Identification and Characterization of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
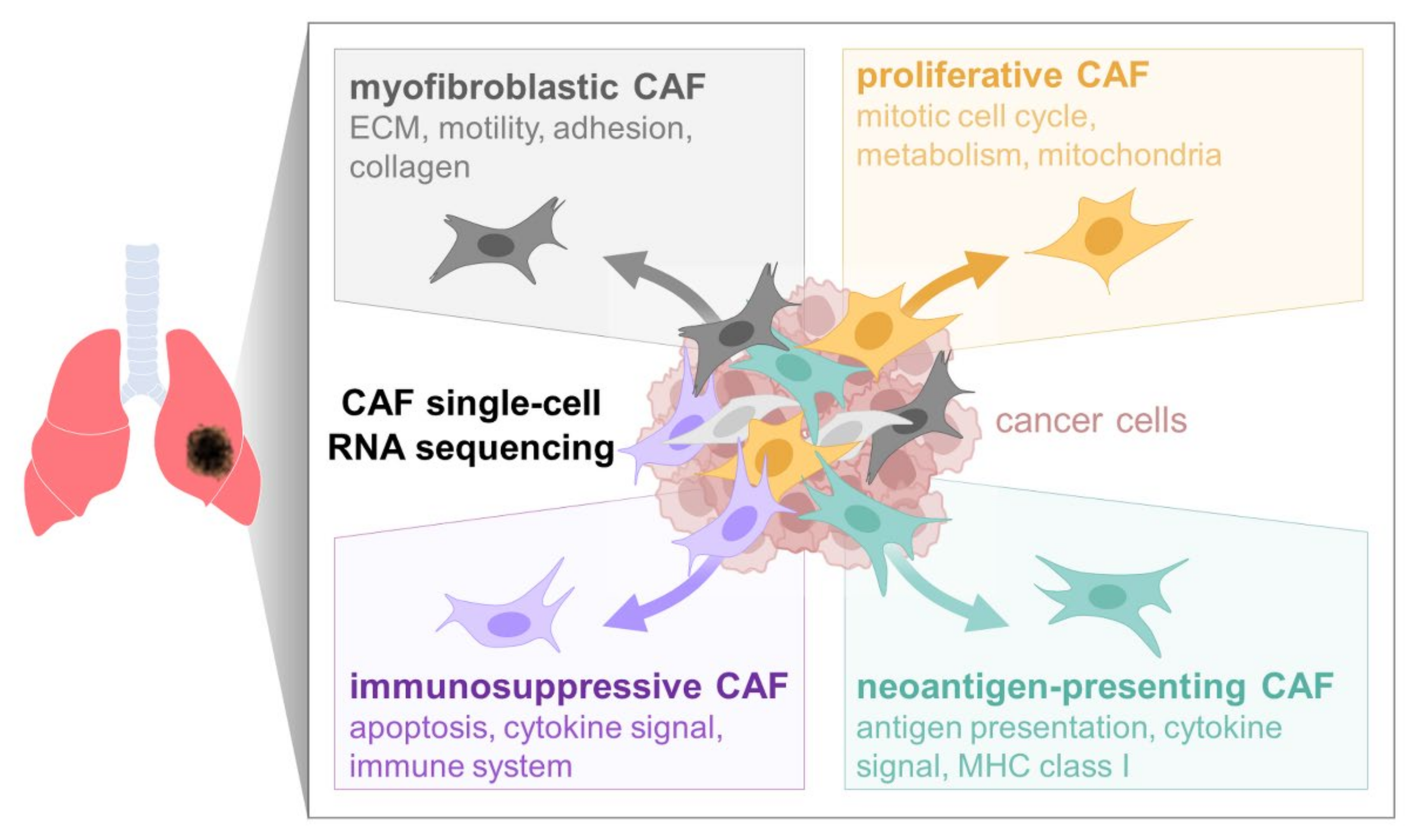
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
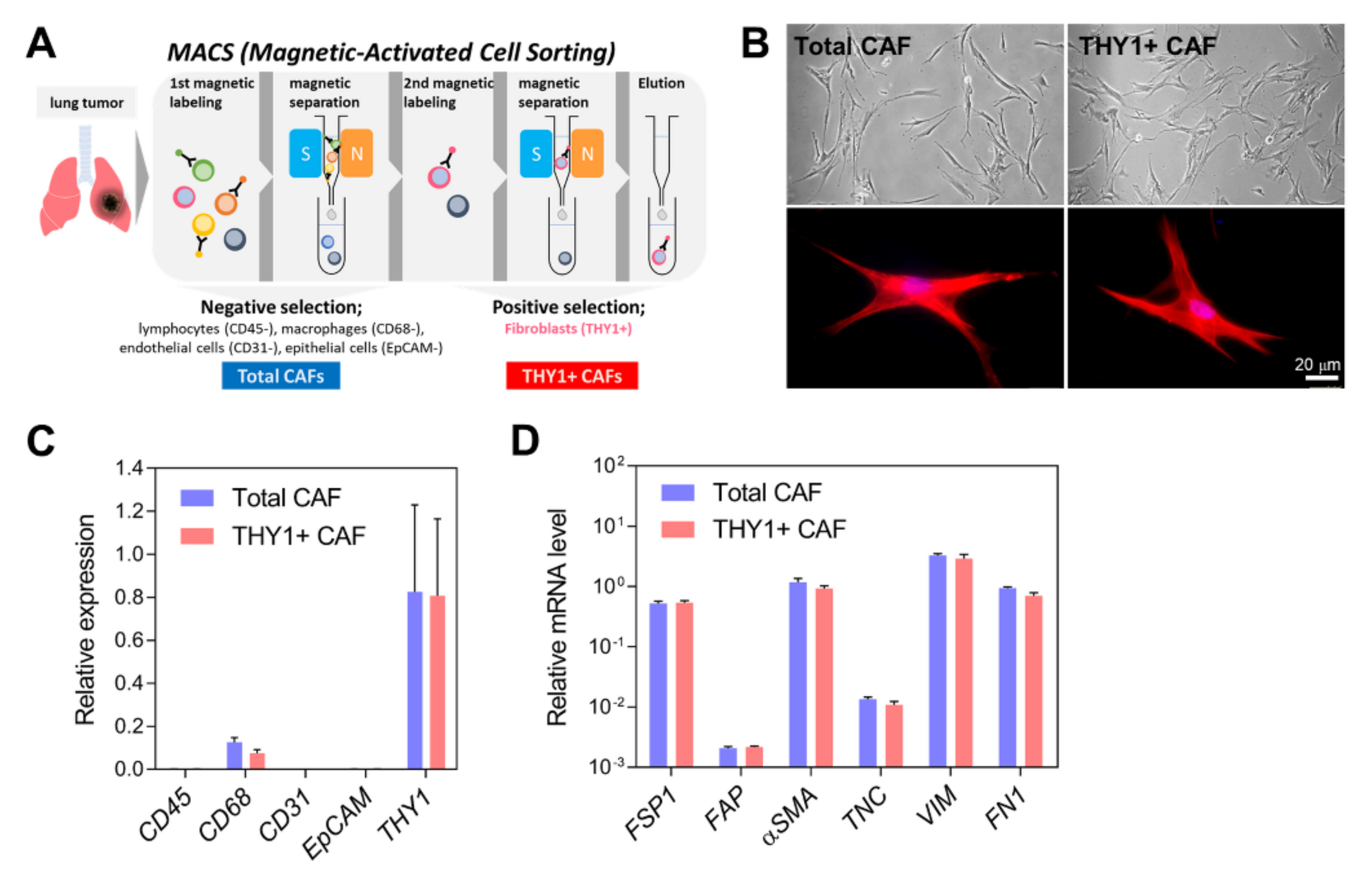
2.1. Isolation of CAFs
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR)
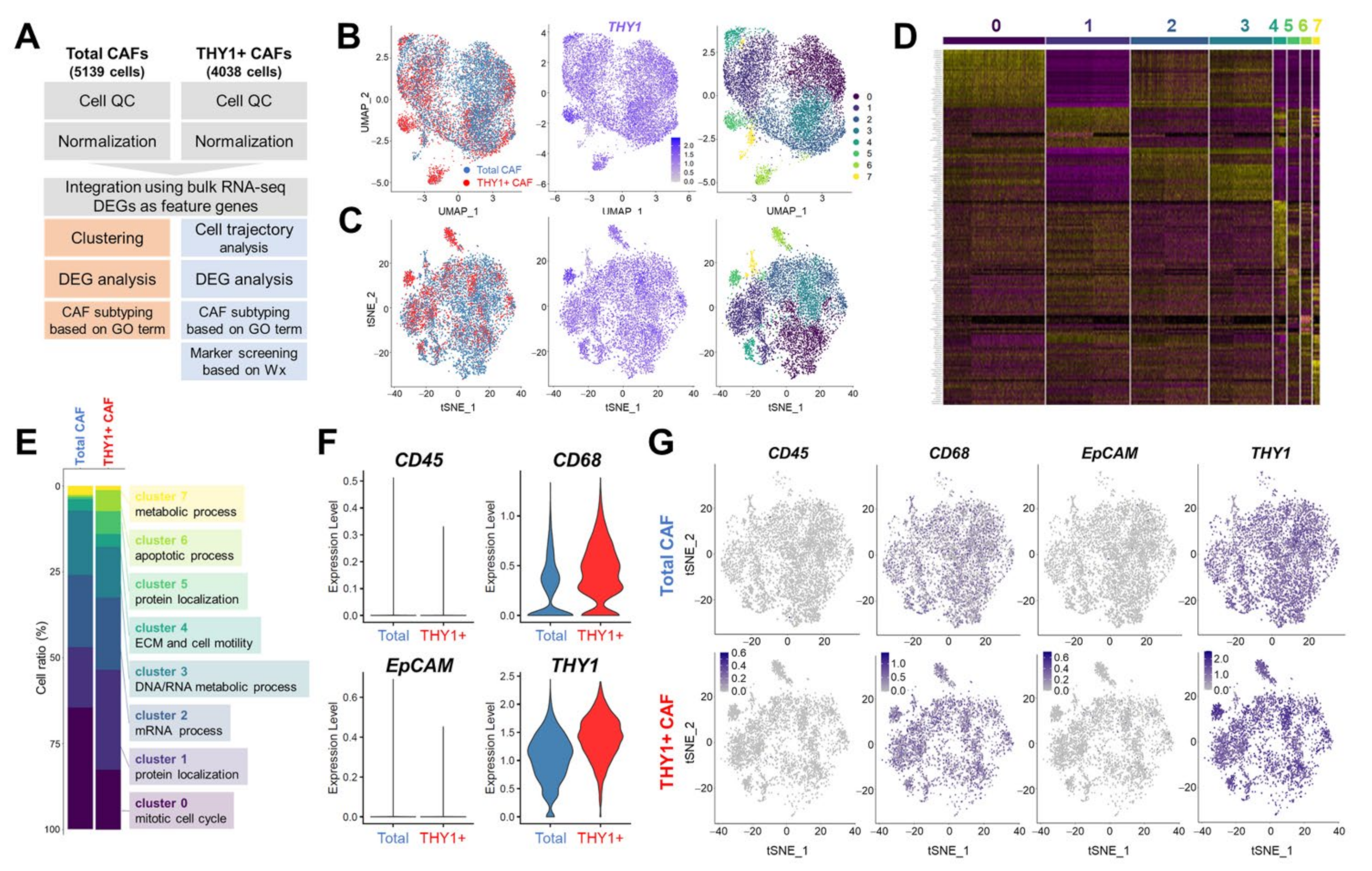
2.4. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.5. Bulk mRNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.6. Unsupervised Clustering
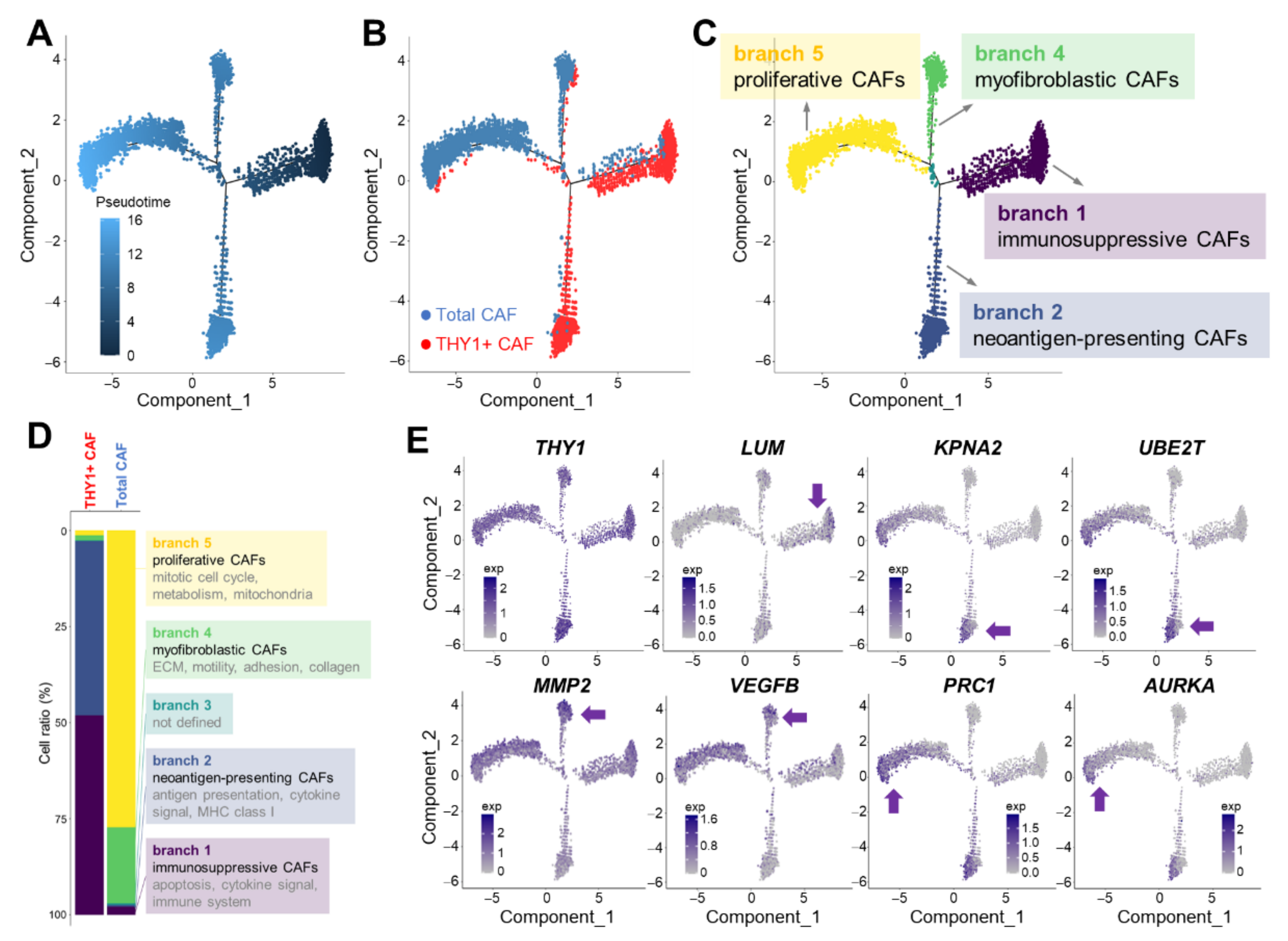
2.7. CAF Subtype Prediction via Trajectory Analysis
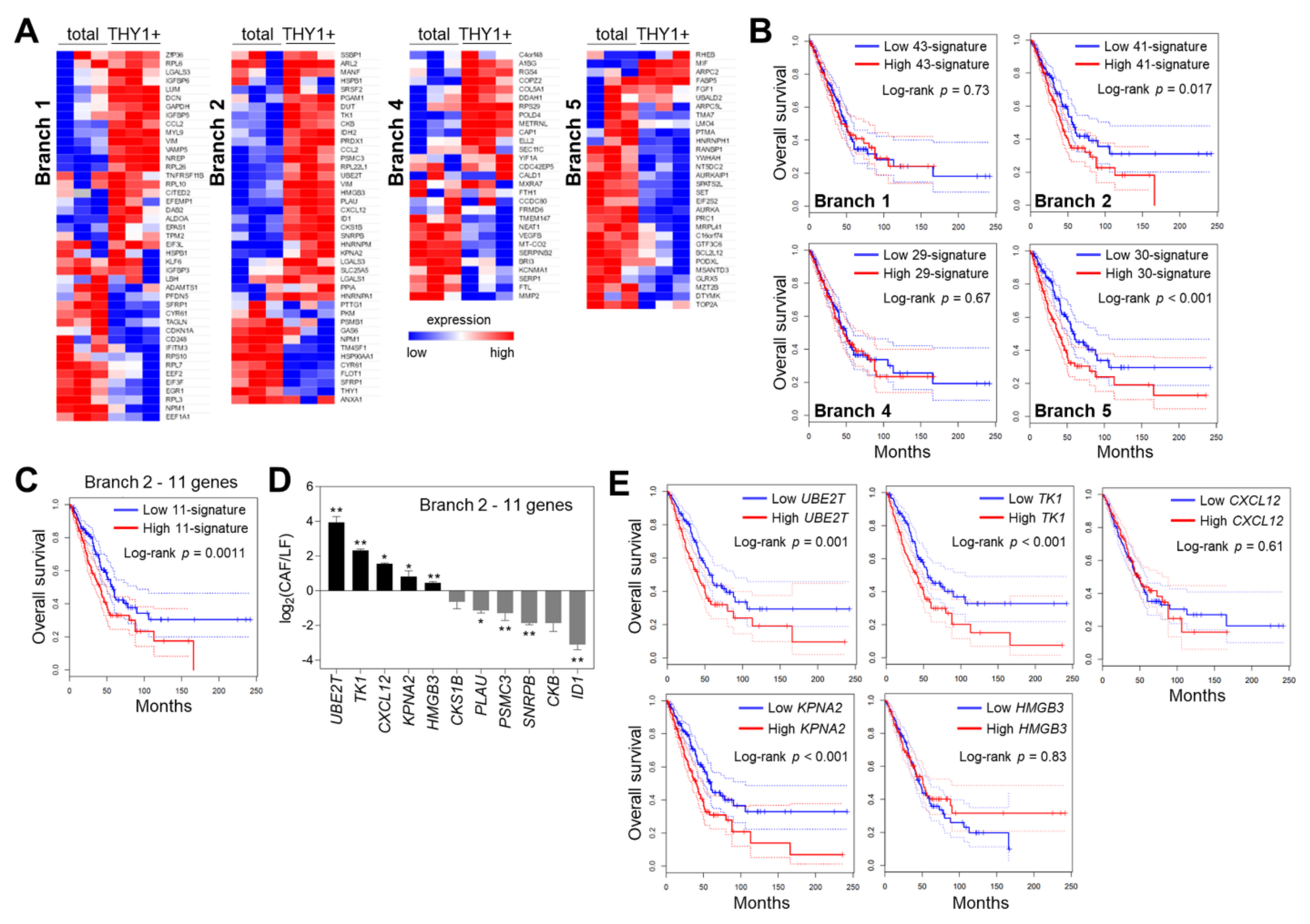
2.8. Survival Analysis
2.9. Mouse Experiments
2.10. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of CAFs from Human Lung Adenocarcinoma
3.2. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-seq) of Human Lung CAFs
3.3. Cell Trajectory Analysis of CAF scRNA-seq Data
3.4. Characterization of Branch-Specific Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Palma, M.; Biziato, D.; Petrova, T.V. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Natl. Cancer 2017, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Kim, J.S. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators of Interactions between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J.S.; Chun, S.H.; Hong, S.A.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, K.; Kang, J.L.; Ko, Y.H.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts activated by miR-196a promote the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2021, 508, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Sakai, R. Direct Interaction between Carcinoma Cells and Cancer Associated Fibroblasts for the Regulation of Cancer Invasion. Cancers 2015, 7, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.; Andl, T.; Zhang, Y. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Build and Secure the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Mariotto, A.B.; Rowland, J.H.; Yabroff, K.R.; Alfano, C.M.