Treatment Strategies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Common and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: Drug Sensitivity Based on Exon Classification, and Structure-Function Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
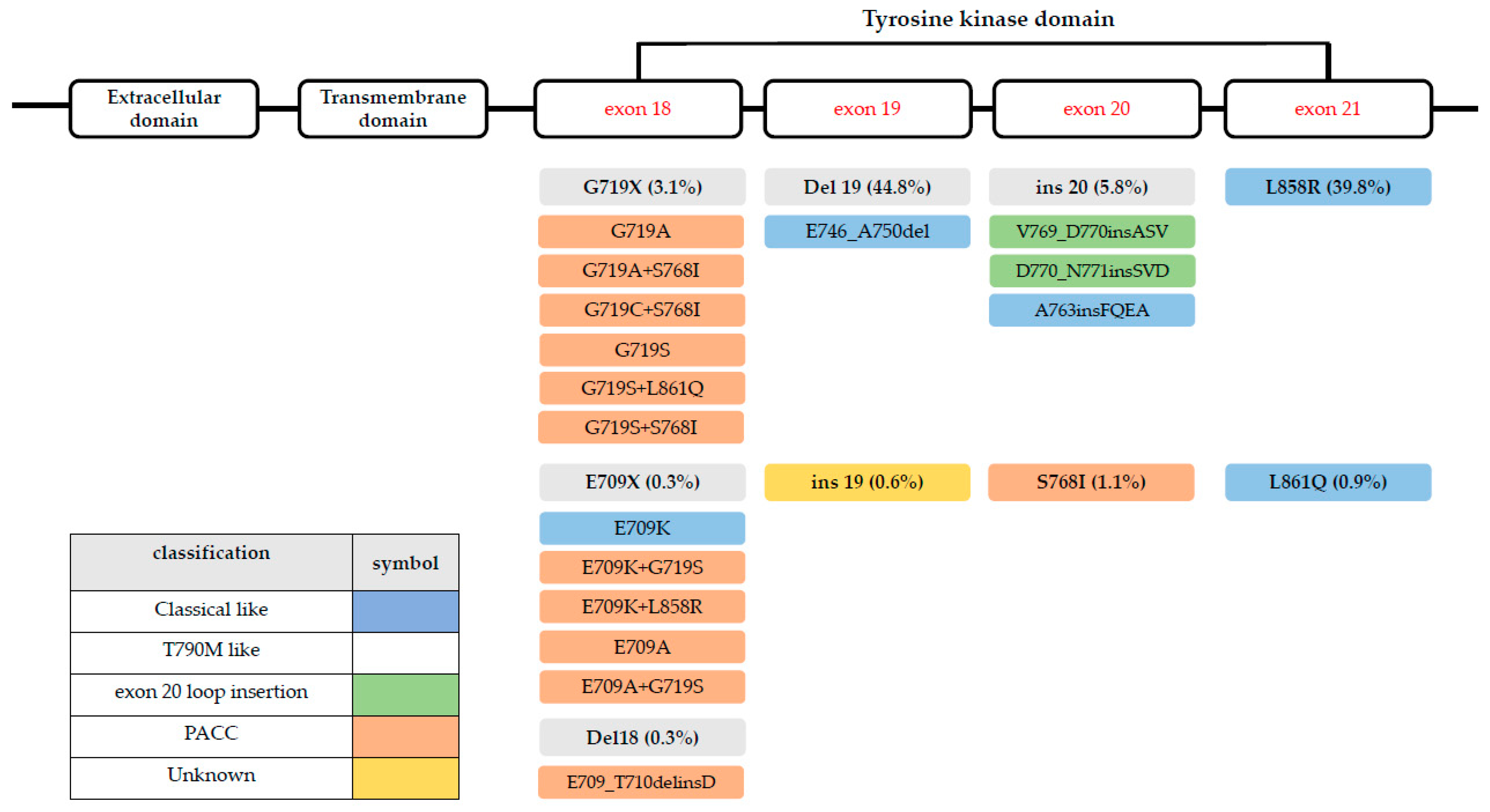
2. Clinical Features and Molecular Characteristics of EGFR-Mutant NSCLC
3. Treatment for Common EGFR Mutations
3.1. EGFR-TKI
3.2. EGFR-TKI Combined with Chemotherapy
3.3. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC
4. Treatment for Uncommon EGFR Mutations (Other Than Exon 20 Insertions)
4.1. Treatment for Major Uncommon Mutations in NSCLC
4.2. Treatment for Other Uncommon EGFR-Mutated NSCLC
4.3. Compound EGFR Mutations in NSCLC
4.4. Treatment for De Novo T790M Mutations in NSCLC
5. Development of Treatment in EGFR Exon 20 Insertions
6. Structural-Based Classification
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sequist, L.V.; Soria, J.-C.; Goldman, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Varga, A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Solomon, B.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. Rociletinib in EGFR-Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgillo, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Fasano, M.; Ciardiello, F. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs: Lung cancer. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Nafa, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Lau, C.; Reva, B.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y. Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene and related genes as determinants of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors sensitivity in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amelia, T.; Kartasasmita, R.E.; Ohwada, T.; Tjahjono, D.H. Structural Insight and Development of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno, A.; Hidalgo, M. Pharmacogenomics of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2006, 1766, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Carotenuto, A.; Rachiglio, A.; Gallo, M.; Maiello, M.R.; Aldinucci, D.; Pinto, A.; Normanno, N. The role of the EGFR signaling in tumor microenvironment. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 214, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Ponce Aix, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, C.H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.K.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Schuler, M.; Popat, S.; Miura, S.; Heeke, S.; Park, K.; Märten, A.; Kim, E.S. Afatinib for the Treatment of NSCLC Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Database of 693 Cases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Veggel, B.; de Langen, A.J.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Monkhorst, K.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Thunnissen, E.; Smit, E.F. Afatinib and Cetuximab in Four Patients With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Positive Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eide, I.J.Z.; Helland, A.; Ekman, S.; Mellemgaard, A.; Hansen, K.H.; Cicenas, S.; Koivunen, J.; Gronberg, B.H.; Brustugun, O.T. Osimertinib in T790M-positive and -negative patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (the TREM-study). Lung Cancer 2020, 143, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Shou, T.; Luo, Y.; Tang, W. Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 or exon 21 mutations after tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuchi, T.; Shingyoji, M.; Itakura, M.; Yokoi, S.; Moriya, Y.; Tamura, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Ashinuma, H.; Kawasaki, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. Frequency of brain metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer, and their association with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 20, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R.; Sánchez-Torres, J.M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Massutí, B.; Reguart, N.; Mayo, C.; Lianes, P.; Queralt, C.; Guillem, V.; Salinas, P.; et al. Brain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib: The importance of EGFR mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-Line Afatinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Common Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations and Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballard, P.; Yates, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kim, D.W.; Yang, J.C.; Cantarini, M.; Pickup, K.; Jordan, A.; Hickey, M.; Grist, M.