Expression Profiles of ID and E2A in Ovarian Cancer and Suppression of Ovarian Cancer by the E2A Isoform E47
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TCGA Data
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Transfection, Cell Cycle Analysis, and FACS
2.4. Apoptosis Analysis
2.5. Microarray Analysis
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
2.7. Animal Studies
2.8. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Analysis
2.9. IHC Scoring
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
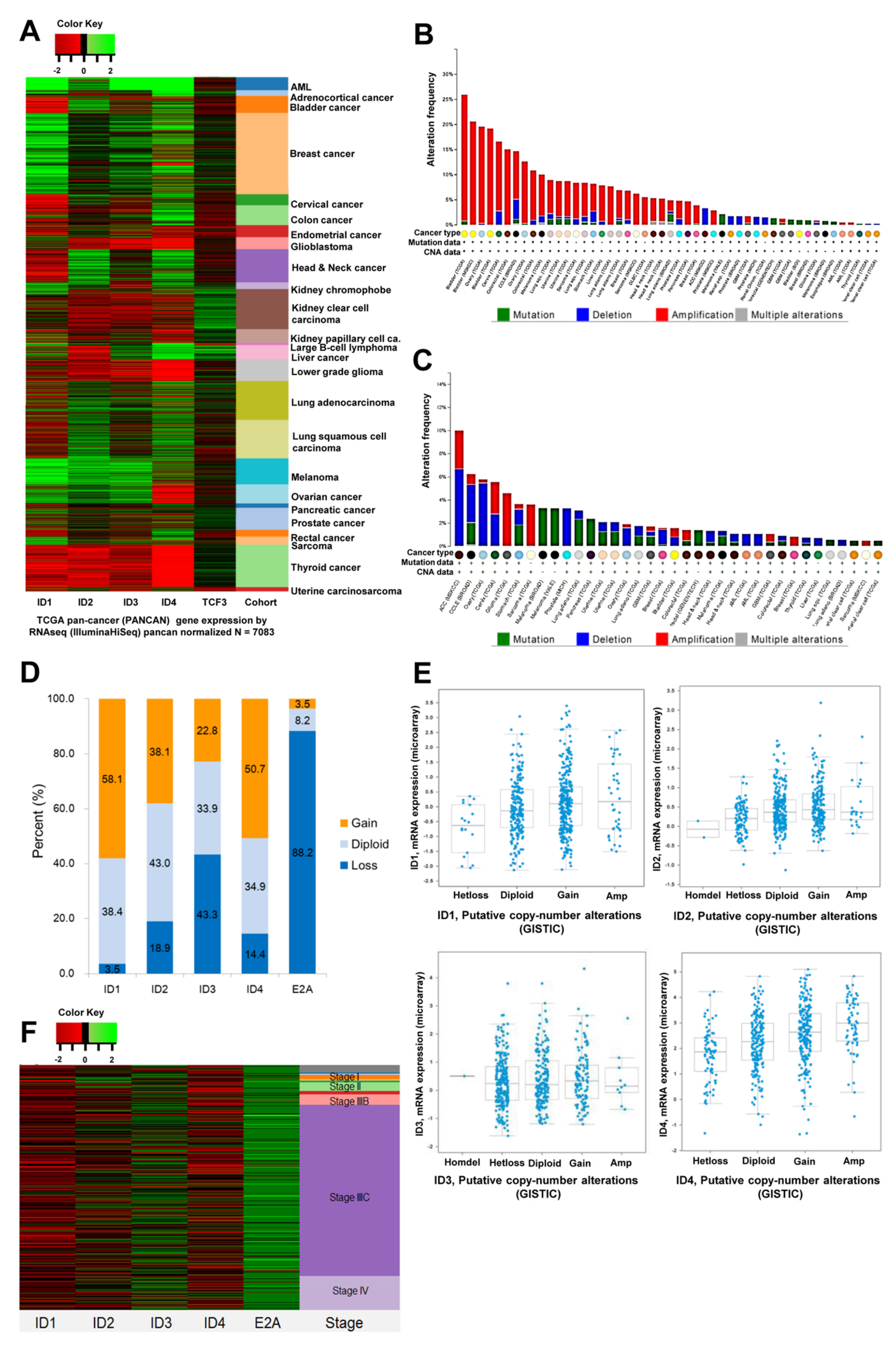
3.1. Expression of ID and E2A Genes in Ovarian Cancer
3.2. Methylation Levels of ID and E2A Genes in Different Stages of Ovarian Cancer
3.3. Association of ID and E2A alterations with Overall Survival
3.4. Clinical Validity of ID and E2A Alterations in Ovarian Cancer Patients
3.5. Induction of the E2A Splice Variant E47 Causes Cell Growth Arrest in Ovarian Cancer Cells
3.6. E47 Induces Global Changes in the Expression Levels of Genes Associated with Cell Cycle, Cancer, and Tissue Differentiation
3.7. E47 Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Formation In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, S. An overview of the basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Pooter, R.F.; Kee, B.L. E proteins and the regulation of early lymphocyte development. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 238, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massari, M.E.; Murre, C. Helix-loop-helix proteins: Regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnold, J.M.; Mok, S.C.; Purdie, D.; Chenevix-Trench, G. Decreased expression of the id3 gene at 1p36.1 in ovarian adenocarcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Israel, M.A.; Hernandez, M.-C.; Florio, M.; Andres-Barquin, P.J.; Mantani, A.; Carter, J.H.; Julin, C.M. Id gene expression as a key mediator of tumor cell biology. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1726s–1730s. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Q.; Singh, J.; Murata, K.; Itahana, Y.; Parrinello, S.; Liang, S.H.; Gillett, C.E.; Campisi, J.; Desprez, P.-Y. A role for id-1 in the aggressive phenotype and steroid hormone response of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Kebebew, E.; Treseler, P.A.; Duh, Q.Y.; Clark, O.H. The helix-loop-helix transcription factor, id-1, is overexpressed in medullary thyroid cancer. Surgery 2000, 128, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.D.; Atherton, G.T. Coupling of cell growth control and apoptosis functions of id proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyden, D.; Young, A.Z.; Zagzag, D.; Yan, W.; Gerald, W.; O’Reilly, R.; Bader, B.L.; Hynes, R.O.; Zhuang, Y.; Manova, K.; et al. Id1 and id3 are required for neurogenesis, angiogenesis and vascularization of tumour xenografts. Nature 1999, 401, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minn, A.J.; Gupta, G.P.; Siegel, P.M.; Bos, P.D.; Shu, W.; Giri, D.D.; Viale, A.; Olshen, A.B.; Gerald, W.L.; Massagué, J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005, 436, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.P.; Perk, J.; Acharyya, S.; de Candia, P.; Mittal, V.; Todorova-Manova, K.; Gerald, W.L.; Brogi, E.; Benezra, R.; Massagué, J. Id genes mediate tumor reinitiation during breast cancer lung metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19506–19511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindl, M.; Schoppmann, S.F.; Ströbel, T.; Heinzl, H.; Leisser, C.; Horvat, R.; Birner, P. Level of id-1 protein expression correlates with poor differentiation, enhanced malignant potential, and more aggressive clinical behavior of epithelial ovarian tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.C.; Lam, K.Y.; Law, S.; Wong, J.; Srivastava, G. Identification of differentially expressed genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (escc) by cdna expression array: Overexpression of fra-1, neogenin, id-1, and cdc25b genes in escc. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schindl, M.; Oberhuber, G.; Obermair, A.; Schoppmann, S.F.; Karner, B.; Birner, P. Overexpression of id-1 protein is a marker for unfavorable prognosis in early-stage cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5703–5706. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Lahmy, R.; Riha, C.; Yang, C.; Jakubison, B.L.; van Niekerk, J.; Staub, C.; Wu, Y.; Gates, K.; Dong, D.S.; et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor e47 reprograms human pancreatic cancer cells to a quiescent acinar state with reduced tumorigenic potential. Pancreas 2015, 44, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, A.; Li, P.; Quan, Y.; Feng, B.; Chen, X.; Mao, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, M. E2a suppresses invasion and migration by targeting yap in colorectal cancer cells. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, A.; Zhao, H.; Quan, Y.; Jin, R.; Feng, B.; Zheng, M. E2a predicts prognosis of colorectal cancer patients and regulates cancer cell growth by targeting mir-320a. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, M.; Chirlaque Lopez, M.D.; Agresti, R.; Sánchez Pérez, M.J.; Holleczek, B.; Bielska-Lasota, M.; Dimitrova, N.; Innos, K.; Katalinic, A.; Langseth, H.; et al. Survival of women with cancers of breast and genital organs in europe 1999-2007: Results of the eurocare-5 study. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2191–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgiou, M.; Salanti, G.; Pavlidis, N.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Survival benefits with diverse chemotherapy regimens for ovarian cancer: Meta-analysis of multiple treatments. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, R.J., Jr.; Alvarez, R.D.; Armstrong, D.K.; Burger, R.A.; Chen, L.M.; Copeland, L.; Crispens, M.A.; Gershenson, D.M.; Gray, H.J.; Hakam, A.; et al. Ovarian cancer, version 2.2013. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2013, 11, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mern, D.S.; Hasskarl, J.; Burwinkel, B. Inhibition of id proteins by a peptide aptamer induces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Cheung, H.W.; von Maltzhan, G.; Agrawal, A.; Cowley, G.S.; Weir, B.A.; Boehm, J.S.; Tamayo, P.; Karst, A.M.; Liu, J.F.; et al. Targeted tumor-penetrating sirna nanocomplexes for credentialing the ovarian cancer oncogene id4. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, R.; Engel, I.; Fallahi-Sichani, M.; Petrie, H.T.; Murre, C. Gene expression patterns define novel roles for e47 in cell cycle progression, cytokine-mediated signaling, and t lineage development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9976–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Hao, E.; Kiselyuk, A.; Shapiro, J.; Shields, D.J.; Lowy, A.; Levine, F.; Itkin-Ansari, P. The id3/e47 axis mediates cell-cycle control in human pancreatic ducts and adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murre, C.; McCaw, P.S.; Baltimore, D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, myod, and myc proteins. Cell 1989, 56, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Brennan, T.J.; Li, L.; Edmondson, D.; Olson, E.N. Inefficient homooligomerization contributes to the dependence of myogenin on e2a products for efficient DNA binding. Mol. Cell. Biol 1991, 11, 3633–3641. [Google Scholar]
- Lassar, A.B.; Buskin, J.N.; Lockshon, D.; Davis, R.L.; Apone, S.; Hauschka, S.D.; Weintraub, H. Myod is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell 1989, 58, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-P.; Kadesch, T. B-cell-specific DNA binding by an e47 homodimer. Mol. Cell. Biol 1995, 15, 4518–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, J.W.; Deed, R.W.; Inoue, T.; Balzi, M.; Becciolini, A.; Faraoni, P.; Potten, C.S.; Norton, J.D. Expression of id helix-loop-helix proteins in colorectal adenocarcinoma correlates with p53 expression and mitotic index. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8803–8810. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, J.D. Id helix-loop-helix proteins in cell growth, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3897–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezra, R.; Davis, R.L.; Lockshon, D.; Turner, D.L.; Weintraub, H. The protein id: A negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell 1990, 61, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasorella, A.; Uo, T.; Iavarone, A. Id proteins at the cross-road of development and cancer. Oncogene 2001, 20, 8326–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Gordon, G.M.