PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
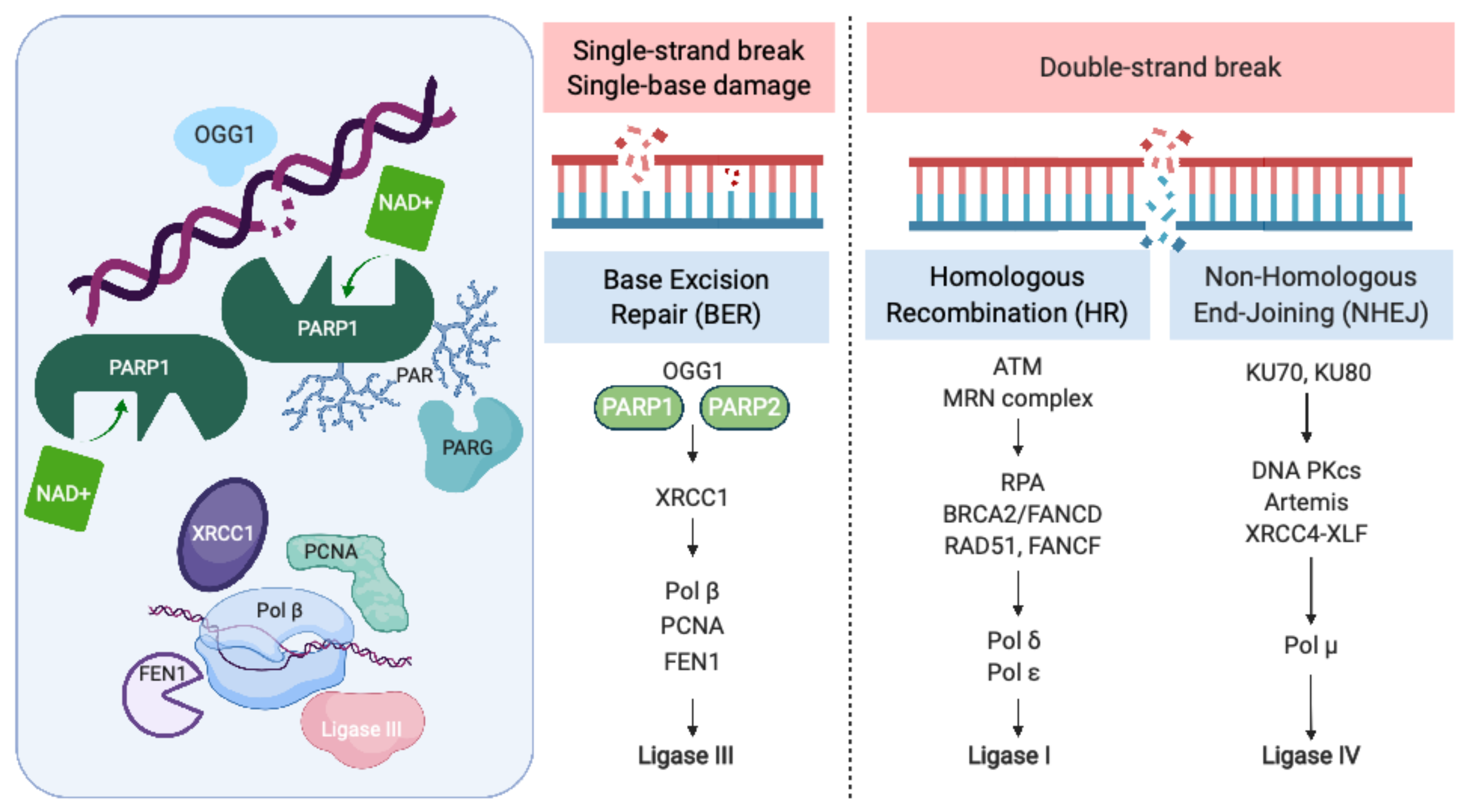
2. PARP Inhibitor Mechanism of Action
3. Biomarkers of Response to PARP Inhibitors in SCLC
4. PARP Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy
5. Synthetic Lethality Downstream of PARP Inhibitors
6. Combining PARP and Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
7. Restoring Tumor Cell Inflammatory Signaling to Enhance PARP Inhibitor Response
8. Orthogonal Approaches
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socinski, M.A.; Smit, E.F.; Lorigan, P.; Konduri, K.; Reck, M.; Szczesna, A.; Blakely, J.; Serwatowski, P.; Karaseva, N.A.; Ciuleanu, T.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed plus carboplatin compared with etoposide plus carboplatin in chemotherapy-naive patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4787–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, D.R.; Townley, P.M.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Fang, L.; Adiguzel, I.; Huang, J.E.; Karlin, D.A.; Faoro, L.; Scappaticci, F.A.; Socinski, M.A. Randomized phase II study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Results from the SALUTE trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.C.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Lopez-Martin, J.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Kao, S.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Delord, J.P.; Gao, B.; Planchard, D.; Gottfried, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab After Two or More Lines of Previous Therapy in Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic SCLC: Results From the KEYNOTE-028 and KEYNOTE-158 Studies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ready, N.E.; Ott, P.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Hann, C.L.; de Braud, F.; Antonia, S.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Moreno, V.; Atmaca, A.; et al. Nivolumab Monotherapy and Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the CheckMate 032 Randomized Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczesna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Ozguroglu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.E.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Tsekov, H.; Shparyk, Y.; Cucevia, B.; Juhasz, G.; Thatcher, N.; Ross, G.A.; Dane, G.C.; Crofts, T. Phase III trial comparing supportive care alone with supportive care with oral topotecan in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5441–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pawel, J.; Schiller, J.H.; Shepherd, F.A.; Fields, S.Z.; Kleisbauer, J.P.; Chrysson, N.G.; Stewart, D.J.; Clark, P.I.; Palmer, M.C.; Depierre, A.; et al. Topotecan versus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine for the treatment of recurrent small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, J.R.; von Pawel, J.; Pujol, J.L.; Papai, Z.; Quoix, E.; Ardizzoni, A.; Poulin, R.; Preston, A.J.; Dane, G.; Ross, G. Phase III study of oral compared with intravenous topotecan as second-line therapy in small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2086–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, J.L.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Uwer, L.; Hureaux, J.; Guisier, F.; Carmier, D.; Madelaine, J.; Otto, J.; et al. A Randomized Non-Comparative Phase II Study of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Atezolizumab or Chemotherapy as Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the IFCT-1603 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgensztern, D.; Besse, B.; Greillier, L.; Santana-Davila, R.; Ready, N.; Hann, C.L.; Glisson, B.S.; Farago, A.F.; Dowlati, A.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine in Third-Line and Beyond Patients with DLL3-Expressing, Relapsed/Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the Phase II TRINITY Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6958–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Vicente, D.; Ciuleanu, T.; Gettinger, S.; Peters, S.; Horn, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Pardo, N.