FGF/FGFR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Carcinogenesis to Recent Therapeutic Intervention
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
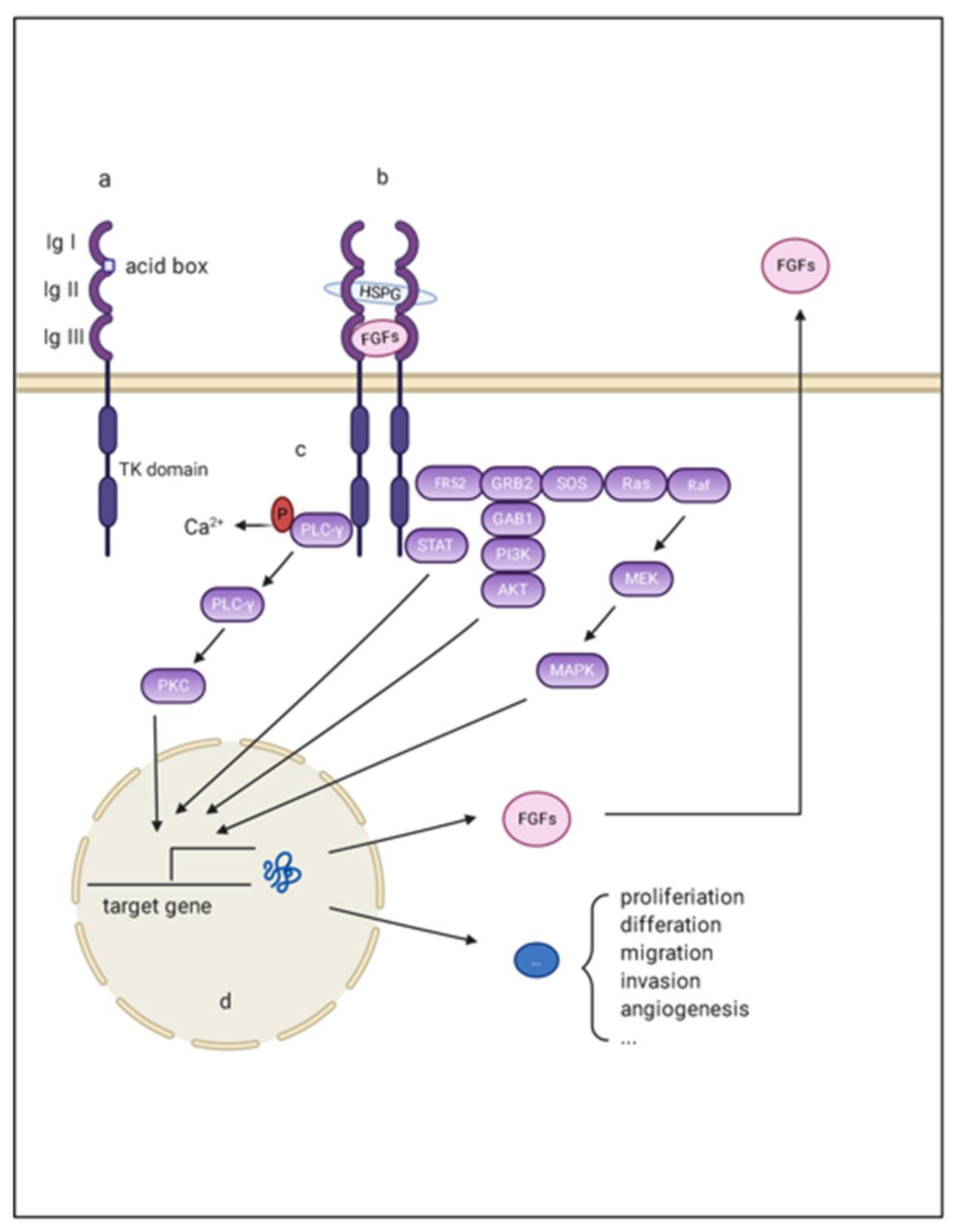
2. The FGF/FGFR System
2.1. FGF, FGFR, and Co-Factor
2.2. FGF/FGFR Downstream Signaling
3. Deregulation of FGF/FGFR in HCC
3.1. FGF2
3.2. FGF8 Subfamily
3.3. FGF9
3.4. FGF19 Subfamily
3.5. Other FGFs in HCC
3.6. FGFRs in HCC
4. Aberrate FGF/FGFR Signaling
4.1. Mutation
4.2. Amplification
5. FGF/FGFR Signaling in Angiogenesis
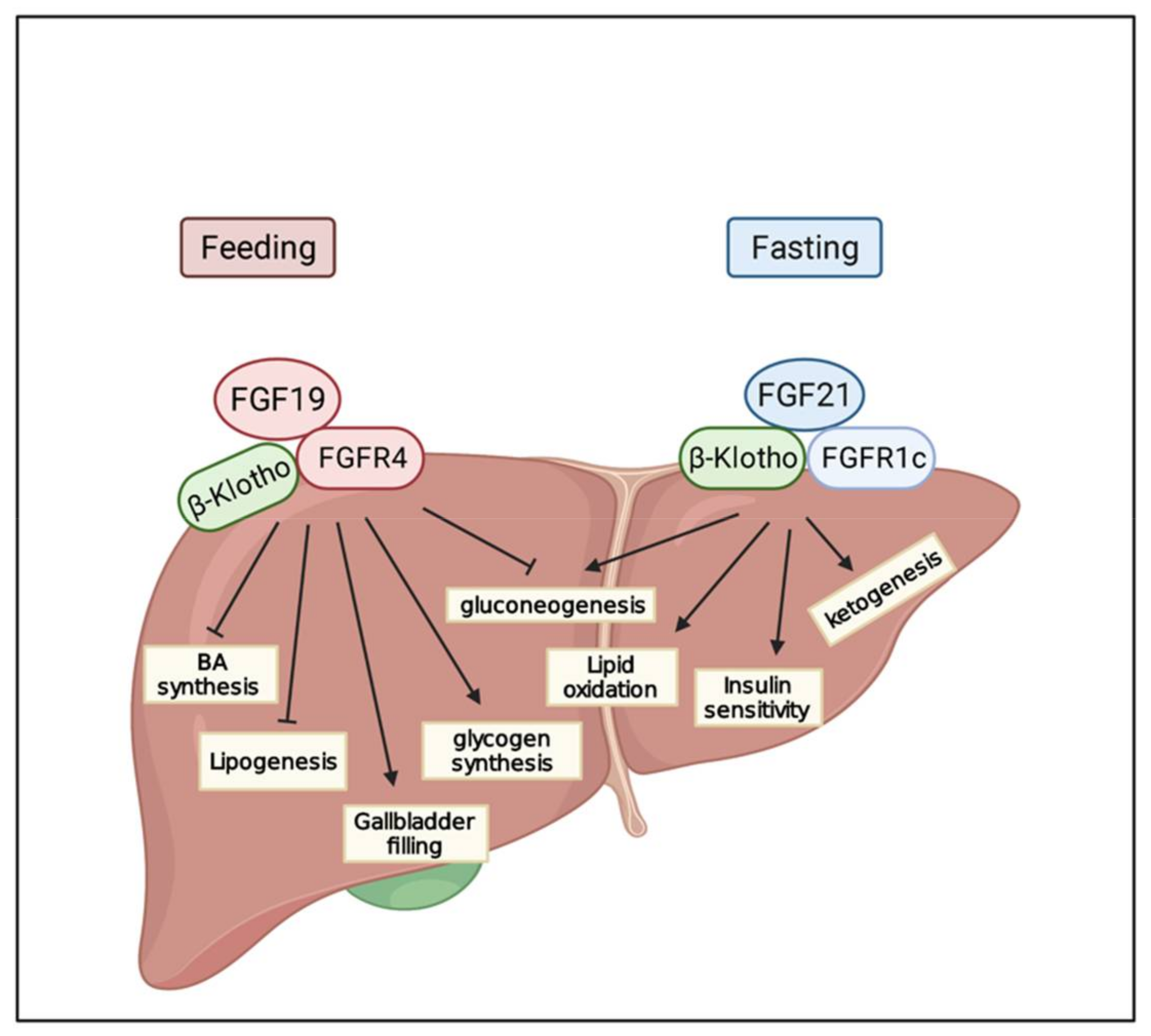
6. FGF/FGFR Signaling in Metabolism
6.1. FGF19
6.2. FGF21
7. FGF/FGFR and Tumor Metastasis
8. FGF/FGFR and Drug Resistance
9. Targeting FGF/FGFR
9.1. Multitarget Kinase Inhibitors
9.2. Pan-FGFR Inhibitors
9.3. FGFR4 Inhibitors
9.3.1. Irreversible Inhibitors
9.3.2. Reversible Inhibitors
9.4. Combined Therapy
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, M.S. Recent progress in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 1990, 2, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Grose, R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: From development to cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Su, N.; Yang, J.; Tan, Q.; Huang, S.; Jin, M.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Luo, F.; et al. FGF/FGFR signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, R.; Pearson, A.; Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Johnson, D.; Mackay, A.; Welti, J.C.; Natrajan, R.; Reynolds, A.R.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashworth, A.; et al. FGFR signaling promotes the growth of triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5275–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jomrich, G.; Hudec, X.; Harpain, F.; Winkler, D.; Timelthaler, G.; Mohr, T.; Marian, B.; Schoppmann, S.F. Expression of FGF8, FGF18, and FGFR4 in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinomas. Cells 2019, 8, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stehbens, S.J.; Ju, R.J.; Adams, M.N.; Perry, S.R.; Haass, N.K.; Bryant, D.M.; Pollock, P.M. FGFR2-activating mutations disrupt cell polarity to potentiate migration and invasion in endometrial cancer cell models. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs213678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szybowska, P.; Kostas, M.; Wesche, J.; Wiedlocha, A.; Haugsten, E.M. Cancer Mutations in FGFR2 Prevent a Negative Feedback Loop Mediated by the ERK1/2 Pathway. Cells 2019, 8, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chae, Y.K.; Hong, F.; Vaklavas, C.; Cheng, H.H.; Hammerman, P.; Mitchell, E.P.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Ivy, S.P.; Gray, R.J.; Li, S.; et al. Phase II study of AZD4547 in patients with tumors harboring aberrations in the FGFR pathway: Results from the NCI-MATCH Trial (EAY131) subprotocol W. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, S.K.; Garbi, M.; Zampieri, N.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Ornitz, D.M.; Goldfarb, M.; Mohammadi, M. Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Homologous Factors Share Structural but Not Functional Homology with FGFs. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34226–34236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. Protein family review: Fibroblast growth factors. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinina, J.; Dutta, K.; Ilghari, D.; Beenken, A.; Goetz, R.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Cowburn, D.; Mohammadi, M. The alternatively spliced acid box region plays a key role in FGF receptor autoinhibition. Structure 2012, 20, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holzmann, K.; Grunt, T.; Heinzle, C.; Sampl, S.; Steinhoff, H.; Reichmann, N.; Kleiter, M.; Hauck, M.; Marian, B. Alternative splicing of fibroblast growth factor receptor IgIII loops in cancer. J. Nucleic Acids 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuro-o, M. The Klotho proteins in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzina, E.S.; Ung, P.M.U.; Mohanty, J.; Tome, F.; Choi, J.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, A.; Schlessinger, J.; et al. Structures of ligand-occupied β-Klotho complexes reveal a molecular mechanism underlying endocrine FGF specificity and activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7819–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.C.; Shiizaki, K.; Kuro-O, M.; Moe, O.W. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and klotho: Physiology and pathophysiology of an endocrine network of mineral metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Sola, G.; Uriarte, I.; Ujue Latasa, M.; Urtasun, R.; Bárcena-Varela, M.; Elizalde, M.; Jiménez, M.; Rodriguez-Ortigosa, C.M.; Corrales, F.J.; Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 15/19 in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.H.; Hadari, Y.R.; Gotoh, N.; Guy, G.R.; Schlessinger, J.; Lax, I. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by fibroblast growth factor receptors is mediated by coordinated recruitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6074–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kin, M.; Sata, M.; Ueno, T.; Torimura, T.; Inuzuka, S.; Tsuji, R.; Sujaku, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Sugawara, H.; Tamaki, S.; et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor regulates proliferation and motility of human hepatoma cells by an autocrine mechanism. J. Hepatol. 1997, 27, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, L.J.; Cao, R.; Hedlund, E.M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wetterskog, D.; Funa, K.; Bråkenhielm, E.; Cao, Y. Angiogenic factors FGF2 and PDGF-BB synergistically promote murine tumor neovascularization and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2766–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shigesawa, T.; Maehara, O.; Suda, G.; Natsuizaka, M.; Kimura, M.; Shimazaki, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamada, R.; Kitagataya, T.; Nakamura, A.; et al. Lenvatinib suppresses cancer stem-like cells in HCC by inhibiting FGFR1–3 signaling, but not FGFR4 signaling. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, H.; Tatsumi, T.; Kohga, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Aketa, H.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Hiramatsu, N.; Kanto, T.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 enhances NK sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Park, H.; Chhim, S.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, W.; Queen, C.; Kim, J.K. A Novel Monoclonal Antibody to Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Effectively Inhibits Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Xenografts. Bone 2014, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauglhofer, C.; Sagmeister, S.; Schrottmaier, W.; Fischer, C.; Rodgarkia-Dara, C.; Mohr, T.; Stättner, S.; Bichler, C.; Kandioler, D.; Wrba, F.; et al. Upregulation of the fibroblast growth factor 8 subfamily in human hepatocellular carcinoma for cell survival and neoangiogenesis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpain, F.; Ahmed, M.A.; Hudec, X.; Timelthaler, G.; Jomrich, G.; Müllauer, L.; Selzer, E.; Dörr, W.; Bergmann, M.; Holzmann, K.; et al. FGF8 induces therapy resistance in neoadjuvantly radiated rectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pei, Y.; Sun, X.; Guo, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, F.; Jing, H.; Liang, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, P. FGF8 promotes cell proliferation and resistance to EGFR inhibitors via upregulation of EGFR in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heer, R.; Douglas, D.; Mathers, M.E.; Robson, C.N.; Leung, H.Y. Fibroblast growth factor 17 is over-expressed in human prostate cancer. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yin, D.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L. Inhibition of the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through fibroblast growth factor 18 suppressed by miR-139. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Wu, F.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chan, A.K.Y.; Liu, L.; Kwan, J.S.H.; et al. FGF18, a prominent player in FGF signaling, promotes gastric tumorigenesis through autocrine manner and is negatively regulated by miR-590-5p. Oncogene 2019, 38, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paur, J.; Valler, M.; Sienel, R.; Taxauer, K.; Holzmann, K.; Marian, B.; Unterberger, A.; Mohr, T.; Berger, W.; Gvozdenovich, A.; et al. Interaction of FGF9 with FGFR3-IIIb/IIIc, a putative driver of growth and aggressive behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, T.; Freese, K.; Dietrich, P.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 is expressed by activated hepatic stellate cells and promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gunewardena, S.; Li, F.; Matye, D.J.; Chen, C.; Chao, X.; Jung, T.; Zhang, Y.; Czerwiński, M.; Ni, H.M.; et al. An FGF15/19-TFEB regulatory loop controls hepatic cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Doughtie, A.; Cui, G.; Li, X.; Pandit, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Martin, R. Upregulation of fibroblast growth factor 19 and its receptor associates with progression from fatty liver to hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52329–52339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawey, E.T.; Chanrion, M.; Cai, C.