Hypoxia and ERα Transcriptional Crosstalk Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Proliferation Assay and TUNEL Assay
2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry (FACS)
2.4. Antibodies and Immunofluorescence
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. RNA Extraction and RT qPCR
2.7. Microarray Preparation
2.8. Microarray Analysis
2.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.10. ChIP-Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) and Data Analysis
2.11. Clinical Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hypoxia Dampens ERα Expression Level and Modulates E2 Sensitivity at the Cellular Level
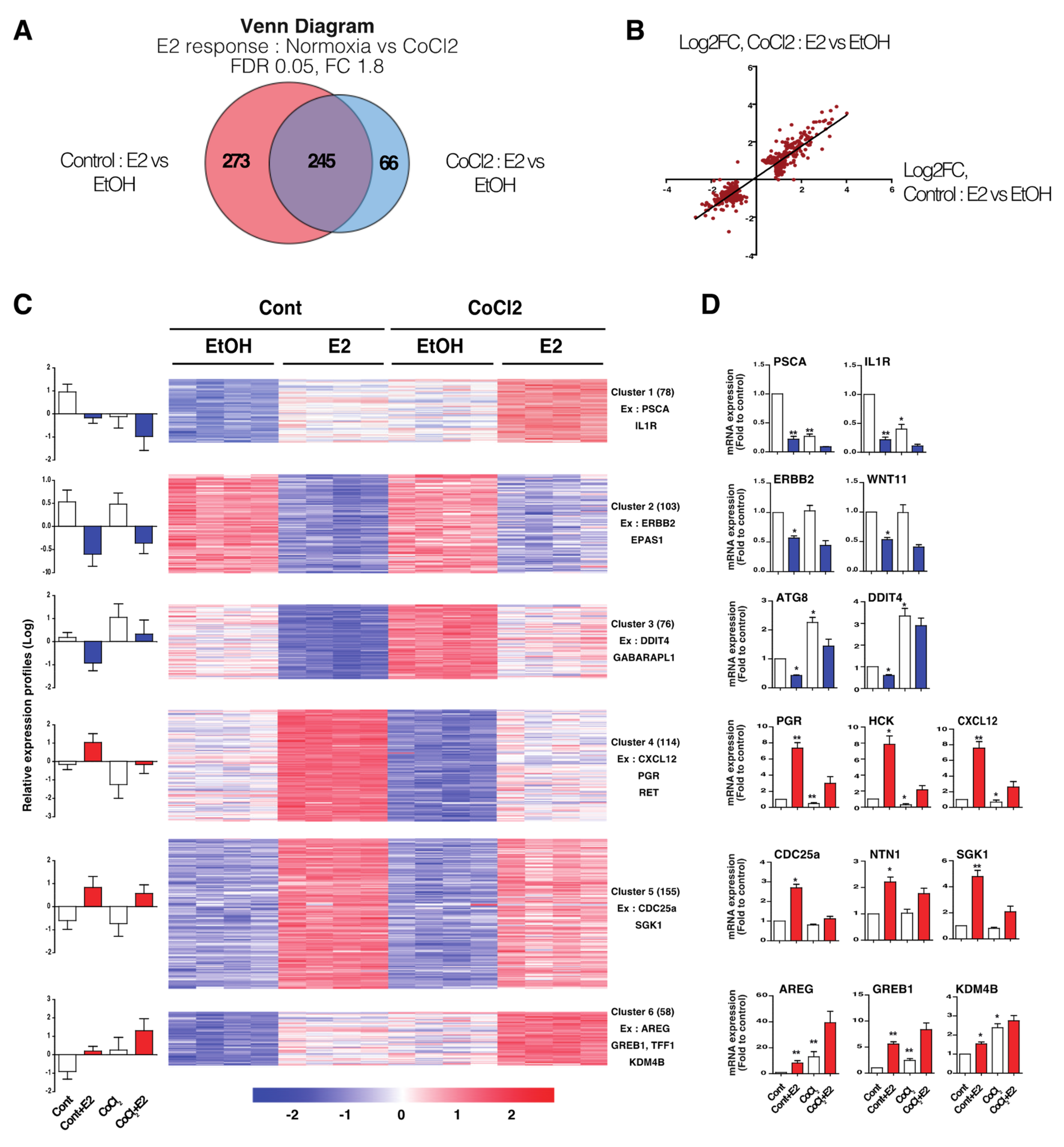
3.2. Hypoxia-Induced E2-Dependant Transcription Reprogramming
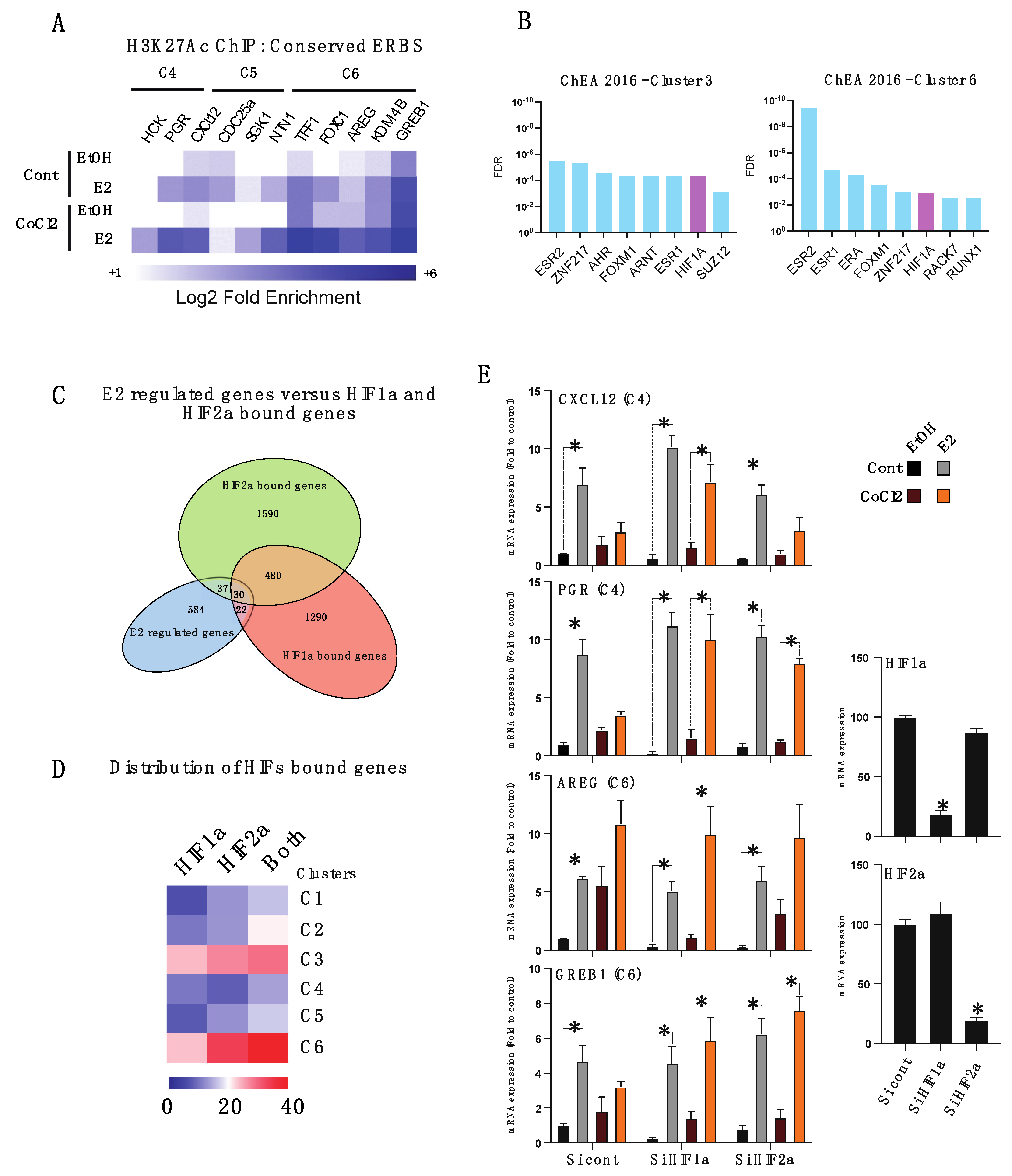
3.3. Hypoxia-Induced Chromatin-ERα Interaction Reprogramming
3.4. HIFα Factors Compensate ERα Loss and Sustain Expression of Specific ERα Target Genes
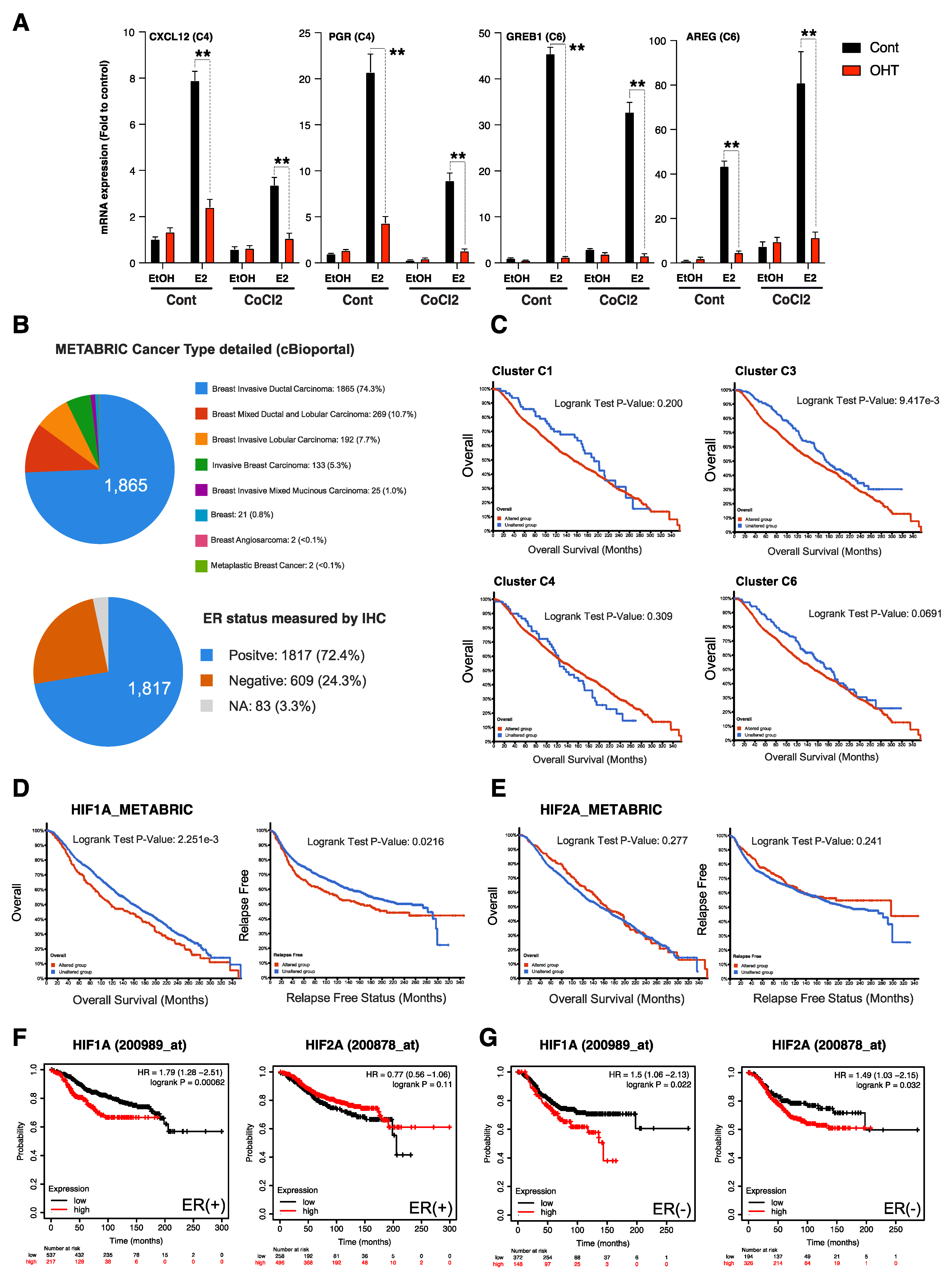
3.5. HIFα-Hypoxia-ERα Crosstalk Correlates with Poor Survival in ER+ Luminal Breast Cancers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnal, J.-F.; Lenfant, F.; Metivier, R.; Flouriot, G.; Henrion, D.; Adlanmerini, M.; Fontaine, C.; Gourdy, P.; Chambon, P.; Katzenellenbogen, B.; et al. Membrane and Nuclear Estrogen Receptor Alpha Actions: From Tissue Specificity to Medical Implications. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1045–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørile, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Ress, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanker, A.B.; Sudhan, D.R.; Arteaga, C.L. Overcoming Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Yelensky, R.; Buchwalter, G.; Frampton, G.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Ferrer-Lozano, J.; Perez-Fidalgo, J.A.; Cristofanilli, M.; Gómez, H.; et al. Emergence of Constitutively Active Estrogen Receptor-α Mutations in Pretreated Advanced Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giltnane, J.M.; Hutchinson, K.E.; Stricker, T.P.; Formisano, L.; Young, C.D.; Estrada, M.V.; Nixon, M.J.; Du, L.; Sanchez, V.; Ericsson, P.G.; et al. Genomic Profiling of ER+ Breast Cancers after Short-Term Estrogen Suppression Reveals Alterations Associated with Endocrine Resistance. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, U.; Cohen, O.; Kapstad, C.; Cuoco, M.S.; Waks, A.G.; Wander, S.A.; Painter, C.; Freeman, S.; Persky, N.S.; Marini, L.; et al. Acquired HER2 Mutations in ER + Metastatic Breast Cancer Confer Resistance to Estrogen Receptor–Directed Therapies. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, P.S.H.; Kim, E.; Pon, C.K.; Gill, A.J.; Moore, K.; Spillane, A.J.; Benn, D.E.; Baxter, R.C. Breast Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Induce Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brechbuhl, H.M.; Finlay-Schultz, J.; Yamamoto, T.M.; Gillen, A.E.; Cittelly, D.M.; Tan, A.C.; Sams, S.B.; Pillai, M.M.; Elias, A.D.; Robinson, W.A.; et al. Fibroblast Subtypes Regulate Responsiveness of Luminal Breast Cancer to Estrogen. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehanno, C.; Fernandez-Calero, T.; Habauzit, D.; Avner, S.; Percevault, F.; Jullion, E.; Le Goff, P.; Coissieux, M.M.; Muenst, S.; Marin, M.; et al. Nuclear Accumulation of MKL1 in Luminal Breast Cancer Cells Impairs Genomic Activity of ERα and Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, M.Y.; Powis, G. Passing the Baton: The HIF Switch. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P.; Hockel, M.; Mayer, A. Detection and Characterization of Tumor Hypoxia Using PO2 Histography. Antioxid Redox Signal 2007, 9, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The Role of Hypoxia in Cancer Progression, Angiogenesis, Metastasis, and Resistance to Therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Review Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Physiology and Medicine. Cell 2012, 148, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chang, G.W.; Clifford, S.C.; Vaux, E.C.; Cockman, M.E.; Wykoff, C.C.; Pugh, C.W.; Maher, E.R.; Ratcliffe, P.J. The Tumour Suppressor Protein VHL Targets Hypoxia-Inducible Factors for Oxygen-Dependent Proteolysis. Nature 1999, 399, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schito, L.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors: Master Regulators of Cancer Progression. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurebayashi, J.; Otsuki, T.; Moriya, T.; Sonoo, H. Hypoxia Reduces Hormone Responsiveness of Human Breast Cancer Cells. JPN J. Cancer Res. 2001, 92, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.; Park, C.; Lee, Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha Represses the Transcription of the Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y. Cobalt Chloride-Induced Estrogen Receptor Alpha down-Regulation Involves Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifeddine, R.; Dreiem, A.; Tomkiewicz, C.; Fulchignoni-Lataud, M.C.; Brito, I.; Danan, J.L.; Favaudon, V.; Barouki, R.; Massaad-Massade, L. Hypoxia and Estrogen Co-Operate to Regulate Gene Expression in T-47D Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 104, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; AlTahan, A.; Jones, D.T.; Buffa, F.M.; Bridges, E.; Interiano, R.B.; Qu, C.; Vogt, N.; Li, J.