Anti-Cancer Role and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
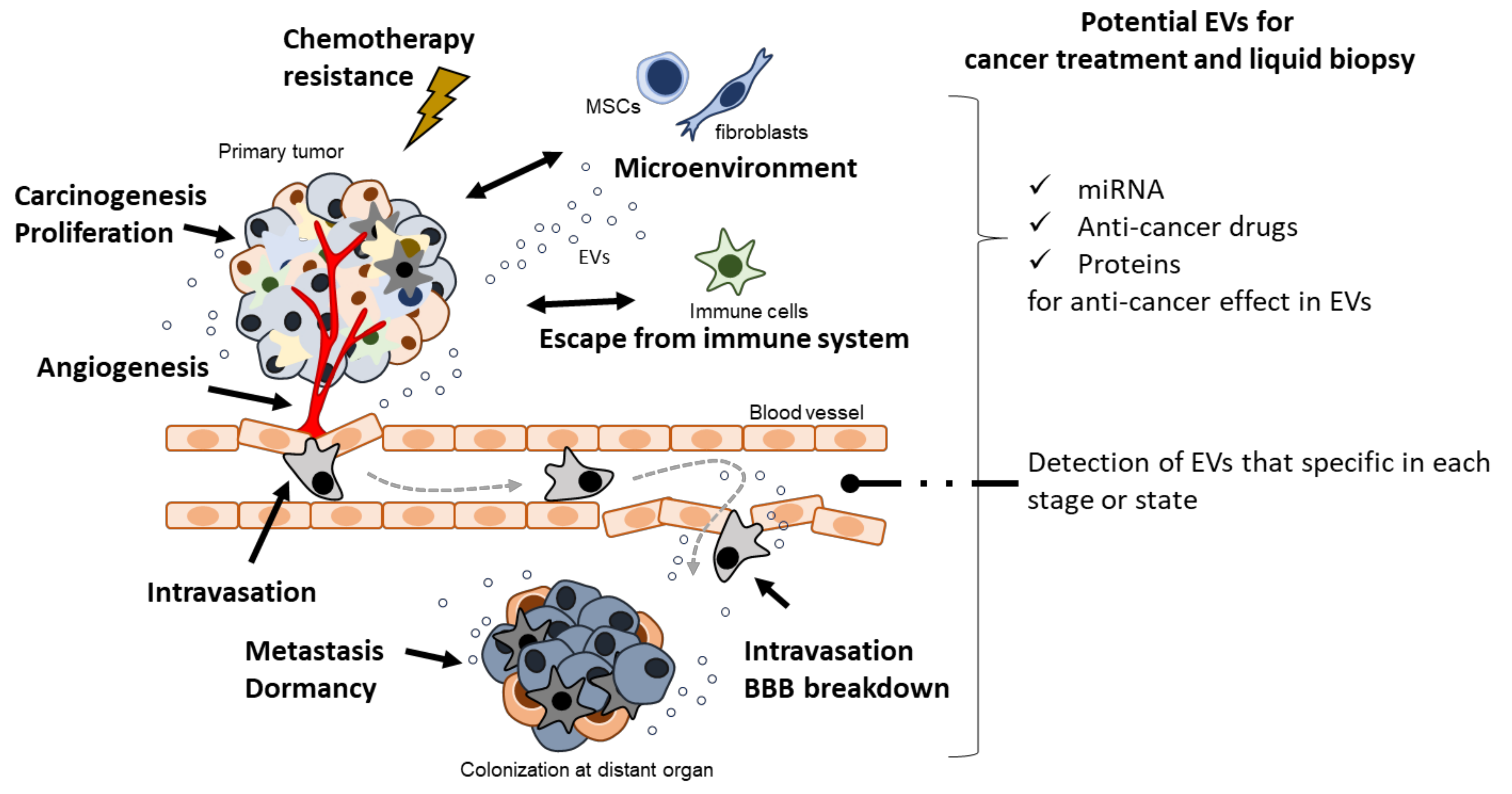
2. Carcinogenesis
3. Proliferation
4. Angiogenesis and Intravasation
5. Metastasis
6. Escape from Immune System
7. Chemotherapeutic Stress
8. Potential of EVs for Liquid Biopsy
9. Potential of EVs for Cancer Treatment
10. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutz, H.U.; Lomant, A.J.; McMillan, P.; Wehrli, E. Rearrangements of integral membrane components during in vitro aging of sheep erythrocyte membranes. J. Cell Biol. 1977, 74, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, G.; Hedström, M. Restoration of detergent-inactivated adenosine triphosphatase activity of human prostatic fluid with concanavalin A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1977, 483, 483–486. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000527447790078X?via%3Dihub (accessed on 15 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.; Schmidt, U.; Lutz, H.U. On the mechanism of vesicle release from ATP-depleted human red blood cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1981, 649, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweig, S.E.; Tokuyasu, K.T.; Singer, S.J. Member-associated changes during erythropoiesis. On the mechanism of maturation of reticulocytes to erythrocytes. J. Supramol. Struct. Cell. Biochem. 1981, 17, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.; Heuser, J.; Stahl, P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 97, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.; Heuser, J.; Stahl, P. Endocytosis and intracellular processing of transferrin and colloidal gold-transferrin in rat reticulocytes: Demonstration of a pathway for receptor shedding. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1984, 35, 256–263. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=6151502%5Buid%5D. (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Pan, B.T.; Teng, K.; Wu, C.; Adam, M.; Johnstone, R.M. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Mathew, A.; Mason, A.B.; Teng, K. Exosome formation during maturation of mammalian and avian reticulocytes: Evidence that exosome release is a major route for externalization of obsolete membrane proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 1991, 147, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, S.J.; Raposo, G. As we wait: Coping with an imperfect nomenclature for extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Théry, C. Extracellular vesicles or exosomes? On primacy, precision, and popularity influencing a choice of nomenclature. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1648167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Micallef, J.; Lhotak, V.; May, L.; Guha, A.; Rak, J. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Tabi, Z. Exosomes and the MICA-NKG2D system in cancer. Blood Cells. Mol. Dis. 2005, 34, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent exosomal transfer of angiogenic micrornas regulate cancer cell metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10849–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, N.; Kosaka, N.; Ono, M.; Katsuda, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tamura, K.; Lötvall, J.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Brain metastatic cancer cells release microRNA-181c-containing extracellular vesicles capable of destructing blood-brain barrier. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.M.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zitvogel, L.; Regnault, A.; Lozier, A.; Wolfers, J.; Flament, C.; Tenza, D.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: Dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida-Aoki, N.; Tominaga, N.; Takeshita, F.; Sonoda, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. Disruption of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy against Cancer Metastasis. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M.-C.; Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Fonsato, V.; Tetta, C. Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): Exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuura, K.; de Giorgi, V.; Schechterly, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Farci, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Alter, H.J. Circulating let-7 levels in plasma and extracellular vesicles correlate with hepatic fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2016, 64, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tsai, M.-H.; Shumilov, A.; Baccianti, F.; Tsao, S.W.; Poirey, R.; Delecluse, H.-J. Epstein-Barr virus ncRNA from a nasopharyngeal carcinoma induces an inflammatory response that promotes virus production. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butin-Israeli, V.; Bui, T.M.; Wiesolek, H.L.; Mascarenhas, L.; Lee, J.J.; Mehl, L.C.; Knutson, K.R.; Adam, S.A.; Goldman, R.D.; Beyder, A.; et al. Neutrophil-induced genomic instability impedes resolution of inflammation and wound healing. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, M.; Osti, D.; Richichi, C.; Ortensi, B.; del Bene, M.; Fornasari, L.; Beznoussenko, G.; Mironov, A.; Rappa, G.; Cuomo, A.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of CLIC1 protein is a novel mechanism for the regulation of glioblastoma growth. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31413–31427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.L.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kogure, T.; Yan, I.K.; Lin, W.-L.; Patel, T. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA TUC339: A Mechanism of Intercellular Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takasugi, M.; Okada, R.; Takahashi, A.; Chen, D.V.; Watanabe, S.; Hara, E. Small extracellular vesicles secreted from senescent cells promote cancer cell proliferation through EphA2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.; Dickman, C.; Towle, R.; Jabalee, J.; Javer, A.; Garnis, C. Extracellular vesicle secretion of miR-142-3p from lung adenocarcinoma cells induces tumor promoting changes in the stroma through cell-cell communication. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Wood, J.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Involvement of extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) in tumor cell responses to chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, D.-K.; Yoon, C.M.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Gho, Y.S. Egr-1 activation by cancer-derived extracellular vesicles promotes endothelial cell migration via ERK1/2 and JNK signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, H.; Peng, R.; Fang, F.; Mao, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Dai, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Feng, N.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer progression via exosome-mediated miR-95 transfer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9729–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iempridee, T. Long non-coding RNA H19 enhances cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of cervical cancer cell lines. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Meng, X.; Wu, M.; Han, J.; Tan, X. Exosomal zinc transporter ZIP4 promotes cancer growth and is a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2946–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Kang, H. Loss of microRNA-30e induced by extracellular vesicles from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer progression by binding to CTHRC1. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 118, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.-C.; Huang, J.-Y.; Wei, Z.-Y.; Li, Z.-X.; Guo, S.-C. EWSAT1 Acts in Concert with Exosomes in Osteosarcoma Progression and Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis: The “Double Stacking Effect”. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, e2000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Xing, Z.; Guo, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Z. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-155 overexpression in extracellular vesicles promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting FOXO3. Aging 2021, 13, 9613–9626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Yi, J.; Dong, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Miao, L.; Zhou, W. miR-365 secreted from M2 Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through the BTG2/FAK/AKT axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4671–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Yue, P.; Li, X. M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promote gastric cancer progression via a microRNA-130b-3p/MLL3/GRHL2 signaling cascade. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.-X.; Chen, C.-J.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Liu, J.-X.; Lin, F.-J. Extracellular vesicle-derived circ_SLC19A1 promotes prostate cancer cell growth and invasion through the miR-497/septin 2 pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.K.; Greening, D.W.; Hanssen, E.G.; Zhu, H.-J.; Simpson, R.J.; Mathias, R.A. Oncogenic epithelial cell-derived exosomes containing Rac1 and PAK2 induce angiogenesis in recipient endothelial cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19709–19722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Hepatocellular carcinoma cell-derived extracellular vesicles encapsulated microRNA-584-5p facilitates angiogenesis through PCK1-mediated nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 125, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lum, D.; Druso, J.E.; Blank, B.; Wilson, K.F.; Welm, A.; Antonyak, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. A class of extracellular vesicles from breast cancer cells activates VEGF receptors and tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannafon, B.N.; Carpenter, K.J.; Berry, W.L.; Janknecht, R.; Dooley, W.C.; Ding, W.-Q. Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.-Y.; Wei, J.-X.; Lv, L.-H.; Han, Q.-F.; Yang, W.-B.; Li, G.-L.; Wang, P.-X.; Wu, S.-B.; Duan, J.-X.; Zhuo, W.-F.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 induces angiogenesis via exosomes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Ming, P.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Xu, X.; Ge, W. The extracellular vesicles secreted by lung cancer cells in radiation therapy promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-23a. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.-H.; Liou, G.-G.; Liu, S.-H.; Chang, J.S.; Hsiao, J.-R.; Yen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wu, W.-L.; Chang, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-W. Laminin γ2-enriched extracellular vesicles of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells enhance in vitro lymphangiogenesis via integrin α3-dependent uptake by lymphatic endothelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2795–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.; Dickman, C.; MacLellan, S.; Towle, R.; Jabalee, J.; Lam, S.; Garnis, C. Selective secretion of microRNAs from lung cancer cells via extracellular vesicles promotes CAMK1D-mediated tube formation in endothelial cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83913–83924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoumi-Dehghi, S.; Babashah, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M. microRNA-141-3p-containing small extracellular vesicles derived from epithelial ovarian cancer cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis through activating the JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 14, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, L.; Bian, H.; Hu, J.; Li, D.; Xia, C.; Xu, H. Tumor-Derived EV-Encapsulated miR-181b-5p Induces Angiogenesis to Foster Tumorigenesis and Metastasis of ESCC. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, S.; He, Z.; Huang, H.; Yao, Z.; Miao, Y.; Cai, C.; Zou, F. MCU-dependent negative sorting of miR-4488 to extracellular vesicles enhances angiogenesis and promotes breast cancer metastatic colonization. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6975–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, B.; Mei, J.; Peng, X.; Wu, Z. Extracellular vesicles-encapsulated microRNA-10a-5p shed from cancer-associated fibroblast facilitates cervical squamous cell carcinoma cell angiogenesis and tumorigenicity via Hedgehog signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aday, S.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Chamorro-Jorganes, A.; Anwar, M.; Goldsmith, M.; Beazley-Long, N.; Sahoo, S.; Dogra, N.; Sweaad, W.; Catapano, F.; et al. Bioinspired artificial exosomes based on lipid nanoparticles carrying let-7b-5p promote angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2239–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Schattschneider, J.; Blechner, C.; Krisp, C.; Schlüter, H.; Schweizer, M.; Nalaskowski, M.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Windhorst, S. Tubulin Tyrosine Ligase Like 4 (TTLL4) overexpression in breast cancer cells is associated with brain metastasis and alters exosome biogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Lv, M.; Yu, Q.; Bao, J.; Lou, K.; Li, X. MicroRNA-370-3p shuttled by breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles induces fibroblast activation through the CYLD/Nf-κB axis to promote breast cancer progression. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2021, 35, e21383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W. LncRNA HLA-F-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by inducing PFN1 in colorectal cancer-derived extracellular vesicles and mediating macrophage polarization. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, L.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.X.; Culbertson, B.; Zhou, A.Y.; Goga, A.; Goodarzi, H. Cancer cells exploit an orphan RNA to drive metastatic progression. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.-P.; Luo, L.-J.; Chen, H.-Z.; Chen, Q.-T.; Bian, X.-L.; Wu, S.-F.; Zhou, J.-X.; Zhao, W.-X.; Liu, J.-M.; Wang, X.-M.; et al. Ectosomal PKM2 Promotes HCC by Inducing Macrophage Differentiation and Remodeling the Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cell. 2020, 78, 1192–1206.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Koyama, K.; Ota, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Yamakita, K.; Fujii, S.; Kitano, Y. The Interaction Between Long Non-coding RNA HULC and MicroRNA-622 via Transfer by Extracellular Vesicles Regulates Cell Invasion and Migration in Human Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Long, Q.; Zeng, H.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, L. Small extracellular vesicles containing miR-30a-3p attenuate the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SNAP23 gene. Oncogene 2021, 40, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Dong, F.; Xin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C. Breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles transfer miR-182-5p and promote breast carcinogenesis via the CMTM7/EGFR/AKT axis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, G.; Yue, M.; Wang, L. Extracellular vesicles-derived microRNA-222 promotes immune escape via interacting with ATF3 to regulate AKT1 transcription in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Kosaka, N.; Tominaga, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Takahashi, R.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuda, H.; Tamura, K.; Ochiya, T. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells contain a microRNA that promotes dormancy in metastatic breast cancer cells. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Lin, F.; Ding, R.; Wang, W.; Hong, W. Extracellular vesicles carrying miR-193a derived from mesenchymal stem cells impede cell proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer by downregulating FAK. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zeng, J.; Lin, D.; Xia, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, L.; Zeng, C. Extracellular vesicles derived from cancer-associated fibroblast carries miR-224-5p targeting SLC4A4 to promote the proliferation, invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricklefs, F.L.; Alayo, Q.; Krenzlin, H.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Speranza, M.C.; Nakashima, H.; Hayes, J.L.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Passaro, C.; et al. Immune evasion mediated by PD-L1 on glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Himes, B.T.; Peterson, T.E.; de Mooij, T.; Garcia, L.M.C.; Jung, M.-Y.; Uhm, S.; Yan, D.; Tyson, J.; Jin-Lee, H.J.; Parney, D.; et al. The role of extracellular vesicles and PD-L1 in glioblastoma-mediated immunosuppressive monocyte induction. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesi, G.; Philippidou, D.; Kozar, I.; Kim, Y.J.; Bernardin, F.; van Niel, G.; Wienecke-Baldacchino, A.; Felten, P.; Letellier, E.; Dengler, S.; et al. A new ALK isoform transported by extracellular vesicles confers drug resistance to melanoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ge, X.; Shi, Z.; Yu, C.; Lu, C.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, A.; Wang, X.; Yan, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic glioma stem-like cells confer temozolomide resistance on glioblastoma by delivering miR-30b-3p. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1763–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Guo, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Gong, J.; Li, W. Tumor-released lncRNA H19 promotes gefitinib resistance via packaging into exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3438–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xavier, C.P.R.; Castro, I.; Caires, H.R.; Ferreira, D.; Cavadas, B.; Pereira, L.; Santos, L.L.; Oliveira, M.J.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Chitinase 3-like-1 and fibronectin in the cargo of extracellular vesicles shed by human macrophages influence pancreatic cancer cellular response to gemcitabine. Cancer Lett. 2021, 501, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Effects of long noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) existing in extracellular vesicles on the occurrence and multidrug resistance of esophageal cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Gen, H. Exosomal Long Non-coding RNA HOTTIP Increases Resistance of Colorectal Cancer Cells to Mitomycin via Impairing MiR-214-Mediated Degradation of KPNA3. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 582723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, X.; Yu, J.; Lu, X.; Qian, Q.; Qian, W. Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA RP11-838N2. 4 promotes erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.; Ren, M.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Deng, M.; Li, C. Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA PART1 induces gefitinib resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, K.; Ye, M.; He, X.; Zhang, F.; Han, J. Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA-SNHG14 promotes trastuzumab chemoresistance in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, K.; Kume, H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kawashima, A.; Ujike, T.; Nagahara, A.; Uemura, M.; Miyagawa, Y.; Tomonaga, T.; Nonomura, N. Proteomic analysis of urinary extracellular vesicles from high Gleason score prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M.; de Menezes, R.; Misovic, B.; Wachalska, M.; Geldof, A.; Zini, N.; de Reijke, T.; Wurdinger, T.; Vis, A.; et al. Non-invasive prostate cancer detection by measuring miRNA variants (isomiRs) in urine extracellular vesicles. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22566–22578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hur, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.A.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, K.Y. Extracellular vesicle-based EGFR genotyping in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from treatment-naive non-small cell lung cancer patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Nakashima, C.; Sato, A.; Harada, Y.; Sueoka, E.; Kimura, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Sueoka-Aragane, N. Origin of circulating free DNA in patients with lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.-K.; Park, J.; Ku, J.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Sunkara, V.; Ha, H.K.; Cho, Y.-K. Urine-based liquid biopsy: Non-invasive and sensitive AR-V7 detection in urinary EVs from patients with prostate cancer. Lab Chip 2018, 19, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Plazas, X.; Altuna-Coy, A.; Alves-Santiago, M.; Vila-Barja, J.; García-Fontgivell, J.F.; Martínez-González, S.; Segarra-Tomás, J.; Chacón, M.R. Liquid Biopsy-Based Exo-oncomiRNAs Can Predict Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness. Cancers 2021, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydbring, P.; de Petris, L.; Zhang, Y.; Brandén, E.; Koyi, H.; Novak, M.; Kanter, L.; Hååg, P.; Hurley, J.; Tadigotla, V.; et al. Exosomal RNA-profiling of pleural effusions identifies adenocarcinoma patients through elevated miR-200 and LCN2 expression. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Soboļevska, K.; Ābols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Šantare, D.; Rudņickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Maehara, S.; Matsubayashi, J.; Otaki, Y.; Kajiwara, N.; Ohira, T.; Minna, J.D.; Ikeda, N. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 has prognostic relevance and is a therapeutic target for high-grade neuroendocrine lung cancers. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, J.M.; Vyas, A.D.; Qiu, Y.; Messer, K.S.; White, R.; Heller, M.J. Integrated Analysis of Exosomal Protein Biomarkers on Alternating Current Electrokinetic Chips Enables Rapid Detection of Pancreatic Cancer in Patient Blood. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3311–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Gong, Y.; An, G. Extracellular vesicle-delivered miR-505-5p, as a diagnostic biomarker of early lung adenocarcinoma, inhibits cell apoptosis by targeting TP53AIP1. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osteikoetxea, X.; Benke, M.; Rodriguez, M.; Pálóczi, K.; Sódar, B.W.; Szvicsek, Z.; Szabó-Taylor, K.; Vukman, K.V.; Kittel, Á.; Wiener, Z.; et al. Detection and proteomic characterization of extracellular vesicles in human pancreatic juice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.S.; Ciprani, D.; O’Shea, A.; Liss, A.S.; Yang, R.; Fletcher-Mercaldo, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Castillo, C.F.; Weissleder, R. Extracellular Vesicle Analysis Allows for Identification of Invasive IPMN. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1345–1358.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ota, Y.; Kogure, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Yamakita, K.; Kitano, Y.; Fujii, S.; Haneda, M.; Patel, T.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicle-encapsulated HULC is a potential biomarker for human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Harada, T.; Fumoto, K.; Osugi, Y.; Sada, R.; Maehara, N.; Hikita, H.; Mori, S.; Eguchi, H.; et al. CKAP4, a DKK1 Receptor, Is a Biomarker in Exosomes Derived from Pancreatic Cancer and a Molecular Target for Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yugawa, K.; Yoshizumi, T.; Mano, Y.; Itoh, S.; Harada, N.; Ikegami, T.; Kohashi, K.; Oda, Y.; Mori, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression through downregulation of exosomal miR-150-3p. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Surg. Oncol. Br. Assoc. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Lowry, M.C.; Corcoran, C.; Martinez, V.G.; Daly, M.; Rani, S.; Gallagher, W.M.; Radomski, M.W.; MacLeod, R.A.F.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32774–32789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, M.F.; Rappa, G.; Karbanová, J.; Vanier, C.; Morimoto, C.; Corbeil, D.; Lorico, A. Anti-human CD9 antibody Fab fragment impairs the internalization of extracellular vesicles and the nuclear transfer of their cargo proteins. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4408–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Piontek, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Selaru, F.M. Exosome miR-335 as a novel therapeutic strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.; Almeida, F. Exosome-Based Vaccines: History, Current State, and Clinical Trials. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, V.; Nowicki, M.O.; Idriss, M.; Jimenez, M.A.; Lugli, G.; Hayes, J.L.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Zane, R.E.; Passaro, C.; Ligon, K.L.; et al. The functional synergism of microRNA clustering provides therapeutically relevant epigenetic interference in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues-Junior, D.M.; Pelarin, M.F.d.; Nader, H.B.; Vettore, A.L.; Pinhal, M.A.S. MicroRNA-1252-5p Associated with Extracellular Vesicles Enhances Bortezomib Sensitivity in Multiple Myeloma Cells by Targeting Heparanase. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, W. Extracellular vesicle encapsulated microRNA-320a inhibits endometrial cancer by suppression of the HIF1α/VEGFA axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. microRNA-375 released from extracellular vesicles of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells exerts anti-oncogenic effects against cervical cancer. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xin, H.; Lu, L. Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA-424 exerts inhibitory function in ovarian cancer by targeting MYB. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells-derived microRNA-203-containing extracellular vesicles alleviate non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating the DTL/p21 axis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Mao, W. Vascular endothelial cell-derived exosomal miR-30a-5p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma malignant progression by targeting CCNE2. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feo, A.; Sciandra, M.; Ferracin, M.; Felicetti, F.; Astolfi, A.; Pignochino, Y.; Picci, P.; Carè, A.; Scotlandi, K. Exosomes from CD99-deprived Ewing sarcoma cells reverse tumor malignancy by inhibiting cell migration and promoting neural differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, H.; Jahangard, Y.; Nikkhah, M.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J.; Mowla, S.J. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Exosomes Packed With a miR-21-Sponge Construct in a Rat Model of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; Niu, J.; Guo, W. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting TRA2B. Cancer Lett. 2020, 490, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, X. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles impede the progression of cervical cancer via the miR-144-3p/CEP55 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1867–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldari, S.; di Rocco, G.; Magenta, A.; Picozza, M.; Toietta, G. Extracellular Vesicles-Encapsulated MicroRNA-125b Produced in Genetically Modified Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation. Cells 2019, 8, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Yin, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, X. Delivery of mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles with enriched miR-185 inhibits progression of OPMD. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gladkova, N.; Umezu, T.; Imanishi, S.; Kawana, C.; Ohyashiki, J.H.; Ohyashiki, K. Effect of the extracellular component of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells from healthy donors on hematologic neoplasms and their angiogenesis. Hum. Cell. 2020, 33, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, K.; Loridas, S. Pulmonary oxidative stress, inflammation and cancer: Respirable particulate matter, fibrous dusts and ozone as major causes of lung carcinogenesis through reactive oxygen species mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 3886–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (Inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J.Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppé, J.-P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the p53 Tumor Suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loarca, L.; de Assuncao, T.M.; Jalan-Sakrikar, N.; Bronk, S.; Krishnan, A.; Huang, B.; Morton, L.; Trussoni, C.; Bonilla, L.M.; Krueger, E.; et al. Development and characterization of cholangioids from normal and diseased human cholangiocytes as an in vitro model to study primary sclerosing cholangitis. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, R.; Crasta, K. Exosomes as emerging pro-tumorigenic mediators of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, C.C.T.; Wong, C.K.C. Characterization of stanniocalcin-1 expression in macrophage differentiation. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyadet, S.; Sotillo, J.; Smout, M.; Cantacessi, C.; Jones, M.K.; Johnson, M.S.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Potriquet, J.; Laohaviroj, M.; et al. Carcinogenic liver fluke secretes extracellular vesicles that promote cholangiocytes to adopt a tumorigenic phenotype. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliano, M.; Mangino, G.; Chiantore, M.V.; Zangrillo, M.S.; Accardi, R.; Tommasino, M.; Fiorucci, G.; Romeo, G. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins affect the cell microenvironment by classical secretion and extracellular vesicles delivery of inflammatory mediators. Cytokine 2018, 106, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, S.-W. Exosomal Transmission of MicroRNA from HCV Replicating Cells Stimulates Transdifferentiation in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Deeke, S.A.; Ning, Z.; Starr, A.E.; Butcher, J.; Li, J.; Mayne, J.; Cheng, K.; Liao, B.; Li, L.; et al. Metaproteomics reveals associations between microbiome and intestinal extracellular vesicle proteins in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Silvers, C.R.; Messing, E.M.; Lee, Y.F. Bladder cancer extracellular vesicles drive tumorigenesis by inducing the unfolded protein response in endoplasmic reticulum of nonmalignant cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3207–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urciuoli, E.; Giorda, E.; Scarsella, M.; Petrini, S.; Peruzzi, B. Osteosarcoma-derived extracellular vesicles induce a tumor-like phenotype in normal recipient cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6158–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherer, W.F.; Syverton, J.T.; Gey, G.O. Studies on the propagation in vitro of poliomyelitis viruses. IV. Viral multiplication in a stable strain of human malignant epithelial cells (strain HeLa) derived from an epidermoid carcinoma of the cervix. J. Exp. Med. 1953, 97, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haga, H.; Yan, I.K.; Takahashi, K.; Wood, J.; Zubair, A.; Patel, T. Tumour cell-derived extracellular vesicles interact with mesenchymal stem cells to modulate the microenvironment and enhance cholangiocarcinoma growth. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 24900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, P.; Liang, Y.; Long, M.; Liu, H.; Mao, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the in vitro proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through the activation of the ERK pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czystowska-Kuzmicz, M.; Sosnowska, A.; Nowis, D.; Ramji, K.; Szajnik, M.; Chlebowska-Tuz, J.; Wolinska, E.; Gaj, P.; Grazul, M.; Pilch, Z.; et al. Small extracellular vesicles containing arginase-1 suppress T-cell responses and promote tumor growth in ovarian carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, T.; Kawahara, H.; Kimura, R.; Dong, Y.; Jiapaer, S.; Sabit, H.; Zhang, J.; Yoshida, T.; Nakada, M.; Hanayama, R. Glioma-derived extracellular vesicles promote tumor progression by conveying WT1. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xue, J.; Ling, M.; Sun, J.; Xiao, T.; Dai, X.; Sun, Q.; Cheng, C.; Xia, H.; Wei, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-15b in extracellular vesicles from arsenite-treated macrophages promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinomas by blocking the LATS1-mediated Hippo pathway. Cancer Lett. 2021, 497, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Wei, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote lung adenocarcinoma growth by transferring miR-410. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.; Coller, J. RNA in unexpected places: Long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Mytar, B.; Weglarczyk, K.; Szatanek, R.; Kijowski, J.; Siedlar, M. Protumorogenic Potential of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Folia Biol. 2020, 66, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- De Andrade, A.; de Oliveira, C.E.; Dourado, M.R.; Macedo, C.; Winck, F.V.; Leme, A.F.P.; Salo, T.; Coletta, R.D.; Freitas, R.d.; Galvão, H.C. Extracellular vesicles from oral squamous carcinoma cells display pro- and anti-angiogenic properties. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Man, Q.W.; Xiong, X.P.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, W.M.; Jia, J.; Sun, Z.J.; et al. Clinical Significance and Roles in Angiogenesis of Circulating Microparticles in Oral Cancer. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfati, M.; Avivi, I.; Brenner, B.; Katz, T.; Aharon, A. Extracellular vesicles of multiple myeloma cells utilize the proteasome inhibitor mechanism to moderate endothelial angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2019, 22, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, R.; Zappulli, V.; Sammarco, A.; Murillo, O.D.; Cheah, P.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tai, E.; Ting, D.T.; Wei, Z.; Roth, M.E.; et al. Glioma-Derived miRNA-Containing Extracellular Vesicles Induce Angiogenesis by Reprogramming Brain Endothelial Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2065–2074.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zang, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, F.; Sun, B.; Qi, D.; Li, X.; Kong, J.; Jin, D.; et al. Small extracellular vesicle-bound vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promotes angiogenesis in a bevacizumab-resistant manner. Cancer Lett. 2020, 492, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Hernandez, A.; Leal-Orta, E.; Ramirez-Ricardo, J.; Cortes-Reynosa, P.; Thompson-Bonilla, R.; Salazar, E.P. Linoleic acid induces secretion of extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells that mediate cellular processes involved with angiogenesis in HUVECs. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021, 153, 106519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Ramírez, P.; Greening, D.W.; Andrés, G.; Gopal, S.K.; Martín-Villar, E.; Renart, J.; Simpson, R.J.; Quintanilla, M. Podoplanin is a component of extracellular vesicles that reprograms cell-derived exosomal proteins and modulates lymphatic vessel formation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16070–16089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindoso, R.S.; Collino, F.; Camussi, G. Extracellular vesicles derived from renal cancer stem cells induce a pro-tumorigenic phenotype in mesenchymal stromal cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7959–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigelt, B.; Peterse, J.L.; Veer, L.J.v. Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, N.; Katsuda, T.; Ochiya, T. Micromanaging of tumor metastasis by extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L. Comments on hematogenous metastatic patterns in humans as revealed by autopsy. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1992, 10, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Hernandez, O.; Serna-Marquez, N.; Castillo-Sanchez, R.; Salazar, E.P. Extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stimulated with linoleic acid promote an EMT-like process in MCF10A cells. Prostaglandins. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2014, 91, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, M.W.; Li, M.; Giovanazzi, A.; Fleming, R.L.; Tabet, E.I.; Nakano, I.; Würdinger, T.; Chiocca, E.A.; Tian, T.; Tannous, B.A. Extracellular Vesicles Induce Mesenchymal Transition and Therapeutic Resistance in Glioblastomas through NF-κB/STAT3 Signaling. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, e1900312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetti, D.; Perelli, L.; Colella, F.; Ricciardi-Tenore, C.; Scoarughi, G.L.; Barbato, G.; Boninsegna, A.; de Maria, R.; Sgambato, A. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound affects growth, differentiation, migration, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5363–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, M.; Watanabe, N.; Watanabe, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Sato, A.; Fujisaki, M.; Kubota, S.; Monzen, S.; Maruyama, A.; Nanashima, N.; et al. Exosomes derived from SW480 colorectal cancer cells promote cell migration in HepG2 hepatocellular cancer cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopatina, T.; Favaro, E.; Danilova, L.; Fertig, E.J.; Favorov, A.V.; Kagohara, L.T.; Martone, T.; Bussolati, B.; Romagnoli, R.; Albera, R.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Tumor Endothelial Cells Spread Immunosuppressive and Transforming Signals Through Various Recipient Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhaneni, K.C.; Hassler, M.-Y.; Abraham, A.; Whitt, J.; Mo, Y.-Y.; Atfi, A.; Pochampally, R. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells under Stress Increase Osteosarcoma Migration and Apoptosis Resistance via Extracellular Vesicle Mediated Communication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, R.; Wang, H.; Loo, D.; Martin, S.; Cumming, A.; Cai, N.; Lane, R.; Ponce, N.S.; Topkas, E.; Inder, K.; et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by highly metastatic clonal variants of osteosarcoma preferentially localize to the lungs and induce metastatic behaviour in poorly metastatic clones. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43570–43587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Colorectal cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles establish an inflammatory premetastatic niche in liver metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörsam, B.; Bösl, T.; Reiners, K.S.; Barnert, S.; Schubert, R.; Shatnyeva, O.; Zigrino, P.; Engert, A.; Hansen, H.P.; von Strandmann, E.P. Hodgkin Lymphoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Change the Secretome of Fibroblasts Toward a CAF Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš, E.; Ābols, A.; Bušs, A.; Zandberga, E.; Palviainen, M.; Siljander, P.; Linē, A. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Hypoxic Colorectal Cancer Cells Confer Metastatic Phenotype to Non-metastatic Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5139–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Kagawa, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Kuwada, K.; Kajioka, H.; Yoshimoto, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Kuroda, S.; Yoshida, R.; Tazawa, H.; et al. Extracellular vesicles shed from gastric cancer mediate protumor macrophage differentiation. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Kudo, K.; Higuchi, H.; Otsuka, H.; Tanaka, M.; Fukunishi, N.; Araki, T.; Takamatsu, M.; Ino, Y.; Kimura, Y.; et al. Proteomic and phospholipidomic characterization of extracellular vesicles inducing tumor microenvironment in Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomas. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2021, 35, e21505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumontet, E.; Pangault, C.; Roulois, D.; Desoteux, M.; Léonard, S.; Marchand, T.; Latour, M.; Legoix, P.; Loew, D.; Dingli, F.; et al. Extracellular vesicles shed by follicular lymphoma B cells promote polarization of the bone marrow stromal cell niche. Blood 2021, 138, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.; Teles, S.P.; Azevedo, M.; Oliveira, P.; Carvalho, J.; Oliveira, C. Gastric Cancer Extracellular Vesicles Tune the Migration and Invasion of Epithelial and Mesenchymal Cells in a Histotype-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Ricardo, J.; Leal-Orta, E.; Martínez-Baeza, E.; Ortiz-Mendoza, C.; Breton-Mora, F.; Herrera-Torres, A.; Elizalde-Acosta, I.; Cortes-Reynosa, P.; Thompson-Bonilla, R.; Salazar, E.P. Circulating extracellular vesicles from patients with breast cancer enhance migration and invasion via a Src-dependent pathway in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1932–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, M.R.; Korvala, J.; Åström, P.; de Oliveira, C.E.; Cervigne, N.K.; Mofatto, L.S.; Bastos, D.C.; Messetti, A.C.P.; Graner, E.; Leme, A.F.P.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts induce the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1578525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sceneay, J.; Smyth, M.J.; Möller, A. The pre-metastatic niche: Finding common ground. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Liu, S.; Jiang, X.; Shang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cao, C.; Xiao, H. Cancer Cell Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Contribute to Recipient Cell Metastasis Through Promoting HGF/c-Met Pathway. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, L.; Calore, F.; Braggio, D.A.; Zewdu, A.; Deshmukh, A.A.; Fadda, P.; Lopez, G.; Wabitsch, M.; Song, C.; Leight, J.L.; et al. MDM2 Derived from Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma Extracellular Vesicles Induces MMP2 Production from Preadipocytes. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4911–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barenholz-Cohen, T.; Merkher, Y.; Haj, J.; Shechter, D.; Kirchmeier, D.; Shaked, Y.; Weihs, D. Lung mechanics modifications facilitating metastasis are mediated in part by breast cancer-derived extracellular vesicles. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, S.E.; McMahon, K.M.; Plebanek, M.P.; Calvert, A.E.; Feliciano, T.J.; Parrish, S.; Tavora, F.; Mega, A.; de Souza, A.; Carneiro, B.A.; et al. Prostate cancer extracellular vesicles mediate intercellular communication with bone marrow cells and promote metastasis in a cholesterol-dependent manner. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 10, e12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.A.; Mazariegos, M.S.; Capuano, A.; Ximénez-Embún, P.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Recio, J.Á.; Muñoz, E.; Al-Shahrour, F.; Muñoz, J.; Megías, D.; et al. Inactivation of EMILIN-1 by Proteolysis and Secretion in Small Extracellular Vesicles Favors Melanoma Progression and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, C.A.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dower, C.M.; Sundstrom, J.; Wang, H.-G. Chemotherapy-Induced Upregulation of Small Extracellular Vesicle-Associated PTX3 Accelerates Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.; Fonseka, P.; Sanwlani, R.; Gangoda, L.; Chee, S.H.; Keerthikumar, S.; Spurling, A.; Chitti, S.V.; Zanker, D.; Ang, C.-S.; et al. Oral administration of bovine milk-derived extracellular vesicles induces senescence in the primary tumor but accelerates cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, G.N.; Loyall, J.; Maguire, O.; Iyer, V.; Kelleher, R.J.J.; Minderman, H.; Wallace, P.K.; Odunsi, K.; Balu-Iyer, S.V.; Bankert, R.B. Exosomes Associated with Human Ovarian Tumors Harbor a Reversible Checkpoint of T-cell Responses. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cianciaruso, C.; Beltraminelli, T.; Duval, F.; Nassiri, S.; Hamelin, R.; Mozes, A.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Torres, G.C.; Torchia, B.; Ries, C.H.; et al. Molecular Profiling and Functional Analysis of Macrophage-Derived Tumor Extracellular Vesicles. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3062–3080.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford, S. Is it time for a new paradigm for systemic cancer treatment? Lessons from a century of cancer chemotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, A.M.; Wolchok, J.D.; Old, L.J. Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hendrix, A.; Hernot, S.; Lemaire, M.; de Bruyne, E.; van Valckenborgh, E.; Lahoutte, T.; de Wever, O.; Vanderkerken, K.; Menu, E. Bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes as communicators in drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2014, 124, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.-Y.; You, S.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Freeman, M.R.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, J. Extracellular vesicles shed from gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer regulate the tumor microenvironment. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Cavalli, I.J.; Malheiros, D.; Ribeiro, E.M.d.F.; Cavalli, L.R. Extracellular vesicles from triple-negative breast cancer cells promote proliferation and drug resistance in non-tumorigenic breast cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Kim, H.S.; Bojmar, L.; Gyan, K.E.; Cioffi, M.; Hernandez, J.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Rodrigues, G.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle and Particle Biomarkers Define Multiple Human Cancers. Cell 2020, 182, 1044–1061.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Mori, K.; Sunayama, H.; Takano, E.; Kitayama, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Hirose, Y.; Inubushi, S.; Sasaki, R.; Tanino, H. Antibody-Conjugated Signaling Nanocavities Fabricated by Dynamic Molding for Detecting Cancers Using Small Extracellular Vesicle Markers from Tears. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6617–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, C.N.; Siddiqui, K.M.; Al-Zahrani, A.A.; Pardhan, S.; Brett, S.I.; Guo, Q.Q.; Yang, J.; Wolf, P.; Power, N.E.; Durfee, P.N.; et al. Prostate extracellular vesicles in patient plasma as a liquid biopsy platform for prostate cancer using nanoscale flow cytometry. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8839–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bijnsdorp, I.V.; Maxouri, O.; Kardar, A.; Schelfhorst, T.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; Vis, A.; van Moorselaar, R.J.; Jimenez, C.R. Feasibility of urinary extracellular vesicle proteome profiling using a robust and simple, clinically applicable isolation method. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1313091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotland, T.; Ekroos, K.; Kauhanen, D.; Simolin, H.; Seierstad, T.; Berge, V.