Proton Therapy in the Management of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
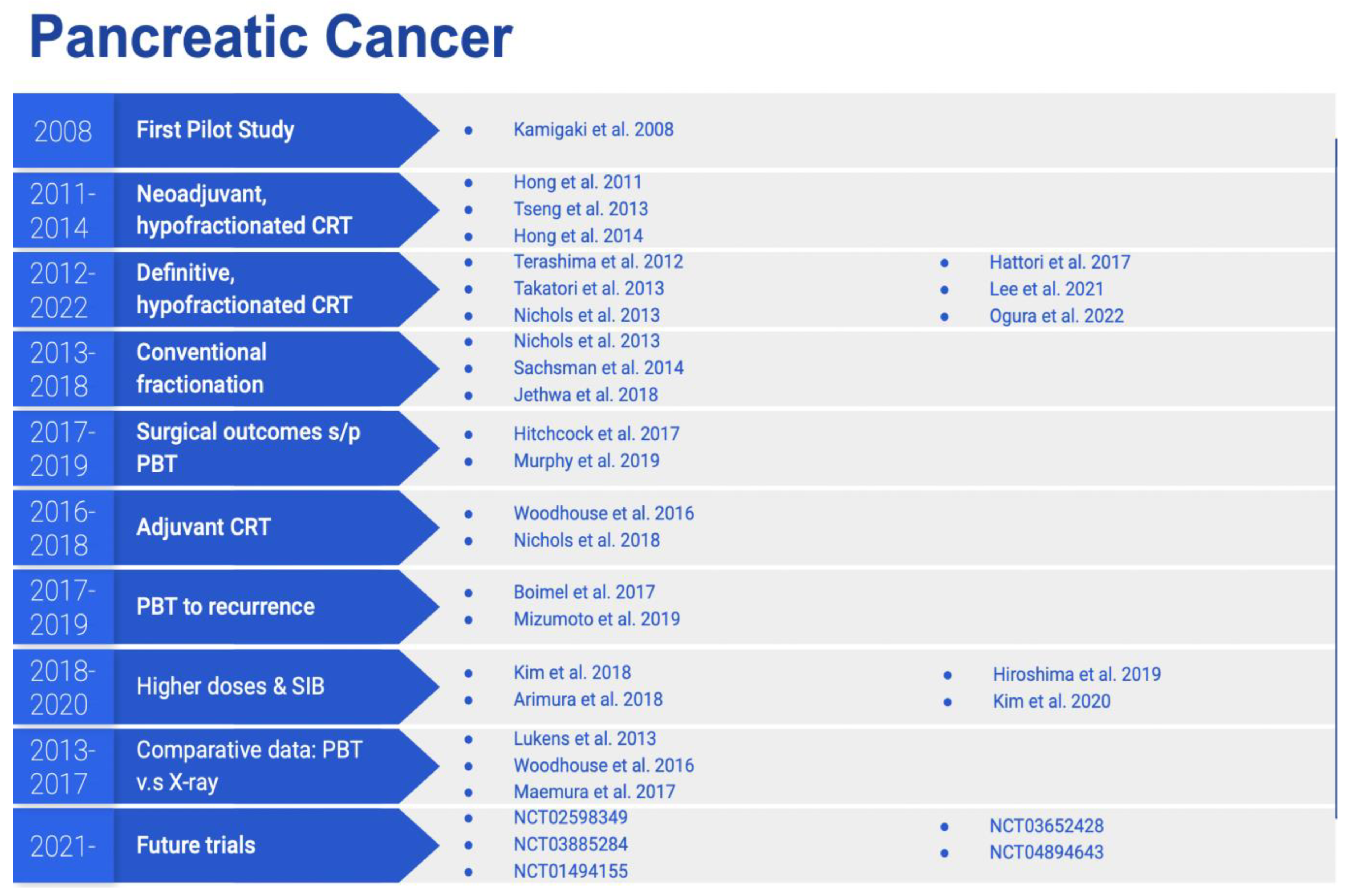
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Dosimetric Data
4. Clinical Data
5. Prospective Trials
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Pancreatic Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- De Ruysscher, D.; Niedermann, G.; Burnet, N.G.; Siva, S.; Lee, A.W.; Hegi-Johnson, F. Author Correction: Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, R.; Grosshans, D. Proton therapy—Present and future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 109, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. 2022. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Jones, C.M.; Radhakrishna, G.; Aitken, K.; Bridgewater, J.; Corrie, P.; Eatock, M.; Goody, R.; Ghaneh, P.; Good, J.; Grose, D.; et al. Considerations for the treatment of pancreatic cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic: The UK consensus position. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, P.W.; Chen, X.; Hall, W.A.; Erickson, B.A.; Li, A. Estimation of the Alpha-beta Ratio for Chemoradiation of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Chen, J.; Dong, M.; Wang, Y.; Ou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, S.; et al. Charged Particle Irradiation for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 775597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Sedor, G.; Ellsworth, P.; Scarborough, J.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; Oliver, D.E.; Eschrich, S.A.; Kattan, M.W.; Torres-Roca, J.F. Pan-cancer prediction of radiotherapy benefit using genomic-adjusted radiation dose (GARD): A cohort-based pooled analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteijne, E.; van Dam, J.L.; Suker, M.; Janssen, Q.P.; Groothuis, K.; Akkermans-Vogelaar, J.M.; Besselink, M.G.; Bonsing, B.A.; Buijsen, J.; Busch, O.R.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Versus Upfront Surgery for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Dutch Randomized PREOPANC Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Hammel, P.; Hebbar, M.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Raoul, J.L.; Choné, L.; Francois, E.; Artru, P.; Biagi, J.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkenbijl, J.H.; Jeekel, J.; Sahmoud, T.; van Pel, R.; Couvreur, M.L.; Veenhof, C.H.; Arnaud, J.P.; Gonzalez, D.G.; de Wit, L.T.; Hennipman, A.; et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy and 5-fluorouracil after curative resection of cancer of the pancreas and periampullary region: Phase III trial of the EORTC gastrointestinal tract cancer cooperative group. Ann. Surg. 1999, 230, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Stocken, D.D.; Friess, H.; Bassi, C.; Dunn, J.A.; Hickey, H.; Beger, H.; Fernandez-Cruz, L.; Dervenis, C.; Lacaine, F.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Chemoradiotherapy and Chemotherapy after Resection of Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyngold, M.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Varghese, A.M.; Fiasconaro, M.; Zinovoy, M.; Romesser, P.B.; Wu, A.; Hajj, C.; Cuaron, J.J.; Tuli, R.; et al. Association of Ablative Radiation Therapy with Survival among Patients with Inoperable Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutenberg, M.S.; Nichols, R.C. Proton beam radiotherapy for pancreas cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 11, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Lin, S.H.; Simone, C.B. Clinical outcomes and toxicities of proton radiotherapy for gastrointestinal neoplasms: A systematic review. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 644–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H.; Beltran, C.; Both, S.; Dong, L.; Flanz, J.; Furutani, K.; Grassberger, C.; Grosshans, D.R.; Knopf, A.C.; Langendijk, J.A.; et al. Roadmap: Proton therapy physics and biology. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 05RM01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurlo, A.; Lomax, A.; Hoess, A.; Bortfeld, T.; Russo, M.; Goitein, G.; Valentini, V.; Marucci, L.; Capparella, R.; Loasses, A. The role of proton therapy in the treatment of large irradiation volumes: A comparative planning study of pancreatic and biliary tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiung-Stripp, D.C.; McDonough, J.; Masters, H.M.; Levin, W.P.; Hahn, S.M.; Jones, H.A.; Metz, J.M. Comparative treatment planning between proton and x-ray therapy in pancreatic cancer. Med. Dosim. 2001, 26, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.; Amos, R.A.; Briere, T.M.; Beddar, S.; Crane, C.H. Dose escalation with proton or photon radiation treatment for pancreatic cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.R.; Kachnic, L.A.; Adams, J.; Crowley, E.M.; Alexander, B.M.; Mamon, H.J.; Fernandez-Del Castillo, C.; Ryan, D.P.; DeLaney, T.F.; Hong, T.S. Dosimetric Feasibility of Hypofractionated Proton Radiotherapy for Neoadjuvant Pancreatic Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.Y.; Nichols, R.C., Jr.; Huh, S.N.; Ho, M.W.; Li, Z.; Zaiden, R.; Awad, Z.T.; Ahmed, B.; Hoppe, B.S. Proton therapy may allow for comprehensive elective nodal coverage for patients receiving neoadjuvant radiotherapy for localized pancreatic head cancers. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 4, 374–379. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, R.C., Jr.; Huh, S.N.; Prado, K.L.; Byong, Y.Y.; Sharma, N.K.; Ho, M.W.; Hoppe, B.S.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Li, Z.; Regine, W.F. Protons Offer Reduced Normal-Tissue Exposure for Patients Receiving Postoperative Radiotherapy for Resected Pancreatic Head Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Dionisi, F.; Tang, S.; Ingram, M.; Hung, C.Y.; Prionas, E.; Lichtenwalner, P.; Butterwick, I.; Zhai, H.; Yin, L.; et al. A comprehensive dosimetric study of pancreatic cancer treatment using three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT), intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), volumetric-modulated radiation therapy (VMAT), and passive-scattering and modulated-scanning proton therapy (PT). Med. Dosim. 2014, 39, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slater, J.M.; Ling, T.C.; Mifflin, R.; Nookala, P.; Grove, R.; Ly, A.M.; Patyal, B.; Slater, J.D.; Yang, G.Y. Protons Offer Reduced Tissue Exposure for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2014, 1, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.F.; Mayekar, S.U.; Zhai, H.; Both, S.; Apisarnthanarax, S.; Metz, J.M.; Plastaras, J.P.; Ben-Josef, E. A dosimetric comparison of proton and photon therapy in unresectable cancers of the head of pancreas. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 081711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz, S.; Stützer, K.; Zschaeck, S.; Jakobi, A.; Troost, E.G. Comparison of different treatment planning approaches for intensity-modulated proton therapy with simultaneous integrated boost for pancreatic cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz, S.; Wlodarczyk, W.; Frosch, S.; Zschaeck, S.; Troost, E.G. Dose-escalated simultaneously integrated boost photon or proton therapy in pancreatic cancer in an in-silico study: Gastrointestinal organs remain critical. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raturi, V.P.; Hojo, H.; Hotta, K.; Baba, H.; Takahashi, R.; Rachi, T.; Nakamura, N.; Zenda, S.; Motegi, A.; Tachibana, H.; et al. Radiobiological model-based approach to determine the potential of dose-escalated robust intensity-modulated proton radiotherapy in reducing gastrointestinal toxicity in the treatment of locally advanced unresectable pancreatic cancer of the head. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuong, M.D.; Yam, M.; Li, Z.; Langen, K.M.; Regine, W.F.; Mehta, M.P.; Morris, C.G.; Huh, S.N.; Snider, J.W.; Rutenberg, M.S.; et al. Is Pencil Beam Scanning Dosimetrically Advantageous Compared to Passively Scattered Proton Therapy for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, E172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Narita, Y.; Kato, T.; Takemasa, K.; Sato, H.; Ikeda, T.; Harada, T.; Oyama, S.; Murakami, M. Dosimetric impact of simulated changes in large bowel content during proton therapy with simultaneous integrated boost for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houweling, A.C.; Crama, K.; Visser, J.; Fukata, K.; Rasch, C.R.; Ohno, T.; Bel, A.; Van Der Horst, A. Comparing the dosimetric impact of interfractional anatomical changes in photon, proton and carbon ion radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer patients. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolde, K.; Naumann, P.; Dávid, C.; Kachelriess, M.; Lomax, A.J.; Weber, D.C.; Saito, N.; Burigo, L.N.; Pfaffenberger, A.; Zhang, Y. Comparing the effectiveness and efficiency of various gating approaches for PBS proton therapy of pancreatic cancer using 4D-MRI datasets. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 085011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolde, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chaudhri, N.; Dávid, C.; Kachelrieß, M.; Lomax, A.J.; Naumann, P.; Saito, N.; Weber, D.C.; Pfaffenberger, A. 4DMRI-based investigation on the interplay effect for pencil beam scanning proton therapy of pancreatic cancer patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sio, T.T.; Beltran, C.J.; Ashman, J.B.; Wurgler, S.K.; Hoeft, K.A.; Miller, R.C. Scanning Beam Stereotactic Body Proton Therapy (SBPT) for Pancreatic Cancer: A Dosimetric Feasibility Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sio, T.T.; Merrell, K.W.; Beltran, C.J.; Ashman, J.B.; Hoeft, K.A.; Miller, R.C.; Whitaker, T.J.; Wurgler, S.K.; Tryggestad, E.J. Spot-scanned pancreatic stereotactic body proton therapy: A dosimetric feasibility and robustness study. Phys. Med. 2016, 32, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Gao, X.S.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Xi, C.; Jia, C.; Xie, M.; Lyu, F.; Ding, X. Investigate the Dosimetric and Potential Clinical Benefits Utilizing Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy With Simultaneous Integrated Boost Technique for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Comparison Between Photon and Proton Beam Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 747532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Range uncertainties in proton therapy and the role of Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lee, H.C.; Duan, X.; Shen, C.; Zhou, L.; Jia, X.; Yang, M. Comprehensive analysis of proton range uncertainties related to stopping-power-ratio estimation using dual-energy CT imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhu, X.R.; Park, P.C.; Titt, U.; Mohan, R.; Virshup, G.; Clayton, J.E.; Dong, L. Comprehensive analysis of proton range uncertainties related to patient stopping-power-ratio estimation using the stoichiometric calibration. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Hooshangnejad, H.; Chen, C.C.; Ding, K. A Beam-Specific Optimization Target Volume for Stereotactic Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Therapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.; Wohlfahrt, P.; Hofmann, C.; Möhler, C.; Menkel, S.; Tschiche, M.; Krause, M.; Troost, E.G.; Enghardt, W.; Richter, C. Reduction of clinical safety margins in proton therapy enabled by the clinical implementation of dual-energy CT for direct stopping-power prediction. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 166, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryggestad, E.J.; Liu, W.; Pepin, M.D.; Hallemeier, C.L.; Sio, T.T. Managing treatment-related uncertainties in proton beam radiotherapy for gastrointestinal cancers. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 11, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.D.; Feng, Z.; Shin, E.J.; He, J.; Waters, K.M.; Coquia, S.; DeJong, R.; Rosati, L.M.; Su, L.; Li, D.; et al. A Novel Absorbable Radiopaque Hydrogel Spacer to Separate the Head of the Pancreas and Duodenum in Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, A.; Free, J.; Wagenaar, D.; Deffet, S.; Knopf, A.C.; Langendijk, J.A.; Both, S. Validation of the proton range accuracy and optimization of CT calibration curves utilizing range probing. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 03NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engwall, E.; Fredriksson, A.; Glimelius, L. 4D robust optimization including uncertainties in time structures can reduce the interplay effect in proton pencil beam scanning radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 4020–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Patel, S.H.; Shan, J.; Schild, S.E.; Vargas, C.E.; Wong, W.W.; Ding, X.; Bues, M.; Liu, W. Robust Optimization for Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy to Redistribute High Linear Energy Transfer from Nearby Critical Organs to Tumors in Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamigaki, T.; Murakami, M.; Matsumoto, I.; Toyama, H.; Fujita, T.; Takase, S.; Sakai, T.; Ajiki, T.; Ku, Y.; Hishikawa, Y.; et al. A phase I study of proton beam therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Analysis of feasibility and anti-tumor effect. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.S.; Ryan, D.P.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Mamon, H.J.; Kwak, E.L.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Adams, J.; Yeap, B.; Winrich, B.; DeLaney, T.F.; et al. Phase I Study of Preoperative Short-Course Chemoradiation with Proton Beam Therapy and Capecitabine for Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Head. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.S.; Ryan, D.P.; Borger, D.R.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Deshpande, V.; Shinagare, S.; Wo, J.Y.; Boucher, Y.; et al. A Phase 1/2 and Biomarker Study of Preoperative Short Course Chemoradiation with Proton Beam Therapy and Capecitabine Followed by Early Surgery for Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.D.; Wo, J.Y.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Adams, J.; Depauw, N.; Mamon, H.J.; Hong, T.S. Dosimetric predictors of nausea and vomiting: An exploratory analysis of a prospective phase I/II trial with neoadjuvant accelerated short-course radiotherapy and capecitabine for resectable pancreatic cancer. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 2, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Terashima, K.; Demizu, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Jin, D.; Mima, M.; Fujii, O.; Niwa, Y.; Takatori, K.; Kitajima, N.; Sirakawa, S.; et al. A phase I/II study of gemcitabine-concurrent proton radiotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer without distant metastasis. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 103, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatori, K.; Terashima, K.; Yoshida, R.; Horai, A.; Satake, S.; Ose, T.; Kitajima, N.; Kinoshita, Y.; Demizu, Y.; Fuwa, N. Upper gastrointestinal complications associated with gemcitabine-concurrent proton radiotherapy for inoperable pancreatic cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 49, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.C., Jr.; Hoppe, B.S. RE: Takatori K, Terashima K, Yoshida R, Horai A, Satake S, Ose T, Kitajima N, Kinoshita Y, Demizu Y, Fuwa N. Upper gastrointestinal complications associated with gemcitabine-concurrent proton radiotherapy for inoperable pancreatic cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2013; (E-pub only). J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 4, E33–E34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Hirano, A.; Iwata, H.; Ogino, H.; Yamashita, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Nakajima, K.; Baba, F.; Sasaki, S.; Senoo, K.; et al. Image-Guided Hypofractionated Proton Therapy and Concurrent Chemotherapy for Inoperable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Toxicities and Preliminary Outcomes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, E153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Komatsu, S.; Terashima, K.; Toyama, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Takahashi, D.; Suga, M.; Nishimura, N.; Tai, K.; Kido, M.; et al. Surgical spacer placement for proton radiotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic body and tail cancers: Initial clinical results. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Terashima, K.; Nanno, Y.; Park, S.; Suga, M.; Takahashi, D.; Matsuo, Y.; Sulaiman, N.S.; Tokumaru, S.; Okimoto, T.; et al. Factors associated with long-term survival in gemcitabine-concurrent proton radiotherapy for non-metastatic locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A single-center retrospective study. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, R.C., Jr.; George, T.J.; Zaiden, R.A., Jr.; Awad, Z.T.; Asbun, H.J.; Huh, S.; Ho, M.W.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Morris, C.G.; Hoppe, B.S. Proton therapy with concomitant capecitabine for pancreatic and ampullary cancers is associated with a low incidence of gastrointestinal toxicity. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachsman, S.; Nichols, R.C., Jr.; Morris, C.G.; Zaiden, R.; Johnson, E.A.; Awad, Z.; Bose, D.; Ho, M.W.; Huh, S.N.; Li, Z.; et al. Proton Therapy and Concomitant Capecitabine for Non-Metastatic Unresectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2014, 1, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethwa, K.R.; Tryggestad, E.J.; Whitaker, T.J.; Giffey, B.T.; Kazemba, B.D.; Neben-Wittich, M.A.; Merrell, K.W.; Haddock, M.G.; Hallemeier, C.L. Initial experience with intensity modulated proton therapy for intact, clinically localized pancreas cancer: Clinical implementation, dosimetric analysis, acute treatment-related adverse events, and patient-reported outcomes. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, K.E.; Nichols, R.C.; Morris, C.G.; Bose, D.; Hughes, S.J.; Stauffer, J.A.; Celinski, S.A.; Johnson, E.A.; Zaiden, R.A.; Mendenhall, N.P.; et al. Feasibility of pancreatectomy following high-dose proton therapy for unresectable pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2017, 9, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.E.; Wo, J.Y.; Ryan, D.P.; Clark, J.W.; Jiang, W.; Yeap, B.Y.; Drapek, L.C.; Ly, L.; Baglini, C.V.