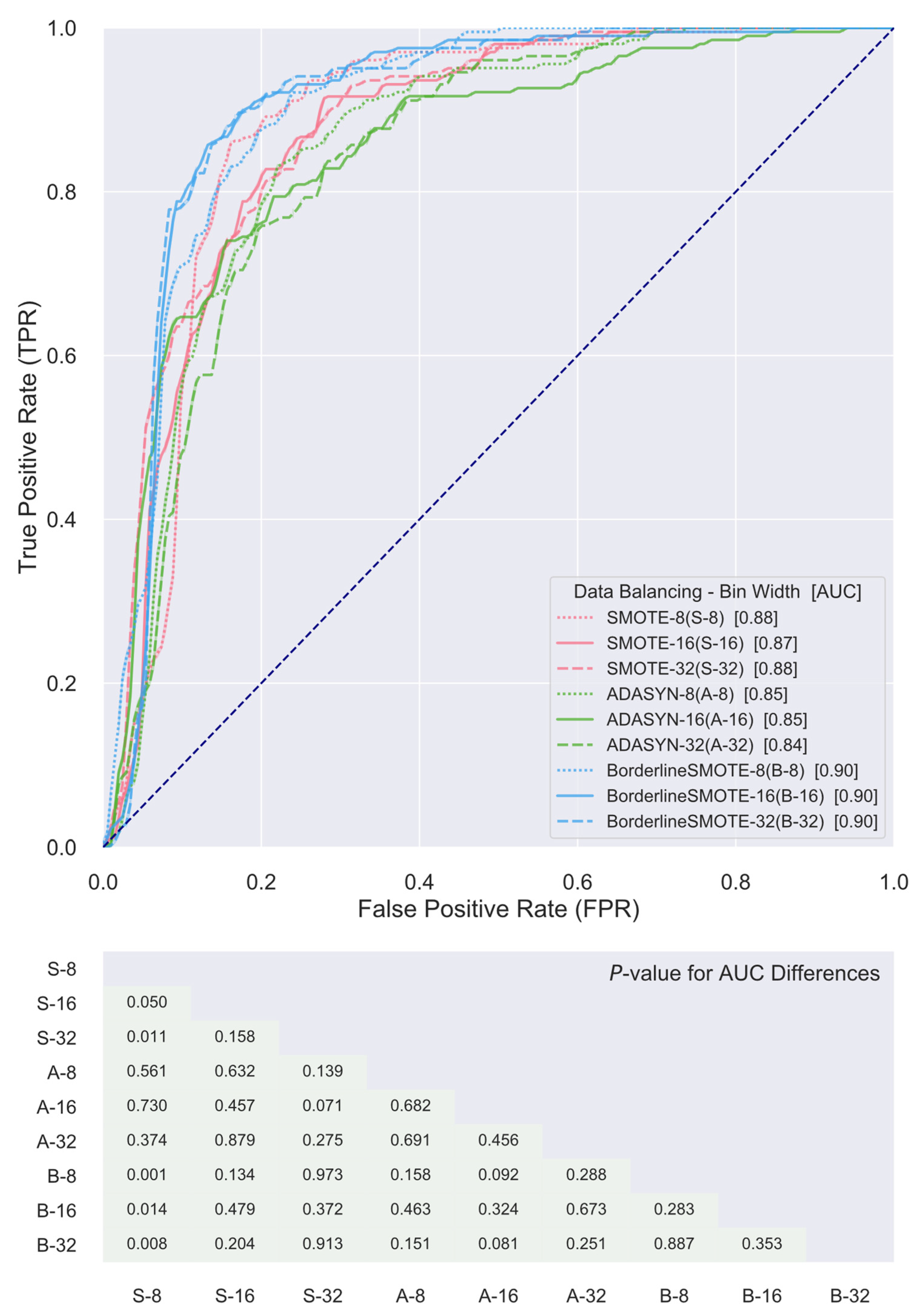
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, N.G.; Tan, D.S.; Tan, V.K.; Wang, W.; Hwang, J.; Tan, N.C.; Sivanandan, R.; Tan, H.K.; Lim, W.T.; Ang, M.K.; et al. Randomized trial comparing surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with advanced, nonmetastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: 10-year update and subset analysis. Cancer 2015, 121, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, K.C.; Tan, E.H.; Wee, J.; Lim, D.; Tai, B.C.; Khoo, M.L.; Goh, C.; Leong, S.S.; Tan, T.; Fong, K.W.; et al. Surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy in stage III/IV nonmetastatic squamous cell head and neck cancer: A randomised comparison. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garden, A.S.; Dong, L.; Morrison, W.H.; Stugis, E.M.; Glisson, B.S.; Frank, S.J.; Beadle, B.M.; Gunn, G.B.; Schwartz, D.L.; Kies, M.S.; et al. Patterns of disease recurrence following treatment of oropharyngeal cancer with intensity modulated radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; Lu, C.; et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fakhry, C.; Zhang, Q.; Nguyen-Tân, P.F.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Weber, R.S.; Lambert, L.; Trotti, A.M.; Barrett, W.L.; Thorstad, W.L.; Jones, C.U.; et al. Development and Validation of Nomograms Predictive of Overall and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With Oropharyngeal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 4057–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Jasem, J.; Jones, B.L.; Robin, T.P.; McDermott, J.D.; Bhatia, S.; Raben, D.; Jimeno, A.; Bowles, D.W.; Karam, S.D. Predictors of overall survival in human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal cancer using the National Cancer Data Base. Oral Oncol. 2016, 56, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yom, S.; Torres-Saavedra, P.; Caudell, J.; Waldron, J.; Gillison, M.; Truong, M.; Jordan, R.; Subramaniam, R.; Yao, M.; Chung, C.; et al. NRG-HN002: A Randomized Phase II Trial for Patients With p16-Positive, Non-Smoking-Associated, Locoregionally Advanced Oropharyngeal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillison, M.L.; Trotti, A.M.; Harris, J.; Eisbruch, A.; Harari, P.M.; Adelstein, D.J.; Jordan, R.C.K.; Zhao, W.; Sturgis, E.M.; Burtness, B.; et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab or cisplatin in human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (NRG Oncology RTOG 1016): A randomised, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, H.; Robinson, M.; Hartley, A.; Kong, A.; Foran, B.; Fulton-Lieuw, T.; Dalby, M.; Mistry, P.; Sen, M.; O’Toole, L.; et al. Radiotherapy plus cisplatin or cetuximab in low-risk human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (De-ESCALaTE HPV): An open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Head and Neck Cancers (Version: 3.2021); NCCN: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, S.P.; Zeevi, T.; Baumeister, P.; Reichel, C.; Sharaf, K.; Forghani, R.; Kann, B.H.; Judson, B.L.; Prasad, M.L.; Burtness, B.; et al. Potential Added Value of PET/CT Radiomics for Survival Prognostication beyond AJCC 8th Edition Staging in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Head and Neck Quantitative Imaging Working Group. Investigation of radiomic signatures for local recurrence using primary tumor texture analysis in oropharyngeal head and neck cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.Y.Y.; Su, J.; Huang, S.H.; Ghoraie, L.S.; Xu, W.; Chan, B.; Yip, K.W.; Giuliani, M.; Bayley, A.; Kim, J.; et al. Radiomic Biomarkers to Refine Risk Models for Distant Metastasis in HPV-related Oropharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallières, M.; Kay-Rivest, E.; Perrin, L.J.; Liem, X.; Furstoss, C.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Khaouam, N.