Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
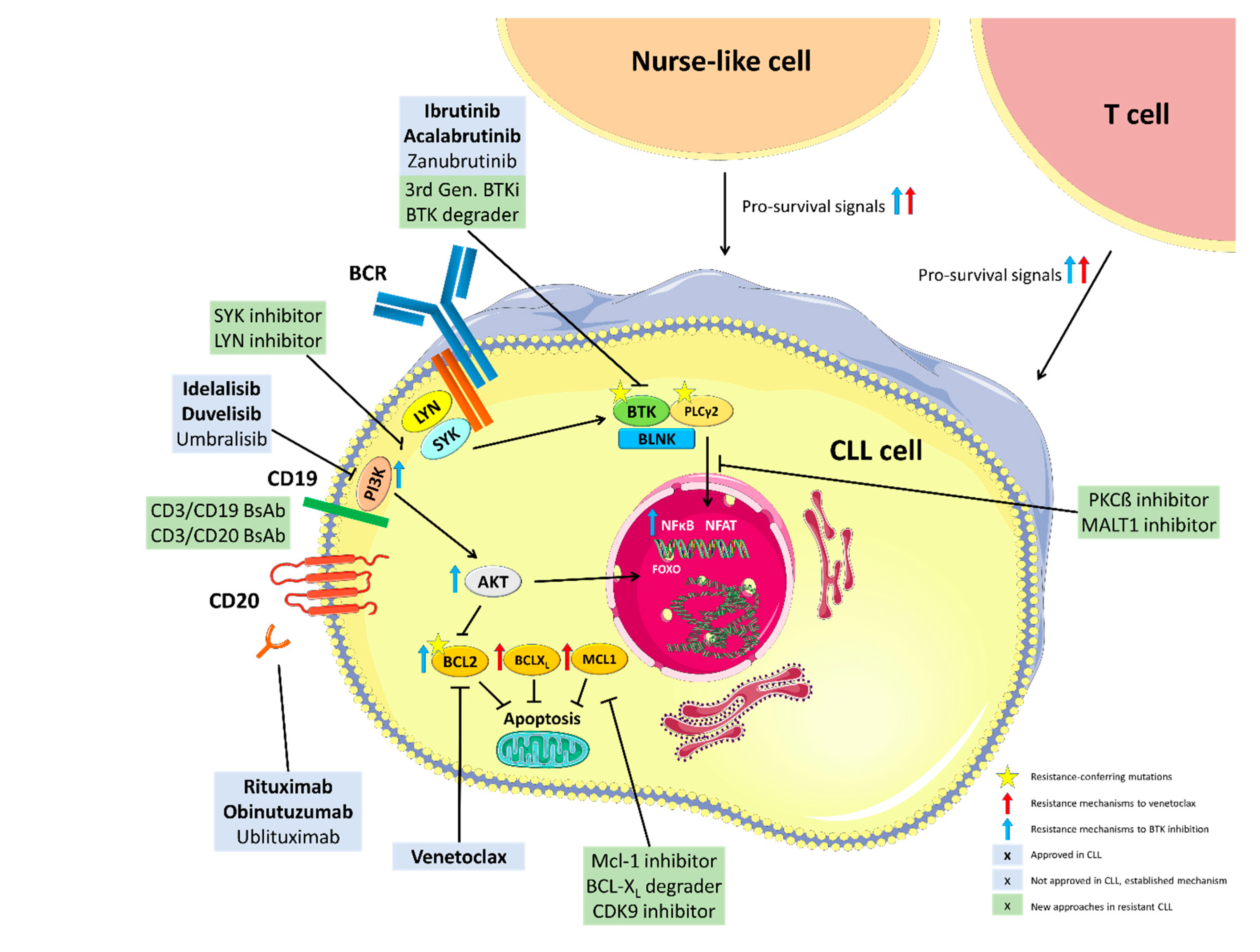
2. Mechanisms of Resistance to BTK Inhibition
2.1. Genetic Mechanisms of Resistance to BTK Inhibition
2.2. Non-Genetic Mechanisms of Resistance to Ibrutinib
3. Mechanisms of Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors
4. Mechanisms of Venetoclax Resistance
4.1. Mutations in BCL2 and Alterations in Cancer-Related Genes
4.2. Changes in Cellular Metabolism/Bcl-2 Family Members
5. Strategies to Prevent Resistance to Novel Agents
- In the pivotal studies, acquired BTK and BCL2 mutations could be detected months and even years [11,21] before the patients fulfilled the iwCLL criteria [77] of clinical disease progression. Following these observations, Woyach and colleagues initiated a prospective study on 112 patients receiving ibrutinib monotherapy and performed serial screening for known resistance mutations [33]. They demonstrated that mutations in BTK and PLCG2 occurred early and clearly correlated with consequent clinical disease progression and could thus be used as a biomarker for relapse and an opportunity to adapt treatment [33]. Hence, a future strategy could be to monitor resistance similarly to strategies in antiviral treatments as for example HIV.
- Constant selection pressure by administering continuous monotherapies with BTKis or Bcl-2 inhibitors might contribute to the acquisition of resistance mutations in a significant number of patients. Hence, avoiding constant drug exposure and selection of BTKi- and venetoclax-resistant clones by using time-limited treatment approaches could be another option to circumvent the development of resistance.
- Another promising strategy to circumvent the acquisition of resistance to novel agents is the development of next generation inhibitors which bind non-covalently to the target kinase and are therefore still active in CLL cells harboring the most common resistance mutations.
