Circulating Tumor DNA Early Kinetics Predict Response of Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy: Validation Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Interpretation of ctDNA Kinetics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Validation Cohort
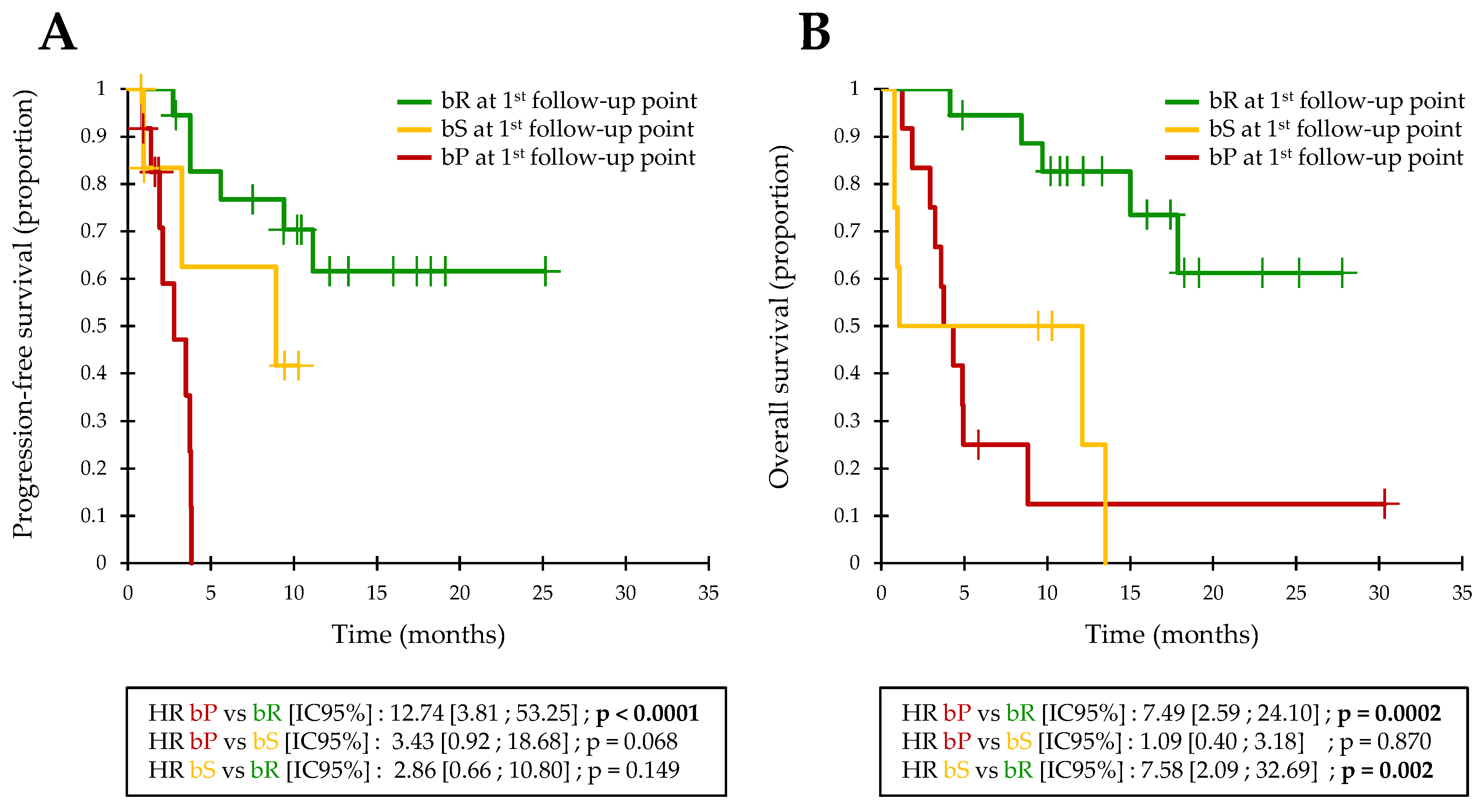
3.2. Early ctDNA Monitoring in Validation Cohort
3.3. Pooled Analysis
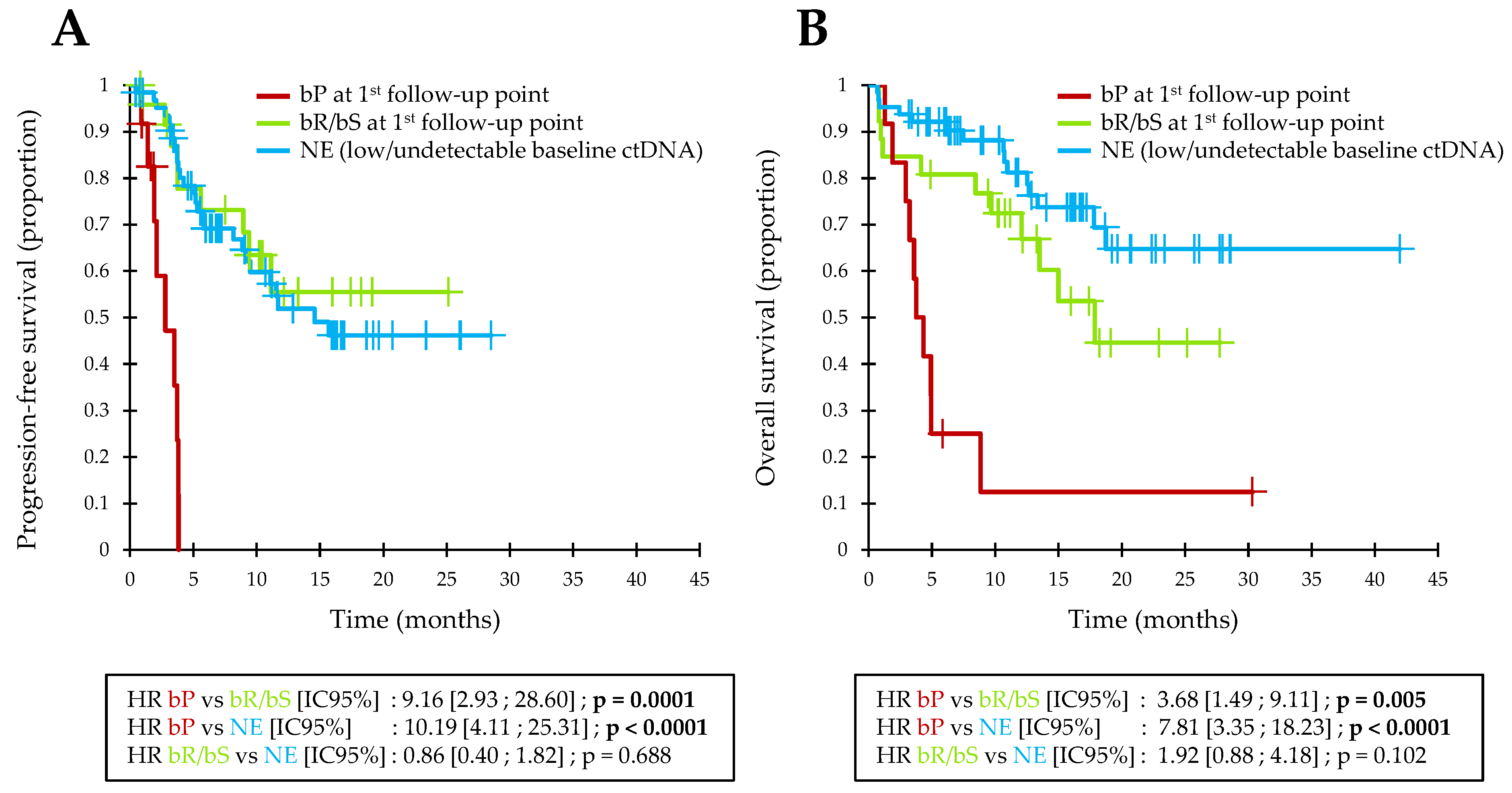
3.4. Early ctDNA Monitoring in Pooled Analysis
3.5. Prognostic Value of Baseline ctDNA Detection
3.6. Biological Follow-Up Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in Previously Untreated Melanoma without BRAF Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Minor, D.; D’Angelo, S.; Neyns, B.; Smylie, M.; Miller, W.H.; Gutzmer, R.; Linette, G.; Chmielowski, B.; Lao, C.D.; et al. Overall Survival in Patients with Advanced Melanoma Who Received Nivolumab Versus Investigator’s Choice Chemotherapy in CheckMate 037: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Dummer, R.; Smylie, M.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Puzanov, I.; Dummer, R.; Schadendorf, D.; Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Hodi, F.S.; Schachter, J.; Pavlick, A.C.; Lewis, K.D.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Investigator-Choice Chemotherapy for Ipilimumab-Refractory Melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): A Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Schachter, J.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Minor, D.; Ribas, A.; Lebbe, C.; O’Hagan, A.; Arya, N.; Guckert, M.; Schadendorf, D.; Kefford, R.F.; Grob, J.-J.; et al. Phase II Trial (BREAK-2) of the BRAF Inhibitor Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3205–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.J.; Gremel, G.; Marshall, A.; Myers, K.A.; Fisher, N.; Dunn, J.A.; Dhomen, N.; Corrie, P.G.; Middleton, M.R.; Lorigan, P.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Predicts Survival in Patients with Resected High-Risk Stage II/III Melanoma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Saw, R.P.; Thompson, J.F.; Lo, S.; Spillane, A.J.; Shannon, K.F.; Stretch, J.R.; Howle, J.; Menzies, A.M.; Carlino, M.S.; et al. Pre-Operative CtDNA Predicts Survival in High-Risk Stage III Cutaneous Melanoma Patients. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Sandhu, S.; Lee, R.J.; Li, J.; Callahan, J.; Ftouni, S.; Dhomen, N.; Middlehurst, P.; Wallace, A.; Raleigh, J.; et al. Prediction and Monitoring of Relapse in Stage III Melanoma Using Circulating Tumor DNA. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.; Kowalik, A.; Gos, A.; Wasag, B.; Lugowska, I.; Jurkowska, M.; Krawczynska, N.; Kosela-Paterczyk, H.; Switaj, T.; Teterycz, P.; et al. Cell-Free DNA BRAF V600E Measurements during BRAF Inhibitor Therapy of Metastatic Melanoma: Long-Term Analysis. Tumori 2020, 300891619900928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seremet, T.; Jansen, Y.; Planken, S.; Njimi, H.; Delaunoy, M.; El Housni, H.; Awada, G.; Schwarze, J.K.; Keyaerts, M.; Everaert, H.; et al. Undetectable Circulating Tumor DNA (CtDNA) Levels Correlate with Favorable Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma Patients Treated with Anti-PD1 Therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmamed, M.F.; Fernández-Landázuri, S.; Rodríguez, C.; Zárate, R.; Lozano, M.D.; Zubiri, L.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Martín-Algarra, S.; González, A. Quantitative Cell-Free Circulating BRAFV600E Mutation Analysis by Use of Droplet Digital PCR in the Follow-up of Patients with Melanoma Being Treated with BRAF Inhibitors. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.C.-H.; Weiss, J.; Hudson, C.; Christophi, C.; Cebon, J.; Behren, A.; Dobrovic, A. Monitoring Response to Therapy in Melanoma by Quantifying Circulating Tumour DNA with Droplet Digital PCR for BRAF and NRAS Mutations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuer, M.; Meersseman, G.; Van Den Herrewegen, S.; Jansen, Y.; Chevolet, I.; Bott, A.; Wilgenhof, S.; Seremet, T.; Jacobs, B.; Buyl, R.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of BRAF V600 Mutant Circulating Cell-Free Tumor DNA as a Tool for Therapeutic Monitoring in Metastatic Melanoma Patients Treated with BRAF/MEK Inhibitors. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F.; Huang, H.J.; Claes, B.; Falchook, G.S.; Fu, S.; Hong, D.; Ramzanali, N.M.; Nitti, G.; Cabrilo, G.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; et al. BRAF Mutation Testing in Cell-Free DNA from the Plasma of Patients with Advanced Cancers Using a Rapid, Automated Molecular Diagnostics System. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbreteau, G.; Vallée, A.; Knol, A.-C.; Théoleyre, S.; Quéreux, G.; Frénard, C.; Varey, E.; Hofman, P.; Khammari, A.; Dréno, B.; et al. Circulating Tumour DNA Is an Independent Prognostic Biomarker for Survival in Metastatic BRAF or NRAS-Mutated Melanoma Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, E.J.; Velculescu, V.E.; Pritchard, T.S.; Sausen, M.; Pardoll, D.M.; Topalian, S.L.; Diaz, L.A. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis as a Real-Time Method for Monitoring Tumor Burden in Melanoma Patients Undergoing Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, E.S.; Rizos, H.; Reid, A.L.; Boyd, S.C.; Pereira, M.R.; Lo, J.; Tembe, V.; Freeman, J.; Lee, J.H.J.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA to Monitor Treatment Response and Detect Acquired Resistance in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42008–42018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Long, G.V.; Boyd, S.; Lo, S.; Menzies, A.M.; Tembe, V.; Guminski, A.; Jakrot, V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Mann, G.J.; et al. Circulating Tumour DNA Predicts Response to Anti-PD1 Antibodies in Metastatic Melanoma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbreteau, G.; Vallée, A.; Knol, A.