Ficus dubia Latex Extract Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway in Inflammatory Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Condition
2.3. The Experimental Design of Non-Inflammatory and Inflammatory Model
2.4. Measurement of Relative Cell Viability Using MTT Assay
2.5. Determination of Colony Formation by Colony Formation Assay
2.6. Analysis of Cell Cycle Arrest by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Analysis of Apoptosis Induction by Flow Cytometry
2.8. Measurement of Proteins Related to Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subsection Effect of FDLE on Cell Viability in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines and Normal Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast Cell (NIH3T3) by MTT Assay
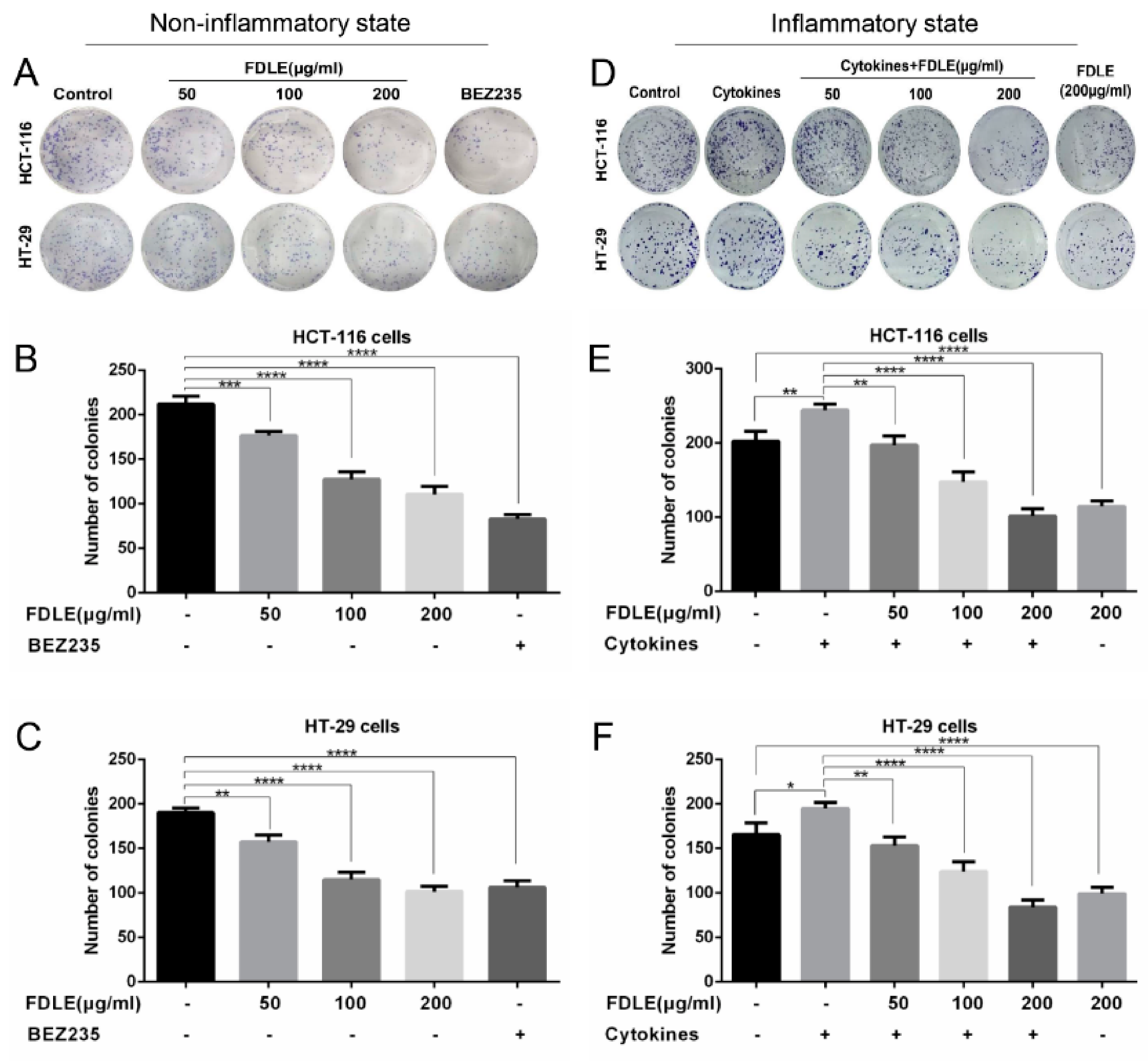
3.2. Effects of FDLE on Growth Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines by Colony Formation Assay
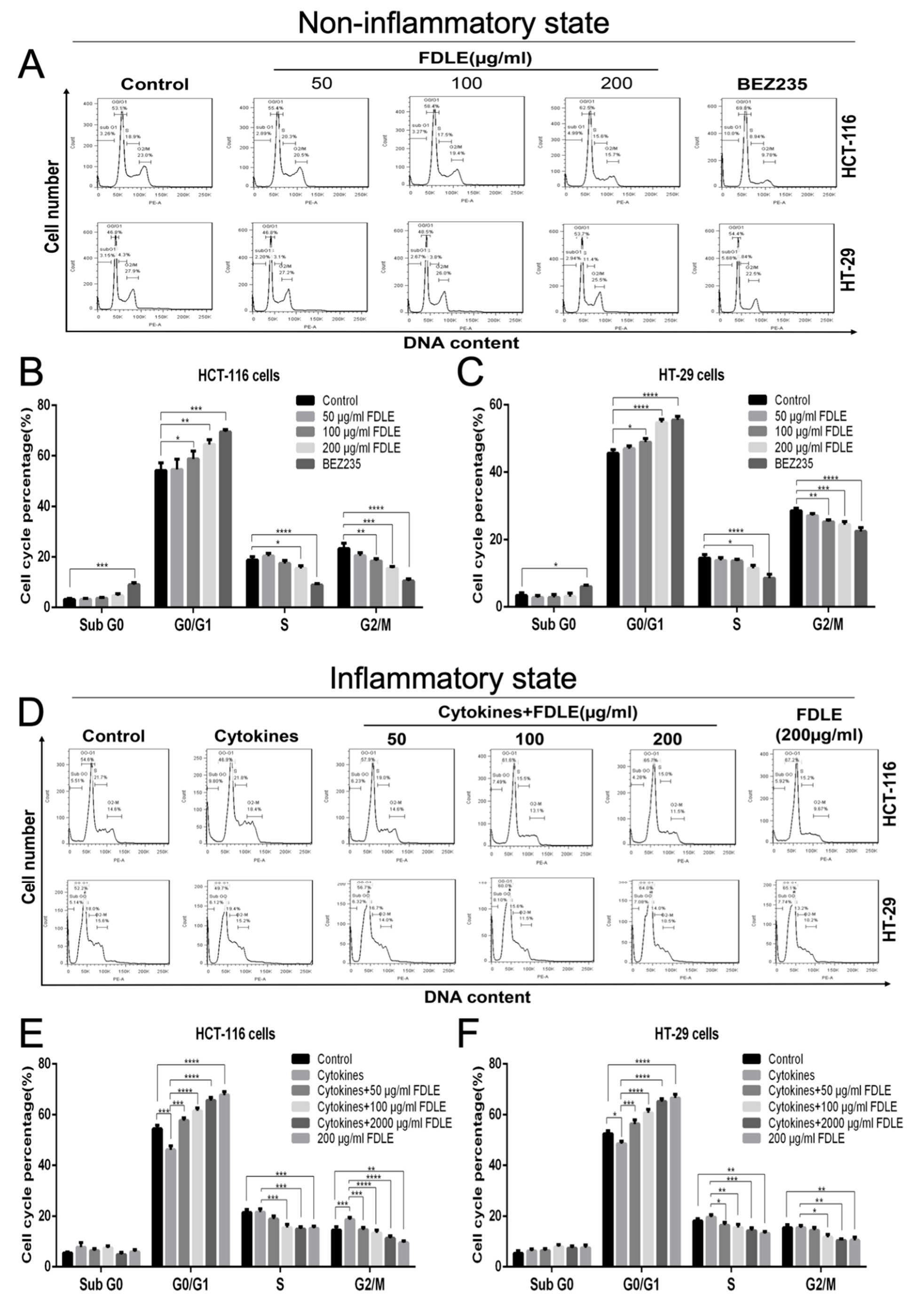
3.3. Effects of FDLE on Cell Cycle Arrest in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines by Flow Cytometer
3.4. Effect of FDLE on NF-κB-Mediated Proteins Related to Cell Cycle by Western Blot
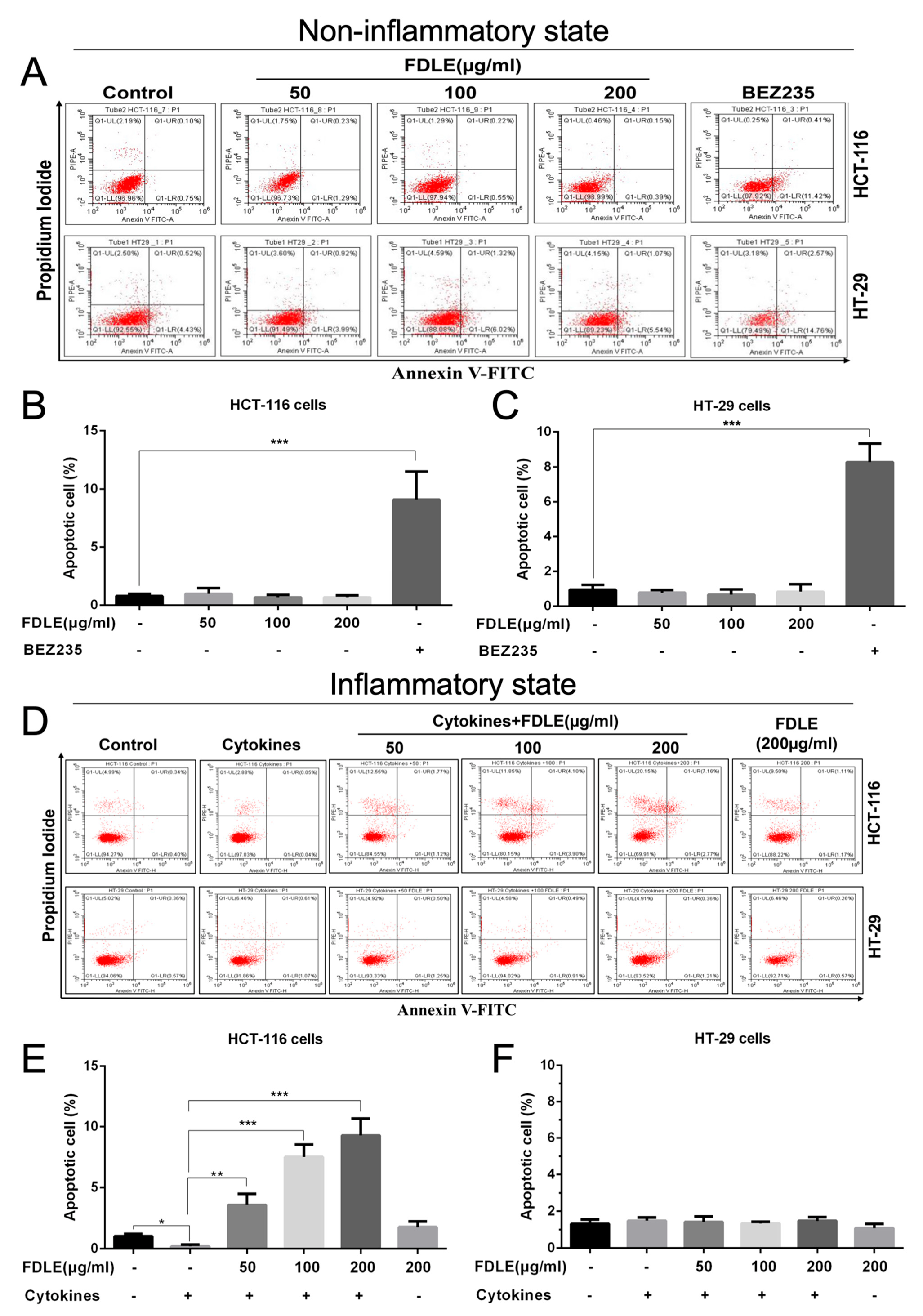
3.5. Effects of FDLE on Apoptosis Induction of Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines by Flow Cytometry
3.6. The Effect of FDLE on NF-ΚB Mediated Expression of Apoptotic Proteins and Activation of Caspase Enzymes by Western Blot
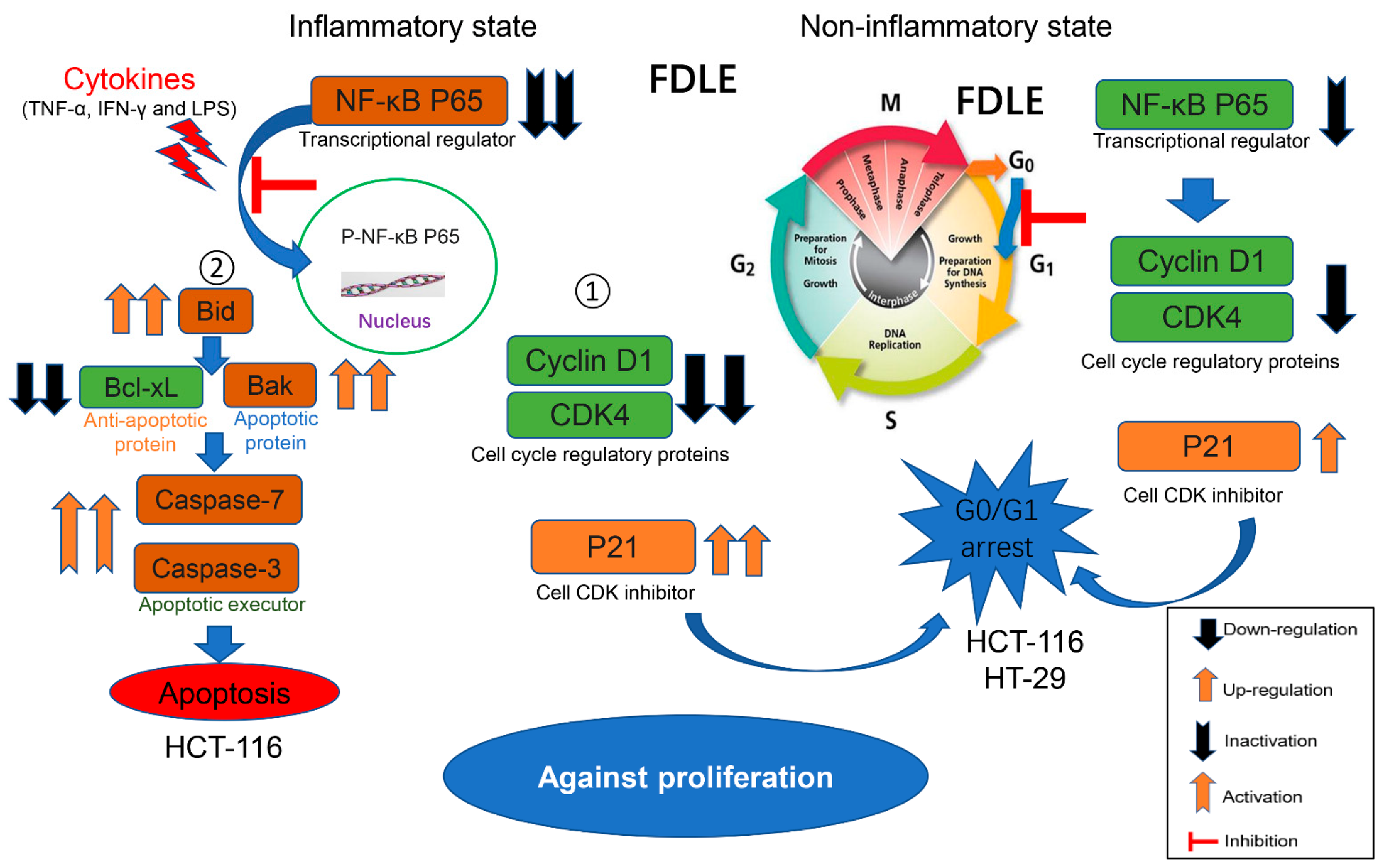
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, A.G.; Lundsmith, E.T.; Hamilton, K.E. Inflammation and colorectal cancer. Curr. Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2017, 13, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Eun, C.S.; Han, D.S. Intestinal microbiota, chronic inflammation, and colorectal cancer. Intest. Res. 2018, 16, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ieda, T.; Tazawa, H.; Okabayashi, H.; Yano, S.; Shigeyasu, K.; Kuroda, S.; Ohara, T.; Noma, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Nishizaki, M. Visualization of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in an inflammatory microenvironment–colorectal cancer network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.