Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
| PKI | Other Name | Known Targets (IC50 Value in nM) | Source | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-769662 | AMPK (800; EC50) | LC Laboratories (Woburn, MA, USA) | [42] | |
| AT7867 | AKT2 (17), PKA (20), AKT1 (32), AKT3 (47), p70S6K (85) | Selleck Chemicals (Houston, TX, USA) | [43] | |
| AT9283 | JAK3 (1.1), JAK2 (1.2), AURKA (~3.0), AURKB (~3.0), ABL1T315I (4) | [44] | ||
| AZD1152-HQPA | Barasertib, AZD2811 | AURKB (0.37) | [45] | |
| AZD1480 | JAK2 (0.26) | [46] | ||
| BI 2536 | PLK1 (0.83), PLK2 (3.5) | [47,48] | ||
| BIX 02189 | MEK5 (1.5) | [49] | ||
| BML-275 | Dorsomorphin, Compound C | AMPK (109; Ki) | Tocris Bioscience (Bristol, UK) | [50] |
| Bosutinib | SKI-606 | ABL (1), SRC (1.2) | LC Laboratories | [51,52] |
| Chelerythrine | PKC (660) | [53] | ||
| CHIR-99021 | CT99021 | GSK3β (6.7), GSK3α (10) | Selleck Chemicals | [54] |
| CI-1040 | PD184352 | MEK1 (17), MEK2 (17) | [55] | |
| CP690550 | Tofacitinib | JAK3 (1), JAK2 (20) | LC Laboratories | [56] |
| CYC116 | AURKA (8; Ki), AURKB (9; Ki), VEGFR2 (44; Ki), FLT3 (44; Ki) | Selleck Chemicals | [57] | |
| Danusertib | PHA-739358 | AURKA (13), ABL (25), RET (31), TRKA (31), FGFR1 (47), AURKC (61), AURKB (79) | [58] | |
| Enzastaurin | LY317615 | PKCβ (6), PKCα (39), PKCγ (83), PKCε (110) | [59] | |
| Fasudil | HA-1077 | ROCK2 (330) | LC Laboratories | [60] |
| FR 180204 | ERK2 (140), ERK1 (310) | Tocris Bioscience | [61] | |
| GDC-0879 | AR-00341677 | BRAF (0.13) | Selleck Chemicals | [62] |
| GW 843682X | PLK1 (2.2), PLK3 (9.1) | Tocris Bioscience | [63] | |
| I3M | GSK3β (190) | Calbiochem (San Diego, CA, USA) | [64] | |
| IKK 16 | IKK Inhibitor VII | IKK2 (40), IKK complex (70), IKK1 (200) | Tocris Bioscience | [65] |
| Imatinib | STI571, CGP057148B, Gleevec | PDGFR (100), c-KIT (100), v-ABL (600) | LC Laboratories | [66] |
| INCB018424 | Ruxolitinib | JAK2 (2.8), JAK1 (3.3) | Selleck Chemicals | [67] |
| JNJ-7706621 | CDK2/Cyclin E (3), CDK2/Cyclin A (4), CDK1/Cyclin B (9), AURKA (11), AURKB (15) | [68] | ||
| KU-55933 | ATM (12.9) | [69] | ||
| LY2228820 | Ralimetinib | P38α (7) | [70] | |
| MLN8237 | Alisertib | AURKA (1.2) | [71] | |
| Nilotinib | AMN-107 | Bcr-Abl (<30) | LC Laboratories | [72] |
| NSC 109555 | CHK2 (200) | Tocris Bioscience | [73] | |
| NU 7441 | KU-57788 | DNA-PK (14) | [74] | |
| PD-0325901 | Mirdametinib | MEK (0.33) | Selleck Chemicals | [75] |
| PD407824 | CHK1 (47), WEE1 (97) | Tocris Bioscience | [76] | |
| PF-4708671 | p70S6K1 (160) | Selleck Chemicals | [77] | |
| PF 573228 | FAK (4) | Tocris Bioscience | [78] | |
| PKC412 | Midostaurin, CGP 41251 | PKCα (22), PKCγ (24), PKCβ1 (30), PKCβ2 (31), PPK (38) | LC Laboratories | [79] |
| PLX-4032 | Vemurafenib | SRMS (18), ACK (19), BRAF (31), C-RAF (48), MAP4K5 (51) | Selleck Chemicals | [80] |
| PLX-4720 | BRAFV600E (13), C-RAF1Y340D/Y341D (6.7) | [81] | ||
| Ro-31-8220 | Bisindolylmaleimide IX | PKCα (5), PKCβ2 (14), PKCβ1 (24), PKCε (24), PKCγ (27) | Calbiochem | [82] |
| Roscovitine | Seliciclib, CYC202 | CDK5/P35 (160) | LC Laboratories | [83] |
| SB216763 | GSK3α (34.3), GSK3β (~34.3) | Selleck Chemicals | [84] | |
| SB 218078 | CHK1 (15) | Tocris Bioscience | [85] | |
| SNS-032 | BMS-387032 | CDK9/Cyclin T (4) | Selleck Chemicals | [86] |
| SNS-314 | AURKC (3), AURKA (9), AURKB (31) | [87] | ||
| SP600125 | NSC75890 | JNK1 (40), JNK2 (40), AURKA (60), TRKA (70) | [88] | |
| TBCA | CK2 (110) | Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA) | [89] | |
| TCS 2312 | CHK1 (60; EC50) | Tocris Bioscience | [90] | |
| TC PIM-1-1 | SC 204330 | PIM (50) | [91] | |
| TCS PIM-1-4a | SMI-4a | PIM1 (17) | [92] | |
| Tozasertib | VX-680, MK-0457 | AURKA (0.6; Ki), AURKC (4.6; Ki), AURKB (18; Ki), FLT3 (30; Ki), BCL-ABL (30; Ki) | LC Laboratories | [93,94] |
| TPCA-1 | GW683965 | IKK2 (17.9) | Tocris Bioscience | [95] |
| U0126 | MEK2 (60), MEK1 (70) | Promega (Madison, WI, USA) | [96] | |
| VX-702 | P38α (4–20) | Selleck Chemicals | [97] | |
| Y-27632 | ROCK1 (140; Ki); ROCK2 (300; Ki) | [98,99] | ||
| ZM-447439 | AURKA (110), AURKB (130) | [100] |
2.2. PKI Screening
2.3. Clonogenic Survival Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Antibody Array
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
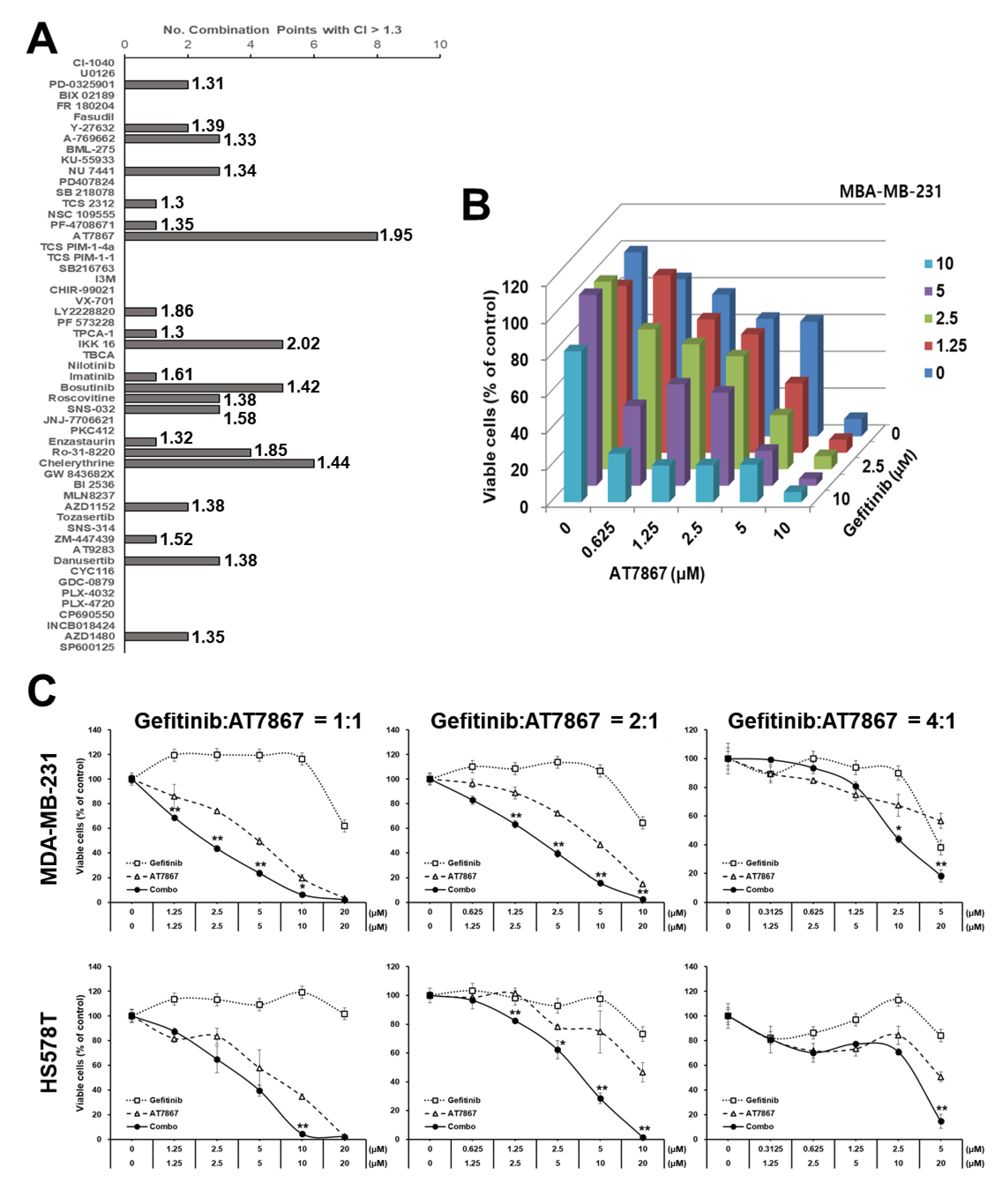
3.1. Identification of AT7867 as a Potentiator of Gefitinib in MDA-MB-231 Cells
3.2. Induction of Tetraploid Cells by AT7867
3.3. Gefitinib and AT7867 Reduced TNBC Cell Survival
3.4. Regulation of Signaling Pathways in TNBC Cells by Gefitinib and AT7867 Treatment
3.5. Upregulation of the MEK/ERK Pathway by Gefitinib and AT7867
3.6. Synergistic Enhancement of the Anti-Proliferative Effect of Gefitinib and AT7867 via the Inhibition of the MEK Pathway
3.7. Induction of Cell Death by Gefitinib and AT7867 and PD-0325901
3.8. Blocking Long-Term Survival of TNBC Cells Using Gefitinib and AT7867 and PD-0326901
3.9. Regulation of Signaling Pathways in TNBC Cells by Gefitinib and AT7867 and PD-0326901
