Core-Clock Genes Regulate Proliferation and Invasion via a Reciprocal Interplay with MACC1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Generation in HCT116
2.3. Lentivirus Production
2.4. Transduction with Lentiviral Vectors
2.5. Bioluminescence Measurements
2.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis (Reverse Transcription) and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.7. Western Blotting and Immunoprecipitation
2.8. Cell Cycle Assay
2.9. Proliferation Assay
2.10. Apoptosis Assay
2.11. Migration Assay
2.12. Chemotaxis Invasion Assay
2.13. Rhythmicity Analysis
2.14. Differential Correlation Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
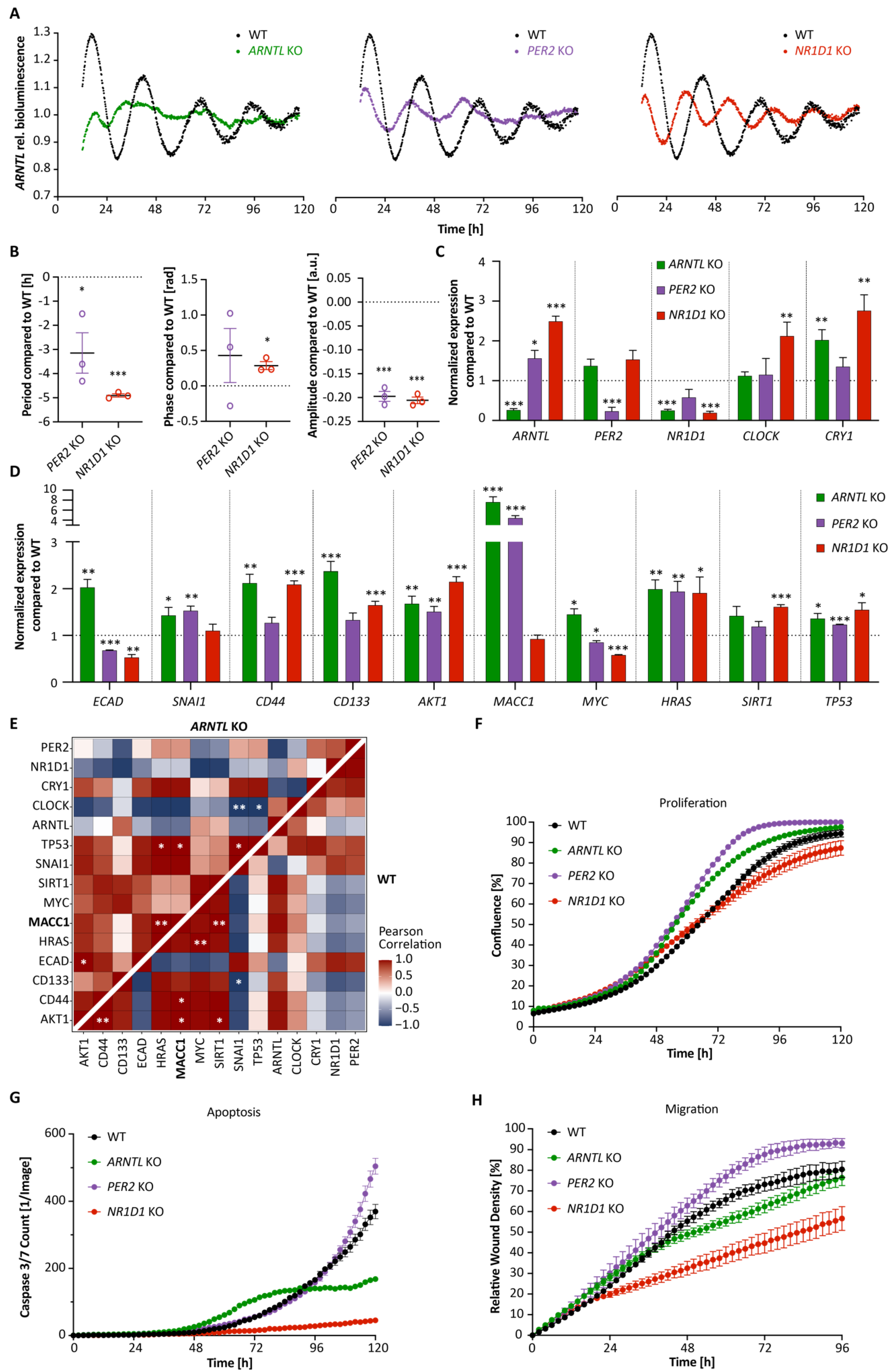
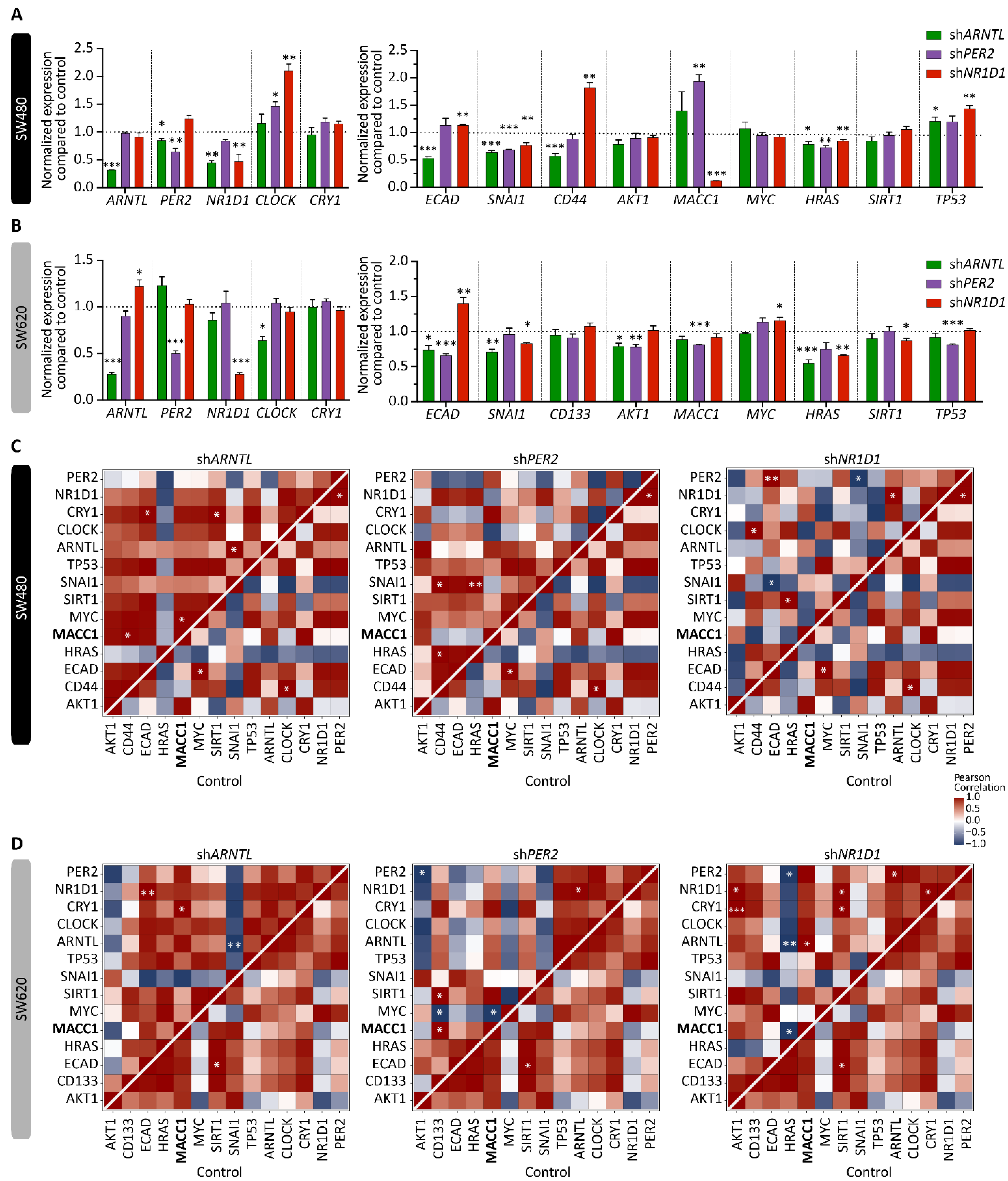
3.1. Core-Clock Manipulation Disrupts the Circadian Clock Network and Affects Expression of Genes Involved in Cell Cycle, EMT and Migration
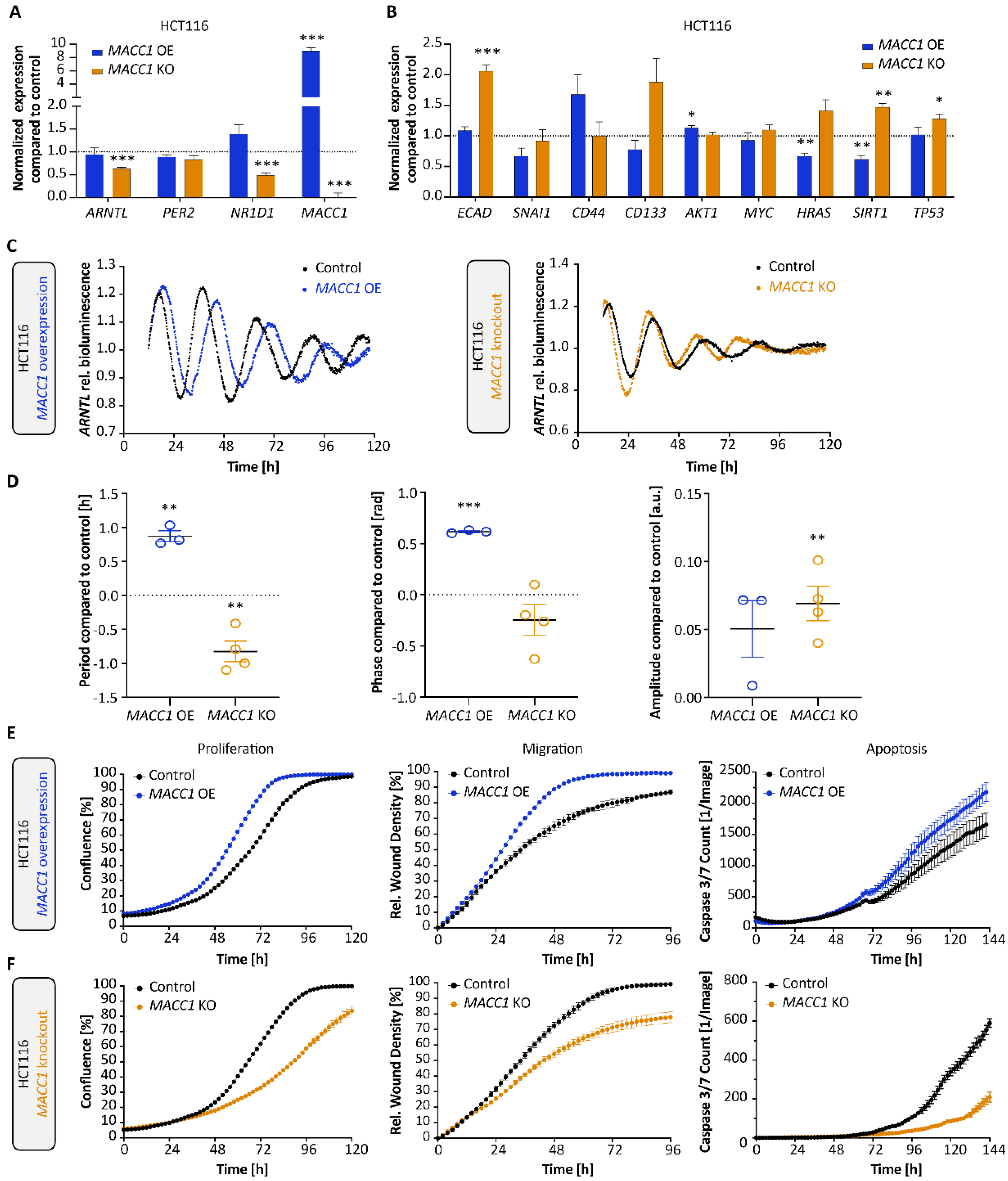
3.2. MACC1 Affects Both the Cellular Circadian Clock and Cancer Properties
3.3. Cell Cycle Dynamics Are Altered in CRC upon KO of CC Genes
3.4. Clock Alteration Affects MACC1 Rhythmic Protein Expression and Cell Invasion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sulli, G.; Lam, M.T.Y.; Panda, S. Interplay between Circadian Clock and Cancer: New Frontiers for Cancer Treatment. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lahens, N.F.; Ballance, H.I.; Hughes, M.E.; Hogenesch, J.B. A circadian gene expression atlas in mammals: Implications for biology and medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16219–16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mure, L.S.; Le, H.D.; Benegiamo, G.; Chang, M.W.; Rios, L.; Jillani, N.; Ngotho, M.; Kariuki, T.; Dkhissi-Benyahya, O.; Cooper, H.M.; et al. Diurnal transcriptome atlas of a primate across major neural and peripheral tissues. Science 2018, 359, eaao0318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patke, A.; Young, M.W.; Axelrod, S. Molecular mechanisms and physiological importance of circadian rhythms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Albrecht, U.; Bass, J.; Brown, S.A.; Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Gachon, F.; Green, C.B.; Hastings, M.H.; Helfrich-Forster, C.; Hogenesch, J.B.; et al. Medicine in the Fourth Dimension. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Selby, C.P.; Yang, Y.