Interleukin (IL)-9 Supports the Tumor-Promoting Environment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Intracellular Signaling Pathways Activated by IL-9
3. Implications of IL-9 Secretion in Disease
4. The Pro- and Anti-Tumoral Functions of IL-9
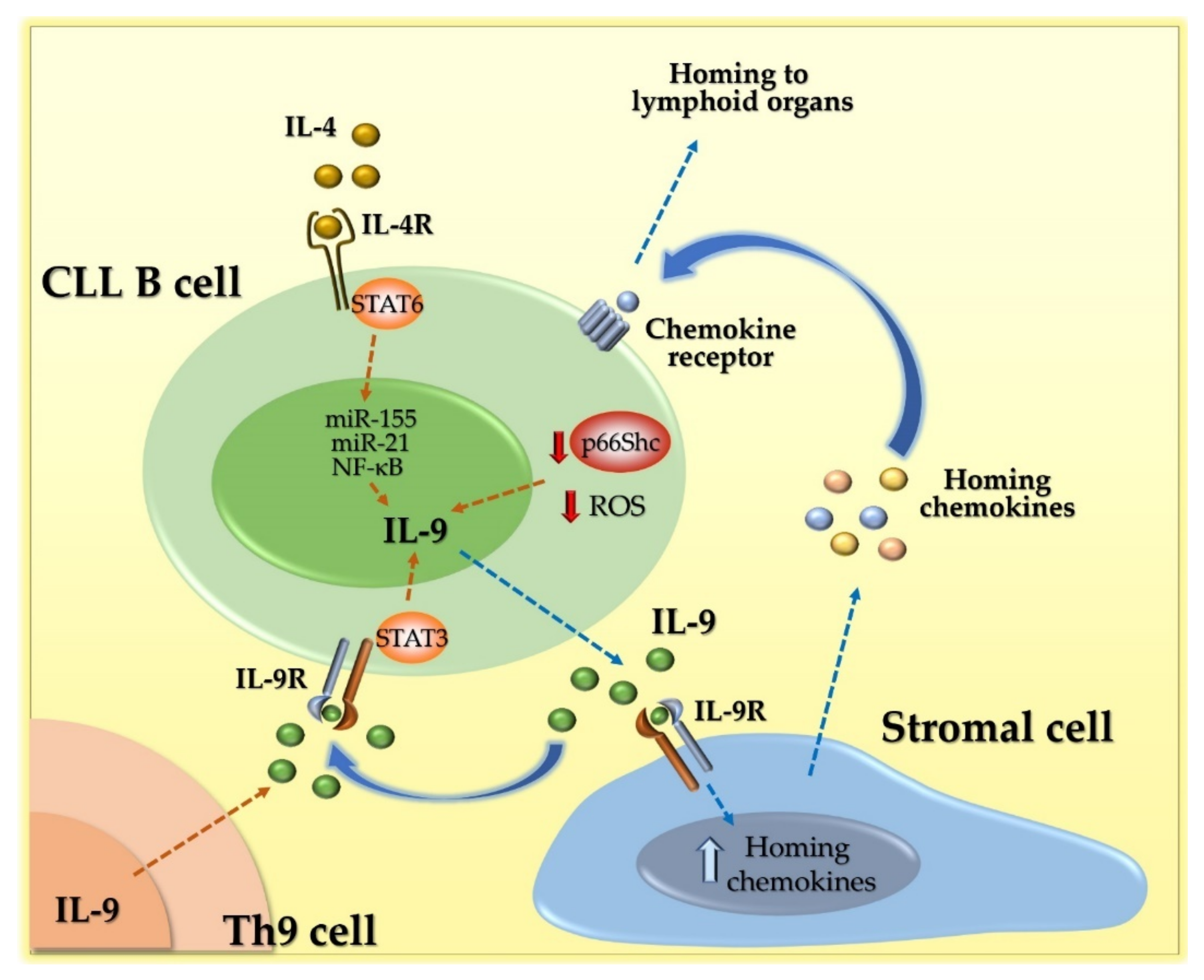
5. IL-9 Acts as a Pro-Tumoral Soluble Factor in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berraondo, P.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Ochoa, M.C.; Etxeberria, I.; Aznar, M.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Castañón, E.; Melero, I. Cytokines in clinical cancer immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic Inflammation and Cytokines in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Brummer, G.; Acevedo, D.; Cheng, N. Cytokine Regulation of Metastasis and Tumorigenicity. Adv. Cancer Res. 2016, 132, 265–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.Q.; Du, W.L.; Cai, M.H.; Yao, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Mou, X.Z. The roles of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cell. Immunol. 2020, 353, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.T.; Appenheimer, M.M.; Evans, S.S. The two faces of IL-6 in the tumor microenvironment. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortezaee, K. Immune escape: A critical hallmark in solid tumors. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Tan, Z.W.; Zhu, P.; Tan, N.S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment—Accomplices in tumor malignancy. Cell. Immunol. 2019, 343, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, D.; Grant, R.; Mishra, P.; Nilubol, N. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor in Manipulating the Immunological Response of Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.F.; Chan, M.K.K.; Li, J.S.F.; Chan, A.S.W.; Tang, P.C.T.; Leung, K.T.; To, K.F.; Lan, H.Y.; Tang, P.M.K. Tgf-β signaling: From tissue fibrosis to tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfo, V.; Romaniello, D.; Mazzeschi, M.; Sgarzi, M.; Grilli, G.; Morselli, A.; Manzan, B.; Rihawi, K.; Lauriola, M. Roles of il-1 in cancer: From tumor progression to resistance to targeted therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Feng, L.; Qu, H.; Lu, K.; Li, P.; Lv, X.; Wang, X. Overexpression of IL-9 induced by STAT3 phosphorylation is mediated by miR-155 and miR-21 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 3064–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrussi, L.; Manganaro, N.; Capitani, N.; Ulivieri, C.; Tatangelo, V.; Libonati, F.; Finetti, F.; Frezzato, F.; Visentin, A.; D’Elios, M.M.; et al. Enhanced IL-9 secretion by p66Shc-deficient CLL cells modulates the chemokine landscape of the stromal microenvironment. Blood 2021, 137, 2182–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis, K.S.; Corrigan, A.E.; Dadah, H.; George, A.M.; Keshwara, S.M.; Sideris, M.; Szabados, B. Cytokine-based cancer immunotherapy: Challenges and opportunities for IL-10. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 3247–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Musolino, C.; Tonacci, A.; Pioggia, G.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S. Clinico-biological implications of modified levels of cytokines in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A possible therapeutic role. Cancers 2020, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalapour, S.; Karin, M. Pas de Deux: Control of Anti-tumor Immunity by Cancer-Associated Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 51, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, M.; Anwar, M.A.; Choi, S. Molecular interactions between innate and adaptive immune cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and their therapeutic implications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselager, M.V.; Kater, A.P.; Eldering, E. Proliferative Signals in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia; What Are We Missing? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 592205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, I.M.; Reed, J.C. Microenvironmental interactions and survival of CLL B-cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Li, R.; Gu, Y.; Fei, Y.; Jin, K.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, K.; Wang, J.; et al. Intratumoral interleukin-9 delineates a distinct immunogenic class of gastric cancer patients with better prognosis and adjuvant chemotherapeutic response. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1856468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, Q.; Brady, T.J.; Xiao, H.; Wakefield, M.R.; Fang, Y. The Role of Interleukin-9 in Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noelle, R.J.; Nowak, E.C. Cellular sources and immune functions of interleukin-9. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Huang, L.; Cai, W.; Su, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. IL-9 and IL-9-producing cells in tumor immunity. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhoen, M.; Uyttenhove, C.; van Snick, J.; Helmby, H.; Westendorf, A.; Buer, J.; Martin, B.; Wilhelm, C.; Stockinger, B. Transforming growth factor-β “reprograms” the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrikant, P.A.; Rao, R.; Li, Q.; Kesterson, J.; Eppolito, C.; Mischo, A.; Singhal, P. Regulating functional cell fates in CD8 T cells. Immunol. Res. 2010, 46, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hong, B.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Qian, J.; Yi, Q. Tumor-specific IL-9-producing CD8+ Tc9 cells are superior effector than type-I cytotoxic Tc1 cells for adoptive immunotherapy of cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantourout, P.; Hayday, A. Six-of-the-best: Unique contributions of γδ T cells to immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, M.; Willimann, K.; Moser, B. Immunology: Professional antigen-presentation function by human γδ cells. Science 2005, 309, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliponsky, A.M.; Romani, L. The contribution of mast cells to bacterial and fungal infection immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Lee, J.B.; Liu, B.; Ohta, S.; Wang, P.Y.; Kartashov, A.V.; Mugge, L.; Abonia, J.P.; Barski, A.; Izuhara, K.; et al. Induction of Interleukin-9-Producing Mucosal Mast Cells Promotes Susceptibility to IgE-Mediated Experimental Food Allergy. Immunity 2015, 43, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, S.; Ganesan, V.; Sharma, A.; Zeng, C.; Waggoner, L.; Smith, A.; Kim, C.H.; Licona-Limón, P.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Flavell, R.A.; et al. IL-4–BATF signaling directly modulates IL-9 producing mucosal mast cell (MMC9) function in experimental food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetè, S.; Nicoletti, M.; Sagginp, A.; Maccauro, G.; Rosati, M.; Conti, F.; Cianchetti, E.; Tripodi, D.; Toniato, E.; Fulcheri, M.; et al. Interleukin-9 and mast cells. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Renauld, J.C. Interleukin 9 and its receptor: An overview of structure and function. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malka, Y.; Hornakova, T.; Royer, Y.; Knoops, L.; Renauld, J.C.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Henis, Y.I. Ligand-independent homomeric and heteromeric complexes between interleukin-2 or -9 receptor subunits and the γ chain. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33569–33577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Sun, H.B.; Tsang, M.L.S.; McMahel, J.; Grigsby, S.; Yin, T.; Yang, Y.C. Critical cytoplasmic domains of human interleukin-9 receptor α chain in interleukin-9-mediated cell proliferation and signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21334–23140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.J.; Lin, J.X.; O’Shea, J.J. The γ c Family of Cytokines: Basic Biology to Therapeutic Ramifications. Immunity 2019, 50, 832–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauert, J.H.; Lui, K.D.; You, Y.; Lai, S.Y.; Goldsmith, M.A. Heteromerization