The Debatable Benefit of Gross-Total Resection of Brain Metastases in a Comprehensive Treatment Setting
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Data Collection
2.2. Surgery
2.3. Assessment of Tumor Burden, Eloquence, Extent of Tumor Resection, and Potential in-Brain Recurrence
- 0 = no residual tumor (GTR)
- 1 = ≤5% residual tumor
- 2 = 5–20% residual tumor
- 3 = >20% residual tumor
- 1–3 = sub-total resection (STR)
- (1)
- local recurrence (LR): at resection cavity only
- (2)
- distant recurrence (DR): distant without contact to resection cavity
- (3)
- combined recurrence (CR): combination of LR and DR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Baseline Clinical Data
3.2. Treatment-Related Parameters
3.3. Cerebral Disease Control and Overall Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Shamy, G.; Sawaya, R. Management of Brain Metastases: The Indispensable Role of Surgery. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 92, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; DeAngelis, L.M. Treatment of Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabouret, E.; Chinot, O.; Metellus, P.; Tallet, A.; Viens, P.; Gonçalves, A. Recent Trends in Epidemiology of Brain Metastases: An Overview. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar]
- Carapella, C.M.; Gorgoglione, N.; Oppido, P.A. The Role of Surgical Resection in Patients with Brain Metastases. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecht, C.J.; Haaxma-Reiche, H.; Noordijk, E.M.; Padberg, G.W.; Voormolen, J.H.C.; Hoekstra, F.H.; Tans, J.T.J.; Lambooij, N.; Metsaars, J.A.L.; Wattendorff, A.R.; et al. Treatment of Single Brain Metastasis: Radiotherapy Alone or Combined with Neurosurgery. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 33, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Walsh, J.W.; Dempsey, R.J.; Maruyama, Y.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Macdonald, J.S.; Young, B. A Randomized Trial of Surgery in the Treatment of Single Metastases to the Brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, M.A.; Rapp, M.; Bühner, J.; Slotty, P.J.; Reichelt, D.; Sadat, H.; Dibué-Adjei, M.; Steiger, H.-J.; Turowski, B.; Sabel, M. Early Postoperative Magnet Resonance Tomography after Resection of Cerebral Metastases. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2015, 157, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesel, B.; Thomé, C.M.; Weiss, T.; Jakola, A.S.; Darlix, A.; Pellerino, A.; Furtner, J.; Kerschbaumer, J.; Freyschlag, C.F.; Wick, W.; et al. Perioperative Imaging in Patients Treated with Resection of Brain Metastases: A Survey by the European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO) Youngsters Committee. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesrud, I.C.; Schulz, M.K.; Marcovic, L.; Kristensen, B.W.; Pedersen, C.B.; Kristiansen, C.; Poulsen, F.R. Early Postoperative MRI after Resection of Brain Metastases-Complete Tumour Resection Associated with Prolonged Survival. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2019, 161, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, O.; Benoit, B.; Cross, P.; Da Silva, V.; Esche, B.; Lesiuk, H.; Gonsalves, C. Prognostic Factors Derived from Recursive Partition Analysis (RPA) of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) Brain Metastases Trials Applied to Surgically Resected and Irradiated Brain Metastatic Cases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 42, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, J.W.; Han, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.-K.; Kim, C.-Y.; Paek, S.H.; Jung, H.-W. The Role of Surgical Resection in the Management of Brain Metastasis: A 17-Year Longitudinal Study. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendulkar, R.D.; Liu, S.W.; Barnett, G.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Toms, S.A.; Jin, T.; Suh, J.H. RPA Classification Has Prognostic Significance for Surgically Resected Single Brain Metastasis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, J.M.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Diniz, J.M.; de Abreu, B.M.; Kamimura, F.; Sousa, U.O.; Botelho, R.V.; de Oliveira, M.F. Analysis of Survival in Patients with Brain Metastases Treated Surgically: Impact of Age, Gender, Oncologic Status, Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, Number and Localization of Lesions, and Primary Cancer Site. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2018, 64, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho-Díaz, B.; Lorenzana-Mendoza, N.A.; Chávez-Hernandez, J.D.; González-Aguilar, A.; Reyes-Soto, G.; Herrera-Gómez, Á. Clinical Manifestations and Location of Brain Metastases as Prognostic Markers. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2019, 43, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumert, B.G.; Rutten, I.; Dehing-Oberije, C.; Twijnstra, A.; Dirx, M.J.M.; Debougnoux-Huppertz, R.M.T.L.; Lambin, P.; Kubat, B. A Pathology-Based Substrate for Target Definition in Radiosurgery of Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Rajky, O.; Winkler, F.; Bartsch, R.; Furtner, J.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Goodman, S.L.; Weller, M.; Schittenhelm, J.; Preusser, M. Invasion Patterns in Brain Metastases of Solid Cancers. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raore, B.; Schniederjan, M.; Prabhu, R.; Brat, D.J.; Shu, H.-K.; Olson, J.J. Metastasis Infiltration: An Investigation of the Postoperative Brain-Tumor Interface. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Kim, Y.Z.; Nam, B.H.; Shin, S.H.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Zo, J.I.; Lee, S.H. Reduced Local Recurrence of a Single Brain Metastasis through Microscopic Total Resection. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 110, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, M.A.; Dibué, M.; Santacroce, A.; Zella, S.M.; Niemann, L.; Steiger, H.-J.; Rapp, M.; Sabel, M. The Tumour Is Not Enough or Is It? Problems and New Concepts in the Surgery of Cerebral Metastases. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, M.A.; Rapp, M.; Slotty, P.J.; Turowski, B.; Sadat, H.; Smuga, M.; Dibué-Adjei, M.; Steiger, H.-J.; Szelényi, A.; Sabel, M. Incidence of Local In-Brain Progression after Supramarginal Resection of Cerebral Metastases. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2015, 157, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Ahmed, S.; McAleer, M.F.; Weinberg, J.S.; Li, J.; Brown, P.; Settle, S.; Prabhu, S.S.; Lang, F.F.; Levine, N.; et al. Post-Operative Stereotactic Radiosurgery versus Observation for Completely Resected Brain Metastases: A Single-Centre, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.E.; Scott, C.; Murray, K.; Curran, W. Validation of the RTOG Recursive Partitioning Analysis (RPA) Classification for Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 47, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.G.; Byhardt, R. Recursive Partitioning Analysis (RPA) of Prognostic Factors in Three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) Brain Metastases Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.F.; Clark, A.; Jensen, R.L.; Bernstein, M.; Guha, A.; Carrabba, G.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Kim, W.; Liau, L.M.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Multiinstitutional Validation of the University of California at San Francisco Low-Grade Glioma Prognostic Scoring System: Clinical Article. JNS 2009, 111, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E.P.; Mathew, M.; Tam, M.; King, J.V.; Kunnakkat, S.D.; Parker, E.C.; Golfinos, J.G.; Gruber, M.L.; Narayana, A. In volved Field Radiation Therapy after Surgical Resection of Solitary Brain Metastases–Mature Results. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, K.; Narita, Y.; Miyakita, Y.; Ohno, M.; Sumi, M.; Mayahara, H.; Kayama, T.; Shibui, S. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Surgery Followed by Local Brain Radiotherapy and Surgery Followed by Whole Brain Radiotherapy in Patients with Single Brain Metastasis: Single-Center Retrospective Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, e475–e480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igaki, H.; Harada, K.; Umezawa, R.; Miyakita, Y.; Ohno, M.; Takahashi, M.; Sumi, M.; Inaba, K.; Murakami, N.; Ito, Y.; et al. Outcomes of Surgery Followed by Local Brain Radiotherapy Compared with Surgery Followed by Whole Brain Radiotherapy for Single Brain Metastasis. Tumori 2017, 103, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.M.; Vatner, R.E.; Tam, M.; Golfinos, J.G.; Narayana, A.; Kondziolka, D.; Silverman, J.S. Resection Followed by Involved-Field Fractionated Radiotherapy in the Management of Single Brain Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatiboglu, M.A.; Wildrick, D.M.; Sawaya, R. The Role of Surgical Resection in Patients with Brain Metastases. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroński, M.; Arbit, E.; Burt, M.; Galicich, J.H. Survival after Surgical Treatment of Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer: A Follow-up Study of 231 Patients Treated between 1976 and 1991. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 83, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rades, D.; Veninga, T.; Hornung, D.; Wittkugel, O.; Schild, S.E.; Gliemroth, J. Single Brain Metastasis: Whole-Brain Irradiation plus Either Radiosurgery or Neurosurgical Resection. Cancer 2012, 118, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitoh, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Shiba, M.; Yoshida, S.; Sekine, Y.; Baba, M.; Iizasa, T.; Kubota, M. Prognostic Factors in Surgical Treatment of Solitary Brain Metastasis after Resection of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 1999, 24, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.J.; Gluck, D.S.; Konchingeri, R.H. Surgical Resection of Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 1996, 138, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Bendix, C.; Rapp, M.; Mijderwijk, H.