5.1. Time-Limited Combination Treatments
| Name/Identifier | Experimental Treatment Arm | Phase | TN vs. R/R | Efficacy (Experimental Treatment Arm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venetoclax + anti-CD20 antibody | |||||
| MURANO NCT02005471 | Venetoclax + rituximab | 3 | R/R | Post-treatment uMRD rate: 62% 5-year PFS/ 5-year OS: 51.1%/82.1% | Seymour et al. 2018 [8] |
| CLL14 NCT02242942 | Venetoclax + obinutuzumab | 3 | TN | Post-treatment uMRD: 75.5% 4-year PFS/ 4-year OS: 74%/85.3% | Fischer et al. 2019 [7] |
| CLL2-BAG NCT02401503 | (Bendamustine) + venetoclax + Obinutuzumab | 2 | TN, R/R | Post-treatment uMRD: 87% 15-month PFS/ 15-month OS: 92%/95% | Cramer et al. 2018 [63] |
| Venetoclax + BTK inhibitor | |||||
| CAPTIVATE NCT02910583 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 2 | TN | 1-year uMRD rate: 73% 30-month PFS: >95% | Wierda et al. 2020 [85] |
| NCT02756897 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 2 | TN | 1-year uMRD rate: 61% 1-year PFS/1-yeary OS: 98%/99% | Jain et al. 2019 [28] |
| CLARITY 2015-003422-14 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 2 | TN | 1-year uMRD rate: 53% | Hillmen et al. 2019 [27] |
| VISION NCT03226301 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 2 | R/R | 15-month uMRD rate: 55% | Niemann et al. 2020 [29] |
| Triple combinations | |||||
| NCT02427451 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib + obinutuzumab | 2 | TN, R/R | Post-treatment uMRD rate TN: 67% Post-treatment uMRD rate R/R: 50% | Rogers et al. 2020 [30] |
| CLL2-GIVe NCT02758665 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib + obinutuzumab | 2 | TN | Post-treatment uMRD rate: 81% | Huber et al. 2020 [86] |
| CLL-003 NCT02296918 | Acalabrutinib + venetoclax + obinutuzumab | 1b | TN, R/R | 10-month uMRD rate: 71% 18-month PFS/18-month OS: 100%/100% | Woyach et al. 2020 [87] |
| NCT03580928 | Acalabrutinib + venetoclax + obinutuzumab | 2 | TN | 16-month uMRD rate: 84% | Davids et al. 2020 [88] |
| NCT03824483 | Zanubrutinib + venetoclax + obinutuzumab | 2 | TN | Overall uMRD rate: 92% | Soumerai et al. 2020 [89] |
5.2. Non-Covalent BTK Inhibitors and BTK Degraders
6. Treatment Options in Case of Clinical Resistance to Novel Agents
6.1. Optimal Sequencing of Approved Agents
6.2. Other B-Cell Receptor Pathway-Targeting Approaches
6.3. Other Currently Investigated Non-Cellular Experimental Treatments
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burger, J.A. Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Eichhorst, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 391, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Tedeschi, A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Li, J.; et al. Ibrutinib as Initial Therapy for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Harrington, B.; O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Schuh, A.; Devereux, S.; Chaves, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Awan, F.T.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Tandon, M.; Dixon, M.; Robrecht, S.; Warburton, S.; Humphrey, K.; Samoylova, O.; et al. Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab in Patients with CLL and Coexisting Conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Ibrutinib-Rituximab or Chemoimmunotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Furman, R.R.; Liu, T.M.; Ozer, H.G.; Zapatka, M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Xue, L.; Li, D.H.; Steggerda, S.M.; Versele, M.; et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Barr, P.M.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Regimens versus Chemoimmunotherapy in Older Patients with Untreated CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, P.; Dohner, H.; Ritgen, M.; Bottcher, S.; Busch, R.; Dietrich, S.; Bunjes, D.; Cohen, S.; Schubert, J.; Hegenbart, U.; et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation provides durable disease control in poor-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Long-term clinical and MRD results of the German CLL Study Group CLL3X trial. Blood 2010, 116, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, P.; Schnaiter, A.; Zenz, T.; Böttcher, S.; Rossi, M.; Paschka, P.; Bühler, A.; Dietrich, S.; Busch, R.; Ritgen, M.; et al. TP53, SF3B1, and NOTCH1 mutations and outcome of allotransplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Six-year follow-up of the GCLLSG CLL3X trial. Blood 2013, 121, 3284–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, I.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Dietrich, S.; Bottcher, S.; Zeis, M.; Stadler, M.; Bittenbring, J.; Uharek, L.; Scheid, C.; Hegenbart, U.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for high-risk CLL: 10-year follow-up of the GCLLSG CLL3X trial. Blood 2017, 130, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, P.; Ghia, P.; Schetelig, J.; van Gelder, M.; Kimby, E.; Michallet, M.; Moreno, C.; Robak, T.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Montserrat, E. High-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of pathway inhibitors: Integrating molecular and cellular therapies. Blood 2018, 132, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Hamadani, M.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Ghia, P.; Anasetti, C.; Dreger, P.; Montserrat, E.; Perales, M.A.; Alyea, E.P.; et al. Clinical Practice Recommendations for Use of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia on Behalf of the Guidelines Committee of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tausch, E.; Close, W.; Dolnik, A.; Bloehdorn, J.; Chyla, B.; Bullinger, L.; Döhner, H.; Mertens, D.; Stilgenbauer, S. Venetoclax resistance and acquired BCL2 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, e434–e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herling, C.D.; Abedpour, N.; Weiss, J.; Schmitt, A.; Jachimowicz, R.D.; Merkel, O.; Cartolano, M.; Oberbeck, S.; Mayer, P.; Berg, V.; et al. Clonal dynamics towards the development of venetoclax resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blombery, P.; Anderson, M.A.; Gong, J.N.; Thijssen, R.; Birkinshaw, R.W.; Thompson, E.R.; Teh, C.E.; Nguyen, T.; Xu, Z.; Flensburg, C.; et al. Acquisition of the Recurrent Gly101Val Mutation in BCL2 Confers Resistance to Venetoclax in Patients with Progressive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestieri, G.; Terzi di Bergamo, L.; Wan Loh, J.; Spina, V.; Rossi, D. Mechanisms of adaptation to ibrutinib in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. EHA Library 2020, 294974, S154. [Google Scholar]
