Whole-Genome Sequencing of Retinoblastoma Reveals the Diversity of Rearrangements Disrupting RB1 and Uncovers a Treatment-Related Mutational Signature
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. All Retinoblastoma Tumours Harbour At Least One RB1 Mutation
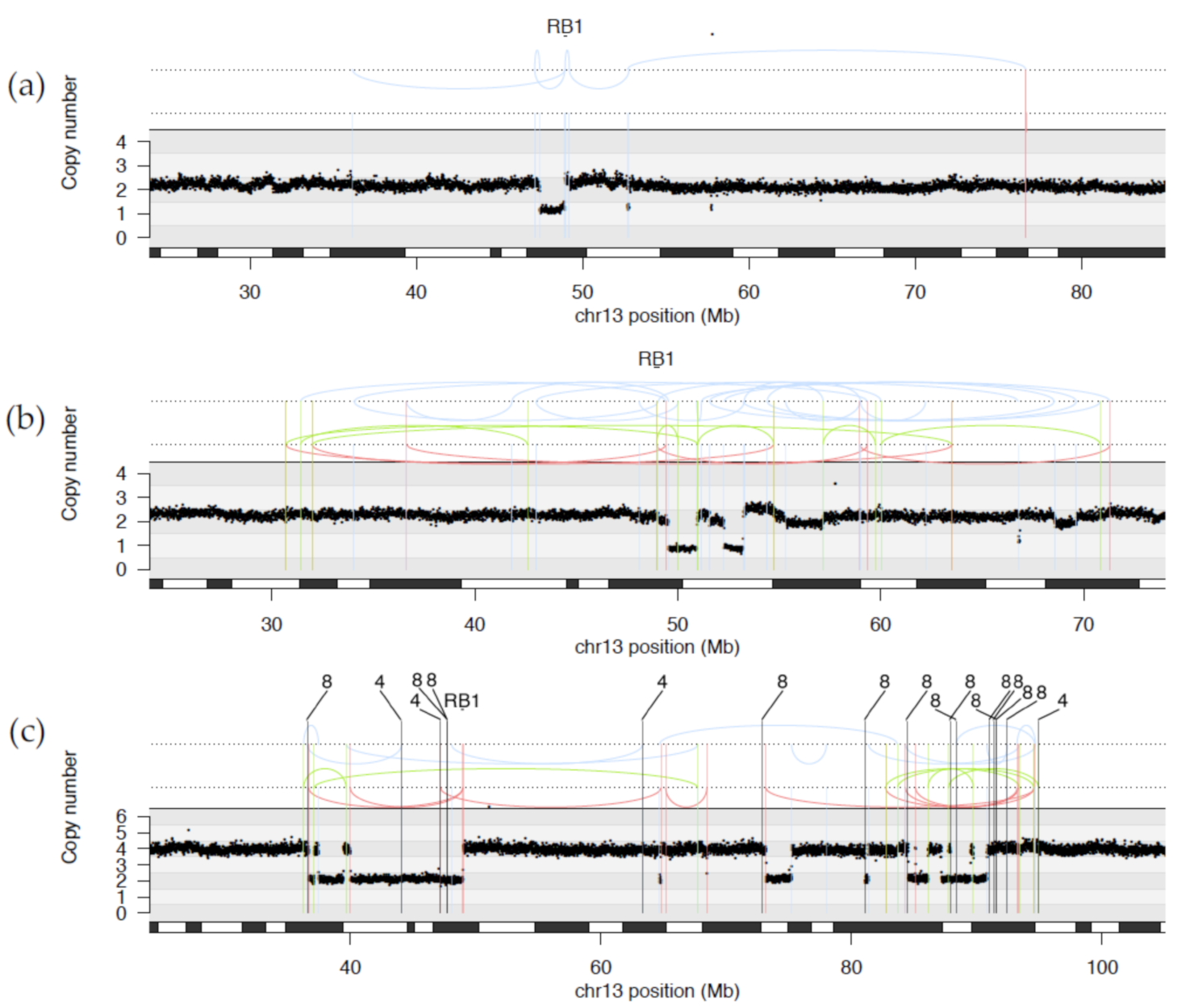
2.1.1. WGS Reveals Novel RB1 Disruptions by Structural Variation
2.1.2. Diverse Rearrangements Transect RB1
2.1.3. WGS Provides Clarification of Ambiguous Clinical Testing Results
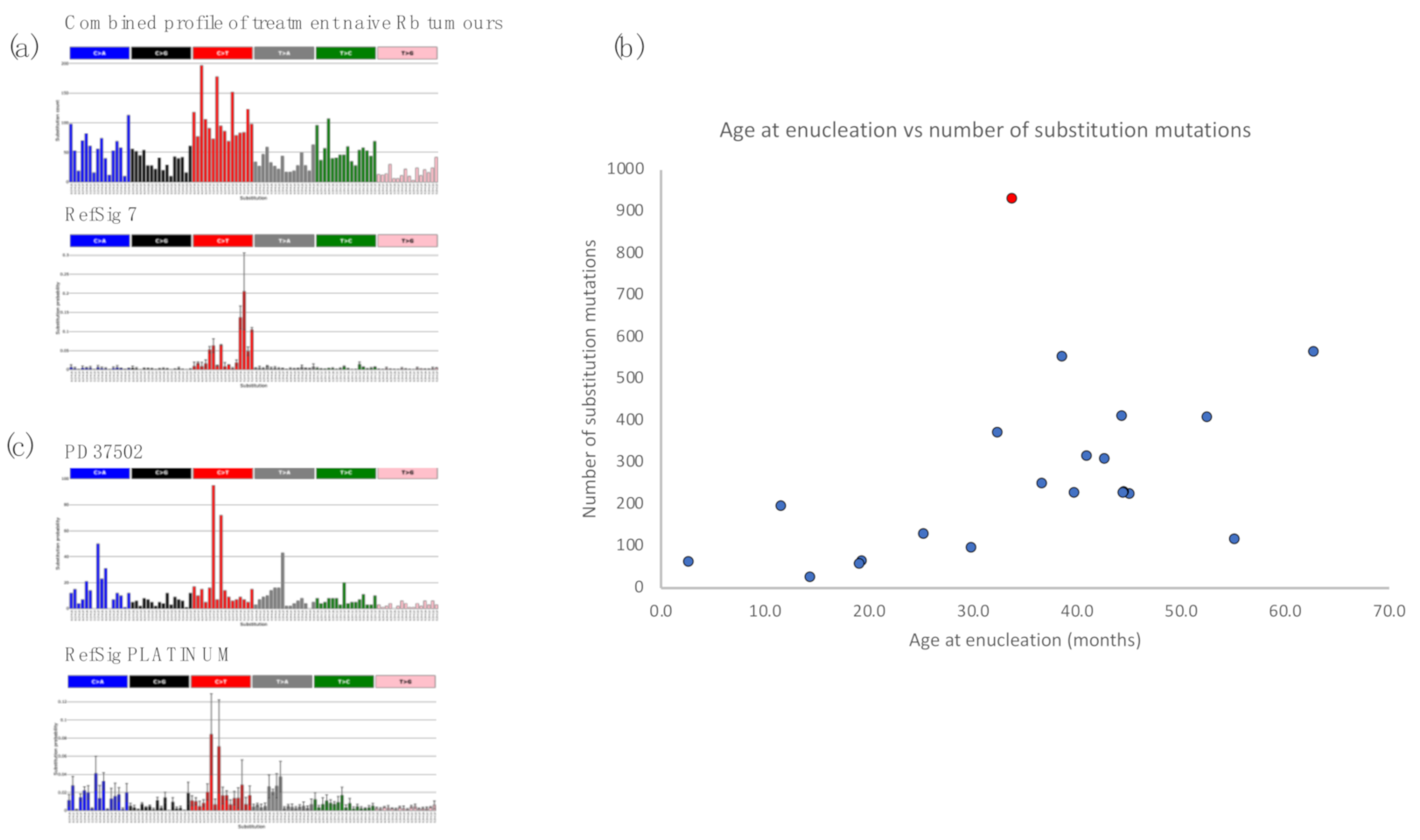
2.2. Retinoblastoma Tumours Harbour a Low Burden of Mutations
2.3. Retinoblastomas Are Not Driven by Ultraviolet Damage
2.4. Insights from Analysis of Independent Tumours in a Bilateral Retinoblastoma Case
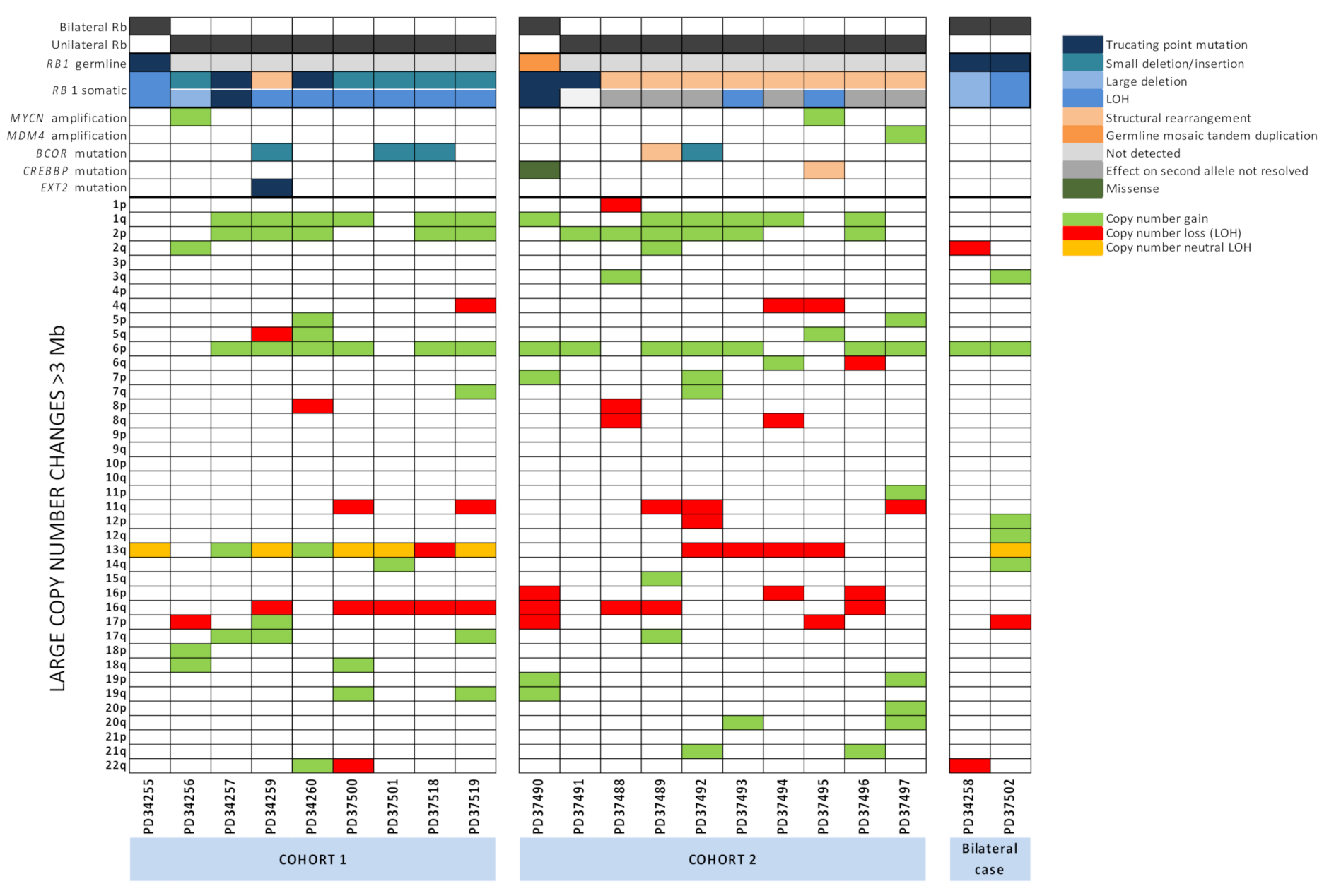
2.5. Large-Scale Copy Number Changes
2.6. RB1 Mutations and N-MYC Dysregulation Are Not Mutually Exclusive and N-MYC Dysregulation Is Universal
2.7. Other Potential Driver Mutations Identified in Retinoblastoma Tumours
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Details
4.2. Tissue Processing and DNA/RNA Extraction
4.3. mRNA Expression Profiling
4.4. Analysis of mRNAseq Data
4.5. Clinical RB1 Mutation Screening
4.6. Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.7. ASCAT Copy Number Analysis
4.8. Mutational Signature Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friend, S.H.; Bernards, R.; Rogelj, S.; Weinberg, R.A.; Rapaport, J.M.; Albert, D.M.; Dryja, T.P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature 1986, 323, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Bookstein, R.; Hong, F.; Young, L.J.; Shew, J.Y.; Lee, E.Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: Cloning, identification, and sequence. Science 1987, 235, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, F.D.; Huang, H.J.; To, H.; Young, L.J.; Oro, A.; Bookstein, R.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, W.H. Structure of the human retinoblastoma gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5502–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, S.J.; Schneider, R.; Bauer, U.M.; Bannister, A.J.; Morrison, A.; O’Carroll, D.; Firestein, R.; Cleary, M.; Jenuwein, T.; Herrera, R.E.; et al. Rb targets histone H3 methylation and HP1 to promoters. Nature 2001, 412, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.M.; Deng, Z.; Kang, H.; Lieberman, P.M. Cell cycle association of the retinoblastoma protein Rb and the histone demethylase LSD1 with the Epstein-Barr virus latency promoter Cp. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3428–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collard, T.J.; Urban, B.C.; Patsos, H.A.; Hague, A.; Townsend, P.A.; Paraskeva, C.; Williams, A.C. The retinoblastoma protein (Rb) as an anti-apoptotic factor: Expression of Rb is required for the anti-apoptotic function of BAG-1 protein in colorectal tumour cells. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, C. Roles of pRB in the Regulation of Nucleosome and Chromatin Structures. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5959721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.A.; Price, K.; Kolkiewicz, K.; Hack, S.; Reddy, M.A.; Hungerford, J.L.; Kingston, J.E.; Onadim, Z. Spectrum of RB1 mutations identified in 403 retinoblastoma patients. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonfeld, S.J.; Kleinerman, R.A.; Abramson, D.H.; Seddon, J.M.; Tucker, M.A.; Morton, L.M. Long-term risk of subsequent cancer incidence among hereditary and nonhereditary retinoblastoma survivors. Br. J. Cancer 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, G.J.; Sanders, B.M.; Kingston, J.E. Second primary neoplasms in patients with retinoblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 1986, 53, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onadim, Z.; Hogg, A.; Baird, P.N.; Cowell, J.K. Oncogenic point mutations in exon 20 of the RB1 gene in families showing incomplete penetrance and mild expression of the retinoblastoma phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6177–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lohmann, D.R.; Gerick, M.; Brandt, B.; Oelschlager, U.; Lorenz, B.; Passarge, E.; Horsthemke, B. Constitutional RB1-gene mutations in patients with isolated unilateral retinoblastoma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 61, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rushlow, D.; Piovesan, B.; Zhang, K.; Prigoda-Lee, N.L.; Marchong, M.N.; Clark, R.D.; Gallie, B.L. Detection of mosaic RB1 mutations in families with retinoblastoma. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, A.G., Jr. Mutation and cancer: Statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dommering, C.J.; Mol, B.M.; Moll, A.C.; Burton, M.; Cloos, J.; Dorsman, J.C.; Meijers-Heijboer, H.; van der Hout, A.H. RB1 mutation spectrum in a comprehensive nationwide cohort of retinoblastoma patients. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rushlow, D.E.; Mol, B.M.; Kennett, J.Y.; Yee, S.; Pajovic, S.; Theriault, B.L.; Prigoda-Lee, N.L.; Spencer, C.; Dimaras, H.; Corson, T.W.; et al. Characterisation of retinoblastomas without RB1 mutations: Genomic, gene expression, and clinical studies. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afshar, A.R.; Pekmezci, M.; Bloomer, M.M.; Cadenas, N.J.; Stevers, M.; Banerjee, A.; Roy, R.; Olshen, A.B.; Van Ziffle, J.; Onodera, C.