D-Mannose Slows Glioma Growth by Modulating Myeloperoxidase Activity
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tumor Cell Cultures
2.2. In Vivo Animal Study
2.3. In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging
2.4. In Vivo MR Imaging
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.6. Leukocyte Isolation and Stimulation
2.7. MPO ELISA and Activity Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
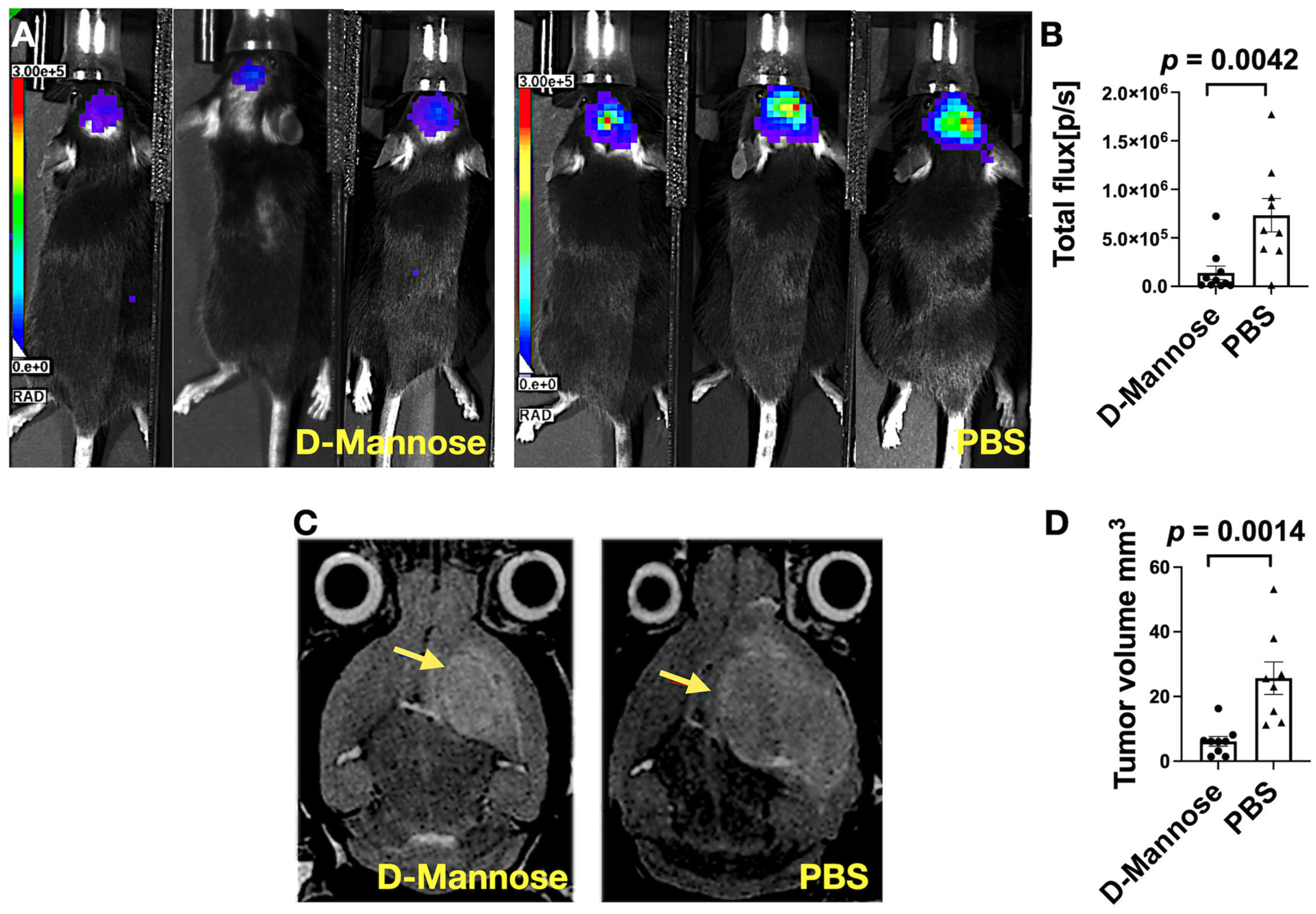
3.1. Bioluminescence (BLI) and MRI Imaging Revealed D-Mannose Treatment Slows Glioma Growth
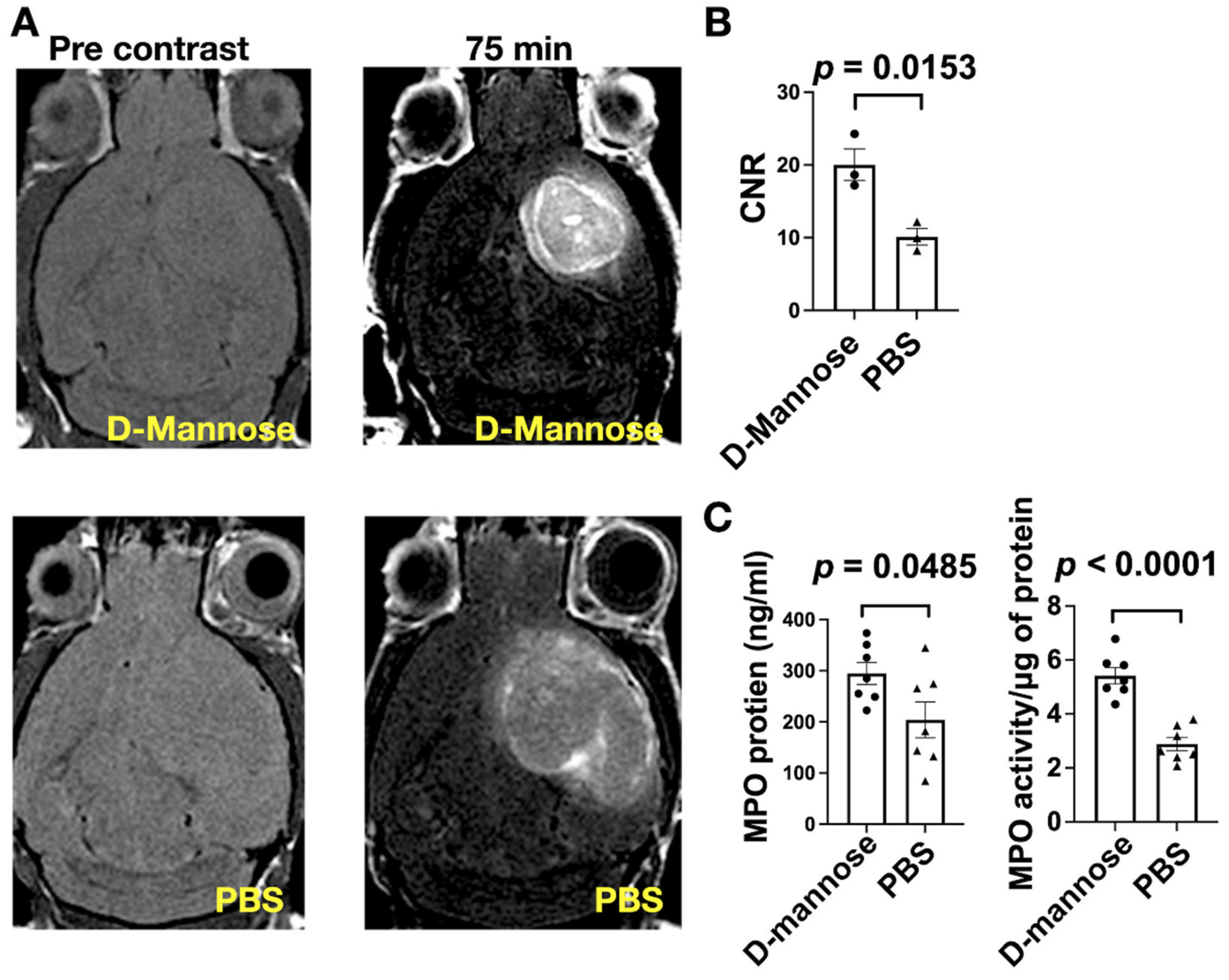
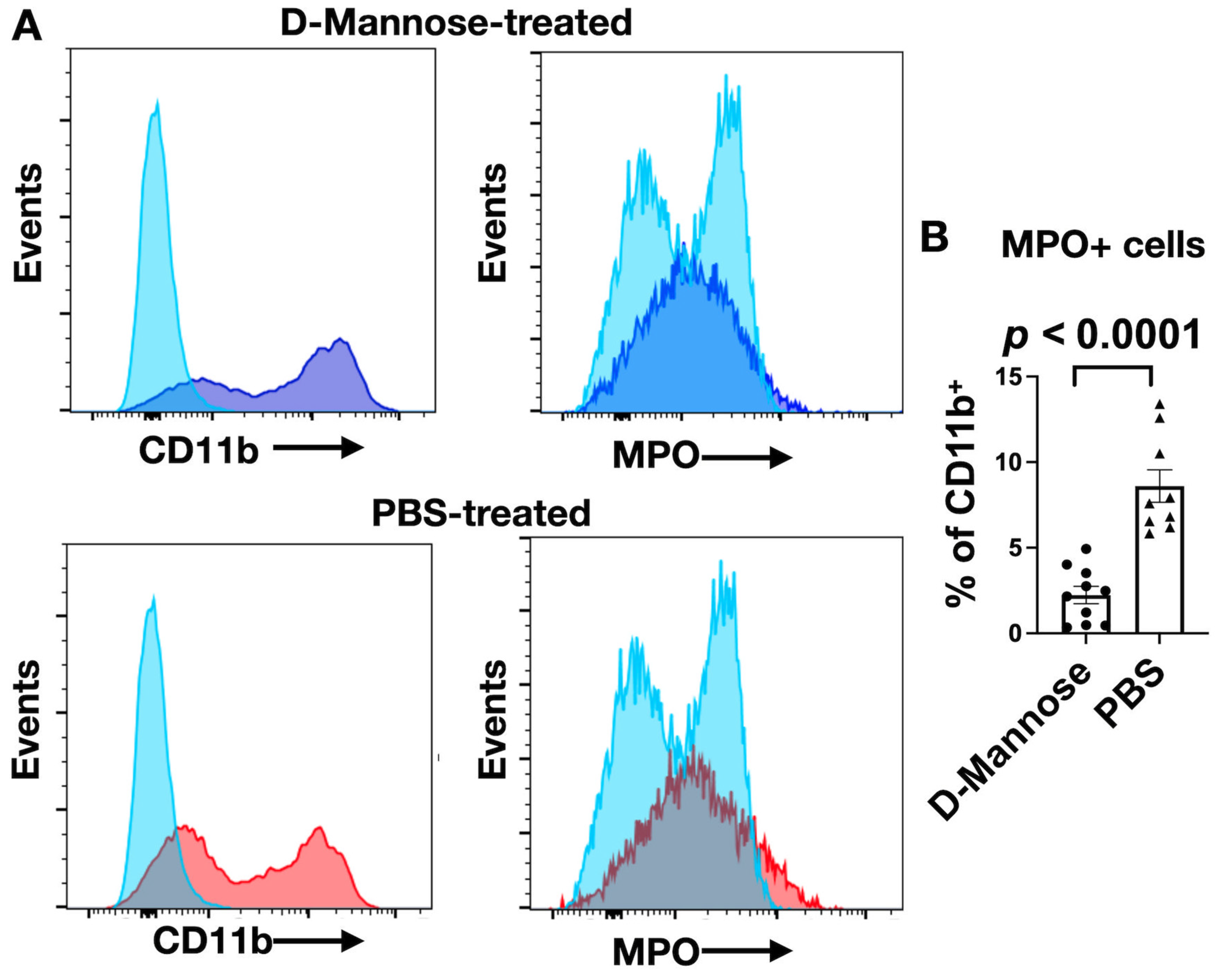
3.2. D-Mannose Increases MPO Amount and Activity In Vivo
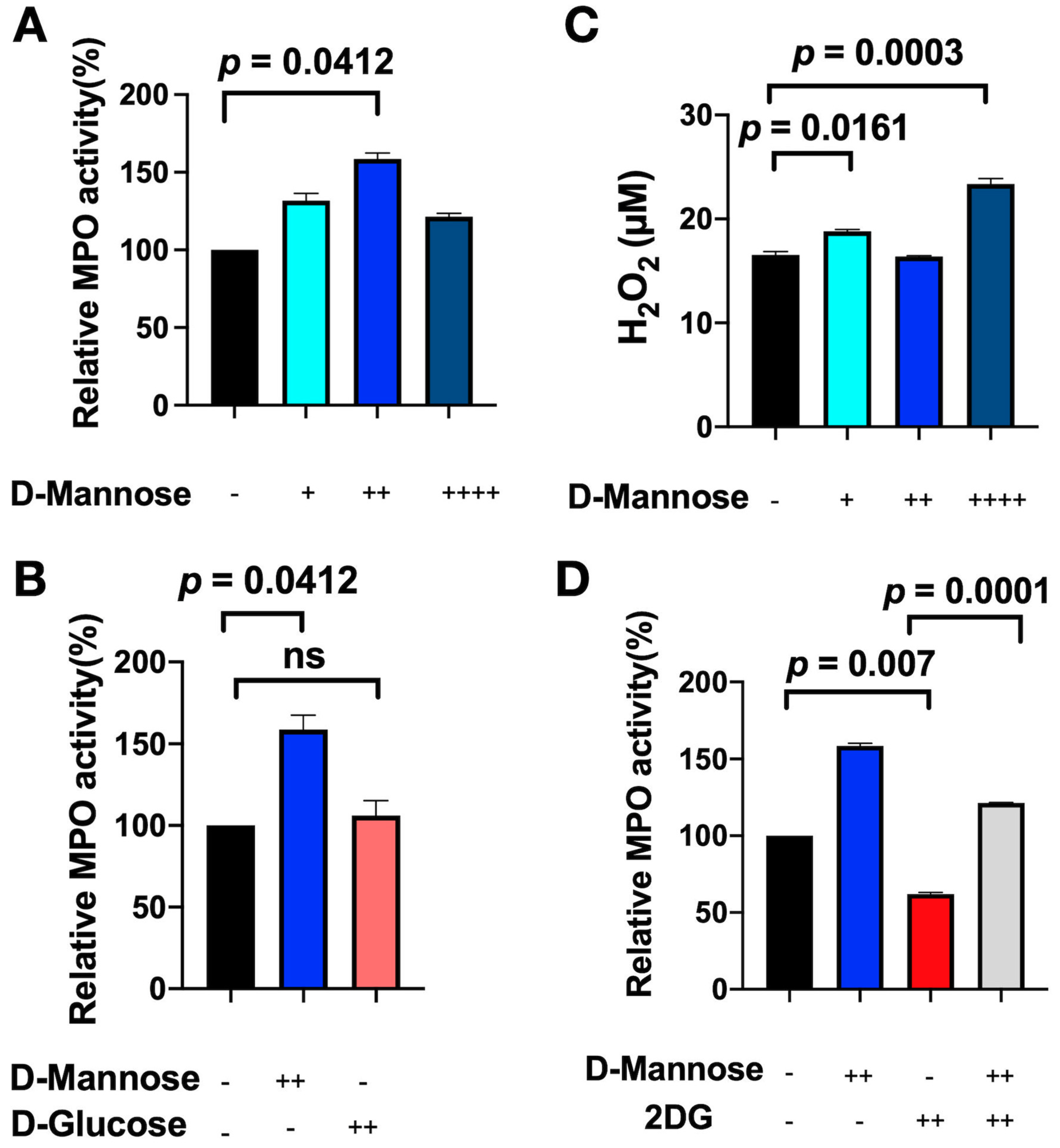
3.3. D-Mannose Increases MPO Activity In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Cordova, S.; Shastri, A.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Yasmin, H.; Klein, L.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. Molecular Heterogeneity and Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, H.A. Radiotherapy plus adjuvant temozolomide for the treatment of glioblastoma—A paradigm shift. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro. Oncol. 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Mendes, R.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R. Targeting Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurelac, I.; Umesh Ganesh, N.; Iorio, M.; Porcelli, A.M.; Gasparre, G. The multifaceted effects of metformin on tumor microenvironment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisimoto, Y.; Diebold, B.A.; Cosentino-Gomes, D.; Lambeth, J.D. Nox4: A hydrogen peroxide-generating oxygen sensor. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aratani, Y.; Kura, F.; Watanabe, H.; Akagawa, H.; Takano, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Dinauer, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Koyama, H. Relative contributions of myeloperoxidase and NADPH-oxidase to the early host defense against pulmonary infections with Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Med. Mycol. 