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz, L.K.; Cryns, V.L.; Symmans, W.F.; Sneige, N. Triple Negative Breast Carcinoma and the Basal Phenotype: From Expression Profiling to Clinical Practice. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2007, 14, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.; Pambid, M.R.; Jayanthan, A.; Dorr, A.; Los, G.; Dunn, S.E. The Dawn of Targeted Therapies for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Snapshot of Investigational Drugs in Phase I and II Trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drug 2020, 29, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Hung, M.-C.; Yamaguchi, H. A Perspective on Anti-EGFR Therapies Targeting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brenton, J.D.; Carey, L.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Caldas, C. Molecular Classification and Molecular Forecasting of Breast Cancer: Ready for Clinical Application? J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7350–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes and Preclinical Models for Selection of Targeted Therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification and Use of Biomarkers in Treatment Strategies for Triple-negative Breast Cancer Subtypes. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, C.; Mazouni, C.; Hess, K.R.; André, F.; Tordai, A.; Mejia, J.A.; Symmans, W.F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy and Long-Term Survival in Patients With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, F.; Enright, K.; Dent, R.; Dranitsaris, G.; Myers, J.; Flynn, C.; Fralick, M.; Kumar, R.; Clemons, M. Survival Outcomes for Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Implications for Clinical Practice and Trial Design. Clin. Breast Cancer 2009, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Shah, A.N.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; Cruz, M.R.; Mahalingam, D.; Carneiro, B.A.; Chae, Y.K.; Cristofanilli, M.; Gradishar, W.J.; Giles, F.J. Targeting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: New Discoveries and Practical Insights for Drug Development. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 53, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Features and Patterns of Recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Brown, M.M.; Bae, I. Targeting Mutant P53 by a SIRT1 Activator YK-3-237 Inhibits the Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Kong, H.-S.; Grindrod, S.; et al. Novel Carbazole Inhibits Phospho-STAT3 through Induction of Protein–Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN6. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6342–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.J.; Yi, Y.W.; Hou, S.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Bae, I.; Brown, M.L. Disruption of STAT3-DNMT1 Interaction by SH-I-14 Induces Re-Expression of Tumor Suppressor Genes and Inhibits Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Tumor. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 83457–83468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eccles, S.A. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Erb-B/HER Family in Normal and Malignant Breast Biology. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Pines, G. The ERBB Network: At Last, Cancer Therapy Meets Systems Biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Dunn, E.F.; Harari, P.M. Understanding Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors—Impact on Future Treatment Strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulkifli, A.A.; Tan, F.H.; Putoczki, T.L.; Stylli, S.S.; Luwor, R.B. STAT3 Signaling Mediates Tumour Resistance to EGFR Targeted Therapeutics. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 451, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB Signalling Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Truica, C.I. Challenges in the Development of Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Therapies in Breast Cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.B.; Kim, J.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. Exploring Protein Kinase Inhibitors: Potentiating Gemcitabine Efficacy in Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2012, 41, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Hong, Y.B.; Cho, C.H.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. Exploring Protein Kinase Inhibitors: Unveiling Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2012, 41, 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duong, H.; Hong, Y.B.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.; Yi, Y.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Wang, A.; Zhao, W.; Cho, C.H.; Seong, Y.; et al. Inhibition of Checkpoint Kinase 2 (CHK2) Enhances Sensitivity of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cells to Gemcitabine. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Wang, A.; Bae, I. Inhibition of Constitutively Activated Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT Pathway Enhances Antitumor Activity of Chemotherapeutic Agents in Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene 1-defective Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Hong, W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, A.; Seong, Y.; Bae, I. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway Potentiates Cytotoxicity of EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.-Q.; Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Bae, I.; Jang, Y.-J.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Combination of Dasatinib and Gemcitabine Reduces the ALDH1A1 Expression and the Proliferation of Gemcitabine-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer MIA PaCa-2 Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 2132–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duong, H.-Q.; Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Hong, Y.B.; Tang, W.; Wang, A.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. Inhibition of NRF2 by PIK-75 Augments Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 44, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Heijkants, R.C.