Simple Summary
Composite/synchronous lymphoma is a rare entity, for which the histopathological diagnosis is difficult due to the co-occurrence of at least two lymphomas, sometimes mixed in the same anatomical site. In the present review, we gathered available data on composite lymphomas associating a classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) with another lymphoma. We report the clinical, histopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular data for each composite lymphoma. These data reinforce the hypothesis of a common clonal origin and a transdifferentiation phenomenon during lymphomagenesis. One of the greatest challenges for the pathologist is to differentiate real Hodgkin cells of cHL from Hodgkin-like cells associated with a non-Hodgkin lymphoma, in order to individualize both contingents for the diagnosis. In contrast, the clinician’s challenge is to optimally treat these rare composite pathologies as a single clinical entity. This review could thus be a useful diagnostic support for pathologists and could help clinicians improve management of these uncommon lymphomas.
Abstract
The co-occurrence of several lymphomas in a patient defines composite/synchronous lymphoma. A common cellular origin has been reported for both contingents of such entities. In the present review, we aimed to gather the available data on composite lymphomas associating a classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) with another lymphoma, to better understand the plasticity of mature B and T-cells. This review highlights that >70% of patients with a composite lymphoma are ≥55 years old, with a male predominance. The most reported associations are cHL with follicular lymphoma or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, with over 130 cases reported. The cHL contingent is often of mixed cellularity type, with a more frequent focal/weak CD20 expression (30% to 55.6%) compared to de novo cHL, suggesting a particular pathophysiology. Moreover, Hodgkin cells may express specific markers of the associated lymphoma (e.g., BCL2/BCL6 for follicular lymphoma and Cyclin D1 for mantle cell lymphoma), sometimes combined with common BCL2/BCL6 or CCND1 rearrangements, respectively. In addition, both contingents may share similar IgH/IgK rearrangements and identical pathogenic variants, reinforcing the hypothesis of a common clonal origin. Finally, cHL appears to be endowed with a greater plasticity than previously thought, supporting a common clonal origin and a transdifferentiation process during lymphomagenesis of composite lymphomas.
1. Literature Review Section
Introduction
A composite lymphoma is defined by the presence of at least two lymphomas in the same anatomical site [1]. However, the co-occurrence of several lymphomas in distinct locations, at the same time, is also accepted to qualify composite/synchronous lymphomas [2,3], as initially defined by Custer et al. in 1954 [4]. Indeed, synchronous and composite lymphomas might share the same pathophysiology, since common cellular origins have been identified between both contingents of these entities [5]. Due to the simultaneous occurrence of different lymphomas, these pathologies are interesting prototypes for studying the cellular plasticity that occurs during lymphomagenesis.
Among composite lymphomas, those associating a classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) contingent have been of great interest since the beginning of the 21st century. Initially considered to be a coincidental association of two different morphological pathologies [2], common molecular abnormalities have been identified between both contingents of these lymphomas. Moreover, studies have also reported (i) common gene translocations (BCL2, BCL6, CCND1) [6,7,8,9,10]; (ii) common IgH and/or IgK rearrangements encoding the heavy and light immunoglobulin chains, respectively [10,11,12,13]; and (iii) common pathogenic variants (TP53, BCL2, EP300, BCOR, KMT2D, ARID1A, SF3B1) [8,10] between both contingents. To date, cHL have been reported in association with nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphomas (NLPHL), B-cell lymphomas (follicular lymphomas, mantle cell lymphomas, marginal zone lymphomas, diffuse large B-cell lymphomas), and T-cell lymphomas [5]. The clinical behavior of cHL/B-cell composite lymphomas appears to be more indolent than that of cHL/B-cell sequential lymphomas, which are defined as several lymphomas arising consecutively in a patient [10,14,15,16]. However, the distinction between composite and sequential lymphomas is not always obvious in clinical practice. Although the lymphomagenesis process of composite lymphomas seems to differ from that of de novo cHL [17], this process remains to be deciphered. As previously suggested, the plasticity of mature B-cells may be responsible for a transdifferentiation phenomenon in the case of cHL/follicular composite lymphomas [10].
However, the main data reported on composite lymphomas are only based on case reports and small series, preventing a comprehensive clinical, histopathological, molecular, and pathophysiological study. In this review, composite lymphoma cases associating a cHL with another B or T-cell lymphoma were gathered from the literature, in order to increase understanding of cHL plasticity.
2. Materials and Methods
The data collection was performed from July to August 2022, on the PubMed Central (PMC) archives (NCBI), using the keywords “composite lymphoma(s)”, “synchronous lymphoma(s)”, “composite AND Hodgkin”, “synchronous AND Hodgkin”, without limit regarding the year of publication (from 1977 to 2022). One reviewer (A.T.) sorted all the articles found, to perform a first selection of those meeting the inclusion criteria. In addition, an exhaustive study of the reference section of each article was carried out. Then, all articles selected were checked independently by another reviewer (A.T.-G.).
Inclusion criteria were (i) the co-occurrence of a cHL with other lymphoma(s) diagnosed at the same time, regardless of their location or the patient’s history; and (ii) the presence of two or more distinct, well-defined, and histopathologically proven non-cutaneous lymphomas. Exclusion criteria were (i) NLPHL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) without a cHL contingent associated; (ii) absence of simultaneous occurrence (sequential lymphoma); (iii) association of cHL and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), which is known as a transformation process rather than a composite pathology; (iv) the presence of Hodgkin-like cells occurring in an NHL; and (v) report(s) including the diagnosis of cHL with negative CD30 “Hodgkin cells”. After the final selection, all articles included were separated into six groups: composite lymphoma associating a cHL and either: (i) NLPHL; (ii) follicular lymphoma; (iii) mantle cell lymphoma; (iv) marginal zone lymphoma; (v) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL); or (vi) T-cell lymphoma. The clinical, laboratory, histopathological, and molecular data from each article available in English were collected. As the chemotherapy treatment that was used was different from one study to another, lymphoma treatments were classified into four groups: cHL-like, B-cell lymphoma-like, T-cell lymphoma-like, and composite lymphoma-like chemotherapy. The latter included combinations of cHL-like chemotherapy and another lymphoma treatment (see Supplementary Text S1 for the classification of treatments). Of note, for the cHL/follicular composite lymphomas previously published by our group [10], more details have been added herein due to the ongoing follow-up of these patients in our center in Lyon, France.
The results of all included studies have been compiled in tables (see Supplementary Materials). Then, the frequencies of the variables from all studies were described as percentages and medians for dichotomous and continuous values, respectively.
