Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Modulators of Cancer Drug Resistance
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
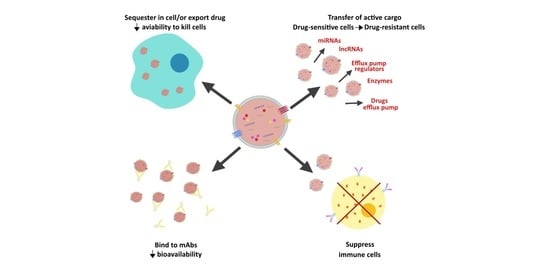
2. EVs and Cancer Drug Resistance
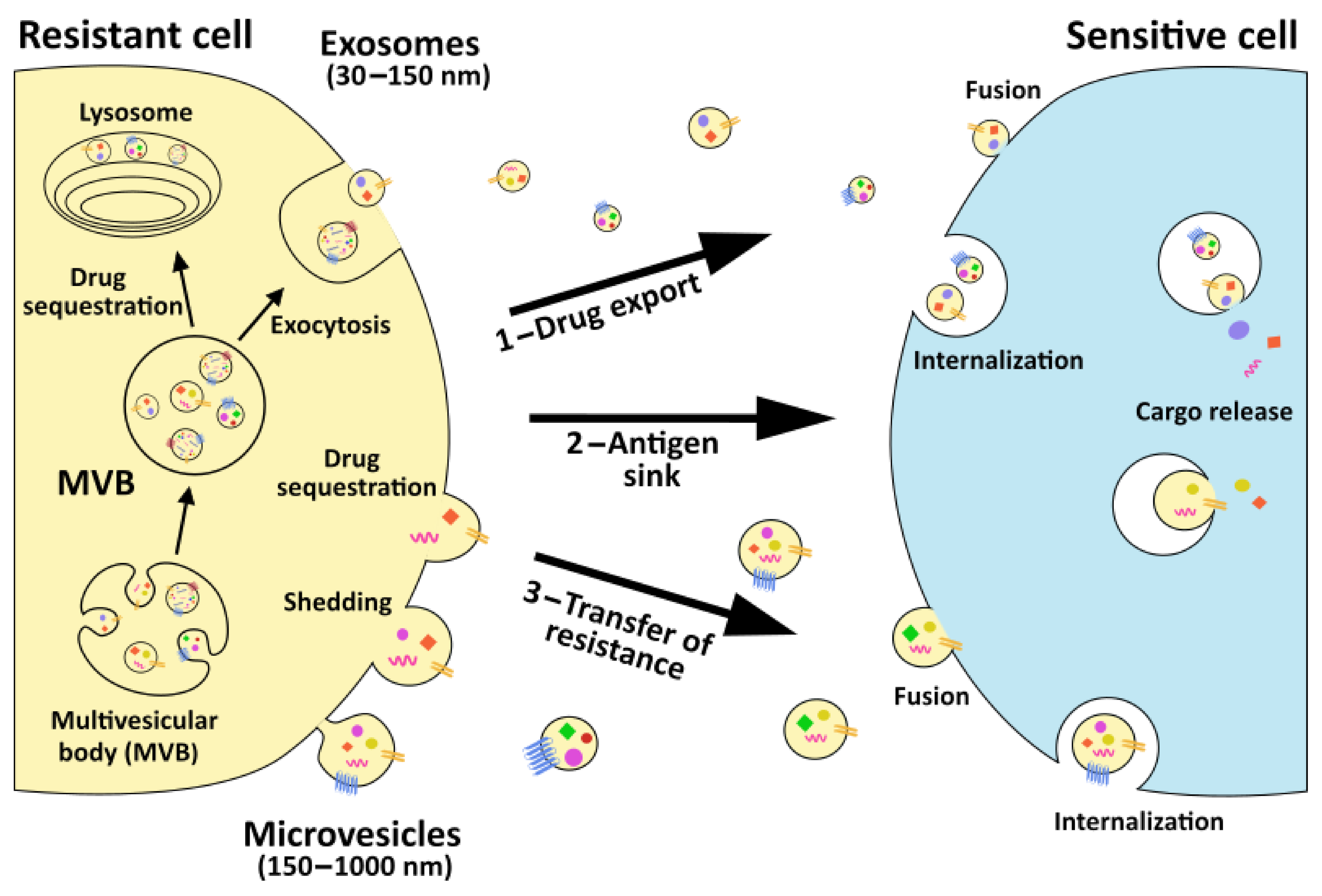
2.1. EVs and Drug Sequestration at Intracellular and Extracellular Levels
2.2. EVs and Acquisition of a Multidrug Resistant Phenotype
2.3. EVs and Horizontal Transfer of Pro-Survival Proteins and RNAs
| miRNA | Tumor | Drug | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-19b | Colorectal cancer, leukemia | Oxaliplatin, daunorubicin | [66,67] |
| miR-20a | Leukemia | Daunorubicin | [67] |
| miR-21 | Oral squamous cell carcinoma, leukemia, breast cancer | Cisplatin, multidrug | [68,69] |
| miR-34a | Colon cancer, prostate cancer | 5-FU, docetaxel | [70,71] |
| miR-31-5p | Renal cell carcinoma | Sorafenib | [58] |
| miR-96 | Lung cancer | Cisplatin | [72] |
| miR-100-5p | Lung cancer | Cisplatin | [73] |
| miR-134 | Breast cancer | Multidrug | [74] |
| miR-145 | Colon cancer | 5-FU | [70] |
| miR-155 | Breast cancer, lung cancer | Doxorubicin, paclitaxel, gemcitabine | [59,75,76] |
| miR-155-5p | Breast cancer | Docetaxel, doxorubicin | [35] |
| miR-211-5p | Melanoma | Vemurafenib | [77] |
| miR-221/222 | Breast cancer | Tamoxifen | [78] |
| miR-222 | Breast cancer | Adriamycin, docetaxel | [79,80] |
| miR-222-3p | Lung cancer | Gemcitabine | [81] |
| miR-365 | Leukemia | Imatinib | [82] |
| miR-425-3p | Lung cancer | Cisplatin | [60,83] |
| miR-744 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Sorafenib | [61] |
| miR-761 | Synovial sarcoma | Pazopanib | [84] |
| miR-1238 | Glioblastoma | Temozolomide | [62] |
| miR-1246 | Breast cancer | Multidrug | [85] |
| lncRNA | Tumor | Drug | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| linc-AGAP2-AS1 | Breast cancer | Trastuzumab | [86] |
| lncARSR | Renal cell carcinoma | Sunitinib | [64] |
| lncHNF1A-AS1 | Cervical cancer | Cisplatin | [87] |
| lncHOTTIP | Gastric cancer | Cisplatin | [65] |
| linc-ROR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Sorafenib | [88] |
| linc-SBF2-AS1 | Glioblastoma | Temozolomide | [89] |
| lincSNHG14 | Breast cancer | Trastuzumab | [90] |
| linc-VLDLR | Hepatocellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer | Multidrug | [91,92] |
2.4. EVs and Interactions with Stromal and Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment
2.5. EVs and Modulation of Cancer Stem Cell-Like Features
2.6. EVs as Tools to Monitor Response to Cancer Treatment
2.7. Strategies to Overcome EV-Related Cancer Drug Resistance
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.; Wang, M. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Lam, E.W.F.; Sun, Y. Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Old stories, but new tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Liu, C.; Bi, Z.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Song, Y.Y.Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Comprehensive landscape of extracellular vesicle-derived RNAs in cancer initiation, progression, metastasis and cancer immunology. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shedden, K.; Xie, X.T.; Chandaroy, P.; Chang, Y.T.; Rosania, G.R. Expulsion of small molecules in vesicles shed by cancer cells: Association with gene expression and chemosensitivity profiles. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4331–4337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Federici, C.; Petrucci, F.; Caimi, S.; Cesolini, A.; Logozzi, M.; Borghi, M.; D’Ilio, S.; Lugini, L.; Violante, N.; Azzarito, T.; et al. Exosome release and low pH belong to a framework of resistance of human melanoma cells to cisplatin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Safaei, R.; Larson, B.J.; Cheng, T.C.; Gibson, M.A.; Otani, S.; Naerdemann, W.; Howell, S.B. Abnormal lysosomal trafficking and enhanced exosomal export of cisplatin in drug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ifergan, I.; Scheffer, G.L.; Assaraf, Y.G. Novel extracellular vesicles mediate an ABCG2-dependent anticancer drug sequestration and resistance. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10952–10958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapuy, B.; Koch, R.; Radunski, U.; Corsham, S.; Cheong, N.; Inagaki, N.; Ban, N.; Wenzel, D.; Reinhardt, D.; Zapf, A.; et al. Intracellular ABC transporter A3 confers multidrug resistance in leukemia cells by lysosomal drug sequestration. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aung, T.; Chapuy, B.; Vogel, D.; Wenzel, D.; Oppermann, M.; Lahmann, M.; Weinhage, T.; Menck, K.; Hupfeld, T.; Koch, R.; et al. Exosomal evasion of humoral immunotherapy in aggressive B-cell lymphoma modulated by ATP-binding cassette transporter A3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15336–15341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciravolo, V.; Huber, V.; Ghedini, G.C.; Venturelli, E.; Bianchi, F.; Campiglio, M.; Morelli, D.; Villa, A.; Della Mina, P.; Menard, S.; et al. Potential role of HER2-overexpressing exosomes in countering trastuzumab-based therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battke, C.; Ruiss, R.; Welsch, U.; Wimberger, P.; Lang, S.; Jochum, S.; Zeidler, R. Tumour exosomes inhibit binding of tumour-reactive antibodies to tumour cells and reduce ADCC. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setroikromo, R.; Zhang, B.; Reis, C.R.; Mistry, R.H.; Quax, W.J. Death Receptor 5 Displayed on Extracellular Vesicles Decreases TRAIL Sensitivity of Colon Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J.I.; Haber, M.; Henderson, M.J.; Norris, M.D. ABC transporters in cancer: More than just drug efflux pumps. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ughachukwu, P.; Unekwe, P. Efflux pump-mediated resistance in chemotherapy. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, K.; Tiriveedhi, V. Perplexing Role of P-Glycoprotein in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, A.; Mehta, B.M.; Niu, X.; Kang, G.; Villafania, L.; Way, D.; Polycarpe, D.; Sadelain, M.; Larson, S.M. Intercellular transfer of P-glycoprotein mediates acquired multidrug resistance in tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bebawy, M.; Combes, V.; Lee, E.; Jaiswal, R.; Gong, J.; Bonhoure, A.; Grau, G.E.R. Membrane microparticles mediate transfer of P-glycoprotein to drug sensitive cancer cells. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, D.; Lima, R.T.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Intercellular Transfer of Cancer Drug Resistance Traits by Extracellular Vesicles. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhu, X.; Chen, W.; Zhong, S.; Hu, Q.; Ma, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Zhao, J. Exosomes mediate drug resistance transfer in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and a probable mechanism is delivery of P-glycoprotein. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 10773–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, C.; Rani, S.; O’Brien, K.; O’Neill, A.; Prencipe, M.; Sheikh, R.; Webb, G.; McDermott, R.; Watson, W.; Crown, J.; et al. Docetaxel-Resistance in Prostate Cancer: Evaluating Associated Phenotypic Changes and Potential for Resistance Transfer via Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.F.; Pokharel, D.; Bebawy, M. MRP1 and its role in anticancer drug resistance. Drug Metab. Rev. 2015, 47, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.F.; Luk, F.; Gong, J.; Jaiswal, R.; Grau, G.E.R.; Bebawy, M. Microparticles mediate MRP1 intercellular transfer and the re-templating of intrinsic resistance pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 76, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Pal, K.; Sharma, A.K.; Dutta, S.K.; Lau, J.S.; Yan, I.K.; Wang, E.; Elkhanany, A.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Sanyal, A.; et al. GAIP interacting protein C-Terminus regulates autophagy and exosome biogenesis of pancreatic cancer through metabolic pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentires-Alj, M.; Barbu, V.; Fillet, M.; Chariot, A.; Relic, B.; Jacobs, N.; Gielen, J.; Merville, M.-P.; Bours, V. NF-kappaB transcription factor induces drug resistance through MDR1 expression in cancer cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, X.; Sarmiento, C.; Tan, T.; Zhu, H. Regulation of multidrug resistance by microRNAs in anti-cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathidevi, S.; Munirajan, A.K. Akt in cancer: Mediator and more. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Dai, Q.; Su, X.; Fu, J.; Feng, X.; Peng, J. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: The framework of malignant behavior. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4587–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Luo, D.; Jiang, C.; Ding, Y. Exosomes derived from HCC cells induce sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma both in vivo and in vitro. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vella, L.J.; Behren, A.; Coleman, B.; Greening, D.W.; Hill, A.F.; Cebon, J. Intercellular Resistance to BRAF Inhibition Can Be Mediated by Extracellular Vesicle-Associated PDGFRβ. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Cavalli, I.J.; Malheiros, D.; de Souza Fonseca Ribeiro, E.M.; Cavalli, L.R. Extracellular vesicles from triple-negative breast cancer cells promote proliferation and drug resistance in non-tumorigenic breast cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Aspe, J.R.; Asumen, M.G.; Almaguel, F.; Odumosu, O.; Acevedo-Martinez, S.; De Leon, M.; Langridge, W.H.R.; Wall, N.R. Extracellular, cell-permeable survivin inhibits apoptosis while promoting proliferative and metastatic potential. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Jutzy, J.M.S.; Aspe, J.R.; McGregor, D.W.; Neidigh, J.W.; Wall, N.R. Survivin is released from cancer cells via exosomes. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Jutzy, J.M.S.; Valenzuela, M.M.A.; Turay, D.; Aspe, J.R.; Ashok, A.; Mirshahidi, S.; Mercola, D.; Lilly, M.B.; Wall, N.R. Plasma-derived exosomal survivin, a plausible biomarker for early detection of prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreger, B.; Johansen, E.; Cerione, R.; Antonyak, M. The Enrichment of Survivin in Exosomes from Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Paclitaxel Promotes Cell Survival and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, S.; Warshall, C.; Bandyopadhyay, C.; Dutta, D.; Chandran, B. Interactions between exosomes from breast cancer cells and primary mammary epithelial cells leads to generation of reactive oxygen species which induce DNA damage response, stabilization of p53 and autophagy in epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hazawa, M.; Tomiyama, K.; Saotome-Nakamura, A.; Obara, C.; Yasuda, T.; Gotoh, T.; Tanaka, I.; Yakumaru, H.; Ishihara, H.; Tajima, K. Radiation increases the cellular uptake of exosomes through CD29/CD81 complex formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutschelknaus, L.; Peters, C.; Winkler, K.; Yentrapalli, R.; Heider, T.; Atkinson, M.J.; Moertl, S. Exosomes Derived from Squamous Head and Neck Cancer Promote Cell Survival after Ionizing Radiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arscott, W.T.; Tandle, A.T.; Zhao, S.; Shabason, J.E.; Gordon, I.K.; Schlaff, C.D.; Zhang, G.; Tofilon, P.J.; Camphausen, K.A. Ionizing radiation and glioblastoma exosomes: Implications in tumor biology and cell migration. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckland N. Z.) 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dorayappan, K.D.P.; Wanner, R.; Wallbillich, J.J.; Saini, U.; Zingarelli, R.; Suarez, A.A.; Cohn, D.E.; Selvendiran, K. Hypoxia-induced exosomes contribute to a more aggressive and chemoresistant ovarian cancer phenotype: A novel mechanism linking STAT3/Rab proteins. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3806–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, R.-X.; Chan, K.-W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Tan, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. Exosomal transfer of p-STAT3 promotes acquired 5-FU resistance in colorectal cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, J. Epithelial mesenchymal transition and lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2010, 2, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lobb, R.J.; van Amerongen, R.; Wiegmans, A.; Ham, S.; Larsen, J.E.; Möller, A. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal non-small cell lung cancer cells promote chemoresistance. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-D.; Wang, C.-S.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chien, K.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Lin, K.-H. Overexpression of CLIC1 in human gastric carcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. Proteomics 2007, 7, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, C.; Shi, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, J. CLIC1 Promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer by Regulating the MAPK/AKT Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.-L.; Tian, L.; Chen, J.-Q. Exosome-mediated transfer of CLIC1 contributes to the vincristine-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 462, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocati, N.; Masulli, M.; Di Ilio, C.; Federici, L. Glutathione transferases: Substrates, inihibitors and pro-drugs in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Wang, D.D.; Li, J.; Xu, H.Z.; Shen, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.Y.; Zhong, S.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Tang, J.H. Predictive role of GSTP1-containing exosomes in chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer. Gene 2017, 623, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilting, R.H.; Dannenberg, J.H. Epigenetic mechanisms in tumorigenesis, tumor cell heterogeneity and drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2012, 15, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, C.; Cui, W.; Wang, L. DNA Methyltransferases in Cancer: Biology, Paradox, Aberrations, and Targeted Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.-L.; Zhuang, T.; Xing, B.