Understanding and Targeting Natural Killer Cell-Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Interactions in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. NK Cell Function and Activity in Normal Biology and Malignancies
3. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts
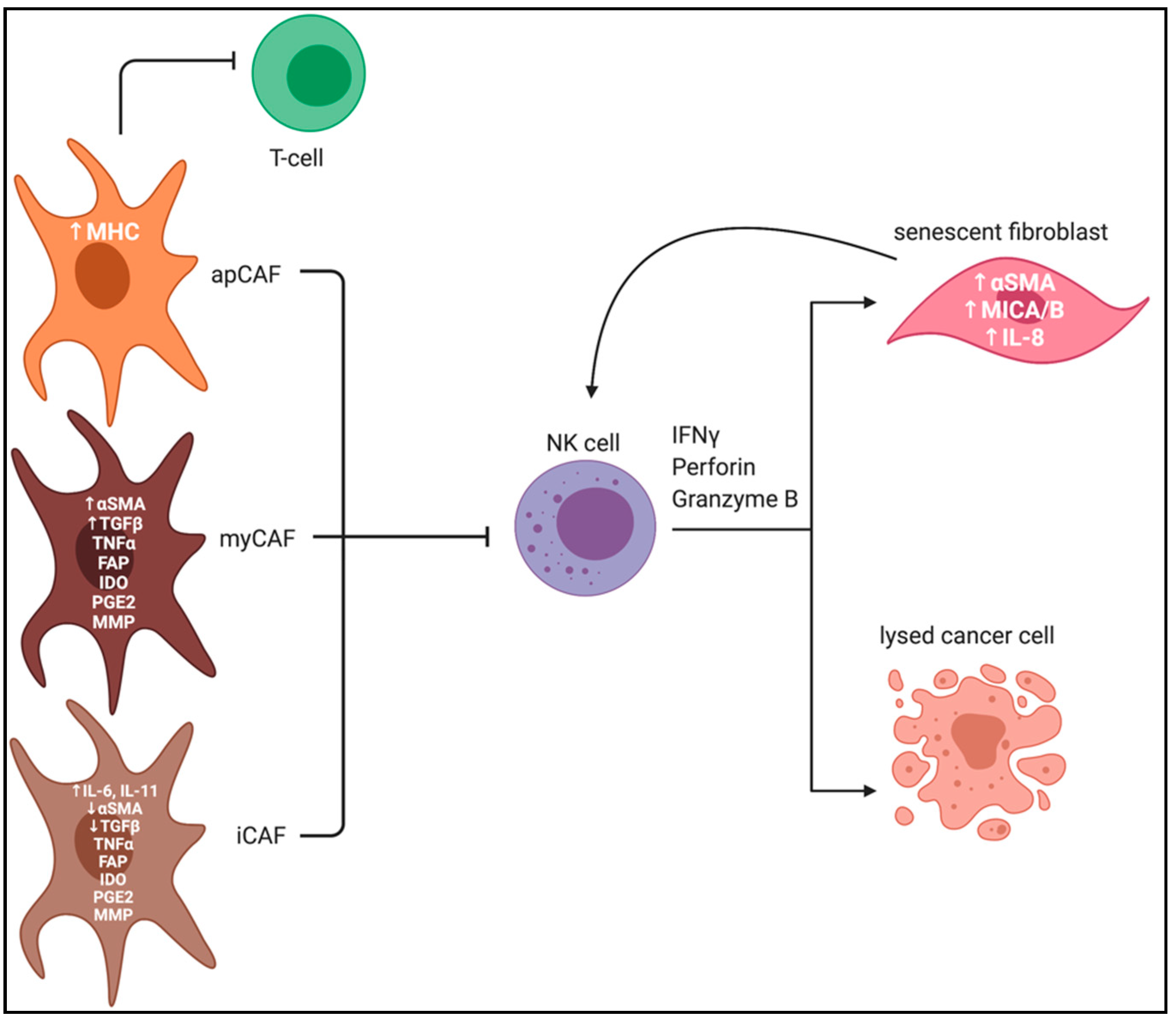
CAF Heterogeneity and Plasticity
4. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast and Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment
CAFs and NK Cells in PDAC TME
5. Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts
5.1. Targeting αSMA+ CAFs in PDAC
5.2. Targeting Shh Signaling in CAFs in PDAC and Other Malignancies
5.3. Targeting NetG1+ CAFs in PDAC
5.4. Targeting FAP+ CAFs in PDAC
6. Other Approaches to Exploiting NK Cell Function in PDAC
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, M.A.; Fehniger, T.A.; Caligiuri, M.A. The Biology of Human Natural Killer-Cell Subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, E.; Onate, M.K.; Sherman, M.H. Fibroblast Heterogeneity in the Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Erwei, S. Turning Foes to Friends: Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 18, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujino, T.; Seshimo, I.; Yamamoto, H.; Ngan, C.Y.; Ezumi, K.; Takemasa, I.; Ikeda, M.; Sekimoto, M.; Matsuura, N.; Monden, M. Stromal Myofibroblasts predict disease recurrence for colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laklai, H.; Miroshnikova, Y.A.; Pickup, M.W.; Collisson, E.R.; Kim, G.E.; Barrett, A.S.; Hill, R.C.; Lakins, J.N.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Mouw, J.K.; et al. Genotype tunes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissue tension to induce matricellular fibrosis and tumor progression. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öhlund, D.; Handly-Santana, A.; Biffi, G.; Elyada, E.; Almeida, A.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Corbo, V.; Oni, T.E.; Hearn, S.A.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Distinct Populations of Inflammatory Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, Y.; Hocine, H.R.; Gentric, G.; Pelon, F.; Bernard, C.; Bourachot, B.; Lameiras, S.; Albergante, L.; Bonneau, C.; Guyward, A.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Fibroblast Clusters Linked to Immunotherapy Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebleu, V.S.; Raghu, K. A Peek into Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Origins, Functions and Translational Impact. Dis. Models Mech. 2018, 11, dmm029447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tchou, J.; Zhang, P.J.; Yingtai, B.; Satija, C.; Marjumdar, R.; Stephen, T.L.; Lo, A.; Chen, H.; Miles, C.; June, C.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Expression by Stromal Cells and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Human Breast Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, S.; Beziat, V.; Dhedin, N.; Vernant, J.P.; Debre, P.; Vieillard, V. HLA-E Upregulation on IFN-γ-Activated AML Blasts Impairs CD94/NKG2A-Dependent NK Cytolysis after Haplo-Mismatched Hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 43, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Fcγ Receptors as Regulators of Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habif, G.; Crinier, A.; André, P.; Vivier, E.; Narni-Mancinelli, E. Targeting Natural Killer Cells in Solid Tumors. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, G.; Antonangeli, F.; Bonanni, V.; Santoni, A. Dysregulation of Chemokine/Chemokine Receptor Axes and NK Cell Tissue Localization during Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.; Hong, D.L.; Atzberger, A.; Kollnberger, S.; Filer, A.D.; Buckley, C.D.; McMichael, A.; Enver, T.; Bowness, P. CD56bright Human NK Cells Differentiate into CD56dim Cells: Role of Contact with Peripheral Fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, S.; Girdhari, L. The Molecular Mechanism of Natural Killer Cells Function and Its Importance in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabry, M.; Lowdell, M.W. NK Cells and Cancer. Nat. Kill. Cells 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasbender, F.; Widera, A.; Hengstler, J.G.; Watzl, C. Natural Killer Cells and Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.R.; Trindade, E.S.; Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, F. Tumor Microenvironment-Associated Extracellular Matrix Components Regulate NK Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Munari, E.; Bertaina, A.; Moretta, F.; Zotto, G.D.; Pietra, G.; et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S. Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity and Its Regulation by Inhibitory Receptors. Immunology 2018, 154, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; Nattermann, J.; Feldmann, G.; Sievers, E.; Frank, S.; Strehl, J.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Activated γδ T cells express the natural cytotoxicity receptor natural killer p44 and show cytotoxic activity against myeloma cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 144, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, D.V.; Fogli, M.; Hudspeth, K.; Gomes de Silva, M.; Maavilio, D.; Silva-Santos, B. Differentiation of human peripheral blood Vδ1+ T cells expressing the natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp30 for recognition of lymphoid leukemia cells. Blood 2011, 118, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iguchi-Manaka, A.; Kai, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Shibata, K.; Tahara-Hanaoka, S.; Honda, S.; Yasui, T.; Kikutani, H.; Shibuya, K.; Shibuya, A. Accelerated tumor growth in mice deficient in DNAM-1 receptor J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinet, L.; Smyth, M.J. Balancing Natural Killer Cell Activation through Paired Receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacson, B.; Mandelboim, O. Natural Killer Cells Control Metastasis via Structural Editing of Primary Tumors in Mice. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, Z.; Wakefield, M.R.; Xiao, H.; Bai, Q.; Fang, Y. The role of IL-11 in immunity and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 373, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves-Maia, M.; Gache, Y.; Basante, M.; Cosson, E.; Salavagione, E.; Muller, M.; Bernerd, F.; Avril, M.F.; Schaub, S.; Sarasin, A.; et al. NK Cell and Fibroblast-Mediated Regulation of Skin Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invasion by CLEC2A Is Compromised in Xeroderma Pigmentosum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, W.N.; Isaacs, J.T.; Denmeade, S.R. Rationale Behind Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein-Expressing Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts as a Novel Chemotherapeutic Strategy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newhook, N.; Fudge, N.; Grant, M. NK Cells Generate Memory-Type Responses to Human Cytomegalovirus-Infected Fibroblasts. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanietsky, N.; Rovis, T.L.; Glasner, A.; Seidel, E.; Tsukerman, P.; Yamin, R.; Enk, J.; Jonjic, S.; Mandelboim, O. Mouse TIGIT Inhibits NK-Cell Cytotoxicity upon Interaction with PVR. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2138–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L. NK Cell Receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 359–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.M.; Bickel, M.; Wiesmann, U.N.; Spörri, B. Natural Killer Cells Activate Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Cytokine 2000, 12, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsamo, M.; Scordamaglia, F.; Pietra, G.; Manzini, C.; Cantoni, C.; Boitano, M.; Queirolo, P.; Vermi, W.; Facchetti, F.; Moretta, A.; et al. Melanoma-Associated Fibroblasts Modulate NK Cell Phenotype and Antitumor Cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20847–20852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sungur, C.M.; Murphy, W.J. Utilization of Mouse Models to Decipher Natural Killer Cell Biology and Potential Clinical Applications. Hematology 2013, 2013, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasner, A.; Levi, A.; Enk, J.; Isaacson, B.; Viukov, S.; Orlanski, S.; Scope, A.; Neuman, T.; Enk, C.; Hanna, J.; et al. NKp46 Receptor-Mediated Interferon-γ Production by Natural Killer Cells Increases Fibronectin 1 to Alter Tumor Architecture and Control Metastasis. Immunity 2018, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, L.; Safta-Saadoun, T.B.; Gourbeix, J.; Cavalcanti, A.; Rober, C.; Favre, G.; Chouaib, S.; Thiery, J. Melanoma-Associated Fibroblasts Decrease Tumor Cell Susceptibility to NK Cell-Mediated Killing through Matrix-Metalloproteinases Secretion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19780–19794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okumura, G.; Iguchi-Manaka, A.; Murata, R.; Yamashita-Kanemaru, Y.; Shibuya, A.; Shibuya, K. Tumor-Derived Soluble CD155 Inhibits DNAM-1–Mediated Antitumor Activity of Natural Killer Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, W.; Xi, X.; Hao, Z.; Li, W.; Kong, Y.; Cui, L.; Ma, C.; Ba, D.; He, W. RAE1E2, a soluble isoform of the UL16-binding protein RAET1E produced by tumor cells, inhibits NKG2D-mediated NK cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18922–18928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, Z.L.; Luo, Z.; Wei, W.; Liang, S.; Gao, T.L.; Lu, Y.B. Hypoxia-induced shedding of MICA and HIF1A-mediated immune escape of pancreatic cancer cells from NK cells: Role of circ_0000977/miR-153 axis. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansems, M.; Span, P.N. The Tumor Microenvironment and Radiotherapy Response; a Central Role for Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 22, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitopoulou, E. Tumour Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer: Immune Landscape Is Dictated by Molecular and Histopathological Features. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yi, S.; Liu, W.; Jia, C.; Wang, G.; Hua, X.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G. Colorectal Carcinoma-Derived Fibroblasts Modulate Natural Killer Cell Phenotype and Antitumor Cytotoxicity. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q. Crosstalk between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Immune Cells in Cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasmim, M.; Messai, Y.; Ziani, L.; Thiery, J.; Bouhris, J.H.; Noman, M.Z.; Chouaib, S. Critical Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Shaping NK Cell Functions: Implication of Hypoxic Stress. Front. Immunol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jewett, A.; Kos, J.; Fong, Y.; Ko, M.W.; Safaei, T.; Nanut, M.P.; Kaur, K. NK Cells Shape Pancreatic and Oral Tumor Microenvironments; Role in Inhibition of Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narra, K.; Mullins, S.R.; Lee, H.O.; Strzemkowski-Brun, B.; Magalong, K.; Christiansen, V.J.; McKee, P.A.; Egleston, B.; Cohen, S.J.; Weiner, L.M.; et al. Phase II Trial of Single Agent Val-BoroPro (Talabostat) Inhibiting Fibroblast Activation Protein in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebeau, A.M.; Brennen, W.N.; Aggarwal, S.; Denmeade, S.R. Targeting the Cancer Stroma with a Fibroblast Activation Protein-Activated Promelittin Protoxin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, A.; Wang, L.C.S.; Scholler, J.; Monslow, J.; Avery, D.; Newick, K.; O’Briend, S.; Evans, R.A.; Bajor, D.J.; Clendenin, C.; et