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Cao, X.; Eynullazada, K.; Sancar, A. Circadian regulation of c-MYC in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21609–21617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, T.; Kim, J.K.; Liu, J.; Vila-Caballer, M.; Stauffer, P.E.; Tyson, J.J.; Finkielstein, C.V. Model-driven experimental approach reveals the complex regulatory distribution of p53 by the circadian factor Period 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13516–13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Relogio, A.; Thomas, P.; Medina-Perez, P.; Reischl, S.; Bervoets, S.; Gloc, E.; Riemer, P.; Mang-Fatehi, S.; Maier, B.; Schafer, R.; et al. Ras-mediated deregulation of the circadian clock in cancer. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Minami, I.; Kadotani, H.; Todo, T.; Nishida, E. Circadian clock-controlled diurnal oscillation of Ras/ERK signaling in mouse liver. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2013, 89, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinouchi, K.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Metabolic rivalry: Circadian homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoccoli, G.; Panza, A.; Valvano, M.R.; Palumbo, O.; Carella, M.; Pazienza, V.; Biscaglia, G.; Tavano, F.; Di Sebastiano, P.; Andriulli, A.; et al. Clock gene expression levels and relationship with clinical and pathological features in colorectal cancer patients. Chronobiol. Int. 2011, 28, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.L.; Luo, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.J.; Chen, D.L.; Huang, P.; Xu, R.H. Overexpression of the circadian clock gene Bmal1 increases sensitivity to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gery, S.; Komatsu, N.; Baldjyan, L.; Yu, A.; Koo, D.; Koeffler, H.P. The circadian gene per1 plays an important role in cell growth and DNA damage control in human cancer cells. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.L.; Papp, S.J.; Chan, A.B.; Henriksson, E.; Jordan, S.D.; Kriebs, A.; Nguyen, M.; Wallace, M.; Li, Z.; Metallo, C.M.; et al. CRY2 and FBXL3 Cooperatively Degrade c-MYC. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Meng, X.; Wu, J.; Pan, C.; Ying, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, W. Cryptochrome 1 overexpression correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giacchetti, S.; Bjarnason, G.; Garufi, C.; Genet, D.; Iacobelli, S.; Tampellini, M.; Smaaland, R.; Focan, C.; Coudert, B.; Humblet, Y.; et al. Phase III trial comparing 4-day chronomodulated therapy versus 2-day conventional delivery of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin as first-line chemotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer: The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Chronotherapy Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3562–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innominato, P.F.; Karaboue, A.; Focan, C.; Chollet, P.; Giacchetti, S.; Bouchahda, M.; Ulusakarya, A.; Torsello, A.; Adam, R.; Levi, F.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of chronomodulated irinotecan, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin combination as first- or second-line treatment against metastatic colorectal cancer: Results from the International EORTC 05011 Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 148, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innominato, P.; Komarzynski, S.; Karaboue, A.; Ulusakarya, A.; Bouchahda, M.; Haydar, M.; Bossevot-Desmaris, R.; Mocquery, M.; Plessis, V.; Levi, F. Home-Based e-Health Platform for Multidimensional Telemonitoring of Symptoms, Body Weight, Sleep, and Circadian Activity: Relevance for Chronomodulated Administration of Irinotecan, Fluorouracil-Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin at Home-Results From a Pilot Study. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2018, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innominato, P.F.; Komarzynski, S.; Palesh, O.G.; Dallmann, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Giacchetti, S.; Ulusakarya, A.; Bouchahda, M.; Haydar, M.; Ballesta, A.; et al. Circadian rest-activity rhythm as an objective biomarker of patient-reported outcomes in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basti, A.; Fior, R.; Yalin, M.; Povoa, V.; Astaburuaga, R.; Li, Y.; Naderi, J.; Godinho Ferreira, M.; Relogio, A. The Core-Clock Gene NR1D1 Impacts Cell Motility In Vitro and Invasiveness in A Zebrafish Xenograft Colon Cancer Model. Cancers 2020, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, U.; Walther, W.; Arlt, F.; Schwabe, H.; Smith, J.; Fichtner, I.; Birchmeier, W.; Schlag, P.M. MACC1, a newly identified key regulator of HGF-MET signaling, predicts colon cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, H.; Walther, W.; Zincke, F.; Kobelt, D.; Imbastari, F.; Erdem, M.; Kortum, B.; Dahlmann, M.; Stein, U. MACC1-the first decade of a key metastasis molecule from gene discovery to clinical translation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhr, L.; El-Athman, R.; Scrima, R.; Cela, O.; Carbone, A.; Knoop, H.; Li, Y.; Hoffmann, K.; Laukkanen, M.O.; Corcione, F.; et