-H.; Li, N.; Li, Q. Exosomal DNMT1 mediates cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; He, J.; Min, L.; He, Y.; Guan, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Extracellular vesicles transmitted miR-31-5p promotes sorafenib resistance by targeting MLH1 in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikamori, M.; Yamada, D.; Eguchi, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Kishimoto, T.; Tomimaru, Y.; Asaoka, T.; Noda, T.; Wada, H.; Kawamoto, K.; et al. MicroRNA-155 controls exosome synthesis and promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuwen, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Fan, M.; Xu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Shu, Y. Prognostic Role of Circulating Exosomal miR-425-3p for the Response of NSCLC to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Qiu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, G.; Li, X. Exosomal MiR-744 Inhibits Proliferation and Sorafenib Chemoresistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PAX2. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 7209–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Yan, W.; You, Y. Exosomal transfer of miR-1238 contributes to temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.-C.; Ni, J.-J.; Cui, W.-Y.; Wang, B.-Y.; Zhuo, W. Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.-J.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Sun, W.; Li, X.-F.; et al. Exosome-Transmitted lncARSR Promotes Sunitinib Resistance in Renal Cancer by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, B.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Bu, J.; Yao, L. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of lncRNA HOTTIP Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulating HMGA1/miR-218 Axis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2019, 12, 11325–11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, C. Suppressing the secretion of exosomal miR-19b by gw4869 could regulate oxaliplatin sensitivity in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouvy, C.; Wannez, A.; Laloy, J.; Chatelain, C.; Dogné, J.-M. Transfer of multidrug resistance among acute myeloid leukemia cells via extracellular vesicles and their microRNA cargo. Leuk. Res. 2017, 62, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, G.; Sun, D.; Lei, M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Exosomes containing miR-21 transfer the characteristic of cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN and PDCD4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2017, 49, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Souza, P.S.; Cruz, A.L.S.; Viola, J.P.B.; Maia, R.C. Microparticles induce multifactorial resistance through oncogenic pathways independently of cancer cell type. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Khoo, F.; Kumazaki, M.; Shinohara, H.; Miki, K.; Yamada, N. Extracellular Disposal of Tumor-Suppressor miRs-145 and -34a via Microvesicles and 5-FU Resistance of Human Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, C.; Rani, S.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-34a is an intracellular and exosomal predictive biomarker for response to docetaxel with clinical relevance to prostate cancer progression. Prostate 2014, 74, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, J.; Mei, S.; Wu, D.; Mu, Z.; Chen, B.; Xie, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, J. Circulating exosomal microRNA-96 promotes cell proliferation, migration and drug resistance by targeting LMO7. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yu, S.; Zhou, L.; Shi, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Shen, B.; Liu, S.; Yan, D.; Feng, J. Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cell–derived exosomes increase cisplatin resistance of recipient cells in exosomal miR-100–5p-dependent manner. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, K.; Lowry, M.C.; Corcoran, C.; Martinez, V.G.; Daly, M.; Rani, S.; Gallagher, W.M.; Radomski, M.W.; MacLeod, R.A.F.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32774–32789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, J.C.; Lima, N.D.S.; Sarian, L.O.; Matheu, A.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Derchain, S.F.M. Exosome-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance via miR-155 transfer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, G.K.; Khan, M.A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Zubair, H.; Patton, M.C.; Singh, S.; Khushman, M.; Singh, A.P. Exosomes confer chemoresistance to pancreatic cancer cells by promoting ROS detoxification and miR-155-mediated suppression of key gemcitabine-metabolising enzyme, DCK. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lunavat, T.R.; Cheng, L.; Einarsdottir, B.O.; Olofsson Bagge, R.; Veppil Muralidharan, S.; Sharples, R.A.; Lässer, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Hill, A.F.; Nilsson, J.A.; et al. BRAFV600 inhibition alters the microRNA cargo in the vesicular secretome of malignant melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5930–E5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Lai, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J. Exosomal miR-221/222 enhances tamoxifen resistance in recipient ER-positive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Lv, M.M.; Chen, W.X.