Microscopic photographs were obtained using Aperio ImageScope software v12.3.3 (Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany) after slide scanning using Aperio AT2 scanner (Leica Biosystems). Figures and Supplementary Figure S1 were created using BioRender (BioRender, Toronto, Canada; BioRender.com). All the figures included in the present review (main text and Supplementary Material) are original.
This systematic review was written according to the PRISMA 2020 Checklist (prisma-statement.org; see Supplementary Table S1).
3. Results
3.1. Article Selection Process for Final Analysis
More than 700 articles were retrieved in PubMed. After an initial screening, 108 articles, published from 1977 to 2022, were identified as “composite/synchronous lymphomas with a Hodgkin lymphoma”. Among them, nine articles were not included: (i) one because both contingents (cHL/NLPHL) had the same immunohistochemical phenotype and were difficult to individualize [18]; (ii) eight because the second contingent was a cutaneous lymphoproliferation (T-cell lymphoma, mycosis fungoid, or lymphomatoid papulosis) [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
Among the remaining 99 articles, 26 were excluded from the final analysis because they met at least one exclusion criterion: (i) six NLPHL/NHL composite lymphomas without cHL contingent [27,28,29,30,31,32]; (ii) two cHL with an Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder [33] or EBV mucocutaneous ulcer [34]; (iii) one with CD30 negative Hodgkin cells [35]; (iv) four with Hodgkin-like cells within an NHL [36,37,38,39]; (v) two sequential lymphomas [40,41]; (vi) ten probable transformations of CCL into cHL [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51]; and (vii) one because the final diagnosis could be considered ambiguous [52].
As a result, 73 original articles reporting composite lymphomas with a cHL contingent were included in the final analysis. The flow diagram of article inclusion/exclusion is presented in Supplementary Figure S1 [53].
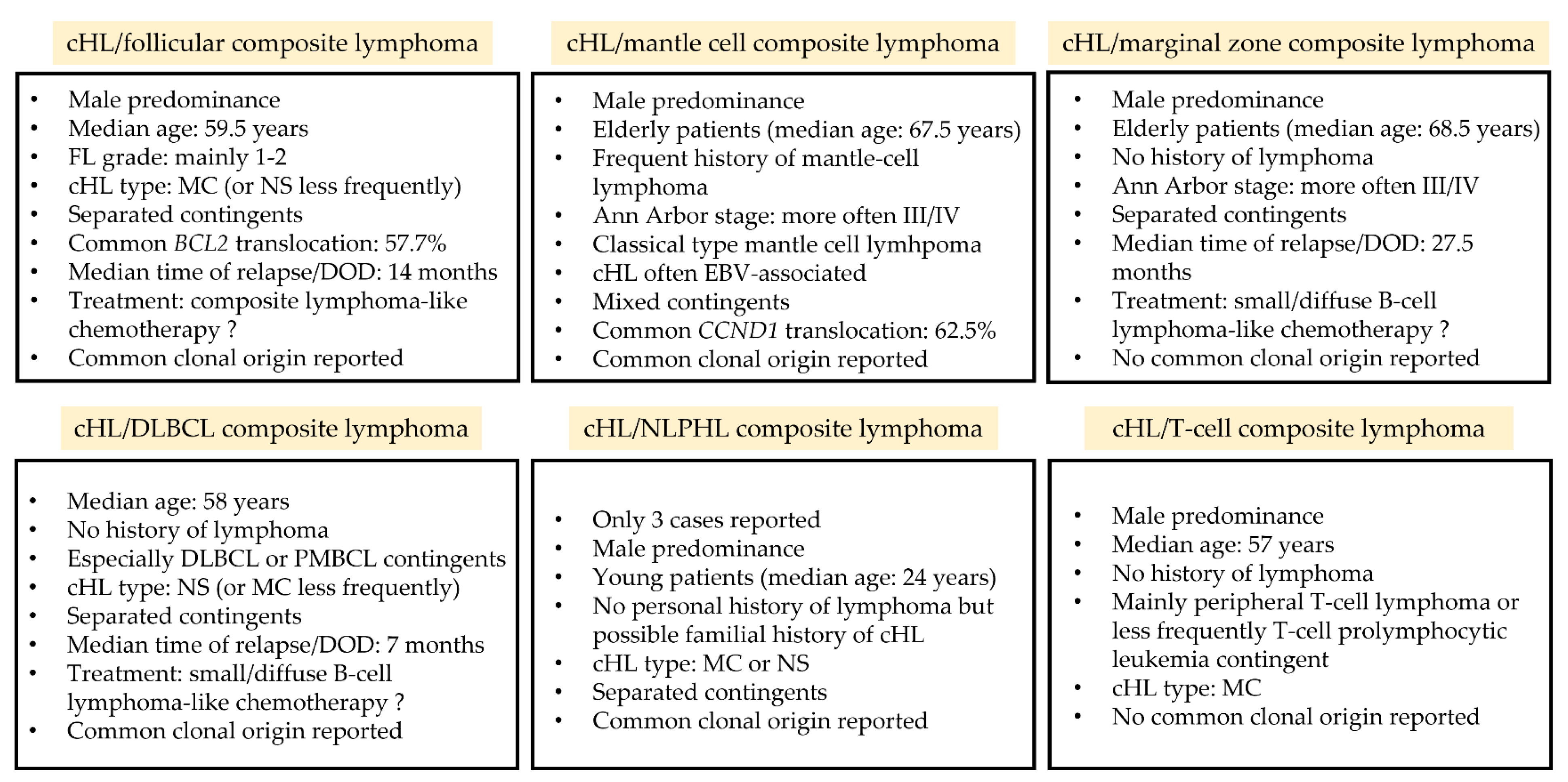
3.2. cHL and Follicular Composite Lymphomas
A total of 76 cHL/follicular composite lymphomas from 20 articles were analyzed [3,6,10,11,12,14,15,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66].
3.2.1. Clinical and Laboratory Data
The median age was 59.5 years (ranging from 35 to 84), and the male/female ratio was 2. At presentation, 59.2% (45/76) of patients had no history of lymphoma, 1.3% (1/76) had a previous history of cHL, 7.9% (6/76) had a previous history of follicular lymphoma, associated with a DLBCL in one case. The history of lymphoma was not specified in 32.9% (25/76) of cases. The median follow-up time was 23.5 months (ranging from 0.75 to 171 months). Fourteen patients relapsed after remission: five as follicular lymphoma, three as cHL, and six without other specification. For patients who relapsed/died from lymphoma, the median relapse time was 14 months (ranging from 1 to 108 months). Clinical and laboratory data are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, and Supplementary Table S2.