-L.; Baban, D.; et al. Estrogen Receptor-α Directly Regulates the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Pathway Associated with Antiestrogen Response in Breast Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15172–15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habauzit, D.; Le Quément, C.; Zhadobov, M.; Martin, C.; Aubry, M.; Sauleau, R.; Le Dréan, Y. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Contribution of Thermal and the Specific Effects in Cellular Response to Millimeter Wave Exposure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintin, J.; Le Peron, C.; Palierne, G.; Bizot, M.; Cunha, S.; Serandour, A.A.; Avner, S.; Henry, C.; Percevault, F.; Belaud-Rotureau, M.-A.; et al. Dynamic Estrogen Receptor Interactomes Control Estrogen-Responsive Trefoil Factor (TFF) Locus Cell-Specific Activities. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 2418–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, T.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.S. Identifying ChIP-Seq Enrichment Using MACS. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sérandour, A.A.; Avner, S.; Oger, F.; Bizot, M.; Percevault, F.; Lucchetti-Miganeh, C.; Palierne, G.; Gheeraert, C.; Barloy-Hubler, F.; Péron, C.L.; et al. Dynamic Hydroxymethylation of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Marks Differentiation-Associated Enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8255–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ortiz, J.A.; Taing, L.; Meyer, C.A.; Lee, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shin, H.; Wong, S.S.; Ma, J.; Lei, Y.; et al. Cistrome: An Integrative Platform for Transcriptional Regulation Studies. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, C.Y.; Bristor, D.; Hiller, M.; Clarke, S.L.; Schaar, B.T.; Lowe, C.B.; Wenger, A.M.; Bejerano, G. GREAT Improves Functional Interpretation of Cis-Regulatory Regions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmel, F.; Primig, M. The Annotation, Mapping, Expression and Network (AMEN) Suite of Tools for Molecular Systems Biology. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métivier, R.; Penot, G.; Hübner, M.R.; Reid, G.; Brand, H.; Koš, M.; Gannon, F. Estrogen Receptor-α Directs Ordered, Cyclical, and Combinatorial Recruitment of Cofactors on a Natural Target Promoter. Cell 2003, 115, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, D.R.; Blancher, C.; Copley, R.R.; Pollard, P.J.; Gleadle, J.M.; Ragousis, J.