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; et al. Total Neoadjuvant Therapy with FOLFIRINOX in Combination with Losartan Followed by Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.C.; Morris, C.G.; Prabhu, K.; Hartsell, W.F.; Cahlon, O.; Apisarnthanarax, S.; McGee, L.; Vargas, C.E. Postoperative proton therapy for pancreatic cancer patients enrolled on the Proton Collaborative Group (PCG) registry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, T.; Terashima, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Nagano, F.; Demizu, Y.; Mima, M.; Sulaiman, N.S.; Tokumaru, S.; Okimoto, T.; Toyama, H.; et al. Proton Radiotherapy for Isolated Local Recurrence of Primary Resected Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boimel, P.J.; Berman, A.T.; Li, J.; Apisarnthanarax, S.; Both, S.; Lelionis, K.; Larson, G.L.; Teitelbaum, U.; Lukens, J.N.; Ben-Josef, E.; et al. Proton beam reirradiation for locally recurrent pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2017, 8, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, T.; Kondo, N.; Matsuyama, M.; Kitano, I.; Mukoyoshi, T.; Nagata, I.; Ogino, T. Proton Beam Therapy for Inoperable Stage III Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, E68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroshima, Y.; Fukumitsu, N.; Saito, T.; Numajiri, H.; Murofushi, K.N.; Ohnishi, K.; Nonaka, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Okumura, T.; Sakurai, H. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy using proton beams for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 136, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, W.J.; Woo, S.M.; Kim, H.; Oh, E.S.; Lee, J.H.; Han, S.S.; Park, S.J.; Suh, Y.G.; Moon, S.H.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Simultaneous Integrated Boost-Proton Beam Therapy for Localized Pancreatic Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818783879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, W.J.; Woo, S.M.; Oh, E.S.; Youn, S.H.; Jang, H.Y.; Han, S.S.; Park, S.J.; Suh, Y.G.; Moon, S.H.; et al. Efficacy and feasibility of proton beam radiotherapy using the simultaneous integrated boost technique for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukens, J.N.; Mick, R.; Demas, K.L.; Apisarnthanarax, S.; Metz, J.M.; McCall, D.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Teitelbaum, U.; Both, S.; Plastaras, J.P. Acute Toxicity of Proton Versus Photon Chemoradiation Therapy for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Cohort Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, S311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, K.D.; Elrakhawy, M.; Jain, A.; Ben-Josef, E.; Metz, J.M.; Plastaras, J.P.; Lukens, J.N. Acute Toxicity of Proton Versus Photon Adjuvant Chemoradiation in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer: A Cohort Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, E208–E209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemura, K.; Mataki, Y.; Kurahara, H.; Kawasaki, Y.; Iino, S.; Sakoda, M.; Ueno, S.; Arimura, T.; Higashi, R.; Yoshiura, T.; et al. Comparison of proton beam radiotherapy and hyper-fractionated accelerated chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.V.; Deek, M.P.; Jackson, J.F.; Hill, C.S.; Sehgal, S.; He, J.; Zheng, L.; Herman, J.M.; Meyer, J.; Narang, A.K. Vertebral body and splenic irradiation are associated with lymphopenia in localized pancreatic cancer treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, A.T.; Ye, X.; Ellsworth, S.G.; Smith, J.A.; Narang, A.K.; Garg, T.; Campian, J.; Laheru, D.A.; Zheng, L.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. The Association Between Chemoradiation-related Lymphopenia and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 38, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Shiraishi, Y.; Verma, V.; Jiang, W.; Song, J.; Hobbs, B.P.; Lin, S.H. Lymphocyte-Sparing Effect of Proton Therapy in Patients with Esophageal Cancer Treated with Definitive Chemoradiation. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2018, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, B.; Ng, S.P.; Liu, A.Y.; Avila, S.; Tao, R.; Holliday, E.B.; Brownlee, Z.; Kaseb, A.; Lee, S.; Raghav, K.; et al. Radiation-Associated Lymphopenia and Outcomes of Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Radiotherapy. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proton Collaborative Group; University of Florida Health. Proton Radiation for Unresectable, Borderline Resectable, or Medically Inoperable Carcinoma of the Pancreas; Proton Collaborative Group: Warrenville, IL, USA; University of Florida Health: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Georgetown University. Study of Proton Therapy in Adjuvant Pancreatic Cancer; Georgetown University: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Massachusetts General Hospital. Short Course Radiation Therapy with Proton or Photon Beam Capecitabine and Hydroxychloroquine for Resectable Pancreatic Cancer; Massachusetts General Hospital: Boston, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- University of Maryland, Baltimore. Phase I Nab-Paclitaxel Plus Gemcitabine with Proton Therapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (LAPC); University of Maryland, Baltimore: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EBG MedAustron GmbH; Landesklinkum Wiener Neustadt. Preoperative, Proton- Radiotherapy Combined with Chemotherapy for Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer; EBG MedAustron GmbH; Landesklinkum Wiener Neustadt: Wiener Neustadt, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jolissaint, J.S.; Reyngold, M.; Bassmann, J.; Seier, K.P.; Gönen, M.; Varghese, A.M.; Kenneth, H.Y.; Park, W.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Balachandran, V.P.; et al. Local Control and Survival After Induction Chemotherapy and Ablative Radiation Versus Resection for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with Vascular Involvement. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Liang, J.; Burleson, S.; Subashi, E.; Scripes, P.G.; Tringale, K.R.; Romesser, P.B.; Reyngold, M.; Crane, C.H. Feasibility of ablative stereotactic body radiation therapy of pancreas cancer patients on a 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance-linac system using abdominal compression. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 19, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Year | Study Design | N | Comparison | OS | PFS | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lukens et al. | 2013 | Prospective | 13 | Grade 3 | |||
| PBT | NA | NA | 8% | ||||
| 3D-CRT or VMAT | NA | NA | 24% | ||||
| p-value | 0.36 | ||||||
| Woodhouse et al. | 2016 | Retrospective | 105 | Grade 3 1 | |||
| Proton | NA | NA | 5% | ||||
| Photon | NA | NA | 18% | ||||
| p-value | 0.079 | ||||||
| Maemura et al. | 2017 | Prospective | 25 | Median OS | TTP 2 | Grade 3 3 | |
| Proton | 22.3 months | 15.4 months | No hematological 1/10 non-heme | ||||
| Photon (HART) | 23.4 months | 4/15 hematological No non-heme | |||||
| p-value | N.S. | N.S. | NA | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobeissi, J.M.; Simone, C.B., II; Lin, H.; Hilal, L.; Hajj, C. Proton Therapy in the Management of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112789
Kobeissi JM, Simone CB II, Lin H, Hilal L, Hajj C. Proton Therapy in the Management of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(11):2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112789
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobeissi, Jana M., Charles B. Simone, II, Haibo Lin, Lara Hilal, and Carla Hajj. 2022. "Proton Therapy in the Management of Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 11: 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112789
APA StyleKobeissi, J. M., Simone, C. B., II, Lin, H., Hilal, L., & Hajj, C. (2022). Proton Therapy in the Management of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 14(11), 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112789