of the γ(c) chain with the interleukin-9 receptor subunit leads to STAT activation and prevention of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9255–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kubatzky, K.F.; Mitra, D.K. An update on interleukin-9: From its cellular source and signal transduction to its role in immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Uyttenhove, C.; Van Roost, E.; DeLestré, B.; Donckers, D.; Van Snick, J.; Renauld, J.C. A single tyrosine of the interleukin-9 (IL-9) receptor is required for STAT activation, antiapoptotic activity, and growth regulation by IL-9. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 4710–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Grasso, L.; Atkins, J.M.; Stevens, M.; Louahed, J.; Levitt, R.C.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Renauld, J.C. Role of insulin receptor substrate-2 in interleukin-9-dependent proliferation. FEBS Lett. 2000, 482, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenush, L.; White, M.F. The IRS-signalling system during insulin and cytokine action. BioEssays 1997, 19, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Louahed, J.; Dumoutier, L.; Stevens, M.; Renauld, J.C. MAP kinase activation by interleukin-9 in lymphoid and mast cell lines. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ksionda, O.; Melton, A.A.; Bache, J.; Tenhagen, M.; Bakker, J.; Harvey, R.; Winter, S.S.; Rubio, I.; Roose, J.P. RasGRP1 overexpression in T-ALL increases basal nucleotide exchange on Ras rendering the Ras/PI3K/Akt pathway responsive to protumorigenic cytokines. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3658–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, D.; Demoulin, J.B.; Renauld, J.C. Interleukin 9 induces expression of three cytokine signal inhibitors: Cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein, suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS)-2 and SOCS-3, but only SOCS-3 overexpression suppresses interleukin 9 signalling. Biochem. J. 2001, 353, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, D.J. Negative regulators of cytokine signal transduction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, V.; Reichenbach, P.; Renauld, J.C. Duration of STAT5 activation influences the response of interleukin-2 receptor alpha gene to different cytokines. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1999, 10, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-C.; Ruscetti, S.K.; Kirken, R.A.; Dai, R.M.; Li, C.-C.H. Involvement of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway in the Degradation of Nontyrosine Kinase-Type Cytokine Receptors of IL-9, IL-2, and Erythropoietin. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6372–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesbert, F.; Malardé, V.; Dautry-Varsat, A. Ubiquitination of the common cytokine receptor γc and regulation of expression by an ubiquitination/deubiquitination machinery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do-Thi, V.A.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S. Crosstalk between the producers and immune targets of il-9. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Ferrante, A.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R.; Triolo, G. Interleukin-9 and T helper type 9 cells in rheumatic diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.C.; Sehra, S.; Goswami, R.; Yao, W.; Yu, Q.; Stritesky, G.L.; Jabeen, R.; McKinley, C.; Ahyi, A.N.; Han, L.; et al. The transcription factor PU.1 is required for the development of IL-9-producing T cells and allergic inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Gao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Bian, F.; Chi, W.; Liu, Z.; de Paiva, C.S.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; et al. IL-33/ST2/IL-9/IL-9R signaling disrupts ocular surface barrier in allergic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu-Raychaudhuri, S.; Abria, C.