-J.; von Sass, C.; Dibué-Adjei, M.; Cornelius, J.F.; Steiger, H.-J.; Turowski, B.; Sabel, M.; Kamp, M.A. Risk Factors for In-Brain Local Progression in Elderly Patients after Resection of Cerebral Metastases. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stummer, W.; Pichlmeier, U.; Meinel, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Zanella, F.; Reulen, H.-J.; ALA-Glioma Study Group. Fluorescence-Guided Surgery with 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Resection of Malignant Glioma: A Randomised Controlled Multicentre Phase III Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayas, A.W.; Grau, S.; Jablonska, K.; Ruess, D.; Ruge, M.; Marnitz, S.; Goldbrunner, R.; Kocher, M. Postoperative Local Fractionated Radiotherapy for Resected Single Brain Metastases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2018, 194, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schackert, G.; Lindner, C.; Petschke, S.; Leimert, M.; Kirsch, M. Retrospective Study of 127 Surgically Treated Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases: Indication, Prognostic Factors, and Outcome. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirati, M.; Nahed, B.V.; Andrews, D.; Chen, C.C.; Olson, J.J. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on Treatment Options for Adults With Multiple Metastatic Brain Tumors. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, E180–E182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venur, V.A.; Cohen, J.V.; Brastianos, P.K. Targeting Molecular Pathways in Intracranial Metastatic Disease. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venur, V.A.; Leone, J.P. Targeted Therapies for Brain Metastases from Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schödel, P.; Jünger, S.T.; Wittersheim, M.; Reinhardt, H.C.; Schmidt, N.-O.; Goldbrunner, R.; Proescholdt, M.; Grau, S. Surgical Resection of Symptomatic Brain Metastases Improves the Clinical Status and Facilitates Further Treatment. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 7503–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintea, B.; Baumert, B.; Kinfe, T.M.; Gousias, K.; Parpaley, Y.; Boström, J.P. Early Motor Function after Local Treatment of Brain Metastases in the Motor Cortex Region with Stereotactic Radiotherapy/Radiosurgery or Microsurgical Resection: A Retrospective Study of Two Consecutive Cohorts. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villà, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant Whole-Brain Radiotherapy versus Observation after Radiosurgery or Surgical Resection of One to Three Cerebral Metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952-26001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Age [median; (range)] | 62 (19–87) |
| Gender [n; (%)] | |
| Male | 88 (44.7) |
| Female | 109 (55.3) |
| Primary [n; (%)] | |
| Lung (NSCLC) | 92 (46.7) |
| Melanoma | 20 (10.2) |