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Molecular lipid species in urinary exosomes as potential prostate cancer biomarkers. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 70, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Wunsch, B.H.; Dogra, N.; Ahsen, M.E.; Lee, K.; Yadav, K.K.; Weil, R.; Pereira, M.A.; Patel, J.V.; Duch, E.A.; et al. Integrated nanoscale deterministic lateral displacement arrays for separation of extracellular vesicles from clinically-relevant volumes of biological samples. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3913–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdbrügger, U.; Blijdorp, C.J.; Bijnsdorp, I.V.; Borràs, F.E.; Burger, D.; Bussolati, B.; Byrd, J.B.; Clayton, A.; Dear, J.W.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M.; et al. Urinary extracellular vesicles: A position paper by the Urine Task Force of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadal, M.; Herrero, C.; López-Rodrigo, O.; Castells, M.; de la Fuente, A.; Vigués, F.; Bassas, L.; Larriba, S. Impact of Extracellular Vesicle Isolation Methods on Downstream Mirna Analysis in Semen: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Z.; Shang, Z.; Sun, K.; Niu, X.; Qian, L.; Fan, L.-Y.; Cao, C.-X.; Xiao, H. Facile preparation of salivary extracellular vesicles for cancer proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakur, A.; Qiu, G.; Ng, S.-P.; Guan, J.; Yue, J.; Lee, Y.; Wu, C.-M.L. Direct detection of two different tumor-derived extracellular vesicles by SAM-AuNIs LSPR biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, A.; Venturelli, E.; Brizzi, M.F. Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Liquid Biopsy-Based Diagnosis for the Central Nervous System, Head and Neck, Lung, and Gastrointestinal Cancers: Current and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vykoukal, J.; Sun, N.; Aguilar-Bonavides, C.; Katayama, H.; Tanaka, I.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Capello, M.; Fujimoto, J.; Aguilar, M.; Wistuba, I.I.; et al. Plasma-derived extracellular vesicle proteins as a source of biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95466–95480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, S.K.; Sänger, H.; Krawczyk, M.; Julich-Haertel, H.; Willms, A.; Ligocka, J.; Azkargorta, M.; Mocan, T.; Kahlert, C.; Kruk, B.; et al. Synergistic effects of extracellular vesicle phenotyping and AFP in hepatobiliary cancer differentiation. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver. 2020, 40, 3103–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobra, G.; Bukva, M.; Szabo, Z.; Bruszel, B.; Harmati, M.; Gyukity-Sebestyen, E.; Jenei, A.; Szucs, M.; Horvath, P.; Biro, T.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Serum May Serve as Signal-Enhancers for the Monitoring of CNS Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, K.E.; Lowe, C.J.; Mahajan, S.; Suttmann, R.; Nguy, T.; Reichelt, M.; Yang, J.; Melendez, R.; Li, Y.; Molinero, L.; et al. Enrichment of circulating tumor-derived extracellular vesicles from human plasma. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 490, 112936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Gu, Y.; Kang, B.; Heskia, F.; Pachot, A.; Bonneville, M.; Wei, P.; Liang, J. PD-L1 detection on circulating tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (T-EVs) from patients with lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2441–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novizio, N.; Belvedere, R.; Pessolano, E.; Tosco, A.; Porta, A.; Perretti, M.; Campiglia, P.; Filippelli, A.; Petrella, A. Annexin A1 Released in Extracellular Vesicles by Pancreatic Cancer Cells Activates Components of the Tumor Microenvironment, through Interaction with the Formyl-Peptide Receptors. Cells 2020, 9, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Bhagwat, N.; Black, T.; Yee, S.S.; Na, Y.-J.; Fisher, S.; Kim, J.; Carpenter, E.L.; Stanger, B.Z.; Issadore, D. miRNA Profiling of Magnetic Nanopore-Isolated Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3688–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Kwak, K.J.; Shi, J.; Yu, B.; Sheng, Y.; Lee, L.J. Overhang molecular beacons encapsulated in tethered cationic lipoplex nanoparticles for detection of single-point mutation in extracellular vesicle-associated RNAs. Biomaterials 2018, 183, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.-J.; Jin, D.-D.; Jiang, F.; Liu, J.-X.; Qu, L.-S.; Ni, W.-K.; Liu, Z.-X.; Lu, C.-H.; Ni, R.-Z.; Zhu, J.; et al. Characterization and proteomic profiling of pancreatic cancer-derived serum exosomes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Qian, L.; Zhao, J.; Zong, H.; Kang, B.; et al. Plasma extracellular vesicle long RNA profiling identifies a diagnostic signature for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gut 2020, 69, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Kimchi, E.T.; Manjunath, Y.; Gajagowni, S.; Stuckel, A.J.; Kaifi, J.T. RNA cargos in extracellular vesicles derived from blood serum in pancreas associated conditions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; LaRiviere, M.J.; Ko, J.; Till, J.E.; Christensen, T.; Yee, S.S.; Black, T.A.; Tien, K.; Lin, A.; Shen, H.; et al. A Multianalyte Panel Consisting of Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs and mRNAs, cfDNA, and CA19-9 Shows Utility for Diagnosis and Staging of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3248–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Gu, Y. Membrane Feature-Inspired Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9860–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Kim, D.U.; Lucas, F.A.S.; Castillo, J.; Allenson, K.; Mulu, F.C.; Stephens, B.M.; Huang, J.; Semaan, A.; Guerrero, P.A.; et al. Circulating Nucleic Acids Are Associated With Outcomes of Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 108–118.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.R.; Han, K.; Han, Y.; Kang, N.; Shin, T.-S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-K.; et al. Microbiome Markers of Pancreatic Cancer Based on Bacteria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Acquired from Blood Samples: A Retrospective Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julich-Haertel, H.; Urban, S.K.; Krawczyk, M.; Willms, A.; Jankowski, K.; Patkowski, W.; Kruk, B.; Krasnodębski, M.; Ligocka, J.; Schwab, R.; et al. Cancer-associated circulating large extracellular vesicles in cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelaiz, A.; Azkargorta, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Santos-Laso, A.; Lapitz, A.; Perugorria, M.J.; Erice, O.; Gonzalez, E.; Jimenez-Agüero, R.; Lacasta, A.; et al. Serum extracellular vesicles contain protein biomarkers for primary sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1125–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Hu, T.; Liu, J.; Su, J.; Sun, J.; Ming, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, N.; Chen, H.; Zhou, M. Genomic instability-derived plasma extracellular vesicle-microRNA signature as a minimally invasive predictor of risk and unfavorable prognosis in breast cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.H.; Espinoza-Sánchez, N.A.; El-Damen, A.; Fahim, S.A.; Badawy, M.A.; Greve, B.; El-Shinawi, M.; Götte, M.; Ibrahim, S.A. Small extracellular vesicle-encapsulated miR-181b-5p, miR-222-3p and let-7a-5p: Next generation plasma biopsy-based diagnostic biomarkers for inflammatory breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Lin, W.; Qi, P.; Xu, M.-D.; Wu, X.; Ni, S.; Huang, D.; Weng, W.-W.; Tan, C.; Sheng, W.; et al. Circulating Long RNAs in Serum Extracellular Vesicles: Their Characterization and Potential Application as Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2016, 25, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tominaga, N.; Hagiwara, K.; Katsuda, T.; Ochiya, T. Dark side of the exosome: The role of the exosome in cancer metastasis and targeting the exosome as a strategy for cancer therapy. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Asghari, M.H.; Goel, A. The therapeutic triad of extracellular vesicles: As drug targets, as drugs, and as drug carriers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, S.R.; Lagerweij, T.; Pérez-Lanzón, M.; Ho, X.D.; Léveillé, N.; Melo, S.A.; Cleton-Jansen, A.-M.; Jordanova, E.S.; Roncuzzi, L.; Greco, M.; et al. Blocking Tumor-Educated MSC Paracrine Activity Halts Osteosarcoma Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. A novel platform for cancer therapy using extracellular vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 95, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzidaki, E.; Vlachou, I.; Elka, A.; Georgiou, E.; Papadimitriou, M.; Iliopoulos, A.; Papasotiriou, I. The use of serum extracellular vesicles for novel small molecule inhibitor cell delivery. Anticancer Drugs 2019, 30, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomatto, M.A.C.; Bussolati, B.; D’Antico, S.; Ghiotto, S.; Tetta, C.; Brizzi, M.F.; Camussi, G. Improved Loading of Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Encapsulate Antitumor miRNAs. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 13, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garofalo, M.; Villa, A.; Brunialti, E.; Crescenti, D.; Dell’Omo, G.; Kuryk, L.; Vingiani, A.; Mazzaferro, V.; Ciana, P. Cancer-derived EVs show tropism for tissues at early stage of neoplastic transformation. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.S.; Li, S.M.; Bago, J.R.; Klyachko, N.L.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Therapy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, H.; Noh, G.J.; Lee, E.S. pH-responsive hyaluronate-anchored extracellular vesicles to promote tumor-targeted drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Ji, T.; Zhu, M.; Anderson, G.J.; Wei, J.; Nie, G. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, F.; Xiong, W.; Song, S.; Yin, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; et al. Mononuclear phagocyte system blockade using extracellular vesicles modified with CD47 on membrane surface for myocardial infarction reperfusion injury treatment. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 121000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, G.; Tong, J.; Fang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Cheng, G.; He, X.; et al. Aptamer-Conjugated Extracellular Nanovesicles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.K.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, R.; Wang, P.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Zhang, C.-G.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.-B.; Ding, W.; et al. Exosomal levels of miRNA-21 from cerebrospinal fluids associated with poor prognosis and tumor recurrence of glioma patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26971–26981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsuda, T.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Han, S.; Wan, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, H. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles confer antitumor activity in preclinical treatment of breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vracar, T.C.; Zuo, J.; Park, J.; Azer, D.; Mikhael, C.; Holliday, S.A.; Holsey, D.; Han, G.; VonMoss, L.; Neubert, J.K.; et al. Enoxacin and bis-enoxacin stimulate 4T1 murine breast cancer cells to release extracellular vesicles that inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Kalimuthu, S.; Oh, J.M.; Gangadaran, P.; Baek, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Enhancement of antitumor potency of extracellular vesicles derived from natural killer cells by IL-15 priming. Biomaterials 2019, 191, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Camargo, L.C.B.; Guaddachi, F.; Bergerat, D.; Ourari, N.; Coillard, L.; Parietti, V.; le Bras, M.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Jauliac, S. Extracellular vesicles produced by NFAT3-expressing cells hinder tumor growth and metastatic dissemination. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Terminology | Exosomes | Microvesicles | Apoptotic Bodies |
| Origin | Multivesicle body | Plasma membrane | Plasma membrane |
| Size | 50–150 nm | 100–1000 nm | 100–5000 nm |
| Marker proteins | CD9, CD63, Tsg101 etc. | Integrins, Selectins, CD40 etc. | Annexin V, thrombospondin, C3b etc. |
| References | [1,3] | [1,23] | [1,24] |
| Proteins | miRNAs | lncRNAs | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenesis | let-7 [25] | EBER2 [26] | ||
| miR-23a, miR-155 [27] | ||||
| Proliferation | CLIC1 [28] | miR-410 [29] | TU399 [30] | |
| EphA2 [31] | miR-142-3p [32] | lncRNA-VLDLR [33] | ||
| L1CAM [34] | miR-95 [35] | lncRNA-H19 [36] | ||
| ZIP4 [37] | miR-30e [38] | EWSAT1 [39] | ||
| hypoxia-induced miR-155 [40] | ||||
| miR-365 [41] | ||||
| miR-130b-3p [42] | ||||
| miR-497 [43] | ||||
| Angiogenesis | Rac1, PAK2 [44] | miR-584-5p [45] | ||
| VEGF90K [46] | miR-23b, miR-320b [47] | |||
| angiopoietin-2 [48] | miR-23a [49] | |||
| laminin γ2 [50] | miR143-3p, miR145-5p [51] | |||
| miR-141-3p [52] | ||||
| miR-81b-5p [53] | ||||
| miR-4488 [54] | ||||
| miR-10a-5p [55] | ||||
| le-7b-5p [56] | ||||
| Metastasis | TTLL4 [57] | miR-370-3p [58] | HLA-F-AS1 [59] | orphan RNA [60] |
| PKM2 [61] | miR-181c [19] | HUCL [62] | ||
| miR-30a-3p [63] | ||||
| miR-185-2p [64] | ||||
| MSC-miR222 [65] | ||||
| miR-30e [38] | ||||
| miR-23b [66] | ||||
| miR-193a [67] | ||||
| miR-622 [62] | ||||
| miR-224-5p [68] | ||||
| Escape from immune system | PD-1 [69,70] | miR-222 [65] | ||
| Chemotherapeutic stress | ALK [71] | miR-30b-3p [72] | H19 [73] | |
| Vasconcelos, Chitinase 3-like-1 and fibronectin [74] | VLDLR [33,75] | |||
| HOTPIT [76] | ||||
| RP11-838N2.4 [77] | ||||
| PART1 [78] | ||||
| SNHG14 [79] |
| Proteins | miRNAs | lncRNAs | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid biopsy | FABp5 [80] | miR-21, miR-375, miR-204 [81] | - | cell-free DNA [82,83] |
| Androgen-receptor splice vairiant 7 [84] | miR-221-3p, miR-222-3p, miR-31-5p [85] | |||
| Lipocalin-2 [86] | miR-375, miR-200c-3p, miR-21-5p [87] | |||
| UCHL1 [88] | miR-200 [86] | |||
| GPC1 [89,90] | miR-505-5p [91] | |||
| mucins, CFTR, MDR1 [92,93] | miR-193a-5p, miR-551b-5p [94] | |||
| ZIP4 [37] | miR-133b [95] | |||
| CKAP4, DKK1 receptor [96] | miR-150-3p [97] | |||
| Annexin A1 [98] | ||||
| Cancer treatment | anti-CD63 antibody, anti-CD9 antibody [22] | miR-134 [99] | - | - |
| CD9 Fab fragment [100] | miR-355-5p [101] | |||
| cell-free vaccine [21,102] | miR-124, miR-128, and miR137 [103] | |||
| mir-1252-5p [104] | ||||
| miR-320a [105] | ||||
| miR-375 [106] | ||||
| miR-424 [107] | ||||
| miR-203 [108] | ||||
| miR-30a [109] | ||||
| miR199a-3p [110] | ||||
| miR-21-sponge construct [111] | ||||
| miR-206 [112] | ||||
| miR-193a [67] | ||||
| miR-144-3p [113] | ||||
| miR-125b [114] | ||||
| mi-185 [115] | ||||
| miR-16-5p [116] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tominaga, N. Anti-Cancer Role and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers 2021, 13, 6303. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246303
Tominaga N. Anti-Cancer Role and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers. 2021; 13(24):6303. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246303
Chicago/Turabian StyleTominaga, Naoomi. 2021. "Anti-Cancer Role and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles" Cancers 13, no. 24: 6303. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246303
APA StyleTominaga, N. (2021). Anti-Cancer Role and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers, 13(24), 6303. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246303