2002, 40, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellani, L.W.; Chang, J.J.; Wang, X.; Lusis, A.J.; Reynolds, W.F. Transgenic mice express human MPO -463G/A alleles at atherosclerotic lesions, developing hyperlipidemia and obesity in -463G males. J. Lipid. Res. 2006, 47, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maki, R.A.; Tyurin, V.A.; Lyon, R.C.; Hamilton, R.L.; DeKosky, S.T.; Kagan, V.E.; Reynolds, W.F. Aberrant expression of myeloperoxidase in astrocytes promotes phospholipid oxidation and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3158–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.K.; Pennathur, S.; Perier, C.; Tieu, K.; Teismann, P.; Wu, D.C.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Vila, M.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Heinecke, J.W.; et al. Ablation of the inflammatory enzyme myeloperoxidase mitigates features of Parkinson’s disease in mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6594–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagra, R.M.; Becher, B.; Tourtellotte, W.W.; Antel, J.P.; Gold, D.; Paladino, T.; Smith, R.A.; Nelson, J.R.; Reynolds, W.F. Immunohistochemical and genetic evidence of myeloperoxidase involvement in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 78, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, V.; Leach, D.A.; Zinonos, I.; Ponomarev, V.; Licari, G.; Liapis, V.; Ingman, W.V.; Anderson, P.; DeNichilo, M.O.; Evdokiou, A. Inflammatory peroxidases promote breast cancer progression in mice via regulation of the tumour microenvironment. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.N.