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. IL-9, a local growth factor for synovial T cells in inflammatory arthritis. Cytokine 2016, 79, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Sande, M.G.; Baeten, D.L. Immunopathology of synovitis: From histology to molecular pathways. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, C.; Baldari, C.T. Regulation of T cell activation and differentiation by extracellular vesicles and their pathogenic role in systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis. Molecules 2017, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Thome, R.; Konno, S.; Mari, E.R.; Rasouli, J.; Hwang, D.; Boehm, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.-X.; Ciric, B.; et al. IL-9 Controls Central Nervous System Autoimmunity by Suppressing GM-CSF Production. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, U.; Van Snick, J.; Campanile, F.; Silla, S.; Giampietri, A.; Vacca, C.; Renauld, J.-C.; Fioretti, M.C.; Puccetti, P. IL-9 Protects Mice from Gram-Negative Bacterial Shock: Suppression of TNF-α, IL-12, and IFN-γ, and Induction of IL-10. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4197–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yi, Q. Anticancer Tc9 cells: Long-lived tumor-killing T cells for adoptive therapy. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e28542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hong, S.; Li, H.; Park, J.; Hong, B.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; He, J.; et al. Th9 cells promote antitumor immune responses in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4160–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwar, R.; Schlapbach, C.; Xiao, S.; Kang, H.S.; Elyaman, W.; Jiang, X.; Jetten, A.M.; Khoury, S.J.; Fuhlbrigge, R.C.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Robust tumor immunity to melanoma mediated by interleukin-9-producing T cells. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végran, F.; Berger, H.; Boidot, R.; Mignot, G.; Bruchard, M.; Dosset, M.; Chalmin, F.; Rébé, C.; Dérangère, V.; Ryffel, B.; et al. The transcription factor IRF1 dictates the IL-21-dependent anticancer functions of T H9 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, Y.; Zheng, X.; Brunn, D.; Raifer, H.; Picard, F.; Zhang, Y.; Winter, H.; Guenther, S.; Weigert, A.; Weigmann, B.; et al. Microenvironmental Th9 and Th17 lymphocytes induce metastatic spreading in lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3560–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, J. Effect of TH9/IL-9 on the growth of gastric cancer in nude mice. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Mao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Dong, X.; Zhao, X. IL-9 Exerts Antitumor Effects in Colon Cancer and Transforms the Tumor Microenvironment In Vivo. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819857737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Sakurai, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Tsuda, M.; Kataoka, T.R.; Hirata, M.; Nishie, M.; Nojiri, T.; Kumazoe, M.; et al. Alteration of specific cytokine expression patterns in patients with breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.P.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Zhu, R.; Lv, C.Q.; Tang, H.T.; Sun, D.W. Th9 cells promote antitumor immunity via IL-9 and IL-21 and demonstrate atypical cytokine expression in breast cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 52, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lai, R.; Lin, Q.; Lau, E.; Thomazy, D.M.; Calame, D.; Ford, R.J.; Kwak, L.W.; Kirken, R.A.; Amin, H.M. Autocrine release of interleukin-9 promotes Jak3-dependent survival of ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma cells. Blood 2006, 108, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Snick, J.; Houssiau, F.; Proost, P.; Van Damme, J.; Renauld, J.C. I-309/T cell activation gene-3 chemokine protects murine T cell lymphomas against dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2570–2576. [Google Scholar]
