Radiation Recall Pneumonitis: A Rare Syndrome That Should Be Recognized
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
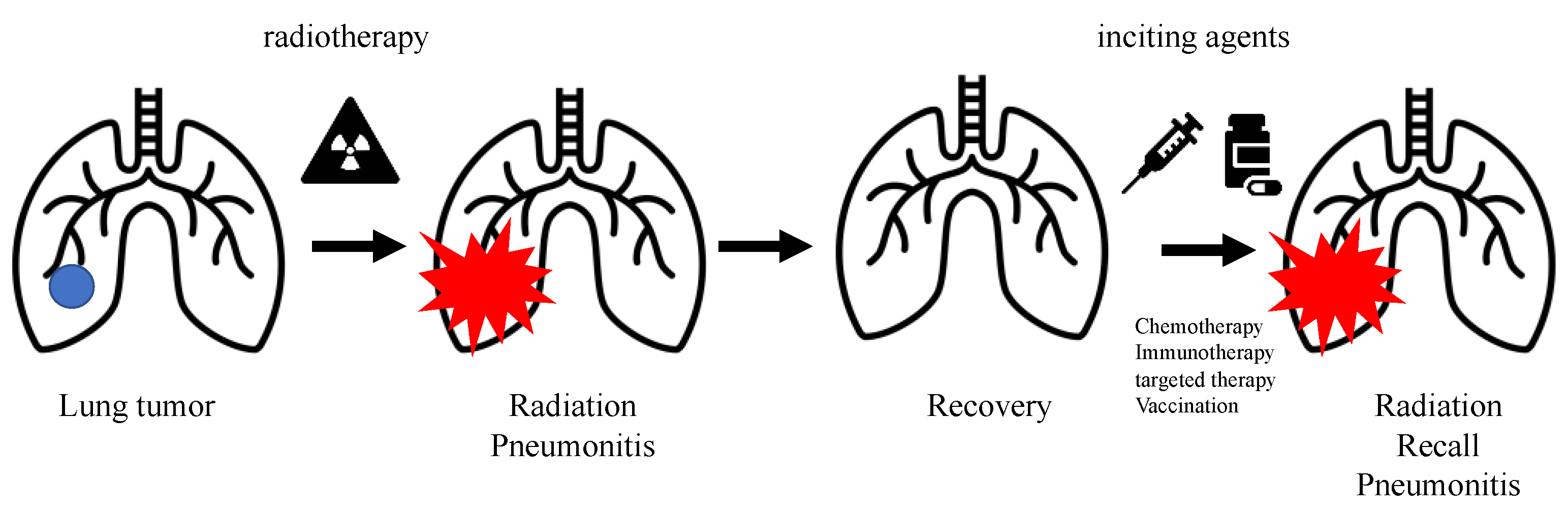
1. Introduction
2. Chemotherapy-Induced RRP
3. Immunotherapy-Induced RRP
4. Targeted Therapy-Induced RRP
4.1. Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)–Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs)
4.2. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Receptors
4.3. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Inhibitors
4.4. Human Epithelial Growth Factor-2 (HER-2) Inhibitors
4.5. BRAF Inhibitors
5. Vaccination-Induced RRP
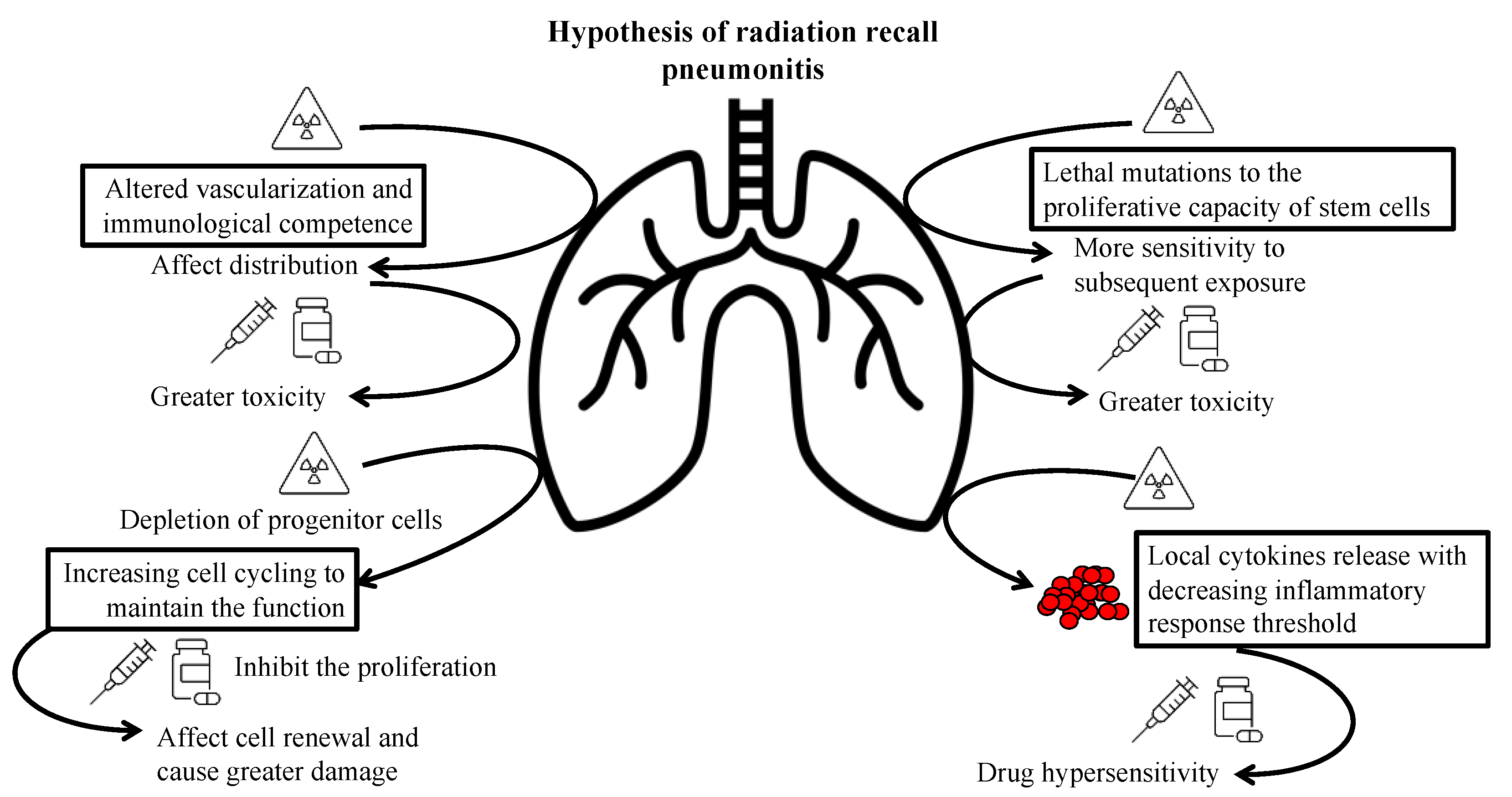
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azria, D.; Magné, N.; Zouhair, A.; Castadot, P.; Culine, S.; Ychou, M.; Stupp, R.; Van Houtte, P.; Dubois, J.B.; Ozsahin, M. Radiation recall: A well recognized but neglected phenomenon. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2005, 31, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Extermann, M.; Vogt, N.; Forni, M.; Dayer, P. Radiation recall in a patient with breast cancer treated for tuberculosis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, L.A.; Yoo, E.K.; Junkins-Hopkins, J.M.; VanVoorhees, A.S. Photo recall effect in association with cefazolin. Cutis 2004, 73, 79–80, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, B.R. Radiation recall induced by tamoxifen. Lancet 1992, 340, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadir, R.; Liebmann, J. Radiation reaction recall following simvastatin therapy: A new observation. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 1995, 7, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLnerney, D.P.; Bullimore, J. Reactivation of radiation pneumonitis by adriamycin. Br. J. Radiol. 1977, 50, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B.; Tattersall, S.F. Recall of radiation pneumonitis after intrapleural administration of doxorubicin. Med. J. Aust. 1983, 1, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, V.G.; Juillard, G.J.; Bajada, C.L.; Parker, R.G. Radiation recall dermatitis and pneumonitis in a patient treated with paclitaxel. Cancer 1995, 76, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarte, S.; Wagner, K.; Karstens, J.H.; Bremer, M. RRP induced by gemcitabine. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2007, 183, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Ji, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. RRP induced by chemotherapy after thoracic radiotherapy for lung cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Stuart, D.; Keyes, M. Radiation recall reaction induced by adjuvant trastuzumab (herceptin). Case Rep. Med. 2009, 2009, 307894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaverdian, N.; Lisberg, A.E.; Bornazyan, K.; Veruttipong, D.; Goldman, J.W.; Formenti, S.C.; Garon, E.B.; Lee, P. Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: A secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibaki, R.; Akamatsu, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Koh, Y.; Yamamoto, N. Nivolumab induced RRP after two years of radiotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1404–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, K.; Ghaly, M.; Esposito, M.; Barnaby, K.; Seetharamu, N. RRP in the setting of immunotherapy and radiation: A focused review. Future Sci. OA 2019, 5, FSO378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Lalezari, F.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Aerts, J.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.N.; de Langen, A.J.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs. Pembrolizumab Alone on Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the PEMBRO-RT Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xing, L.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. RRP Induced by Anti-PD-1 Blockade: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itamura, H.; Ohguri, T.; Yahara, K.; Nakahara, S.; Kakinouchi, S.; Morisaki, T.; Yatera, K.; Tanaka, F.; Korogi, Y. Pembrolizumab-induced RRP After the Resolution of Typical Asymptomatic Radiation Pneumonitis. J. UOEH 2020, 42, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Li, M.; Yu, J. RRP induced by PD-1/PD-L1 blockades: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, F.; Desir, C.; Ben Mustapha, S.; Mievis, C.; Coucke, P.; Hustinx, R. Incidence, risk factors, and CT characteristics of RRP induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor in lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 157, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, P.; Sumner, W.; Cornell, M.; Sandhu, A.; Murphy, J.D.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.; Bruggeman, A.; Kim, S.S.; Randall, J.M.; Sharabi, A.B. RRP After Treatment with Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy: A Case Series and Review of Literature. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 662954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, S.; Zhu, H. RRP Induced by Sintilimab: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; Oudard, S.; Hutson, T.E.; Porta, C.; Bracarda, S.; Grünwald, V.; Thompson, J.A.; Figlin, R.A.; Hollaender, N.; et al. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrimali, R.K.; McPhail, N.J.; Correa, P.D.; Fraser, J.; Rizwanullah, M. Trastuzumab-induced radiation recall dermatitis--first reported case. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2009, 21, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, C.; Janssen, S.; Karstens, J.H.; Welte, T.; Morgan, M.; Ganser, A.; Grünwald, V. Recall pneumonitis during systemic treatment with sunitinib. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 2119–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.; Gauchan, D.; Ramaekers, R.; Norvell, M.; Copur, M.S. RRP During Systemic Treatment with Everolimus. Oncol. Res. 2014, 22, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forschner, A.; Zips, D.; Schraml, C.; Röcken, M.; Iordanou, E.; Leiter, U.; Weide, B.; Garbe, C.; Meier, F. Radiation recall dermatitis and radiation pneumonitis during treatment with vemurafenib. Melanoma Res. 2014, 24, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Jeong, N.J.; Lee, Y.