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, M.H. Deglycosylation influences the oxidation activity and antigenicity of myeloperoxidase. Nephrology (Carlton) 2018, 23, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.S.; O’Prey, J.; Cardaci, S.; Barthet, V.J.A.; Sakamaki, J.I.; Beaumatin, F.; Roseweir, A.; Gay, D.M.; Mackay, G.; Malviya, G.; et al. Mannose impairs tumour growth and enhances chemotherapy. Nature 2018, 563, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranjcec, B.; Papes, D.; Altarac, S. D-mannose powder for prophylaxis of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: A randomized clinical trial. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, L.; Cui, L.; Zhu, X. Mannose: Good player and assister in pharmacotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartner, S.L.; Williams, T.J. Modulation of interleukin-1 induced thymocyte proliferation by D-mannose. Thymus 1992, 19, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, U.; Bhattacharyya, S. Inhibition by monosaccharides of tumor associated macrophages mediated antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity to autologous tumor cells. Neoplasma 1987, 34, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Binello, E.; Qadeer, Z.A.; Kothari, H.P.; Emdad, L.; Germano, I.M. Stemness of the CT-2A Immunocompetent Mouse Brain Tumor Model: Characterization In Vitro. J. Cancer 2012, 3, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riva, M.; Wouters, R.; Weerasekera, A.; Belderbos, S.; Nittner, D.; Thal, D.R.; Baert, T.; Giovannoni, R.; Gsell, W.; Himmelreich, U.; et al. CT-2A neurospheres-derived high-grade glioma in mice: A new model to address tumor stem cells and immunosuppression. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio044552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakimoto, H.; Johnson, P.R.; Knipe, D.M.; Chiocca, E.A. Effects of innate immunity on herpes simplex virus and its ability to kill tumor cells. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Xie, Q.; Shen, Y.; Lu, G.