al. Tumor-Promoting Desmoplasia Is Disrupted by Depleting FAP-Expressing Stromal Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, A.; Li, C.P.; Buza, E.L.; Blomberg, R.; Govindaraju, P.; Avery, D.; Monslow, J.; Hsiao, M.; Puré, E. Fibroblast Activation Protein Augments Progression and Metastasis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Yin, W.; Dang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Fan, J.; He, R. FAP Promotes Immunosuppression by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment via STAT3–CCL2 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4124–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, C.C. Talabostat. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Xiao, L.; Joo, K.I.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Conti, P.S.; Wang, P. A Potent Immunotoxin Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein for Treatment of Breast Cancer in Mice. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 138, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arteel, G.E. Silencing a Killer Among Us: Ethanol Impairs Immune Surveillance of Activated Stellate Cells by Natural Killer Cells. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Apte, M.V.; Wilson, J.S.; Lugea, A.; Pandol, S.J. A Starring Role for Stellate Cells in the Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachem, M.G.; Schünemann, M.; Ramadani, M.; Siech, M.; Beger, H.; Buck, A.; Zhou, S.; Schmid-Kotsas, A.; Adler, G. Pancreatic Carcinoma Cells Induce Fibrosis by Stimulating Proliferation and Matrix Synthesis of Stellate Cells. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, M.; Schmidy, C.; Ringel, J.; Kluth, M.; Müller, P.; Nizze, H.; Jesnowski, R. Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Induces Desmoplasia in an Experimental Model of Human Pancreatic Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 550–555. [Google Scholar]
- Elyada, E.; Bolisetty, M.; Laise, P.; Flynn, W.F.; Courtois, E.T.; Burkhart, R.A.; Teinor, J.A.; Belleau, P.; Biffi, G.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. Cross-Species Single-Cell Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Reveals Antigen-Presenting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.A.; Kim, J.; Jeon, S.; Shin, M.H.; Kwon, J.; Kim, T.J.; Im, K.; Han, Y.; Kwon, W.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Defective Localization With Impaired Tumor Cytotoxicity Contributes to the Immune Escape of NK Cells in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Front. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radaeva, S.; Sun, R.; Jaruga, B.; Nguyen, V.T.; Tian, Z.; Gao, B. Natural Killer Cells Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Killing Activated Stellate Cells in NKG2D-Dependent and Tumor Necrosis Factor–Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand–Dependent Manners. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.B.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, W.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-Expressing Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts Synergizes with Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, M.; Meng, F.; Sun, R. Activated Pancreatic Stellate Cells Inhibit NK Cell Function in the Human Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 16, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kang, T.H.; Yoo, W.; Choi, H.; Jo., S.; Kong, K.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, D.; et al. An Antibody Designed to Improve Adoptive NK-Cell Therapy Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Progression in a Murine Model. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Pentchena-Hoang, T.; Carstens, J.L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.C.; Simpson, T.R.; Laklai, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Kahlert, C.; Novitskiy, S.V.; et al. Depletion of Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts and Fibrosis Induces Immunosuppression and Accelerates Pancreas Cancer with Reduced Survival. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanley, C.J.; Mellone, M.; Ford, K.; Thirdborough, S.M.; Mellows, T.; Frampton, S.J.; Smith, D.M.; Harden, E.; Szyndralewiez, C.; Bullock, M.; et al. Targeting the Myofibroblastic Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Phenotype Through Inhibition of NOX4. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 110, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pausch, T.M.; Aue, E.; Wirsik, N.M.; Valls, A.F.; Shen, Y.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Hackert, T.; Schneider, M.; Schmidt, T. Metastasis-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Angiogenesis in Metastasized Pancreatic Cancer via the CXCL8 and the CCL2 Axes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, A.D.; Oberstein, P.E.; Thomas, D.H.; Mirek, E.T.; Palermo, C.F.; Sastra, S.A.; Dekleva, E.N.; Saunders, T.; Becerra, C.P.; Tattersall, I.W.; et al. Stromal Elements Act to Restrain, Rather Than Support, Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, K.; Omura, N.; Hong, S.M.; Griffith, M.; Vincent, A.; Borges, M.; Goggins, M. Overexpression of Smoothened Activates the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Pitaressi, J.R.; Cuitiño, M.C.; Kladney, R.D.; Woelke, S.A.; Sizemore, G.M.; Nayak, S.G.; Egriboz, O.; Schweickery, P.G.; Yu, L.; et al. Genetic Ablation of Smoothened in Pancreatic Fibroblasts Increases Acinar–Ductal Metaplasia. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Fisher, G.G., Jr.; Li, R. Natural Killer Cell and Stroma Abundance Are Independently Prognostic and Predict Gastric Cancer Chemotherapy Benefit. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francescone, R.; Vendramini-Costa, D.B.; Franco-Barraza, J.; Wagner, J.; Muir, A.; Lau, A.N.; Gabitova, L.; Pazina, T.; Gupta, S.; Luong, T.; et al. Netrin G1 promote pancreatic tumorigenesis through cancer associated fibroblast driven nutritional support and immunosuppression. Cancer Discov. 2020, CD-20-0775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerensen, M.M.; Ros, W.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Robbrecht, D.; Rohrberg, K.S.; Martin-Liberal, J.; Lassen, U.N.; Bermejo, I.M.; Lolkema, M.P.; Tabernero, J. Safety, PK/PD, and anti-tumor activity of RO6874281, an engineered variant of interleukin-2 (IL-2v) targeted to tumor-associated fibroblasts via binding to fibroblast activation protein (FAP). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, I.; Alvarez, E.C.; Mau-Sorensen, M.; Lassen, U.N.; Lolkema, M.P.; Robbrecht, D.G.; Gomez-Roca, C.A.; Martin-Liberal, J.; Tabernero, J.; Ros, W. Clincal activity, safety, and PK/PD from a phase I study of RO6874281, a fibroblast activation protein (FAP) targeted interleukin-2 variant (IL-2v). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscetti, M.; Leibold, J.; Bott, M.J.; Fennell, M.; Kulick, A.; Salgado, N.R.; Chen, C.C.; Ho, Y.J.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Feucht, J.; et al. NK Cell–Mediated Cytotoxicity Contributes to Tumor Control by a Cytostatic Drug Combination. Science 2018, 362, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gürlevik, E.; Fleischmann-Mundy, B.; Brooks, J.; Demir, I.E.; Steiger, K.; Ribback, S.; Yevsa, T.; Woller, N.; Kloos, A.; Ostroumov, D.; et al. Administration of Gemcitabine After Pancreatic Tumor Resection in Mice Induces an Antitumor Immune Response Mediated by Natural Killer Cells. Gastroenterology 2016, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawson, D.W.