Combined Luteolin and Indole-3-Carbinol Synergistically Constrains ERα-Positive Breast Cancer by Dual Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Pathway in Cultured Cells and Xenograft Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Combination of LUT and I3C Synergistically Inhibits ER+ Breast Cancer Cells Growth
2.2. Combination of LUT and I3C Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in ER+ Breast Cancer Cells
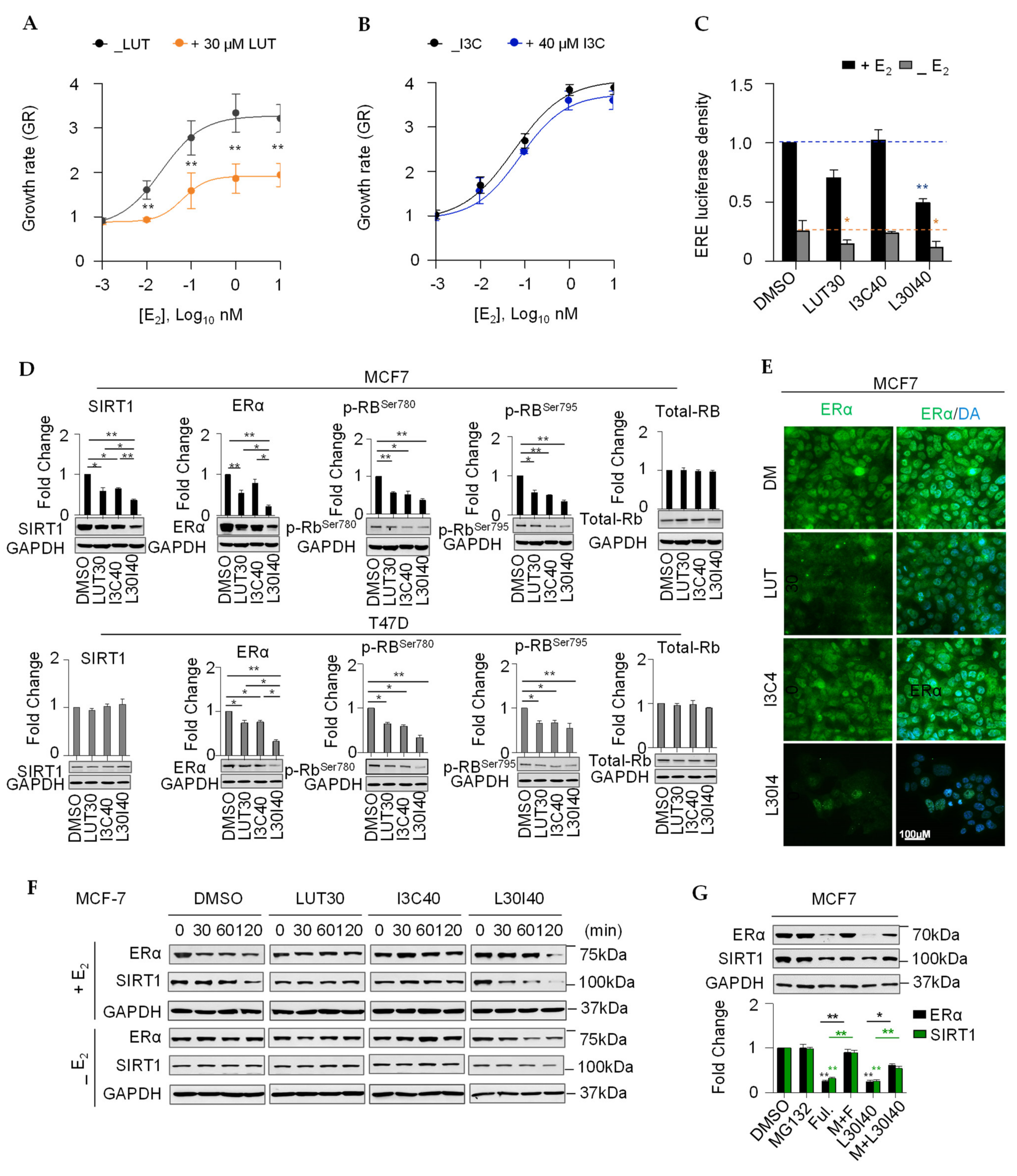
2.3. Combination of LUT and I3C Suppresses E2-Induced MCF7 Cell Growth through Modulating ERα Levels
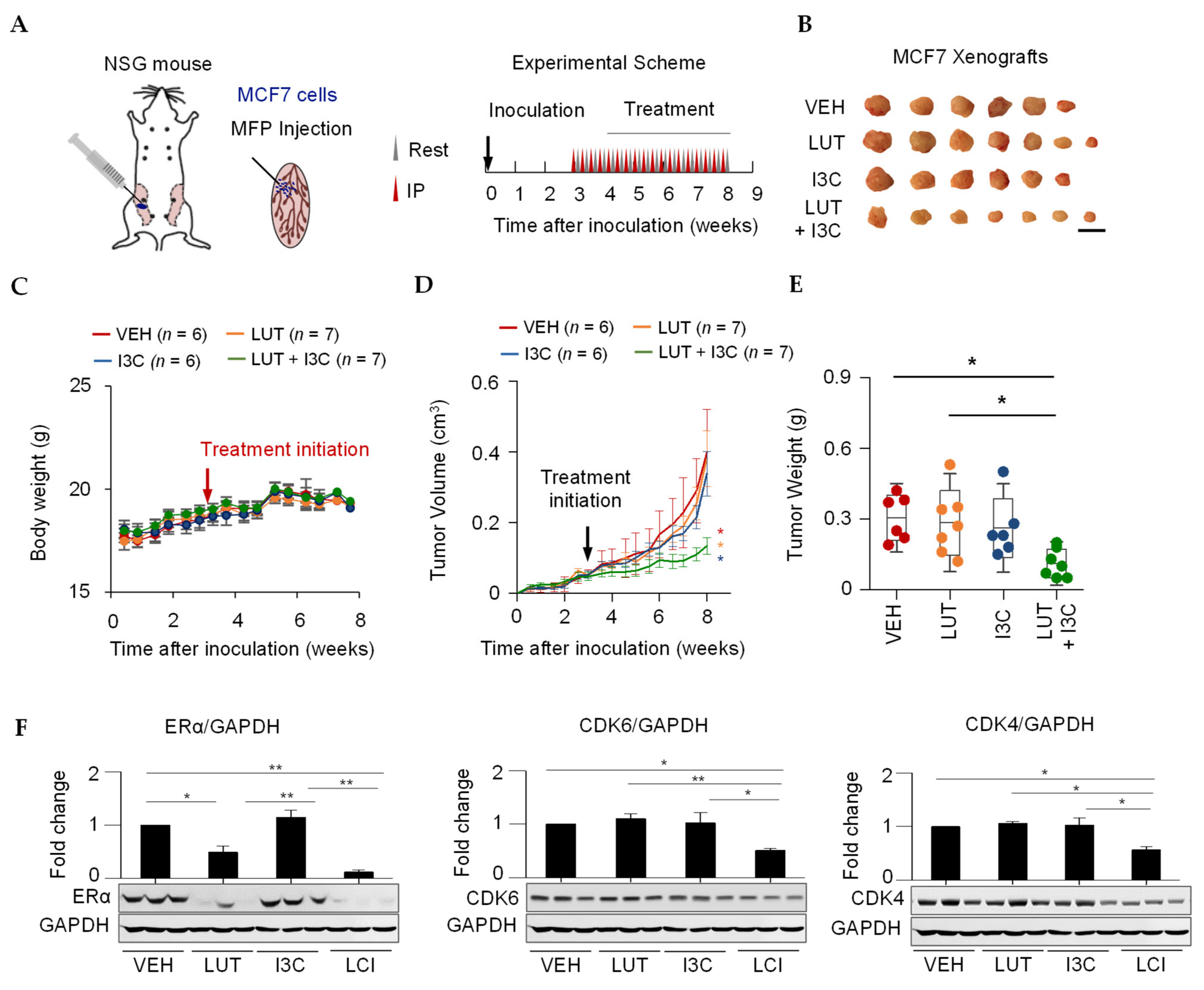
2.4. Combination of LUT and I3C Suppresses MCF7 Xenograft Tumor Growth
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment Reagents
4.2. Cell Viability and Dose-Response Curve Fitting
4.3. Pairwise Combinations Screening
4.4. Cell Cycle Assay
4.5. Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.6. ERE Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.7. Immunoblotting, Immunoprecipitation, and Immunofluorescence Staining Experiments
4.8. Xenograft Mice Study
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeSantis, C.E.; Ma, J.; Gaudet, M.M.; Newman, L.A.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, C.D.; Migliaccio, I.; Malorni, L.; Guarducci, C.; Biganzoli, L.; Di Leo, A. Challenges in the management of advanced, ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, S.; Haytowitz, D.B. USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400525/Data/Flav/Flav3.2.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Wang, L.-M.; Xie, K.-P.; Huo, H.-N.; Shang, F.; Zou, W.; Xie, M.-J. Luteolin inhibits proliferation induced by IGF-1 pathway dependent ERalpha in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Woo, J.S.; Kwon, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, K.H. Luteolin induces apoptotic cell death through AIF nuclear translocation mediated by activation of ERK and p38 in human breast cancer cell lines. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-W.; Zhang, H.-D.; Mao, L.; Mao, C.-F.; Chen, W.; Cui, M.; Ma, R.; Cao, H.-X.; Jing, C.-W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Luteolin Inhibits Breast Cancer Development and Progression In Vitro and In Vivo by Suppressing Notch Signaling and Regulating MiRNAs. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1693–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseeva, E.P.; Fox, L.H.; Howells, L.M.; Temple, L.A.F.; Manson, M.M. Indole-3-carbinol-induced death in cancer cells involves EGFR downregulation and is exacerbated in a 3D environment. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, E.J.; Liu, B.D.; Bjeldanes, L.F.; Firestone, G.L. Indole-3-carbinol Inhibits CDK6 Expression in Human MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells by Disrupting Sp1 Transcription Factor Interactions with a Composite Element in the CDK6 Gene Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22332–22340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, J.A.; Campana, R.; Wei, C.; Su, C.H.; Hanks, A.M.; Bornmann, W.G.; Keyomarsi, K. Indole-3-carbinol and its N-alkoxy derivatives preferentially target ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2587–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Saito, M.; Endo, N.; Kugawa, F.; Ueno, A. Luteolin Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cytotoxicity to MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.