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zender, L.; Zhao, A.; Busuttil, R.W.; Yee, H.; Stein, L.; et al. Identification of a Therapeutic Strategy Targeting Amplified FGF19 in Liver Cancer by Oncogenomic Screening. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholes, K.; Guillet, S.; Tomlinson, E.; Hillan, K.; Wright, B.; Frantz, G.D.; Pham, T.A.; Dillard-Telm, L.; Tsai, S.P.; Stephan, J.-P.; et al. A Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massafra, V.; Milona, A.; Vos, H.R.; Burgering, B.M.T.; Van Mil, S.W.C. Quantitative liver proteomics identifies FGF19 targets that couple metabolism and proliferation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y. Defects in mTORC1 Network and mTORC1-STAT3 Pathway Crosstalk Contributes to Non-inflammatory Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Du, F.; Dang, Y.; Li, X.; Qian, M.; Feng, W.; Qiao, C.; Fan, D.; Nie, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 19–Mediated Upregulation of SYR-Related High-Mobility Group Box 18 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis by Transactivating Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 and Fms-Related Tyrosine Kinase 4. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1712–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Sola, G.; Uriarte, I.; Latasa, M.U.; Jimenez, M.; Barcena-Varela, M.; Santamaría, E.; Urtasun, R.; Rodriguez-Ortigosa, C.; Prieto, J.; Berraondo, P.; et al. Bile acids, FGF15/19 and liver regeneration: From mechanisms to clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, C.; Li, Y.; Nian, C.; Li, J.; et al. FGF15 Activates Hippo Signaling to Suppress Bile Acid Metabolism and Liver Tumorigenesis. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 460–474.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.Y.; Huang, S.; Shi, K.Q.; Zhao, C.C.; Chen, L.L.; Braddock, M.; Chen, Y.P.; Feng, W.K.; Zheng, M.H. The role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the pathogenesis of liver disease: A novel predictor and therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Martin, R.C.; Shi, X.; Pandit, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, W.; Tan, M.; Bai, O.; Meng, X.; et al. Lack of FGF21 promotes NASH-HCC transition via hepatocyte-TLR4-IL-17A signaling. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9923–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.L.; Teijeiro, A.; Burén, S.; Tummala, K.S.; Yilmaz, M.; Waisman, A.; Theurillat, J.P.; Perna, C.; Djouder, N. Metabolic Inflammation-Associated IL-17A Causes Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allerstorfer, S.; Sonvilla, G.; Fischer, H.; Gauglhofer, C.; Setinek, U.; Marosi, C.; Buchroithner, J.; Pichler, J.; Silye, R.; Mohr, T.; et al. UKPMC Funders Group autocrine and paracrine activities. Nature 2010, 27, 4180–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, M.; Ishiwata, T.; Beger, H.G.; Korc, M. Fibroblast growth factor-5 stimulates mitogenic signaling and is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer: Evidence for autocrine and paracrine actions. Oncogene 1997, 15, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Deng, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. Downregulation of fibroblast growth factor 5 inhibits cell growth and invasion of human nonsmall-cell lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 8238–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Chang, R.M.; Yu, L.; Lei, X.; Xiao, S.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.Y. MicroRNA-188-5p suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting FGF5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Qiu, H.; Ke, S.; Hu, S.; Yu, S.; Zou, S. The fibroblast growth factor receptor 2-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway plays is important in regulating excision repair cross-complementary gene 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fautrel, A.; Andrieux, L.; Musso, O.; Boudjema, K.; Guillouzo, A.; Langouët, S. Overexpression of the two nucleotide excision repair genes ERCC1 and XPC in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropiquet, F.; Giri, D.; Kwabi-addo, B.; Mansukhani, A.; Ittmann, M. Increased expression of fibroblast growth factor 6 in human prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4245–4250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armand, A.S.; Laziz, I.; Chanoine, C. FGF6 in myogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2006, 1763, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komiya, A.; Watanabe, A.; Yasuda, K.; Fuse, H. Enhanced paracrine FGF10 expression promotes formation of multifocal prostate adenocarcinoma and an increase in epithelial androgen receptor. Nippon Rinsho. Jpn. J. Clin. Med. 2010, 68 (Suppl. S7), 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ingram, L.; Kim, S.; Beharry, Z.; Cooper, J.A.; Cai, H. Paracrine Fibroblast Growth Factor Initiates Oncogenic Synergy with Epithelial FGFR/Src Transformation in Prostate Tumor Progression. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.H.; Zhou, B.S.; Chu, P.G.; Chen, W.G.; Chung, C.; Shih, J.; Hwu, P.; Yeh, C.; Lopez, R.; Yen, Y. Over-expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paur, J.; Nika, L.; Maier, C.; Moscu-Gregor, A.; Kostka, J.; Huber, D.; Mohr, T.; Heffeter, P.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kappel, S.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 isoforms: Novel therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology 2015, 62, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, H.K.; Pok, S.; Streit, S.; Ruhe, J.E.; Hart, S.; Lim, K.S.; Loo, H.L.; Aung, M.O.; Lim, S.G.; Ullrich, A. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 regulates proliferation, anti-apoptosis and alpha-fetoprotein secretion during hepatocellular carcinoma progression and represents a potential target for therapeutic intervention. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauglhofer, C.; Paur, J.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Wingelhofer, B.; Huber, D.; Naegelen, I.; Pirker, C.; Mohr, T.; Heinzle, C.; Holzmann, K.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4: A putative key driver for the aggressive phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2331–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Martino, E.; Tomlinson, D.C.; Knowles, M.A. A decade of FGF receptor research in bladder cancer: Past, present, and future challenges. Adv. Urol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshimoto, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Murata, K.; Noda, S.E.; Miyasaka, Y.; Hamamoto, J.; Furuya, M.; Hirato, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Ohno, T.; et al. Mutation profiling of uterine cervical cancer patients treated with definitive radiotherapy. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Shen, B.; Cheng, X.; Ma, D.; Jing, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Peng, C.; Qiu, W. Phenotypic and signaling consequences of a novel aberrantly spliced transcript FGF Receptor-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4205–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Feng, H.; Liang, J.; Jing, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, L.; Shen, B.; Cheng, X.; Su, L.; Qiu, W. FGFR3△7–9 promotes tumor progression via the phosphorylation and destabilization of ten-eleven translocation-2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arao, T.; Ueshima, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagai, T.; Kimura, H.; Hagiwara, S.; Sakurai, T.; Haji, S.; Kanazawa, A.; Hidaka, H.; et al. FGF3/FGF4 amplification and multiple lung metastases in responders to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Learned, R.M.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Non-cell-autonomous activation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling mediates FGF19-driven hepatocarcinogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Haq, F.; Sung, C.O.; Choi, J.; Hong, S.M.; Eo, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Shin, J.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; et al. Characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with FGF19 amplification assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization: A large cohort study. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziol, M.; Poté, N.; Amaddeo, G.; Laurent, A.; Nault, J.-C.; Oberti, F.; Costentin, C.; Michalak, S.; Bouattour, M.; Francoz, C.; et al. Macrotrabecular-massive hepatocellular carcinoma: A distinctive histological subtype with clinical relevance. Hepatology 2018, 68, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, J.; Couchy, G.; Imbeaud, S.; Amaddeo, G.; Letouzé, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; Laurent, C.; Hajji, Y.; Azoulay, D.