-C.; Théoleyre, S.; Quéreux, G.; Varey, E.; Khammari, A.; Dréno, B.; Denis, M.G. Quantitative Monitoring of Circulating Tumor DNA Predicts Response of Cutaneous Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25265–25276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M.; Lo, S.; Guminski, A.; Whitbourne, K.; Peranec, M.; Scolyer, R.; Kefford, R.F.; Rizos, H.; et al. Association Between Circulating Tumor DNA and Pseudoprogression in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Treated with Anti–Programmed Cell Death 1 Antibodies. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Váraljai, R.; Wistuba-Hamprecht, K.; Seremet, T.; Diaz, J.M.S.; Nsengimana, J.; Sucker, A.; Griewank, K.; Placke, J.-M.; Horn, P.A.; von Neuhoff, N.; et al. Application of Circulating Cell-Free Tumor DNA Profiles for Therapeutic Monitoring and Outcome Prediction in Genetically Heterogeneous Metastatic Melanoma. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselmann, V.; Gebhardt, C.; Brechtel, I.; Duda, A.; Czerwinski, C.; Sucker, A.; Holland-Letz, T.; Utikal, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Neumaier, M. Liquid Profiling of Circulating Tumor DNA in Plasma of Melanoma Patients for Companion Diagnostics and Monitoring of BRAF Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, M.M.; Wiggins, J.M.; Corless, B.C.; Long, G.V.; Flaherty, K.T.; Schadendorf, D.; Nathan, P.D.; Robert, C.; Ribas, A.; Davies, M.A.; et al. Circulating Tumour DNA in Patients with Advanced Melanoma Treated with Dabrafenib or Dabrafenib plus Trametinib: A Clinical Validation Study. Lancet Oncol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Q.; Raleigh, J.M.; Callahan, J.; Vergara, I.A.; Ftouni, S.; Hatzimihalis, A.; Colebatch, A.J.; Li, J.; Semple, T.; Doig, K.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis and Functional Imaging Provide Complementary Approaches for Comprehensive Disease Monitoring in Metastatic Melanoma. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, J.; Keller, L.; Schiller, F.; Graf, E.; Rafei-Shamsabadi, D.; Wehrle, J.; Follo, M.; Philipp, U.; Hussung, S.; Pfeifer, D.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Allows Early Treatment Monitoring in BRAF- and NRAS-Mutant Malignant Melanoma. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, G.T.; Weiner, L.M.; Atkins, M.B. Predictive Biomarkers for Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e542–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumeh, P.C.; Harview, C.L.; Yearley, J.H.; Shintaku, I.P.; Taylor, E.J.M.