Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microbiota, Inflammatory Mediators and CRC
2.1. Tumor Necrosis Factor
2.2. Nuclear Factor Kappa B
2.3. Interleukin-1
2.4. Interleukin-6
2.5. Interleukin-10
2.6. Interleukin-17
2.7. Interferons
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, R.N. Role of inflammation and inflammatory mediators in colorectal cancer. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2014, 125, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mariani, F.; Sena, P.; Roncucci, L. Inflammatory pathways in the early steps of colorectal cancer development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9716–9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera-Guillem, E.; Nyhus, J.K.; Wolford, C.C.; Friece, C.R.; Sampsel, J.W. Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by tumor-infiltrating macrophages essentially supports tumor angiogenesis, and IgG immune complexes potentiate the process. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 7042–7049. [Google Scholar]
- Markman, J.L.; Shiao, S.L. Impact of the immune system and immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, C.; McLean, M.H.; Durum, S.K. Cytokine Tuning of Intestinal Epithelial Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, K.A.; Schulz, H.M.; Regner, E.H.; Severs, E.L.; Hendrickson, J.D.; Mehta, G.; Whitney, A.K.; Ir, D.; Ohri, N.; Robertson, C.E.; et al. Bacteroidales recruit IL-6-producing intraepithelial lymphocytes in the colon to promote barrier integrity. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Kelly, C.J.; Battista, K.D.; Schaefer, R.; Lanis, J.M.; Alexeev, E.E.; Wang, R.X.; Onyiah, J.C.; Kominsky, D.J.; Colgan, S.P. Microbial-Derived Butyrate Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function through IL-10 Receptor-Dependent Repression of Claudin-2. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Tato, C.M.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Cayatte, C.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Judo, M.; Ayanoglu, G.; McClanahan, T.K.; et al. Interleukin-23-Independent IL-17 Production Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Permeability. Immunity 2015, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dieterich, W.; Schink, M.; Zopf, Y. Microbiota in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Man, W.H.; de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.; Bogaert, D. The microbiota of the respiratory tract: Gatekeeper to respiratory health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampersaud, R.; Randis, T.M.; Ratner, A.J. Microbiota of the upper and lower genital tract. Semin. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2012, 17, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, C.; Barnich, N.; Nguyen, H.T.T. Microbiota, Inflammation and Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, R.; Gao, Z.; Huang, L.; Qin, H. Gut microbiota and colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.H.; Yu, J. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, L.F.; Wasmer, M.H.; Rau, T.T.; Krebs, P. Cytokine-Induced Modulation of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.W.; Karin, M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.P.; Antoine, J.M.; Midtvedt, T.; van Hemert, S. Manipulating the gut microbiota to maintain health and treat disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 25877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, V.B. Therapeutic manipulation of the microbiota: Past, present, and considerations for the future. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ericsson, A.C.; Franklin, C.L. Manipulating the Gut Microbiota: Methods and Challenges. ILAR J. 2015, 56, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling in macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C. Anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Mol. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbola, S.O.; Sahnan, K.; Warusavitarne, J.; Hart, A.; Tozer, P. Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coates, L.C.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Bennett, A.N.; Emery, P. Anti-TNF Therapy in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Insights for the Clinician. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2010, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busquets, D.; Mas-de-Xaxars, T.; Lopez-Siles, M.; Martinez-Medina, M.; Bahi, A.; Sabat, M.; Louvriex, R.; Miquel-Cusachs, J.O.; Garcia-Gil, J.L.; Aldeguer, X. Anti-tumour Necrosis Factor Treatment with Adalimumab Induces Changes in the Microbiota of Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borruel, N.; Carol, M.; Casellas, F.; Antolin, M.; de Lara, F.; Espin, E.; Naval, J.; Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.R. Increased mucosal tumour necrosis factor alpha production in Crohn’s disease can be downregulated ex vivo by probiotic bacteria. Gut 2002, 51, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burrello, C.; Garavaglia, F.; Cribiu, F.M.; Ercoli, G.; Lopez, G.; Troisi, J.; Colucci, A.; Guglietta, S.; Carloni, S.; Guglielmetti, S.; et al. Therapeutic faecal microbiota transplantation controls intestinal inflammation through IL10 secretion by immune cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Li, F.; Qin, Z. TNF Receptor 2 Makes Tumor Necrosis Factor a Friend of Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Keku, T.O.; Martin, C.; Galanko, J.; Woosley, J.T.; Schroeder, J.C.; Satia, J.A.; Halabi, S.; Sandler, R.S. Circulating levels of inflammatory cytokines and risk of colorectal adenomas. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Obeed, O.A.; Alkhayal, K.A.; Al Sheikh, A.; Zubaidi, A.M.; Vaali-Mohammed, M.A.; Boushey, R.; McKerrow, J.H.; Abdulla, M.H. Increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha is associated with advanced colorectal cancer stages. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18390–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popivanova, B.K.; Kitamura, K.; Wu, Y.; Kondo, T.; Kagaya, T.; Kaneko, S.; Oshima, M.; Fujii, C.; Mukaida, N. Blocking TNF-alpha in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with chronic colitis. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Cao, H.; Cover, T.L.; Whitehead, R.; Washington, M.K.; Polk, D.B. Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iida, N.; Dzutsev, A.; Stewart, C.A.; Smith, L.; Bouladoux, N.; Weingarten, R.A.; Molina, D.A.; Salcedo, R.; Back, T.; Cramer, S.; et al. Commensal bacteria control cancer response to therapy by modulating the tumor microenvironment. Science 2013, 342, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gharaibeh, R.Z.; Newsome, R.C.; Jobin, C. Amending microbiota by targeting intestinal inflammation with TNF blockade attenuates development of colorectal cancer. Nature Cancer 2020, 1, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, G.; Petit, C.R.; Marcq, I.; Boury, M.; Oswald, E.; Nougayrede, J.P. Escherichia coli induces DNA damage in vivo and triggers genomic instability in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11537–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell. Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naugler, W.E.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB and cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.J.; Ratnam, N.M.; Byrd, J.C.; Guttridge, D.C. NF-kappaB functions in tumor initiation by suppressing the surveillance of both innate and adaptive immune cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Quezada, B.A.; Santana-Bejarano, U.F.; Corona-Rivera, A.; Pimentel-Gutierrez, H.J.; Silva-Cruz, R.; Ortega-De-la-Torre, C.; Franco-Topete, R.; Franco-Topete, K.; Centeno-Flores, M.W.; Maciel-Gutierrez, V.M.; et al. Expression profile of NF-kappaB regulated genes in sporadic colorectal cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7344–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.M.; Liu, H.L. Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 10, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, R.; Hua, F.; Qiu, Z.; Song, Y.; Bai, C.; et al. Gut microbiota regulate tumor metastasis via circRNA/miRNA networks. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1788891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Weng, W.; Peng, J.; Hong, L.; Yang, L.; Toiyama, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Increases Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells and Tumor Development in Mice by Activating Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling to Nuclear Factor-kappaB, and Up-regulating Expression of MicroRNA-21. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahu, U.; Choudhury, A.; Parvez, S.; Biswas, S.; Kar, S. Induction of intestinal stemness and tumorigenicity by aberrant internalization of commensal non-pathogenic E. coli. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Wong, C.C.; Tong, L.; Chu, E.S.H.; Ho Szeto, C.; Go, M.Y.Y.; Coker, O.O.; Chan, A.W.H.; Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Peptostreptococcus anaerobius promotes colorectal carcinogenesis and modulates tumour immunity. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.J.; Houston, A.; Brint, E. IL-1 Family Members in Cancer; Two Sides to Every Story. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabay, C.; Lamacchia, C.; Palmer, G. IL-1 pathways in inflammation and human diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Kurata, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, S.; Masumoto, J. The role of interleukin-1 in general pathology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Lu, J. The Role of Interleukins in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2323–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sconocchia, G.; Eppenberger-Castori, S.; Zlobec, I.; Karamitopoulou, E.; Arriga, R.; Coppola, A.; Caratelli, S.; Spagnoli, G.C.; Lauro, D.; Lugli, A.; et al. HLA class II antigen expression in colorectal carcinoma tumors as a favorable prognostic marker. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elaraj, D.M.; Weinreich, D.M.; Varghese, S.; Puhlmann, M.; Hewitt, S.M.; Carroll, N.M.; Feldman, E.D.; Turner, E.M.; Alexander, H.R. The role of interleukin 1 in growth and metastasis of human cancer xenografts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Han, G.C.; Wang, R.X.; Xiao, H.; Hou, C.M.; Guo, R.F.; Dou, Y.; Shen, B.F.; Li, Y.; et al. Neutrophil infiltration favors colitis-associated tumorigenesis by activating the interleukin-1 (IL-1)/IL-6 axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrieva-Posocco, O.; Dzutsev, A.; Posocco, D.F.; Hou, V.; Yuan, W.; Thovarai, V.; Mufazalov, I.A.; Gunzer, M.; Shilovskiy, I.P.; Khaitov, M.R.; et al. Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Interleukin-1 Control Microbial Invasion and Tumor-Elicited Inflammation in Colorectal Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mertens, M.; Singh, J.A. Anakinra for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. J Rheumatol 2009, 36, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isambert, N.; Hervieu, A.; Rebe, C.; Hennequin, A.; Borg, C.; Zanetta, S.; Chevriaux, A.; Richard, C.; Derangere, V.; Limagne, E.; et al. Fluorouracil and bevacizumab plus anakinra for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard therapies (IRAFU): A single-arm phase 2 study. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1474319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Simon, A.; van der Meer, J.W. Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, S.U.; Kamada, N.; Munoz-Planillo, R.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, D.; Koizumi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Himpsl, S.D.; Browne, H.P.; Lawley, T.D.; et al. Distinct Commensals Induce Interleukin-1beta via NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Monocytes to Promote Intestinal Inflammation in Response to Injury. Immunity 2015, 42, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couturier-Maillard, A.; Froux, N.; Piotet-Morin, J.; Michaudel, C.; Brault, L.; Le Berichel, J.; Senechal, A.; Robinet, P.; Chenuet, P.; Jejou, S.; et al. Interleukin-22-deficiency and microbiota contribute to the exacerbation of Toxoplasma gondii-induced intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorak, R.N.; Feagan, B.G.; Hotte, N.; Leddin, D.; Dieleman, L.A.; Petrunia, D.M.; Enns, R.; Bitton, A.; Chiba, N.; Pare, P.; et al. The probiotic VSL#3 has anti-inflammatory effects and could reduce endoscopic recurrence after surgery for Crohn’s disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogier, R.; Ederveen, T.H.A.; Boekhorst, J.; Wopereis, H.; Scher, J.U.; Manasson, J.; Frambach, S.; Knol, J.; Garssen, J.; van der Kraan, P.M.; et al. Aberrant intestinal microbiota due to IL-1 receptor antagonist deficiency promotes IL-17- and TLR4-dependent arthritis. Microbiome 2017, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincon, M. Interleukin-6: From an inflammatory marker to a target for inflammatory diseases. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.H.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Role of STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgart, S.; Ellenrieder, V.