Immunonutrition Changes Inflammatory Response in Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
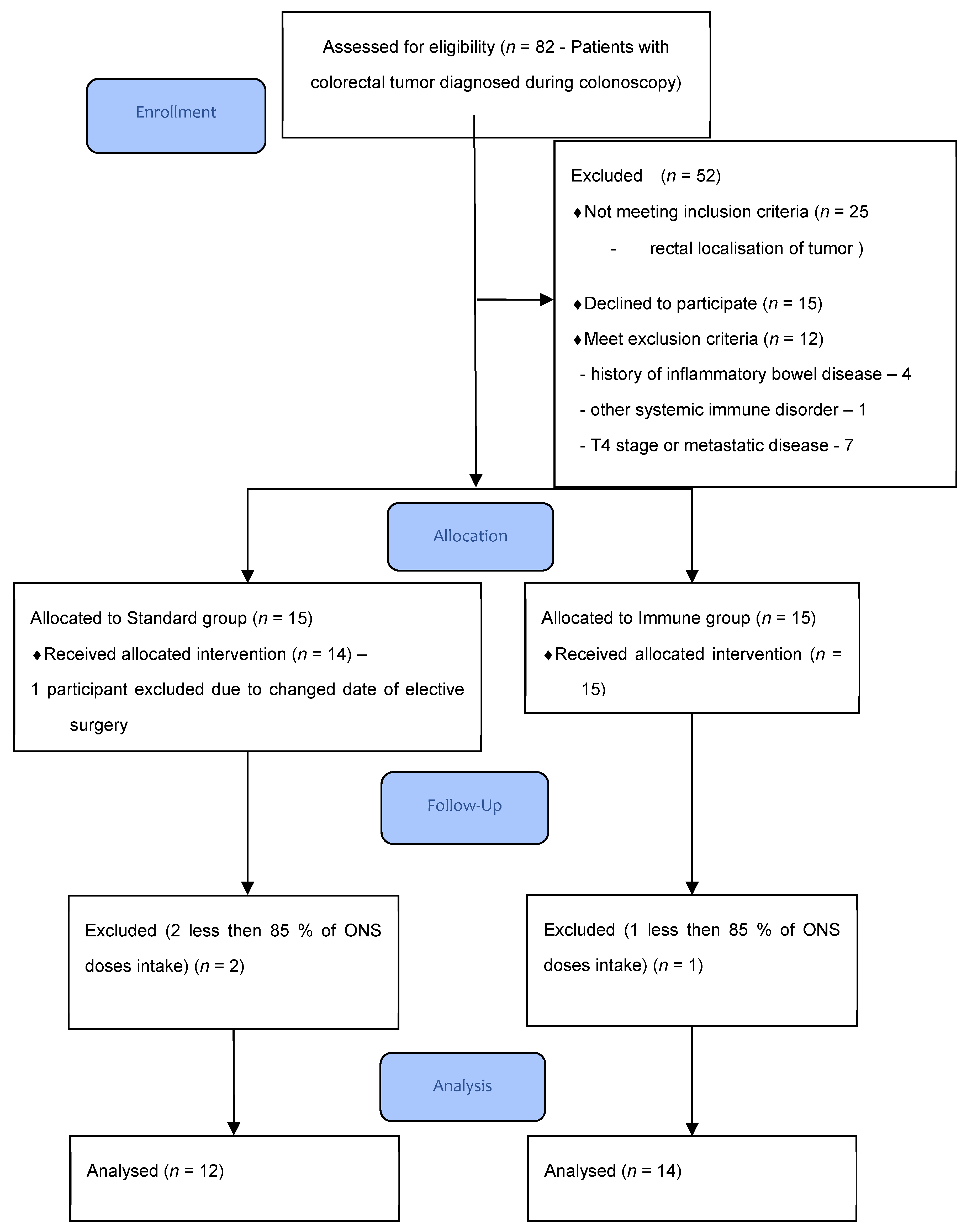
2.1. Patients
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Randomization
2.4. Study Protocol
2.5. Intervention
2.6. Perioperative Care
2.7. Tissue Tumor Cytokine Concentration Measurement
2.8. Tissue Tumor Neutrophile Infiltration Assessment
2.9. End Point Criteria
2.9.1. Primary Outcome
2.9.2. Secondary Outcomes
2.10. Sample Size Calculation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
The Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nygren, J.; Thacker, J.; Carli, F.; Fearon, K.C.; Norderval, S.; Lobo, D.N.; Ljungqvist, O.; Soop, M.; Ramirez, J. Guidelines for perioperative care in elective rectal/pelvic surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society recommendations. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burden, S.; Todd, C.; Hill, J.; Lal, S. Pre-operative nutrition support in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, Cd008879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.; et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Yang, M.; Guo, N.; Ma, X.; Bu, Y.; et al. Immunonutrition vs Standard Nutrition for Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (Part 1). J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 742–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, X.; Xin, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J. Effect of immunonutrition on colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2018, 33, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lind, D.S. Arginine and cancer. J. Nutr. 2004, 134 (Suppl. 10), 2837S–2841S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Koussa, H.; El Mais, N.; Maalouf, H.; Abi-Habib, R.; El-Sibai, M. Arginine deprivation: A potential therapeutic for cancer cell metastasis? A review. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, F.; Kashfi, K.; Nath, N. The dual role of iNOS in cancer. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Generator Liczb Losowych. Available online: https://www.naukowiec.org/kalkulatory/liczby-losowe.html (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Pisarska, M.; Torbicz, G.; Gajewska, N.; Rubinkiewicz, M.; Wierdak, M.; Major, P.; Budzyński, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Pędziwiatr, M. Compliance with the ERAS Protocol and 3-Year Survival After Laparoscopic Surgery for Non-metastatic Colorectal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 2552–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magierowska, K.; Korbut, E.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Surmiak, M.; Chmura, A.; Bakalarz, D.; Buszewicz, G.; Wójcik, D.; Śliwowski, Z.; Ginter, G.; et al. Oxidative gastric mucosal damage induced by ischemia/reperfusion and the mechanisms of its prevention by carbon monoxide-releasing tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Yeom, S.S.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, H.R. Effect of preoperative immunonutrition on outcomes of colon cancer surgery: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Pozzo, C.; Strippoli, A.; Bria, E.; Tortora, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Effects of nutritional interventions on nutritional status in patients with gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 38, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.L.; Oh, E.S.; Lee, R.W.; Finucane, T.E. Serum Albumin and Prealbumin in Calorically Restricted, Nondiseased Individuals: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 1023.e1–1023.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prieto, I.; Montemuiño, S.; Luna, J.; de Torres, M.V.; Amaya, E. The role of immunonutritional support in cancer treatment: Current evidence. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariette, C. Immunonutrition. J. Visc. Surg. 2015, 152 (Suppl. 1), S14–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, N. Chemokines and cancer: New immune checkpoints for cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 51, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines in cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klampfer, L. Cytokines, inflammation and colon cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwirner, N.W.; Domaica, C.I. Cytokine regulation of natural killer cell effector functions. Biofactors 2010, 36, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillerey, C. NK Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1273, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjević, G.M.; Vuletić, A.M.; Mirjačić Martinović, K.M.; Larsen, A.K.; Jurišić, V.B. The role of cytokines in the regulation of NK cells in the tumor environment. Cytokine 2019, 117, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.T.; Naismith, J.H. TNF alpha and the TNF receptor superfamily: Structure-function relationship(s). Microsc Res. Tech. 2000, 50, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. TNF-alpha in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Horssen, R.; Ten Hagen, T.L.; Eggermont, A.M. TNF-alpha in cancer treatment: Molecular insights, antitumor effects, and clinical utility. Oncologist 2006, 11, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Yang, L.; Shen, R.; Kong, B.; Chen, W.; Liang, J.; Tang, G.; Zhang, B. Th17 cells regulate the production of CXCL1 in breast cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 56, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Quay, J.; Koren, H.S.; Haskill, J.S. Constitutive and stimulated MCP-1, GRO alpha, beta, and gamma expression in human airway epithelium and bronchoalveolar macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, L278–L286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Grotendorst, G.R. Cloning and sequencing of a new gro transcript from activated human monocytes: Expression in leukocytes and wound tissue. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 5596–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jin, R.; Chen, R.; Huang, Z. Complementary action of CXCL1 and CXCL8 in pathogenesis of gastric carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, W.A.; Jian, S.F.; Fan, H.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Interaction between Tumor-Associated Dendritic Cells and Colon Cancer Cells Contributes to Tumor Progression via CXCL1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spaks, A. Role of CXC group chemokines in lung cancer development and progression. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S164–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, A.; Sekido, N.; Akahoshi, T.; Wada, T.; Mukaida, N.; Matsushima, K. Essential involvement of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in acute inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 56, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, R.; Erikson, J.S.; West, D.C.; Kinsella, A.R.; Slavin, J.; Christmas, S.E. Interleukin-8 as an autocrine growth factor for human colon carcinoma cells in vitro. Cytokine 2000, 12, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J. Myeloperoxidase-derived oxidation: Mechanisms of biological damage and its prevention. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buijs, N.; van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A.; Langius, J.A.; Leemans, C.R.; Kuik, D.J.; Vermeulen, M.A.; van Leeuwen, P.A. Perioperative arginine-supplemented nutrition in malnourished patients with head and neck cancer improves long-term survival. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albaugh, V.L.; Pinzon-Guzman, C.; Barbul, A. Arginine-Dual roles as an onconutrient and immunonutrient. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Yang, B.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, D. Effect of Marine-Derived n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Major Eicosanoids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis from 18 Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mocellin, M.C.; Fernandes, R.; Chagas, T.R.; Trindade, E. A meta-analysis of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids effects on circulating acute-phase protein and cytokines in gastric cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, N.; Atkinson, C.; Thomas, S.; Lewis, S.J. Immunonutrition for patients undergoing surgery for head and neck cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, Cd010954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, G.M.; Tian, X.; Liang, H.; Yi, L.J.; Zhou, J.G.; Zeng, Z.; Shuai, T.; Ou, Y.X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Role of Enteral Immunonutrition in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2015, 94, e1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Group 1 IMMUNE | Group 2 CONTROL | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 14 | 12 | - |
| Females, n (%) | 7 (50.0%) | 7 (58.3%) | 0.6708 |
| Males, n (%) | 7 (50.0%) | 5 (41.7%) | |
| Mean age, years ± SD | 69.9 ± 10.9 | 68.4 ± 7.62 | 0.6908 |
| Body mass index (BMI), kg/m2 ± SD | 29.2 ± 5.5 | 27.8 ± 3.9 | 0.2565 |
| ASA 1, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 1 (8.3%) | 0.8402 |
| ASA 2, n (%) | 8 (57.1%) | 8 (66.7%) | |
| ASA 3, n (%) | 5 (35.7%) | 3 (25.0%) | |
| Any comorbidity, n (%) | 12 (85.7%) | 8 (66.7%) | 0.2504 |
| Cardiovascular, n (%) | 5 (35.7%) | 3 (25.0%) | 0.5551 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 10 (71.4%) | 7 (36.1%) | 0.4849 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 2(14.2%) | 3 (25.0%) | 0.4895 |
| Renal disease, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 1 (8.3%) | 0.7587 |
| Other comorbidity, n (%) | 2 (14.2%) | 1 (8.3%) | 0.9095 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 3 (21.4%) | 2 (16.7%) | 0.6357 |
| AJCC Stage I, n (%) | 3 (21.4%) | 2 (16.7%) | 0.4241 |
| AJCC Stage II, n (%) | 4 (28.6%) | 6 (50.0%) | |
| AJCC Stage III, n (%) | 6 (42.9%) | 2 (16.7%) | |
| AJCC Stage IV, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 2 (16.7%) | |
| NRS 2000 median, (IQR) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 0.7970 |
| Tumor location | |||
| Cecum, n (%) | 3 (21.4%) | 2 (16.7%) | 0.7865 |
| Ascending colon, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 3 (5.5%) | |
| Transvers colon n (%) | 2 (14.2%) | 1 (36.1%) | |
| Descending colon n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 1 (11.1%) | |
| Sigmoid colon, n (%) | 7 (50.0%) | 5 (41.7%) | |
| Grading | |||
| G1 | 3 (21.4%) | 1(8.3%) | 0.6533 |
| G2 | 10(71.5%) | 11(91.7%) | |
| G3 | 1 (7.1%) | - |
| Parameter | Group 1 IMMUNE | Group 2 CONTROL | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 14 | 12 | - |
| Median WBC before intervention, 103/mL (IQR) | 6.60 (5.33–8.31) | 8.11 (6.16–9.28) | 0.1983 |
| Median WBC after intervention, 103/mL (IQR) | 6.49 (5.59–8.96) | 7.34 (6.06–8.15) | 0.9350 |
| p-value | 0.2945 | 0.5751 | |
| Median neutrophil before intervention, 103/mL (IQR) | 4.25 (5.40–2.15) | 4.90 (3.20–5.80) | 0.1063 |
| Median neutrophil after intervention, 103/mL (IQR) | 3.80 (2.82–5.50) | 4.72 (2.94–5.20) | 0.7281 |
| p-value | 0.9165 | 0.9528 | |
| Median lymphocytes before intervention, 103/mL (IQR) | 1.74 (1.57–2.47) | 1.80 (1.53–2.46) | 0.9128 |
| Median lymphocytes after intervention, 103/mL (IQR) | 1.83 (1.50–2.60) | 1.86 (1.56–2.44) | 0.8167 |
