Identification of EGFR-Related LINC00460/mir-338-3p/MCM4 Regulatory Axis as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Preparation and Processing
2.2. Identify Different Expression RNAs in LUAD
2.3. Construction of ceRNA Network
2.4. Survival Analysis
2.5. Total RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining and Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Enrichment Analysis and Interaction Network
2.8. Mutation Analysis
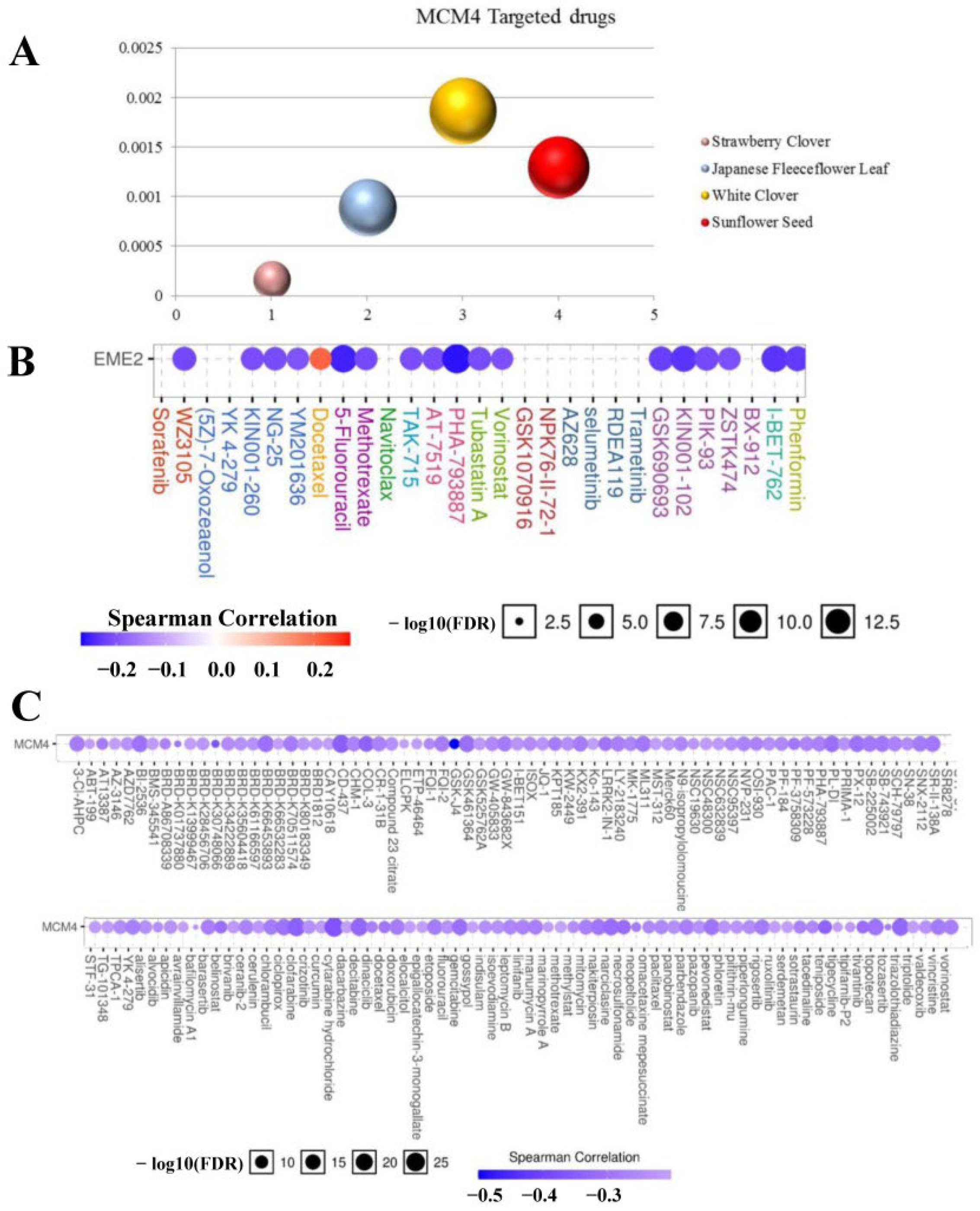
2.9. Targeted Drug Analysis of MCM4
2.10. Immune Correlates
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression and Prognostic Value of EGFR in LUAD
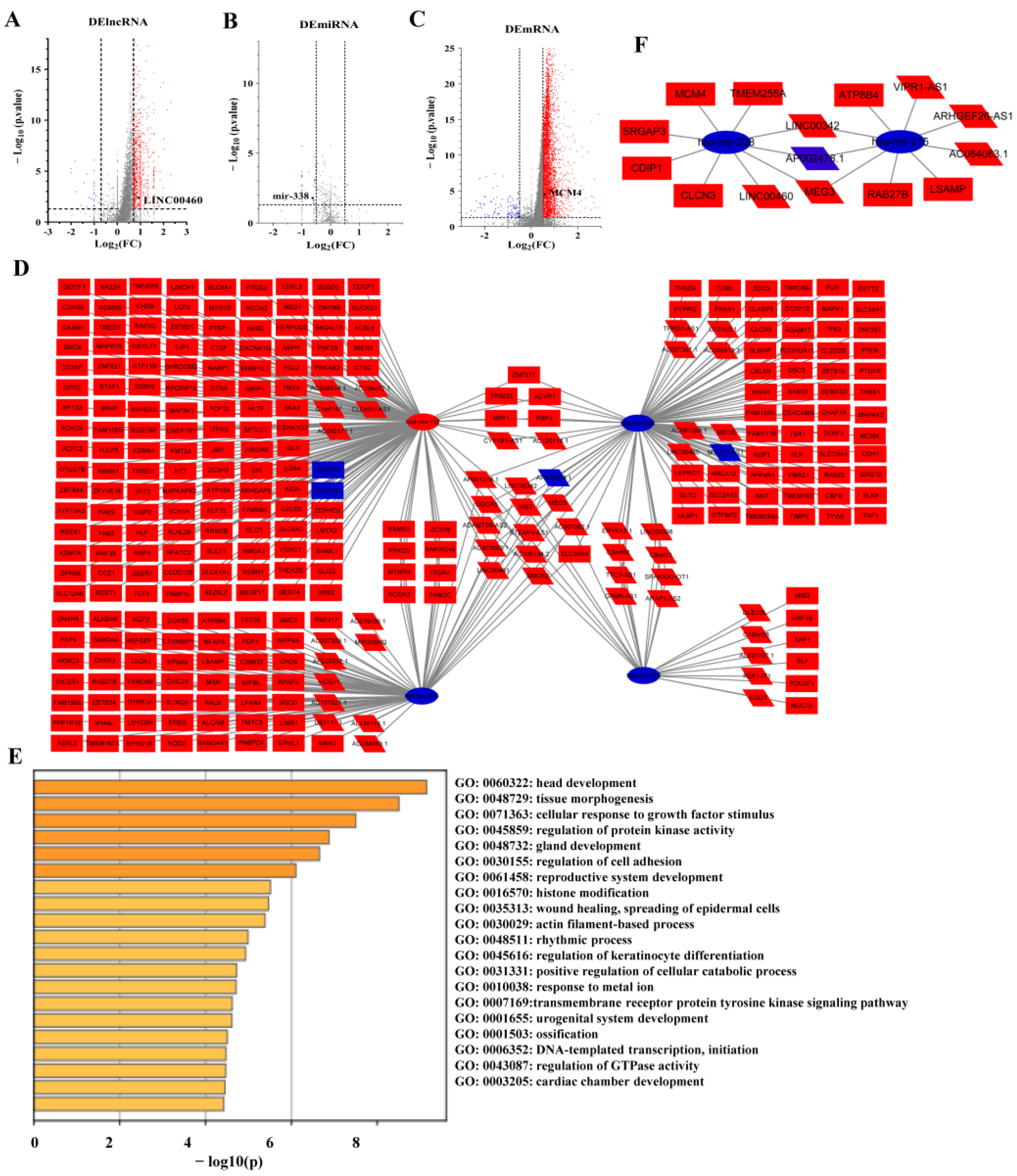
3.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
3.3. ceRNA Regulatory Network
3.4. Construction of a ceRNA Network Model with LUAD Prognostic Specificity
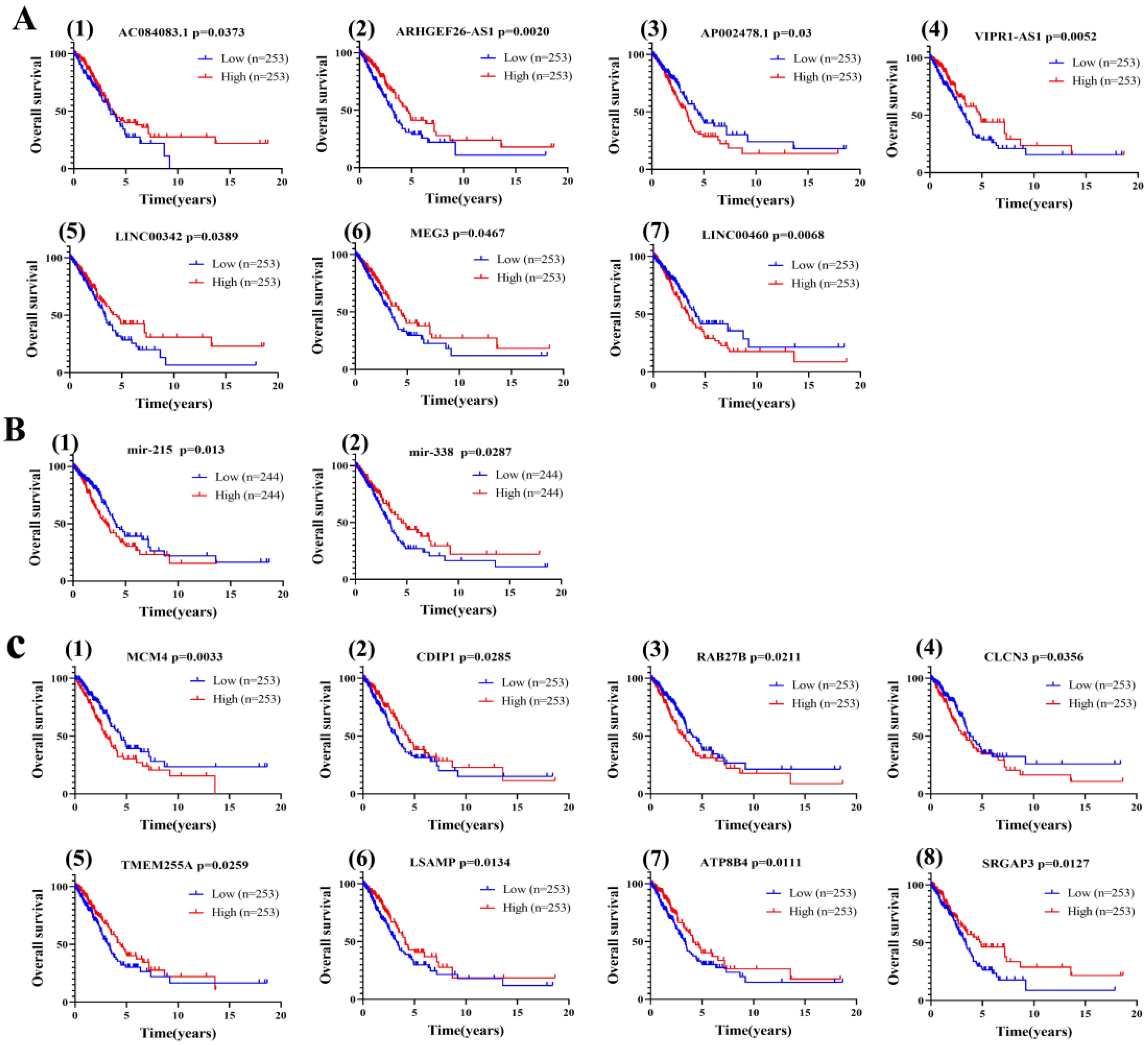
3.5. Effect of Different Expression Patterns of LINC00460-mir-338-3p-MCM4 Axis on OS of LUAD
3.6. Clinical Relevance of LINC00460/MCM4 Axis in LUAD Patients
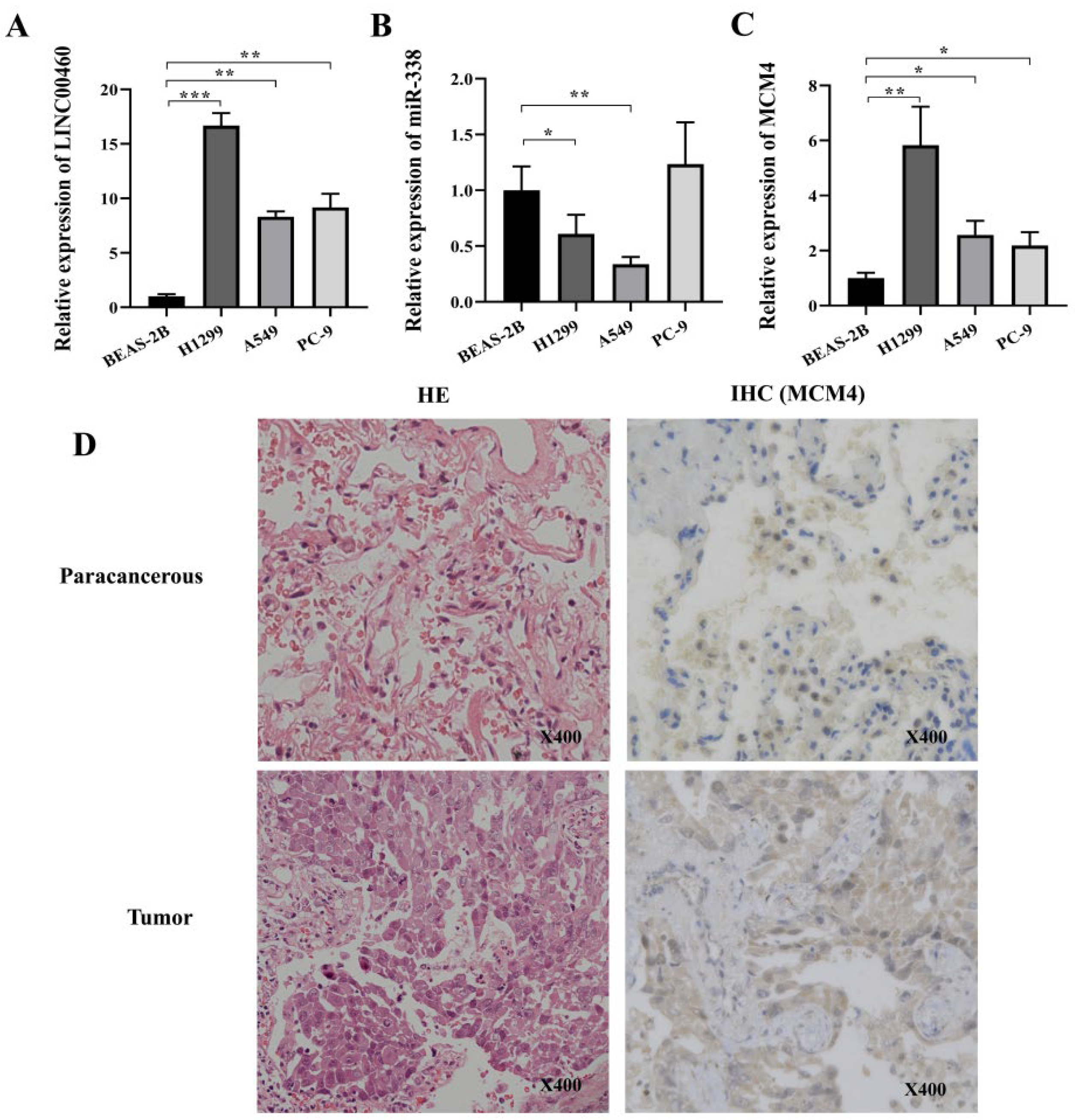
3.7. Validation of LINC00460/MCM4 Axis Expression Levels
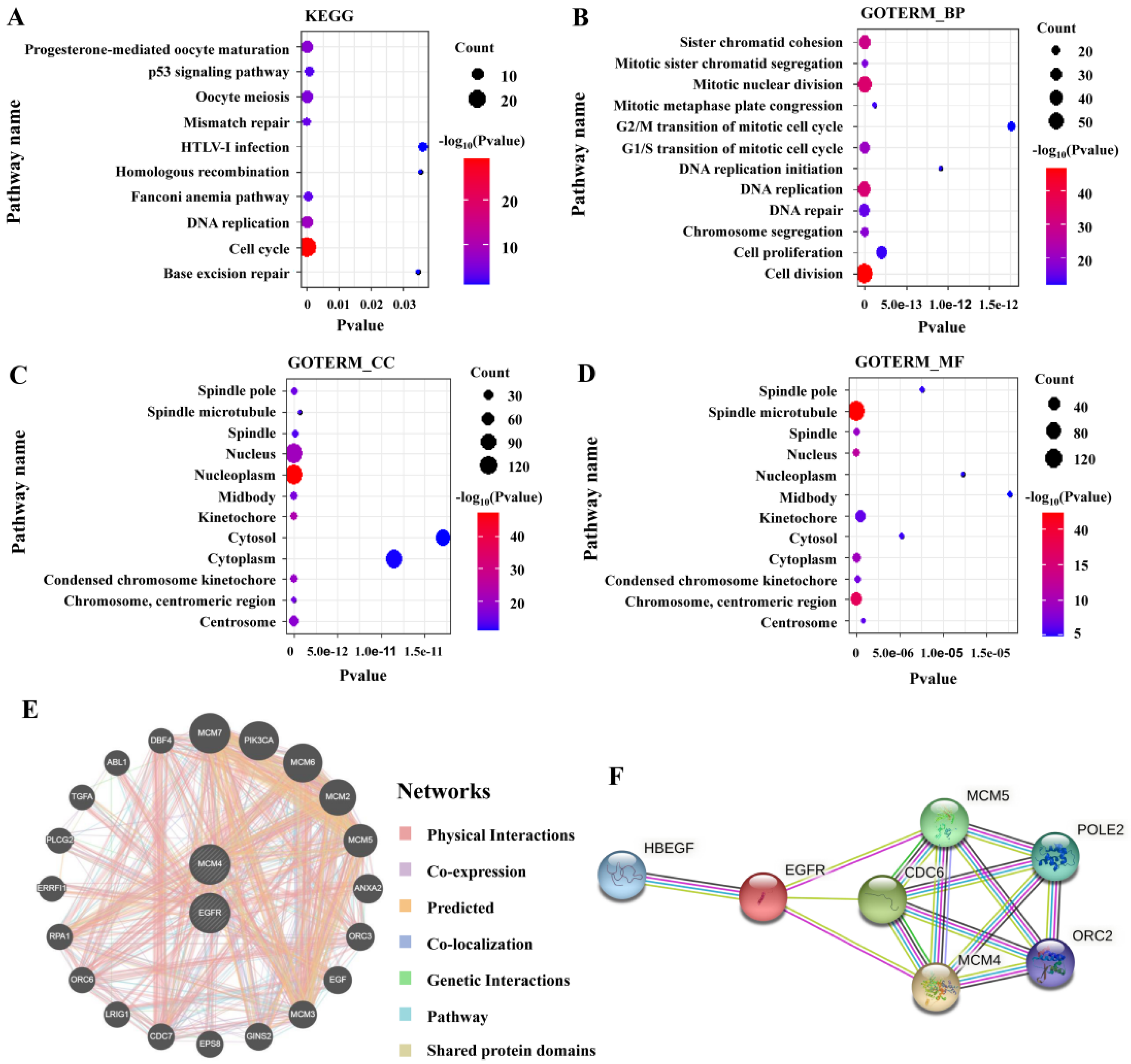
3.8. Enrichment Analysis and Interaction Network of MCM4-Related Genes
3.9. Potential Drugs Targeting MCM4
3.10. Correlation between Immune Infiltration and Expression of MCM4 in LUAD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Pang, Z.; Li, G.; Gu, T. Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Graeff, P.; Crijns, A.P.G.; De Jong, S.; Boezen, M.; Post, W.J.; De Vries, E.G.E.; Van Der Zee, A.G.J.; De Bock, G.H. Modest effect of p53, EGFR and HER-2/neu on prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, D.; Sun, L. High levels of EGFR expression in tumor stroma are associated with aggressive clinical features in epithelial ovarian cancer. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2016, 9, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takada, K.; Toyokawa, G.; Tagawa, T.; Kohashi, K.; Shimokawa, M.; Akamine, T.; Takamori, S.; Hirai, F.; Shoji, F.; Okamoto, T.; et al. PD-L1 expression according to the EGFR status in primary lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2018, 116, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gately, K.; Forde, L.; Cuffe, S.; Cummins, R.; Kay, E.W.; Feuerhake, F.; O’Byrne, K.J. High coexpression of both EGFR and IGF1R correlates with poor patient prognosis in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaggi, G.; Novello, S.; Torri, V.; Leonardo, E.; De Giuli, P.; Borasio, P.; Mossetti, C.; Ardissone, F.; Lausi, P.; Scagliotti, G.V. Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression correlates with a poor prognosis in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Yang, J.C.H.; Mok, T.S.; Loong, H.H. Overview of current systemic management of EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i3–i9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G.; Shih, J.Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, R.F.; Zhu, M.L.; Liu, M.M.; Xu, Y.T.; Yuan, L.L.; Bian, J.; Xia, Y.Z.; Kong, L.Y. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: From molecular mechanisms to clinical research. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.R.; Jänne, P.A. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, S.; He, Z.; Chen, T.; Guo, X.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, J. Long noncoding RNA 00976 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through OTUD7B by sponging miR-137 involving EGFR/MAPK pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; You, Z.; Yin, Y.; Liu, L.; Kang, Y.; Li, S.; Ning, S.; Li, H.; Gong, Y.; et al. LncRNA TINCR favors tumorigenesis via STAT3–TINCR–EGFR-feedback loop by recruiting DNMT1 and acting as a competing endogenous RNA in human breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.D.; Ren, X.; Cai, M.