- Spina, V.; Forestieri, G.; Zucchetto, A.; Bruscaggin, A.; Bittolo, T.; Terzi di Bergamo, L.; Szenes, E.; Condoluci, A.; Tissino, E.; De Paoli, L.; et al. Mechanisms of Adaptation to Ibrutinib in High Risk Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guièze, R.; Liu, V.M.; Rosebrock, D.; Jourdain, A.A.; Hernández-Sánchez, M.; Martinez Zurita, A.; Sun, J.; Ten Hacken, E.; Baranowski, K.; Thompson, P.A.; et al. Mitochondrial Reprogramming Underlies Resistance to BCL-2 Inhibition in Lymphoid Malignancies. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 369–384.e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselager, M.V.; Kielbassa, K.; Ter Burg, J.; Bax, D.J.C.; Fernandes, S.M.; Borst, J.; Tam, C.; Forconi, F.; Chiodin, G.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Changes in Bcl-2 members in response to ibrutinib or venetoclax uncover functional hierarchy in determining resistance to venetoclax in CLL. Blood 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Pluta, A.; Wach, M.; Lysak, D.; Kozak, T.; Simkovic, M.; Kaplan, P.; Kraychok, I.; Illes, A.; de la Serna, J.; et al. ASCEND: Phase III, Randomized Trial of Acalabrutinib Versus Idelalisib Plus Rituximab or Bendamustine Plus Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Opat, S.; D’Sa, S.; Jurczak, W.; Lee, H.P.; Cull, G.; Owen, R.G.; Marlton, P.; Wahlin, B.E.; Sanz, R.G.; et al. A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia: The ASPEN study. Blood 2020, 136, 2038–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmen, P.; Rawstron, A.C.; Brock, K.; Muñoz-Vicente, S.; Yates, F.J.; Bishop, R.; Boucher, R.; MacDonald, D.; Fegan, C.; McCaig, A.; et al. Ibrutinib Plus Venetoclax in Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: The CLARITY Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Keating, M.; Thompson, P.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.; Borthakur, G.; Takahashi, K.; Estrov, Z.; Fowler, N.; Kadia, T.; et al. Ibrutinib and Venetoclax for First-Line Treatment of CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, C.U.; Levin, M.D.; Dubois, J.; Kersting, S.; Enggaard, L.; Veldhuis, G.J.; Mous, R.; Mellink, C.H.M.; Dobber, J.A.; Poulsen, C.B.; et al. Venetoclax and Ibrutinib for Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Andersen, B.L.; Awan, F.T.; Bhat, S.A.; Dean, A.; Lucas, M.; Banks, C.; et al. Phase II Study of Combination Obinutuzumab, Ibrutinib, and Venetoclax in Treatment-Naïve and Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3626–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Woyach, J.A.; Zhao, W.; Caruthers, S.; Tu, H.; Coleman, J.; Byrd, J.C.; Johnson, A.J.; Lozanski, G. PLCG2 C2 domain mutations co-occur with BTK and PLCG2 resistance mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia undergoing ibrutinib treatment. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1645–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Coleman, J.; Jones, D.; et al. BTK(C481S)-Mediated Resistance to Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.M.; Letestu, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Fleury, C.; Lazarian, G.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Nollet, D.; Guieze, R.; Feugier, P.; et al. Prevalence of BTK and PLCG2 mutations in a real-life CLL cohort still on ibrutinib after 3 years: A FILO group study. Blood 2019, 134, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Galanina, N.; Guo, A.; Lee, J.; Kadri, S.; Van Slambrouck, C.; Long, B.; Wang, W.; Ming, M.; Furtado, L.V.; et al. Identification of a structurally novel BTK mutation that drives ibrutinib resistance in CLL. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68833–68841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Landau, D.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Bozic, I.; Zhang, H.; Sarosiek, K.; Wang, L.; Stewart, C.; Fan, J.; Hoellenriegel, J.; et al. Clonal evolution in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia developing resistance to BTK inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosson, A.; Chapiro, E.; Bougacha, N.; Lambert, J.; Herbi, L.; Cung, H.A.; Algrin, C.; Keren, B.; Damm, F.; Gabillaud, C.; et al. Gain in the short arm of chromosome 2 (2p+) induces gene overexpression and drug resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Analysis of the central role of XPO1. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiestner, A.; Ghia, P.; Byrd, J.C.; Ahn, I.E.; Moreno, C.; O’Brien, S.M.; Jones, D.; Cheung, L.W.K.; Chong, E.; Kwei, K.; et al. Rarity of B-Cell Receptor Pathway Mutations in Progression-Free Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) during First-Line Versus Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Treatment with Ibrutinib. Blood 2020, 136, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, K.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.R.; Lozanski, A.; Doong, T.-J.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Jones, D.; et al. Resistance to Acalabrutinib in CLL Is Mediated Primarily by BTK Mutations. Blood 2019, 134, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Liu, X.; Munshi, M.; Xu, L.