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; et al. Histological subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma are related to gene mutations and molecular tumour classification. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaibori, M.; Sakai, K.; Ishizaki, M.; Matsushima, H.; de Velasco, M.A.; Matsui, K.; Iida, H.; Kitade, H.; Kwon, A.H.; Nagano, H.; et al. Increased FGF19 copy number is frequently detected in hepatocellular carcinoma with a complete response after sorafenib treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 49091–49098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeo, S.; Arai, H.; Kusano, N.; Harada, T.; Furuya, T.; Kawauchi, S.; Oga, A.; Hirano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Okita, K.; et al. Examination of oncogene amplification by genomic DNA microarray in hepatocellular carcinomas: Comparison with comparative genomic hybridization analysis. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2001, 130, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, M.S. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Duda, D.G.; Sahani, D.V.; Jain, R.K. HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions. Bone 2014, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, C.; Heymach, J.; Overman, M.; Tran, H.; Kopetz, S. Beyond VEGF: Inhibition of the Fibroblast Growth Factor Pathway and Antiangiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshiji, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Yoshii, J.; Ikenaka, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Hicklin, D.J.; Huber, J.; Nakatani, T.; Tsujinoue, H.; Yanase, K.; et al. Synergistic effect of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavri, G.T.; Zachary, I.C.; Baskerville, P.A.; Martin, J.F.; Erusalimsky, J.D. Basic fibroblast growth factor upregulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Synergistic interaction with hypoxia. Circulation 1995, 92, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xie, K.; Zhang, L.; Yao, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Fang, J. Dual blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) exhibits potent anti-angiogenic effects. Cancer Lett. 2016, 377, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.R.; Morishita, Y.; Iwata, C.; Iwasaka, S.; Watabe, T.; Ouchi, Y.; Miyazono, K.; Miyazawa, K. VEGF-A and FGF-2 synergistically promote neoangiogenesis through enhancement of endogenous PDGF-B-PDGFRβ signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3759–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, P.; Wang, Y.; Dai, C.; Tao, C.; Wu, F.; Xie, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Ye, L.; et al. Ribosomal protein S15a promotes tumor angiogenesis via enhancing Wnt/β-catenin-induced FGF18 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1220–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jing, X.; Cheng, X.; Ma, D.; Jin, Z.; Yang, W.; Qiu, W. FGFR3 promotes angiogenesis-dependent metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via facilitating MCP-1-mediated vascular formation. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, M.; Wirz, W.; Tag, C.G.; Gressner, A.M.; Wycislo, M.; Müller, R.; Kiefer, P. Fibroblast growth factor 16 and 18 are expressed in human cardiovascular tissues and induce on endothelial cells migration but not proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kir, S.; Beddow, S.A.; Samuel, V.T.; Miller, P.; Previs, S.F.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E.; Shulman, G.I.; Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. FGF19 as a Postprandial, Insulin-Independent Activator of Hepatic Protein and Glycogen Synthesis Serkan. Bone 2011, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, K.H.; Li, T.; Owsley, E.; Strom, S.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acids activate fibroblast growth factor 19 signaling in human hepatocytes to inhibit cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase gene expression. Hepatology 2009, 49, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Kuro-o, M.; Razzaque, M.S. Molecular Regulation of Phosphate Metabolism by Fibroblast Growth Factor-23-Klotho System. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhatre, K.N.; Wakula, P.; Klein, O.; Bisping, E.; Völkl, J.; Pieske, B.; Heinzel, F.R. Crosstalk between FGF23- and angiotensin II-mediated Ca2+ signaling in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4403–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, S.; Kaneko, I.; Tatsumi, S.; Segawa, H.; Miyamoto, K.I. Vitamin D and type II sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters. Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 180, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.-J.; Briz, O. Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Chavan, H.; Matye, D.; Ni, H.M.; Chiang, J.Y.L.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Ding, W.X.; Li, T. Targeting the Enterohepatic Bile Acid Signaling Induces Hepatic Autophagy via a CYP7A1–AKT–mTOR Axis in Mice. CMGH 2017, 3, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.; Moschetta, A.; Bookout, A.L.; Peng, L.; Umetani, M.; Holmstrom, S.R.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Gerard, R.D.; et al. Identification of a hormonal basis for gallbladder filling. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1253–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, M.K.; Pissios, P.; Kennedy, A.R.; Koukos, G.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Hepatic Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is Regulated by PPARα and Is a Key Mediator of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Ketotic States. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inagaki, T.; Dutchak, P.; Zhao, G.; Ding, X.; Gautron, L.; Parameswara, V.; Li, Y.; Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Esser, V.; et al. Endocrine Regulation of the Fasting Response by PPARα-Mediated Induction of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Tian, H.; Lam, K.S.L.; Lin, S.; Hoo, R.C.L.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N.; Wang, Y.; Bornstein, S.R.; Xu, A.; et al. Adiponectin mediates the metabolic effects of FGF21 on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murata, Y.; Nishio, K.; Mochiyama, T.; Konishi, M.; Shimada, M.; Ohta, H.; Itoh, N. Fgf21 Impairs Adipocyte Insulin Sensitivity in Mice Fed a Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Ketogenic Diet. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, G.; Kumar, G.; Chan, S.; Fisher, F.M.; Ma, Y.; Vardeh, H.G.; Nasser, I.A.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Deficiency of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) promotes hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in mice on a long term obesogenic diet. Mol. Metab. 2018, 13, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Takahashi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Krausz, K.W.; Smith, P.B.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J. Role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the early stage of NASH induced by methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, F.; Shao, T.; Barve, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is required for the therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG against fructose-induced fatty liver in mice. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lv, F.; Liang, G.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L.; Shi, L.; Teng, Y. FGF19 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by modulating the GSK3β/β- catenin signaling cascade via FGFR4 activation. Oncotarget 2015, 19, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Ye, S.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Lin, X. Small hepatitis B virus surface antigen promotes malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced FGF19/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2020, 499, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.S.; Tan, L.; Smith, A.; Gray, N.S.; Wendt, M.K. Covalent targeting of fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibits metastatic breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNiel, E.A.; Tsichlis, P.N. Analyses of publicly available genomics resources define FGF-2-expressing bladder carcinomas as EMT-prone, proliferative tumors with low mutation rates and high expression of CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-l1. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunwobi, O.O.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C. Cyclooxygenase-2 and Akt mediate multiple growth-factor-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Wu, H.J.; Zhang, H.F.; Fang, S.Q.; Zeng, R. miR-143-3p inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating its target gene FGF1. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, V.; Cornella, H.; Moeini, A.; Vidal, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Sia, D.; Peix, J.; Cabellos, L.; Alsinet, C.; Torrecilla, S.; et al. Tumour initiating cells and IGF/FGF signalling contribute to sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2015, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Huang, S.; Hu, C.A.A.; Teng, Y. FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatlen, M.A.