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Oncogenic transcription factors: Cornerstones of inflammation-linked pancreatic carcinogenesis. Gut 2013, 62, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knupfer, H.; Preiss, R. Serum interleukin-6 levels in colorectal cancer patients--a summary of published results. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2010, 25, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Szmitkowski, M.; Makinen, M.J.; Li, P.; Xia, D.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Serum Interleukin-6 in Colorectal Cancer. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.; Fantini, M.C.; Schramm, C.; Lehr, H.A.; Wirtz, S.; Nikolaev, A.; Burg, J.; Strand, S.; Kiesslich, R.; Huber, S.; et al. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 2004, 21, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldner, M.J.; Foersch, S.; Neurath, M.F. Interleukin-6--a key regulator of colorectal cancer development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, R.; Sun, G.; Peng, L.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Y. Pilot study of cytokine changes evaluation after fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with ulcerative colitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaldetti, M.; Bessler, H. Probiotic strains modulate cytokine production and the immune interplay between human peripheral blood mononucear cells and colon cancer cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, G.; Xie, M.; Yu, H.; Chen, H. Intestinal dysbacteriosis activates tumor-associated macrophages to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burrello, C.; Giuffre, M.R.; Macandog, A.D.; Diaz-Basabe, A.; Cribiu, F.M.; Lopez, G.; Borgo, F.; Nezi, L.; Caprioli, F.; Vecchi, M.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Controls Murine Chronic Intestinal Inflammation by Modulating Immune Cell Functions and Gut Microbiota Composition. Cells 2019, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, P.V.; Hao, L.; Offermanns, S.; Medzhitov, R. The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2247–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segain, J.P.; Raingeard de la Bletiere, D.; Bourreille, A.; Leray, V.; Gervois, N.; Rosales, C.; Ferrier, L.; Bonnet, C.; Blottiere, H.M.; Galmiche, J.P. Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through NFkappaB inhibition: Implications for Crohn’s disease. Gut 2000, 47, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Peng, W.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Peng, Y.; Fu, X. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes M2 polarization of macrophages in the microenvironment of colorectal tumours via a TLR4-dependent mechanism. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, K.N.; Blount, D.G.; Riley, E.M. IL-10: The master regulator of immunity to infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.K.; Boukhaled, G.M.; Condotta, S.A.; Mazouz, S.; Guthmiller, J.J.; Vijay, R.; Butler, N.S.; Bruneau, J.; Shoukry, N.H.; Krawczyk, C.M.; et al. Interleukin-10 Directly Inhibits CD8(+) T Cell Function by Enhancing N-Glycan Branching to Decrease Antigen Sensitivity. Immunity 2018, 48, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, R.; Lohler, J.; Rennick, D.; Rajewsky, K.; Muller, W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 1993, 75, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesler, P.; Fuss, I.J.; Strober, W. Experimental Models of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mannino, M.H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Bai, Q.; Wakefield, M.R.; Fang, Y. The paradoxical role of IL-10 in immunity and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; O’Garra, A. IL-10 Family Cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: From Basic Science to Clinical Translation. Immunity 2019, 50, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocellin, S.; Panelli, M.C.; Wang, E.; Nagorsen, D.; Marincola, F.M. The dual role of IL-10. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.Z.; Patil, P.; Gude, R.P. Role of STAT3 in cancer metastasis and translational advances. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 421821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbrink, K.; Jonuleit, H.; Muller, G.; Schuler, G.; Knop, J.; Enk, A.H. Interleukin-10-treated human dendritic cells induce a melanoma-antigen-specific anergy in CD8(+) T cells resulting in a failure to lyse tumor cells. Blood 1999, 93, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Terai, M.; Tamura, Y.; Alexeev, V.; Mastrangelo, M.J.; Selvan, S.R. Interleukin 10 in the tumor microenvironment: A target for anticancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Res. 2011, 51, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumm, J.B.; Emmerich, J.; Zhang, X.; Chan, I.; Wu, L.; Mauze, S.; Blaisdell, S.; Basham, B.; Dai, J.; Grein, J.; et al. IL-10 elicits IFNgamma-dependent tumor immune surveillance. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naing, A.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Autio, K.A.; Ott, P.A.; Patel, M.R.; Wong, D.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Pant, S.; Whiteside, M.; Rasco, D.R.; et al. Safety, Antitumor Activity, and Immune Activation of Pegylated Recombinant Human Interleukin-10 (AM0010) in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3562–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.; Infante, J.R.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Chan, I.H.; Shen, C.; Ratti, N.P.; Rojo, B.; Autio, K.A.; Wong, D.J.; Patel, M.R.; et al. PEGylated IL-10 (Pegilodecakin) Induces Systemic Immune Activation, CD8(+) T Cell Invigoration and Polyclonal T Cell Expansion in Cancer Patients. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.M.; Ojcius, D.M.; Garaud, F.; Roth, C.; Maxwell, E.; Li, Z.; Rong, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Catino, J.J.; et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits tumor metastasis through an NK cell-dependent mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, N.; Beaty, T.L.; Jackson, M.J.; Fulton, A.M. Antimetastatic and antitumor activities of Interleukin 10 in a murine model of breast cancer. Jnci. J. Natl. Cancer I. 1996, 88, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, Y.; Oka, A.; Liu, B.; Herzog, J.W.; Eun, C.S.; Fan, T.J.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.; Carroll, I.M.; Hansen, J.J.; Chen, L.; et al. Microbiota maintain colonic homeostasis by activating TLR2/MyD88/PI3K signaling in IL-10-producing regulatory B cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 3702–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Gong, H.; Li, N.; Wu, K.Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, K.J.; Wen, L.Z.; Xiao, X.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Ameliorates Experimentally Induced Colitis in Mice by Upregulating AhR. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arthur, J.C.; Perez-Chanona, E.; Muhlbauer, M.; Tomkovich, S.; Uronis, J.M.; Fan, T.J.; Campbell, B.J.; Abujamel, T.; Dogan, B.; Rogers, A.B.; et al. Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing activity of the microbiota. Science 2012, 338, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moseley, T.A.; Haudenschild, D.R.; Rose, L.; Reddi, A.H. Interleukin-17 family and IL-17 receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporeale, A.; Poli, V. IL-6, IL-17 and STAT3: A holy trinity in auto-immunity? Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2012, 17, 2306–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onishi, R.M.; Gaffen, S.L. Interleukin-17 and its target genes: Mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease. Immunology 2010, 129, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, S.; Andoh, A.; Bamba, S.; Ogawa, A.; Hata, K.; Araki, Y.; Bamba, T.; Fujiyama, Y. Increased expression of interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2003, 52, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, T.; Ishikawa, F.; Kondo, M.; Kakiuchi, T. The Role of IL-17 and Related Cytokines in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3908061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Kang, H.; Fung, A.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, D. The role of interleukin 17 in tumour proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 623759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Shen, J.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shang, L.; Jin, S.; Cao, S.; Che, D.; Liu, F.; Yu, Y. Interleukin-17 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells via the STAT3/GIV signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, S.; Girault, A.; Ohresser, M.; Lereclus, E.; Paintaud, G.; Lecomte, T.; Raoul, W. Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting the IL-17/IL-17RA Axis: An Opportunity to Improve the Efficiency of Anti-VEGF Therapy in Fighting Metastatic Colorectal Cancer? Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2018, 17, e109–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Choo, J.; Heo, G.; Yoo, J.W.; Jung, Y.; Rhee, S.H.; Im, E. miR-23a-3p is a Key Regulator of IL-17C-Induced Tumor Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Kim, M.K.; Di Caro, G.; Wong, J.; Shalapour, S.; Wan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Wu, L.W.; et al. Interleukin-17 receptor a signaling in transformed enterocytes promotes early colorectal tumorigenesis. Immunity 2014, 41, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Do Thi, V.A.; Park, S.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S. The Membrane-Bound Form of IL-17A Promotes the Growth and Tumorigenicity of Colon Cancer Cells. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X.; Xie, W.; Long, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, B. IL-17 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes angiogenesis via stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells in colorectal carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. The human commensal Bacteroides fragilis binds intestinal mucin. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toprak, N.U.; Yagci, A.; Gulluoglu, B.M.; Akin, M.L.; Demirkalem, P.; Celenk, T.; Soyletir, G. A possible role of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Rhee, K.J.; Albesiano, E.; Rabizadeh, S.; Wu, X.; Yen, H.R.; Huso, D.L.; Brancati, F.L.; Wick, E.; McAllister, F.; et al. A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.L.; Lee, S.M.; Li, J.; Tran, G.; Jabri, B.; Chatila, T.A.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 2011, 332, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Wang, K.; Mucida, D.; Stewart, C.A.; Schnabl, B.; Jauch, D.; Taniguchi, K.; Yu, G.Y.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Hung, K.E.; et al. Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature 2012, 491, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crow, M.K.; Ronnblom, L. Type I interferons in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Lupus Sci. Med. 2019, 6, e000336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makris, S.; Paulsen, M.; Johansson, C. Type I Interferons as Regulators of Lung Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopitar-Jerala, N. The Role of Interferons in Inflammation and Inflammasome Activation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.J.; Ashkar, A.A. The Dual Nature of Type I and Type II Interferons. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Franco, S.; Turdo, A.; Todaro, M.; Stassi, G. Role of Type I and II Interferons in Colorectal Cancer and Melanoma. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arico, E.; Castiello, L.; Capone, I.; Gabriele, L.; Belardelli, F. Type I Interferons and Cancer: An Evolving Story Demanding Novel Clinical Applications. Cancers 2019, 11, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnette, B.C.; Liang, H.; Lee, Y.; Chlewicki, L.; Khodarev, N.N.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.X.; Auh, S.L. The efficacy of radiotherapy relies upon induction of type i interferon-dependent innate and adaptive immunity. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katlinski, K.V.; Gui, J.; Katlinskaya, Y.V.; Ortiz, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carbone, C.J.; Beiting, D.P.; Girondo, M.A.; Peck, A.R.; et al. Inactivation of Interferon Receptor Promotes the Establishment of Immune Privileged Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sistigu, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Vacchelli, E.; Chaba, K.; Enot, D.P.; Adam, J.; Vitale, I.; Goubar, A.; Baracco, E.E.; Remedios, C.; et al. Cancer cell-autonomous contribution of type I interferon signaling to the efficacy of chemotherapy. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Goncalves, R.M.