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab (nivo) monotherapy versus chemotherapy (chemo) in recurrent small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Results from CheckMate 331. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cision PR Newswire. Jazz Pharmaceuticals and PharmaMar Announce Results of ATLANTIS Phase 3 Study Evaluating Zepzelca™ in Combination with Doxorubicin for Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer Following One Prior Platinum-containing Line; News Release; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Dublin, Ireland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Trigo, J.; Subbiah, V.; Besse, B.; Moreno, V.; Lopez, R.; Sala, M.A.; Peters, S.; Ponce, S.; Fernandez, C.; Alfaro, V.; et al. Lurbinectedin as second-line treatment for patients with small-cell lung cancer: A single-arm, open-label, phase 2 basket trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Small Cell Lung Cancer V1.2021-11 August. Available online: https://www.nccn.org (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Takahashi, T.; Nau, M.M.; Chiba, I.; Birrer, M.J.; Rosenberg, R.K.; Vinocour, M.; Levitt, M.; Pass, H.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D. p53: A frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science 1989, 246, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, C.H.; Hsieh, C.L.; Gazdar, A.F.; Johnson, B.E.; Sakaguchi, A.Y.; Naylor, S.L.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, E.Y. Altered structure and expression of the human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J.; McCormick, F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilfou, J.T.; Lowe, S.W. Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Wang, J.; Nilsson, M.B.; Fujimoto, J.; Saintigny, P.; Yordy, J.; Giri, U.; Peyton, M.; Fan, Y.H.; Diao, L.; et al. Proteomic profiling identifies dysregulated pathways in small cell lung cancer and novel therapeutic targets including PARP1. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Poirier, J.T.; Byers, L.A.; Dive, C.; Dowlati, A.; George, J.; Heymach, J.V.; Johnson, J.E.; Lehman, J.M.; MacPherson, D.; et al. Molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer: A synthesis of human and mouse model data. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, D. PARP and PARG inhibitors in cancer treatment. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 360–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. PARP inhibitors: Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science 2017, 355, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, N.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, P.C.; Boss, D.S.; Yap, T.A.; Tutt, A.; Wu, P.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Mortimer, P.; Swaisland, H.; Lau, A.; O’Connor, M.J.; et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barayan, R.; Ran, X.; Lok, B.H. PARP inhibitors for small cell lung cancer and their potential for integration into current treatment approaches. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6240–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilie, P.G.; Gay, C.M.; Byers, L.A.; O’Connor, M.J.; Yap, T.A. PARP Inhibitors: Extending Benefit Beyond BRCA-Mutant Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3759–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Mina, L.; Chugh, R.; Glaspy, J.; Rafii, S.; Kaye, S.; Sachdev, J.; Heymach, J.; Smith, D.C.; et al. Phase I, Dose-Escalation, Two-Part Trial of the PARP Inhibitor Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Germline BRCA1/2 Mutations and Selected Sporadic Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woll, P.; Gaunt, P.; Steele, N.; Ahmed, S.; Mulatero, C.; Shah, R. P1.07–015 STOMP: A UK National Cancer Research Network randomised, double blind, multicentre phase II trial of olaparib as maintenance therapy in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S704–S705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sica, G.L.; Wagner, L.I.; Wade, J.L., 3rd; Srkalovic, G.; Lash, B.W.; Leach, J.W.; Leal, T.B.; Aggarwal, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Etoposide in Combination With Veliparib or Placebo for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ECOG-ACRIN 2511 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, B.H.; Gardner, E.E.; Schneeberger, V.E.; Ni, A.; Desmeules, P.; Rekhtman, N.; de Stanchina, E.; Teicher, B.A.; Riaz, N.; Powell, S.N.