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Demos, M.G.; Kofides, A.; Guerrera, M.L.; Chan, G.G.; Patterson, C.J.; et al. BTK(Cys481Ser) drives ibrutinib resistance via ERK1/2 and protects BTK(wild-type) MYD88-mutated cells by a paracrine mechanism. Blood 2018, 131, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, I.; Bodo, J.; Hill, B.T.; Hsi, E.D.; Almasan, A. Targeting BCL-2 in B-cell malignancies and overcoming therapeutic resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, M.F.; Kuil, A.; Geest, C.R.; Eldering, E.; Chang, B.Y.; Buggy, J.J.; Pals, S.T.; Spaargaren, M. The clinically active BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 targets B-cell receptor- and chemokine-controlled adhesion and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 2590–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, S.E.M.; Mustafa, R.Z.; Jones, J.; Wong, D.H.; Farooqui, M.; Wiestner, A. Treatment with Ibrutinib Inhibits BTK- and VLA-4-Dependent Adhesion of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4642–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodin, G.; Dutton, D.; Martino, E.A.; Drennan, S.; Tracy, I.; Ondrisova, L.; Henderson, I.; D’Avola, A.; Pitsillidou, C.; Mraz, M.; et al. High Surface IgM Levels Associate with Shorter Response Duration and Bypass of the BTK Blockade during Ibrutinib Therapy in CLL Patients. Blood 2019, 134, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drennan, S.; Chiodin, G.; D’Avola, A.; Tracy, I.; Johnson, P.W.; Trentin, L.; Steele, A.J.; Packham, G.; Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F. Ibrutinib Therapy Releases Leukemic Surface IgM from Antigen Drive in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissard, F.; Fournié, J.J.; Quillet-Mary, A.; Ysebaert, L.; Poupot, M. Nurse-like cells mediate ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissard, F.; Tosolini, M.; Ligat, L.; Quillet-Mary, A.; Lopez, F.; Fournié, J.-J.; Ysebaert, L.; Poupot, M. Nurse-like cells promote CLL survival through LFA-3/CD2 interactions. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 52225–52236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorcari, S.; Maffei, R.; Audrito, V.; Martinelli, S.; Ten Hacken, E.; Zucchini, P.; Grisendi, G.; Potenza, L.; Luppi, M.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Ibrutinib modifies the function of monocyte/macrophage population in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65968–65981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompot, E.; Van Damme, M.; Pieters, K.; Vermeersch, M.; Perez-Morga, D.; Mineur, P.; Maerevoet, M.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L.; et al. Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, R.R.; Sharman, J.P.; Coutre, S.E.; Cheson, B.D.; Pagel, J.M.; Hillmen, P.; Barrientos, J.C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Kipps, T.J.; Flinn, I.; et al. Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinn, I.W.; Hillmen, P.; Montillo, M.; Nagy, Z.; Illes, A.; Etienne, G.; Delgado, J.; Kuss, B.J.; Tam, C.S.; Gasztonyi, Z.; et al. The phase 3 DUO trial: Duvelisib vs. ofatumumab in relapsed and refractory CLL/SLL. Blood 2018, 132, 2446–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Ljungström, V.; Tausch, E.; Agathangelidis, A.; Scheffold, A.; Scarfo, L.; Jebaraj, B.M.C.; Owen, C.J.; Barrientos, J.C.; Zapatka, M.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Revealed No Recurrent Mutations within the PI3K Pathway in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients Progressing Under Idelalisib Treatment. Blood 2016, 128, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffold, A.; Jebaraj, B.M.C.; Tausch, E.; Bloehdorn, J.; Ghia, P.; Yahiaoui, A.; Dolnik, A.; Blätte, T.J.; Bullinger, L.; Dheenadayalan, R.P.; et al. IGF1R as druggable target mediating PI3K-δ inhibitor resistance in a murine model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huw, L.Y.; O’Brien, C.; Pandita, A.; Mohan, S.; Spoerke, J.M.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hampton, G.M.; Wilson, T.R.; Lackner, M.R. Acquired PIK3CA amplification causes resistance to selective phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors in breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, D.; Castel, P.; Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Won, H.H.; Ellis, H.; Ebbesen, S.H.; Ainscough, B.J.; Ramu, A.; Iyer, G.; et al. Convergent loss of PTEN leads to clinical resistance to a PI(3)Kα inhibitor. Nature 2015, 518, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, I.; Kasar, S.; McWilliams, E.M.; Itchaki, G.; Tyekucheva, S.; Livitz, D.; Leshchiner, I.; Dong, S.; Fernandes, S.M.; Getz, G.; et al. Activating MAPK Pathway Mutations Mediate Primary Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Blood 2018, 132, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letai, A.G. Diagnosing and exploiting cancer’s addiction to blocks in apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.E.; Plunkett, W.; McConnell, K.; Keating, M.J.; McDonnell, T.J. Bcl-2 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its correlation with the induction of apoptosis and clinical outcome. Leukemia 1996, 10, 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Boghaert, E.R.; Ackler, S.L.; Catron, N.D.; Chen, J.; Dayton, B.D.; Ding, H.; Enschede, S.H.; Fairbrother, W.J.; et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Zhang, C.; Tandon, M.; Sinha, A.; Fink, A.M.; Robrecht, S.; Samoylova, O.; Liberati, A.M.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Opat, S.; et al. Venetoclax plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab for previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL14): Follow-up results from a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.A.; Deng, J.; Seymour, J.F.; Tam, C.; Kim, S.Y.; Fein, J.; Yu, L.; Brown, J.R.; Westerman, D.; Si, E.G.; et al. The BCL2 selective inhibitor venetoclax induces rapid onset apoptosis of CLL cells in patients via a TP53-independent mechanism. Blood 2016, 127, 3215–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Bahlo, J.; Robrecht, S.; Langerbeins, P.