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. Involvement of mannose receptor in the preventive effects of mannose in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 641, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulli, B.; Ali, M.; Forghani, R.; Schob, S.; Hsieh, K.L.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Linnoila, J.J.; Chen, J.W. Measuring myeloperoxidase activity in biological samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Sosnovik, D.; Chen, J.W.; Panizzi, P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Aikawa, E.; Libby, P.; Swirski, F.K.; Weissleder, R. Activatable magnetic resonance imaging agent reports myeloperoxidase activity in healing infarcts and noninvasively detects the antiinflammatory effects of atorvastatin on ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation 2008, 117, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleijn, A.; Chen, J.W.; Buhrman, J.S.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Iwamoto, Y.; Lamfers, M.L.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.O.; Rabkin, S.D.; Weissleder, R.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Distinguishing inflammation from tumor and peritumoral edema by myeloperoxidase magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4484–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.W.; Breckwoldt, M.O.; Aikawa, E.; Chiang, G.; Weissleder, R. Myeloperoxidase-targeted imaging of active inflammatory lesions in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain 2008, 131, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breckwoldt, M.O.; Chen, J.W.; Stangenberg, L.; Aikawa, E.; Rodriguez, E.; Qiu, S.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Weissleder, R. Tracking the inflammatory response in stroke in vivo by sensing the enzyme myeloperoxidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18584–18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronald, J.A.