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Street, D.; Kaufmann, A.M.; Vaughan, A.; Fisher, S.G.; Hunter, M.; Schreckenberger, C.; Potkul, R.K.; Gissmann, L.; Qiao, L. Interferon-gamma enhances susceptibility of cervical cancer cells to lysis by tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 1997, 65, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.A.; Hardy, K.J. Role of interferon-gamma in immune cell regulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 58, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvat, B.L.; Seth, P.; Jetten, A.M. The role of p27Kip1 in gamma interferon-mediated growth arrest of mammary epithelial cells and related defects in mammary carcinoma cells. Oncogene 1997, 14, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Z.; Schwartzkopff, J.; Pradera, F.; Kammertoens, T.; Seliger, B.; Pircher, H.; Blankenstein, T. A critical requirement of interferon gamma-mediated angiostasis for tumor rejection by CD8+ T cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4095–4100. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.F.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, G.M.; Chen, H.T.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Z.H. Sustained low-level expression of interferon-gamma promotes tumor development: Potential insights in tumor prevention and tumor immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.R. The Interferon-Gamma Paradox in Cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitbarek, A.; Alkie, T.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Astill, J.; Rodriguez-Lecompte, J.C.; Parkinson, J.; Nagy, E.; Sharif, S. Gut microbiota modulates type I interferon and antibody-mediated immune responses in chickens infected with influenza virus subtype H9N2. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinohe, T.; Pang, I.K.; Kumamoto, Y.; Peaper, D.R.; Ho, J.H.; Murray, T.S.; Iwasaki, A. Microbiota regulates immune defense against respiratory tract influenza A virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5354–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Moreno de Leblanc, A.; Perdigon, G. Yogurt feeding inhibits promotion and progression of experimental colorectal cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, BR96–BR104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zadka, L.; Kulus, M.J.; Kurnol, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Glatzel-Plucinska, N.; Jurek, T.; Czuba, M.; Nowak, A.; Chabowski, M.; Janczak, D.; et al. The expression of IL10RA in colorectal cancer and its correlation with the proliferation index and the clinical stage of the disease. Cytokine 2018, 110, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razi, S.; Baradaran Noveiry, B.; Keshavarz-Fathi, M.; Rezaei, N. IL-17 and colorectal cancer: From carcinogenesis to treatment. Cytokine 2019, 116, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

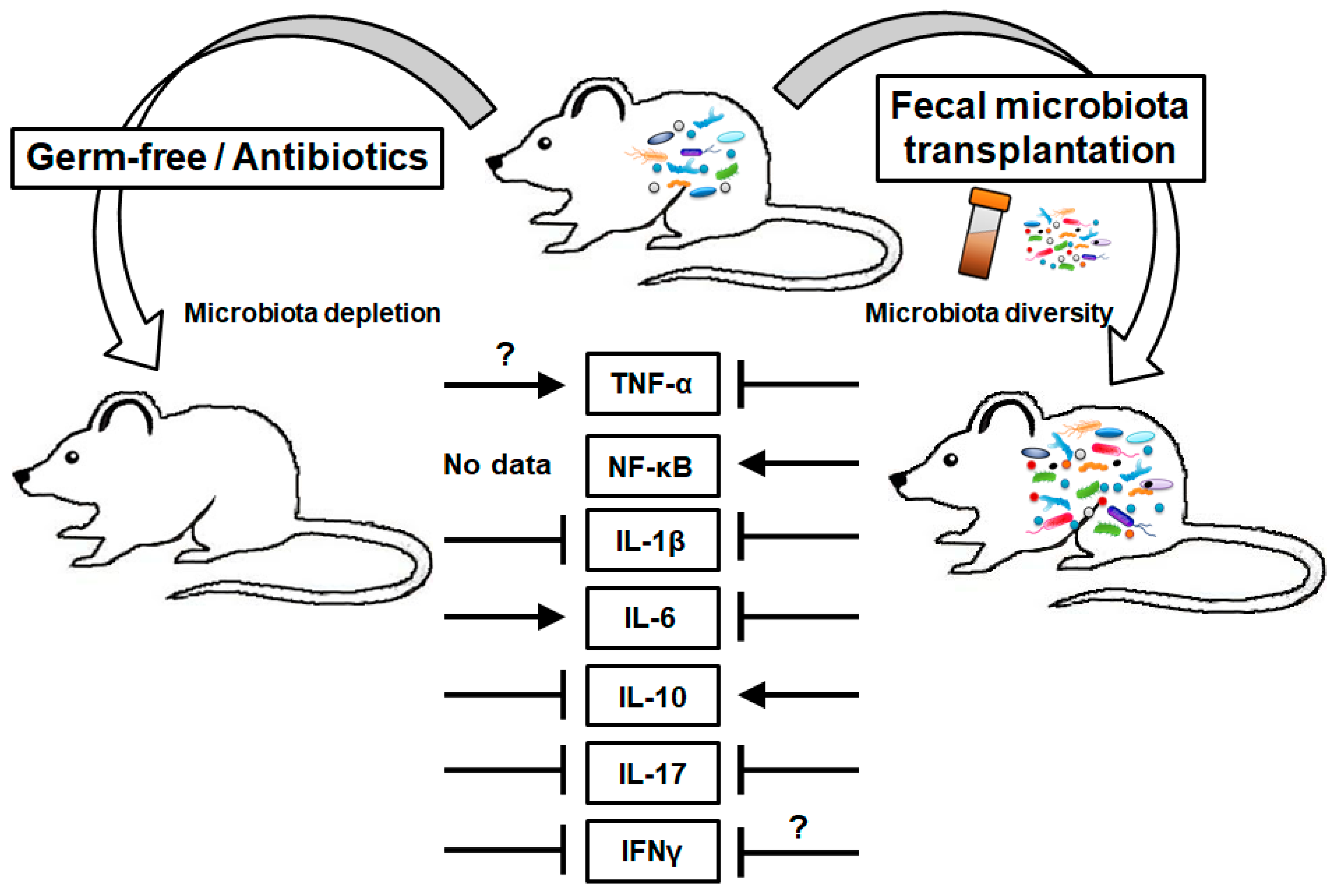
| Mediators | Roles in CRC | Status in CRC | Status in GF or ABX-Treated Animal | Modulation by Exogenous Microbiota |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | Dual [28] | ↑ [29,30] | ↓ in tumor under immunotherapy [33] ↑ in serum [74] | ↓ by FMT under DSS [27] |
| NF-κB | Promote [39] | ↑ [42] | - | ↑ by P. anaerobius [47] |
| IL-1 | Dual [51,55] | ↑, IL-1β [52] | ↓ in LP under DSS [59] ↓ in SI under T. gondii infection [60] | ↓ by FMT under DSS [27] ↓ by VSL#3 under CD [61] |
| IL-6 | Promote [68] | ↑ [52,68] | ↑ in serum [74] | ↓ by FMT under UC [72] ↓ by FMT under DSS [75] ↓ by mixture of 6 strains under LPS [73] |
| IL-10 | Controversial [51] | ↑ [134] | ↓ in colon [94] | ↑ by FMT [27,94,95] |
| IL-17 | Promote [106,135] | ↑ [114,135] | ↓ in CD4+ T cell [113] ↓ in colon [94] | ↓ by FMT under DSS [75] |
| IFNs | Suppress (α, β) [122] Controversial (γ) [124,129,130] | ↓ IFNAR1 [122] | ↓ α, β in ileum under viral infection [131] ↓ γ in T cells under viral infection [132] ↓ β, γ in SI under T. gondii infection [60] | ↑ γ by L. delbrueckii, S. thermophilus under DMH-induced CRC [133] ↓ γ by FMT under DSS [75] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, G.; Lee, Y.; Im, E. Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040734
Heo G, Lee Y, Im E. Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040734
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Gwangbeom, Yunna Lee, and Eunok Im. 2021. "Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development of Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 4: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040734
APA StyleHeo, G., Lee, Y., & Im, E. (2021). Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 13(4), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040734