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.J.; Shen, H.; Zhong, S.L.; Tang, J.H.; et al. Exosomes from adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells transmit drug resistance partly by delivering miR-222. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 3227–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-X.; Cai, Y.-Q.; Lv, M.-M.; Chen, L.; Zhong, S.-L.; Ma, T.-F.; Zhao, J.-H.; Tang, J.-H. Exosomes from docetaxel-resistant breast cancer cells alter chemosensitivity by delivering microRNAs. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 9649–9659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Ma, C.; Zhou, T.; Dong, X.; Luo, Q.; Geng, L.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; et al. Exosomes derived from gemcitabine-resistant cells transfer malignant phenotypic traits via delivery of miRNA-222-3p. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, Q.-H.; Wang, X.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.-G.; Li, S.-Q.; Liu, X.-Q.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.-M.; Jiang, Y.-H.; et al. Exosomes derived from imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells mediate a horizontal transfer of drug-resistant trait by delivering miR-365. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 362, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yuwen, D.; Chen, J.; Zheng, B.; Gao, J.; Fan, M.; Xue, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Shu, Y.; et al. Exosomal transfer of cisplatin-induced mir-425-3p confers cisplatin resistance in NSCLC through activating autophagy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8121–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiozawa, K.; Shuting, J.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T.; Kondo, T. Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA-761 enhances pazopanib resistance in synovial sarcoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H.; Yu, Q. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-1246 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting CCNG2 in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, M.; Xing, P.; Yan, X.; Xie, B. Increased Expression of Exosomal AGAP2-AS1 (AGAP2 Antisense RNA 1) In Breast Cancer Cells Inhibits Trastuzumab-Induced Cell Cytotoxicity. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wei, J.; Yang, F.; Pang, X.; Shi, F.; Wei, Y.; Liao, B.; Wang, J. Exosomal lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 affects cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer cells through regulating microRNA-34b/TUFT1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Kogure, T.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of long non-coding RNA ROR modulates chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Lu, C.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, A.; You, Y. Exosomal transfer of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 enhances chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, K.; Ye, M.; He, X.; Zhang, F.; Han, J. Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA-SNHG14 promotes trastuzumab chemoresistance in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Wood, J.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Involvement of extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) in tumor cell responses to chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.T.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.H. Effects of long noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) existing in extracellular vesicles on the occurrence and multidrug resistance of esophageal cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthebane, D.A.; Rowe, A.; Thomford, N.E.; Shipanga, H.; Munro, D.; Mazeedi, M.A.M.A.; Almazyadi, H.A.M.; Kallmeyer, K.; Dandara, C.; Pepper, M.S.; et al. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Chemoresistance: To Survive, Keep Your Enemies Closer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.; Lee, S.; Youn, H.; Kim, E.; Kim, W.; Youn, B. The role of tumor microenvironment in therapeutic resistance. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3933–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchihara, T.; Miyake, K.; Yonemura, A.; Komohara, Y.; Itoyama, R.; Koiwa, M.; Yasuda, T.; Arima, K.; Harada, K.; Eto, K.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Containing Annexin A6 Induces FAK-YAP Activation by Stabilizing β1 Integrin, Enhancing Drug Resistance. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3222–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.L.