al. The Circadian Clock Regulates Metabolic Phenotype Rewiring Via HKDC1 and Modulates Tumor Progression and Drug Response in Colorectal Cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juneja, M.; Kobelt, D.; Walther, W.; Voss, C.; Smith, J.; Specker, E.; Neuenschwander, M.; Gohlke, B.O.; Dahlmann, M.; Radetzki, S.; et al. Statin and rottlerin small-molecule inhibitors restrict colon cancer progression and metastasis via MACC1. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2000784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahlmann, M.; Werner, R.; Kortum, B.; Kobelt, D.; Walther, W.; Stein, U. Restoring Treatment Response in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting MACC1-Dependent ABCB1 Expression in Combination Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pliatsika, V.; Rigoutsos, I. “Off-Spotter”: Very fast and exhaustive enumeration of genomic lookalikes for designing CRISPR/Cas guide RNAs. Biol. Direct. 2015, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodgkins, A.; Farne, A.; Perera, S.; Grego, T.; Parry-Smith, D.J.; Skarnes, W.C.; Iyer, V. WGE: A CRISPR database for genome engineering. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3078–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, B.; Lorenzen, S.; Finger, A.M.; Herzel, H.; Kramer, A. Searching Novel Clock Genes Using RNAi-Based Screening. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2130, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlucci, M.; Krisciunas, A.; Li, H.; Gibas, P.; Koncevicius, K.; Petronis, A.; Oh, G. DiscoRhythm: An easy-to-use web application and R package for discovering rhythmicity. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 1952–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, A.T.; Katsyv, I.; Song, W.M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, B. DGCA: A comprehensive R package for Differential Gene Correlation Analysis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunger, M.K.; Wilsbacher, L.D.; Moran, S.M.; Clendenin, C.; Radcliffe, L.A.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Simon, M.C.; Takahashi, J.S.; Bradfield, C.A. Mop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals. Cell 2000, 103, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Tian, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X. Systematic Studies of the Circadian Clock Genes Impact on Temperature Compensation and Cell Proliferation Using CRISPR