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Wang, C.S.; Sultanem, K.; et al. Radiomics strategies for risk assessment of tumour failure in head-and-neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogowicz, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Guckenberger, M.; Riesterer, O. Combined CT radiomics of primary tumor and metastatic lymph nodes improves prediction of loco-regional control in head and neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brkic, F.F.; Kadletz-Wanke, L.; Kenner, L.; Fureder, T.; Jank, B.; Brunner, M.; Heiduschka, G. An analysis of distant metastasis cases from HPV-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2021, 49, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimura, H.; Soufi, M.; Kamezawa, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Yamada, M. Radiomics with artificial intelligence for precision medicine in radiation therapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, J.J.; Torres-Roca, J.F.; Gillies, R.J.; Enderling, H.; Kim, S.; Rishi, A.; Moros, E.G.; Harrison, L.B. The future of personalised radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e266–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligson, N.D.; Knepper, T.C.; Ragg, S.; Walko, C.M. Developing Drugs for Tissue-Agnostic Indications: A Paradigm Shift in Leveraging Cancer Biology for Precision Medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and operating a public information repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elhalawani, H.; Mohamed, A.S.; White, A.L.; Zafereo, J.; Wong, A.J.; Berends, J.E.; AboHashem, S.; Williams, B.; Aymard, J.M.; Kanwar, A. Matched computed tomography segmentation and demographic data for oropharyngeal cancer radiomics challenges. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170077. [Google Scholar]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossberg, A.J.; Mohamed, A.S.; Elhalawani, H.; Bennett, W.C.; Smith, K.E.; Nolan, T.S.; Williams, B.; Chamchod, S.; Heukelom, J.; Kantor, M.E. Imaging and clinical data archive for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregoire, V.; Evans, M.; Le, Q.T.; Bourhis, J.; Budach, V.; Chen, A.; Eisbruch, A.; Feng, M.; Giralt, J.; Gupta, T.; et al. Delineation of the primary tumour Clinical Target Volumes (CTV-P) in laryngeal, hypopharyngeal, oropharyngeal and oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: AIRO, CACA, DAHANCA, EORTC, GEORCC, GORTEC, HKNPCSG, HNCIG, IAG-KHT, LPRHHT, NCIC CTG, NCRI, NRG Oncology, PHNS, SBRT, SOMERA, SRO, SSHNO, TROG consensus guidelines. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larue, R.T.; van Timmeren, J.E.; de Jong, E.E.; Feliciani, G.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Schreurs, W.M.; Sosef, M.N.; Raat, F.H.; van der Zande, F.H.; Das, M. Influence of gray level discretization on radiomic feature stability for different CT scanners, tube currents and slice thicknesses: A comprehensive phantom study. Acta Oncol. 2017, 56, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc. IEEE 1979, 67, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Dogan, N.; Stoyanova, R.; Ford, J. Evaluation of radiomic texture feature error due to MRI acquisition and reconstruction: A simulation study utilizing ground truth. Phys. Med. 2018, 50, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Young, L.A.; Johnson, P.B. Quantitative radiomics: Validating image textural features for oncological PET in lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 129, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, M.M. Texture analysis using gray level run lengths. Comput. Graphic. Image Process. 1975, 4, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.; Dogan, N.; Young, L.; Yang, F. Quantitative Radiomics: Impact of Pulse Sequence Parameter Selection on MRI-Based Textural Features of the Brain. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 1729071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoecker, W.V.; Chiang, C.S.; Moss, R.H. Texture in skin images: Comparison of three methods to determine smoothness. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 1992, 16, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Simpson, G.; Young, L.; Ford, J.; Dogan, N.; Wang, L. Impact of contouring variability on oncological PET radiomics features in the lung. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wee, W.G. Neighboring gray level dependence matrix for texture classification. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 23, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.B.; Young, L.A.; Lamichhane, N.; Patel, V.; Chinea, F.M.; Yang, F. Quantitative imaging: Correlating image features with the segmentation accuracy of PET based tumor contours in the lung. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Normalizing Data in Encyclopedia of Research Design; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S. ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), Hong Kong, China, 1–8 June 2008; pp. 1322–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Wang, W.-Y.; Mao, B.-H. Borderline-SMOTE: A new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Peng, H. Minimum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2005, 3, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, K.-R.; Anderson, C.W.; Birch, G.E. Linear and nonlinear methods for brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J.; Bach, F. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; pp. 1137–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 398. [Google Scholar]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.M.; Daly, M.E.; Farwell, D.G.; Vazquez, E.; Courquin, J.; Lau, D.H.; Purdy, J.A. Quality of life among long-term survivors of head and neck cancer treated by intensity-modulated radiotherapy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Ridge, J.A.; Li, T.; Lango, M.N.; Churilla, T.M.; Bauman, J.R.; Galloway, T.J. Long-term toxicities in 10-year survivors of radiation treatment for head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2017, 71, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citrin, D.; Mansueti, J.; Likhacheva, A.; Sciuto, L.; Albert, P.S.; Rudy, S.F.; Cooley-Zgela, T.; Cotrim, A.; Solomon, B.; Colevas, A.D.; et al. Long-term outcomes and toxicity of concurrent paclitaxel and radiotherapy for locally advanced head-and-neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machtay, M.; Moughan, J.; Farach, A.; Martin-O’Meara, E.; Galvin, J.; Garden, A.S.; Weber, R.S.; Cooper, J.S.; Forastiere, A.; Ang, K.K. Hypopharyngeal dose is associated with severe late toxicity in locally advanced head-and-neck cancer: An RTOG analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, C.B.; Baxi, S.S.; Atoria, C.L.; O’Neill, J.P.; Henman, M.C.; Sherman, E.J.; Lee, N.Y.; Pfister, D.G.; Elkin, E.B. Treatment-related toxicities in older adults with head and neck cancer: A population-based analysis. Cancer 2015, 121, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rich, B.J.; Schumacher, L.D.; Sargi, Z.B.; Masforroll, M.; Kwon, D.; Zhao, W.; Rueda-Lara, M.A.; Freedman, L.M.; Elsayyad, N.; Samuels, S.E.; et al. Opioid use patterns in patients with head and neck cancer receiving radiation therapy: Single-institution retrospective analysis characterizing patients who did not require opioid therapy. Head Neck 2021, 43, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C.C.; Seiwert, T.Y.; MacCracken, E.; Blair, E.A.; Agrawal, N.; Melotek, J.M.; Portugal, L.; Brisson, R.J.; Gooi, Z.; Spiotto, M.T.; et al. Dose and Volume De-Escalation for Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer is Associated with Favorable Posttreatment Functional Outcomes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.M.; Kimple, R.J.; Lin, A.; Karam, S.D.; Margalit, D.N.; Chua, M.L.K. De-Escalation Strategies in HPV-Associated Oropharynx Cancer-Are we Putting the Cart Before the Horse? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitler, J.J.; Switchenko, J.M.; Dignam, J.J.; McDonald, M.W.; Saba, N.F.; Shin, D.M.; Magliocca, K.R.; Cassidy, R.J.; El-Deiry, M.W.