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.L.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Liao, Z.; Hess, K.; Chance, W.W.; Zhuang, Y.; Jensen, G.; Xu, T.; Komaki, R.; Gomez, D.R. Prognosis and predictors of site of first metastasis after definitive radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Pusztai, L.; Swanton, C. Cancer heterogeneity: Implications for targeted therapeutics. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.; Lin, K.; Li, X.; Yuan, X.; Xu, P.; Ni, P.; Xu, D. Redefining Tumor-Associated Macrophage Subpopulations and Functions in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoschek, M.; Oskolkov, N.; Bocci, M.; Lövrot, J.; Larsson, C.; Sommarin, M.; Madsen, C.D.; Lindgren, D.; Pekar, G.; Karlsson, G.; et al. Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, L.; Hou, Y.; Xiong, M.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, K. Single-cell RNA sequencing highlights the role of inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts in bladder urothelial carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast (CAF) Heterogeneity and Targeting Therapy of CAFs in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 655152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, Y.; Hocine, H.R.; Gentric, G.; Pelon, F.; Bernard, C.; Bourachot, B.; Lameiras, S.; Albergante, L.; Bonneau, C.; Guyard, A.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Fibroblast Clusters Linked to Immunotherapy Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1330–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Mao, T.; Cui, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, F.; Xiao, X.; et al. Single-cell analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies a novel fibroblast subtype associated with poor prognosis but better immunotherapy response. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, J.K. Dissecting Cellular Heterogeneity Using Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyada, E.; Bolisetty, M.; Laise, P.; Flynn, W.F.; Courtois, E.T.; Burkhart, R.A.; Teinor, J.A.; Belleau, P.; Biffi, G.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. Cross-Species Single-Cell Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Reveals Antigen-Presenting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puram, S.V.; Tirosh, I.; Parikh, A.S.; Patel, A.P.; Yizhak, K.; Gillespie, S.; Rodman, C.; Luo, C.L.; Mroz, E.A.; Emerick, K.S.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrechts, D.; Wauters, E.; Boeckx, B.; Aibar, S.; Nittner, D.; Burton, O.; Bassez, A.; Decaluwé, H.; Pircher, A.; Van den Eynde, K.; et al. Phenotype molding of stromal cells in the lung tumor microenvironment. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roybal, J.D.; Zang, Y.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; Gibbons, D.L.; Baird, B.N.; Alvarez, C.; Thilaganathan, N.; Liu, D.D.; Saintigny, P.; et al. miR-200 Inhibits Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Invasion and Metastasis by Targeting Flt1/VEGFR1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Smibert, P.; Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Hill, A.; Packer, J.; Lin, D.; Ma, Y.-A.; Trapnell, C. Single-cell mRNA quantification and differential analysis with Census. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Shin, B.; Shim, W.S.; Choi, Y.; Kang, K.; Kang, K. Wx: A neural network-based feature selection algorithm for transcriptomic data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottfried, E.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Weber, A.; Rehli, M.; Peuker, A.; Müller, A.; Kastenberger, M.; Brockhoff, G.; Andreesen, R.; Kreutz, M. Expression of CD68 in Non-Myeloid Cell Types. Scand. J. Immunol. 2008, 67, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berge, K.; de Bézieux, H.R.; Street, K.; Saelens, W.; Cannoodt, R.; Saeys, Y.; Dudoit, S.; Clement, L. Trajectory-based differential expression analysis for single-cell sequencing data. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakins, M.A.; Ghorani, E.; Munir, H.; Martins, C.P.; Shields, J.D. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce antigen-specific deletion of CD8+ T Cells to protect tumour cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareeda, A.; Negm, O.H.; Green, A.; Nolan, C.C.; Tighe, P.; Albarakati, N.; Sultana, R.; Madhusudan, S.; Ellis, I.; A Rakha, E. KPNA2 is a nuclear export protein that contributes to aberrant localisation of key proteins and poor prognosis of breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.-I.; Wang, C.-L.; Chen, C.-D.; Wu, C.-C.; Liang, Y.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-S.; Yu, J.-S.; Yu, C.-J. Importin subunit alpha-2 is identified as a potential biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer by integration of the cancer cell secretome and tissue transcriptome. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.; Baba, H.; Yoshida, N.; Miyake, K.; Yasuda, T.; Uchihara, T.; Tan, P.; Ishimoto, T. Biological heterogeneity and versatility of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4887–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieniec, K.A.; Butler, L.M.; Worthley, D.L.; Woods, S.L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts—heroes or villains? Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinugasa, Y.; Matsui, T.; Takakura, N. CD44 Expressed on Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Is a Functional Molecule Supporting the Stemness and Drug Resistance of Malignant Cancer Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Stem Cells 2013, 32, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmik, M.; Ullmann, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Haan, S.; Letellier, E. In search of definitions: Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their markers. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schliekelman, M.J.; Creighton, C.J.; Baird, B.N.; Chen, Y.; Banerjee, P.; Bota-Rabassedas, N.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Roybal, J.D.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Thy-1+ Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Adversely Impact Lung Cancer Prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankova, D.; Chen, Y.; Terajima, M.; Schliekelman, M.J.; Baird, B.N.; Fahrenholtz, M.; Sun, L.; Gill, B.J.; Vadakkan, T.J.; Kim, M.P.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Induce a Collagen Cross-link Switch in Tumor Stroma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luecken, M.D.; Theis, F.J. Current best practices in single-cell RNA-seq analysis: A tutorial. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2019, 15, e8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, E.; Burchell, J.; Dazzi, F.; Sarker, D.; Beatson, R. Apoptosis in the Pancreatic Cancer Tumor Microenvironment—The Double-Edged Sword of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cells 2021, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, T.S.; Galleu, A.; Von Bonin, M.; Bornhäuser, M.; Dazzi, F. Apoptotic mesenchymal stromal cells induce prostaglandin E2 in monocytes: Implications for the monitoring of mesenchymal stromal cell activity. Haematologica 2019, 104, e438–e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sueoka, N.; Lee, H.-Y.; Wiehle, S.; Cristiano, R.J.; Fang, B.; Ji, L.; Roth, J.A.; Hong, W.K.; Cohen, P.; Kurie, J.M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 activates programmed cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2000, 19, 4432–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Shen, J.; Shi, J.; Shen, C.; Xu, P.; Chang, H.; Xia, X.; Xu, L.; Jianhong, S.; et al. IGFBP6 Regulates Cell Apoptosis and Migration in Glioma. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liso, A.; Capitanio, N.; Gerli, R.; Conese, M. From fever to immunity: A new role for IGFBP-6? J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4588–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Fan, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Lv, J.; Pan, X.; Qu, F.; et al. IFITM3 promotes bone metastasis of prostate cancer cells by mediating activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yánez, D.C.; Sahni, H.; Ross, S.; Solanki, A.; Lau, C.; Papaioannou, E.; Barbarulo, A.; Powell, R.; Lange, U.C.; Adams, D.J.; et al. IFITM proteins drive type 2 T helper cell differentiation and exacerbate allergic airway inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajapaksa, U.S.; Jin, C.; Dong, T. Malignancy and IFITM3: Friend or Foe? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 593245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ajani, J.A.; Sushovan, G.; Ochi, N.; Hwang, R.; Hafley, M.; Johnson, R.L.; Bresalier, R.; Logsdon, C.D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Galectin-3 Mediates Tumor Cell–Stroma Interactions by Activating Pancreatic Stellate Cells to Produce Cytokines via Integrin Signaling. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruvolo, P.P. Galectin 3 as a guardian of the tumor microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, G.S.; Poutahidis, T.; Erdman, S.E.; Kirsch, R.; Riddell, R.H.; Diamandis, E.P. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Drive the Progression of Metastasis through both Paracrine and Mechanical Pressure on Cancer Tissue. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dominguez, C.X.; Müller, S.; Keerthivasan, S.; Koeppen, H.; Hung, J.; Gierke, S.; Breart, B.; Foreman, O.; Bainbridge, T.W.; Castiglioni, A.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Stromal Evolution into LRRC15+ Myofibroblasts as a Determinant of Patient Response to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 232–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, K.; Hong, Y.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.