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing of Retinoblastoma Identifies Pathogenic Alterations beyond RB1 Inactivation That Correlate with Aggressive Histopathologic Features. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, J.; Nagahawatte, P.; Finkelstein, D.; Richards-Yutz, J.; Valentine, M.; Ma, J.; Mullighan, C.; Song, G.; Chen, X.; Wilson, M.; et al. RB1 gene inactivation by chromothripsis in human retinoblastoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kooi, I.E.; Mol, B.M.; Massink, M.P.; Ameziane, N.; Meijers-Heijboer, H.; Dommering, C.J.; van Mil, S.E.; de Vries, Y.; van der Hout, A.H.; Kaspers, G.J.; et al. Somatic genomic alterations in retinoblastoma beyond RB1 are rare and limited to copy number changes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Benavente, C.A.; McEvoy, J.; Flores-Otero, J.; Ding, L.; Chen, X.; Ulyanov, A.; Wu, G.; Wilson, M.; Wang, J.; et al. A novel retinoblastoma therapy from genomic and epigenetic analyses. Nature 2012, 481, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.H.; Richards, A.L.; Mandelker, D.L.; Berger, M.F.; Walsh, M.F.; Dunkel, I.J.; Donoghue, M.T.A.; Abramson, D.H. Molecular Changes in Retinoblastoma beyond RB1: Findings from Next-Generation Sequencing. Cancers 2021, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, I.E.; Mol, B.M.; Massink, M.P.; de Jong, M.C.; de Graaf, P.; van der Valk, P.; Meijers-Heijboer, H.; Kaspers, G.J.; Moll, A.C.; Te Riele, H.; et al. A Meta-Analysis of Retinoblastoma Copy Numbers Refines the List of Possible Driver Genes Involved in Tumor Progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grobner, S.N.; Worst, B.C.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Buchhalter, I.; Kleinheinz, K.; Rudneva, V.A.; Johann, P.D.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Segura-Wang, M.; Brabetz, S.; et al. The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers. Nature 2018, 555, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Edmonson, M.N.; Gawad, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Rusch, M.C.; Easton, J.; et al. Pan-cancer genome and transcriptome analyses of 1,699 paediatric leukaemias and solid tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helleday, T.; Eshtad, S.; Nik-Zainal, S. Mechanisms underlying mutational signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, M.L. Is sunlight an aetiological agent in the genesis of retinoblastoma? Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jemal, A.; Devesa, S.S.; Fears, T.R.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Retinoblastoma incidence and sunlight exposure. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivolta, C.; Royer-Bertrand, B.; Rimoldi, D.; Schalenbourg, A.; Zografos, L.; Leyvraz, S.; Moulin, A. UV light signature in conjunctival melanoma; not only skin should be protected from solar radiation. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 61, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Royer-Bertrand, B.; Torsello, M.; Rimoldi, D.; El Zaoui, I.; Cisarova, K.; Pescini-Gobert, R.; Raynaud, F.; Zografos, L.; Schalenbourg, A.; Speiser, D.; et al. Comprehensive Genetic Landscape of Uveal Melanoma by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johansson, P.; Aoude, L.G.; Wadt, K.; Glasson, W.J.; Warrier, S.K.; Hewitt, A.W.; Kiilgaard, J.F.; Heegaard, S.; Isaacs, T.; Franchina, M.; et al. Deep sequencing of uveal melanoma identifies a recurrent mutation in PLCB4. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4624–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Jones, P.H.; Wedge, D.C.; Sale, J.E.; Campbell, P.J.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Stratton, M.R. Clock-like mutational processes in human somatic cells. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Degasperi, A.; Amarante, T.D.; Czarnecki, J.; Shooter, S.; Zou, X.; Glodzik, D.; Morganella, S.; Nanda, A.S.; Badja, C.; Koh, G.; et al. A practical framework and online tool for mutational signature analyses show inter-tissue variation and driver dependencies. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klutz, M.; Brockmann, D.; Lohmann, D.R. A parent-of-origin effect in two families with retinoblastoma is associated with a distinct splice mutation in the RB1 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lillington, D.M.; Goff, L.K.; Kingston, J.E.; Onadim, Z.; Price, E.; Domizio, P.; Young, B.D. High level amplification of N-MYC is not associated with adverse histology or outcome in primary retinoblastoma tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, H.R.; Hodgson, K.; Schwalbe, E.; Coxhead, J.; Sinclair, N.; Zou, X.; Cockell, S.; Husain, A.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Rajan, N. Epigenetic modifiers DNMT3A and BCOR are recurrently mutated in CYLD cutaneous syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, V.; Tiacci, E.; Holmes, A.B.; Kohlmann, A.; Martelli, M.P.; Kern, W.; Spanhol-Rosseto, A.; Klein, H.U.; Dugas, M.; Schindela, S.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of BCOR in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Blood 2011, 118, 6153–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimaras, H.; Khetan, V.; Halliday, W.; Orlic, M.; Prigoda, N.L.; Piovesan, B.; Marrano, P.; Corson, T.W.; Eagle, R.C., Jr.; Squire, J.A.; et al. Loss of RB1 induces non-proliferative retinoma: Increasing genomic instability correlates with progression to retinoblastoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, R.D.; Liu, S.G.; Zhao, X.X.; Cui, L.; Yue, Z.X.; Li, W.J.; Chen, Z.P.; Li, Z.G.; Rao, Q.; et al. Low CREBBP expression is associated with adverse long-term outcomes in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2017, 99, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Ramis-Zaldivar, J.E.; Bonzheim, I.; Steinhilber, J.; Muller, I.; Haake, A.; Yu, S.C.; Raffeld, M.; Fend, F.; Salaverria, I.; et al. CREBBP gene mutations are frequently detected in in situ follicular neoplasia. Blood 2018, 132, 2687–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stickens, D.; Clines, G.; Burbee, D.; Ramos, P.; Thomas, S.; Hogue, D.; Hecht, J.T.; Lovett, M.; Evans, G.A. The EXT2 multiple exostoses gene defines a family of putative tumour suppressor genes. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewens, K.G.; Bhatti, T.R.; Moran, K.A.; Richards-Yutz, J.; Shields, C.L.; Eagle, R.C.; Ganguly, A. Phosphorylation of pRb: Mechanism for RB pathway inactivation in MYCN-amplified retinoblastoma. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Fang, Y.; Lee, T.C.; Forrest, D.; Gregory-Evans, C.; Almeida, D.; Liu, A.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Abramson, D.H.; Cobrinik, D. Retinoblastoma has properties of a cone precursor tumor and depends upon cone-specific MDM2 signaling. Cell 2009, 137, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.L.; Singh, H.P.; Wang, L.; Qi, D.L.; Poulos, B.K.; Abramson, D.H.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Cobrinik, D. Rb suppresses human cone-precursor-derived retinoblastoma tumours. Nature 2014, 514, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, A.; Shields, C.L. Differential gene expression profile of retinoblastoma compared to normal retina. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Targeting oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, H.; Glodzik, D.; Morganella, S.; Yates, L.R.; Staaf, J.; Zou, X.; Ramakrishna, M.; Martin, S.; Boyault, S.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; et al. HRDetect is a predictor of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficiency based on mutational signatures. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.; Morganella, S.; Purdie, C.A.; Jang, S.J.; Borgen, E.; Russnes, H.; Glodzik, D.; Zou, X.; Viari, A.; Richardson, A.L.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Breast Cancers with Mismatch Repair Deficiency. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4755–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzog, S.; Lohmann, D.R.; Buiting, K.; Schuler, A.; Horsthemke, B.; Rehder, H.; Rieder, H. Marked differences in unilateral isolated retinoblastomas from young and older children studied by comparative genomic hybridization. Hum. Genet. 