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of Osimertinib with Other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastases Models, and Early Evidence of Clinical Brain Metastases Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Han, J.Y.; Katakami, N.; Kim, H.R.; Hodge, R.; Kaur, P.; Brown, A.P.; Ghiorghiu, D.; et al. CNS Efficacy of Osimertinib in Patients With T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Data From a Randomized Phase III Trial (AURA3). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo, M.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; Nogami, N.; et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients With Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Peled, N.; Tufman, A.; Servidio, L.; Li, J.; Taylor, R.; Zhao, J. P47.11 COMPEL: Chemotherapy With/Without Osimertinib in Patients With EGFRm Advanced NSCLC and Progression on First-Line Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, Y.; Morita, S.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Gemma, A.; Takahashi, K.; Fujita, Y.; Harada, T.; Minato, K.; et al. Gefitinib Alone Versus Gefitinib Plus Chemotherapy for Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer With Mutated Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: NEJ009 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, V.; Patil, V.M.; Joshi, A.; Menon, N.; Chougule, A.; Mahajan, A.; Janu, A.; Purandare, N.; Kumar, R.; More, S.; et al. Gefitinib Versus Gefitinib Plus Pemetrexed and Carboplatin Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, S.; Mizutani, T.; Shibata, T.; Niho, S.; Kurata, T.; Nakamura, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohe, Y. P2.06-023 A Phase III Study Comparing Gefitinib and Inserted Cisplatin plus Pemetrexed with Gefitinib for EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Squamous NSCLC: Topic: Phase III. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Feng, P.H.; Karaseva, N.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, C.K.; Poltoratskiy, A.; Yanagitani, N.; Marshall, R.; Huang, X.; et al. Osimertinib plus platinum-pemetrexed in newly diagnosed epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: Safety run-in results from the FLAURA2 study. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, T.; Kato, T.; Nishio, M.; Goto, K.; Atagi, S.; Hosomi, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Hida, T.; Maemondo, M.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): An open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; Yoshimori, K.; et al. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Fukuhara, T.; Saito, H.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; et al. NEJ026: Final overall survival analysis of bevacizumab plus erlotinib treatment for NSCLC patients harboring activating EGFR-mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisberg, A.; Cummings, A.; Goldman, J.W.; Bornazyan, K.; Reese, N.; Wang, T.; Coluzzi, P.; Ledezma, B.; Mendenhall, M.; Hunt, J.; et al. A Phase II Study of Pembrolizumab in EGFR-Mutant, PD-L1+, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Naïve Patients With Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, S.; Gettinger, S.; Johnson, M.L.; Jänne, P.A.; Garassino, M.C.; Christoph, D.; Toh, C.K.; Rizvi, N.A.; Chaft, J.E.; Carcereny Costa, E.; et al. Phase II Trial of Atezolizumab As First-Line or Subsequent Therapy for Patients With Programmed Death-Ligand 1-Selected Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (BIRCH). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garassino, M.C.; Cho, B.-C.; Kim, J.-H.; Mazières, J.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Lena, H.; Corral Jaime, J.; Gray, J.E.; Powderly, J.; Chouaid, C.; et al. Durvalumab as third-line or later treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ATLANTIC): An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Cooper, W.; Links, M.; Gebski, V.; Herbst, R.S.; Gralla, R.J.; Mok, T.; Yang, J.C. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Associated With Survival Among Patients Treated With Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socinski, M.A.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, X.; Zhou, J.; Bao, Z.; Fan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shu, Y.; Guo, R.; et al. MA11.06 A PII Study of Toripalimab, a PD-1 mAb, in Combination with Chemotherapy in EGFR+ Advanced NSCLC Patients Failed to Prior EGFR TKI Therapies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.; Hui, R.; Carbone, D.; Park, K.; Carrigan, M.; Xu, X.; Dang, T.; Chih-Hsin Yang, J. P1.01-81 Phase 3 Study of Pemetrexed-Platinum with or without Pembrolizumab for TKI-Resistant/EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC: KEYNOTE-789. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, K.; Yang, J.C.H.; Park, K.; Ohe, Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Gainor, J.; Blackwood-Chirchir, A.; Yang, R.; Chang, I.F.; Mok, T. 481TiP Checkmate 722: A phase 3 trial of nivolumab with chemotherapy or ipilimumab vs chemotherapy in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutation, T790M-negative stage IV or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, ix154–ix155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Sakai, K.; Fujita, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Sakai, D.; Kitagawa, C.; Naito, T.; Takeda, K.; Okamoto, I.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Study Comparing Nivolumab With Carboplatin-Pemetrexed for Patients With EGFR Mutation-Positive Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Who Acquire Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Not Due to a Secondary T790M Mutation: Rationale and Protocol Design for the WJOG8515L Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Goldman, J.W.; Gettinger, S.N.; Borghaei, H.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ready, N.E.; Gerber, D.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Juergens, R.A.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 012): Results of an open-label, phase 1, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gubens, M.A.; Sequist, L.V.; Stevenson, J.P.; Powell, S.F.; Villaruz, L.C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Langer, C.J.; Patnaik, A.; Borghaei, H.; Jalal, S.I.; et al. Pembrolizumab in combination with ipilimumab as second-line or later therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: KEYNOTE-021 cohorts D and H. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Cho, E.N.; Park, H.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Lim, S.; Youn, J.P.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Compound EGFR mutation is frequently detected with co-mutations of actionable genes and associated with poor clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, D.B. Kinase inhibitor-responsive genotypes in EGFR mutated lung adenocarcinomas: Moving past common point mutations or indels into uncommon kinase domain duplications and rearrangements. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.C.H.; Sequist, L.V.; Geater, S.L.; Tsai, C.-M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Schuler, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yu, C.-J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Zhou, C.; et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: A combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Minegishi, Y.; Yoshizawa, H.; Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Sugawara, S.; Isobe, H.; Harada, M.; Ishii, Y.; Gemma, A.; et al. Effectiveness of Gefitinib against Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with the Uncommon EGFR Mutations G719X and L861Q. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Yang, C.-T.; Shih, J.-Y.; Huang, M.-S.; Su, W.-C.; Lai, R.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Hsiao, S.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment Response in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas with G719X/L861Q/S768I Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; An, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.U.; Kang, E.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Ahn, M.S.; Lee, M.H.; Sun, J.M.; et al. Osimertinib for Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase II Trial (KCSG-LU15-09). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Aredo, J.V.; Piper-Vallillo, A.; Huppert, L.; Rotow, J.K.; Husain, H.; Stewart, S.L.; Cobb, R.; Wakelee, H.A.; Blakely, C.M.; et al. Osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with atypical EGFR activating mutations: A retrospective multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, Y.; Shimokawa, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Mizutani, H.; Wakui, H.; Murakami, S.; Atagi, S.; Minato, K.; Seike, M.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Uncommon EGFR mutations conducted with osimertinib in patients with NSCLC: A study protocol of phase 2 study (UNICORN/TCOG1901). Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Shih, J.Y. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on uncommon E709X epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 6137–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.K.; Ko, J.C.; Yang, J.C.; Shih, J.Y. Afatinib is effective in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma with uncommon EGFR p.L747P and p.L747S mutations. Lung Cancer 2019, 133, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohsaka, S.; Nagano, M.; Ueno, T.; Suehara, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Shimada, N.; Takahashi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takamochi, K.; Takahashi, F.; et al. A method of high-throughput functional evaluation of EGFR gene variants of unknown significance in cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, A.; Franchina, T.; Ricciardi, G.; Battaglia, A.; Picciotto, M.; Adamo, V. Heterogeneous Responses to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Patients with Uncommon EGFR Mutations: New Insights and Future Perspectives in this Complex Clinical Scenario. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passaro, A.; Prelaj, A.; Bonanno, L.; Tiseo, M.; Tuzi, A.; Proto, C.; Chiari, R.; Rocco, D.; Genova, C.; Sini, C.; et al. Activity of EGFR TKIs in Caucasian Patients With NSCLC Harboring Potentially Sensitive Uncommon EGFR Mutations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e186–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Sun, J.M.; Min, Y.J.; Cho, E.K.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer except both exon 19 deletion and exon 21 L858R: A retrospective analysis in Korea. Lung Cancer 2015, 87, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Song, Z.-G.; Jiao, S.-C. Efficacy analysis of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on rare non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring complex EGFR mutations. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, C.H.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3812–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, C.; Molina, M.A.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Giménez-Capitán, A.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Gervais, R.; Massuti, B.; Wei, J.; Moran, T.; et al. The Impact of EGFR T790M Mutations and BIM mRNA Expression on Outcome in Patients with EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Treated with Erlotinib or Chemotherapy in the Randomized Phase III EURTAC Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maheswaran, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Nagrath, S.; Ulkus, L.; Brannigan, B.; Collura, C.V.; Inserra, E.; Diederichs, S.; Iafrate, A.J.; Bell, D.W.; et al. Detection of Mutations in EGFR in Circulating Lung-Cancer Cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, K.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Li, K.-C.; Kuo, M.-L.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Chan, W.-K.; Ho, B.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yu, S.-L.; et al. Pretreatment Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) T790M Mutation Predicts Shorter EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Response Duration in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akamatsu, H.; Toi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Fujimoto, D.; Tachihara, M.; Furuya, N.; Otani, S.; Shimizu, J.; Katakami, N.; Azuma, K.; et al. Efficacy of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab vs Osimertinib in Patients With EGFR T790M–Mutated Non—Small Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: West Japan Oncology Group 8715L Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riess, J.W.; Gandara, D.R.; Frampton, G.M.; Madison, R.; Peled, N.; Bufill, J.A.; Dy, G.K.; Ou, S.I.; Stephens, P.J.; McPherson, J.D.; et al. Diverse EGFR Exon 20 Insertions and Co-Occurring Molecular Alterations Identified by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Lo, P.C.; Nishino, M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Lindeman, N.I.; Butaney, M.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A. Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Costa, D.B. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: Preclinical data and clinical implications. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e23–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau-Faller, M.; Prim, N.; Ruppert, A.M.; Nanni-Metéllus, I.; Lacave, R.; Lacroix, L.; Escande, F.; Lizard, S.; Pretet, J.L.; Rouquette, I.; et al. Rare EGFR exon 18 and exon 20 mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer on 10 117 patients: A multicentre observational study by the French ERMETIC-IFCT network. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, J.; Sima, C.S.; Rodriguez, K.; Busby, N.; Nafa, K.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J.; Kris, M.G.; Arcila, M.E.; Yu, H.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions in advanced lung adenocarcinomas: Clinical outcomes and response to erlotinib. Cancer 2015, 121, 3212–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voon, P.J.; Tsui, D.W.; Rosenfeld, N.; Chin, T.M. EGFR exon 20 insertion A763-Y764insFQEA and response to erlotinib—Letter. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2614–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, H.S.; Ahn, H.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, J.; Sym, S.J.; Park, J.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, D.B.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer and resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Park, E.; Yun, C.H.; Sng, N.J.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yeo, W.L.; Huberman, M.S.; Cohen, D.W.; Nakayama, S.; Ishioka, K.; et al. Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Ding, P.N.; Lord, S.J.; Inoue, A.; Zhou, C.; Mitsudomi, T.; Rosell, R.; Pavlakis, N.; Links, M.; et al. Impact of Specific Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations and Clinical Characteristics on Outcomes After Treatment With EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Versus Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, P.; Gergis, C.; Viray, H.; Varkaris, A.; Fujii, M.; Rangachari, D.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Kobayashi, I.S.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA Is a Unique Exon 20 Insertion Mutation That Displays Sensitivity to Approved and In-Development Lung Cancer EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Li, J.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, H.S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.H.; Wang, Y. Osimertinib for Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring diverse EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Lung Cancer 2021, 152, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riely, G.J.; Neal, J.W.; Camidge, D.R.; Spira, A.I.; Piotrowska, Z.; Costa, D.B.; Tsao, A.S.; Patel, J.D.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Bazhenova, L.; et al. Activity and Safety of Mobocertinib (TAK-788) in Previously Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations from a Phase I/II Trial. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Felip, E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Positive Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1/2 Open-label Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Tan, Z.; Carter, B.W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Poteete, A.; Estrada-Bernal, A.; et al. Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon 20–selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Goldman, J.W.; Clarke, J.M.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Piotrowska, Z.; Chu, D.; Bhat, G.; Lebel, F.M.; Socinski, M.A. Poziotinib shows activity and durability of responses in subgroups of previously treated EGFR exon 20 NSCLC patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Yu, H.A.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Koczywas, M.; Smit, E.F.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lee, V.H.-F.; Soo, R.A.; Wrangle, J.M.; Spira, A.I.; et al. Safety and activity of CLN-081 (TAS6417) in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 insertion mutations (Ins20). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Pyo, K.H.; Park, C.W.; Heo, S.G.; Yun, M.R.; Lim, S.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET Bispecific Antibody, in Diverse Models of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Driven NSCLC. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, S.; Lipfert, L.; Chevalier, K.; Bushey, B.S.; Henley, B.; Lenhart, R.; Sendecki, J.; Beqiri, M.; Millar, H.J.; Packman, K.; et al. Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an Fc Enhanced EGFR/cMet Bispecific Antibody, Induces Receptor Downmodulation and Antitumor Activity by Monocyte/Macrophage Trogocytosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; John, T.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.S.; Shu, C.A.; Kim, D.-W.; Ramirez, S.V.; Spira, A.I.; Sabari, J.K.; Han, J.-Y.; et al. Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an anti-EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion (exon20ins)-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabari, J.K.; Shu, C.A.; Park, K.; Leighl, N.; Mitchell, P.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Viteri, S.; Spira, A.; et al. OA04.04 Amivantamab in Post-platinum EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S108–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Wang, M.; Mitchell, P.; Fang, J.; Nian, W.; Chiu, C.-H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, W.-C.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Preliminary safety and efficacy results from phase 1 studies of DZD9008 in NSCLC patients with EGFR Exon20 insertion mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.V.; Villaruz, L.C.; Lee, V.H.F.; Zhu, V.W.; Baik, C.S.; Sacher, A.; McCoach, C.E.; Nguyen, D.; Li, J.Y.C.; Pacheco, J.M.; et al. LBA61 First analysis of RAIN-701: Study of tarloxotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) EGFR Exon 20 insertion, HER2-activating mutations other solid tumours with NRG1/ERBB gene fusions. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.; Horn, L.; Gettinger, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Riely, G.J.; Wang, B.; Fu, Y.; Chand, V.K.; et al. Dual inhibition of EGFR with afatinib and cetuximab in kinase inhibitor-resistant EGFR-mutant lung cancer with and without T790M mutations. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Le, X.; Vijayan, R.S.K.; Hicks, J.K.; Heeke, S.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Udagawa, H.; Skoulidis, F.; Tran, H.; et al. Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Nature 2021, 597, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Morabito, A.; Hao, D.; Yang, C.T.; Soo, R.A.; Yang, J.C.; Gucalp, R.; Halmos, B.; Wang, L.; Marten, A.; et al. Sequential afatinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated analysis of the observational GioTag study. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- To, C.; Beyett, T.S.; Jang, J.; Feng, W.W.; Bahcall, M.; Haikala, H.M.; Shin, B.H.; Heppner, D.E.; Rana, J.K.; Leeper, B.A.; et al. An allosteric inhibitor against the therapy-resistant mutant forms of EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Exon | Mutation | Frequency (%) | In Vitro Sensitivity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gefitinib/Erlotinib | Afatinib | Osimertinib | |||
| 18 | G719X | 3.0–3.1 | intermediate | sensitive | intermediate-sensitive |
| E709X | 0.3 | E709K intermediate | sensitive | sensitive | |
| del 18 | 0.3 | intermediate | sensitive | sensitive | |
| 19 | del 19 | 44.8–45.0 | sensitive | sensitive | sensitive |
| ins 19 | <0.6 | intermediate | intermediate-sensitive | intermediate-sensitive | |
| 20 | ins 20 | >5.8 | resistant except A763_Y764insFQEA | resistant-sensitive | intermediate-sensitive |
| S768I | <1.5 | intermediate | intermediate-sensitive | sensitive | |
| 21 | L858R | 35.0–39.8 | sensitive | sensitive | sensitive |
| L861Q | 0.9–3.0 | intermediate | intermediate-sensitive | intermediate-sensitive | |
| Agents | Trial | Phase | Number of Patients | ORR (%) | PFS (Months) | OS (Months) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobocertinib | EXCLAIM | 1/2 | 96 | 23 | 7.3 a | 24.0 | [85,86] |
| Mobocertinib | EXCLAIM-2 | 3 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NCT04129502 |
| Poziotinib | ZENITH20-1 | 2 | 115 | 15 | 4.2 | NA | [88] |
| TAS6417 | NCT04036682 | 1/2 | 17 | 35 | NA | NA | [89] |
| BDTX-189 | NCT04209465 | 1/2 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NCT04209465 |
| Amivantamab | CHRYSALIS | 1 | 81 | 40 | 8.3 | NA | [92] |
| Amivantamab + chemotherapy | PAPILLON | 3 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NCT04538664 |
| DZD9008 | NCT03974022 | 1 | 97 | 48.4 | NA | NA | [95] |
| Tarloxotinib | NCT03805841 | 2 | 11 | 0 | NA | NA | [96] |
| Afatinib + cetuximab | NCT03727724 | 2 | NA | NA | NA | NA | [19] |
| necitumumab + osimertinib | NCT02496663 | 1 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NCT02496663 |
| Amivantamab + lazertinib | NCT04487080 | 3 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NCT04487080 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitadai, R.; Okuma, Y. Treatment Strategies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Common and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: Drug Sensitivity Based on Exon Classification, and Structure-Function Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14102519
Kitadai R, Okuma Y. Treatment Strategies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Common and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: Drug Sensitivity Based on Exon Classification, and Structure-Function Analysis. Cancers. 2022; 14(10):2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14102519
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitadai, Rui, and Yusuke Okuma. 2022. "Treatment Strategies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Common and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: Drug Sensitivity Based on Exon Classification, and Structure-Function Analysis" Cancers 14, no. 10: 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14102519
APA StyleKitadai, R., & Okuma, Y. (2022). Treatment Strategies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Common and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: Drug Sensitivity Based on Exon Classification, and Structure-Function Analysis. Cancers, 14(10), 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14102519