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasic, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. PD-1 Blockade Induces Responses by Inhibiting Adaptive Immune Resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, A.I.; Loo, K.; Pauli, M.L.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, R.; Sandoval, P.M.; Taravati, K.; Tsai, K.; Nosrati, A.; Nardo, L.; Alvarado, M.D.; et al. Tumor Immune Profiling Predicts Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Human Melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, N.; Wessel, T.; Marks, J. Digital PCR Modeling for Maximal Sensitivity, Dynamic Range and Measurement Precision. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbreteau, G.; Charpentier, S.; Vallée, A.; Denis, M.G. Use of Circulating Tumoral DNA to Guide Treatment for Metastatic Melanoma. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood-Bouwens, C.M.; Haslem, D.; Moulton, B.; Almeda, A.F.; Lee, H.; Heestand, G.M.; Nadauld, L.D.; Ji, H.P. Therapeutic Monitoring of Circulating DNA Mutations in Metastatic Cancer with Personalized Digital PCR. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bis, S.; Tsao, H. Melanoma Genetics: The Other Side. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, X.Y.; Singh, A.; Osman, N.; Piva, T.J. Role Played by Signalling Pathways in Overcoming BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Walker, A.; Gagnon, R.; Mazumdar, J.; Casey, M.; Long, G.V.; Schadendorf, D.; Flaherty, K.; Kefford, R.; Hauschild, A.; Hwu, P.; et al. Correlation of BRAF Mutation Status in Circulating-Free DNA and Tumor and Association with Clinical Outcome across Four BRAFi and MEKi Clinical Trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Kong, Y.; Si, L.; Cui, C.; Sheng, X.; Chi, Z.; Dai, J.; Yu, S.; Ma, M.; Wu, X.; et al. Clinical Significance of BRAFV600E Mutation in Circulating Tumor DNA in Chinese Patients with Melanoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanikou, E.; Haselmann, V.; Markou, A.; Duda, A.; Utikal, J.; Neumaier, M.; Lianidou, E.S. Direct Comparison Study between Droplet Digital PCR and a Combination of Allele-Specific PCR, Asymmetric Rapid PCR and Melting Curve Analysis for the Detection of BRAF V600E Mutation in Plasma from Melanoma Patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbet-Llopart, N.; Potrony, M.; Tell-Martí, G.; Carrera, C.; Barreiro, A.; Aguilera, P.; Podlipnik, S.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J.; Puig-Butillé, J.A. Detection of Cell-Free Circulating BRAFV600E by Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction in Patients with and without Melanoma under Dermatological Surveillance. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Evaluation Criteria | Definition |
|---|---|
| biological Response (bR) | Statistically significant decrease in ctDNA concentration compared to baseline, considering the accuracy of the measurement at both points (one-sided Z-test, α = 2.5%) |