2001, 108, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillington, D.M.; Kingston, J.E.; Coen, P.G.; Price, E.; Hungerford, J.; Domizio, P.; Young, B.D.; Onadim, Z. Comparative genomic hybridization of 49 primary retinoblastoma tumors identifies chromosomal regions associated with histopathology, progression, and patient outcome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 36, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Wal, J.E.; Hermsen, M.A.; Gille, H.J.; Schouten-Van Meeteren, N.Y.; Moll, A.C.; Imhof, S.M.; Meijer, G.A.; Baak, J.P.; van der Valk, P. Comparative genomic hybridisation divides retinoblastomas into a high and a low level chromosomal instability group. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 56, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, E.A.; Kolkiewicz, K.; Patel, R.; Hashim, S.; Karaa, E.; Scheimberg, I.; Sagoo, M.S.; Reddy, M.A.; Onadim, Z. Detection and reporting of RB1 promoter hypermethylation in diagnostic screening. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Davies, H.; Staaf, J.; Ramakrishna, M.; Glodzik, D.; Zou, X.; Martincorena, I.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Martin, S.; Wedge, D.C.; et al. Landscape of somatic mutations in 560 breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature 2016, 534, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| RB1 Mutations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cohort 1: Tumours with Biallelic Mutations Previously Identified | ||
| Tumour | RB1 mutation allele 1 | RB1 mutation allele 2 |
| PD34255 | Germline c.1421+1G>C ESS splice a | LOH a |
| PD34256 | Somatic c.1420_1421+30del32 a | Somatic deletion exons 18 to 27 a |
| PD34257 | Somatic c.1421+2T>A ESS splice a | Somatic c.1333C>T p. (R445 *) a |
| PD34259 | Somatic Rearrangement resulting in deletion exon 2 a | LOH a |
| PD34260 | Somatic c.1363C>T p.(R455*) a | LOH a |
| PD37500 | Somatic c.266_229delTTAAp.(T77fs*33) a | LOH a |
| PD37501 | Somatic c.393_396dupCTTT p.(N133fs*2) a | LOH a |
| PD37518 | Somatic c.1389dupA p.(E464fs*11) a | LOH a |
| PD37519 | Somatic c.173delC p.(T58fs*7) a | LOH a |
| Cohort 2: Tumours with One or Zero Previously Identified Mutations | ||
| PD37490 | Somatic c.763C>T p.(R255*) a | Germline mosaic duplication of exons 12–17 c |
| PD37491 | Somatic c.1072C>T p.(R358*) a | Not detected |
| PD37488 | Complex intrachromosomal rearrangements, 4 break points in RB1.d | Effect on second allele could not be resolved |
| PD37489 | Complex intrachromosomal rearrangement, 3 break points in RB1. One copy lost due to deletion of exons 1–6. b | Effect on second allele could not be resolved |