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Activity Correlates with SLFN11 Expression and Demonstrates Synergy with Temozolomide in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, E.E.; Lok, B.H.; Schneeberger, V.E.; Desmeules, P.; Miles, L.A.; Arnold, P.K.; Ni, A.; Khodos, I.; de Stanchina, E.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Chemosensitive Relapse in Small Cell Lung Cancer Proceeds through an EZH2-SLFN11 Axis. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, E.; Kunkel, M.; Evans, D.; Silvers, T.; Delosh, R.; Laudeman, J.; Ogle, C.; Reinhart, R.; Selby, M.; Connelly, J.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer Screen of Oncology Drugs, Investigational Agents, and Gene and microRNA Expression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietanza, M.C.; Waqar, S.N.; Krug, L.M.; Dowlati, A.; Hann, C.L.; Chiappori, A.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Woo, K.M.; Cardnell, R.J.; Fujimoto, J.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Temozolomide in Combination With Either Veliparib or Placebo in Patients With Relapsed-Sensitive or Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, J.; Feng, Y.; Yu, G.K.; Ru, Y.; Tang, S.W.; Shen, Y.; Pommier, Y. Resistance to PARP inhibitors by SLFN11 inactivation can be overcome by ATR inhibition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76534–76550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapkin, B.J.; George, J.; Christensen, C.L.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Dries, R.; Sundaresan, T.; Phat, S.; Myers, D.T.; Zhong, J.; Igo, P.; et al. Genomic and Functional Fidelity of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farago, A.F.; Yeap, B.Y.; Stanzione, M.; Hung, Y.P.; Heist, R.S.; Marcoux, J.P.; Zhong, J.; Rangachari, D.; Barbie, D.A.; Phat, S.; et al. Combination Olaparib and Temozolomide in Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1372–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.A.; Tong, P.; Cardnell, R.J.; Sen, T.; Li, L.; Gay, C.M.; Masrorpour, F.; Fan, Y.; Bara, R.O.; Feng, Y.; et al. Dynamic variations in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), ATM, and SLFN11 govern response to PARP inhibitors and cisplatin in small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28575–28587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Park, E.M.; Diao, L.; Groves, S.M.; Heeke, S.; Nabet, B.Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Solis, L.M.; Lu, W.; et al. Patterns of transcription factor programs and immune pathway activation define four major subtypes of SCLC with distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Zhang, G.; Deng, X.; Rossi, M.R.; Switchenko, J.M.; Doho, G.H.; Chen, Z.; Kim, S.; Strychor, S.; Christner, S.M.; et al. Poly (ADP) ribose polymerase enzyme inhibitor, veliparib, potentiates chemotherapy and radiation in vitro and in vivo in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, B.A.; Silvers, T.; Selby, M.; Delosh, R.; Laudeman, J.; Ogle, C.; Reinhart, R.; Parchment, R.; Krushkal, J.; Sonkin, D.; et al. Small cell lung carcinoma cell line screen of etoposide/carboplatin plus a third agent. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1952–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Khan, S.A.; Gerber, D.E.; Dowell, J.; Moss, R.A.; Belani, C.P.; Hann, C.L.; Aggarwal, C.; Ramalingam, S.S. A phase 1 safety study of veliparib combined with cisplatin and etoposide in extensive stage small cell lung cancer: A trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E2511). Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrafi, F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Byers, L.A.; Garralda, E.; Lolkema, M.P.; Sangha, R.S.; Viteri, S.; Chae, Y.K.; Camidge, D.R.; Gabrail, N.Y.; et al. A Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Veliparib Combined with Carboplatin and Etoposide in Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer and Other Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietanza, M.C.; Kadota, K.; Huberman, K.; Sima, C.S.; Fiore, J.J.; Sumner, D.K.; Travis, W.D.; Heguy, A.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Holodny, A.I.; et al. Phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with relapsed sensitive or refractory small cell lung cancer, with assessment of methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase as a potential biomarker. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, L.R.; Bankovich, A.J.; Anderson, W.C.; Aujay, M.A.; Bheddah, S.; Black, K.; Desai, R.; Escarpe, P.A.; Hampl, J.; Laysang, A.; et al. A DLL3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate eradicates high-grade pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor-initiating cells in vivo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 302ra136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Pietanza, M.C.; Bauer, T.M.; Ready, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Glisson, B.S.; Byers, L.A.; Johnson, M.L.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Robert, F.; et al. Rovalpituzumab tesirine, a DLL3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate, in recurrent small-cell lung cancer: A first-in-human, first-in-class, open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.B.; Evers, G.; Kerkhoff, A.; Mohr, M.; Schliemann, C.; Berdel, W.E.; Schmidt, L.H. Future Options of Molecular-Targeted Therapy in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Heist, R.S.; Starodub, A.N.; Camidge, D.R.; Kio, E.A.; Masters, G.A.; Purcell, W.T.; Guarino, M.J.; Misleh, J.; Schneider, C.J.; et al. Therapy of Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) with a Topoisomerase-I-inhibiting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Targeting Trop-2, Sacituzumab Govitecan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5711–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, J.H.; Lok, B.H.; Ma, J.; Bell, A.; de Stanchina, E.; Poirier, J.T.; Rudin, C.M. Talazoparib Is a Potent Radiosensitizer in Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines and Xenografts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5143–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, V.; Schenk, M.W.; Baker, K.; Gomes, F.; Lallo, A.; Frese, K.K.; Forster, M.; Dive, C.; Blackhall, F. Targeting DNA damage in SCLC. Lung Cancer 2017, 114, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretic, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardnell, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Diao, L.; Fan, Y.H.; Masrorpour, F.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Mills, G.B.; Minna, J.D.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Proteomic markers of DNA repair and PI3K pathway activation predict response to the PARP inhibitor BMN 673 in small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.; Tong, P.; Stewart, C.A.; Cristea, S.; Valliani, A.; Shames, D.S.; Redwood, A.B.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, L.; Glisson, B.S.; et al. CHK1 Inhibition in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Produces Single-Agent Activity in Biomarker-Defined Disease Subsets and Combination Activity with Cisplatin or Olaparib. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3870–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallo, A.; Frese, K.K.; Morrow, C.J.; Sloane, R.; Gulati, S.; Schenk, M.W.; Trapani, F.; Simms, N.; Galvin, M.; Brown, S.; et al. The Combination of the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib and the WEE1 Inhibitor AZD1775 as a New Therapeutic Option for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5153–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.W.; Thomas, A.; Murai, J.; Trepel, J.B.; Bates, S.E.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Pommier, Y. Overcoming Resistance to DNA-Targeted Agents by Epigenetic Activation of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) Expression with Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Alu, A.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. cGAS-STING pathway in cancer biotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhao, W.; Ju, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Labrie, M.; Yap, T.A.; Mills, G.B.; Peng, G. PARPi Triggers the STING-Dependent Immune Response and Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Independent of BRCAness. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Niimi, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Permata, T.B.M.; Hagiwara, Y.; Isono, M.; Nuryadi, E.; Sekine, R.; Oike, T.; Kakoti, S.; et al. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Xia, W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M.K.; Hsu, J.M.; Hsu, J.L.; Yu, W.H.; Du, Y.; Lee, H.H.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Upregulates PD-L1 Expression and Enhances Cancer-Associated Immunosuppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3711–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabanon, R.M.; Muirhead, G.; Krastev, D.B.; Adam, J.; Morel, D.; Garrido, M.; Lamb, A.; Henon, C.; Dorvault, N.; Rouanne, M.; et al. PARP inhibition enhances tumor cell-intrinsic immunity in ERCC1-deficient non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Kim, H.J.; Wang, Q.; Kearns, M.; Jiang, T.; Ohlson, C.E.; Li, B.B.; Xie, S.; Liu, J.F.; Stover, E.H.; et al. PARP Inhibition Elicits STING-Dependent Antitumor Immunity in Brca1-Deficient Ovarian Cancer. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2972–2980.e2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Chen, L.; Corte, C.M.D.; Morikawa, N.; Fujimoto, J.; Cristea, S.; Nguyen, T.; Diao, L.; Li, L.; et al. Targeting DNA Damage Response Promotes Antitumor Immunity through STING-Mediated T-cell Activation in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Vilimas, R.; Trindade, C.; Erwin-Cohen, R.; Roper, N.; Xi, L.; Krishnasamy, V.; Levy, E.; Mammen, A.; Nichols, S.; et al. Durvalumab in Combination with Olaparib in Patients with Relapsed SCLC: Results from a Phase II Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.; Ross, K.; Kim, S.; De Jonge, M.; Barlesi, F.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Domchek, S.; Lee, J.; Angell, H.; Bui, K.; et al. P1.15-004 An Open-Label, Multitumor Phase II Basket Study of Olaparib and Durvalumab (MEDIOLA): Results in Patients with Relapsed SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S2044–S2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyraud, F.; Italiano, A. Combined PARP Inhibition and Immune Checkpoint Therapy in Solid Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponath, P.; Menezes, D.; Pan, C.; Chen, B.; Oyasu, M.; Strachan, D.; LeBlanc, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.T.; Rangan, V.S.; et al. A Novel, Fully Human Anti-fucosyl-GM1 Antibody Demonstrates Potent In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity in Preclinical Models of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5178–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, D.; Rivard, C.; Yu, H.; Bunn, P.; Suda, K.; Ren, S.; Pickard, S.L.; Laszlo, V.; Harko, T.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; et al. Neuroendocrine subtypes of small cell lung cancer differ in terms of immune microenvironment and checkpoint molecule distribution. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1947–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadas, I.; Thummalapalli, R.; Kim, J.W.; Kitajima, S.; Jenkins, R.W.; Christensen, C.L.; Campisi, M.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gjini, E.; et al. Tumor innate immunity primed by specific interferon-stimulated endogenous retroviruses. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, M.L.; Sparbier, C.E.; Chan, K.L.; Chan, Y.C.; Kersbergen, A.; Lam, E.Y.N.; Azidis-Yates, E.; Vassiliadis, D.; Bell, C.C.; Gilan, O.; et al. An Evolutionarily Conserved Function of Polycomb Silences the MHC Class I Antigen Presentation Pathway and Enables Immune Evasion in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 385–401.e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, J.T.; Gardner, E.E.; Connis, N.; Moreira, A.L.; de Stanchina, E.; Hann, C.L.; Rudin, C.M. DNA methylation in small cell lung cancer defines distinct disease subtypes and correlates with high expression of EZH2. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5869–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakashev, S.; Fukumoto, T.; Zhao, B.; Lin, J.; Wu, S.; Fatkhutdinov, N.; Park, P.H.; Semenova, G.; Jean, S.; Cadungog, M.G.; et al. EZH2 Inhibition Sensitizes CARM1-High, Homologous Recombination Proficient Ovarian Cancers to PARP Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 157–167.e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapkin, B.J.; Rudin, C.M. Advances in Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Translational Research. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yin, Q.; Kuss, P.; Maliga, Z.; Millan, J.L.; Wu, H.; Mitchison, T.J. Hydrolysis of 2′3′-cGAMP by ENPP1 and design of nonhydrolyzable analogs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, L.; Daniels, C.M.; Nettleship, J.E.; Rahman, N.; McPherson, R.L.; Ong, S.E.; Kato, K.; Nureki, O.; Leung, A.K.; Ahel, I. ENPP1 processes protein ADP-ribosylation in vitro. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 3371–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, M.A.; Yu, L.L.; Yu, X. Targeting dePARylation for cancer therapy. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, J.T.; George, J.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Berns, A.; Brambilla, E.; Byers, L.A.; Carbone, D.; Chen, H.J.; Christensen, C.L.; Dive, C.; et al. New Approaches to SCLC Therapy: From the Laboratory to the Clinic. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratigos, M.; Matikas, A.; Voutsina, A.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V. Targeting angiogenesis in small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meder, L.; Schuldt, P.; Thelen, M.; Schmitt, A.; Dietlein, F.; Klein, S.; Borchmann, S.; Wennhold, K.; Vlasic, I.; Oberbeck, S.; et al. Combined VEGF and PD-L1 Blockade Displays Synergistic Treatment Effects in an Autochthonous Mouse Model of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4270–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Barry, W.T.; Birrer, M.; Lee, J.M.; Buckanovich, R.J.; Fleming, G.F.; Rimel, B.; Buss, M.K.; Nattam, S.; Hurteau, J.; et al. Combination cediranib and olaparib versus olaparib alone for women with recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: A randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardnell, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Mukherjee, S.; Diao, L.; Tong, P.; Stewart, C.A.; Masrorpour, F.; Fan, Y.; Nilsson, M.; Shen, Y.; et al. Activation of the PI3K/mTOR Pathway following PARP Inhibition in Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.M.; Diao, L.; Stewart, C.A.; Xi, Y.; Cardnell, R.J.; Swisher, S.G.; Roth, J.A.; Glisson, B.S.; Wang, J.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Abstract 3772: Inter- and intra-tumoral variations in ASCL1, NEUROD1, and POU2F3 transcriptional programs underlie three distinct molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.M.; Byers, L.A. PARP Inhibition Combined with Immune Checkpoint Blockade in SCLC: Oasis in an Immune Desert or Mirage? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study Population | Drug(s) | Response Rate | PFS (Months) | OS (Months) | Unique Trial Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with ≤1 prior treatment regimen30 | Talazoparib | 9% | 11.1 weeks | ||