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Engelke, A.; Fink, A.M.; Fischer, K.; Tausch, E.; et al. Bendamustine followed by obinutuzumab and venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL2-BAG): Primary endpoint analysis of a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Puvvada, S.D.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Brown, J.R.; Gressick, L.; et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Eichhorst, B.; Schetelig, J.; Coutre, S.; Seymour, J.F.; Munir, T.; Puvvada, S.D.; Wendtner, C.M.; Roberts, A.W.; Jurczak, W.; et al. Venetoclax in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Eichhorst, B.; Schetelig, J.; Hillmen, P.; Seymour, J.F.; Coutre, S.; Jurczak, W.; Mulligan, S.P.; Schuh, A.; Assouline, S.; et al. Venetoclax for Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia With 17p Deletion: Results From the Full Population of a Phase II Pivotal Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkinshaw, R.W.; Gong, J.N.; Luo, C.S.; Lio, D.; White, C.A.; Anderson, M.A.; Blombery, P.; Lessene, G.; Majewski, I.J.; Thijssen, R.; et al. Structures of BCL-2 in complex with venetoclax reveal the molecular basis of resistance mutations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blombery, P.; Thompson, E.R.; Nguyen, T.; Birkinshaw, R.W.; Gong, J.N.; Chen, X.; McBean, M.; Thijssen, R.; Conway, T.; Anderson, M.A.; et al. Multiple BCL2 mutations cooccurring with Gly101Val emerge in chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression on venetoclax. Blood 2020, 135, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tausch, E.; Stilgenbauer, S. Response to Comment by Jonathan Weiss et al. Haematologica 2019, 104, e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Peifer, M.; Herling, C.D.; Frenzel, L.P.; Hallek, M. Acquisition of the recurrent Gly101Val mutation in BCL2 confers resistance to venetoclax in patients with progressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Comment to Tausch et al.). Haematologica 2019, 104, e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, S.; Hill, B.T.; Mazumder, S.; Singh, K.; Devecchio, J.; Choudhary, G.; Rybicki, L.A.; Kalaycio, M.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Houghton, J.A.; et al. An antiapoptotic BCL-2 family expression index predicts the response of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to ABT-737. Blood 2011, 118, 3579–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punnoose, E.A.; Leverson, J.D.; Peale, F.; Boghaert, E.R.; Belmont, L.D.; Tan, N.; Young, A.; Mitten, M.; Ingalla, E.; Darbonne, W.C.; et al. Expression Profile of BCL-2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1 Predicts Pharmacological Response to the BCL-2 Selective Antagonist Venetoclax in Multiple Myeloma Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Chan, Y.-C.; Tam, C.S.; Hunter, T.; Vassiliadis, D.; Teh, C.E.; Thijssen, R.; Yeh, P.; Wong, S.Q.; Ftouni, S.; et al. Dynamic molecular monitoring reveals that SWI–SNF mutations mediate resistance to ibrutinib plus venetoclax in mantle cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, K.; Wienand, K.; Ryan, J.A.; Chen, L.; Villalobos-Ortiz, M.; Mandato, E.; Stachura, J.; Letai, A.; Lawton, L.N.; Chapuy, B.; et al. Targeted inhibition of PI3Kα/δ is synergistic with BCL-2 blockade in genetically defined subtypes of DLBCL. Blood 2019, 133, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, G.S.; Al-Harbi, S.; Mazumder, S.; Hill, B.T.; Smith, M.R.; Bodo, J.; Hsi, E.D.; Almasan, A. MCL-1 and BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderquist, R.S.; Crawford, L.; Liu, E.; Lu, M.; Agarwal, A.; Anderson, G.R.; Lin, K.H.; Winter, P.S.; Cakir, M.; Wood, K.C. Systematic mapping of BCL-2 gene dependencies in cancer reveals molecular determinants of BH3 mimetic sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Dohner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Jaglowski, S.; Byrd, J.C.; Bannerji, R.; Blum, K.A.; Fox, C.P.; Furman, R.R.; Hillmen, P.; Kipps, T.J.; Montillo, M.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Complete Response to Ibrutinib in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Pooled Analysis of 2 Clinical Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.W.; Ma, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Coutre, S.E.; Davids, M.S.; Eichhorst, B.; Hallek, M.; Byrd, J.C.; Humphrey, K.; Zhou, L.; et al. Efficacy of venetoclax in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia is influenced by disease and response variables. Blood 2019, 134, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Gomez, F.; Lamothe, B.; Woyach, J.A.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Gandhi, V. Pharmacological and Protein Profiling Suggests Venetoclax (ABT-199) as Optimal Partner with Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3705–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, D.; Dousset, C.; Brosseau, C.; Touzeau, C.; Maïga, S.; Moreau, P.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; Le Gouill, S.; Amiot, M. Biological rational for sequential targeting of Bruton tyrosine kinase and Bcl-2 to overcome CD40-induced ABT-199 resistance in mantle cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Isik, E.; Fernandes, S.M.; Brown, J.R.; Letai, A.; Davids, M.S. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibition increases BCL-2 dependence and enhances sensitivity to venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, A.; Akhtar, S.; Yousaf, H.; Manna, A.; Paulus, S.M.; Bashir, Y.; Caulfield, T.R.; Kuranz-Blake, M.; Chitta, K.; Wang, X.; et al. Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia cells devoid of BTKC481S or CXCR4WHIM-like mutations acquire resistance to ibrutinib through upregulation of Bcl-2 and AKT resulting in vulnerability towards venetoclax or MK2206 treatment. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Wilson, C.; Tandon, M.; Ching, T.; Fink, A.