Tools. Biology 2021, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Athman, R.; Fuhr, L.; Relogio, A. A Systems-Level Analysis Reveals Circadian Regulation of Splicing in Colorectal Cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoccoli, G.; Colangelo, T.; Panza, A.; Rubino, R.; De Cata, A.; Tiberio, C.; Valvano, M.R.; Pazienza, V.; Merla, G.; Augello, B.; et al. Deregulated expression of cryptochrome genes in human colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serchov, T.; Jilg, A.; Wolf, C.T.; Radtke, I.; Stehle, J.H.; Heumann, R. Ras Activity Oscillates in the Mouse Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and Modulates Circadian Clock Dynamics. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Guarente, L. SIRT1 mediates central circadian control in the SCN by a mechanism that decays with aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafi, A.A.; Knudsen, K.E. Cancer and the Circadian Clock. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3806–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y. Roles of circadian clocks in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Gaddameedhi, S.; Selby, C.P.; Ye, R.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Kemp, M.G.; Hu, J.; Lee, J.H.; Ozturk, N. Circadian clock, cancer, and chemotherapy. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, T.; Takenoshita, S.; Akaike, M.; Kunisaki, C.; Fujii, S.; Nozaki, A.; Numata, K.; Shiozawa, M.; Rino, Y.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Expression of circadian genes correlates with liver metastasis and outcomes in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; Lu, C.; Bei, Y.; Qian, R.; Hua, L. Upregulation of circadian gene ‘hClock’ contribution to metastasis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lin, J.; Qian, R.; Hua, L.; Lu, C. BMAL1 induces colorectal cancer metastasis by stimulating exosome secretion. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, J.E.; Price, T.S.; DiTacchio, L.; Panda, S.; Fitzgerald, G.A.; Hogenesch, J.B. Network features of the mammalian circadian clock. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, B.J.; Hsieh, A.L.; Sengupta, A.; Krishnanaiah, S.Y.; Stine, Z.E.; Walton, Z.E.; Gouw, A.M.; Venkataraman, A.; Li, B.; Goraksha-Hicks, P.; et al. MYC Disrupts the Circadian Clock and Metabolism in Cancer Cells. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aroca-Siendones, M.I.; Moreno-SanJuan, S.; Puentes-Pardo, J.D.; Verbeni, M.; Arnedo, J.; Escudero-Feliu, J.; Garcia-Costela, M.; Garcia-Robles, A.; Carazo, A.; Leon, J. Core Circadian Clock Proteins as Biomarkers of Progression in Colorectal Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 8, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulli, G.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Taub, P.R.; Panda, S. Training the Circadian Clock, Clocking the Drugs, and Drugging the Clock to Prevent, Manage, and Treat Chronic Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, F.; Chan, P.; Pan, Y.; Soni, S.; Qu, M.; Spiller, E.R.; Castanon, S.; Roussos Torres, E.T.; Mumenthaler, S.M.; Kay, S.A.; et al. Clocking cancer: The circadian clock as a target in cancer therapy. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3187–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, A.; Van Gelder, R.N. Clocks, cancer, and chronochemotherapy. Science 2021, 371, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulli, G.; Rommel, A.; Wang, X.; Kolar, M.J.; Puca, F.; Saghatelian, A.; Plikus, M.V.; Verma, I.M.; Panda, S. Pharmacological activation of REV-ERBs is lethal in cancer and oncogene-induced senescence. Nature 2018, 553, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Saberifar, S.; Hashemi, F.; Hushmandi, K.; Hashemi, F.; Moghadam, E.R.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Najafi, M.; Garg, M. Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Printezi, M.I.; Kilgallen, A.B.; Bond, M.J.G.; Stibler, U.; Putker, M.; Teske, A.J.; Cramer, M.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Huitema, A.D.R.; et al. Toxicity and efficacy of chronomodulated chemotherapy: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e129–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.W.; Le Sage, C.; Larrieu, D.; Demir, M.; Jackson, S.P. CRISPR-Cas9(D10A) nickase-based genotypic and phenotypic screening to enhance genome editing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target Gene | gRNA Seq (without PAM)—(5′ –> 3′) | Cas9 Type |
|---|---|---|
| ARNTL | ACAGACAAAGATGACCCTCA | pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP |
| ARNTL | TTATCACACTACGGAGTCGA | pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP |
| ARNTL | CTGGACATTGCGTTGCATGT TAGATAAACTTACTGTGCTA | Cas9D10A-GFP (AIO-GFP) |
| PER2 | GACCAACGAAAACTGCTCCA | pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP |
| PER2 | GAACACAACCCATCTACAAG | pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP |
| PER2 | CCCCGTGGAGCAGTTTTCGT GCAGTGACTGTGACGACAGT | Cas9D10A-GFP (AIO-GFP) |