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Smoking, age, nodal disease, T stage, p16 status, and risk of distant metastases in patients with squamous cell cancer of the oropharynx. Cancer 2019, 125, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setton, J.; Caria, N.; Romanyshyn, J.; Koutcher, L.; Wolden, S.L.; Zelefsky, M.J.; Rowan, N.; Sherman, E.J.; Fury, M.G.; Pfister, D.G.; et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of oropharyngeal cancer: An update of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfieri, S.; Carenzo, A.; Platini, F.; Serafini, M.S.; Perrone, F.; Galbiati, D.; Sponghini, A.P.; Depenni, R.; Vingiani, A.; Quattrone, P.; et al. Tumor Biomarkers for the Prediction of Distant Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Sturgis, E.M.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, P.; Wang, J.R.; Wei, Q.; Li, G. Genetic Variants Predict Clinical Outcomes of HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients after Definitive Radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaka, A.S.; Nowacki, N.B.; Kumar, B.; Zhao, S.; Old, M.O.; Agrawal, A.; Ozer, E.; Carrau, R.L.; Schuller, D.E.; Kumar, P.; et al. Notch1 Overexpression Correlates to Improved Survival in Cancer of the Oropharynx. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, N.; Sherman, E.; Pei, X.; Schoder, H.; Grkovski, M.; Paudyal, R.; Katabi, N.; Selenica, P.; Yamaguchi, T.N.; Ma, D.; et al. Precision Radiotherapy: Reduction in Radiation for Oropharyngeal Cancer in the 30 ROC Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabroff, K.R.; Zhao, J.; de Moor, J.S.; Sineshaw, H.M.; Freedman, A.N.; Zheng, Z.; Han, X.; Rai, A.; Klabunde, C.N. Factors Associated With Oncologist Discussions of the Costs of Genomic Testing and Related Treatments. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, P.; Liang, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Luo, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Xing, L.; Huang, M.; et al. A radiomics approach based on support vector machine using MR images for preoperative lymph node status evaluation in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5374–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Coroller, T.P.; Grossmann, P.; Zeleznik, R.; Kumar, A.; Bussink, J.; Gillies, R.J.; Mak, R.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Deep learning for lung cancer prognostication: A retrospective multi-cohort radiomics study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marino, M.A.; Pinker, K.; Leithner, D.; Sung, J.; Avendano, D.; Morris, E.A.; Jochelson, M. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Radiomics Analysis for Noninvasive Breast Cancer Characterization: Initial Results. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Thomas, M.A.; Dehdashti, F.; Grigsby, P.W. Temporal analysis of intratumoral metabolic heterogeneity characterized by textural features in cervical cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Young, L.; Grigsby, P. Predictive value of standardized intratumoral metabolic heterogeneity in locally advanced cervical cancer treated with chemoradiation. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2016, 26, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.; Folkert, M.; Liu, H.; Jiang, S.; Sher, D.; Wang, J. Multifaceted radiomics for distant metastasis prediction in head & neck cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 155009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, I.; Alvarez, M.; Hidalgo, R.; Pajares, B.; Garcia-Anaya, M.J.; Toledo, M.D.; Trigo, J.M.; Lupiañez-Perez, Y.; Medina, J.A.; Jaime Gomez-Millan, J. Causes of death in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy and systemic therapy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxi, S.S.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Patil, S.M.; Pfister, D.G.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Elkin, E.B. Causes of death in long-term survivors of head and neck cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Demographic | Median or Occurrence | Range or Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 195 | 87% |
