Assessment of the Molecular Heterogeneity of E-Cadherin Expression in Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cases and Histological Review
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Macrodissection and DNA Extraction
2.4. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.4.1. Library Construction
2.4.2. Alignment and QC
2.4.3. Variant Calling
2.4.4. MuTect2 Pipeline
2.4.5. Strelka2 Pipeline
2.4.6. MuSE Pipeline
2.4.7. Annotations of Variants
2.4.8. Selecting High Confidence Calls
2.4.9. Post Hoc Variant Filtering
- (1)
- Remove multiallelic sites;
- (2)
- Exclude common variants with prevalence >1% in gnomAD database;
- (3)
- Remove variants with tumour allele frequency <0.01;
- (4)
- Filter for variants with depth <10 in both tumour and matched normal sample;
- (5)
- Keep variants with reads supporting alternate allele in tumour sample ≥ 5 and reads supporting the alternative allele in matched normal sample ≤ 2;
- (6)
- Remove synonymous variants.
2.4.10. Identification of Recurrent Mutations
2.4.11. Tumour Subclonal Deconvolution
2.4.12. Copy Number Analysis
2.4.13. Single-Base Substitutions (SBS) Signature Analysis
2.5. DNA Methylation Pre-Processing and Analysis
2.6. Data Availability
3. Results
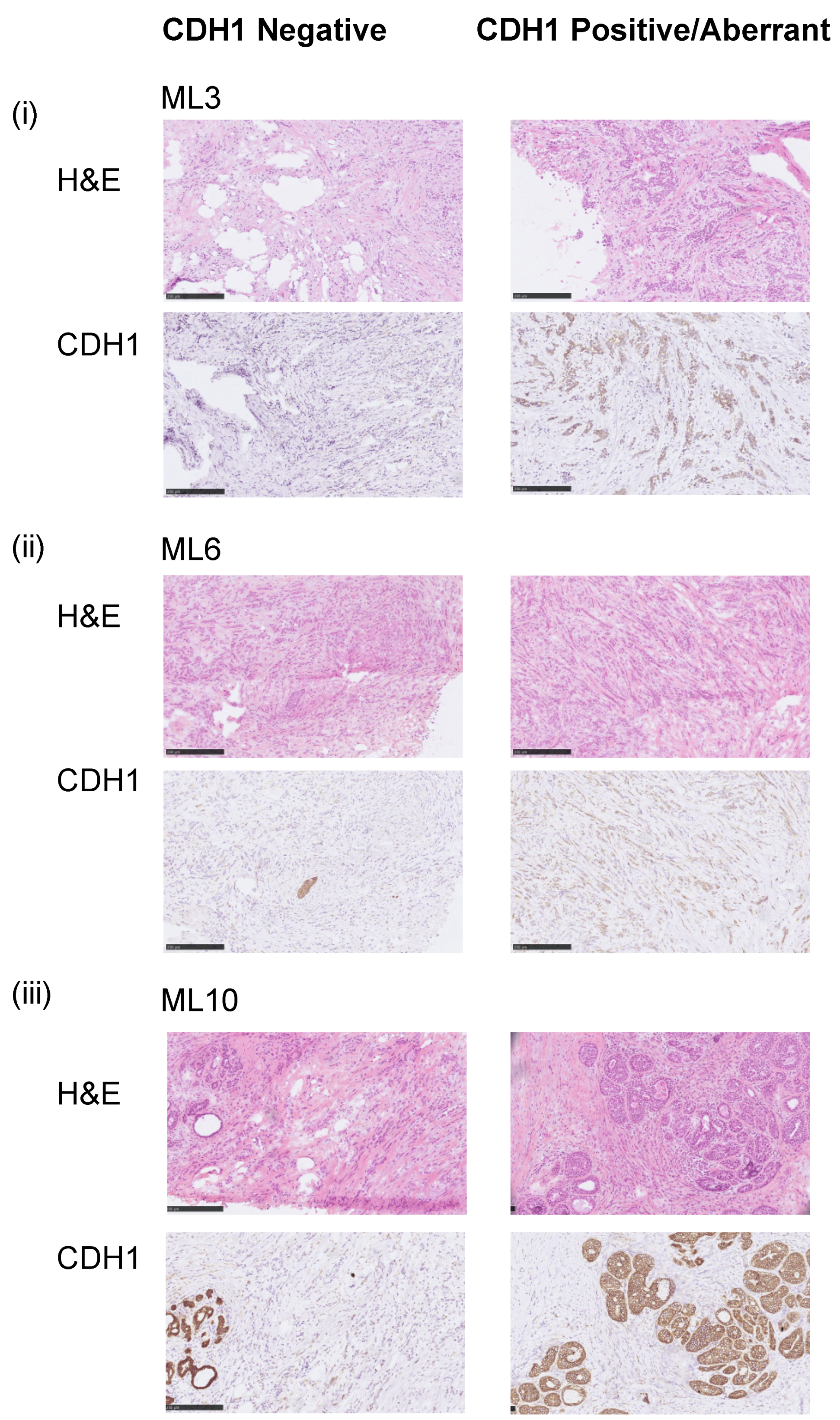
3.1. Assessment of the E-Cadherin Pathway in E-Cadherin Negative and Aberrant/Positive Components of E-Cadherin Heterogeneous Breast Cancers
3.2. E-Cadherin Negative and Aberrant Components of EcadhetILC Are Clonally Related
3.3. E-Cadherin Negative and Aberrant/Positive Components of E-Cadherin Heterogeneous Breast Cancers Show Similar Driver Alterations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Kalinowski, L.; Simpson, P.T.; Lakhani, S.R. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: The increasing importance of this special subtype. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Lakhani, S.R.; Simpson, P.T. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Morphology, biomarkers and omics. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestalozzi, B.C.; Zahrieh, D.; Mallon, E.; Gusterson, B.A.; Price, K.N.; Gelber, R.D.; Holmberg, S.B.; Lindtner, J.; Snyder, R.; Thurlimann, B.; et al. Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: Combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3006–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luveta, J.; Parks, R.M.; Heery, D.M.; Cheung, K.L.; Johnston, S.J. Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer as a Distinct Disease: Implications for Therapeutic Strategy. Oncol. Ther. 2020, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Lv, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Yi, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: A special histological type compared with invasive ductal carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriello, G.; Gatza, M.L.; Beck, A.H.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Rhie, S.K.; Pastore, A.; Zhang, H.; McLellan, M.; Yau, C.; Kandoth, C.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Droufakou, S.; Deshmane, V.; Roylance, R.; Hanby, A.; Tomlinson, I.; Hart, I.R. Multiple ways of silencing E-cadherin gene expression in lobular carcinoma of the breast. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarrio, D.