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, S. Exosome-derived miR-27a produced by PSC-27 cells contributes to prostate cancer chemoresistance through p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Rong, Y.; Kuang, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, D.; Lou, W. Exosomal miRNA-106b from cancer-associated fibroblast promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 383, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Shi, J.; Lu, E.; Chen, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Ruan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Kong, F.; Guan, M. Long noncoding RNA CCAL transferred from fibroblasts by exosomes promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1700–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au Yeung, C.L.; Co, N.N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.L.; Kwan, S.Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Yuan, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, W.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hendrix, A.; Hernot, S.; Lemaire, M.; De Bruyne, E.; Van Valckenborgh, E.; Lahoutte, T.; De Wever, O.; Vanderkerken, K.; Menu, E. Bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes as communicators in drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2014, 124, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Han, H.; Song, S.; Yi, N.; Qian, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Hong, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Li, Z.; et al. Exosome-Transmitted PSMA3 and PSMA3-AS1 Promote Proteasome Inhibitor Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, I.; Cherdyntseva, N.; Liu, T.; Patysheva, M.; Rakina, M.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Interaction of tumor-associated macrophages and cancer chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1596004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binenbaum, Y.; Fridman, E.; Yaari, Z.; Milman, N.; Schroeder, A.; Ben David, G.; Shlomi, T.; Gil, Z. Transfer of miRNA in Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Induces Drug Resistance in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5287–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, P.; Chen, L.; Yuan, X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, G.; Ma, Y.; Shen, L. Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, H.; Yin, X.; Yang, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Feng, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Y. Macrophages derived exosomes deliver miR-223 to epithelial ovarian cancer cells to elicit a chemoresistant phenotype. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandari, S.K.; Purushothaman, A.; Ramani, V.C.; Brinkley, G.J.; Chandrashekar, D.S.; Varambally, S.; Mobley, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Brown, E.E.; Vlodavsky, I.; et al. Chemotherapy induces secretion of exosomes loaded with heparanase that degrades extracellular matrix and impacts tumor and host cell behavior. Matrix Biol. 2018, 65, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challagundla, K.B.; Wise, P.M.; Neviani, P.; Chava, H.; Murtadha, M.; Xu, T.; Kennedy, R.; Ivan, C.; Zhang, X.; Vannini, I.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of microRNAs Within the Tumor Microenvironment and Neuroblastoma Resistance to Chemotherapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Teng, M.W.L.; Smyth, M.J. Resistance to PD1/PDL1 checkpoint inhibition. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, S.; Xu, M.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X.-J.; Ji, J. Resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade cancer immunotherapy: Mechanisms, predictive factors, and future perspectives. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, J.A.; Zhang, R.R.; Kuo, J.S. Extracellular Vesicles Containing PD-L1 Contribute to Immune Evasion in Glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 2018, 83, E98–E100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreola, G.; Rivoltini, L.; Castelli, C.; Huber, V.; Perego, P.; Deho, P.; Squarcina, P.; Accornero, P.; Lozupone, F.; Lugini, L.; et al. Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, V.; Fais, S.; Iero, M.; Lugini, L.; Canese, P.; Squarcina, P.; Zaccheddu, A.; Colone, M.; Arancia, G.; Gentile, M.; et al. Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: Role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Wieckowski, E.; Taylor, D.D.; Reichert, T.E.; Watkins, S.; Whiteside, T.L. Fas ligand-positive membranous vesicles isolated from sera of patients with oral cancer induce apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Abusamra, A.J.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, M.; Ichim, T.E.; Chin, J.L.; Min, W.