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.M. Long non-coding RNAs: An emerging powerhouse in the battle between life and death of tumor cells. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 26, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Z.; Xu, F.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, X.; McDonald, J.M.; Chen, Y. The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances pancreatic cancer resistance to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10390–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui, H.; Al-Ghafari, A.; Choudhry, H.; Al Doghaither, H. Roles of long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer tumorigenesis: A review. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, B.; Sun, L.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, C. Competitive Endogenous RNA (ceRNA) Regulation Network of lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA in Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of Aberrantly Expressed ceRNA network in gastric cancer with and without H.pylori infection. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Song, S.; Yang, H.; Han, F.; Liu, F.; Hu, Y. Long intergenic non-coding LINC00657 regulates tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-190a-3p. Aging 2019, 11, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, M.; Ying, X.; Li, B.; Cao, F.; Cheng, S.; Xiao, B.; Cheng, M.; Liang, L.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of PTEN-related ceRNA network revealing the key pathways WDFY3-AS2-miR-21-5p/miR-221-3p/miR-222-3p-TIMP3 as potential biomarker in tumorigenesis and prognosis of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2022, 61, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Jie, W. ZEB1-AS1/miR-133a-3p/LPAR3/EGFR axis promotes the progression of thyroid cancer by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Ding, Z.-B.; Xi, H.P.; Wang, G.W. lncRNA SNHG16 promotes glioma tumorigenicity through miR-373/EGFR axis by activating PI3K/AKT pathway. Genomics 2020, 112, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirker, R.; Pereira, J.R.; Von Pawel, J.; Krzakowski, M.; Ramlau, R.; Park, K.; De Marinis, F.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Paz-Ares, L.; Störkel, S.; et al. EGFR expression as a predictor of survival for first-line chemotherapy plus cetuximab in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Analysis of data from the phase 3 FLEX study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Hirsch, F.R.; Rossi, E.; Bartolini, S.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Bemis, L.; Haney, J.; Witta, S.; Danenberg, K.; Domenichini, I.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Shi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Fu, D.; Bai, J.; Ma, Y. WT1-AS / IGF2BP2 Axis Is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma According to ceRNA Network Comprehensive Analysis Combined with Experiments. Cells 2022, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, L.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Gerding, L.P.; Custers, E.E.M.; Van Den Berg, E.; Jolink, W.M.T.; Schreuder, F.H.B.M.; Küsters, B.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Verbeek, M.M. Disturbed balance in the expression of MMP9 and TIMP3 in cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related intracerebral haemorrhage. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Alexander, R.; Yao, Y.; MacLennan, G.T.; Pan, C.X.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Montironi, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A. The landscape of EGFR pathways and personalized management of non-small-cell lung cancer. Futur. Oncol. 2011, 7, 519–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanno, N.; De Luca, A.; Bianco, C.; Strizzi, L.; Mancino, M.; Maiello, M.R.; Carotenuto, A.; De Feo, G.; Caponigro, F.; Salomon, D.