Regulation of Interleukin-36γ/IL-36R Signaling Axis by PIN1 in Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Culture and TRANSFECTION
2.3. CRISPR/Cas9 KO System
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay Using 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) Incorporation
2.5. Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. Anchorage-Independent Cellular Transformation Assay (Soft Agar Assay)
2.7. Luciferase Assay
2.8. Tumorigenicity Assay in BALB/c Mice
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
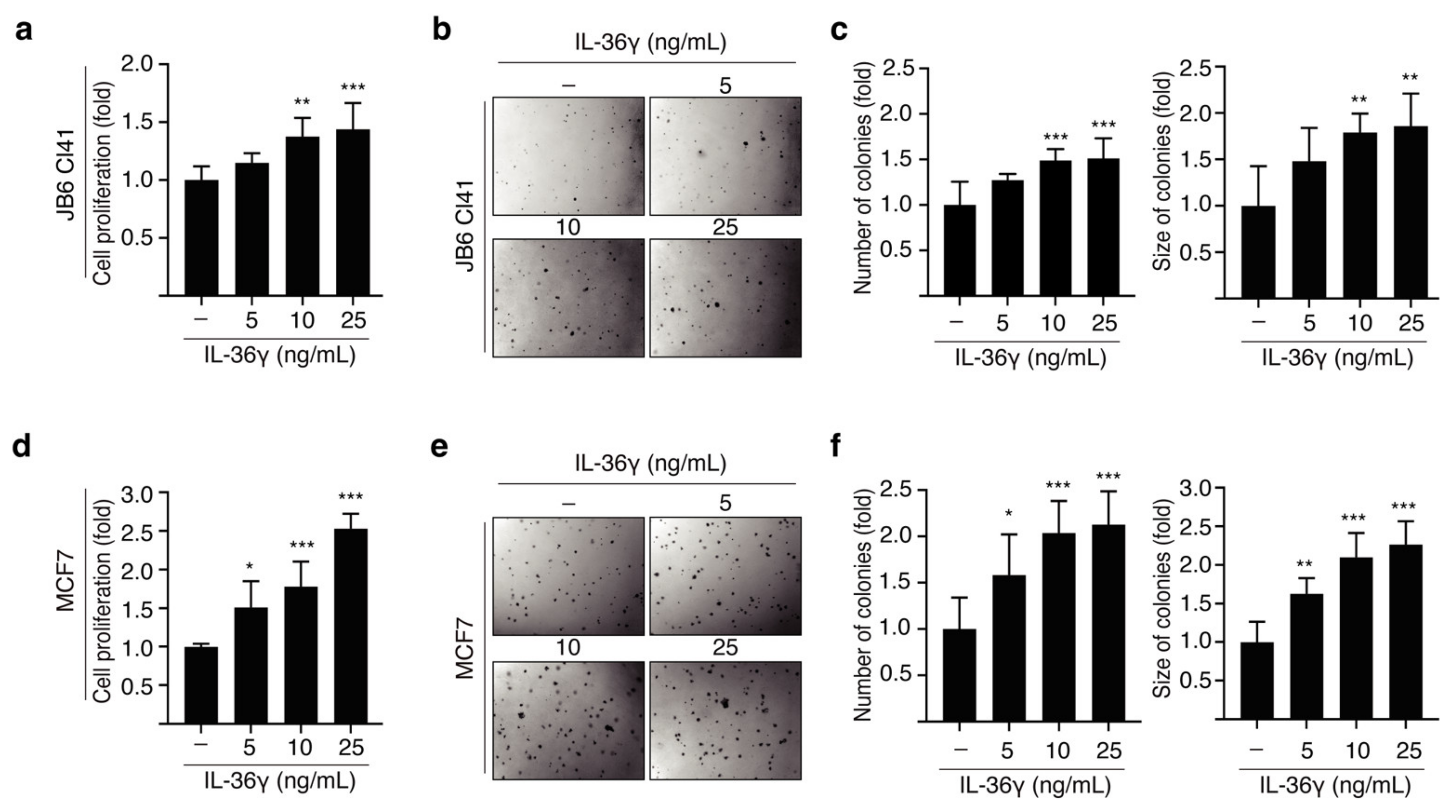
3.1. IL-36γ Induced Proliferation and Anchorage-Independent Growth of JB6 Cl41 and MCF7 Cells
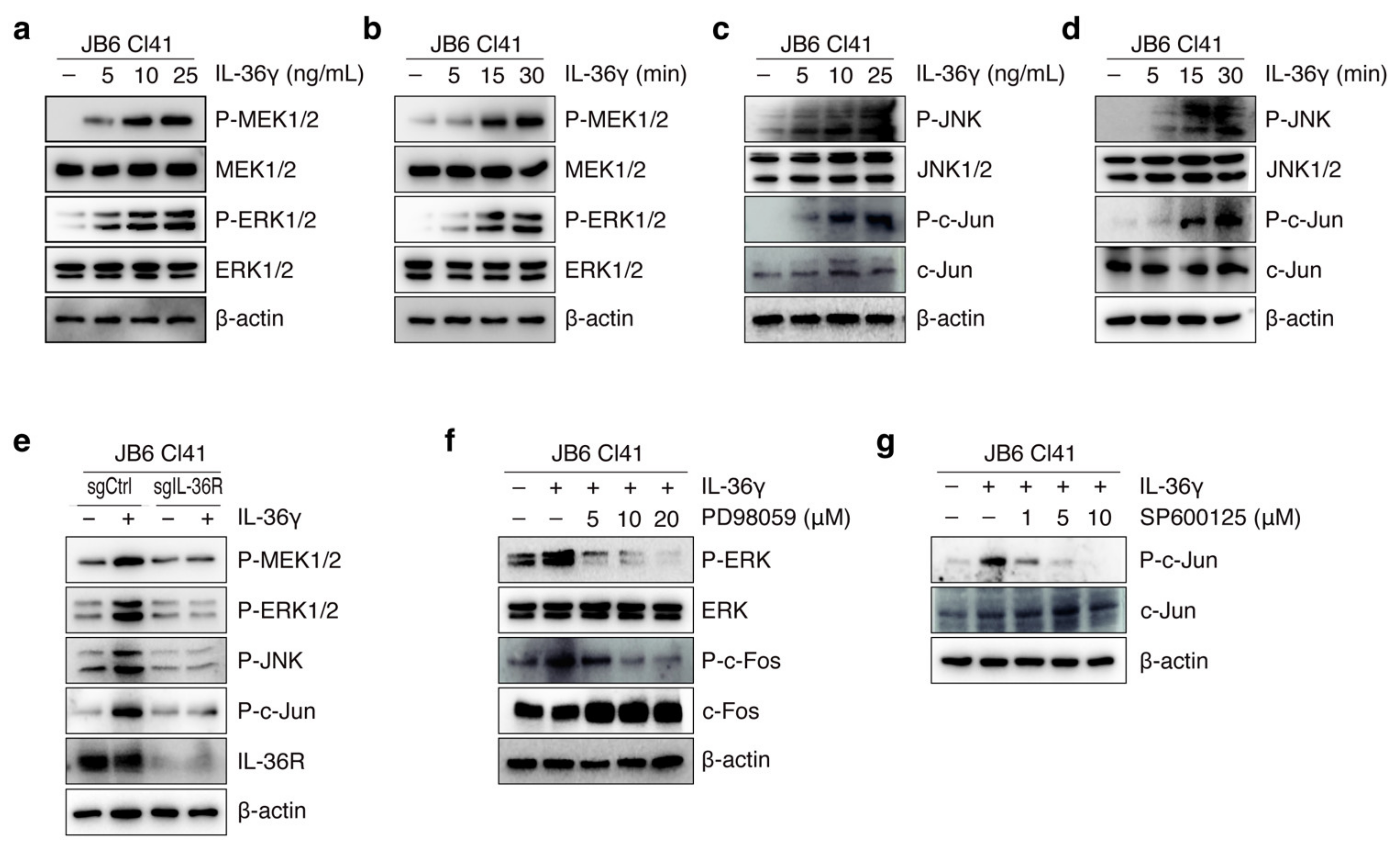
3.2. IL-36γ Induced MEK/ERK and JNK/c-Jun Signaling Pathways via IL36R in JB6 Cl41 Cells
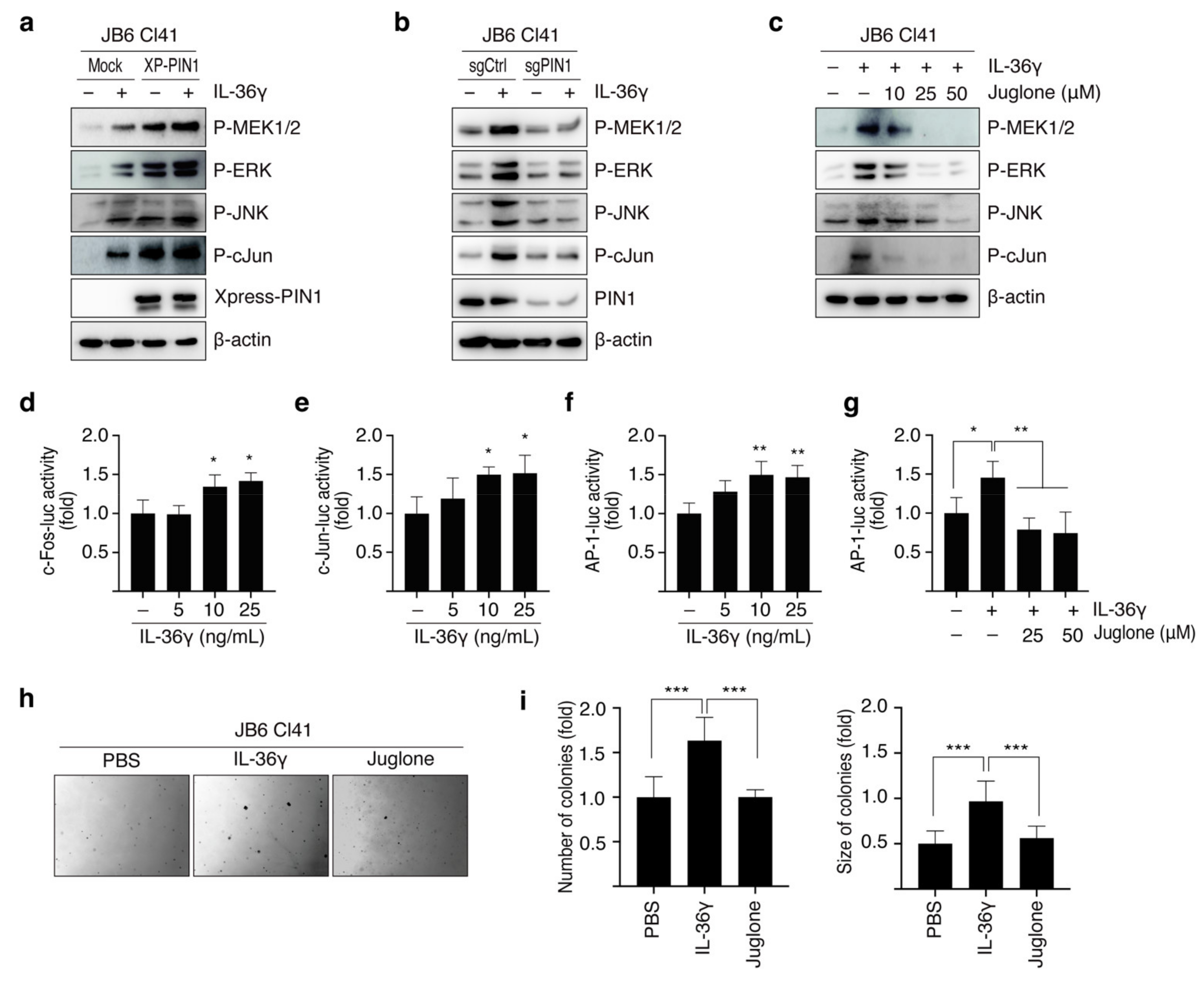
3.3. PIN1 Regulates IL-36γ-Induced MEK/ERK and JNK/c-Jun Signaling Pathways in MCF7 Cells
3.4. PIN1 Promotes IL-36γ-Induced AP-1 Activity and Anchorage-Independent Growth of MCF7 Cells
3.5. PIN1 Regulates IL-36γ-Induced 4T1 Cell Proliferation and Mammary Gland Tumorigenesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, J.M.; Rasanayagam, S.; Engel, C.; Rizzo, J. State of the evidence 2017: An update on the connection between breast cancer and the environment. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Coussens, L.M. Inflammation and breast cancer. Balancing immune response: Crosstalk between adaptive and innate immune cells during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Huertas, C.S.; Mitchell, A.; Plebanski, M. Tumor-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and the Emerging Diagnostic Devices for Cancer Detection and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 692142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquivel-Velázquez, M.; Ostoa-Saloma, P.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Castro, J.I.; Morales-Montor, J. The Role of Cytokines in Breast Cancer Development and Progression. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Castro, K.E.N.; Castro, J.I.; García-Zepeda, E.; Carrero, J.C.; Morales-Montor, J. The Role of Chemokines in Breast Cancer Pathology and Its Possible Use as Therapeutic Targets. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 849720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, R.K.; Nandi, A.; Thacker, G.; Murali, H.; Kim, S.; Baldeon, M.; Tobias, J.; Blanco, M.A.; et al. Loss of ELF5–FBXW7 stabilizes IFNGR1 to promote the growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through interferon-γ signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.J.; Houston, A.; Brint, E. IL-1 Family Members in Cancer; Two Sides to Every Story. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carey, A.; Edwards, D.K.; Eide, C.A.; Newell, L.; Traer, E.; Medeiros, B.C.; Pollyea, D.A.; Deininger, M.W.; Collins, R.H.; Tyner, J.W.; et al. Identification of Interleukin-1 by Functional Screening as a Key Mediator of Cellular Expansion and Disease Progression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 3204–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, S.-C.; Kim, G.; Yun, H.J.; Ahn, S.-G.; Choi, H.S. Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes epithelial cell transformation and breast tumorigenesis via upregulation of COT activity. Oncogene 2014, 34, 4928–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Zhu, F.; Tian, R.; Shi, C.; Xu, M.; et al. Blocking NF-κB Is Essential for the Immunotherapeutic Effect of Recombinant IL18 in Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5939–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, G.; Wang, A.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Xue, Y. Interleukin-37 suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Hu, H.; Lu, Z. Interleukin-38 Suppresses Cell Migration and Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Colorectal Cancer Cell Through Negatively Regulating Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases Signaling. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2021, 41, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teufel, L.U.; Arts, R.J.; Netea, M.G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Joosten, L.A. IL-1 family cytokines as drivers and inhibitors of trained immunity. Cytokine 2021, 150, 155773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.; Arend, W.; Sims, J.; Smith, D.; Blumberg, H.; O’Neill, L.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Pizarro, T.; Hoffman, H.; Bufler, P.; et al. IL-1 family nomenclature. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, M.; Scheiermann, P.; Härdle, L.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Mühl, H. IL-36γ/IL-1F9, an Innate T-bet Target in Myeloid Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 41684–41696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, E.; Sims, J.; Nicklin, M.; O’Neill, L.A. Annotating genes with potential roles in the immune system: Six new members of the IL-1 family. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towne, J.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Douangpanya, J.; Lipsky, B.P.; Shen, M.; Gabel, C.A.; Sims, J.E. Interleukin-36 (IL-36) Ligands Require Processing for Full Agonist (IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) or Antagonist (IL-36Ra) Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42594–42602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Towne, J.E.; Garka, K.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Virca, G.D.; Sims, J.E. Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 Signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to Activate the Pathway Leading to NF-κB and MAPKs. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13677–13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Hong, J.T. Roles of NF-κB in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases and Their Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Nishida, A.; Takahashi, K.; Hidaka, K.; Imaeda, H.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Andoh, A. Interleukin(IL)-36α and IL-36γ Induce Proinflammatory Mediators from Human Colonic Subepithelial Myofibroblasts. Front. Med. 2015, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magne, D.; Palmer, G.; Barton, J.L.; Mézin, F.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Bas, S.; Duffy, T.; Noger, M.; Guerne, P.-A.; Nicklin, M.J.H.; et al. The new IL-1 family member IL-1F8 stimulates production of inflammatory mediators by synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, A.; Xing, X.; Guzman, A.M.; Riblett, M.; Loyd, C.M.; Ward, N.L.; Wohn, C.; Prens, E.P.; Wang, F.; Maier, L.E.; et al. IL-1F5, -F6, -F8, and -F9: A Novel IL-1 Family Signaling System That Is Active in Psoriasis and Promotes Keratinocyte Antimicrobial Peptide Expression. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Feng, C.; Weinstein, A.; Xia, R.; Wen, W.; Lv, Q.; Zuo, S.; Tang, P.; Yang, X.; et al. IL-36γ Transforms the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Type 1 Lymphocyte-Mediated Antitumor Immune Responses. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, K.; O’Donnell, C.; Bendix, M.; Keogh, S.; Byrne, J.; O’Riordain, M.; Neary, P.; Houston, A.; Brint, E. IL-36 signalling enhances a pro-tumorigenic phenotype in colon cancer cells with cancer cell growth restricted by administration of the IL-36R antagonist. Oncogene 2022, 41, 2672–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Dong, H.; Wang, P.; Xu, Z.; Xian, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Lou, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhong, B. IL-36 γ and IL-36Ra Reciprocally Regulate Colon Inflammation and Tumorigenesis by Modulating the Cell–Matrix Adhesion Network and Wnt Signaling. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.P.; Liou, Y.-C.; Zhou, X.Z. Pinning down proline-directed phosphorylation signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Hasei, S.; Yamamotoya, T.; Honda, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Sakoda, H.; Fujishiro, M.; Ono, H.; Ito, H.; Okabe, T.; et al. Pathological Role of Pin1 in the Development of DSS-Induced Colitis. Cells 2021, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Xue, Z.; Fan, G.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Li, G.; Da, Y. Pin1 Promotes NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK Pathway in Septic Shock. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.; Kim, G.; Bhattarai, P.; Kim, J.-Y.; Choi, H. Interleukin-34-CSF1R Signaling Axis Promotes Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, P.; Namgoong, G.M.; Kang, B.S.; Woo, E.-R.; Choi, H.S. The Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 Enhances HER-2 Expression and Cellular Transformation via Its Interaction with Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Kinase 1. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wulf, G.M.; Ryo, A.; Wulf, G.G.; Lee, S.W.; Niu, T.; Petkova, V.; Lu, K.P. Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3459–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Queen, D.; Ediriweera, C.; Liu, L. Function and Regulation of IL-36 Signaling in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landskron, G.; De La Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic Inflammation and Cytokines in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boersma, B.; Jiskoot, W.; Lowe, P.; Bourquin, C. The interleukin-1 cytokine family members: Role in cancer pathogenesis and potential therapeutic applications in cancer immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 62, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochkov, Y.A.; Hanson, K.M.; Keles, S.; Brockman-Schneider, R.A.; Jarjour, N.N.; Gern, J.E. Rhinovirus-induced modulation of gene expression in bronchial epithelial cells from subjects with asthma. Mucosal Immunol. 2009, 3, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balato, A.; Mattii, M.; Caiazzo, G.; Raimondo, A.; Patruno, C.; Balato, N.; Ayala, F.; Lembo, S. IL-36γ Is Involved in Psoriasis and Allergic Contact Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovach, M.A.; Che, K.; Brundin, B.; Andersson, A.; Asgeirsdottir, H.; Padra, M.; Lindén, S.K.; Qvarfordt, I.; Newstead, M.W.; Standiford, T.J.; et al. IL-36 Cytokines Promote Inflammation in the Lungs of Long-Term Smokers. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; He, H.; Xu, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shi, L.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. Association between interleukin-36γ and tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibe, K.; Backert, I.; Wirtz, S.; Hueber, A.; Schett, G.; Vieth, M.; Probst, H.C.; Bopp, T.; Neurath, M.F.; Neufert, C. IL-36R signalling activates intestinal epithelial cells and fibroblasts and promotes mucosal healing in vivo. Gut 2016, 66, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibe, K.; Kersten, C.; Schmied, A.; Vieth, M.; Primbs, T.; Carlé, B.; Knieling, F.; Claussen, J.