| p-value | 0.4421 | 0.9528 | |
| Median plasma protein before intervention, g/L (IQR) | 65.4 (59.0–72.0) | 68.0 (68.8–73.4) | 0.4250 |
| Median plasma protein after intervention, g/L (IQR) | 69.5 (64.0–72.0) | 67.5 (59.5–70.0) | 0.3913 |
| p-value | 0.7221 | 0.4990 | |
| Median plasma albumin before intervention, g/L (IQR) | 38.6 (35.9–42.0) | 42.0 (38.1–50,2) | 0.9212 |
| Median plasma albumin after intervention, g/L (IQR) | 40.0 (35.0–44.7) | 39.9 (35.6–43.0) | 0.2390 |
| p-value | 0.8588 | 0.2626 |
| Group 1—IMMUNE | p-Value | Group 2—CONTROL | p-Value | p-Value of Comparison of Changes in Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α (pg/100 ug total protein) mean ± SD | 27.79 ± 14.01 | 31.63 ± 13.28 | 0.551 | 35.68 ± 24.41 | 21.54 ± 6.84 | 0.038 | 0.049 |
| CXCL8 (pg/100 ug total protein) mean ± SD | 2608.87 ± 1715.15 | 2676.41 ± 1530.15 | 0.910 | 2975.93 ± 1484.04 | 1584.85 ± 1659.84 | 0.041 | 0.095 |
| SDF-1a (pg/100 ug total protein) median (IQR) | 399.94 (319.78–469.63) | 469.63 (395.47–565.72) | 0.477 | 421.01 (384.89–501.80) | 358.68 (333.02–371.16) | 0.823 | 0.205 |
| CXCL6 (pg/100 ug total protein) median (IQR) | 247.73 (109.53–467.97) | 241.76 (155.02–372.85) | 0.309 | 238.11 (103.41–371.02) | 133.14 (92.60–197.79) | 0.671 | 0.640 |
| CXCL2 (pg/100 ug total protein) mean ± SD | 625.63 ± 793.10 | 879.19 ± 1008.23 | 0.438 | 631.87 ± 570.80 | 301.03 ± 287.39 | 0.407 | 0.261 |
| MPO (pg/100 ug total protein) mean ± SD | 54,176.82 ± 36,077.57 | 63,096.97 ± 38,509.00 | 0.473 | 51,313.49 ± 21,340.86 | 51,114.38 ± 30,976.68 | 0.935 | 0.655 |
| CXCL1 (pg/100 ug total protein) median (IQR) | 1902.86 (1170.34–3517.76) | 2698.27 (1538.14–5124.70) | 0.821 | 2144.59 (808.68–5933.12) | 953.75 (457.85–1534.60) | 0.403 | 0.032 |
| Parameter | Group 1 IMMUNE | Group 2 CONTROL | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 14 | 12 | - |
| Median superficial neutrophil infiltration before intervention, n/HPF (IQR) | 47 (31.5–82) | 61 (35–88) | 0.5022 |
| Median superficial neutrophil infiltration after intervention, n/HPF (IQR) | 39 (31–57) | 59 (50–86) | 0.0033 |
| p-value | 0.2651 | 0.1709 | |
| Median deep neutrophil infiltration before intervention, n/HPF (IQR) | 51 (27.5–93.5) | 54 (28–87) | 0.9341 |
| Median deep neutrophil infiltration after intervention, n/HPF (IQR) | 36 (27–50) | 37 (31–50) | 0.7775 |
| p-value | 0.0865 | 0.6071 | |
| Median change in combined superficial and deep neutrophil infiltration before and after intervention, n/HPF (IQR) | −21 (−80.5–68.5) | −5 (−45–64) | 0.5458 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wierdak, M.; Surmiak, M.; Milian-Ciesielska, K.; Rubinkiewicz, M.; Rzepa, A.; Wysocki, M.; Major, P.; Kłęk, S.; Pędziwiatr, M. Immunonutrition Changes Inflammatory Response in Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Cancers 2021, 13, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061444
Wierdak M, Surmiak M, Milian-Ciesielska K, Rubinkiewicz M, Rzepa A, Wysocki M, Major P, Kłęk S, Pędziwiatr M. Immunonutrition Changes Inflammatory Response in Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061444
Chicago/Turabian StyleWierdak, Mateusz, Marcin Surmiak, Katarzyna Milian-Ciesielska, Mateusz Rubinkiewicz, Anna Rzepa, Michał Wysocki, Piotr Major, Stanisław Kłęk, and Michał Pędziwiatr. 2021. "Immunonutrition Changes Inflammatory Response in Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061444
APA StyleWierdak, M., Surmiak, M., Milian-Ciesielska, K., Rubinkiewicz, M., Rzepa, A., Wysocki, M., Major, P., Kłęk, S., & Pędziwiatr, M. (2021). Immunonutrition Changes Inflammatory Response in Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Cancers, 13(6), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061444