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 2006, 366, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Chu, H.; Yao, Y. Intrinsic resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with activating EGFR mutations. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2016, 9, 3711–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okabe, T.; Okamoto, I.; Tamura, K.; Terashima, M.; Yoshida, T.; Satoh, T.; Takada, M.; Fukuoka, M.; Nakagawa, K. Differential constitutive activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cells bearing EGFR gene mutation and amplification. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlsson, J.; Wester, K.; De La Torre, M.; Malmström, P.U.; Gårdmark, T. EGFR-expression in primary urinary bladder cancer and corresponding metastases and the relation to HER2-expression on the possibility to target these receptors with radionuclides. Radiol. Oncol. 2015, 49, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.R.; Chitale, D.; Riely, G.J.; Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Rusch, V.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. Clinical testing experience and relationship to EGFR gene copy number and immunohistochemical expression. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Sun, D.; Gou, Q.; Ke, X.; Gong, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Zhou, J.K.; Guo, C.; Xia, Z.; Liu, L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA linc00460 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration in lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 420, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, J.; Kinoshita, I.; Shimizu, Y.; Kikuchi, E.; Takeda, K.; Aburatani, H.; Oizumi, S.; Konishi, J.; Kaga, K.; Matsuno, Y.; et al. Minichromosome maintenance (MCM) protein 4 as a marker for proliferation and its clinical and clinicopathological significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 72, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zitello, E.; Guo, R.; Deng, Y. The function of LncRNAs and their role in