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Dogrusöz, M.; de Lange, M.J.; van der Velden, P.A.; van der Burg, S.H.; Jager, M.J.; Verdijk, R.M. Targeting of the MAPK and AKT Pathways in Conjunctival Melanoma Shows Potential Synergy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 58021–58036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; Park, J.-S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Co-Treatment with BEZ235 Enhances Sensitivity of BRCA1-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Olaparib. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3829–3838. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.W.; You, K.; Bae, E.J.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. Dual Inhibition of EGFR and MET Induces Synthetic Lethality in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Ribosomal Protein S6. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayub, A.; Yip, W.K.; Seow, H.F. Dual Treatments Targeting IGF-1R, PI3K, MTORC or MEK Synergize to Inhibit Cell Growth, Induce Apoptosis, and Arrest Cell Cycle at G1 Phase in MDA-MB-231 Cell Line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 75, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiello, M.R.; D’Alessio, A.; Bevilacqua, S.; Gallo, M.; Normanno, N.; Luca, A.D. EGFR and MEK Blockade in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 2778–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Inhibition of RPTOR Overcomes Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; McLaughlin, R.P.; van der Noord, V.; Foekens, J.A.; Martens, J.W.M.; van Westen, G.; Zhang, Y.; van de Water, B. Multi-Targeted Kinase Inhibition Alleviates MTOR Inhibitor Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 178, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajor, M.; Graczyk-Jarzynka, A.; Marhelava, K.; Kurkowiak, M.; Rahman, A.; Aura, C.; Russell, N.; Zych, A.O.; Firczuk, M.; Winiarska, M.; et al. Triple Combination of Ascorbate, Menadione and the Inhibition of Peroxiredoxin-1 Produces Synergistic Cytotoxic Effects in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattarawat, P.; Wallace, S.; Pfisterer, B.; Odoi, A.; Wang, H.-C.R. Formulation of a Triple Combination Gemcitabine plus Romidepsin + Cisplatin Regimen to Efficaciously and Safely Control Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Tumor Development. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; He, Q.; Williams, K.P.; Scott, J.E. Identification of a Triple Drug Combination That Is Synergistically Cytotoxic for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Using a Novel Combination Discovery Approach. SLAS Discov. 2020, 25, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-J.; Yi, Y.-W.; Kim, J.H. In Situ Monitoring of Bindings between Dasatinib and Its Target Protein Kinases Using Magnetic Nanoparticles in Live Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16466–16467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkovsky, N.; Berezov, A. BIBW-2992, a Dual Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs Lond. Engl. 2000 2008, 9, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kakefuda, R.; Tajima, N.; Sowa, Y.; Sakai, T. Antitumor Activities of JTP-74057 (GSK1120212), a Novel MEK1/2 Inhibitor, on Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines in Vitro and in Vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.I.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.; Hong, D.; Lim, H.; Cho, K.; Jung, N.; Yi, Y.W. Application of a Non-Hazardous Vital Dye for Cell Counting with Automated Cell Counters. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 492, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cool, B.; Zinker, B.; Chiou, W.; Kifle, L.; Cao, N.; Perham, M.; Dickinson, R.; Adler, A.; Gagne, G.; Iyengar, R.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Small Molecule AMPK Activator That Treats Key Components of Type 2 Diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grimshaw, K.M.; Hunter, L.-J.K.; Yap, T.A.; Heaton, S.P.; Walton, M.I.; Woodhead, S.J.; Fazal, L.; Reule, M.; Davies, T.G.; Seavers, L.C.; et al. AT7867 Is a Potent and Oral Inhibitor of AKT and P70 S6 Kinase That Induces Pharmacodynamic Changes and Inhibits Human Tumor Xenograft Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howard, S.; Berdini, V.; Boulstridge, J.A.; Carr, M.G.; Cross, D.M.; Curry, J.; Devine, L.A.; Early, T.R.; Fazal, L.; Gill, A.L.; et al. Fragment-Based Discovery of the Pyrazol-4-Yl Urea (AT9283), a Multitargeted Kinase Inhibitor with Potent Aurora Kinase Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ikezoe, T.; Nishioka, C.; Tasaka, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Kuwayama, Y.; Komatsu, N.; Bandobashi, K.; Togitani, K.; Koeffler, H.P.; et al. AZD1152, a Novel and Selective Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Growth Arrest, Apoptosis, and Sensitization for Tubulin Depolymerizing Agent or Topoisomerase II Inhibitor in Human Acute Leukemia Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derenzini, E.; Lemoine, M.; Buglio, D.; Katayama, H.; Ji, Y.; Davis, R.E.; Sen, S.; Younes, A. The JAK Inhibitor AZD1480 Regulates Proliferation and Immunity in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2011, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steegmaier, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Baum, A.; Lénárt, P.; Petronczki, M.; Krššák, M.; Gürtler, U.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Lieb, S.; Quant, J.; et al. BI 2536, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Polo-like Kinase 1, Inhibits Tumor Growth In Vivo. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Yap, J.L.; Yoshioka, M.; Lanning, M.E.; Fountain, R.N.; Raje, M.; Scheenstra, J.A.; Strovel, J.W.; Fletcher, S. BRD4 Structure–Activity Relationships of Dual PLK1 Kinase/BRD4 Bromodomain Inhibitor BI-2536. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tatake, R.J.; O’Neill, M.M.; Kennedy, C.A.; Wayne, A.L.; Jakes, S.; Wu, D.; Kugler, S.Z.; Kashem, M.A.; Kaplita, P.; Snow, R.J. Identification of Pharmacological Inhibitors of the MEK5/ERK5 Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Myers, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Fenyk-Melody, J.; Wu, M.; Ventre, J.; Doebber, T.; Fujii, N.; et al. Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Mechanism of Metformin Action. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschelli, D.H.; Ye, F.; Wang, Y.D.; Dutia, M.; Johnson, S.L.; Wu, B.; Miller, K.; Powell, D.W.; Yaczko, D.; Young, M.; et al. Optimization of 4-Phenylamino-3-Quinolinecarbonitriles as Potent Inhibitors of Src Kinase Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golas, J.M.; Arndt, K.; Etienne, C.; Lucas, J.; Nardin, D.; Gibbons, J.; Frost, P.; Ye, F.; Boschelli, D.H.; Boschelli, F. SKI-606, a 4-Anilino-3-Quinolinecarbonitrile Dual Inhibitor of Src and Abl Kinases, Is a Potent Antiproliferative Agent against Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cells in Culture and Causes Regression of K562 Xenografts in Nude Mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.-L.; Lee, M.C.; Tan, K.O.; Yang, L.-K.; Lee, A.S.Y.; Flotow, H.; Fu, N.Y.; Butler, M.S.; Soejarto, D.D.; Buss, A.D.; et al. Identification of Chelerythrine as an Inhibitor of BclXL Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20453–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ring, D.B.; Johnson, K.W.; Henriksen, E.J.; Nuss, J.M.; Goff, D.; Kinnick, T.R.; Ma, S.T.; Reeder, J.W.; Samuels, I.; Slabiak, T.; et al. Selective Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Inhibitors Potentiate Insulin Activation of Glucose Transport and Utilization In Vitro and In Vivo. Diabetes 2003, 52, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebolt-Leopold, J.S.; Dudley, D.T.; Herrera, R.; Becelaere, K.V.; Wiland, A.; Gowan, R.C.; Tecle, H.; Barrett, S.D.; Bridges, A.; Przybranowski, S.; et al. Blockade of the MAP Kinase Pathway Suppresses Growth of Colon Tumors in Vivo. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changelian, P.S.; Flanagan, M.E.; Ball, D.J.; Kent, C.R.; Magnuson, K.S.; Martin, W.H.; Rizzuti, B.J.; Sawyer, P.S.; Perry, B.D.; Brissette, W.H.; et al. Prevention of Organ Allograft Rejection by a Specific Janus Kinase 3 Inhibitor. Science 2003, 302, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Midgley, C.A.; Scaërou, F.; Grabarek, J.B.; Griffiths, G.; Jackson, W.; Kontopidis, G.; McClue, S.J.; McInnes, C.; Meades, C.; et al. Discovery of N-Phenyl-4-(Thiazol-5-Yl)Pyrimidin-2-Amine Aurora Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4367–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpinelli, P.; Ceruti, R.; Giorgini, M.L.; Cappella, P.; Gianellini, L.; Croci, V.; Degrassi, A.; Texido, G.; Rocchetti, M.; Vianello, P.; et al. PHA-739358, a Potent Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases with a Selective Target Inhibition Profile Relevant to Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3158–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graff, J.R.; McNulty, A.M.; Hanna, K.R.; Konicek, B.W.; Lynch, R.L.; Bailey, S.N.; Banks, C.; Capen, A.; Goode, R.; Lewis, J.E.; et al. The Protein Kinase Cβ–Selective Inhibitor, Enzastaurin (LY317615.HCl), Suppresses Signaling through the AKT Pathway, Induces Apoptosis, and Suppresses Growth of Human Colon Cancer and Glioblastoma Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7462–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono-Saito, N.; Niki, I.; Hidaka, H. H-Series Protein Kinase Inhibitors and Potential Clinical Applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 82, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohori, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Okubo, M.; Sato, K.; Yamazaki, A.; Arakawa, H.; Nishimura, S.; Inamura, N.; Nakajima, H.; Neya, M.; et al. Identification of a Selective ERK Inhibitor and Structural Determination of the Inhibitor–ERK2 Complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.; Belvin, M.; Herter, S.; Hoeflich, K.P.; Murray, L.J.; Wong, L.; Choo, E.F. Pharmacodynamics of 2-{4-[(1E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-5-Yl]-3-(Pyridine-4-Yl)-1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl}ethan-1-Ol (GDC-0879), a Potent and Selective B-Raf Kinase Inhibitor: Understanding Relationships between Systemic Concentrations, Phosphorylated Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1 Inhibition, and Efficacy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansing, T.J.; McConnell, R.T.; Duckett, D.R.; Spehar, G.M.; Knick, V.B.; Hassler, D.F.; Noro, N.; Furuta, M.; Emmitte, K.A.; Gilmer, T.M.; et al. In Vitro Biological Activity of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Polo-like Kinase 1. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclerc, S.; Garnier, M.; Hoessel, R.; Marko, D.; Bibb, J.A.; Snyder, G.L.; Greengard, P.; Biernat, J.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Mandelkow, E.