-W. Systemic inflammatory response as a prognostic factor in patients with cancer. J. Korean Tradit. Oncol. 2012, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ullman, T.A.; Itzkowitz, S.H. Intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1807–1816.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Lin, C.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Q.I.N.; Hoffman, R.M.; Singh, S.R.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, W.E.I.; Yang, S.; Ye, J. TRAF6-Mediated Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion in LPS-induced Colorectal Cancer Cells Is Regulated by miR-140. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, T.; Sershen, C.L.; May, E.E. Investigating the role of TNF-α and IFN-γ activation on the dynamics of iNOS gene expression in LPS stimulated macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savio, M.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Scarlata, C.; Orgiu, M.; Accardo, G.; Sardar, A.S.; Moccia, F.; Stivala, L.A.; Brusotti, G. Anti-inflammatory properties of Bellevalia saviczii root extract and its isolated homoisoflavonoid (dracol) are mediated by modification on calcium signaling. Molecules 2019, 24, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolcet, X.; Llobet, D.; Pallares, J.; Matias-Guiu, X. NF-kB in development and progression of human cancer. Virchows Arch. 2005, 446, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. NF-κB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, M.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Edwards, J. NF-κB pathways in the development and progression of colorectal cancer. Transl. Res. 2018, 197, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baig, S.; Seevasant, I.; Mohamad, J.; Mukheem, A.; Huri, H.; Kamarul, T. Potential of apoptotic pathway-targeted cancer therapeutic research: Where do we stand? Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Na, K.; Sang, T.; Wu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. The ethanol extracts of sporoderm-broken spores of Ganoderma lucidum inhibit colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aiello, P.; Sharghi, M.; Mansourkhani, S.M.; Ardekan, A.P.; Jouybari, L.; Daraei, N.; Peiro, K.; Mohamadian, S.; Rezaei, M.; Heidari, M. Medicinal plants in the prevention and treatment of colon cancer. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2075614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kooti, W.; Daraei, N. A review of the antioxidant activity of celery (Apium graveolens L). J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 22, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Cobb, R.E.; Zhao, H. Recent advances in natural product discovery. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chantarasuwan, B.; Thong-Aree, S. Five species of Ficus (Moraceae) new for Thailand. Thai For. Bull. Bot. 2006, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Suttisansanee, U.; Pitchakarn, P.; Ting, P.; Inthachat, W.; Thiyajai, P.; Rodthayoy, D.; Karinchai, J.; Chantarasuwan, B.; Nuchuchua, O.; Temviriyanukul, P. Health-promoting bioactivity and in vivo genotoxicity evaluation of a hemiepiphyte fig, Ficus dubia. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2269–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansriniyom, C.; Nooin, R.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Wongwanakul, R.; Petpiroon, N.; Srinuanchai, W.; Chantarasuwan, B.; Pitchakarn, P.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Nuchuchua, O. Tandem mass spectrometry of aqueous extract from Ficus dubia sap and its cell-based assessments for use as a skin antioxidant. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodthayoy, D.; Karinchai, J.; Dukaew, N.; Buacheen, P.; Wongnoppavich, A.; Bonness, A.I.; Khantamat, O.; Chantarasuwan, B.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Pitchakarn, P. Effect of Ficusdubia latex and root extracts in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages. Innov. Funct. Foods Asia IFFA 2018, 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Abolmaesoomi, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Junit, S.M.; Ali, J.M. Ficus deltoidea: Effects of solvent polarity on antioxidant and anti-proliferative activities in breast and colon cancer cells. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 28, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltana, H.; Pinon, A.; Limami, Y.; Zaid, Y.; Khalki, L.; Zaid, N.; Salah, D.; Sabitaliyevich, U.Y.; Simon, A.; Liagre, B. Antitumoral activity of Ficus carica L. on colorectal cancer cell lines. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Chantana, W.; Pitchakarn, P.; Subhawa, S.; Chantarasuwan, B.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Chewonarin, T. Ficus dubia Latex Extract Prevent DMH-Induced Rat Colorectal Carcinogenesis Through the Regulation of Xenobiotic Metabolism, Inflammation, Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358084128_Ficus_Dubia_Latex_Extract_Prevent_DMH-Induced_Rat_Colorectal_Carcinogenesis_Through_the_Regulation_of_Xenobiotic_Metabolism_Inflammation_Cell_Proliferation_and_Apoptosis (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Sadeghi Ekbatan, S.; Li, X.-Q.; Ghorbani, M.; Azadi, B.; Kubow, S. Chlorogenic acid and its microbial metabolites exert anti-proliferative effects, S-phase cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer Caco-2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; He, X.; Qiu, X.; Song, Z. In vitro monitoring chlorogenic acid in human urine and serum by a flow injection system exploiting the luminol-dissolved oxygen chemiluminescence reaction. Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, W.-Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z.-L.; Wen, Y.-L.; Zhao, C.-C.; Tao, L.; Li, L.-F.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Astragalin Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Colon Cancer HCT116 Cells by Regulating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 639256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Kim, W.K.; Ha, A.W.; Kim, M.H.; Chang, M.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of lycopene in SW480 human colorectal cancer cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schottelius, A.J.; Dinter, H. Cytokines, NF-κB, microenvironment, intestinal inflammation and cancer. Link Between Inflamm. Cancer 2006, 130, 67–87. [Google Scholar]