Table 1.
Clinical, laboratory, and pathological data.

Table 2.
Treatments for cHL composite lymphomas reported in the literature.
3.2.2. Pathological Data
The cHL contingent was of mixed cellularity-type (MC) or with an abundant granulomatous background in 60.5% (46/76) of cases, nodular sclerosis-type (NS) in 23.7% (18/76), and unclassified in 15.8% (12/76) of cases. The follicular lymphoma contingent was in situ in 1.3% (1/76), grade 1–2 in 53.9% (41/76), grade 3A in 13.2% (10/76), grade 3B in 2.6% (2/76), and unspecified in 28.9% (22/76) of cases. A DLBCL contingent was associated in 7.9% (6/76) of cases. The major contingent was follicular lymphoma and/or DLBCL in 28.9% (22/76), cHL in 13.2% (10/76), and unspecified in 53.9% (41/76) of cases. Both contingents were present in equal quantity in 3.9% (3/76) of cases. Pathological data are presented in Table 1 and Table 3, and Supplementary Table S3.

Table 3.
Immunophenotype of both contingents in cHL composite lymphomas.
3.2.3. Molecular Data
A BCL2 translocation was reported in both contingents in 57.7% (15/26) of cases, and a translocation of BCL6 was identified in 8.3% (1/12) of cases. In addition, a common 16p duplication was also reported in one case.
Similar clonal rearrangements of IgH/IgK were reported in 90% (9/10) of cases. In the only negative case, DNA degradation was reported.
Two cases of cHL/follicular composite lymphomas showed identical pathogenic variants of BCL2, EP300, BCOR, ARID1A, KMT2D, and SF3B1 in both contingents obtained by microdissection. In addition, each contingent showed its own pathogenic variants, such as BCL2, KMT2D, EP300 in the follicular lymphoma contingent, and XPO1, TNFAIP3, and CREBBP in the cHL contingent [10]. Molecular data are detailed in Supplementary Table S3.
3.3. cHL and Mantle Cell Composite Lymphomas
A total of 11 cHL/mantle cell composite lymphomas from 10 articles were analyzed [6,8,9,67,68,69,70,71,72,73].
3.3.1. Clinical and Laboratory Data
The median age was 67.5 years (ranging from 42 to 89), and the male/female ratio was 4. At presentation, 45.5% (5/11) of patients had no history of lymphoma, 54.5% (6/11) had a history of lymphoma (mantle cell lymphoma in five cases and unspecified lymphoproliferation in one case). Data concerning the median follow-up time were not available in 90.9% (10/11) of cases. Clinical and laboratory data are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, and Supplementary Table S4.
3.3.2. Pathological Data
The cHL contingent was of NS-type in 9.1% (1/11), MC-type in 9.1% (1/11), lymphocyte-rich-type (LR) in 18.2% (2/11), and unclassified in 63.6% (7/11) of cases. The mantle cell lymphoma contingents were of classical-type in 90.9% (10/11) and blastoid-type in 9.1% (1/11) of cases. Pathological data are presented in Table 1 and Table 3, and Supplementary Table S5.
3.3.3. Molecular Data
A translocation of CCND1 was reported in both contingents in 62.5% (5/8) of cases.
A similar clonal IgH rearrangement in both contingents was reported in 40% (2/5) of cases, while distinct IgH rearrangements were found in 60% (3/5) of cases. In one patient, a TP53 variant (exon 5, p.Y163C) and a heterozygous deletion of TP53/17p13 were identified. Molecular data are detailed in Supplementary Table S5.
3.4. cHL and Marginal Zone Composite Lymphomas
A total of 21 cHL/marginal zone composite lymphomas from 10 articles were analyzed [6,60,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81].
3.4.1. Clinical and Laboratory Data
The median age was 68.5 years (ranging from 45 to 87), and the male/female ratio was 4. Most patients (76.2%, 16/21) had no history of lymphoma, 14.3% (3/21) had a history of lymphoma (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT), splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL), and lymphoplasmacytoid immunocytoma/lymphoma), and the history of lymphoma was not specified in 9.5% (2/21) of cases. The median follow-up time was 12 months (ranging from 2 to 131 months). For patients who relapsed/died from lymphoma, the median relapse time was 27.5 months (ranging from 7 to 122). Clinical and laboratory data are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, and Supplementary Table S6.
3.4.2. Pathological Data
The cHL contingent was of NS-type in 4.8% (1/21), MC-type in 57.1% (12/21), and unclassified in 38.1% (8/21) of cases. The second contingent was SMZL, MALT, MALT + DLBCL, MZBL, and MZBL + DLBCL in 14.3% (3/21), 33.3% (7/21), 28.6% (6/21), 19% (4/21), and 4.8% (1/21) of patients, respectively. Pathological data are presented in Table 1 and Table 3, and Supplementary Table S7.
3.4.3. Molecular Data
For the only case tested, no t(11;18) translocation and no IgH rearrangement was identified in either of the contingents individualized before testing. Molecular data are detailed in Supplementary Table S7.
3.5. cHL and Diffuse Large B-Cell Composite Lymphomas
A total of 79 cHL/diffuse large B-cell composite lymphomas from 35 articles were analyzed [1,3,6,13,14,16,58,64,66,76,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105].
3.5.1. Clinical and Laboratory Data
The median age was 58 years (ranging from 14 to 84), and the male/female ratio was 1.5. At presentation, 57% (45/79) of patients had no history of lymphoma, 6.3% (5/79) had a history of lymphoma (cHL in two cases, follicular lymphoma in one case, DLBCL in one case, DLBCL and follicular lymphoma in one case), and the history of lymphoma was not specified in 36.7% (29/79) of cases. The median time of follow-up was 12 months (ranging from 0.67 to 124.8 months). Five patients relapsed after complete remission: 60% (3/5) as cHL, 20% (1/5) as DLBCL, and 20% (1/5) had no available data. For patients who relapsed/died from lymphoma, the median relapse time was 7 months (ranging from 1 to 54 months). Clinical and laboratory data are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, and Supplementary Table S8.
3.5.2. Pathological Data
The cHL contingent was of NS-type in 53.2% (42/79), MC-type in 21.5% (17/79), LR-type in 1.3% (1/79), and unclassified/unspecified in 24% (19/79) of cases. The second contingent was DLBCL in 70.9% (56/79), Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma in 1.3% (1/79), primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma in 25.3% (20/79), gray-zone lymphoma in 1.3% (1/79), and high-grade B-cell lymphoma in 1.3% (1/79) of cases. Pathological data are presented in Table 1 and Table 3, and Supplementary Table S9.