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Gemcitabine Activates Natural Killer Cells to Attenuate Pancreatic Cancer Recurrence. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-C.S.; Lo, A.; Scholler, J.; Sun, J.; Majumdar, R.S.; Kapoor, V.; Antzis, M.; Cotner, C.E.; Johnson, L.A.; Durham, A.C.; et al. Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein in Tumor Stroma with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Can Inhibit Tumor Growth and Augment Host Immunity without Severe Toxicity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 2, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, E.; Chinnasamy, D.; Yu, Z.; Morgan, R.A.; Lee, C.C.R.; Restifo, N.P.; Rosenberg, S.A. Immune Targeting of Fibroblast Activation Protein Triggers Recognition of Multipotent Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Cachexia. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautela, J.; Huntington, N.D. IL-15 Signaling in NK Cell Cancer Immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Audenaerde, J.R.M.; De Waele, J.; Marcq, E.; Van Loenhout, J.; Lion, E.; Van den Bergh, J.M.J.; Jesenofsky, R.; Masamune, A.; Roeyen, G.; Pauwels, P.; et al. Interleukin-15 stimulates natural killer cell-mediated killing of both human pancreatic cancer and stellate cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56968–56979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhanovsky, V.; Yon, M.; Dickins, R.A.; Hearn, S.; Simon, J.; Miething, C.; Yee, H.; Zender, L.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence of Activated Stellate Cells Limits Liver Fibrosis. Cell 2008, 134, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| NK Cell Receptor Class/Family | Receptor (Human/Mouse) | Ligand(s) (Human/Mouse) | Activating or Inhibitory |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCR | NKG2D/mNKG2D | MICA/B, ULBPs/Rae-1, H-60, MULT1c | Activating |
| NKG2C/mNKG2C | HLA-E/Qa1b | ||
| NKp30 (human only) | Heparin, HLA-B3 (BAT3), B7H6 | ||
| NKp46/Ncr1 | Heparin/Heparin | ||
| NKp65 (human only) | CLEC2A (skin specific) | ||
| NKp80 (human only) | AICL | ||
| NKp44 (human only) | Heparin, NKp44L | ||
| PCNA | Inhibitory | ||
| CD94-NKG2A/mCD94-NKG2A | HLA-E/Qa1b | Inhibitory | |
| KIR | KIR2DS1/2 | HLA-C1/2 | Activating |
| KIR2DS4 | HLA-A | ||
| KIR3DS1 | HLA-B | ||
| KIR2DL1–3 | HLA-C | Inhibitory | |
| KIR2DL4 | HLA-G | ||
| KIR3DL1 | HLA-B | ||
| KIR3DL2 | HLA-A | ||
| Ly49 (mouse only) | Ly49D | H-2D | Activating |
| Ly49H | M157 | ||
| Ly49A | H-2D | Inhibitory | |
| Ly49C | H-2D | ||
| Ly49I | H-2k | ||
| Ly49P | H-2D | ||
| Ig Superfamily | DNAM-1 (CD226)/mDNAM-1 | CD155, CD122/CD125, CD112 | Activating |
| Other NK cell receptors | TIGIT/mTIGIT | CD155, CD122/CD125, CD112 | Inhibitory |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malchiodi, Z.X.; Weiner, L.M. Understanding and Targeting Natural Killer Cell-Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Interactions in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030405
Malchiodi ZX, Weiner LM. Understanding and Targeting Natural Killer Cell-Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Interactions in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(3):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030405
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalchiodi, Zoe X., and Louis M. Weiner. 2021. "Understanding and Targeting Natural Killer Cell-Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Interactions in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 3: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030405
APA StyleMalchiodi, Z. X., & Weiner, L. M. (2021). Understanding and Targeting Natural Killer Cell-Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Interactions in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 13(3), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030405