-Q.; Xie, K.-P.; Xie, M.-J. Inhibitory effect of luteolin on the proliferation of human breast cancer cell lines induced by epidermal growth factor. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2016, 68, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimoi, K.; Okada, H.; Furugori, M.; Goda, T.; Takase, S.; Suzuki, M.; Hara, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Kinae, N. Intestinal absorption of luteolin and luteolin 7-O-beta-glucoside in rats and humans. FEBS Lett. 1998, 438, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderton, M.J.; Manson, M.M.; Verschoyle, R.D.; Gescher, A.J.; Lamb, J.H.; Farmer, P.B.; Steward, W.P.; Williams, M.L. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Disposition of Indole-3-carbinol and Its Acid Condensation Products after Oral Administration to Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5233–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Layard, M.W.; Basa, P.; Davis, H.L., Jr.; Von Hoff, A.L.; Rozencweig, M.; Muggia, F.M. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 91, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, B.; Finn, R.S.; Turner, N.C. Treating cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. p21 in cancer: Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.L.; Shioda, K.; Coser, K.R.; Rivizzigno, D.; McSweeney, K.R.; Shioda, T. Fulvestrant-induced cell death and pro-teasomal degradation of estrogen receptor alpha protein in MCF-7 cells require the CSK c-Src tyrosine kinase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaverich, B.M.; Shoulars, K.; Rodriguez, M.A. Luteolin Regulation of Estrogen Signaling and Cell Cycle Pathway Genes in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. IJBS 2011, 7, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Marconett, C.N.; Sundar, S.N.; Poindexter, K.M.; Stueve, T.R.; Bjeldanes, L.F.; Firestone, G.L. Indole-3-carbinol triggers aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent estrogen receptor (ER)alpha protein degradation in breast cancer cells disrupting an ERal-pha-GATA3 transcriptional cross-regulatory loop. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Milner, M.J.; Milner, J.A.; Kim, Y.S. Estrogen receptor α as a target for indole-3-carbinol. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.L.; Faller, D.V. SIRT1 represses estrogen-signaling, ligand-independent ERalpha-mediated transcription, and cell proliferation in estrogen-responsive breast cells. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 216, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, J.; An, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z. Relationship between molecular classification and clinicopathological features of young and medium-elderly breast cancer patients. Cancer Cell Res. 2017, 16, 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Hallman, K.; Aleck, K.; Dwyer, B.; Lloyd, V.; Quigley, M.; Sitto, N.; Siebert, A.E.; Dinda, S. The effects of turmeric (curcumin) on tumor suppressor protein (p53) and estrogen receptor (ERalpha) in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer 2017, 9, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Key, T.; Appleby, P.; Barnes, I.; Reeves, G.; Endogenous, H.; Breast Cancer Collaborative, G. Endogenous sex hormones and breast cancer in post-menopausal women: Reanalysis of nine prospective studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 606–616. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, H.B.; Visvanathan, K.; Newcomb, P.A.; Hampton, J.M.; Egan, K.M.; Titus-Ernstoff, L.; Trentham-Dietz, A. Bilateral oophorectomy in relation to risk of post-menopausal breast cancer: Confounding by nonmalignant indications for surgery? Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Tanji, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Noguchi, S. Association of serum estrone levels with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer risk in post-menopausal Japanese women. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2229–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Han, W.; Moon, H.G.; Ahn, S.K.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, T.; Noh, D.Y. Prognostic effect of preoperative serum estradiol level in post-menopausal breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.J.; Reddy, E.P. CDK4: A Key Player in the Cell Cycle, Development, and Cancer. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, M.; Nakamura, M.; Tokuda, E.; Toyosawa, D.; Niwa, T.; Ohuchi, N.; Ishida, T.; Hayashi, S.-I. The p21 levels have the potential to be a monitoring marker for ribociclib in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4907–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigan, A.-S.; Bellutti, F.; Kollmann, K.; Tebb, G.; Sexl, V. CDK6—A review of the past and a glimpse into the future: From cell-cycle control to transcriptional regulation. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Satelli, A.; Moridani, M.; Jenkins, M.; Rao, U.S. Luteolin induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant cancer cells without affecting the drug transporter function: Involvement of cell line-specific apoptotic mechanisms. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 130, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, C.M.; Hsieh, S.J.; Cram, E.J.; Hong, C.; Riby, J.E.; Bjeldanes, L.F.; Firestone, G.L. Indole-3-carbinol and tamoxifen cooperate to arrest the cell cycle of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Virgous, C.; Si, H. Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of combined phytochemicals. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 69, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.T.; Liu, H.; Radhakrishnan, I.; Abdelrahim, M.; Safe, S.; Jordan, V.C. Interaction of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand 6-Methyl-1,3,8-trichlorodibenzofuran with Estrogen Receptor α. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2889–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Milner, J.A. Targets for indole-3-carbinol in cancer prevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qin, C.; Safe, S.H. Flavonoids as aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists/antagonists: Effects of structure and cell context. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottardis, M.M.; Robinson, S.P.; Jordan, V. Estradiol-stimulated growth of MCF-7 tumors implanted in athymic mice: A model to study the tumoristatic action of tamoxifen. J. Steroid Biochem. 1988, 30, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, G.; Vieusseux, J.; Unsworth, A.; Anderson, R.; Britt, K. Low Dose, Low Cost Estradiol Pellets Can Support MCF-7 Tumour Growth in Nude Mice without Bladder Symptoms. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Bulus, N.; Fogo, A.B.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Harris, R.C. YAP Activation in Renal Proximal Tubule Cells Drives Diabetic Renal Interstitial Fibrogenesis. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2446–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschanzky, R.S.; Humphrey, L.E.; Ma, J.; Smith, L.M.; Enke, T.J.; Shukla, S.K.; Dasgupta, A.; Singh, P.K.; Howell, G.M.; Brattain, M.G.; et al. Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases 1/2/6 in Combination with Gemcitabine: A Promising Combination for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Q.; Si, H.; Zhang, L.; Eltom, S.E.; Si, H. Combined Luteolin and Indole-3-Carbinol Synergistically Constrains ERα-Positive Breast Cancer by Dual Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Pathway in Cultured Cells and Xenograft Mice. Cancers 2021, 13, 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092116
Wang X, Zhang L, Dai Q, Si H, Zhang L, Eltom SE, Si H. Combined Luteolin and Indole-3-Carbinol Synergistically Constrains ERα-Positive Breast Cancer by Dual Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Pathway in Cultured Cells and Xenograft Mice. Cancers. 2021; 13(9):2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092116
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoyong, Lijuan Zhang, Qi Dai, Hongzong Si, Longyun Zhang, Sakina E. Eltom, and Hongwei Si. 2021. "Combined Luteolin and Indole-3-Carbinol Synergistically Constrains ERα-Positive Breast Cancer by Dual Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Pathway in Cultured Cells and Xenograft Mice" Cancers 13, no. 9: 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092116
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, L., Dai, Q., Si, H., Zhang, L., Eltom, S. E., & Si, H. (2021). Combined Luteolin and Indole-3-Carbinol Synergistically Constrains ERα-Positive Breast Cancer by Dual Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Pathway in Cultured Cells and Xenograft Mice. Cancers, 13(9), 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092116