3.5.3. Molecular Data
Similar clonal IgH/IgK rearrangements were found in 70% (7/10) of cases. More specifically, in two cases, both identical and different V gene somatic hypermutations were identified in both contingents. In one case, somatic hypermutations of IgVH were increased in the DLBCL contingent (27–28%) compared to the cHL contingent (7–8%). In one case, a TP53 variant was found only in the DLBCL contingent. Molecular data are detailed in Supplementary Table S9.
3.6. cHL and Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Composite Lymphomas
A total of three cHL/NLPHL composite lymphomas from three articles were analyzed [106,107,108].
3.6.1. Clinical and Laboratory Data
The median age was 24 years (ranging from 22 to 48), and the three cases were male. At presentation, no patient had a personal history of lymphoma, but one patient had a family history of cHL (father and two paternal cousins). The follow-up time was available for only one patient (12 months). Clinical and laboratory data are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, and Supplementary Table S10.
3.6.2. Pathological Data
The cHL contingent was of NS-type in 33.3% (1/3) and MC-type in 66.7% (2/3) of cases. MUM1, LMP-1, and p53 immunostainings were each performed in only one case, and found positive in the cHL contingent where they were performed. Similarly, CD79a, MUM1, BOB1, and p53 immunostainings were positive in the only case of NLPHL contingent where they were performed. Pathological data are presented in Table 1 and Table 3, and Supplementary Table S11.
3.6.3. Molecular Data
In one case, an identical clonal IgH rearrangement with the same V gene somatic hypermutations were identified in both contingents. A second different IgH rearrangement was observed in the NLPHL contingent only. For another patient, the IgH repertoire was polyclonal, but both contingents shared a similar clonal IgK rearrangement. Molecular data are detailed in Supplementary Table S11.
3.7. cHL and T-cell Composite Lymphomas
A total of 11 cHL/T-cell composite lymphomas from seven articles were analyzed [60,109,110,111,112,113,114].
3.7.1. Clinical and Laboratory Data
The median age was 57 years (ranging from 19 to 84), and the male/female ratio was 2.7. At presentation, 72.7% (8/11) of patients had no history of lymphoma and 27.3% (3/11) had a history of lymphoma/hematological pathology (a cHL in two cases, a prolymphocytic leukemia in one case). The median follow-up time was 30 months (ranging from 0.75 to 48 months). Clinical and laboratory data are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, and Supplementary Table S12.
3.7.2. Pathological Data
The cHL contingent was of NS-type in 9.1% (1/11), MC-type in 45.5% (5/11), and unclassified in 45.5% (5/11) of cases. The second contingent was peripheral T-cell lymphoma in 72.7% (8/11), T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia in 18.2% (2/11), and cytotoxic CD8+ T-cell lymphoma in 9.1% (1/11) of cases.
Concerning the cHL contingent, no expression of T-cell markers (CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD8), ALK-1, nor LCA/CD45 were observed in the Hodgkin cells. For the T-cell lymphoma contingent, the proliferative index (Ki67) ranged from 40% to 80%. The CD30 immunostaining of T-cell lymphomas was always negative. Concerning the cHL contingent, the LMP-1 immunostaining performed in only one case was positive, while the ALK-1, CD4, and CD8 immunostainings, also performed in only one case, were negative. For the T-cell lymphoma contingent, the CD20 immunostaining performed in only one case was negative. Pathological data are presented in Table 1 and Table 3, and Supplementary Table S13.
3.7.3. Molecular Data
For two cases, a TCR-β and/or TCR-γ rearrangement was identified in both T-cell lymphoma contingents, while a clonal IgH rearrangement was found only in one cHL contingent.
For all the other cases tested, the rearrangements were analyzed on the whole tissue samples (non-individualized contingents). Clonal IgH rearrangements were identified in 83.3% (5/6) of cases, and clonal TCR-β and/or TCR-γ rearrangements were identified in 100% (9/9) of cases. No common clonal B or T rearrangement was reported in either of the individualized contingents of the cHL/T-cell composite lymphomas. Molecular data are detailed in Supplementary Table S13.
4. Discussion
The present systematic review, which gathered the available data from the literature concerning composite lymphomas with a cHL contingent, allowed to describe the clinical, histopathological, and molecular characteristics of these entities, to improve the understanding of lymphomagenesis in these rare lymphomas (Figure 1). Due to the low prevalence of these diseases (<0.5% of lymphomas) [115], no prospective study can be easily performed and the data available are thus based on case reports and small series only. This review highlights that >70% of patients with composite lymphomas are ≥55 years old, suggesting that aging and immunosenescence could be risk factors for developing two lymphomas simultaneously [68]. However, cHL/NLPHL [106,108], cHL/DLBCL [14,66,84,86,89], and cHL/T-cell lymphoma [109] were also reported in younger patients (<35 years old), emphasizing that these pathologies can occur at any age. Histologically, the cHL contingent is very frequently of MC-type, suggesting a particular pathophysiology. Moreover, Hodgkin cells within composite lymphomas often express CD20 in a focal and/or weak manner (from 28.9% to 55.6%), while this expression is reported to be less frequent in de novo cHL (from 12.6 to 28.1%) [116,117,118,119]. These Hodgkin cells may also express markers of the associated lymphoma such as BCL2/BCL6 for follicular lymphoma and Cyclin D1 for mantle cell lymphoma, which may be combined with BCL2/BCL6 and CCND1 rearrangements in both contingents, respectively [3,6,8,10,56,61,62,70,71,72]. These contingents may also share similar IgH/IgK rearrangements and identical pathogenic variants [5,10,56], reinforcing the hypothesis of a common clonal origin. Although the classification of lymphomas, and especially the distinction between germinal center and post-germinal center subgroups, is currently based on cellular origin [120], it appears that the cellular plasticity occurring during lymphomagenesis might be higher than initially thought. Follicular lymphomas, which have a germinal center origin [120], are an ideal illustration of this cellular plasticity, since they have been reported to transform into post-germinal center DLBCL [121,122] or transdifferentiate into myeloid pathologies such as histiocytic/dendritic cell sarcomas in rare instances [123]. The data presented herein thus expand the spectrum of mature B-cell plasticity and the classical limits of lymphomagenesis.