- Peyressatre, M.; Prével, C.; Pellerano, M.; Morris, M.C. Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in human cancers: From small molecules to peptide inhibitors. Cancers 2015, 7, 179–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Anders, L. Signaling through cyclin D-dependent kinases. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1890–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Huo, B.; Li, B.; Jin, Y.; Hu, X. Extracts and components of Ficus carica leaves suppress survival, cell cycle, and migration of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Kang, J.; Song, K.; Park, M.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.; Choi, C.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Oh, S. Inonotus obliquus suppresses proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and tumor growth in mice models by downregulation of β-catenin/NF-κB-signaling pathways. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2013, 11, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Qin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, J. SMAC mimetic birinapant inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by activating the cIAP1/TRAF3 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cen, J.; Jia, Z.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Xia, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Hepatotoxicity induced by isoniazid-lipopolysaccharide through endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and apoptosis pathways in zebrafish. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01639-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillyer, R.L.; Sirinvasin, P.; Joglekar, M.; Sikes, R.A.; van Golen, K.L.; Nohe, A. Differential effects of vitamin D treatment on inflammatory and non-inflammatory breast cancer cell lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Feldman, D. Mechanisms of the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory actions of vitamin D. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yousef, B.A.; Hassan, H.M.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Jiang, Z.-Z. Pristimerin exhibits in vitro and in vivo anticancer activities through inhibition of nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 40, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, H.; Wang, C.; Ni, M.; Fishbein, A.; Mehendale, S.; Xie, J.; Shoyama, A.; Yuan, C. Crocin from Crocus sativus possesses significant anti-proliferation effects on human colorectal cancer cells. Exp. Oncol. 2007, 29, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Heffern, M.C.; Su, T.A.; Chang, C.J.; Toietta, G. Effects of copper chelation on BRAFV600E positive colon carcinoma cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, K.C.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Johannessen, B.; Bruun, J.; Danielsen, S.A.; Bjørnslett, M.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Eknæs, M.; Lind, G.E. Multi-omics of 34 colorectal cancer cell lines-a resource for biomedical studies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calistri, D.; Rengucci, C.; Seymour, I.; Lattuneddu, A.; Polifemo, A.M.; Monti, F.; Saragoni, L.; Amadori, D. Mutation analysis of p53, K-ras, and BRAF genes in colorectal cancer progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 204, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, A.; Mathe, E.; Kato, S.; Ishioka, C.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Hainaut, P.; Olivier, M. Impact of mutant p53 functional properties on TP53 mutation patterns and tumor phenotype: Lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53 database. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Shukla, S.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Ghoshal, U.C. Analysis of p53, K-ras gene mutation & Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with gastric cancer & peptic ulcer disease at a tertiary care hospital in north India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 136, 664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajbouj, K.; Schulze-Luehrmann, J.; Diermeier, S.; Amin, A.; Schneider-Stock, R. The anticancer effect of saffron in two p53 isogenic colorectal cancer cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arisan, E.D.; Ergül, Z.; Bozdağ, G.; Rencüzoğulları, Ö.; Çoker-Gürkan, A.; Obakan-Yerlikaya, P.; Coşkun, D.; Palavan-Ünsal, N. Diclofenac induced apoptosis via altering PI3K/Akt/MAPK signaling axis in HCT 116 more efficiently compared to SW480 colon cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, R.; Gariboldi, M.B.; Passarelli, L.; Monti, E. Role of the p53/p21 system in the response of human colon carcinoma cells to Doxorubicin. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, D.; Coulombe, Y.; Martinez-Marignac, V.L.; Amrein, L.; Grenier, J.; Hodkinson, K.; Masson, J.-Y.; Aloyz, R.; Panasci, L. Irinotecan and DNA-PKcs inhibitors synergize in killing of colon cancer cells. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, R.; Chantana, W.; Pitchakarn, P.; Subhawa, S.; Chantarasuwan, B.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Chewonarin, T. Ficus dubia Latex Extract Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway in Inflammatory Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2022, 14, 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112665
Hu R, Chantana W, Pitchakarn P, Subhawa S, Chantarasuwan B, Temviriyanukul P, Chewonarin T. Ficus dubia Latex Extract Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway in Inflammatory Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers. 2022; 14(11):2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112665
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Rentong, Weerachai Chantana, Pornsiri Pitchakarn, Subhawat Subhawa, Bhanumas Chantarasuwan, Piya Temviriyanukul, and Teera Chewonarin. 2022. "Ficus dubia Latex Extract Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway in Inflammatory Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines" Cancers 14, no. 11: 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112665
APA StyleHu, R., Chantana, W., Pitchakarn, P., Subhawa, S., Chantarasuwan, B., Temviriyanukul, P., & Chewonarin, T. (2022). Ficus dubia Latex Extract Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway in Inflammatory Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers, 14(11), 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112665