| biological Progression (bP) | Statistically significant increase in ctDNA concentration compared to nadir, considering the accuracy of the measurement at both points (one-sided Z-test, α = 2.5%) |
| biological Stability (bS) |
|
| Non-evaluable biological response (NE) |
|
| Total | Undetectable Baseline ctDNA | Detectable Baseline ctDNA | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 49 | 30 | 19 | - | |
| Age m (Q1–Q3) | 63.6 (54.1–74.8) | 65.3 (54.0–77.1) | 60.9 (57.1–70.0) | 0.662 | |
| Tumor thickness m (Q1–Q3) | 3.3 (1.4–3.8) | 2.9 (1.3–3.3) | 3.8 (1.5–6.0) | 0.573 | |
| Number of metastases m (Q1–Q3) | 3.0 (2.0–3.0) | 2.7 (2.0–3.0) | 3.6 (2.0–4.0) | 0.066 | |
| Baseline LDH IU/L; m (Q1–Q3) | 378.3 (195.9–387.7) | 221.2 (195.9–227.9) | 548.5 (275.3–468.3) | 0.026 | |
| Gender | M | 16 | 6 (37%) | 10 (63%) | 0.028 |
| F | 33 | 24 (73%) | 9 (27%) | ||
| Stage | III | 22 | 18 (82%) | 4 (18%) | 0.009 |
| IV | 27 | 12 (44%) | 15 (56%) | ||
| Ulceration | Yes | 20 | 9 (45%) | 11 (55%) | 0.128 |
| No | 19 | 13 (68%) | 6 (32%) | ||
| Presence of lymph node metastasis | Yes | 32 | 17 (53%) | 15 (47%) | 0.135 |
| No | 17 | 13 (76%) | 4 (24%) | ||
| Presence of cutaneous metastasis | Yes | 28 | 20 (71%) | 8 (29%) | 0.139 |
| No | 21 | 10 (48%) | 11 (52%) | ||
| Presence of pulmonary metastasis | Yes | 11 | 6 (55%) | 5 (45%) | 0.729 |
| No | 38 | 24 (63%) | 14 (37%) | ||
| Presence of cerebral metastasis | Yes | 10 | 5 (50%) | 5 (50%) | 0.480 |
| No | 39 | 25 (64%) | 14 (36%) | ||
| Presence of abdominal metastasis | Yes | 14 | 3 (21%) | 11 (79%) | 0.001 |
| No | 35 | 27 (77%) | 8 (23%) | ||
| Presence of bone metastasis | Yes | 9 | 2 (22%) | 7 (78%) | 0.019 |
| No | 40 | 28 (70%) | 12 (30%) | ||
| Mutated gene | NRAS | 33 a | 20 (61%) | 13 (39%) | 1.00 |
| BRAF | 16 b | 10 (63%) | 6 (37%) | ||
| Baseline LDH | >426 IU/L (2 × ULN) | 4 | 0 | 4 (100%) | 0.027 |
| ≤426 IU/L (2 × ULN) | 21 | 13 (62%) | 8 (38%) | ||
| Undetermined | 24 | 17 (71%) | 7 (29%) | ||
| Treatment | Nivolumab monotherapy | 44 | 29 (66%) | 15 (34%) | 0.067 |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 5 | 1 (20%) | 4 (80%) | ||
| Therapeutic line | First line | 32 | 19 (59%) | 13 (41%) | 0.767 |
| ≥second line | 17 | 11 (65%) | 6 (35%) | ||
| Total | Undetectable Baseline ctDNA | Detectable Baseline ctDNA | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (nderivation + nvalidation) | 102 (49 + 53) | 58 | 44 | - | |
| Age m (Q1–Q3) | 63 (54–74.6) | 62.9 (52.4–75.4) | 63.1 (58.3–73.5) | 0.545 | |
| Tumor thickness m (Q1–Q3) | 3.2 (1.5–3.9) | 2.9 (1.4–3.5) | 3.6 (1.6–5.0) | 0.284 | |
| Number of metastases m (Q1–Q3) | 3.9 (2.0–5.0) | 3.7 (2.0–4.0) | 4.2 (2.0–5.3) | 0.011 | |
| Baseline LDH IU/L; m (Q1–Q3) | 293.2 (167.7–290.2) | 194.8 (160.1–223.1) | 397.3 (184.5–456.6) | 0.008 | |
| Gender | M | 45 | 18 (40%) | 27 (60%) | 0.003 |