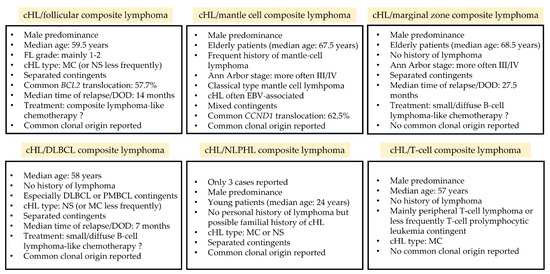
Figure 1.
Key features of composite lymphomas associating a cHL with another lymphoma. cHL: classical Hodgkin lymphoma; DOD: death of disease; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; EBV: Epstein–Barr virus; FL: follicular lymphoma; MC: mixed cellularity; M/F: male/female ratio; NLPHL: nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma; NS: nodular sclerosis; PMBL: primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma.
At diagnosis, the challenge is to differentiate a cHL contingent from Hodgkin-like cells, which can co-occur within B-cell [36,37] or T-cell lymphomas [124,125] (an example of such a differential diagnosis is given in Figure 2). Some criteria must be considered to recognize Hodgkin-like cells: (i) absence of fibrosis and/or cHL stromal reaction (eosinophils, histiocytes) with mixed/non-nodular distribution of Hodgkin cells [18,33,36,39,79]; (ii) absence/weak expression of usual cHL markers such as CD30 [35] or CD15 [36,59]; (iii) diffuse and intense expression of CD45 and multiple B-cell markers [37]. Moreover, since it is classically accepted that the lymphoma pathophysiology follows the lymphoma negation principle [120], the presence of reactive germinal centers and/or post-germinal center immunoblasts with a normal differentiation spectrum are not suggestive of cHL diagnosis [120]. However, the distinction is sometimes difficult to achieve in practice, and especially in the context of EBV lymphoproliferative disorders [33,34] in which the study of EBV latency could be helpful [126].
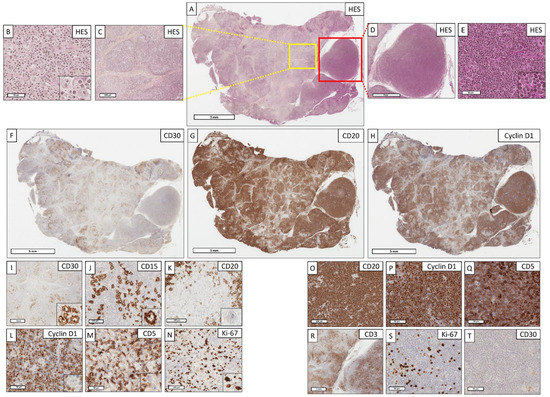
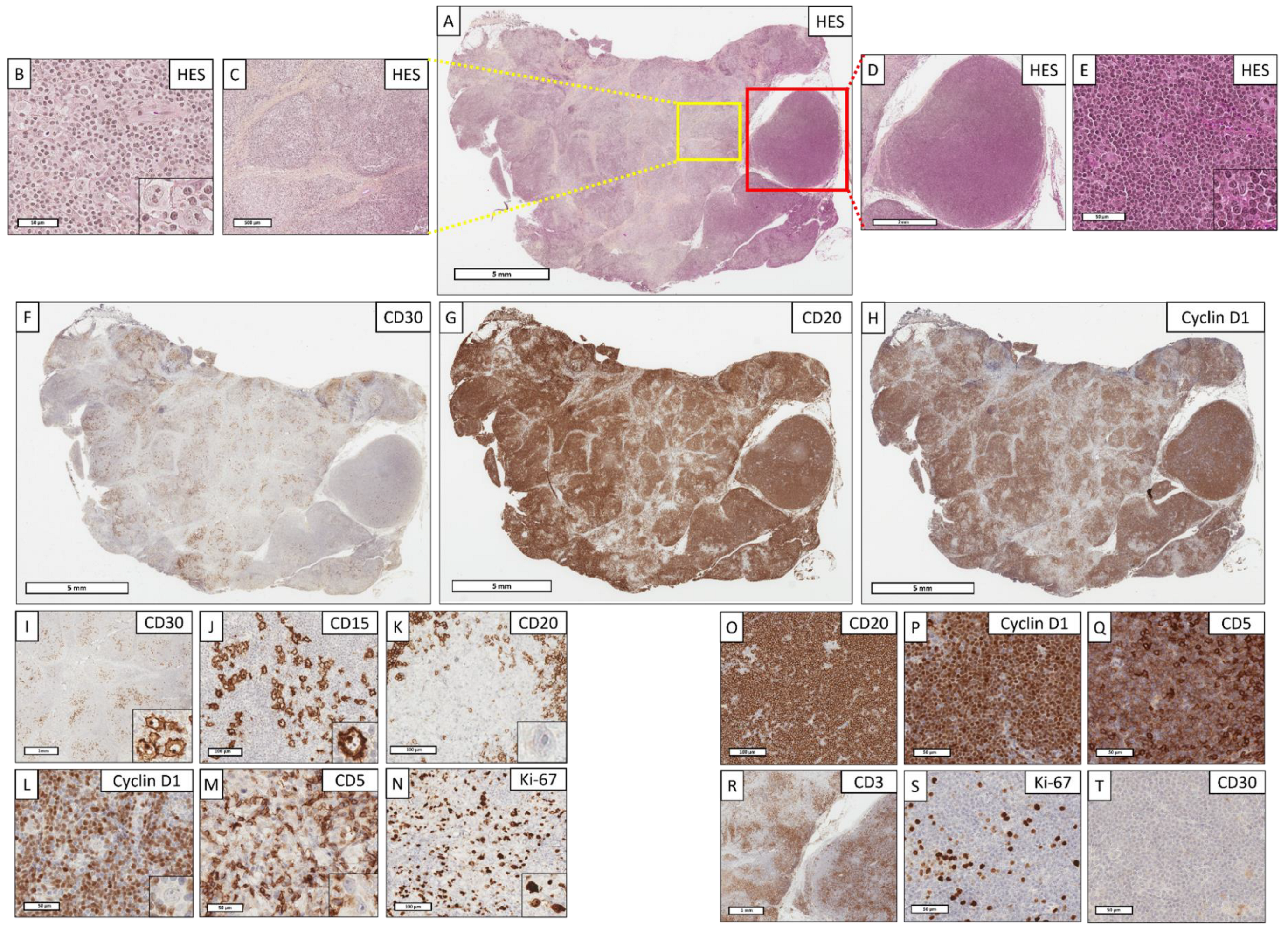
Figure 2.
