Methylation Profiling in Diffuse Gliomas: Diagnostic Value and Considerations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
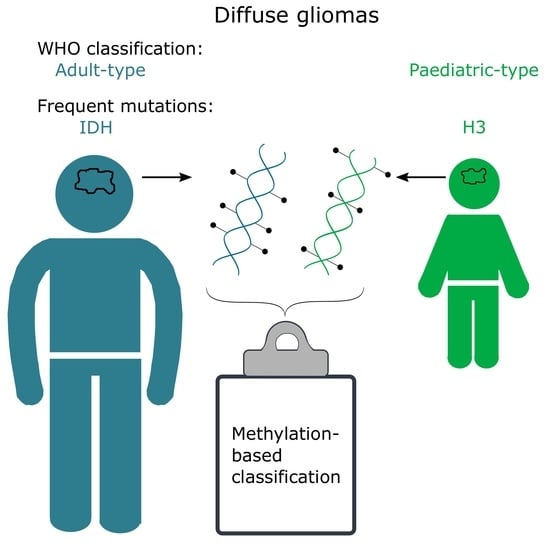
2. Adult vs. Paediatric Gliomas
3. CNS WHO Classification of Diffuse Gliomas
4. DNA Methylation and How Methylation-Based Classification Works
5. Methylation-Based Classification in Diffuse Gliomas and Its Value
6. Considerations Regarding Methylation-Based Classification
7. Heterogeneity in Diffuse Gliomas
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, X.; Jorg, D.J.; Cavalli, F.M.G.; Richards, L.M.; Nguyen, L.V.; Vanner, R.J.; Guilhamon, P.; Lee, L.; Kushida, M.M.; Pellacani, D.; et al. Fate mapping of human glioblastoma reveals an invariant stem cell hierarchy. Nature 2017, 549, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.K.; Wang, J.; Sa, J.K.; Ladewig, E.; Lee, H.O.; Lee, I.H.; Kang, H.J.; Rosenbloom, D.S.; Camara, P.G.; Liu, Z.; et al. Spatiotemporal genomic architecture informs precision oncology in glioblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segerman, A.; Niklasson, M.; Haglund, C.; Bergstrom, T.; Jarvius, M.; Xie, Y.; Westermark, A.; Sonmez, D.; Hermansson, A.; Kastemar, M.; et al. Clonal Variation in Drug and Radiation Response among Glioma-Initiating Cells Is Linked to Proneural-Mesenchymal Transition. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, D.; Witt, H.; Hovestadt, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Jones, D.T.; Konermann, C.; Pfaff, E.; Tonjes, M.; Sill, M.; Bender, S.; et al. Hotspot mutations in H3F3A and IDH1 define distinct epigenetic and biological subgroups of glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartzentruber, J.; Korshunov, A.; Liu, X.Y.; Jones, D.T.; Pfaff, E.; Jacob, K.; Sturm, D.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Quang, D.A.; Tonjes, M.; et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Borresen-Dale, A.L.; et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Dutt, M.; Suraweera, N.; Pfister, S.M.; von Deimling, A.; Brandner, S. Methylation array profiling of adult brain tumours: Diagnostic outcomes in a large, single centre. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Schrimpf, D.; Sturm, D.; Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Chavez, L.; Reuss, D.E.; et al. DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bird, A. DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Kelly, T.K.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cedar, H.; Bergman, Y. Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: Patterns and paradigms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.K.; Qiu, C.; Bernstein, E.; Li, K.; Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Lin, S.P.; Allis, C.D.; et al. DNMT3L connects unmethylated lysine 4 of histone H3 to de novo methylation of DNA. Nature 2007, 448, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danielsson, A.; Nemes, S.; Tisell, M.; Lannering, B.; Nordborg, C.; Sabel, M.; Caren, H. MethPed: A DNA methylation classifier tool for the identification of pediatric brain tumor subtypes. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Barthel, F.P.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Salama, S.R.; Murray, B.A.; Morozova, O.; Newton, Y.; Radenbaugh, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell 2016, 164, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surveillance Research Program, N.C.I. SEER*Explorer: An Interactive Website for SEER Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/explorer/ (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Behjati, S.; Huch, M.; van Boxtel, R.; Karthaus, W.; Wedge, D.C.; Tamuri, A.U.; Martincorena, I.; Petljak, M.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Gundem, G.; et al. Genome sequencing of normal cells reveals developmental lineages and mutational processes. Nature 2014, 513, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gröbner, S.N.; Worst, B.C.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Buchhalter, I.; Kleinheinz, K.; Rudneva, V.A.; Johann, P.D.