| PD37492 | Complex interchromosomal rearrangements, 3 break points in RB1. One copy lost due to deletion of exons 18 to 27. b | Effect on second allele could not be resolved |
| PD37493 | Complex interchromosomal rearrangements. RB1 disrupted by a translocation to chromosome 2. d | LOH a |
| PD37494 | Complex interchromosomal rearrangement, 2 break points in RB1. One copy lost due to deletion of exons 1 to 17. b | Effect on second allele could not be resolved |
| PD37495 | RB1 disrupted by balanced translocations from intron 2 to chromosomes 16 and 18. d | LOH a |
| PD37496 | Complex intrachromosomal rearrangement, 4 break points in RB1. c | Effect on second allele could not be resolved |
| PD37497 | Complex interchromosomal rearrangement, 4 break points in RB1. c | Effect on second allele could not be resolved |
| Bilateral Tumours from a Single Patient | ||
| PD34258 | Germline c.607+1G>T ESS splice a | Somatic deletion exons 8 to 11 |
| PD37502 | Germline c.607+1G>T ESS splice a | LOH |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davies, H.R.; Broad, K.D.; Onadim, Z.; Price, E.A.; Zou, X.; Sheriff, I.; Karaa, E.K.; Scheimberg, I.; Reddy, M.A.; Sagoo, M.S.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Retinoblastoma Reveals the Diversity of Rearrangements Disrupting RB1 and Uncovers a Treatment-Related Mutational Signature. Cancers 2021, 13, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040754
Davies HR, Broad KD, Onadim Z, Price EA, Zou X, Sheriff I, Karaa EK, Scheimberg I, Reddy MA, Sagoo MS, et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Retinoblastoma Reveals the Diversity of Rearrangements Disrupting RB1 and Uncovers a Treatment-Related Mutational Signature. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040754
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavies, Helen R., Kevin D. Broad, Zerrin Onadim, Elizabeth A. Price, Xueqing Zou, Ibrahim Sheriff, Esin Kotiloğlu Karaa, Irene Scheimberg, M. Ashwin Reddy, Mandeep S. Sagoo, and et al. 2021. "Whole-Genome Sequencing of Retinoblastoma Reveals the Diversity of Rearrangements Disrupting RB1 and Uncovers a Treatment-Related Mutational Signature" Cancers 13, no. 4: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040754
APA StyleDavies, H. R., Broad, K. D., Onadim, Z., Price, E. A., Zou, X., Sheriff, I., Karaa, E. K., Scheimberg, I., Reddy, M. A., Sagoo, M. S., Ohnuma, S.-i., & Nik-Zainal, S. (2021). Whole-Genome Sequencing of Retinoblastoma Reveals the Diversity of Rearrangements Disrupting RB1 and Uncovers a Treatment-Related Mutational Signature. Cancers, 13(4), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040754