-P. Tumor exosomes expressing Fas ligand mediate CD8+ T-cell apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2005, 35, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieckowski, E.U.; Visus, C.; Szajnik, M.; Szczepanski, M.J.; Storkus, W.J.; Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-Derived Microvesicles Promote Regulatory T Cell Expansion and Induce Apoptosis in Tumor-Reactive Activated CD8 + T Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3720–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klibi, J.; Niki, T.; Riedel, A.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Souquere, S.; Rubinstein, E.; Moulec, S.L.E.; Guigay, J.; Hirashima, M.; Guemira, F.; et al. Blood diffusion and Th1-suppressive effects of galectin-9-containing exosomes released by Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Blood 2009, 113, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maybruck, B.T.; Pfannenstiel, L.W.; Diaz-Montero, M.; Gastman, B.R. Tumor-derived exosomes induce CD8+ T cell suppressors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Mitchell, J.P.; Court, J.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7458–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szczepanski, M.J.; Szajnik, M.; Welsh, A.; Whiteside, T.L.; Boyiadzis, M. Blast-derived microvesicles in sera from patients with acute myeloid leukemia suppress natural killer cell function via membrane-associated transforming growth factor-β1. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Kuranaga, Y.; Kumazaki, M.; Shinohara, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Akao, Y. Colorectal cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles induce phenotypic alteration of T cells into tumor-growth supporting cells with transforming growth factor-β1-mediated suppression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27033–27043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valenti, R.; Huber, V.; Filipazzi, P.; Pilla, L.; Sovena, G.; Villa, A.; Corbelli, A.; Fais, S.; Parmiani, G.; Rivoltini, L. Human tumor-released microvesicles promote the differentiation of myeloid cells with transforming growth factor-β-mediated suppressive activity on T lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9290–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marzagalli, M.; Raimondi, M.; Fontana, F.; Montagnani Marelli, M.; Moretti, R.M.; Limonta, P. Cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells in melanoma: Possible therapeutic implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.K.; Desai, N.S. Cancer Stem Cells: Acquisition, Characteristics, Therapeutic Implications, Targeting Strategies and Future Prospects. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, R.; Demant, M.; Aung, T.; Diering, N.; Cicholas, A.; Chapuy, B.; Wenzel, D.; Lahmann, M.; Guentsch, A.; Kiecke, C.; et al. Populational equilibrium through exosome-mediated Wnt signaling in tumor progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Qiao, Z.; Kong, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Exosomes mediate intercellular transfer of non–autonomous tolerance to proteasome inhibitors in mixed-lineage leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Dong, C.; Ruan, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, M.; Pizzo, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs Promote Breast Cancer Stemness by Targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3608–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, S.A.; Sinha, G.; Sandiford, O.A.; Williams, L.M.; Engelberth, D.J.; Guiro, K.; Isenalumhe, L.L.; Greco, S.J.; Ayer, S.; Bryan, M.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulate cycling quiescence and early breast cancer dormancy in bone marrow. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5832–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boelens, M.C.; Wu, T.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y.; Yoon, T.; Azzam, D.J.; Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Wiemann, B.Z.; Ishwaran, H.; et al. Exosome transfer from stromal to breast cancer cells regulates therapy resistance pathways. Cell 2014, 159, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, C.F.D.; Serrano, E.; Patrício, M.I.; Val, M.M.; Albuquerque, P.; Fonseca, J.; Gomes, C.M.F.; Abrunhosa, A.J.; Paiva, A.; Carvalho, L.; et al. Stroma-derived IL-6, G-CSF and Activin-A mediated dedifferentiation of lung carcinoma cells into cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.Z.; Sharawat, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Kochat, V.; Equbal, Z.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Kumar, U.; Mathur, S.; Kumar, L.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Aggressive serous epithelial ovarian cancer is potentially propagated by EpCAM+CD45+ phenotype. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2089–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, C.; Mu, L.; Huang, K.; Li, X.; Tao, D.; Wu, Y.; Qin, J. Fibroblast-Derived Exosomes Contribute to Chemoresistance through Priming Cancer Stem Cells in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, G.; Xu, Q.