A cHL/mantle cell composite lymphoma with mixed contingents: how to differentiate Hodgkin cells from Hodgkin-like cells? (A) (Hematoxylin–eosin–saffron (HES), ×4). Lymph node with a completely remodeled architecture. The tumor proliferation is nodular and diffuse. (B) (HES, ×400); (C) (HES, ×40, corresponding to yellow box from (A). The cHL contingent organization is nodular, delimited by a marked collagenous fibrosis/sclerosis. This contingent is composed of a rich epithelioid histiocytic stroma within which are Hodgkin cells with an atypical nucleus and a large eosinophilic nucleolus. (D) (HES, ×16, corresponding to red box from (A); (E) (HES, ×400). The mantle cell lymphoma contingent organization is diffuse and nodular, consisting of small, slightly atypical cells. (F) (CD30, ×4); (G) (CD20, ×4) and (H) (Cyclin D1, ×4). The anti-CD30 antibody highlights the nodular organization of cHL (localized on the left side of the lymph node), whereas the CD20 and Cyclin D1 antibodies at low magnification highlight the mantle cell lymphoma contingent (predominantly localized on the right side of the lymph node, but also mixed with cHL on the left). (I) (CD30, ×20); (J) (CD15, ×200); (K) (CD20, ×400); (L) (Cyclin D1, ×400); (M) (CD5, ×400). Hodgkin cells intensely and diffusely express CD30 and CD15, but do not express CD20, Cyclin D1, or CD5. (N) (Ki67, ×400). The proliferative index highlights the large Hodgkin cells. (O) (CD20, ×200); (P) (Cyclin D1, ×400); (Q) (CD5, ×400); (R) (CD3, ×20); (S) (Ki67, ×400); (T) (CD30, ×400). The mantle cell lymphoma contingent expresses intensely and diffusely CD20, CD5, and Cyclin D1, without expression of CD3. The tumor cells express CD5 less intensely than adjacent reactive T cells, also expressing CD3. The proliferative index is weak (<10%). In this example, the diagnosis is a cHL/mantle cell composite lymphoma rather than Hodgkin-like cells of a mantle cell lymphoma, since there is a compatible architectural change (sclerotic and nodular), a cHL histiocytic stroma, positive cHL markers (CD30 and CD15) [36,59], and a lack of expression of other markers by the cHL contingent (CD20, CD5, Cyclin D1).
4.1. cHL/Follicular Composite Lymphomas
Patients are generally old or middle-aged and without a history of lymphoma. At presentation, a polyadenopathy and a III/IV Ann Arbor stage are observed. The cHL contingent is classically of MC-type, less frequently of NS-type, and is usually separated from the follicular lymphoma contingent, which is more often grade 1–2. Patients treated with a composite lymphoma-like chemotherapy showed a rate of relapse/death slightly decreased compared to other patients, reinforcing the importance of treating both contingents.
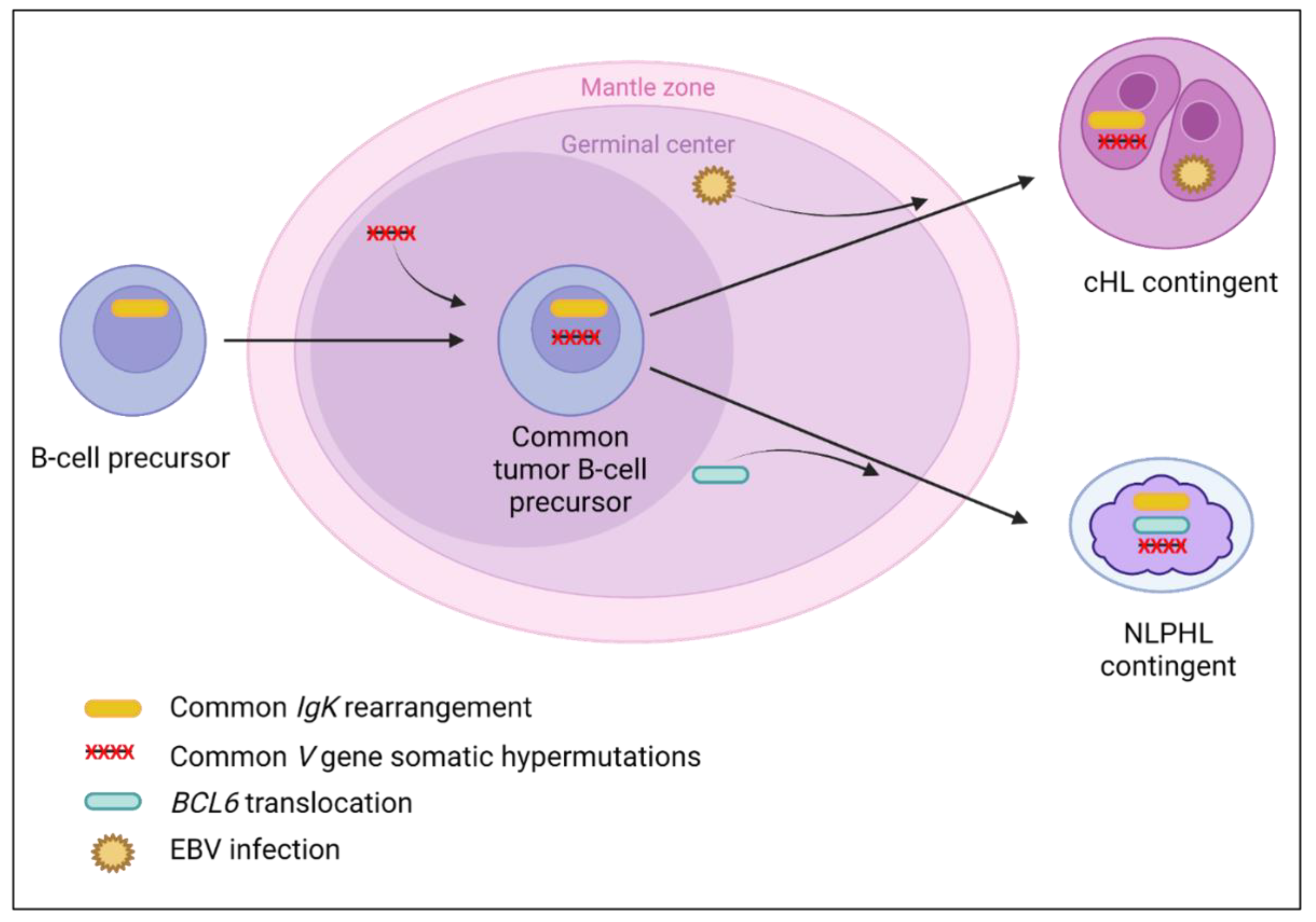
It has been hypothesized that the cHL contingent of composite cHL/follicular lymphomas could be different than de novo cHL [10,56]. In this review, we also observed (i) clinical differences (composite lymphomas occurring at a later age than de novo cHL); (ii) morphological differences (high prevalence of EBER negative cHL-MC compared to de novo cHL-MC which is often EBER positive, reinforcing the hypothesis of a low prevalence of EBV infection in composite lymphomas [66]); (iii) immunohistochemical differences with a higher prevalence of centrofollicular markers and some B-cell markers, questioning a possible response to anti-CD20 therapy of the cHL contingent [57]; and (iv) molecular differences, with BCL2/BCL6 translocations and pathogenic follicular lymphoma-like variants reported in the cHL contingent [3,10,56,61,62]. All these uncommon features suggest a specific pathophysiology of these lymphomas and as shown in Figure 3, a transdifferentiation process of the cHL contingent from a follicular tumor cell could be hypothesized.