- Merz, H.; Houssiau, F.A.; Orscheschek, K.; Renauld, J.C.; Fliedner, A.; Herin, M.; Noel, H.; Kadin, M.; Mueller-Hermelink, H.K.; Van Snick, J.; et al. Interleukin-9 expression in human malignant lymphomas: Unique association with Hodgkin’s disease and large cell anaplastic lymphoma. Blood 1991, 78, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlio, J.P.; Kadin, M.E. Cytokines, genetic lesions and signaling pathways in anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagato, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Kishibe, K.; Takahara, M.; Ogino, T.; Ishii, H.; Oikawa, K.; Aoki, N.; Sato, K.; Kimura, S.; et al. Expression of interleukin-9 in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cell lines and patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8250–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Bijman, M.; Molin, D.; Cormont, F.; Uyttenhove, C.; van Snick, J.; Sundström, C.; Enblad, G.; Nilsson, G. Increased serum levels of interleukin-9 correlate to negative prognostic factors in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2513–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.L.; Gao, J.M.; Li, P.P.; Wang, X. IL-9 contributes to immunosuppression mediated by regulatory T cells and mast cells in B-cell non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Feng, L.; Fang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X. Overexpression of IL-9 receptor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 911–916. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Feng, L.; Ge, X.; Lu, K.; Wang, X. Interleukin-9 promotes cell survival and drug resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dhamija, B.; Marathe, S.; Ghosh, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Karulkar, A.; Sharma, N.; Sengar, M.; Sridhar, E.; Bonda, A.; et al. The Th9 Axis reduces the oxidative stress and promotes the survival of malignant t cells in cutaneous t-cell lymphoma patients. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Griner, L.A.M.; Ju, W.; Duveau, D.Y.; Guha, R.; Petrus, M.N.; Wen, B.; Maeda, M.; Shinn, P.; Ferrer, M.; et al. Selective targeting of JAK/STAT signaling is potentiated by Bcl-xL blockade in IL-2-dependent adult T-cell leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12480–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipps, T.J.; Stevenson, F.K.; Wu, C.J.; Croce, C.M.; Packham, G.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Gribben, J.; Rai, K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hacken, E.; Burger, J.A. Microenvironment interactions and B-cell receptor signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Implications for disease pathogenesis and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shcherbina, V.; Gordiienko, I.; Shlapatska, L.; Gluzman, D.; Sidorenko, S. CD150 and CD180 are negative regulators of IL-10 expression and secretion in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Neoplasma 2021, 68, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.T.; Farren, T.; Agrawal, S.G.; Liu, F.T. Increased autocrine interleukin-6 production is significantly associated with worse clinical outcome in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 13994–14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; McCaw, L.; Li, Y.J.; Zhu, F.; Gorczynski, R.; Duncan, G.S.; Yang, B.; Ben-David, Y.; Spaner, D.E. Microenvironmental interleukin-6 suppresses toll-like receptor signaling in human leukemia cells through miR-17/19A. Blood 2015, 126, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Totero, D.; Meazza, R.; Capaia, M.; Fabbi, M.; Azzarone, B.; Balleari, E.; Gobbi, M.; Cutrona, G.; Ferrarini, M.; Ferrini, S. The opposite effects of IL-15 and IL-21 on CLL B cells correlate with differential activation of the JAK/STAT and ERK1/2 pathways. Blood 2008, 111, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprevotte, E.; Voisin, G.; Ysebaert, L.; Klein, C.; Daugrois, C.; Laurent, G.; Fournie, J.