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Hou, Y. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3932–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, P.; Savini, C.; Kurelac, I.; Chang, Q.; Amato, L.B.; Strillacci, A.; Stepanova, A.; Iommarini, L.; Mastroleo, C.; Daly, L.; et al. Packaging and transfer of mitochondrial DNA via exosomes regulate escape from dormancy in hormonal therapy-resistant breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9066–E9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, N.D.; Elias, M.; Guiro, K.; Bhatia, R.; Greco, S.J.; Bryan, M.; Gergues, M.; Sandiford, O.A.; Ponzio, N.M.; Leibovich, S.J.; et al. Exosomes from differentially activated macrophages influence dormancy or resurgence of breast cancer cells within bone marrow stroma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S. Tumor markers in clinical practice: General principles and guidelines. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2009, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Dommelen, S.M.; van der Meel, R.; van Solinge, W.W.; Coimbra, M.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. Cetuximab treatment alters the content of extracellular vesicles released from tumor cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, L.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Bittner, A.-K.; Hoffmann, O.; Wagner, B.; Santos Manvailer, L.F.; Kimmig, R.; Horn, P.A.; Rebmann, V. Elevated levels of extracellular vesicles are associated with therapy failure and disease progression in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1376153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Re, M.; Marconcini, R.; Pasquini, G.; Rofi, E.; Vivaldi, C.; Bloise, F.; Restante, G.; Arrigoni, E.; Caparello, C.; Grazia Bianco, M.; et al. PD-L1 mRNA expression in plasma-derived exosomes is associated with response to anti-PD-1 antibodies in melanoma and NSCLC. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, V.; Kim, D.U.; San Lucas, F.A.; Castillo, J.; Allenson, K.; Mulu, F.C.; Stephens, B.M.; Huang, J.; Semaan, A.; Guerrero, P.A.; et al. Circulating Nucleic Acids Are Associated With Outcomes of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 108–118.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allenson, K.; Castillo, J.; San Lucas, F.A.; Scelo, G.; Kim, D.U.; Bernard, V.; Davis, G.; Kumar, T.; Katz, M.; Overman, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of mutant KRAS in circulating exosome-derived DNA from early-stage pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, B.; Aebersold, D.M.; Dal Pra, A. Protocol for serum exosomal miRNAs analysis in prostate cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, P.; Mulcahy, L.A.; Furlong, F.; McCarthy, H.O.; Brooks, S.A.; Fabbri, M.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.F. Cisplatin induces the release of extracellular vesicles from ovarian cancer cells that can induce invasiveness and drug resistance in bystander cells. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiao, D.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Cai, J.; Fu, L. Chemotherapeutic drugs stimulate the release and recycling of extracellular vesicles to assist cancer cells in developing an urgent chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melling, G.E.; Carollo, E.; Conlon, R.; Simpson, J.C.; Carter, D.R.F. The Challenges and Possibilities of Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Vehicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R.; Aung, T.; Vogel, D.; Chapuy, B.; Wenzel, D.; Becker, S.; Sinzig, U.; Venkataramani, V.; Von Mach, T.; Jacob, R.; et al. Nuclear trapping through inhibition of exosomal export by indomethacin increases cytostatic efficacy of doxorubicin and pixantrone. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marleau, A.M.; Chen, C.S.; Joyce, J.A.; Tullis, R.H. Exosome removal as a therapeutic adjuvant in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fontana, F.; Carollo, E.; Melling, G.E.; Carter, D.R.F. Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Modulators of Cancer Drug Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040749
Fontana F, Carollo E, Melling GE, Carter DRF. Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Modulators of Cancer Drug Resistance. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040749
Chicago/Turabian StyleFontana, Fabrizio, Emanuela Carollo, Genevieve E. Melling, and David R. F. Carter. 2021. "Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Modulators of Cancer Drug Resistance" Cancers 13, no. 4: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040749
APA StyleFontana, F., Carollo, E., Melling, G. E., & Carter, D. R. F. (2021). Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Modulators of Cancer Drug Resistance. Cancers, 13(4), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040749