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Zheng, J.; et al. Inhibiting Interleukin 36 Receptor Signaling Reduces Fibrosis in Mice With Chronic Intestinal Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1082–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leon, G.; Santana, Y.E.H.; Irwin, N.; Giannoudaki, E.; O’Neill, S.; Csizmadia, I.; Gogarty, M.; Lee, T.J.; Ruane, D.; Long, A.; et al. IL-36 cytokines imprint a colitogenic phenotype on CD4+ T helper cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koss, C.K.; Wohnhaas, C.T.; Baker, J.R.; Tilp, C.; Przibilla, M.; Lerner, C.; Frey, S.; Keck, M.; Williams, C.M.M.; Peter, D.; et al. IL36 is a critical upstream amplifier of neutrophilic lung inflammation in mice. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton, E.; Qiu, H. Interleukin-36 Cytokine/Receptor Signaling: A New Target for Tissue Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, M.; Bart, G.; Penhoat, M.; Amiaud, J.; Brulin, B.; Charrier, C.; Morel, F.; Lecron, J.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M.; Bourreille, A.; et al. Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36α, β and γ, their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segueni, N.; Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Bourigault, M.-L.; Olleros, M.L.; Vesin, D.; Garcia, I.; Ryffel, B.; Quesniaux, V.F.J.; Gabay, C. Limited Contribution of IL-36 versus IL-1 and TNF Pathways in Host Response to Mycobacterial Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramadas, R.A.; Ewart, S.L.; Medoff, B.D.; Levine, A.M. Interleukin-1 Family Member 9 Stimulates Chemokine Production and Neutrophil Influx in Mouse Lungs. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Miller, A.H. Interleukin 1α (IL-1α) induced activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibits glucocorticoid receptor function. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 9, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, S.; Takayama, K.T.; Aizawa, Y.; Koide, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Ohta, T.; Kurimoto, M. Interleukin-18 Activates NF-κB in Murine T Helper Type 1 Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Hawke, N.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB and IKK as therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammouda, M.B.; Ford, A.E.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. The JNK Signaling Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Disorders and Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Cheon, S.; Jung, M.K.; Song, S.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.; Bang, S.I.; Cho, D. Interleukin-18 enhances breast cancer cell migration via down-regulation of claudin-12 and induction of the p38 MAPK pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 459, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-E.; Song, H.; Kim, T.S.; Yoon, D.; Kim, C.-W.; Bang, S.I.; Hur, D.Y.; Park, H.; Cho, D.