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; Im, M. Radiation recall dermatitis and pneumonitis induced by trastuzumab (Herceptin®). Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, e159–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.; Nott, L. RRP induced by erlotinib after palliative thoracic radiotherapy for lung cancer: Case report and literature review. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 12, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Chen, Y.-W.; Wu, M.-H.; Huang, H.-C.; Tsai, C.-M.; Chiu, C.-H. RRP induced by epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2016, 79, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Borja, M.; Parrot, A.; Sroussi, D.; Rivin del Campo, E.; Fallet, V.; Cadranel, J. Dramatic RRP Induced by Osimertinib after Palliative Thoracic Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e224–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steber, C.R.; Ponnatapura, J.; Hughes, R.T.; Farris, M.K. Rapid Development of Clinically Symptomatic RRP Immediately Following COVID-19 Vaccination. Cureus 2021, 13, e14303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, N.M.; Hammer, M.M.; Awad, M.M.; Jacene, H.A. RRP on FDG PET/CT Triggered by COVID-19 Vaccination. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, e281–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinada, K.; Murakami, S.; Yoshida, D.; Saito, H. RRP after COVID-19 vaccination. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, A.; Sjölin-Forsberg, G.; Wilking, N.; Bergh, J. Radiation recall—Another call with tamoxifen. Acta Oncol. 1999, 38, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.B.; Mothersill, C.; Alper, T. High yields of lethal mutations in somatic mammalian cells that survive ionizing radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1986, 50, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.J.; Piedboeuf, B.; Rubin, P.; Williams, J.P.; Baggs, R.; Finkelstein, J.N. Early and persistent alterations in the expression of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels in fibrosis-resistant and sensitive mice after thoracic irradiation. J. Radiat. Res. 1996, 145, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasskarl, J. Everolimus. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meskawi, M.; Valdivieso, R.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Trudeau, V.; Larcher, A.; Karakiewicz, P.I. The Role of Everolimus in Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2015, 2, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Gelber, R.D.; Procter, M.; Goldhirsch, A.; de Azambuja, E.; Castro, G., Jr.; Untch, M.; Smith, I.; Gianni, L.; et al. 11 years’ follow-up of trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive early breast cancer: Final analysis of the HERceptin Adjuvant (HERA) trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drugs (Cases ∑) | Radiotherapy Program # | Time Interval from Radiotherapy * | Time to Onset & | Treatment ∆ | Rechallenge with Same Regimen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adriamycin [6] | Co-60 radiation/ 15 Gy/10 F/ unknown | 4 months | 1 day | Prednisolone 20 mg/day, gradually tapered to 5 mg/day across 3 weeks | No recurrence with concurrent prednisolone 5 mg/day |