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Hamilton, A.M.; Rodriguez, E.; Reynolds, F.; Hegele, R.A.; Rogers, K.A.; Querol, M.; Bogdanov, A.; et al. Enzyme-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging targeting myeloperoxidase identifies active inflammation in experimental rabbit atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation 2009, 120, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rest, R.F.; Farrell, C.F.; Naids, F.L. Mannose inhibits the human neutrophil oxidative burst. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1988, 43, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumann-Page, M.; Furtmuller, P.G.; Hofbauer, S.; Paton, L.N.; Obinger, C.; Kettle, A.J. Inactivation of human myeloperoxidase by hydrogen peroxide. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 539, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigorieva, D.V.; Gorudko, I.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Kostevich, V.A.; Vasilyev, V.B.; Cherenkevich, S.N.; Panasenko, O.M. Myeloperoxidase Stimulates Neutrophil Degranulation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 161, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marth, J.D.; Grewal, P.K. Mammalian glycosylation in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnhold, J.; Flemmig, J. Human myeloperoxidase in innate and acquired immunity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 500, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Veen, B.S.; de Winther, M.P.; Heeringa, P. Myeloperoxidase: Molecular mechanisms of action and their relevance to human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2899–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Antwerpen, P.; Slomianny, M.C.; Boudjeltia, K.Z.; Delporte, C.; Faid, V.; Calay, D.; Rousseau, A.; Moguilevsky, N.; Raes, M.; Vanhamme, L.; et al. Glycosylation pattern of mature dimeric leukocyte and recombinant