-J.; Quillet-Mary, A. Recombinant Human IL-15 Trans -Presentation by B Leukemic Cells from Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Induces Autologous NK Cell Proliferation Leading to Improved Anti-CD20 Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3634–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, E.; Cantó, E.; Vidal, S.; Juarez, C.; Sierra, J.; Briones, J. Interleukin-15 enhances rituximab-dependent cytotoxicity against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and overcomes transforming growth factor beta-mediated immunosuppression. Exp. Hematol. 2011, 39, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Memarian, A.; Asgarian-Omran, H.; Razavi, S.M.; Sarrafnejad, A.; Shokri, F. Downregulation of IL-17-producing T cells is associated with regulatory T cell expansion and disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; McCaw, L.; Spaner, D.E.; Gorczynski, R.M. Targeting the IL-17/IL-6 axis can alter growth of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in vivo/in vitro. Leuk. Res. 2018, 66, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbassy, H.A.; Aboelwafa, R.A.; Ghallab, O.M. Evaluation of Interleukin-9 Expression as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in a Cohort of Egyptian Patients. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2017, 33, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, S.A.; El-Senduny, F.F.; Abousamra, N.K.; Salah El-Din, M.; Youssef, M.M. Oxidative stress in CLL patients leads to activation of Th9 cells: An experimental and comprehensive survey. Immunol. Med. 2020, 43, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Lv, X.; Li, P.; Lu, K.; Wang, X. Role of high expression of IL-9 in prognosis of CLL. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bichi, R.; Shinton, S.A.; Martin, E.S.; Koval, A.; Calin, G.A.; Cesari, R.; Russo, G.; Hardy, R.R.; Croce, C.M. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6955–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchini, A.; Aragno, M.; Vallario, A.; Alfarano, A.; Circosta, P.; Gottardi, D.; Faldella, A.; Rege-Cambrin, G.; Thunberg, U.; Nilsson, K.; et al. MEC1 and MEC2: Two new cell lines derived from B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia in prolymphocytoid transformation. Leuk. Res. 1999, 23, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Lu, K.; Li, P.; Lv, X.; Wang, X. Overexpression of IL-9 induced by STAT6 activation promotes the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2319–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Rozovski, U.; Calin, G.A.; Setoyama, T.; D’Abundo, L.; Harris, D.M.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Grgurevic, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Faderl, S.; et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-3 regulates microRNA gene expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jash, A.; Sahoo, A.; Kim, G.C.; Chae, C.S.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, J.E.; Im, S.H. Nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 (NFAT1)-induced Permissive chromatin modification facilitates nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-mediated interleukin-9 (IL-9) transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15445–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassen, M.; Müller, C.; Arnold, M.; Hültner, L.; Klein-Hessling, S.; Neudörfl, C.; Reineke, T.; Serfling, E.; Schmitt, E. IL-9 and IL-13 Production by Activated Mast Cells Is Strongly Enhanced in the Presence of Lipopolysaccharide: NF-κB Is Decisively Involved in the Expression of IL-9. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4391–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Papakonstantinou, N.; Ntoufa, S.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Rosenquist, R. NF-κB activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A point of convergence of external triggers and intrinsic lesions. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitani, N.; Lucherini, O.M.; Sozzi, E.; Ferro, M.; Giommoni, N.; Finetti, F.; De Falco, G.; Cencini, E.; Raspadori, D.; Pelicci, P.G.; et al. Impaired expression of p66Shc, a novel regulator of B-cell survival, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 3726–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patrussi, L.; Capitani, N.; Ulivieri, C.; Manganaro, N.; Granai, M.; Cattaneo, F.; Kabanova, A.; Mundo, L.; Gobessi, S.; Frezzato, F.; et al. p66Shc deficiency in the Eμ-TCL1 mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia enhances leukemogenesis by altering the chemokine receptor landscape. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrussi, L.; Capitani, N.; Baldari, C.T. Abnormalities in chemokine receptor recycling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3249–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiniz, N.; Beyar Katz, O.; Polliack, A.; Tadmor, T. The Clinical Spectrum of Hepatic Manifestations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmier, D.; Dartigeas, C.; Mankikian, J.; Rousselot-Denis, C.; Lissandre, S.; Diot, P.; Marchand-Adam, S. Serious bronchopulmonary involvement due to chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.N.; Guo, Y.B.; Li, X.; Li, C.L.; Tan, W.P.; Fan, X.L.; Qin, Z.L.; Chen, D.; Wen, W.P.; Zheng, S.G.; et al. ILC2 frequency and activity are inhibited by glucocorticoid treatment via STAT pathway in patients with asthma. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 73, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Yassine, F.; Gadd, M.E.; Qin, H. Driving out chronic lymphocytic leukemia with CAR T-cells. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bi, E.; Ma, X.; Xiong, W.; Qian, J.; Ye, L.; Su, P.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, L.; Yang, M.; et al. Enhanced CAR-T activity against established tumors by polarizing human T cells to secrete interleukin-9. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Song, Z.; Lu, X.; Ma, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Duan, M.; Apetoh, L.; Li, X.; et al. Fas signaling-mediated TH9 cell differentiation favors bowel inflammation and antitumor functions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, C.S.; Kaiser, A.; Paulos, C.M.; Cassard, L.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Heemskerk, B.; Wrzesinski, C.; Borman, Z.A.; Muranski, P.; Restifo, N.P. Type 17 CD8+ T cells display enhanced antitumor immunity. Blood 2009, 114, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visekruna, A.; Ritter, J.; Scholz, T.; Campos, L.; Guralnik, A.; Poncette, L.; Raifer, H.; Hagner, S.; Garn, H.; Staudt, V.; et al. Tc9 cells, a new subset of CD8+ T cells, support Th2-mediated airway inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Gribben, J.G. The microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and other B cell malignancies: Insight into disease biology and new targeted therapies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 24, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patrussi, L.; Capitani, N.; Baldari, C.T. Interleukin (IL)-9 Supports the Tumor-Promoting Environment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 6301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246301
Patrussi L, Capitani N, Baldari CT. Interleukin (IL)-9 Supports the Tumor-Promoting Environment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers. 2021; 13(24):6301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246301
Chicago/Turabian StylePatrussi, Laura, Nagaja Capitani, and Cosima T. Baldari. 2021. "Interleukin (IL)-9 Supports the Tumor-Promoting Environment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Cancers 13, no. 24: 6301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246301
APA StylePatrussi, L., Capitani, N., & Baldari, C. T. (2021). Interleukin (IL)-9 Supports the Tumor-Promoting Environment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers, 13(24), 6301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246301






