IL-2K35C-moFA, a Long-Acting Engineered Cytokine with Decreased Interleukin 2 Receptor α Binding, Improved the Cellular Selectivity Profile and Antitumor Efficacy in a Mouse Tumor Model
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction and Purification of IL-2 Muteins
2.2. FA Conjugation
2.3. RP-HPLC
2.4. Mass Analysis by LC-MS
2.5. Mapping Analysis by LC-MS/MS
2.6. Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. CTLL-2 Cell Proliferation Assay
2.8. p-STAT5 Assay in Treg and CD8+ T Cell
2.9. Animal Experiments
2.10. Half-Life Analysis in Mice
2.11. Immune Cell Phenotyping in Mice
2.12. B16F10 Murine Tumor Model
2.13. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Screen/Design IL-2 Mutants
3.2. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of IL-2K35C
3.3. moFA Conjugation and Identification by LC-MS
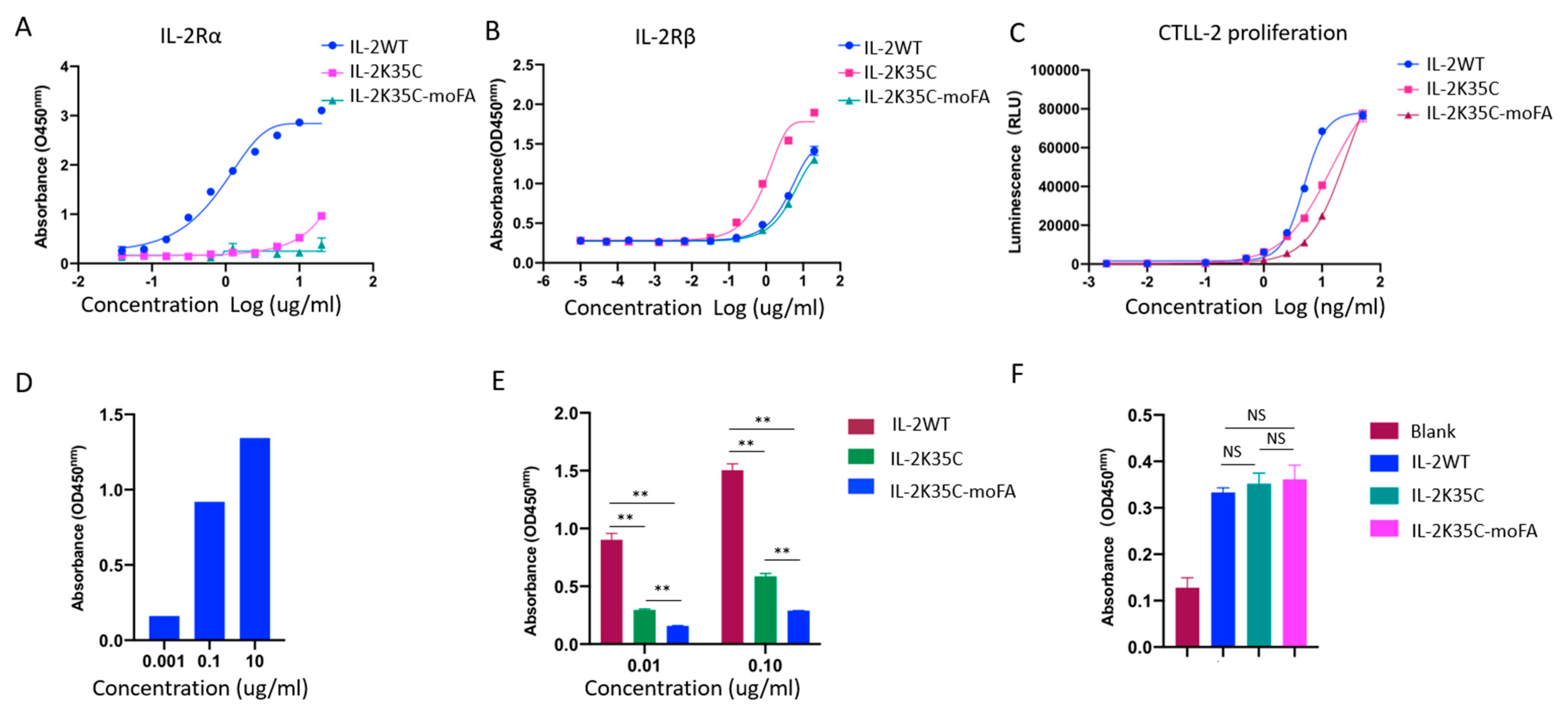
3.4. Binding Affinity to Receptors by ELISA
3.5. Effects on IL-2-Dependent Proliferation of CTLL-2 Cells
3.6. Effects on IL-2-Dependent p-STAT5 of Treg and CD8+ T Cells
3.7. IL-2K35C-moFA Demonstrates Increased Half-Life in Mice
3.8. IL-2K35C-moFA Drives Expansion of CD8+ T and NK Cells in Mice
3.9. Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety in B16F10 Tumor Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robb, R.J.; Smith, K.A. Heterogeneity of human T-cell growth factor (s) due to variable glycosylation. Mol. Immunol. 1981, 18, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuribayashi, K.; Gillis, S.; Kern, D.; Henney, C. Murine NK cell cultures: Effects of interleukin-2 and interferon on cell growth and cytotoxic reactivity. J. Immunol. 1981, 126, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhupkar, P.; Gordon, N. Interleukin-2: Old and new approaches to enhance immune-therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 995, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Sprent, J. The role of interleukin-2 during homeostasis and activation of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.K.; Trotta, E.; Simeonov, D.R.; Marson, A.; Bluestone, J.A. Revisiting IL-2: Biology and therapeutic prospects. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, D.F.; Atkins, M.B. Interleukin-2 therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma—Predictors of response. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkowski, A., III; Wong, M.K. A Re-assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of Interleukin-2 for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Med. Ther. 2009, 1, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.E.; Fisher, J.L.; Flick, H.L.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Alvarez, J.C.; Losey, H.C. ALKS 4230: A novel engineered IL-2 fusion protein with an improved cellular selectivity profile for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ai, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Yang, P.; Liu, G. A novel human IL-2 mutein with minimal systemic toxicity exerts greater antitumor efficacy than wild-type IL-2. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z.; Cao, S.; Deng, S.; Xu, L.; Liang, Y.; Guo, J.; Bian, Y.; et al. A next-generation tumor-targeting IL-2 preferentially promotes tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T-cell response and effective tumor control. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charych, D.H.; Hoch, U.; Langowski, J.L.; Steve, R.L.; Murali, K.A.; Peter, B.K.; Sheng, D.; Liu, X.; Paul, W.S.; Laurie, A.V.; et al. NKTR-214, an engineered cytokine with biased IL2 receptor binding, increased tumor exposure, and marked efficacy in mouse tumor models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolski, R.; Li, P.; Leonard, W.J. Biology and regulation of IL-2: From molecular mechanisms to human therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, G.; Frydecka, I. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) and its receptor (IL-2R) in healthy individuals and with various disease states. Acta Haematol. Pol. 1993, 24, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tahvildari, M.; Dana, R. Low-dose IL-2 therapy in transplantation, autoimmunity, and inflammatory diseases. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2749–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Cho, J.-H.; Sprent, J. The role of interleukin-2 in memory CD8 cell differentiation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 684, 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- Damoiseaux, J. The IL-2–IL-2 receptor pathway in health and disease: The role of the soluble IL-2 receptor. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Jin, Y.; Gan, Y.; Hu, X.; Jia, R.; et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Brand, D.; Zheng, S.G. Targeting IL-2: An unexpected effect in treating immunological diseases. Signal Transduc. Target Ther. 2018, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, J.M.; Blaire, L.O.; Todd, R.; Palanisamy, K.; Ping, W.; Guoxian, C.; David, S.; Wendy, G.H.; Thi-Sau, M.; Qi, W.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor response of an interleukin-2-human serum albumin fusion protein in mice. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
- Adabi, E.; Saebi, F.; Hasan-Abad, A.M.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L.; Kardar, G.A. Evaluation of an albumin-binding domain protein fused to recombinant human IL-2 and its effects on the bioactivity and serum half-life of the cytokine. Iran. Biomed. 2017, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, M.J.; Joolakanti, S.; Hartranft, M.E.; Guley, P.C.; Cho, M.J. A dicarboxylic fatty acid derivative of paclitaxel for albumin-assisted drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3292–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar, A.; Mohsen, A.; Soliman, M.; Younes, G.; Amir, A.; Mohammad, R.T.; Eskandar, K.; Saeid, D. Nanostructure L-asparaginase-fatty acid bioconjugate: Synthesis, preformulation study and biological assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzhals, P. Engineering predictability and protraction in a basal insulin analogue: The pharmacology of insulin detemir. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, S23–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, S.-I.; Amisaki, T. Fatty acid binding to serum albumin: Molecular simulation approaches. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeannette, N.; Malin, B.; Kine, M.K.S.; Algirdas, G.; Bjorn, D.; Inger, S.; Jan, T.A. Human and mouse albumin bind their respective neonatal Fc receptors differently. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14648. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, I.; Moon, H.R.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, K.T.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, K.C.; Youn, Y.S. Preparation and evaluation of palmitic acid-co.njugated exendin-4 with delayed absorption and prolonged circulation for longer hypoglycemia. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 424, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, D.J.; Debler, E.W.; Horton, P.A.; Smith, K.A.; Wilson, I.A. Crystal structure of the IL-2 signaling complex: Paradigm for a heterotrimeric cytokine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milla, M.; Ptacin, J.L.; Ma, L.; Caffaro, C.E.; Aerni, H.R.; San Jose, K.M.; Herman, R.W.; Pavlova, Y.; Chen, D.B.; Ismaili, T.K.; et al. THOR-707, a novel not-alpha IL-2, promotes all key immune system anti-tumoral actions of IL-2 without eliciting vascular leak syndrome (VLS). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacin, J.L.; Caffaro, C.E.; Ma, L.; Caffaro, C.E.; Aerni, H.R.; San JK, M.; Pena, M.J.; Herman, R.W.; Pavlova, Y.; Chen, D.B.; et al. An engineered IL-2 reprogrammed for anti-tumor therapy using a semi-synthetic organism. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. A pharmacological and clinical overview of oral semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Drugs 2021, 81, 1003–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, G.A.; Katsiki, N.; Blundell, J.; Fruhbeck, G.; Kiortsis, D.N. Semaglutide as a promising antiobesity drug. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Sun, L.; Dai, Y.; Avraham, Y.; Liu, C.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, D.; Huang, W.; Qian, H. Novel fatty acid chain modified GLP-1 derivatives with prolonged in vivo glucose-lowering ability and balanced glucoregulatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, M.T.; Frana, L.W.; Sharrow, S.O.; Robb, R.J.; Rosenberg, S. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin 2. I. Half-life and immunologic effects of the Jurkat cell line-derived interleukin 2. J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veronese, F.M.; Mero, A. The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies. BioDrugs 2008, 22, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, C.; Khalili, H.; Lever, R.; Brocchini, S. PEGylation and its impact on the design of new protein-based medicines. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1829–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, Q.; Xu, J.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takakura, T.; Takimoto, A.; Yoshioka, T.; Lian, C.; Chen, C.; et al. PEGylation confers greatly extended half-life and attenuated immunogenicity to recombinant methioninase in primates. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6673–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.M.; Chess, R.B. Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Azadi, A.; Rafiei, P. Pharmacokinetic consequences of pegylation. Drug Deliv. 2006, 13, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.; Wu, B. Effects of pharmaceutical PEGylation on drug metabolism and its clinical concerns. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. 2014, 10, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderschuren, K.; Arranz-Gibert, P.; Khang, M.; Hadar, D.; Gaudin, A.; Yang, F.; Folta-Stogniew, E.; Saltzman, M.W.; Amiram, M.; Isaacs, F.J. Tuning protein half-life in mouse using sequence-defined biopolymers functionalized with lipids. Proc. Acad. Natl. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2103099119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, A.A.; Shegokar, R. Polyethylene glycol (PEG): A versatile polymer for pharmaceutical applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1257–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No. | Oligo |
|---|---|
| 1 | CTCTCCCTGTCTCCGGGTAAACTGGTGCCACGCGGTTCGCCTACTTCAAGTTCTACAAAGAAAACACAGCTACAACTGGAGCATT |
| 2 | TGGTGAGACAGGGATTCTTGTAATTATTAATTCCATTCAAAATCATCTGTAAATCCAGCAGTAAATGCTCCAGTTGTAGCT |
| 3 | AGAATCCCTGTCTCACCAGGATGCTCACATTTAAGTTTTACATGCCCAAGAAGGCCACAGAACTG |
| 4 | GCACTTCCTCCAGAGGTTTGAGTTCTTCTTCTAGACACTGAAGATGTTTCAGTTCTGTGGCCTTCT |
| 5 | ACCTCTGGAGGAAGTGCTAAATTTAGCTCAAAGCAAAAACTTTCACTTAAGACCCAGGGACTTAATCAGC |
| 6 | CATCAGCATATTCACACATGAATGTTGTTTCAGATCCCTTTAGTTCCAGAACTATTACGTTGATATTGCTGATTAAGTCCCTGGG |
| 7 | TCATGTGTGAATATGCTGATGAGACAGCAACCATTGTAGAATTTCTGAACAGATGGATTACCTTTTCTCAAAGCATCATCTCAAC |
| 8 | TTTGTAATCCAGAGGTTGATTGTCGACTCTAGAATCATCAAGTCAGTGTTGAGATGATGCTTTGAGA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Nie, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.; He, Q.; et al. IL-2K35C-moFA, a Long-Acting Engineered Cytokine with Decreased Interleukin 2 Receptor α Binding, Improved the Cellular Selectivity Profile and Antitumor Efficacy in a Mouse Tumor Model. Cancers 2022, 14, 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194742
Wang X, Chen G, Nie L, Wu Z, Wang X, Pan C, Chen X, Zhao X, Zhu J, He Q, et al. IL-2K35C-moFA, a Long-Acting Engineered Cytokine with Decreased Interleukin 2 Receptor α Binding, Improved the Cellular Selectivity Profile and Antitumor Efficacy in a Mouse Tumor Model. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194742
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoze, Gang Chen, Lei Nie, Zhenhua Wu, Xinzeng Wang, Chenxiao Pan, Xuchen Chen, Xiaobei Zhao, Jie Zhu, Qiaojun He, and et al. 2022. "IL-2K35C-moFA, a Long-Acting Engineered Cytokine with Decreased Interleukin 2 Receptor α Binding, Improved the Cellular Selectivity Profile and Antitumor Efficacy in a Mouse Tumor Model" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194742
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, G., Nie, L., Wu, Z., Wang, X., Pan, C., Chen, X., Zhao, X., Zhu, J., He, Q., & Wang, H. (2022). IL-2K35C-moFA, a Long-Acting Engineered Cytokine with Decreased Interleukin 2 Receptor α Binding, Improved the Cellular Selectivity Profile and Antitumor Efficacy in a Mouse Tumor Model. Cancers, 14(19), 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194742