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Genome-Wide Association of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1a and HIF-2a DNA Binding with Expression Profiling of Hypoxia-Inducible Transcripts. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 16767–16775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, C.; Shah, S.P.; Chin, S.F.; Turashvili, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Dunning, M.J.; Speed, D.; Lynch, A.G.; Samarajiwa, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. The Genomic and Transcriptomic Architecture of 2000 Breast Tumours Reveals Novel Subgroups. Nature 2012, 486, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Györffy, B.; Lanczky, A.; Eklund, A.C.; Denkert, C.; Budczies, J.; Li, Q.; Szallasi, Z. An Online Survival Analysis Tool to Rapidly Assess the Effect of 22,277 Genes on Breast Cancer Prognosis Using Microarray Data of 1809 Patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xie, X.; Ye, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, Z.; Yan, S.M.; Yang, L.; Kong, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Regulated FGFR4 Attenuates Ferroptotic Cell Death in Recalcitrant HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardia, A.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Loirat, D.; Punie, K.; Oliveira, M.; Brufsky, A.; Sardesai, S.D.; Kalinsky, K.; Zelnak, A.B.; et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, R.; Tyson, J.J.; Dixon, J.M. Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer—An Overview and Update. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palafox, M.; Monserrat, L.; Bellet, M.; Villacampa, G.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Oliveira, M.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Ibrahimi, N.; Kannan, S.; Mina, L.; et al. High P16 Expression and Heterozygous RB1 Loss Are Biomarkers for CDK4/6 Inhibitor Resistance in ER+ Breast Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiehl, D.P.; Bordoli, M.R.; Abreu-Rodríguez, I.; Wollenick, K.; Schraml, P.; Gradin, K.; Poellinger, L.; Kristiansen, G.; Wenger, R.H. Non-Canonical HIF-2α Function Drives Autonomous Breast Cancer Cell Growth via an AREG-EGFR/ErbB4 Autocrine Loop. Oncogene 2011, 31, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, N.; Xue, Z.; Liu, L.R.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Xie, X.; Zou, Y.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. Synergistic Therapeutic Effect of Combined PDGFR and SGK1 Inhibition in Metastasis-Initiating Cells of Breast Cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2066–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.P.; Chan, T.E.; Lombardo, Y.; Corleone, G.; Rotmensz, N.; Bravaccini, S.; Rocca, A.; Pruneri, G.; McEwen, K.R.; Coombes, R.C.