| NR1D1 | GTTGCGATTGATGCGGACGA | pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP |
| NR1D1 | CGTAGGTGAAGATCTCTCGA | pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP |
| Target Gene | gRNA Seq (No PAM) | #Mismatch | Region Type | Location | % Similarity Compared to WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARNTL | TTATCACACTACGGAGTCGA | 3 | intergenic | ||
| ARNTL | ACAGACAAAGATGACCCTCA | 3 | exonic | 16:89708928-89708950 | 100 |
| PER2 | GACCAACGAAAACTGCTCCA | 3 | intronic | 6:157052704-157052726 | 100 |
| PER2 * | GAACACAACCCATCTACAAG | 3 | intronic | 2:115016664-115016686 | - |
| PER2 | GAACACAACCCATCTACAAG | 3 | intronic | 7:4244707-4244729 | 100 |
| PER2 | GAACACAACCCATCTACAAG | 3 | intronic | 3:161369567-161369589 | 100 |
| NR1D1 | CGTAGGTGAAGATCTCTCGA | 3 | intronic | 12:99265850-99265872 | 100 |
| NR1D1 | GTTGCGATTGATGCGGACGA | 3 | intronic | 17:20085554-20085576 | 100 |
| NR1D1 | GTTGCGATTGATGCGGACGA | 3 | exonic | 8:144581166-144581188 | 100 |
| Target Gene | Forward Primer (5′–> 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–> 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CD44 | ACACAAATGGCTGGTACGTCT | CCGTGGTGTGGTTGAAATGG |
| CD133 | CCCCAGGAAATTTGAGG AAC | TCCAACAATCCATTCCCTGT |
| ECAD | ATTGCAAATTCCTGCCATTC | CTCTTCTCCGCCTCCTTCTT |
| SIRT1 | AGGCCACGGATAGGTCCATA | GTGGAGGTATTGTTTCCGGC |
| MACC1 | TTCTTTTGATTCCTCCGGTGA | ACTCTGATGGGCATGTGCTG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basti, A.; Malhan, D.; Dumbani, M.; Dahlmann, M.; Stein, U.; Relógio, A. Core-Clock Genes Regulate Proliferation and Invasion via a Reciprocal Interplay with MACC1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143458
Basti A, Malhan D, Dumbani M, Dahlmann M, Stein U, Relógio A. Core-Clock Genes Regulate Proliferation and Invasion via a Reciprocal Interplay with MACC1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143458
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasti, Alireza, Deeksha Malhan, Malti Dumbani, Mathias Dahlmann, Ulrike Stein, and Angela Relógio. 2022. "Core-Clock Genes Regulate Proliferation and Invasion via a Reciprocal Interplay with MACC1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143458
APA StyleBasti, A., Malhan, D., Dumbani, M., Dahlmann, M., Stein, U., & Relógio, A. (2022). Core-Clock Genes Regulate Proliferation and Invasion via a Reciprocal Interplay with MACC1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers, 14(14), 3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143458