| Female | 30 | 13% | |
| Age at diagnosis (y) | 57 | 38–81 | |
| Smoking history | Never | 88 | 40% |
| Former | 82 | 36% | |
| Current | 55 | 24% | |
| Tumor subsite | Base of tongue | 118 | 52% |
| Tonsil | 84 | 37% | |
| Not specified | 13 | 6% | |
| Glossopharyngeal sulcus | 8 | 4% | |
| Soft palate | 2 | 1% | |
| AJCC stage | III | 39 | 17% |
| IV | 186 | 83% | |
| T category | T1 | 56 | 25% |
| T2 | 93 | 41% | |
| T3 | 44 | 20% | |
| T4 | 32 | 14% | |
| N category | N0 | 11 | 5% |
| N1 | 32 | 14% | |
| N2 | 178 | 79% | |
| N3 | 4 | 2% | |
| Treatment regimen | Radiation alone | 30 | 14% |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) | 122 | 54% | |
| Induction chemotherapy and radiation alone | 14 | 6% | |
| Induction chemotherapy and concurrent CRT | 59 | 26% |
| Category | Feature |
|---|---|
| Gray-level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) | Autocorrelation (AutoCorr), Cluster Prominence (CluProm), Cluster Shade (CluShd), Cluster Tendency (CluTndy), Contrast (CNST), Correlation (CORR), Difference Average (DiffAvg), Difference Entropy (DiffEpy), Difference Variance (DiffVar), Inverse Difference (ID), Inverse Difference Moment (IDM), Inverse Difference Moment Normalized (IDMN), Inverse Difference Normalized (IDN), Informational Measure of Correlation (IMC1), Informational Measure of Correlation (IMC2), Inverse Variance (IvsVar), Joint Average (JntAvg), Joint Energy (JntEngy), Joint Entropy (JntEpy), Maximal Correlation Coefficient (MCC), Maximum Probability (MaxProb), Sum Average (SumAvg), Sum Entropy (SumEpy), Sum Squares (SumSqr) |
| Gray-level Dependence Matrix (GLDM) | Dependence Entropy (DEPNEPY), Dependence Nonuniformity (DNU), Dependence Nonuniformity Normalized (DNUN), Dependence Variance (DVAR), Gray Level Nonuniformity (GLNU), Gray Level Variance (GLV), High Gray Level Emphasis (HGLE), Large Dependence Emphasis (LDE), Large Dependence High Gray Level Emphasis (LDHGLE), Large Dependence Low Gray Level Emphasis (LDLGLE), Low Gray Level Emphasis (LGLE), Small Dependence Emphasis (SDE), Small Dependence High Gray Level Emphasis (SDHGLE), Small Dependence Low Gray Level Emphasis (SDLGLE) |
| Gray-level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM) | Gray Level Nonuniformity (GLNU), Gray Level Nonuniformity Normalized (GLNUN), Gray Level Variance (GLV), High Gray Level Run Emphasis (HGLRE), Long Run Emphasis (LRE), Long Run High Gray Level Emphasis (LRHGLE), Long Run Low Gray Level Emphasis (LRLGLE), Low Gray Level Run Emphasis (LGLRE), Run Entropy (REPY), Run Length Nonuniformity (RLNU), Run Length Nonuniformity Normalized (RLNUN), Run Percentage (RP), Run Variance (RUNVAR), Short Run Emphasis (SRE), Short Run High Gray Level Emphasis (SRHGLE), Short Run Low Gray Level Emphasis (SRLGLE) |
| Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix (NGTDM) | Busyness (BUSY), Coarseness (COAS), Complexity (CPLX), Contrast (CNST), Strength (STR) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rich, B.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Jin, W.; Johnson, P.; Wang, L.; Yang, F. Radiomics Predicts for Distant Metastasis in Locally Advanced Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225689
Rich B, Huang J, Yang Y, Jin W, Johnson P, Wang L, Yang F. Radiomics Predicts for Distant Metastasis in Locally Advanced Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(22):5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225689
Chicago/Turabian StyleRich, Benjamin, Jianfeng Huang, Yidong Yang, William Jin, Perry Johnson, Lora Wang, and Fei Yang. 2021. "Radiomics Predicts for Distant Metastasis in Locally Advanced Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 22: 5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225689
APA StyleRich, B., Huang, J., Yang, Y., Jin, W., Johnson, P., Wang, L., & Yang, F. (2021). Radiomics Predicts for Distant Metastasis in Locally Advanced Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 13(22), 5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225689