monomeric myeloperoxidase: Glycosylation is required for optimal enzymatic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16351–16359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rymaszewski, A.L.; Tate, E.; Yimbesalu, J.P.; Gelman, A.E.; Jarzembowski, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Pritchard, K.A., Jr.; Vikis, H.G. The role of neutrophil myeloperoxidase in models of lung tumor development. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry. Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/72309/download (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Scaglione, F.; Musazzi, U.M.; Minghetti, P. Considerations on D-mannose Mechanism of Action and Consequent Classification of Marketed Healthcare Products. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 636377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jalali Motlagh, N.; Wang, C.; Kuellenberg, E.G.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Schmidt, S.; Chen, J.W. D-Mannose Slows Glioma Growth by Modulating Myeloperoxidase Activity. Cancers 2021, 13, 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246360
Jalali Motlagh N, Wang C, Kuellenberg EG, Wojtkiewicz GR, Schmidt S, Chen JW. D-Mannose Slows Glioma Growth by Modulating Myeloperoxidase Activity. Cancers. 2021; 13(24):6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246360
Chicago/Turabian StyleJalali Motlagh, Negin, Cuihua Wang, Enrico Giovanni Kuellenberg, Gregory R. Wojtkiewicz, Stephan Schmidt, and John W. Chen. 2021. "D-Mannose Slows Glioma Growth by Modulating Myeloperoxidase Activity" Cancers 13, no. 24: 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246360
APA StyleJalali Motlagh, N., Wang, C., Kuellenberg, E. G., Wojtkiewicz, G. R., Schmidt, S., & Chen, J. W. (2021). D-Mannose Slows Glioma Growth by Modulating Myeloperoxidase Activity. Cancers, 13(24), 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246360