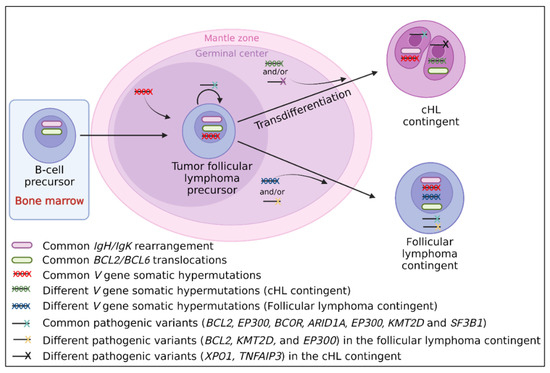
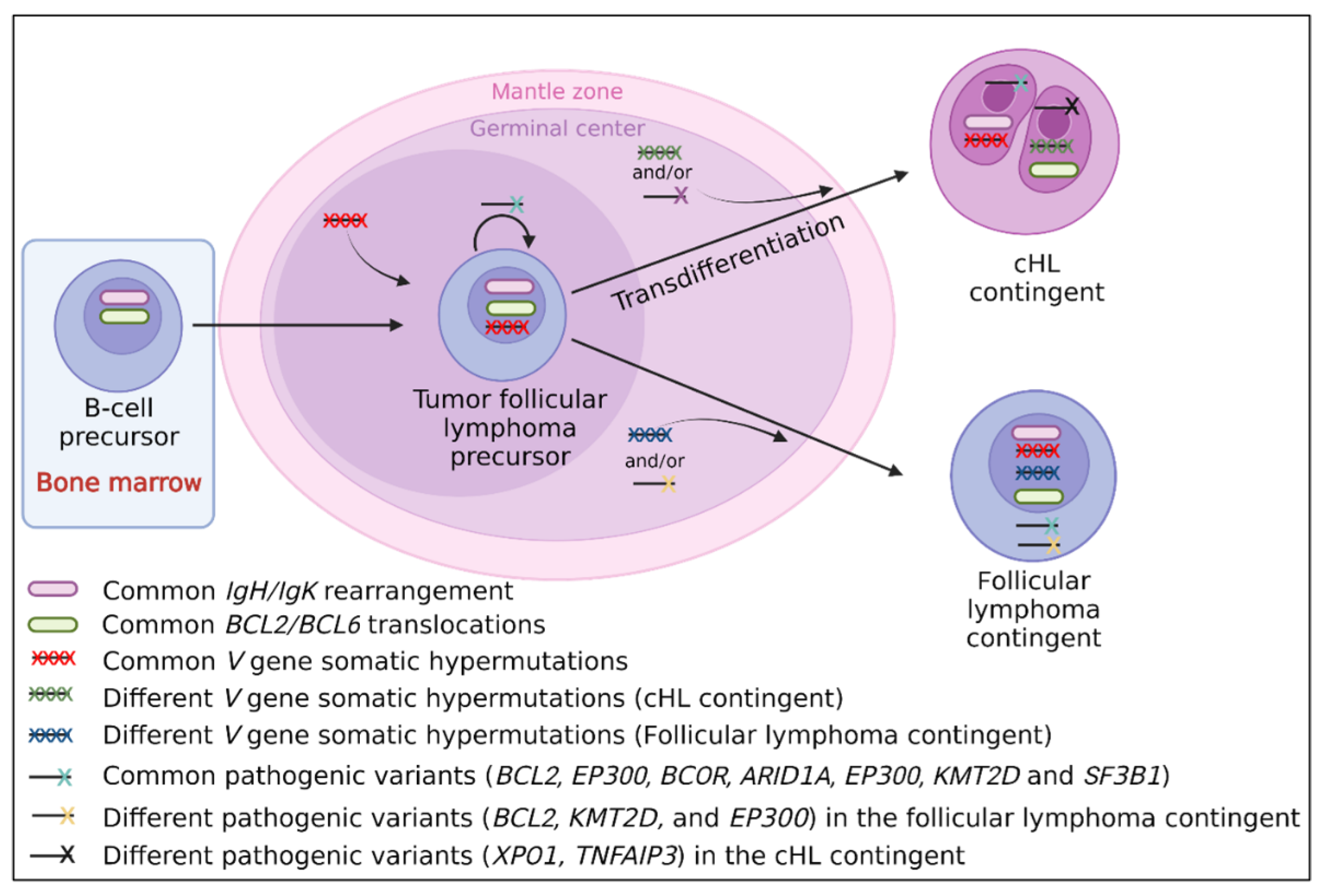
Figure 3.
Suggested transdifferentiation model of a follicular lymphoma precursor into classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) contingent in cHL/follicular composite lymphomas. The transdifferentiation model in this type of composite lymphoma is based on the presence of (i) BCL2/BCL6 translocations in both contingents and similar IgH/IgK rearrangements which take place in early B-cells in the bone marrow [10,123]; (ii) identical V gene somatic hypermutations [6,11,12], indicating that the tumoral precursor matures through the germinal center; (iii) identical driver pathogenic follicular lymphoma-like variants (KMT2D, BCL2, EP300, and ARID1A) [10], indicating that the common tumoral precursor is probably a tumor follicular cell; (iv) different V gene somatic hypermutations between both contingents [6,11,12], indicating that the separation of both contingents takes place during the germinal center step; and (v) different passenger variants, specific to each contingent (XPO1, TNFAIP3 found in the cHL contingent only, and BCL2, KMT2D, and EP300 found in the follicular lymphoma contingent only) [10], indicating that each contingent evolves independently after the transdifferentiation step.