-M.; Ritgen, M.; Tausch, E.; Kreuzer, K.-A.; et al. Clonal Dynamics after Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab Therapy: Novel Insights from the Randomized, Phase 3 CLL14 Trial. Blood 2020, 136, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, W.G.; Tam, C.S.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Kipps, T.J.; Opat, S.; Tedeschi, A.; Badoux, X.C.; Kuss, B.J.; Jackson, S.; et al. Ibrutinib (Ibr) Plus Venetoclax (Ven) for First-Line Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): 1-Year Disease-Free Survival (DFS) Results from the MRD Cohort of the Phase 2 CAPTIVATE Study. Blood 2020, 136, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H.; Edenhofer, S.; Tresckow, J.v.; Grimm, M.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Fürstenau, M.; Dreger, P.; Ritgen, M.; Illmer, T.; et al. CLL2-Give, a Prospective, Open-Label, Multicenter Phase-II Trial of Obinutuzumab (GA101, G), Ibrutinib (I), Plus Venetoclax (VE) in Untreated Patients with CLL with 17P Deletion/TP53 Mutation; EHA: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Woyach, J.A.; Blachly, J.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.R.; Kittai, A.S.; Jianfar, M.; Lozanski, G.; Weiss, D.M.; Andersen, B.L.; et al. Acalabrutinib in Combination with Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab or Rituximab in Patients with Treatment-Naïve or Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2020, 136, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Lampson, B.L.; Tyekucheva, S.; Crombie, J.L.; Ng, S.; Kim, A.I.; Weinstock, M.; Lowney, J.; Pazienza, S.; Montegaard, J.; et al. Updated Safety and Efficacy Results from a Phase 2 Study of Acalabrutinib, Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab (AVO) for Frontline Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Blood 2020, 136, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumerai, J.D.; Mato, A.R.; Carter, J.; Dogan, A.; Hochberg, E.P.; Barnes, J.A.; Hamilton, A.; Abramson, J.S.; Batlevi, C.L.; Joffe, E.; et al. MRD-Driven Time Limited Therapy with Zanubrutinib, Obinutuzumab, and Venetoclax (BOVen) in Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. In Proceedings of the 62nd ASH Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kater, A.P.; Seymour, J.F.; Hillmen, P.; Eichhorst, B.; Langerak, A.W.; Owen, C.; Verdugo, M.; Wu, J.; Punnoose, E.A.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Fixed Duration of Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Eradicates Minimal Residual Disease and Prolongs Survival: Post-Treatment Follow-Up of the MURANO Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrup, R.A.; Owen, C.; D’Rozario, J.; Robak, T.; Kater, A.P.; Montillo, M.; de la Serna, J.; Trněný, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Bataillard, E.; et al. Efficacy of Subsequent Novel Targeted Therapies, Including Repeated Venetoclax-Rituximab (VenR), in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (R/R CLL) Previously Treated with Fixed-Duration Venr in the Murano Study. Blood 2020, 136, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, M.; Hallek, M.; Eichhorst, B. Sequential and combination treatments with novel agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.S.; Quach, H.; Nicol, A.; Badoux, X.; Rose, H.; Prince, H.M.; Leahy, M.F.; Eek, R.; Wickham, N.; Patil, S.S.; et al. Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) plus obinutuzumab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and follicular lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4802–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.S.; Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Burger, J.A.; Cull, G.; Gottlieb, D.; Harrup, R.; Johnston, P.B.; Marlton, P.; Munoz, J.; et al. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. Blood 2019, 134, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, J.N.; Patel, K.; Mato, A.R.; Wierda, W.G.; Pinilla Ibarz, J.; Choi, M.Y.; O’Brien, S.M.; Sharman, J.P.; Shadman, M.; Gladstone, D.E.; et al. Ongoing Results of a Phase 1B/2 Dose-Escalation and Cohort-Expansion Study of the Selective, Noncovalent, Reversible Bruton’S Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Vecabrutinib, in B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2019, 134, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, S.D.; Muhowski, E.M.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Fabian, C.A.; Cheney, C.; Mantel, R.; Smith, L.; Johnson, A.J.; Young, W.B.; et al. Noncovalent inhibition of C481S Bruton tyrosine kinase by GDC-0853: A new treatment strategy for ibrutinib-resistant CLL. Blood 2018, 132, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, A.R.; Pagel, J.M.; Coombs, C.C.; Shah, N.N.; Lamanna, N.; Lech-Marańda, E.; Eyre, T.A.; Woyach, J.A.; Wierda, W.G.; Cheah, C.Y.; et al. LOXO-305, A Next Generation, Highly Selective, Non-Covalent BTK Inhibitor in Previously Treated CLL/SLL: Results from the Phase 1/2 BRUIN Study. Blood 2020, 136, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, S.D.; Mantel, R.; Smith, L.L.; Greene, J.T.; Muhowski, E.M.; Fabian, C.A.; Goettl, V.M.; Tran, M.; Harrington, B.K.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. The BTK Inhibitor ARQ 531 Targets Ibrutinib-Resistant CLL and Richter Transformation. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1300–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, R.; Valle-Argos, B.; Steele, A.J.; Packham, G. Development of PROTACs to address clinical limitations associated with BTK-targeted kinase inhibitors. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2020, 1, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhimschi, A.D.; Armstrong, H.A.; Toure, M.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; Chen, T.L.; Lehman, A.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Johnson, A.J.; Byrd, J.C.; Crews, C.M. Targeting the C481S Ibrutinib-Resistance Mutation in Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Using PROTAC-Mediated Degradation. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3564–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, N.; Song, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhu, J.; Rao, Y. Degradation of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase mutants by PROTACs for potential treatment of ibrutinib-resistant non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Zhang, X.; Lv, D.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Thummuri, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wiegand, J.S.; et al. A selective BCL-XL PROTAC degrader achieves safe and potent antitumor activity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.A.; Mato, A.R.; Wierda, W.G.; Davids, M.S.; Choi, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Furman, R.R.; Lamanna, N.; Barr, P.M.; Zhou, L.; et al. Venetoclax for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia progressing after ibrutinib: An interim analysis of a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Roeker, L.E.; Jacobs, R.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Brander, D.; Shadman, M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Yazdy, M.S.; Perini, G.F.; et al. Assessment of the Efficacy of Therapies Following Venetoclax Discontinuation in CLL Reveals BTK Inhibition as an Effective Strategy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3589–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Barr, P.M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Brander, D.M.; Howlett, C.; Skarbnik, A.P.; Cheson, B.D.; Zent, C.S.; et al. Optimal sequencing of ibrutinib, idelalisib, and venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results from a multicenter study of 683 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Cymbalista, F.; Buske, C.; Hillmen, P.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, F.T.; Schuh, A.; Brown, J.R.; Furman, R.R.; Pagel, J.M.; Hillmen, P.; Stephens, D.M.; Woyach, J.; Bibikova, E.; Charuworn, P.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who are intolerant to ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, F.; Larkin, K.; Gregory, C.T.; Orwick, S.; Doong, T.J.; Lozanski, A.; Lozanski, G.; Misra, S.; Ngankeu, A.; Ozer, H.G.; et al. Novel BCL2 mutations in venetoclax-resistant, ibrutinib-resistant CLL patients with BTK/PLCG2 mutations. Blood 2020, 135, 2192–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunning, M.; Vose, J.; Nastoupil, L.; Fowler, N.; Burger, J.A.; Wierda, W.G.; Schreeder, M.T.; Siddiqi, T.; Flowers, C.R.; Cohen, J.B.; et al. Ublituximab and umbralisib in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastoupil, L.J.; Lunning, M.A.; Vose, J.M.; Schreeder, M.T.; Siddiqi, T.; Flowers, C.R.; Cohen, J.B.; Burger, J.A.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; et al. Tolerability and activity of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A phase 1 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e100–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Zhong, Y.; Lozanski, A.; Lozanski, G.; Dong, S.; Strattan, E.; Lehman, A.; Zhang, X.; Jones, J.A.; et al. Hypermorphic mutation of phospholipase C, γ2 acquired in ibrutinib-resistant CLL confers BTK independency upon B-cell receptor activation. Blood 2015, 126, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.T.; Thirman, M.J.; Patel-Donnelly, D.; Assouline, S.; Rao, A.V.; Ye, W.; Hill, B.; Sharman, J.P. Entospletinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia previously treated with B-cell receptor inhibitors: Results of a phase 2 study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsch, N.; Pallasch, C.; Tausch, E.; Boehme, V.; Ritgen, M.; Liersch, R.; Wacker, A.; Jacobs, G.; Trappe, R.U.; Dreger, P.; et al. A Prospective, Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase 2 Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of the Combination of Tirabrutinib (ONO/GS-4059) and Entospletinib with and without Obinutuzumab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Blood 2019, 134, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Lu, P.; Coffey, G.; Conley, P.; Pandey, A.; Wang, Y.L. Dual SYK/JAK inhibition overcomes ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Cerdulatinib, but not ibrutinib, induces apoptosis of tumor cells protected by the microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12953–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, G.P.; Feng, J.; Betz, A.; Pandey, A.; Birrell, M.; Leeds, J.M.; Der, K.; Kadri, S.; Lu, P.; Segal, J.; et al. Cerdulatinib Pharmacodynamics and Relationships to Tumor Response Following Oral Dosing in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-cell Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gamal, D.; Williams, K.; LaFollette, T.D.; Cannon, M.; Blachly, J.S.; Zhong, Y.; Woyach, J.A.; Williams, E.; Awan, F.T.; Jones, J.; et al. PKC-β as a therapeutic target in CLL: PKC inhibitor AEB071 demonstrates preclinical activity in CLL. Blood 2014, 124, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.S.; Wong, D.H.; Tanios, G.; Iyer, J.R.; Lobelle-Rich, P.; Dadashian, E.L.; Liu, D.; Fontan, L.; Flemington, E.K.; Nichols, C.M.; et al. MALT1 Inhibition Is Efficacious in Both Naïve and Ibrutinib-Resistant Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 7038–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Sarkar, A.; Kismali, G.; Aslan, B.; Ayres, M.; Iles, L.R.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Long, J.P.