the prediction, diagnosis, and prognosis of lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhu, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00460 Promotes the Gefitinib Resistance of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Through Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor by Sponging miR-769-5p. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Du, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The regulation of Neuropilin 1 expression by miR-338-3p promotes non-small cell lung cancer via changes in EGFR signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choy, B.; LaLonde, A.; Que, J.; Wu, T.; Zhou, Z. MCM4 and MCM7, potential novel proliferation markers, significantly correlated with Ki-67, Bmi1, and cyclin E expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and precancerous lesions. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 57, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; McCormick, F. The metabolic landscape of RAS-driven cancers from biology to therapy. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigis, K.M. KRAS Alleles: The Devil Is in the Detail. Trends in Cancer 2017, 3, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A.Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C.G.; Koppada, N.; et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2019, 575, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakar, N.; Bowcut, V.; Baer, B.R.; Ballard, J.A.; Michael, R. The KRASG12C Inhibitor, MRTX849, Provides Insight Toward Therapeutic Susceptibility of KRAS Mutant Cancers in Mouse Models and Patients. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, M.R.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.S.; Hansen, R.; Peters, U.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Babbar, A.; Firdaus, S.J.; Darjania, L.; et al. Targeting KRAS Mutant Cancers with a Covalent G12C-Specific Inhibitor. Cell 2018, 172, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factor | Variable | N | LINC00460 Expression (Median) | p-value | MCM4 Expression (Median) | p-Value | Overall Survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Months (Mean) | 95% CI (Mean) | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) | |||||||