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Foreman, K.E. The helix–loop–helix protein id-1 delays onset of replicative senescence in human endothelial cells. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Cai, J.; Guo, H.; Gu, J.; Tong, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Xia, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Id3 promotes stem cell features and predicts chemotherapeutic response of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1995–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arend, R.C.; Londoño-Joshi, A.I.; Straughn, J.M., Jr.; Buchsbaum, D.J. The wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaraj, A.B.; Joseph, P.; Kovalenko, O.; Singh, S.; Armstrong, A.; Redline, R.; Resnick, K.; Zanotti, K.; Waggoner, S.; DiFeo, A. Critical role of wnt/β-catenin signaling in driving epithelial ovarian cancer platinum resistance. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23720–23734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pai, S.G.; Carneiro, B.A.; Mota, J.M.; Costa, R.; Leite, C.A.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Kaplan, J.B.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: Modulating anticancer immune response. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Broaddus, R.; Sun, L.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. Exon 3 mutations of ctnnb1 drive tumorigenesis: A review. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5492–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, J.J.; Pohl, S.; Deshmukh, A.; Visweswaran, M.; Ward, N.C.; Arfuso, F.; Agostino, M.; Dharmarajan, A. The role of wnt signalling in angiogenesis. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2017, 38, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma, Y.; Westphal, H. Abnormal structure and expression of the p53 gene in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 4196–4199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villarino, N.; Signaevskaia, L.; van Niekerk, J.; Medal, R.; Kim, H.; Lahmy, R.; Scully, K.; Pinkerton, A.; Kim, S.; Lowy, A.; et al. A screen for inducers of bhlh activity identifies pitavastatin as a regulator of p21, rb phosphorylation and e2f target gene expression in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53154–53167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Copy Number | Gene (No, %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID1 | ID2 | ID3 | ID4 | E2A | |
| −2 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.4) | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 26 (4.6) |
| −1 | 20 (3.5) | 106 (18.6) | 246 (43.2) | 82 (14.4) | 477 (83.7) |
| 0 | 219 (38.4) | 245 (43.0) | 193 (33.9) | 199 (34.9) | 47 (8.2) |
| 1 | 289 (50.7) | 195 (34.2) | 118 (20.7) | 223 (39.1) | 18 (3.2) |
| 2 | 42 (7.4) | 22 (3.9) | 12 (2.1) | 66 (11.6) | 2 (0.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-J.; Nam, E.-J.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Itkin-Ansari, P.; Kim, S.-W. Expression Profiles of ID and E2A in Ovarian Cancer and Suppression of Ovarian Cancer by the E2A Isoform E47. Cancers 2022, 14, 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122903
Lee Y-J, Nam E-J, Kim S, Kim Y-T, Itkin-Ansari P, Kim S-W. Expression Profiles of ID and E2A in Ovarian Cancer and Suppression of Ovarian Cancer by the E2A Isoform E47. Cancers. 2022; 14(12):2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122903
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yong-Jae, Eun-Ji Nam, Sunghoon Kim, Young-Tae Kim, Pamela Itkin-Ansari, and Sang-Wun Kim. 2022. "Expression Profiles of ID and E2A in Ovarian Cancer and Suppression of Ovarian Cancer by the E2A Isoform E47" Cancers 14, no. 12: 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122903
APA StyleLee, Y.-J., Nam, E.-J., Kim, S., Kim, Y.-T., Itkin-Ansari, P., & Kim, S.-W. (2022). Expression Profiles of ID and E2A in Ovarian Cancer and Suppression of Ovarian Cancer by the E2A Isoform E47. Cancers, 14(12), 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122903