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals Multi-Step Adaptations to Endocrine Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, S.; Rao, S.V.; Sutton, J.; Cheeseman, D.; Dunn, S.; Papachristou, E.K.; Prada, J.E.G.; Couturier, D.L.; Kumar, S.; Kishore, K.; et al. ARID1A Influences HDAC1/BRD4 Activity, Intrinsic Proliferative Capacity and Breast Cancer Treatment Response. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 87–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-Z.; Xia, L.; Hu, G.-S.; Liu, J.-Y.; Hu, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Peng, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.-J.; Liu, W. Super-Enhancer-Controlled Positive Feedback Loop BRD4/ERα-RET-ERα Promotes ERα-Positive Breast Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, gkac778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, J.A.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Vander Steen, T.; Cuyàs, E.; Oza-Gajera, B.P.; Verdura, S.; Espinoza, I.; Vellon, L.; Mehmi, I.; Lupu, R. Fatty Acid Synthase Confers Tamoxifen Resistance to Er+/Her2+ Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padró, M.; Louie, R.J.; Lananna, B.V.; Krieg, A.J.; Timmerman, L.A.; Chan, D.A. Genome-Independent Hypoxic Repression of Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Breast Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Yoshida, M.; Jimbo, K.; Asaga, S.; Takayama, S.; Tsuda, H. Prognostic Impact of Discordance in Hormone Receptor Status Between Primary and Recurrent Sites in Patients With Recurrent Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2016, 16, e133–e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Lee, S.J.; Yoon, M.H.; Ha, N.C.; Park, B.J. Estrogen Receptor ?? Is a Novel Target of the Von Hippel-Lindau Protein and Is Responsible for the Proliferation of VHL-Deficient Cells under Hypoxic Conditions. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4462–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alam, M.W.; Persson, C.U.; Reinbothe, S.; Kazi, J.U.; Wigerup, C.; Ditzel, H.J.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E.; Jögi, A. HIF2α Contributes to Antiestrogen Resistance via Positive Bilateral Crosstalk with EGFR in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11238–11250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Hong, Q.; Lei, L.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Mo, M.