| First-line ES-SCLC32 | CE + veliparib vs. CE + placebo | 71.9% vs. 65.6% | 6.1 vs. 5.5 | 10.3 vs. 8.9 | Elevated LDH and male gender correlated with benefit |
| First-line ES-SCLC45 | (A) CE+ veliparib -> veliparib (B) CE + veliparib -> placebo (C) CE + placebo -> placebo | 77% 59.3% 63.9% | 5.8 5.7 5.6 | 10.1 10.0 12.4 | |
| Relapsed ES-SCLC36 | TMZ + veliparib vs. TMZ + placebo | 39% vs. 14% | 3.8 vs. 2.0 | 8.2 vs. 7.0 | SLFN11 positive tumors prolonged PFS and OS |
| Relapsed ES-SCLC39 | TMZ + olaparib | 41.7% | 4.2 | 8.5 | Co-clinical PDX trial |
| Relapsed ES-SCLC65 | Durvalumab + olaparib | 10.5% | 1.8 | 4.1 | Inflamed phenotype→ response |
| Relapsed ES-SCLC66 | Durvalumab + olaparib | 5.3% | Olaparib run in |
| Study Population | Drug(s) | Phase | Unique Trial Data | Trial Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES-SCLC | Talazoparib + Atezolizumab maintenance | II | Prospective study of SLFN11 expression | NCT04334941 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | Intermittent low-dose TMZ + continuous Talazoparib | II | Previous trials used intermittent talazoparib | NCT03672773 |
| SCLC | PLX038 (Pegylated SN-38) + rucaparib | I/II | Potential enhancement in DNA damage from formulation of irinotecan metabolite | NCT04209595 |
| ES-SCLC | Olaparib + low-dose radiotherapy | I | Maintenance therapy for stable disease after first-line chemotherapy | NCT03532880 |
| ES-SCLC | Talazoparib + consolidative thoracic XRT | I | Maintenance therapy for stable disease after first-line chemotherapy | NCT04170946 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | AZD1775 (WEE1) | II | Single-arm study | NCT02593019 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | AZD1775 (WEE1) | II | Single-arm study; CDKN2A or MYC mutation required | NCT02688907 |
| ES-SCLC | VX-970 (ATR) + CE or cisplatin (platinum resistant) | I | Flexible enrollment with first-line chemotherapy or relapsed/refractory disease | NCT02157792 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | VX-970 (ATR) + topotecan | I/II | NCT02487095 | |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | Prexasertib (CHK) | II | NCT02735980 | |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | AZD1775 (WEE1) + olaparib | 1b | NCT02511795 | |
| ES-SCLC | Rucaparib + nivolumab | II | Maintenance therapy for stable disease after first-line chemotherapy | NCT03958045 |
| ES-SCLC | Thoracic radiation combined with durvalumab +/− (tremelimumab + olaparib) | I | Maintenance therapy for stable disease after first-line chemotherapy | NCT03923270 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | BMS-986012 +/− nivolumab | I/II | NCT02247349 | |
| ES-SCLC | BMS-986012 + CE | I/II | First-line therapy | NCT02815592 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | Olaparib + cediranib (VEGF) | II | Correlation with DNA repair gene expression | NCT02498613 |
| Relapsed/refractory ES-SCLC | Vistusertib (mTOR) + Navitoclax (Bcl-2) | I/II | On treatment biopsy | NCT03366103 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knelson, E.H.; Patel, S.A.; Sands, J.M. PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses. Cancers 2021, 13, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040727
Knelson EH, Patel SA, Sands JM. PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040727
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnelson, Erik H., Shetal A. Patel, and Jacob M. Sands. 2021. "PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses" Cancers 13, no. 4: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040727
APA StyleKnelson, E. H., Patel, S. A., & Sands, J. M. (2021). PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses. Cancers, 13(4), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040727