| Paclitaxel [8] | Palliative RT/ 43.2 Gy/24 F/ unknown | 12 days | Several hours | Dexamethasone 20 mg once | No recurrence with premedication with 3 doses of dexamethasone 20 mg |
| Cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and vincristine [10] | 3D-CRT/ 60 Gy/30 F/ 15.6 Gy | 71 days | 29 days | Systemic steroids, dose not reported | No |
| Docetaxel [10] | IMRT/ 54 Gy/24 F/ 14.89Gy | 82 days | 51 days | No | |
| Gemcitabine and docetaxel (n = 2) [10] | 3D-CRT/ 62 Gy/34 F/ 14.46 Gy | 87.5 days (range, 81–94 days) | 30 days (range, 22–38 days) | No recurrence with concurrent steroid coverage | |
| Carboplatin and Etoposide [10] | IMRT/ 60 Gy/30 F 13.19 Gy | 94 days | 79 days | No | |
| Navelbine and cisplatin [10] | 3D-CRT/ 52 Gy/26 F 18.19 Gy | 102 days | 42 days | No | |
| Paclitaxel and carboplatin (n = 5) [10] | 3D-CRT (n = 4) and IMRT (n = 1)/ 62.52 Gy/33.2 F/ 17.036 Gy | 105 days (range, 86–202 days) | 71 days (range, 36–169 days) | 1 of 5 patients was rechallenged and no recurrence with concurrent steroid coverage was found | |
| Etoposide and cisplatin [10] | IMRT/ 60 Gy/30 F/ 14.44 Gy | 171 days | 164 days | No |
| Drugs (Cases ∑) | Radiotherapy Program # | Time Interval from Radiotherapy * | Time to Onset & | Treatment ∆ | Rechallenge with Same Regimen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pembrolizumab [16,19] | EBRT/ unknown/unknown/ 5–20 Gy | 14 months | 10 months | Prednisolone 1 mg/kg, followed by a prolonged taper for 3 months | Not reported |
| 3D-CRT/ 64 Gy/32 F/ 15 Gy | 7 months | 1 month | Methylprednisolone 1000 mg/day for 3 days, then prednisolone 60 mg/day tapered in 3 months | Not reported | |
| Nivolumab [15] | Unknown/ 60 Gy/unknown/ unknown | 2 years | 6 weeks | Prednisolone 1 mg/kg, tapered over 4 weeks | Not reported |
| Unknown/ 60 Gy/unknown/ unknown | 2 years | 6 months | Prednisolone 1 mg/kg, tapered over 4 weeks | Not reported | |
| Sintilimab [23] | CCRT/ 60 Gy/30 F/ 13.5 Gy | 11 months | 10 months | Prednisolone 120 mg twice a day, tapered over 4 weeks | Not reported |
| Camrelizumab [18] | SIB/ 63.8 Gy/29 F/ 13.5 Gy | 19 months | 4 months | Prednisolone 80 mg twice a day, tapered over 3 weeks | Not reported |
| Pembrolizumab Nivolumab Atezolizumab (n = 15) [21] | CRT (n = 12) and SBRT (n = 3)/ 60 Gy/unknown/ 11 Gy | 450 days (range, 231–1859 days) | 61 days (range, 4–520 days) | Not reported | Not reported |
| Nivolumab and experimental histone deacetylase inhibitor [22] | IMRT/ 59.4 Gy/33 F/ Unknown | 4.5 years | 2 weeks | Prednisolone 60 mg/day, tapered gradually | Not reported |
| Ipilimumab and pembrolizumab [22] | SBRT/ 25 Gy/5 F/ unknown | Less than half a year | 3 days (second dose) | Expired | Expired |
| Nivolumab and Ipilimumab [22] | CRT/ 30 Gy/10 F/ unknown | 7 months | 11 days (fourth dose) | Prednisolone 50 mg/day, tapered gradually | Not reported |