| Age | ≥60 | 353 | 20 | 0.889 | 3172 | 0.012 | 24.647 | 22.053–27.241 | 0.143 |
| <60 | 134 | 20 | 3690 | 27.515 | 21.747–33.283 | ||||
| Gender | Male | 226 | 17 | 0.112 | 3921.5 | 0.0006 | 25.814 | 21.824–29.804 | 0.984 |
| Female | 261 | 22 | 3077 | 25.109 | 22.086–28.132 | ||||
| Tumor size (T) | >4 | 91 | 27 | 0.245 | 3455 | 0.1273 | 18.420 | 15.265–21.575 | 0.0007 |
| ≤4 | 393 | 19 | 3383 | 27.110 | 24.181–30.04 | ||||
| Lymph node metastasis (N) | Negative | 313 | 16 | 0.0006 | 3282 | 0.0463 | 27.008 | 23.714–30.303 | <0.0001 |
| Positive | 162 | 35 | 3638 | 22.988 | 19.299–26.676 | ||||
| Unknown | 12 | 20 | 2112.5 | 17.478 | 10.683–24.273 | ||||
| Distant metastasis (M) | Negative | 320 | 23 | 0.119 | 3547.5 | 0.021 | 25.963 | 22.97–28.956 | 0.027 |
| Positive | 23 | 24 | 6456 | 23.494 | 15.296–31.692 | ||||
| Unknown | 144 | 15 | 3157.5 | 24.576 | 19.724–29.428 | ||||
| TNM stage | I–II | 376 | 18 | 0.0468 | 3306.5 | 0.0356 | 26.752 | 23.756–29.747 | <0.0001 |
| III–IV | 104 | 25 | 3755 | 19.856 | 16.506–23.206 | ||||
| Unknown | 7 | 57 | 3306 | 37.667 | 9.879–66.355 | ||||
| Factor | Univariate Cox | Multivariate Cox | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) | HR | 95% CI | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) | |
| Age | 1.078 | 0.761–1.528 | 0.671 | |||
| Gender | 0.99 | 0.725–1.351 | 0.948 | |||
| TNM stage | 1.813 | 1.398–2.350 | <0.0001 | |||
| Tumor size(T) | 1.958 | 1.390–2.757 | <0.0001 | 1.543 | 1.101–2.163 | 0.012 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 2.219 | 1.704–2.890 | <0.0001 | 2.051 | 1.563–2.690 | <0.0001 |
| Distant metastasis | 0.954 | 0.798–1.139 | 0.602 | |||
| LINC00460 expression (high/low) | 1.383 | 1.011–1.893 | 0.043 | |||