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Sherwin, C.A.; Rozsahegyi, E.; Rubin, N.; Sheets, M.P.; Kim, J.L.; Miduturu, C.; Bifulco, N.; Brooijmans, N.; et al. Acquired on-target clinical resistance validates fgfr4 as a driver of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Montal, R.; Sia, D.; Finn, R.S. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardini, A.C.; Puzzoni, M.; Montagnani, F.; Marisi, G.; Tamburini, E.; Cucchetti, A.; Solaini, L.; Foschi, F.G.; Conti, F.; Ercolani, G.; et al. Profile of lenvatinib in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Design, development, potential place in therapy and network meta-analysis of hepatitis b and hepatitis c in all phase iii trials. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuma, M.; Uojima, H.; Numata, K.; Hidaka, H.; Toyoda, H.; Hiraoka, A.; Tada, T.; Hirose, S.; Atsukawa, M.; Itokawa, N.; et al. Early changes in circulating FGF19 and ang-2 levels as possible predictive biomarkers of clinical response to lenvatinib therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonbol, M.B.; Riaz, I.B.; Naqvi, S.A.A.; Almquist, D.R.; Mina, S.; Almasri, J.; Shah, S.; Almader-Douglas, D.; Uson Junior, P.L.S.; Mahipal, A.; et al. Systemic Therapy and Sequencing Options in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e204930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, F.; Yoshida, H.; Tateishi, R.; Sato, S.; Kawabe, T.; Obi, S.; Kondo, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Tagawa, K.; Ikeda, M.; et al. A phase I/II trial of the oral antiangiogenic agent TSU-68 in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, Y.; Kanai, F.; Aramaki, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yamakado, K.; Kaneko, S.; Kudo, M.; Imanaka, K.; Kora, S.; et al. A randomised phase II study of TSU-68 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolisation. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Le Coutre, P.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; Talpaz, M.; et al. A phase 2 trial of ponatinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richeldi, L.; Du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FDA. Balversa (Erdafinitib); Janssen Biotech: Horsham, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–21.
- Markham, A. Erdafitinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavine, P.R.; Mooney, L.; Kilgour, E.; Thomas, A.P.; Al-Kadhimi, K.; Beck, S.; Rooney, C.; Coleman, T.; Baker, D.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD4547: An orally bioavailable, potent, and selective inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase family. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2045–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanes, R.; Munthe, E.; Grad, I.; Han, J.; Karlsen, I.; McCormack, E.; Meza-Zepeda, L.; Stratford, E.; Myklebost, O. Preclinical Evaluation of the Pan-FGFR Inhibitor LY2874455 in FRS2-Amplified Liposarcoma. Cells 2019, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javle, M.; Lowery, M.; Shroff, R.T.; Weiss, K.H.; Springfeld, C.; Borad, M.J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Goyal, L.; Sadeghi, S.; Macarulla, T.; et al. Phase II study of BGJ398 in patients with FGFR-Altered advanced cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, H.; Lee, L.Y.; Goh, K.Y.; Ong, R.; Hao, H.-X.; Huang, A.; Wang, Y.; Graus, P.D.; Chow, P.; Chung, A. Infigratinib Mediates Vascular Normalization, Impairs Metastasis, and Improves Chemotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Patterson, A.V.; Smaill, J.B.; Ding, K. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 (FGFR4) Selective Inhibitors as Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy: Advances and Prospects. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagel, M.; Miduturu, C.; Sheets, M.; Rubin, N.; Weng, W.; Stransky, N.; Bifulco, N.; Kim, J.L.; Hodous, B.; Brooijmans, N.; et al. First selective small molecule inhibitor of FGFR4 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas with an activated FGFR4 signaling pathway. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, R.D.; Sarker, D.; Meyer, T.; Yau, T.; Macarulla, T.; Park, J.W.; Choo, S.P.; Hollebecque, A.; Sung, M.W.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. First-in-human phase i study of fisogatinib (BLU-554) validates aberrant FGF19 signaling as a driver event in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, J.J.; Coffey, H.; Corcoran, E.; Tsai, J.; Huang, C.L.; Ichikawa, K.; Prajapati, S.; Hao, M.H.; Bailey, S.; Wu, J.; et al. H3B-6527 Is a potent and selective inhibitor of FGFR4 in FGF19-Driven hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6999–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, S.