| Drugs (Cases ∑) | Radiotherapy Program # | Time Interval from Radiotherapy * | Time to Onset & | Treatment ∆ | Rechallenge with Same Regimen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erlotinib [30] | Palliative/ 30 Gy/12 F/ 10.7Gy | 4 months | 2 months | Prednisolone 50 mg/day, tapered over 4 weeks | No recurrence without mention of steroid coverage |
| Gefitinib and erlotinib (n = 7) [31] | Conventional and conformal RT/ 60 Gy/unknown/ 12.8 Gy | 124 days (range, 80–635 days) | 43 days (range, 18–65 days) | Systemic steroid for grade 3 RRP (n = 3) | No recurrence in patients with grade 1 and 2 RRP without mention of steroid coverage One patient with grade 3 RRP developed interstitial pneumonitis after rechallenge |
| Osimertinib [32] | Hypo-RT/ 55 Gy/20 F/ unknown | 2.5 months | 2 weeks (pre-exposure) | Prednisolone 0.5 mg/kg/day for 1 week | Not reported |
| Sunitinib [26] | Palliative RT/ 30 Gy/unknown/ unknown | 6 months | 5 months | Reduced the sunitinib dose from 50 to 37.5 mg/day | Dose adjustment, no discontinuation of sunitinib |
| Everolimus [27] | Palliative RT/ 39 Gy/13 F/ unknown | 2 months | 1 month | Methylprednisolone followed by oral prednisolone, not reported dose | Not reported |
| Trastuzumab [29] | Unknown/ 50.4 Gy/unknown/ unknown | 2 years | 2 years | Prednisolone 30 mg/day for 2 weeks | Not reported |
| Vemurafenib [28] | 3D-CRT/ 50 Gy/25 F 6.9 Gy | 7 weeks | 3 weeks | Continued vemurafenib ∆ Added prednisolone 150 mg/day for 10 days | No discontinuation of vemurafenib |
| 3D-CRT/ 50 Gy/25 F/ 17.4 Gy | 7 weeks | 4 weeks | Continued vemurafenib ∆ Added prednisolone 60 mg/day for 10 days | No discontinuation of vemurafenib |
| Drugs (Cases ∑) | Radiotherapy Program # | Time interval from Radiotherapy * | Time to Onset & | Treatment ∆ | Rechallenge with Same Regimen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderna COVID-19 vaccine [33] | Unknown/ 45 Gy/15 F/ unknown | 6 months | 3 days (second dose) | Prednisolone 40 mg/day and tapered gradually | Not reported |
| BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine [35] | IMRT/ 60 Gy/30 F/ unknown | 1 year | 19 days (second dose) | Prednisolone 0.5 mg/kg/day and tapered gradually | Not reported |
| mRNA COVID-19 vaccine [34] | Unknown/ 60 Gy/15 F/ unknown | 8 months | 3 months (second dose) | No intervention ∆ | Not reported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jan, P.-R.; Chang, J.W.-C.; Wu, C.-E. Radiation Recall Pneumonitis: A Rare Syndrome That Should Be Recognized. Cancers 2022, 14, 4642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194642
Jan P-R, Chang JW-C, Wu C-E. Radiation Recall Pneumonitis: A Rare Syndrome That Should Be Recognized. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194642
Chicago/Turabian StyleJan, Pei-Rung, John Wen-Cheng Chang, and Chiao-En Wu. 2022. "Radiation Recall Pneumonitis: A Rare Syndrome That Should Be Recognized" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194642
APA StyleJan, P.-R., Chang, J. W.-C., & Wu, C.-E. (2022). Radiation Recall Pneumonitis: A Rare Syndrome That Should Be Recognized. Cancers, 14(19), 4642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194642