-M.; et al. Indirubins Inhibit Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β and CDK5/P25, Two Protein Kinases Involved in Abnormal Tau Phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s Disease a Property Common to Most Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors? J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waelchli, R.; Bollbuck, B.; Bruns, C.; Buhl, T.; Eder, J.; Feifel, R.; Hersperger, R.; Janser, P.; Revesz, L.; Zerwes, H.-G.; et al. Design and Preparation of 2-Benzamido-Pyrimidines as Inhibitors of IKK. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Griffith, D.J.; Druker, B.J.; Wait, C.L.; Ott, K.A.; Zigler, A.J. Inhibition of C-Kit Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activity by STI 571, a Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Blood 2000, 96, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Vaddi, K.; Liu, P.; Manshouri, T.; Li, J.; Scherle, P.A.; Caulder, E.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Waeltz, P.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of the Selective JAK1/2 Inhibitor INCB018424: Therapeutic Implications for the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2010, 115, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, S.; Rugg, C.A.; Gruninger, R.H.; Lin, R.; Fuentes-Pesquera, A.; Connolly, P.J.; Wetter, S.K.; Hollister, B.; Kruger, W.W.; Napier, C.; et al. The In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of JNJ-7706621: A Dual Inhibitor of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases and Aurora Kinases. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9038–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hickson, I.; Zhao, Y.; Richardson, C.J.; Green, S.J.; Martin, N.M.B.; Orr, A.I.; Reaper, P.M.; Jackson, S.P.; Curtin, N.J.; Smith, G.C.M. Identification and Characterization of a Novel and Specific Inhibitor of the Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated Kinase ATM. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 9152–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mader, M.; de Dios, A.; Shih, C.; Bonjouklian, R.; Li, T.; White, W.; de Uralde, B.L.; Sánchez-Martinez, C.; del Prado, M.; Jaramillo, C.; et al. Imidazolyl Benzimidazoles and Imidazo[4,5-b]Pyridines as Potent P38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors with Excellent in Vivo Antiinflammatory Properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.G.; Ecsedy, J.A.; Chakravarty, A.; Silverman, L.; Zhang, M.; Hoar, K.M.; Stroud, S.G.; Chen, W.; Shinde, V.; Huck, J.J.; et al. Characterization of Alisertib (MLN8237), an Investigational Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora A Kinase Using Novel In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Assays. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7614–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisberg, E.; Catley, L.; Wright, R.D.; Moreno, D.; Banerji, L.; Ray, A.; Manley, P.W.; Mestan, J.; Fabbro, D.; Jiang, J.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Combining Nilotinib and Imatinib in Preclinical Models of BCR-ABL+ Leukemias. Blood 2007, 109, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jobson, A.G.; Cardellina, J.H.; Scudiero, D.; Kondapaka, S.; Zhang, H.; Kim, H.; Shoemaker, R.; Pommier, Y. Identification of a Bis-Guanylhydrazone [4,4′-Diacetyldiphenylurea-Bis(Guanylhydrazone); NSC 109555] as a Novel Chemotype for Inhibition of Chk2 Kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leahy, J.J.J.; Golding, B.T.; Griffin, R.J.; Hardcastle, I.R.; Richardson, C.; Rigoreau, L.; Smith, G.C.M. Identification of a Highly Potent and Selective DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase (DNA-PK) Inhibitor (NU7441) by Screening of Chromenone Libraries. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 6083–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.D.; Bridges, A.J.; Dudley, D.T.; Saltiel, A.R.; Fergus, J.H.; Flamme, C.M.; Delaney, A.M.; Kaufman, M.; LePage, S.; Leopold, W.R.; et al. The Discovery of the Benzhydroxamate MEK Inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6501–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.D.; Thompson, A.M.; Booth, R.J.; Dobrusin, E.M.; Kraker, A.J.; Lee, H.H.; Lunney, E.A.; Mitchell, L.H.; Ortwine, D.F.; Smaill, J.B.; et al. 4-Phenylpyrrolo[3,4-c]Carbazole-1,3(2H,6H)-Dione Inhibitors of the Checkpoint Kinase Wee1. Structure−Activity Relationships for Chromophore Modification and Phenyl Ring Substitution. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4896–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L.R.; Alton, G.R.; Richter, D.T.; Kath, J.C.; Lingardo, L.; Chapman, J.; Hwang, C.; Alessi, D.R. Characterization of PF-4708671, a Novel and Highly Specific Inhibitor of P70 Ribosomal S6 Kinase (S6K1). Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slack-Davis, J.K.; Martin, K.H.; Tilghman, R.W.; Iwanicki, M.; Ung, E.J.; Autry, C.; Luzzio, M.J.; Cooper, B.; Kath, J.C.; Roberts, W.G.; et al. Cellular Characterization of a Novel Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14845–14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbro, D.; Buchdunger, E.; Wood, J.; Mestan, J.; Hofmann, F.; Ferrari, S.; Mett, H.; O’Reilly, T.; Meyer, T. Inhibitors of Protein Kinases CGP 41251, a Protein Kinase Inhibitor with Potential as an Anticancer Agent. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 82, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollag, G.; Hirth, P.