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; et al. AMG-176, an Mcl-1 Antagonist, Shows Preclinical Efficacy in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3856–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tron, A.E.; Belmonte, M.A.; Adam, A.; Aquila, B.M.; Boise, L.H.; Chiarparin, E.; Cidado, J.; Embrey, K.J.; Gangl, E.; Gibbons, F.D.; et al. Discovery of Mcl-1-specific inhibitor AZD5991 and preclinical activity in multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, J.; Deckwerth, T.L.; Kerwin, W.S.; Casalini, J.R.; Merrell, A.J.; Grenley, M.O.; Burns, C.; Ditzler, S.H.; Dixon, C.P.; Beirne, E.; et al. Voruciclib, a clinical stage oral CDK9 inhibitor, represses MCL-1 and sensitizes high-risk Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma to BCL2 inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, D.A.; Su, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Buck, S.A.; Edwards, H.; Polin, L.; Kushner, J.; Dzinic, S.H.; White, K.; et al. Inhibition of CDK9 by voruciclib synergistically enhances cell death induced by the Bcl-2 selective inhibitor venetoclax in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Ghia, E.M.; Kidwell, R.L.; Hasan, M.K.; Yu, J.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Pittman, E.; et al. Phase I Trial: Cirmtuzumab Inhibits ROR1 Signaling and Stemness Signatures in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 951–959.e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, B.; Widhopf Ii, G.F.; Rassenti, L.; Shen, Z.; Briggs, S.P.; Kipps, T.J. Wnt5a induces ROR1 to complex with HS1 to enhance migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Ghia, E.M.; Choi, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Messer, K.; et al. Cirmtuzumab blocks Wnt5a/ROR1 stimulation of NF-κB to repress autocrine STAT3 activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Siddiqi, T.; Wierda, W.G.; Barrientos, J.C.; Lamanna, N.; Goldenberg, A.; Isufi, I.; Tuscano, J.; Subbiah, S.; et al. Cirmtuzumab, an Anti-ROR1 Antibody, in Combination with Ibrutinib: Clinical Activity in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) or Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) from a Phase 1/2 Study. Blood 2020, 136, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, E.M.; Lucas, C.R.; Chen, T.; Harrington, B.K.; Wasmuth, R.; Campbell, A.; Rogers, K.A.; Cheney, C.M.; Mo, X.; Andritsos, L.A.; et al. Anti-BAFF-R antibody VAY-736 demonstrates promising preclinical activity in CLL and enhances effectiveness of ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.A.; Flinn, I.W.; McGarry, C.; Gou, L.C.; Hassounah, N.; Woo, J.; Byrd, J.C. Phase Ib Study of Ianalumab (VAY736) and Ibrutinib in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) on Ibrutinib Therapy. Blood 2020, 136, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Ten Hacken, E.; Sivina, M.; Clarke, A.; Thompson, P.A.; Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. The BET inhibitor GS-5829 targets chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and their supportive microenvironment. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrà, G.; Nicoli, P.; Lingua, M.F.; Maffeo, B.; Cartellà, A.; Circosta, P.; Brancaccio, M.; Parvis, G.; Gaidano, V.; Guerrasio, A.; et al. Inhibition of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins increases sensitivity to venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, K.; Powers, J.J.; Achille, A.; Deng, S.; Fonseca, R.; Pabon-Saldana, M.; Quayle, S.N.; Jones, S.S.; Villagra, A.; Sotomayor, E.M.; et al. Silencing of HDAC6 as a therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, K.; Powers, J.J.; Mediavilla-Varela, M.; Achille, A.; Gamal, W.; Quayle, S.; Jones, S.S.; Sahakian, E.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J. HDAC6 Inhibition Alleviates CLL-Induced T-Cell Dysfunction and Enhances Immune Checkpoint Blockade Efficacy in the Eμ-TCL1 Model. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, H.R.; Qi, J.; Cook, E.M.; Nichols, C.; Dadashian, E.L.; Underbayev, C.; Herman, S.E.M.; Saba, N.S.; Keyvanfar, K.; Sun, C.; et al. A CD19/CD3 bispecific antibody for effective immunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the ibrutinib era. Blood 2018, 132, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Horst, H.J.; de Jonge, A.V.; Hiemstra, I.H.; Gelderloos, A.T.; Berry, D.R.; Hijmering, N.J.; de Jong, D.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Zweegman, S.; Breij, E.C.; et al. Duobody-CD3xCD20 Induces Potent Anti-Tumor Activity in Malignant Lymph Node B Cells from Patients with DLBCL, FL and MCL Ex Vivo, Irrespective of Prior Treatment with CD20 Monoclonal Antibodies. Blood 2019, 134, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name/Identifier | Experimental Treatment Arm | Phase | TN vs. R/R |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLAIR 2013-001944-76 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 3 | TN |
| GLOW NCT03462719 | Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 3 | TN |
| CLL13/GAIA NCT02950051 | Venetoclax + rituximab Venetoclax + obinutuzumab Venetoclax + ibrutinib + obinutuzumab | 3 | TN |
| CLL17 NCT04608318 | Venetoclax + obinutuzumab Venetoclax + ibrutinib | 3 | TN |
| ACE-CL-311 NCT03836261 | Acalabrutinib + venetoclax ± obinutuzumab | 3 | TN |
| PreVent-ACaLL NCT03868722 | Venetoclax + acalabrutinib | 2 | TN |
| CLL2-BAAG NCT03787264 | (Bendamustine) + acalabrutinib + venetoclax + obinutuzumab | 2 | R/R |
| CLL2-BZAG NCT04515238 | (Bendamustine) + zanubrutinib + venetoclax + obinutuzumab | 2 | R/R |
| CLLRUmbrella1 NCT02968563 | Tirabrutinib + idelalisib ± obinutuzumab | 2 | R/R |
| CLLRUmbrella2 NCT02983617 | Tirabrutinib + entospletinib ± obinutuzumab | 2 | TN, R/R |
| COSMOS NCT02639910 | Tafasitamab + idelalisib/venetoclax | 2 | R/R |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fürstenau, M.; Eichhorst, B. Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061336
Fürstenau M, Eichhorst B. Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061336
Chicago/Turabian StyleFürstenau, Moritz, and Barbara Eichhorst. 2021. "Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061336
APA StyleFürstenau, M., & Eichhorst, B. (2021). Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers, 13(6), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061336