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, J.; et al. Basal and Therapy-Driven Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Confers Resistance to Endocrine Therapy in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8648–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Searfoss, G.; Krolikowski, D.; Pagnoni, M.; Franks, C.; Clark, K.; Yu, K.T.; Jaye, M.; Ivashchenko, Y. Hypoxia Induces the Expression of the Pro-Apoptotic Gene BNIP3. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Lai, Y.P.; Chen, T.S.; Marthandam Asokan, S.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, K.H.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y. Hypoxia Suppresses Myocardial Survival Pathway through HIF-1α-IGFBP-3-Dependent Signaling and Enhances Cardiomyocyte Autophagic and Apoptotic Effects Mainly via FoxO3a-Induced BNIP3 Expression. Growth Factors 2016, 34, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, N.; Hadden, T.J.; Rishi, A.K. Akt, FoxO and Regulation of Apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade Harper, J.; Adami, G.R.; Wei, N.; Keyomarsi, K.; Elledge, S.J. The P21 Cdk-Interacting Protein Cip1 Is a Potent Inhibitor of G1 Cyclin-Dependent Kinases. Cell 1993, 75, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Tong, T.; Fan, W.; Fan, F.; Antinore, M.J.; Zhu, X.; Mazzacurati, L.; Li, X.; Petrik, K.L.; Rajasekaran, B.; et al. GADD45-Induced Cell Cycle G2-M Arrest Associates with Altered Subcellular Distribution of Cyclin B1 and Is Independent of P38 Kinase Activity. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8696–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Conza, G.; Trusso Cafarello, S.; Loroch, S.; Mennerich, D.; Deschoemaeker, S.; Di Matteo, M.; Ehling, M.; Gevaert, K.; Prenen, H.; Zahedi, R.P.; et al. The MTOR and PP2A Pathways Regulate PHD2 Phosphorylation to Fine-Tune HIF1?? Levels and Colorectal Cancer Cell Survival under Hypoxia. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E.; Braunstein, S.; Formenti, S.; Schneider, R.J. Hypoxia Inhibits Protein Synthesis through a 4E-BP1 and Elongation Factor 2 Kinase Pathway Controlled by MTOR and Uncoupled in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3955–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Bhowmick, N.; Qu, Y.; Chung, S.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cui, X. FOXC1: An Emerging Marker and Therapeutic Target for Cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3957–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Qiu, L.; Hong, Y.; Karnik, T.; Tadros, G.; Mau, B.; Ma, T.; Mu, Y.; New, J.; Louie, R.J.; et al. The Histone Demethylase KDM4B Regulates Peritoneal Seeding of Ovarian Cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. KDM4B Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through