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hardisson, D.; Sanchez-Estevez, C.; Guo, M.; Herman, J.G.; Gamallo, C.; Esteller, M.; Palacios, J. Epigenetic and genetic alterations of APC and CDH1 genes in lobular breast cancer: Relationships with abnormal E-cadherin and catenin expression and microsatellite instability. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Nones, K.; Saunus, J.M.; Da Silva, L.; Newell, F.; Kazakoff, S.; Melville, L.; Jayanthan, J.; Vargas, A.C.; et al. Mixed ductal-lobular carcinomas: Evidence for progression from ductal to lobular morphology. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrajan, R.; Lambros, M.B.; Geyer, F.C.; Marchio, C.; Tan, D.S.; Vatcheva, R.; Shiu, K.K.; Hungermann, D.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Palacios, J.; et al. Loss of 16q in high grade breast cancer is associated with estrogen receptor status: Evidence for progression in tumors with a luminal phenotype? Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbs, D.J.; Bhargava, R.; Chivukula, M. Lobular versus ductal breast neoplasms: The diagnostic utility of p120 catenin. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schackmann, R.C.; van Amersfoort, M.; Haarhuis, J.H.; Vlug, E.J.; Halim, V.A.; Roodhart, J.M.; Vermaat, J.S.; Voest, E.E.; van der Groep, P.; van Diest, P.J.; et al. Cytosolic p120-catenin regulates growth of metastatic lobular carcinoma through Rock1-mediated anoikis resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3176–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbs, D.J.; Schnitt, S.J.; Geyer, F.C.; Weigelt, B.; Baehner, F.L.; Decker, T.; Eusebi, V.; Fox, S.B.; Ichihara, S.; Lakhani, S.R.; et al. Lobular neoplasia of the breast revisited with emphasis on the role of E-cadherin immunohistochemistry. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, L.; Parry, S.; Reid, L.; Keith, P.; Waddell, N.; Kossai, M.; Clarke, C.; Lakhani, S.R.; Simpson, P.T. Aberrant expression of E-cadherin in lobular carcinomas of the breast. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.H.; Ellis, I.; Allison, K.; Brogi, E.; Fox, S.B.; Lakhani, S.; Lazar, A.J.; Morris, E.A.; Sahin, A.; Salgado, R.; et al. The 2019 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the breast. Histopathology 2020, 77, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajrami, I.; Marlow, R.; van de Ven, M.; Brough, R.; Pemberton, H.N.; Frankum, J.; Song, F.; Rafiq, R.; Konde, A.; Krastev, D.B.; et al. E-Cadherin/ROS1 Inhibitor Synthetic Lethality in Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 498–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piscuoglio, S.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Geyer, F.C.; Burke, K.A.; Cowell, C.F.; Martelotto, L.G.; Natrajan, R.; Popova, T.; Maher, C.A.; Lim, R.S.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic heterogeneity in metaplastic carcinomas of the breast. NPJ Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscuoglio, S.; Ng, C.K.; Martelotto, L.G.; Eberle, C.A.; Cowell, C.F.; Natrajan, R.; Bidard, F.C.; De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Wilkerson, P.M.; Mariani, O.; et al. Integrative genomic and transcriptomic characterization of papillary carcinomas of the breast. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1588–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Fan, G.; Luo, Y.; Sun, S.; Han, P.; Wu, Q.; et al. Comparative analysis of clonal evolution among patients with right- and left-sided colon and rectal cancer. iScience 2021, 24, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostin, D.; Kulemin, N.; Naumov, V.; Belova, V.; Kwon, D.; Gorbachev, A. Comparative analysis of novel MGISEQ-2000 sequencing platform vs Illumina HiSeq 2500 for whole-genome sequencing. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cibulskis, K.; Lawrence, M.S.; Carter, S.L.; Sivachenko, A.; Jaffe, D.; Sougnez, C.; Gabriel, S.; Meyerson, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Scheffler, K.; Halpern, A.L.; Bekritsky, M.A.; Noh, E.; Kallberg, M.; Chen, X.; Kim, Y.; Beyter, D.; Krusche, P.; et al. Strelka2: Fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xi, L.; Hughes, D.S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Futreal, P.A.; Wheeler, D.A.; Wang, W. MuSE: Accounting for tumor heterogeneity using a sample-specific error model improves sensitivity and specificity in mutation calling from sequencing data. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Schulz-Trieglaff, O.; Shaw, R.; Barnes, B.; Schlesinger, F.; Kallberg, M.; Cox, A.J.; Kruglyak, S.; Saunders, C.T. Manta: Rapid detection of structural variants and indels for germline and cancer sequencing applications. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1220–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolchik, D.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Sugnet, C.W.; Haussler, D.; Kent, W.J. The UCSC Table Browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq): A curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D61–D65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caravagna, G.; Heide, T.; Williams, M.J.; Zapata, L.; Nichol, D.; Chkhaidze, K.; Cross, W.; Cresswell, G.D.; Werner, B.; Acar, A.; et al. Subclonal reconstruction of tumors by using machine learning and population genetics. Nat. Genet 2020, 52, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, K.M.; Van Loo, P.; Wedge, D.C.; Jones, D.; Menzies, A.; Butler, A.P.; Teague, J.W.; Tarpey, P.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Campbell, P.J. ascatNgs: Identifying Somatically Acquired Copy-Number Alterations from Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 56, 15.9. 1–15.9. 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favero, F.; Joshi, T.; Marquard, A.M.; Birkbak, N.J.; Krzystanek, M.; Li, Q.; Szallasi, Z.; Eklund, A.C. Sequenza: Allele-specific copy number and mutation profiles from tumor sequencing data. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maksimovic, J.; Phipson, B.; Oshlack, A. A cross-package Bioconductor workflow for analysing methylation array data. F1000Res 2016, 5, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidsley, R.; Zotenko, E.; Peters, T.J.; Lawrence, M.G.; Risbridger, G.P.; Molloy, P.; Van Djik, S.; Muhlhausler, B.; Stirzaker, C.; Clark, S.J. Critical evaluation of the Illumina MethylationEPIC BeadChip microarray for whole-genome DNA methylation profiling. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Groot, J.S.; Ratze, M.A.; van Amersfoort, M.; Eisemann, T.; Vlug, E.J.; Niklaas, M.T.; Chin, S.F.; Caldas, C.; van Diest, P.J.; Jonkers, J.; et al. alphaE-catenin is a candidate tumor suppressor for the development of E-cadherin-expressing lobular-type breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2018, 245, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Davies, H.; Staaf, J.; Ramakrishna, M.; Glodzik, D.; Zou, X.; Martincorena, I.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Martin, S.; Wedge, D.C.; et al. Landscape of somatic mutations in 560 breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature 2016, 534, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Greenman, C.D.; Raine, K.; Jones, D.; Hinton, J.; Marshall, J.; Stebbings, L.A.; et al. Mutational processes molding the genomes of 21 breast cancers. Cell 2012, 149, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Petljak, M.; Butler, A.P.; Bolli, N.; Davies, H.R.; Knappskog, S.; Martin, S.; Papaemmanuil, E.; et al. Association of a germline copy number polymorphism of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B with burden of putative APOBEC-dependent mutations in breast cancer. Nat. Genet 2014, 46, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andre, F.; Ciruelos, E.M.; Juric, D.; Loibl, S.; Campone, M.; Mayer, I.A.; Rubovszky, G.; Yamashita, T.; Kaufman, B.; Lu, Y.S.; et al. Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: Final overall survival results from SOLAR-1. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leo, A.; Johnston, S.; Lee, K.S.; Ciruelos, E.; Lonning, P.E.; Janni, W.; O’Regan, R.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Kalev, D.; Egle, D.; et al. Buparlisib plus fulvestrant in postmenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer progressing on or after mTOR inhibition (BELLE-3): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexander, J.; Mariani, O.; Meaudre, C.; Fuhrmann, L.; Xiao, H.; Naidoo, K.; Gillespie, A.; Roxanis, I.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Haider, S.; et al. Assessment of the Molecular Heterogeneity of E-Cadherin Expression in Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020295
Alexander J, Mariani O, Meaudre C, Fuhrmann L, Xiao H, Naidoo K, Gillespie A, Roxanis I, Vincent-Salomon A, Haider S, et al. Assessment of the Molecular Heterogeneity of E-Cadherin Expression in Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(2):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020295
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexander, John, Odette Mariani, Celine Meaudre, Laetitia Fuhrmann, Hui Xiao, Kalnisha Naidoo, Andrea Gillespie, Ioannis Roxanis, Anne Vincent-Salomon, Syed Haider, and et al. 2022. "Assessment of the Molecular Heterogeneity of E-Cadherin Expression in Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 2: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020295
APA StyleAlexander, J., Mariani, O., Meaudre, C., Fuhrmann, L., Xiao, H., Naidoo, K., Gillespie, A., Roxanis, I., Vincent-Salomon, A., Haider, S., & Natrajan, R. (2022). Assessment of the Molecular Heterogeneity of E-Cadherin Expression in Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. Cancers, 14(2), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020295