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Segura-Wang, M.; Brabetz, S.; et al. The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers. Nature 2018, 555, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huether, R.; Dong, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Parker, M.; Wei, L.; Ma, J.; Edmonson, M.N.; Hedlund, E.K.; Rusch, M.C.; et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in epigenetic regulators across 1,000 paediatric cancer genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Edmonson, M.N.; Gawad, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Rusch, M.C.; Easton, J.; et al. Pan-cancer genome and transcriptome analyses of 1,699 paediatric leukaemias and solid tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryall, S.; Tabori, U.; Hawkins, C. Pediatric low-grade glioma in the era of molecular diagnostics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Parsons, D.W.; Jin, G.; McLendon, R.; Rasheed, B.A.; Yuan, W.; Kos, I.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Jones, S.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stichel, D.; Ebrahimi, A.; Reuss, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Ono, T.; Shirahata, M.; Reifenberger, G.; Weller, M.; Hänggi, D.; Wick, W.; et al. Distribution of EGFR amplification, combined chromosome 7 gain and chromosome 10 loss, and TERT promoter mutation in brain tumors and their potential for the reclassification of IDHwt astrocytoma to glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brat, D.J.; Aldape, K.; Colman, H.; Holland, E.C.; Louis, D.N.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Stupp, R.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 3: Recommended diagnostic criteria for “Diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH-wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV”. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesileanu, C.M.S.; Dirven, L.; Wijnenga, M.M.J.; Koekkoek, J.A.F.; Vincent, A.; Dubbink, H.J.; Atmodimedjo, P.N.; Kros, J.M.; van Duinen, S.G.; Smits, M.; et al. Survival of diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH1/2 wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV: A confirmation of the cIMPACT-NOW criteria. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsch, S.; Batchelor, T.T.; Gonzalez Castro, L.N. Diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications of the 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer 2022, 128, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Bailey, S.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Kool, M.; Dufour, C.; Vassal, G.; Milde, T.; et al. Risk stratification of childhood medulloblastoma in the molecular era: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, J.T.; Snuderl, M.; Jones, D.T.; Brathwaite, C.D.; Altman, N.; Lavi, E.; Saffery, R.; Sexton-Oates, A.; Blumcke, I.; Capper, D.; et al. Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young (PLNTY): An epileptogenic neoplasm with oligodendroglioma-like components, aberrant CD34 expression, and genetic alterations involving the MAP kinase pathway. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avery, O.T.; Macleod, C.M.; McCarty, M. Studies on the Chemical Nature of the Substance Inducing Transformation of Pneumococcal Types: Induction of Transformation by a Desoxyribonucleic Acid Fraction Isolated from Pneumococcus Type III. J. Exp. Med. 1944, 79, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wutz, A.; Smrzka, O.W.; Schweifer, N.; Schellander, K.; Wagner, E.F.; Barlow, D.P. Imprinted expression of the Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island. Nature 1997, 389, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouse, S.D.; Shen, Y.; Pellegrini, M.; Cole, S.; Meissner, A.; Van Neste, L.; Jaenisch, R.; Fan, G. Promoter CpG methylation contributes to ES cell gene regulation in parallel with Oct4/Nanog, PcG complex, and histone H3 K4/K27 trimethylation. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B. Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2042–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer: The DNA hypermethylome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, R50–R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, A.; Gaudet, F.; Waghmare, A.; Jaenisch, R. Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA hypomethylation. Science (N.Y.) 2003, 300, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Frigola, J.; Vendrell, E.; Risques, R.A.; Fraga, M.F.; Morales, C.; Moreno, V.; Esteller, M.; Capellà, G.; Ribas, M.; et al. Chromosomal instability correlates with genome-wide DNA demethylation in human primary colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8462–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timp, W.; Bravo, H.C.; McDonald, O.G.; Goggins, M.; Umbricht, C.; Zeiger, M.; Feinberg, A.P.; Irizarry, R.A. Large hypomethylated blocks as a universal defining epigenetic alteration in human solid tumors. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcan, S.; Rohle, D.; Goenka, A.; Walsh, L.A.; Fang, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Campos, C.; Fabius, A.W.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; et al. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype. Nature 2012, 483, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyota, M.; Ahuja, N.; Ohe-Toyota, M.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B.; Issa, J.P. CpG island methylator phenotype in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8681–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noushmehr, H.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Diefes, K.; Phillips, H.S.; Pujara, K.; Berman, B.P.; Pan, F.; Pelloski, C.E.; Sulman, E.P.; Bhat, K.P.; et al. Identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype that defines a distinct subgroup of glioma. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, A.F.; Assenov, Y.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Balint, B.; Siebert, R.; Taniguchi, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Hidalgo, M.; Tan, A.C.; Galm, O.; et al. A DNA methylation fingerprint of 1628 human samples. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moran, S.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Sayols, S.; Musulén, E.; Balañá, C.; Estival-Gonzalez, A.; Moutinho, C.; Heyn, H.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; de Moura, M.C.; et al. Epigenetic profiling to classify cancer of unknown primary: A multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Stichel, D.; Sahm, F.; Jones, D.T.W.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Schmid, S.; Hovestadt, V.; Reuss, D.E.; Koelsche, C.; et al. Practical implementation of DNA methylation and copy-number-based CNS tumor diagnostics: The Heidelberg experience. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 181–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schepke, E.; Löfgren, M.; Pietsch, T.; Olsson Bontell, T.; Kling, T.; Wenger, A.; Ferreyra Vega, S.; Danielsson, A.; Dosa, S.; Holm, S.; et al. DNA methylation profiling improves routine diagnosis of paediatric central nervous system tumours: A prospective population-based study. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2022, 48, e12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priesterbach-Ackley, L.P.; Boldt, H.B.; Petersen, J.K.; Bervoets, N.; Scheie, D.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Gardberg, M.; Brännström, T.; Torp, S.H.; Aronica, E.; et al. Brain tumour diagnostics using a DNA methylation-based classifier as a diagnostic support tool. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2020, 46, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickles, J.C.; Fairchild, A.R.; Stone, T.J.; Brownlee, L.; Merve, A.; Yasin, S.A.; Avery, A.; Ahmed, S.W.; Ogunbiyi, O.; Gonzalez Zapata, J.; et al. DNA methylation-based profiling for paediatric CNS tumour diagnosis and treatment: A population-based study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, T.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Williamson, D.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Mynarek, M.; Rutkowski, S.; Robinson, G.W.; Gajjar, A.; Cavalli, F.; et al. Second-generation molecular subgrouping of medulloblastoma: An international meta-analysis of Group 3 and Group 4 subtypes. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovestadt, V.; Remke, M.; Kool, M.; Pietsch, T.; Northcott, P.A.; Fischer, R.; Cavalli, F.M.; Ramaswamy, V.; Zapatka, M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. Robust molecular subgrouping and copy-number profiling of medulloblastoma from small amounts of archival tumour material using high-density DNA methylation arrays. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Bent, M.J. Interobserver variation of the histopathological diagnosis in clinical trials on glioma: A clinician’s perspective. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreyra Vega, S.; Olsson Bontell, T.; Corell, A.; Smits, A.; Jakola, A.S.; Carén, H. DNA methylation profiling for molecular classification of adult diffuse lower-grade gliomas. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, R.; Schüller, U.; Eckhardt, A.; Filipski, K.; Hartung, T.I.; Harter, P.N.; Divé, I.; Forster, M.T.; Czabanka, M.; Jelgersma, C.; et al. DNA methylation subclasses predict the benefit from gross total tumor resection in IDH-wildtype glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, F.L.; Drexler, R.; Wollmann, K.; Eckhardt, A.; Heiland, D.H.; Sauvigny, T.; Maire, C.; Lamszus, K.; Westphal, M.; Schüller, U.; et al. DNA Methylation subclass Receptor Tyrosine Kinase II (RTK II) is predictive for seizure development in glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovestadt, V.; Zapatka, M. Conumee: Enhanced Copy-Number Variation Analysis Using Illumina DNA Methylation Arrays. R Package Version 1.9.0. Available online: http://bioconductor.org/packages/conumee/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Bady, P.; Sciuscio, D.; Diserens, A.C.; Bloch, J.; van den Bent, M.J.; Marosi, C.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Weller, M.; Mariani, L.; Heppner, F.L.; et al. MGMT methylation analysis of glioblastoma on the Infinium methylation BeadChip identifies two distinct CpG regions associated with gene silencing and outcome, yielding a prediction model for comparisons across datasets, tumor grades, and CIMP-status. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bady, P.; Delorenzi, M.; Hegi, M.E. Sensitivity Analysis of the MGMT-STP27 Model and Impact of Genetic and Epigenetic Context to Predict the MGMT Methylation Status in Gliomas and Other Tumors. J. Mol. Diagn. JMD 2016, 18, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kling, T.; Wenger, A.; Beck, S.; Caren, H. Validation of the MethylationEPIC BeadChip for fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumours. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwala, A.K.; Felix, M.; Friedel, D.; Stichel, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Hinz, F.; Hewer, E.; Schweizer, L.; Dohmen, H.; Pohl, U.; et al. Oligosarcomas, IDH-mutant are distinct and aggressive. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 143, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefers, A.K.; Stichel, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Coras, R.; Pages, M.; Tauziède-Espariat, A.; Varlet, P.; Schwarz, D.; Söylemezoglu, F.; Pohl, U.; et al. Isomorphic diffuse glioma is a morphologically and molecularly distinct tumour entity with recurrent gene fusions of MYBL1 or MYB and a benign disease course. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Witt, H.; Hielscher, T.; Eberhart, C.G.; Mack, S.; Bouffet, E.; Clifford, S.C.; Hawkins, C.E.; French, P.; et al. Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajtler, K.W.; Witt, H.; Sill, M.; Jones, D.T.; Hovestadt, V.; Kratochwil, F.; Wani, K.; Tatevossian, R.; Punchihewa, C.; Johann, P.; et al. Molecular Classification of Ependymal Tumors across All CNS Compartments, Histopathological Grades, and Age Groups. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellison, D.W.; Aldape, K.D.; Capper, D.; Fouladi, M.; Gilbert, M.R.; Gilbertson, R.J.; Hawkins, C.; Merchant, T.E.; Pajtler, K.; Venneti, S.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 7: Advancing the molecular classification of ependymal tumors. Brain Pathol. (Zur. Switz.) 2020, 30, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, O.; Silva-Oliveira, R.; Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Clara, C.; Almeida, J.R.; Carvalho, A.L.; Barata, J.T.; Reis, R.M. In Vitro and In Vivo Analysis of RTK Inhibitor Efficacy and Identification of Its Novel Targets in Glioblastomas. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, A.; Musket, A.; Musich, P.R.; Schweitzer, J.B.; Xie, Q. Receptor tyrosine kinases as druggable targets in glioblastoma: Do signaling pathways matter? Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.; Ferreyra Vega, S.; Schepke, E.; Löfgren, M.; Olsson Bontell, T.; Tisell, M.; Nilsson, D.; Kling, T.; Carén, H. DNA methylation alterations across time and space in paediatric brain tumours. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, H.D.; Nakano, I.; Lazareff, J.A.; Masterman-Smith, M.; Geschwind, D.H.; Bronner-Fraser, M.; Kornblum, H.I. Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15178–15183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.; Mitra, S.S.; Freret, M.E.; Raveh, T.B.; Kim, J.; Masek, M.; Attema, J.L.; Li, G.; Haddix, T.; Edwards, M.S.; et al. Hedgehog-responsive candidate cell of origin for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenger, A.; Larsson, S.; Danielsson, A.; Elbaek, K.J.; Kettunen, P.; Tisell, M.; Sabel, M.; Lannering, B.; Nordborg, C.; Schepke, E.; et al. Stem cell cultures derived from pediatric brain tumors accurately model the originating tumors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18626–18639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Valentim, C.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, R.; Dorsey, J.F.; Fan, Y. Cell plasticity, senescence, and quiescence in cancer stem cells: Biological and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 231, 107985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowell, P.C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science (N.Y.) 1976, 194, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, M.; Burford, A.; Molinari, V.; Kessler, K.; Popov, S.; Clarke, M.; Taylor, K.R.; Pemberton, H.N.; Lord, C.J.; Gutteridge, A.; et al. Functional diversity and cooperativity between subclonal populations of pediatric glioblastoma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.M.; DeWire, M.; Ryall, S.; Buczkowicz, P.; Leach, J.; Miles, L.; Ramani, A.; Brudno, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Drissi, R.; et al. Spatial genomic heterogeneity in diffuse intrinsic pontine and midline high-grade glioma: Implications for diagnostic biopsy and targeted therapeutics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sottoriva, A.; Spiteri, I.; Piccirillo, S.G.; Touloumis, A.; Collins, V.P.; Marioni, J.C.; Curtis, C.; Watts, C.; Tavare, S. Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer evolutionary dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4009–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science (N.Y.) 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenger, A.; Ferreyra Vega, S.; Kling, T.; Bontell, T.O.; Jakola, A.S.; Caren, H. Intratumor DNA methylation heterogeneity in glioblastoma: Implications for DNA methylation-based classification. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, N.; Barthel, F.P.; Anderson, K.J.; Johnson, K.C.; Koopman, T.; Yaqub, M.M.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Barkhof, F.; Pouwels, P.J.W.; et al. Spatial concordance of DNA methylation classification in diffuse glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreyra Vega, S.; Wenger, A.; Kling, T.; Olsson Bontell, T.; Jakola, A.S.; Carén, H. Spatial heterogeneity in DNA methylation and chromosomal alterations in diffuse gliomas and meningiomas. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gempt, J.; Withake, F.; Aftahy, A.K.; Meyer, H.S.; Barz, M.; Delbridge, C.; Liesche-Starnecker, F.; Prokop, G.; Pfarr, N.; Schlegel, J.; et al. Methylation subgroup and molecular heterogeneity is a hallmark of glioblastoma: Implications for biopsy targeting, classification and therapy. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, S.L. MGMT: Its role in cancer aetiology and cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.; Hamilton, S.R.; Burger, P.C.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Inactivation of the DNA repair gene O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase by promoter hypermethylation is a common event in primary human neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malmstrom, A.; Gronberg, B.H.; Marosi, C.; Stupp, R.; Frappaz, D.; Schultz, H.; Abacioglu, U.; Tavelin, B.; Lhermitte, B.; Hegi, M.E.; et al. Temozolomide versus standard 6-week radiotherapy versus hypofractionated radiotherapy in patients older than 60 years with glioblastoma: The Nordic randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.R.; Hudson, A.L.; Khong, P.; Parkinson, J.F.; Dwight, T.; Ikin, R.J.