| Factor | Univariate Cox | Multivariate Cox | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) | HR | 95% CI | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) | |
| Age | 1.078 | 0.761–1.528 | 0.671 | |||
| Gender | 0.99 | 0.725–1.351 | 0.948 | |||
| TNM stage | 1.813 | 1.398–2.350 | <0.0001 | |||
| Tumor size(T) | 1.958 | 1.390–2.757 | <0.0001 | 1.550 | 1.103–2.177 | 0.012 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 2.219 | 1.704–2.890 | <0.0001 | 1.974 | 1.498–2.600 | <0.0001 |
| Distant metastasis | 0.954 | 0.798–1.139 | 0.602 | |||
| MCM4 expression (high/low) | 1.608 | 1.176–2.200 | 0.003 | 1.459 | 1.064–2.000 | 0.019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, M.; Feng, S.; Cao, F.; Deng, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Bai, W. Identification of EGFR-Related LINC00460/mir-338-3p/MCM4 Regulatory Axis as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation. Cancers 2022, 14, 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205073
Jia M, Feng S, Cao F, Deng J, Li W, Zhou W, Liu X, Bai W. Identification of EGFR-Related LINC00460/mir-338-3p/MCM4 Regulatory Axis as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation. Cancers. 2022; 14(20):5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205073
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Mingxi, Shanshan Feng, Fengxi Cao, Jing Deng, Wen Li, Wangyan Zhou, Xiang Liu, and Weidong Bai. 2022. "Identification of EGFR-Related LINC00460/mir-338-3p/MCM4 Regulatory Axis as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation" Cancers 14, no. 20: 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205073
APA StyleJia, M., Feng, S., Cao, F., Deng, J., Li, W., Zhou, W., Liu, X., & Bai, W. (2022). Identification of EGFR-Related LINC00460/mir-338-3p/MCM4 Regulatory Axis as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation. Cancers, 14(20), 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205073