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Xu, G.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y. Characterization of FGF401 as a reversible covalent inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 5890–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Adler, F.; Buhles, A.; Stamm, C.; Fairhurst, R.A.; Kiffe, M.; Sterker, D.; Centeleghe, M.; Wartmann, M.; Kinyamu-Akunda, J.; et al. FGF401, A First-In-Class Highly Selective and Potent FGFR4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of FGF19-Driven Hepatocellular Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 2194–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Jiao, D.; Qin, S.; Chu, Q.; Wu, K.; Li, A. Synergistic effect of immune checkpoint blockade and anti-angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpekris, F.; Voutouri, C.; Baish, J.W.; Duda, D.G.; Munn, L.L.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Jain, R.K. Combining microenvironment normalization strategies to improve cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3728–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Chan, C.K.; Hahn, S.M.; Weissman, I.L.; Jiang, W. Improving immune-vascular crosstalk for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FGF Subfamily | FGF | FGFR |
|---|---|---|
| FGF1 (paracrine) | FGF1 (aFGF) | All FGFRs |
| FGF2 (bFGF) | FGFR1c, FGFR2c, FGFR3-IIIc, FGFR1b, FGFR4 | |
| FGF4 (paracrine) | FGF4 | FGFR1c, FGFR2c, FGFR3c |
| FGF5 | FGFR1c, FGFR2 c | |
| FGF6 | FGFR2b | |
| FGF7 (paracrine) | FGF3 | FGFR1b, FGFR2b |
| FGF7(KGF) | FGFR2b | |
| FGF10 | FGFR2b | |
| FGF22 | FGFR1b, FGFR2b | |
| FGF8 (paracrine) | FGF8 | FGFR2c, FGFR3c, FGFR4 |
| FGF17 | FGFR2c, FGFR3c, FGFR4 | |
| FGF18 | FGFR2c, FGFR3c, FGFR4 | |
| FGF9 (paracrine) | FGF9 | FGFR3b, FGFR3c |
| FGF16 | FGFR2c, FGFR3c, and FGFR4 | |
| FGF20 | FGFR1c | |
| FGF19 (endocrine) | FGF15/19 | FGFR4, FGFR1c, FGFR2c, FGFR3c |
| FGF21 | FGFR1c, FGFR3c | |
| FGF23 | FGFR1c, FGFR2c, FGFR3c, FGFR4 | |
| FGF11 (Intracrine) | FGF11 | |
| FGF12 | ||
| FGF13 | ||
| FGF14 |
| Drug | Drug Target | Conditions | Status | Phase | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regorafenib | VEGFR1–3, PDGFR, RAF kinase, FGFR1–2 | HCC | Not recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT04476329 |
| BLU554 | FGFR4 | HCC | Active, not recruiting | Active, not recruiting | NCT02508467 |
| H3B-6527 | FGFR4 | HCC | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT02834780 |
| Regorafenib + Nivolumab | VEGFR1–3, PDGFR, RAF kinase, FGFR1–2 + PD-1 | HCC | Recruiting | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT04170556 |
| Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib | PD-1 + VEGFR1–3, PDGFR, FGFR1–4, RET | Liver Transplant Complications; HCC Recurrent | Recruiting | Not Applicable | NCT04425226 |
| Durvalumab + Lenvatinib | PD-L1 + VEGFR1–3, PDGFR, FGFR1–4, RET | Liver carcinoma; Liver Transplant; Complications | Recruiting | Not Applicable | NCT04443322 |
| Camrelizumab + Lenvatinib | PD-1 + Multitarget kinase inhibitors | HCC | Recruiting | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT04443309 |
| Lenvatinib + Toripalimab | VEGFR1–3, PDGFR, FGFR1–4, RET + PD-1 | HCC | Recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT04368078 |
| Lenvatinib + TACE versus Sorafenib + TACE | VEGFR1–3, PDGFR, FGFR1–4, RET | HCC; Tumor Thrombus | Enrolling | Phase 4 | NCT04127396 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, T.; Xia, L. FGF/FGFR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Carcinogenesis to Recent Therapeutic Intervention. Cancers 2021, 13, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061360
Wang Y, Liu D, Zhang T, Xia L. FGF/FGFR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Carcinogenesis to Recent Therapeutic Intervention. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061360
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yijun, Danfei Liu, Tongyue Zhang, and Limin Xia. 2021. "FGF/FGFR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Carcinogenesis to Recent Therapeutic Intervention" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061360
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, D., Zhang, T., & Xia, L. (2021). FGF/FGFR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Carcinogenesis to Recent Therapeutic Intervention. Cancers, 13(6), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061360