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ibrahim, P.N.; Cho, H.; Spevak, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Habets, G.; et al. Clinical Efficacy of a RAF Inhibitor Needs Broad Target Blockade in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma. Nature 2010, 467, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Lee, J.T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cho, H.; Mamo, S.; Bremer, R.; Gillette, S.; Kong, J.; Haass, N.K.; et al. Discovery of a Selective Inhibitor of Oncogenic B-Raf Kinase with Potent Antimelanoma Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, S.E.; Parker, P.J.; Nixon, J.S. Isoenzyme Specificity of Bisindolylmaleimides, Selective Inhibitors of Protein Kinase C. Biochem. J. 1993, 294, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, L.; Borgne, A.; Mulner, O.; Chong, J.P.J.; Blow, J.J.; Inagaki, N.; Inagaki, M.; Delcros, J.; Moulinoux, J. Biochemical and Cellular Effects of Roscovitine, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinases Cdc2, Cdk2 and Cdk5. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghlan, M.P.; Culbert, A.A.; Cross, D.A.; Corcoran, S.L.; Yates, J.W.; Pearce, N.J.; Rausch, O.L.; Murphy, G.J.; Carter, P.S.; Cox, L.R.; et al. Selective Small Molecule Inhibitors of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Modulate Glycogen Metabolism and Gene Transcription. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.R.; Gilmartin, A.; Imburgia, C.; Winkler, J.D.; Marshall, L.A.; Roshak, A. An Indolocarbazole Inhibitor of Human Checkpoint Kinase (Chk1) Abrogates Cell Cycle Arrest Caused by DNA Damage. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 566–572. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, A.; Stockett, D.E.; Walker, D.; Arkin, M.R.; Hoch, U.; Fox, J.A.; Hawtin, R.E. SNS-032 Is a Potent and Selective CDK 2, 7 and 9 Inhibitor That Drives Target Modulation in Patient Samples. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 64, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oslob, J.D.; Romanowski, M.J.; Allen, D.A.; Baskaran, S.; Bui, M.; Elling, R.A.; Flanagan, W.M.; Fung, A.D.; Hanan, E.J.; Harris, S.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective Aurora Kinase Inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4880–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.L.; Sasaki, D.T.; Murray, B.W.; O’Leary, E.C.; Sakata, S.T.; Xu, W.; Leisten, J.C.; Motiwala, A.; Pierce, S.; Satoh, Y.; et al. SP600125, an Anthrapyrazolone Inhibitor of Jun N-Terminal Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13681–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagano, M.A.; Poletto, G.; Maira, G.D.; Cozza, G.; Ruzzene, M.; Sarno, S.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Moro, S.; Zagotto, G.; et al. Tetrabromocinnamic Acid (TBCA) and Related Compounds Represent a New Class of Specific Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Zhu, J.; Johnson, M.D.; Chen, P.; Kornmann, J.; Chen, E.; Blasina, A.; Register, J.; Anderes, K.; Rogers, C.; et al. Structure-Based Design of (5-Arylamino-2 H -Pyrazol-3-Yl)-Biphenyl-2‘,4‘-Diols as Novel and Potent Human CHK1 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5253–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheney, I.W.; Yan, S.; Appleby, T.; Walker, H.; Vo, T.; Yao, N.; Hamatake, R.; Hong, Z.; Wu, J.Z. Identification and Structure–Activity Relationships of Substituted Pyridones as Inhibitors of Pim-1 Kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beharry, Z.; Zemskova, M.; Mahajan, S.; Zhang, F.; Ma, J.; Xia, Z.; Lilly, M.; Smith, C.D.; Kraft, A.S. Novel Benzylidene-Thiazolidine-2,4-Diones Inhibit Pim Protein Kinase Activity and Induce Cell Cycle Arrest in Leukemia and Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrington, E.A.; Bebbington, D.; Moore, J.; Rasmussen, R.K.; Ajose-Adeogun, A.O.; Nakayama, T.; Graham, J.A.; Demur, C.; Hercend, T.; Diu-Hercend, A.; et al. VX-680, a Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Aurora Kinases, Suppresses Tumor Growth in Vivo. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, G.M.T.; Charlton, P.A.; Golec, J.M.C.; Pollard, J.R. Structural Basis for Potent Inhibition of the Aurora Kinases and a T315I Multi-Drug Resistant Mutant Form of Abl Kinase by VX-680. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolin, P.L.; Callahan, J.F.; Bolognese, B.J.; Li, Y.H.; Carlson, K.; Davis, T.G.; Mellor, G.W.; Evans, C.; Roshak, A.K. Attenuation of Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis by a Novel, Potent, Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of IκB Kinase 2, TPCA-1 (2-[(Aminocarbonyl)Amino]-5-(4-Fluorophenyl)-3-Thiophenecarboxamide), Occurs via Reduction of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Antigen-Induced T Cell Proliferation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncia, J.V.; Santella, J.B.; Higley, C.A.; Pitts, W.J.; Wityak, J.; Frietze, W.E.; Rankin, F.W.; Sun, J.-H.; Earl, R.A.; Tabaka, A.C.; et al. MEK Inhibitors: The Chemistry and Biological Activity of U0126, Its Analogs, and Cyclization Products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 2839–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliopulos, A.; Mohanlal, R.; Covic, L. Effect of Selective Inhibition of the P38 MAP Kinase Pathway on Platelet Aggregation. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehata, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Satoh, H.; Ono, T.; Kawahara, T.; Morishita, T.; Tamakawa, H.; Yamagami, K.; Inui, J.; Maekawa, M.; et al. Calcium Sensitization of Smooth Muscle Mediated by a Rho-Associated Protein Kinase in Hypertension. Nature 1997, 389, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, T.; Uehata, M.; Tamechika, I.; Keel, J.; Nonomura, K.; Maekawa, M.; Narumiya, S. Pharmacological Properties of Y-27632, a Specific Inhibitor of Rho-Associated Kinases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Ditchfield, C.; Johnson, V.L.; Tighe, A.; Ellston, R.; Haworth, C.; Johnson, T.; Mortlock, A.; Keen, N.; Taylor, S.S. Aurora B Couples Chromosome Alignment with Anaphase by Targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to Kinetochores. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.-Q.; You, K.; Oh, S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Silencing of NRF2 Reduces the Expression of ALDH1A1 and ALDH3A1 and Sensitizes to 5-FU in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Q.; Esteva, F.J. Cross-Talk Between the ErbB/HER Family and the Type I Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. 2008, 13, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouzis, M.V.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Targeting MET as a Strategy to Overcome Crosstalk-Related Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nahta, R.; Yu, D.; Hung, M.-C.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Esteva, F.J. Mechanisms of Disease: Understanding Resistance to HER2-Targeted Therapy in Human Breast Cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2006, 3, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Chang, S.-S.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.-C. Signaling Cross-Talk in the Resistance to HER Family Receptor Targeted Therapy. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baselga, J. Targeting Tyrosine Kinases in Cancer: The Second Wave. Science 2006, 312, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, J.; Reifferscheid, G.; Waldmann, P.; Leyhausen, G.; Geurtsen, W. Genotoxicity of Dental Materials. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1996, 368, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyuhas, O. Ribosomal Protein S6 Phosphorylation Four Decades of Research. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 320, 41–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandarlapaty, S.; Sawai, A.; Scaltriti, M.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.; Grbovic-Huezo, O.; Serra, V.; Majumder, P.K.; Baselga, J.; Rosen, N. AKT Inhibition Relieves Feedback Suppression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Expression and Activity. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, V.; Scaltriti, M.; Prudkin, L.; Eichhorn, P.J.A.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Markman, B.; Rodriguez, O.; Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, S.; et al. PI3K Inhibition Results in Enhanced HER Signaling and Acquired ERK Dependency in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2547–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Sánchez, V.; Kuba, M.G.; Rinehart, C.; Arteaga, C.L. Feedback Upregulation of HER3 (ErbB3) Expression and Activity Attenuates Antitumor Effect of PI3K Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2718–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrett, J.T.; Olivares, M.G.; Rinehart, C.; Granja-Ingram, N.D.; Sánchez, V.; Chakrabarty, A.; Dave, B.; Cook, R.S.; Pao, W.; McKinely, E.; et al. Transcriptional and Posttranslational Up-Regulation of HER3 (ErbB3) Compensates for Inhibition of the HER2 Tyrosine Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5021–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajstura, M.; Halicka, H.D.; Pryjma, J.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Discontinuous Fragmentation of Nuclear DNA during Apoptosis Revealed by Discrete “Sub-G1” Peaks on DNA Content Histograms. Cytom. Part A 2007, 71A, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umansky, S.R.; Korol’, B.A.; Nelipovich, P.A. In Vivo DNA Degradation in Thymocytes of γ-Irradiated or Hydrocortisone-Treated Rats. BBA Nucleic Acids Protein Synth. 1981, 655, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.G.; King, L.E.; Fraker, P.J. Evaluation of Glucocorticoid-induced DNA Fragmentation in Mouse Thymocytes by Flow Cytometry. Cell Prolif. 1991, 24, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.G.; King, L.E.; Fraker, P.J. Comparative Evaluation of Several DNA Binding Dyes in the Detection of Apoptosis-associated Chromatin Degradation by Flow Cytometry. Cytometry 1992, 13, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Traganos, F.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. A Selective Procedure for DNA Extraction from Apoptotic Cells Applicable for Gel Electrophoresis and Flow Cytometry. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 218, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzynkiewicz, Z.; Juan, G.; Li, X.; Gorczyca, W.; Murakami, T.; Traganos, F. Cytometry in Cell Necrobiology: Analysis of Apoptosis and Accidental Cell Death (Necrosis). Cytometry 1997, 27, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, K.M.; Ghanayem, R.B.; Peplinski, S.; Lyerly, H.K.; Devi, G.R. X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein Inhibits Apoptosis in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cells with Acquired Resistance to an ErbB1/2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; You, D.; Jeong, Y.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E. Berberine Down-Regulates IL-8 Expression through Inhibition of the EGFR/MEK/ERK Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. EGFR Promotes the Development of Triple Negative Breast Cancer through JAK/STAT3 Signaling. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohn, J.; Liu, S.; Parinyanitikul, N.; Lee, J.