-I.; Suh, Y.-L.; Ku, B.M.; Eum, H.H.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Fang, P.; Ma, Z.; Xu, L.; Yin, R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: An emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Shi, X.; Zhang, R.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Regulation of proliferation and cell cycle by protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Assoro, A.B.; Ehaddad, T.; Egalanis, E. Aurora-A Kinase as a Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Xu, G.; Zou, C. Cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete FGF-1 to promote ovarian proliferation, migration, and invasion through the activation of FGF-1/FGFR4 signaling. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317712592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X. The emerging roles of KPNA2 in cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Kim, J.S.; Cheon, I.; Kim, S.R.; Chun, S.H.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J.S.; Hong, S.A.; Won, H.S.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143486
Kim D, Kim JS, Cheon I, Kim SR, Chun SH, Kim JJ, Lee S, Yoon JS, Hong SA, Won HS, et al. Identification and Characterization of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143486
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Daeseung, Jeong Seon Kim, Inyoung Cheon, Seo Ree Kim, Sang Hoon Chun, Jae Jun Kim, Sieun Lee, Jung Sook Yoon, Soon Auck Hong, Hye Sung Won, and et al. 2022. "Identification and Characterization of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations in Lung Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143486
APA StyleKim, D., Kim, J. S., Cheon, I., Kim, S. R., Chun, S. H., Kim, J. J., Lee, S., Yoon, J. S., Hong, S. A., Won, H. S., Kang, K., Ahn, Y.-H., & Ko, Y. H. (2022). Identification and Characterization of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 14(14), 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143486