up-Regulation of ZEB1 in Pancreatic Cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2015, 47, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Moons, L.; Luttun, A.; Vincenti, V.; Compernolle, V.; de Mol, M.; Wu, Y.; Bono, F.; Devy, L.; Beck, H.; et al. Synergism between Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Placental Growth Factor Contributes to Angiogenesis and Plasma Extravasation in Pathological Conditions. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coradini, D.; Pellizzaro, C.; Speranza, A.; Daidone, M.G. Hypoxia and Estrogen Receptor Profile Influence the Responsiveness of Human Breast Cancer Cells to Estradiol and Antiestrogens. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallah, J.; Rini, B.I. HIF Inhibitors: Status of Current Clinical Development. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupien, M.; Meyer, C.A.; Bailey, S.T.; Eeckhoute, J.; Cook, J.; Westerling, T.; Zhang, X.; Carroll, J.S.; Rhodes, D.R.; Liu, X.S.; et al. Growth Factor Stimulation Induces a Distinct ER(Alpha) Cistrome Underlying Breast Cancer Endocrine Resistance. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross-Innes, C.S.; Stark, R.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Holmes, K.A.; Ali, H.R.; Dunning, M.J.; Brown, G.D.; Gojis, O.; Ellis, I.O.; Green, A.R.; et al. Differential Oestrogen Receptor Binding Is Associated with Clinical Outcome in Breast Cancer. Nature 2012, 481, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jehanno, C.; Le Goff, P.; Habauzit, D.; Le Page, Y.; Lecomte, S.; Lecluze, E.; Percevault, F.; Avner, S.; Métivier, R.; Michel, D.; et al. Hypoxia and ERα Transcriptional Crosstalk Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194934
Jehanno C, Le Goff P, Habauzit D, Le Page Y, Lecomte S, Lecluze E, Percevault F, Avner S, Métivier R, Michel D, et al. Hypoxia and ERα Transcriptional Crosstalk Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194934
Chicago/Turabian StyleJehanno, Charly, Pascale Le Goff, Denis Habauzit, Yann Le Page, Sylvain Lecomte, Estelle Lecluze, Frédéric Percevault, Stéphane Avner, Raphaël Métivier, Denis Michel, and et al. 2022. "Hypoxia and ERα Transcriptional Crosstalk Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194934
APA StyleJehanno, C., Le Goff, P., Habauzit, D., Le Page, Y., Lecomte, S., Lecluze, E., Percevault, F., Avner, S., Métivier, R., Michel, D., & Flouriot, G. (2022). Hypoxia and ERα Transcriptional Crosstalk Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 14(19), 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194934