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, Z.J.; Vafaee, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity identified at the epigenetic, genetic and transcriptional level in glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.F.; Wheeler, H.R.; Clarkson, A.; McKenzie, C.A.; Biggs, M.T.; Little, N.S.; Cook, R.J.; Messina, M.; Robinson, B.G.; McDonald, K.L. Variation of O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation in serial samples in glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2008, 87, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, C.G.; Lowe, R.; Adams, P.D.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Beck, S.; Bell, J.T.; Christensen, B.C.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Heijmans, B.T.; Horvath, S.; et al. DNA methylation aging clocks: Challenges and recommendations. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kling, T.; Wenger, A.; Carén, H. DNA methylation-based age estimation in pediatric healthy tissues and brain tumors. Aging 2020, 12, 21037–21056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, S.; McAleenan, A.; Kelly, C.; Spiga, F.; Cheng, H.Y.; Dawson, S.; Schmidt, L.; Faulkner, C.L.; Wragg, C.; Jefferies, S.; et al. MGMT promoter methylation testing to predict overall survival in people with glioblastoma treated with temozolomide: A comprehensive meta-analysis based on a Cochrane Systematic Review. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Redfield, J.; Ballo, M.; Michael, M.; Sorenson, J.; Dibaba, D.; Wan, J.; Ramos, G.D.; Pandey, M. Identifying the optimal cutoff point for MGMT promoter methylation status in glioblastoma. CNS Oncol. 2021, 10, Cns74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.; Koch, A.; Pritsch, F.; Schumann, E.; Misch, M.; Hempt, C.; Lenz, K.; Löbel, F.; Paschereit, F.; Heppner, F.L.; et al. Predictive MGMT status in a homogeneous cohort of IDH wildtype glioblastoma patients. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelsche, C.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Sill, M.; Sahm, F.; Reuss, D.E.; Blattner, M.; Worst, B.; Heilig, C.E.; Beck, K.; et al. Sarcoma classification by DNA methylation profiling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Hierarchy | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superfamily | Adult-type diffuse gliomas | Adult-type diffuse gliomas | Paediatric-type diffuse high-grade gliomas |
| Family | Glioblastoma, IDH-wt | Diffuse glioma, IDH mutant | Diffuse paediatric-type high-grade glioma, H3-wt and IDH-wt |
| Class | Glioblastoma, IDH-wt, RTK1 type | Diffuse glioma, IDH-mutant and 1p19q codeleted [oligodendroglial type] | Diffuse paediatric-type high-grade glioma, RTK1 subtype |
| Subclass | Glioblastoma, IDH-wt, RTK1 subtype | Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted | Diffuse paediatric-type high-grade glioma, RTK1 subtype, subclass A |
| Benefits of DNA Methylation Profiling |
|---|
|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Histopathological diagnosis | Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted grade 3 | Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted grade 3 | Glioblastoma, IDH wildtype grade 4 |
| Methylation-based subclass | Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted | Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted | Control tissue, cerebral hemisphere |
| Calibrated score | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.35 |
| Tumour cell content (%) | 72 | 65 | 17 |
| Copy-number alterations (CNA) | 1p/19q codeletion | 1p/19q codeletion | No discernable CNA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wenger, A.; Carén, H. Methylation Profiling in Diffuse Gliomas: Diagnostic Value and Considerations. Cancers 2022, 14, 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225679
Wenger A, Carén H. Methylation Profiling in Diffuse Gliomas: Diagnostic Value and Considerations. Cancers. 2022; 14(22):5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225679
Chicago/Turabian StyleWenger, Anna, and Helena Carén. 2022. "Methylation Profiling in Diffuse Gliomas: Diagnostic Value and Considerations" Cancers 14, no. 22: 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225679