| F | 57 | 40 (70%) | 17 (30%) | ||
| Stage | III | 33 | 25 (76%) | 8 (24%) | 0.010 |
| IV | 69 | 33 (48%) | 36 (52%) | ||
| Ulceration | Yes | 35 | 17 (49%) | 18 (51%) | 0.345 |
| No | 40 | 26 (65%) | 14 (35%) | ||
| Presence of lymph node metastasis | Yes | 80 | 42 (53%) | 38 (48%) | 0.144 |
| No | 22 | 16 (73%) | 6 (27%) | ||
| Presence of cutaneous metastasis | Yes | 59 | 33 (56%) | 26 (44%) | 0.842 |
| No | 43 | 25 (58%) | 18 (42%) | ||
| Presence of pulmonary metastasis | Yes | 32 | 15 (47%) | 17 (53%) | 0.199 |
| No | 70 | 43 (61%) | 27 (39%) | ||
| Presence of cerebral metastasis | Yes | 22 | 13 (59%) | 9 (41%) | 1.00 |
| No | 80 | 45 (56%) | 35 (44%) | ||
| Presence of abdominal metastasis | Yes | 34 | 13 (38%) | 21 (62%) | 0.011 |
| No | 68 | 45 (66%) | 23 (34%) | ||
| Presence of bone metastasis | Yes | 20 | 8 (36%) | 14 (64%) | 0.011 |
| No | 82 | 52 (63%) | 30 (37%) | ||
| Mutated gene | NRAS | 62 a | 36 (58%) | 26 (42%) | 0.839 |
| BRAF | 40 b | 22 (55%) | 18 (45%) | ||
| Baseline LDH | >426 IU/L (2 × ULN) | 9 | 0 | 9 (100%) | 0.001 |
| ≤426 IU/L (2 × ULN) | 61 | 36 (59%) | 25 (41%) | ||
| Undetermined | 32 | 22 (69%) | 10 (31%) | ||
| Treatment | Nivolumab monotherapy | 93 | 55 (59%) | 38 (41%) | 0.169 |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | 9 | 30 (83%) | 6 (17%) | ||
| Therapeutic line | First line | 58 | 33 (57%) | 25 (43%) | 1.000 |
| ≥second line | 44 | 25 (57%) | 19 (43%) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herbreteau, G.; Vallée, A.; Knol, A.-C.; Théoleyre, S.; Quéreux, G.; Varey, E.; Khammari, A.; Dréno, B.; Denis, M.G. Circulating Tumor DNA Early Kinetics Predict Response of Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy: Validation Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081826
Herbreteau G, Vallée A, Knol A-C, Théoleyre S, Quéreux G, Varey E, Khammari A, Dréno B, Denis MG. Circulating Tumor DNA Early Kinetics Predict Response of Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy: Validation Study. Cancers. 2021; 13(8):1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081826
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerbreteau, Guillaume, Audrey Vallée, Anne-Chantal Knol, Sandrine Théoleyre, Gaëlle Quéreux, Emilie Varey, Amir Khammari, Brigitte Dréno, and Marc G. Denis. 2021. "Circulating Tumor DNA Early Kinetics Predict Response of Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy: Validation Study" Cancers 13, no. 8: 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081826
APA StyleHerbreteau, G., Vallée, A., Knol, A.-C., Théoleyre, S., Quéreux, G., Varey, E., Khammari, A., Dréno, B., & Denis, M. G. (2021). Circulating Tumor DNA Early Kinetics Predict Response of Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy: Validation Study. Cancers, 13(8), 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081826