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Mills, G.B.; Ueno, N.T.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. CMET Activation and EGFR-Directed Therapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simiczyjew, A.; Dratkiewicz, E.; Troys, M.V.; Ampe, C.; Styczeń, I.; Nowak, D. Combination of EGFR Inhibitor Lapatinib and MET Inhibitor Foretinib Inhibits Migration of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2018, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Hou, J.-Z.; Niu, J.; Xi, Z.-Q.; Ma, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.-J.; Fang, D.; Li, Q.; Xie, S.-Q. Akt1 Inhibition Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis through EGFR-Mediated β-Catenin Nuclear Accumulation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleisher, B.; Mody, H.; Werkman, C.; Ait-Oudhia, S. Chloroquine Sensitizes MDA-MB-231 Cells to Osimertinib through Autophagy–Apoptosis Crosstalk Pathway. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 11, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrab, A.E.; Bamdad, M.; Bignon, Y.-J.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Aubel, C. Co-Targeting EGFR and MTOR with Gefitinib and Everolimus in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu-Rocca, P.; Orrù, S.; Muroni, M.R.; Sanges, F.; Sotgiu, G.; Ena, S.; Pira, G.; Murgia, L.; Manca, A.; Uras, M.G.; et al. Analysis of PIK3CA Mutations and Activation Pathways in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pao, W.; Wang, T.Y.; Riely, G.J.; Miller, V.A.; Pan, Q.; Ladanyi, M.; Zakowski, M.F.; Heelan, R.T.; Kris, M.G.; Varmus, H.E. KRAS Mutations and Primary Resistance of Lung Adenocarcinomas to Gefitinib or Erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xue, L.; Yang, L. Expression and Clinical Significance of MAPK and EGFR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeusz, C.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Liu, P.; Hayashi, N.; Lluch, A.; Ferrer-Lozano, J.; Hortobágyi, G.N. High ERK Protein Expression Levels Correlate with Shorter Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Oncologist 2012, 17, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholami, S.; Chen, C.-H.; Gao, S.; Lou, E.; Fujisawa, S.; Carson, J.; Nnoli, J.E.; Chou, T.-C.; Bromberg, J.; Fong, Y. Role of MAPK in Oncolytic Herpes Viral Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; O’Brien, C.; Boyd, Z.; Cavet, G.; Guerrero, S.; Jung, K.; Januario, T.; Savage, H.; Punnoose, E.; Truong, T.; et al. In Vivo Antitumor Activity of MEK and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitors in Basal-Like Breast Cancer Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4649–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; McLellan, M.D.; Schmidt, H.; Kalicki-Veizer, J.; McMichael, J.F.; Fulton, L.L.; Dooling, D.J.; Ding, L.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Howard, E.W.; Parris, A.B.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, X. Alcohol Promotes Migration and Invasion of Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells through Activation of P38 MAPK and JNK. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, N.; Kanematsu, S.; Miki, H.; Yoshizawa, K.; Tsubura, A. Requirement of P38 MAPK for a Cell-Death Pathway Triggered by Vorinostat in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 315, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; He, R.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Hou, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Ginsenoside 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis in Vivo by Targeting EGFR-Mediated MAPK Pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.S.; Whittle, M.C.; Nakamura, K.; Abell, A.N.; Midland, A.A.; Zawistowski, J.S.; Johnson, N.L.; Granger, D.A.; Jordan, N.V.; Darr, D.B.; et al. Dynamic Reprogramming of the Kinome in Response to Targeted MEK Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swearingen, A.E.D.V.; Sambade, M.J.; Siegel, M.B.; Sud, S.; McNeill, R.S.; Bevill, S.M.; Chen, X.; Bash, R.E.; Mounsey, L.; Golitz, B.T.; et al. Combined Kinase Inhibitors of MEK1/2 and Either PI3K or PDGFR Are Efficacious in Intracranial Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.J.; Whichard, Z.L.; Corey, S.J. Dasatinib Synergizes with Both Cytotoxic and Signal Transduction Inhibitors in Heterogeneous Breast Cancer Cell Lines—Lessons for Design of Combination Targeted Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2012, 320, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramaswamy, B.; Mrozek, E.; Lustberg, M.; Wesolowski, R.; Layman, R.; Abdel-Rasoul, M.; Timmers, C.; Patrick, R.; Sexton, J.; Macrae, E.; et al. Abstract LB-216: NCI 9455: Phase II Study of Trametinib Followed by Trametinib plus AKT Inhibitor, GSK2141795 in Patients with Advanced Triple Negative Breast Cancer. In Proceedings of the AACR 107th Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 16–20 April 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Cho, J.; Seong, Y.-S. Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061205
You KS, Yi YW, Cho J, Seong Y-S. Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061205
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Kyu Sic, Yong Weon Yi, Jeonghee Cho, and Yeon-Sun Seong. 2021. "Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061205
APA StyleYou, K. S., Yi, Y. W., Cho, J., & Seong, Y.-S. (2021). Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers, 13(6), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061205