| Breast | 27 (13.7) |
| Gastrointestinal | 33 (16.8) |
| Others | 17 (8.6) |
| Cancer of unknown primary | 7 (3.6) |
| Controlled systemic disease [n; (%)] | 63 (32.0) |
| Tumor location [n; (%)] | |
| Frontal | 65 (33.0) |
| Temporal | 29 (14.7) |
| Parietal | 21 (10.7) |
| Temporo-parietal | 3 (1.5) |
| Occipital | 12 (6.1) |
| Cerebellar | 66 (33.5) |
| Basal ganglia | 1 (0.5) |
| Eloquent location [n; (%)] | 74 (37.6) |
| Neurological deficits [%] | |
| Seizures | 15.7 |
| Aphasia | 8.1 |
| Hemiparesis | 29.9 |
| Visual field defects | 6.6 |
| Signs of elevated intracranial pressure | 33 |
| Adjuvant Treatment [n; (%)] | 130 (66.0) |
| Systemic medical treatment | 75 (38.1) |
| Molecular treatment | |
| Postoperative Radiotherapy | |
| Whole brain radiotherapy | 47 (24.9) |
| Partial/focal radiotherapy | 142 (72.1) |
| Stereotactic radiosurgery | 6 (3.0) |
| Scale | Before Surgery | After Surgery | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRC-NPS [n; (%)] | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 25 (12.7) | 110 (55.8) | |
| 2 | 97 (49.2) | 68 (34.5) | |
| 3 | 31 (15.7) | 14 (7.1) | |
| 4 | 44 (22.3) | 4 (2.0) | |
| 5 | 1 (0.5) | ||
| KPS [median; range] | 80 (40–100) | 90 (30–100) | <0.001 |
| RPA group [n; (%)] | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 55 (27.9) | 69 (35.0) | |
| 2 | 96 (48.7) | 121 (61.4) | |
| 3 | 46 (23.4) | 7 (3.6) |
| Parameter | Local Recurrence | Overall Survival | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Log Rank Test (p-Value) | Log Rank Test (p-Value) | Cox Regression (HR 95%CI; p-Value) | |
| Age < 65 years | 0.780 | 0.251 | |
| Gender | 0.144 | 0.100 | |
| Controlled systemic disease | 0.698 | 0.039 | 0.59 0.40–0.88 0.009 |
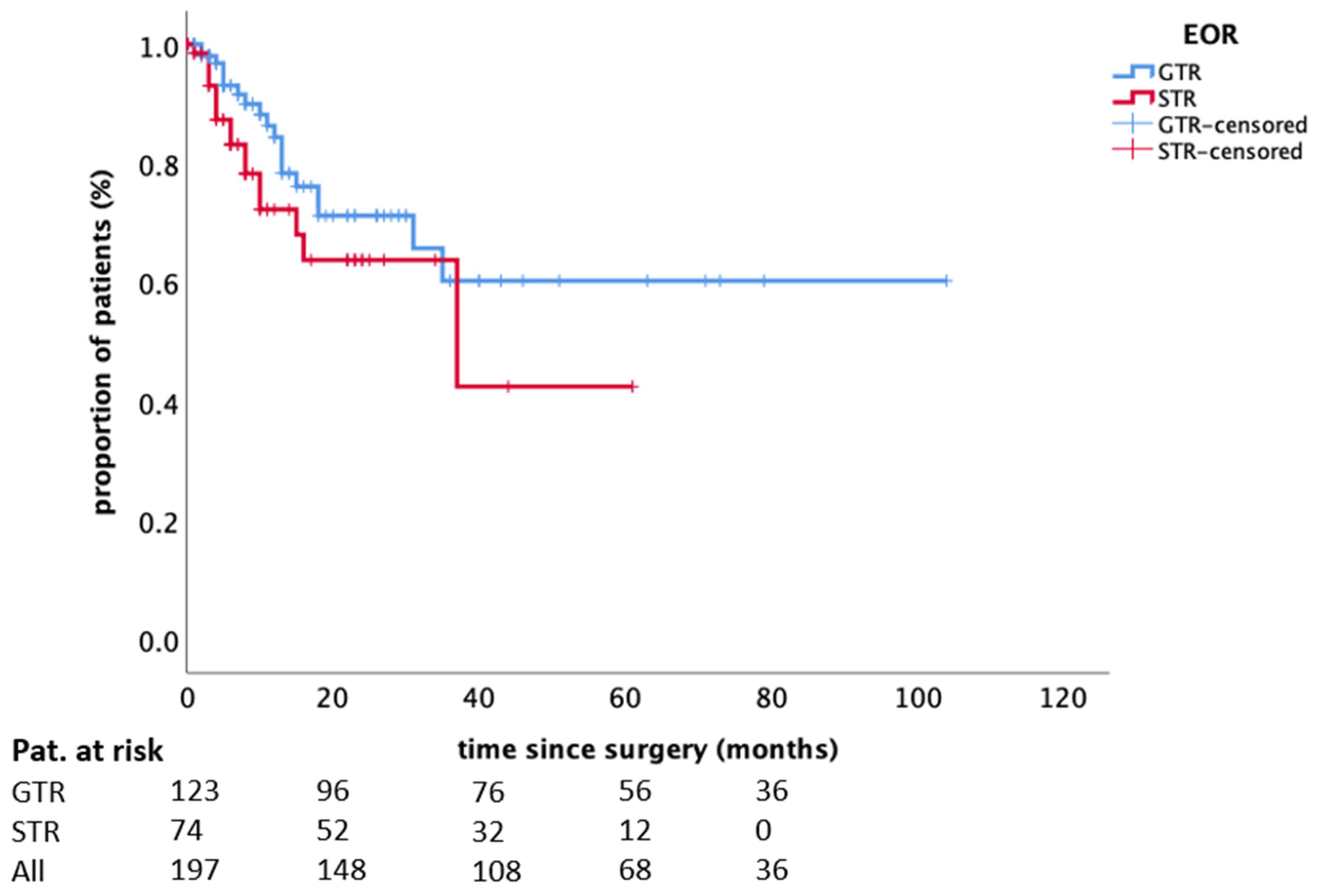
| Extent of resection (GTR vs. STR) | 0.139 | 0.759 | |
| Adjuvant systemic treatment | 0.313 | <0.0001 | 0.45 0.31–0.65 <0.0001 |
| Adjuvant radiotherapy modality (WBRT vs. fRT vs. SRS) | 0.154 | ||
| In-brain recurrence | 0.114 | ||
| Local recurrence | 0.591 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jünger, S.T.; Pennig, L.; Schödel, P.; Goldbrunner, R.; Friker, L.; Kocher, M.; Proescholdt, M.; Grau, S. The Debatable Benefit of Gross-Total Resection of Brain Metastases in a Comprehensive Treatment Setting. Cancers 2021, 13, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061435
Jünger ST, Pennig L, Schödel P, Goldbrunner R, Friker L, Kocher M, Proescholdt M, Grau S. The Debatable Benefit of Gross-Total Resection of Brain Metastases in a Comprehensive Treatment Setting. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061435
Chicago/Turabian StyleJünger, Stephanie T., Lenhard Pennig, Petra Schödel, Roland Goldbrunner, Lea Friker, Martin Kocher, Martin Proescholdt, and Stefan Grau. 2021. "The Debatable Benefit of Gross-Total Resection of Brain Metastases in a Comprehensive Treatment Setting" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061435
APA StyleJünger, S. T., Pennig, L., Schödel, P., Goldbrunner, R., Friker, L., Kocher, M., Proescholdt, M., & Grau, S. (2021). The Debatable Benefit of Gross-Total Resection of Brain Metastases in a Comprehensive Treatment Setting. Cancers, 13(6), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061435