-H. Interleukin-18 is a critical factor for vascular endothelial growth factor-enhanced migration in human gastric cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2006, 26, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, A.; Hidaka, K.; Kanda, T.; Imaeda, H.; Shioya, M.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Kitoh, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Andoh, A. Increased Expression of Interleukin-36, a Member of the Interleukin-1 Cytokine Family, in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.; Zhao, S.; Le, H.T.; Wang, J.; Neurath, M.F.; Neufert, C.; Fiocchi, C.; Rieder, F. IL-36 in chronic inflammation and fibrosis—Bridging the gap? J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e144336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Fan, G.; Zhuo, Q.; Dai, W.; Ye, Z.; Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Pin1 promotes pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis by activation of NF-κB-IL-18 feedback loop. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechama, M.; Kwon, J.; Wei, S.; Kyi, A.T.; Welner, R.S.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Arredouani, M.S.; Asara, J.M.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, C.Y.; et al. The IL-33-PIN1-IRAK-M axis is critical for type 2 immunity in IL-33-induced allergic airway inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garth, J.M.; Reeder, K.M.; Godwin, M.; Mackel, J.; Dunaway, C.W.; Blackburn, J.P.; Steele, C. Correction: IL-33 Signaling Regulates Innate IL-17A and IL-22 Production via Suppression of Prostaglandin E2 during Lung Fungal Infection. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, G.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yun, H.J.; Lim, S.-C.; Choi, H.S. Interleukin-22 promotes epithelial cell transformation and breast tumorigenesis via MAP3K8 activation. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poudel, M.; Bhattarai, P.Y.; Shrestha, P.; Choi, H.S. Regulation of Interleukin-36γ/IL-36R Signaling Axis by PIN1 in Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153654
Poudel M, Bhattarai PY, Shrestha P, Choi HS. Regulation of Interleukin-36γ/IL-36R Signaling Axis by PIN1 in Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis. Cancers. 2022; 14(15):3654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153654
Chicago/Turabian StylePoudel, Muna, Poshan Yugal Bhattarai, Pratikshya Shrestha, and Hong Seok Choi. 2022. "Regulation of Interleukin-36γ/IL-36R Signaling Axis by PIN1 in Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis" Cancers 14, no. 15: 3654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153654
APA StylePoudel, M., Bhattarai, P. Y., Shrestha, P., & Choi, H. S. (2022). Regulation of Interleukin-36γ/IL-36R Signaling Axis by PIN1 in Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis. Cancers, 14(15), 3654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153654