4.2. cHL/Mantle Cell Composite Lymphomas
This entity is rarer than cHL/follicular composite lymphomas, with only a few cases reported in the literature. Patients are classically old males with a history of mantle cell lymphoma, presenting polyadenopathy but without B symptoms. The Ann Arbor stage is usually III/IV, without bone marrow involvement. Both contingents are often mixed with frequent Hodgkin cell CD15 and EBER positivity. As shown in Figure 4, data available could support a transdifferentiation process of cHL from a tumor mantle cell precursor, with some evidence that the cHL contingent could then pass through the germinal center [6,9].
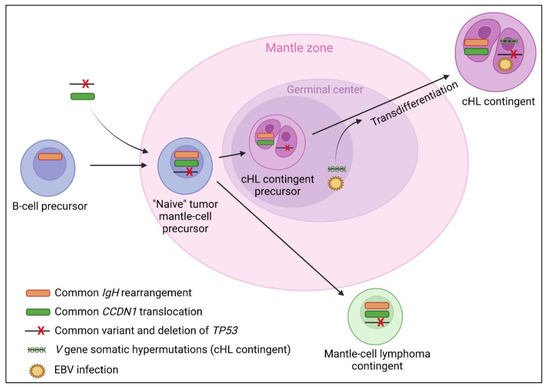
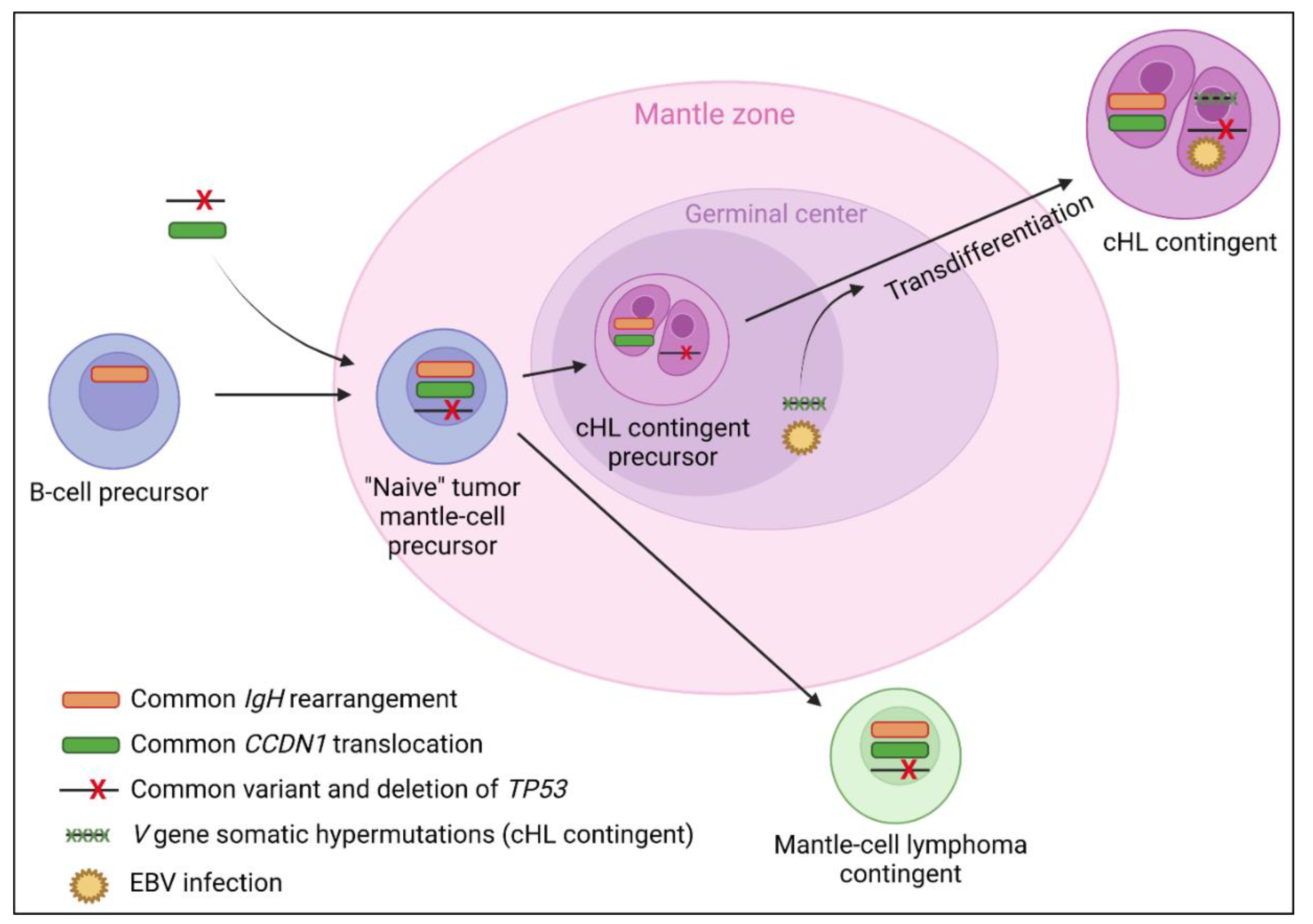
Figure 4.
Suggested lymphomagenesis model for classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL)/mantle cell composite lymphomas. The frequent presence of a mantle cell lymphoma in patient personal history at diagnosis, CCND1 translocations in both contingents [6,8,70,71,72], and similar clonal IgH rearrangements [8,9] between both contingents suggest a transdifferentiation of cHL from a tumoral mantle cell precursor. One study also reported a common pathogenic variant and deletion of TP53 shared by both contingents [8]. There is evidence that the cHL contingent could evolve through the germinal center with the presence of V gene somatic hypermutations reported in the cHL contingent only [6,9]. The passage through the germinal center of a subclone of the mantle cell lymphoma precursor, with the apparition of V gene somatic hypermutations, could be implicated in the transdifferentiation event [9] as could the EBV infection of a tumoral mantle cell precursor, which is very prevalent in the cHL contingent (75%) and never reported in the mantle cell lymphoma contingent. However, 25% of the cHL contingents do not express EBER and/or LMP-1, which suggests that the latter assumption alone is not sufficient to fully explain the lymphomagenesis of the cHL contingent. Although the origin of mantle cell lymphoma from a naive B-cell of the mantle zone is yet to be commonly accepted [123], one study also reported the presence of V gene somatic hypermutations in both cHL and mantle cell lymphoma contingents [8], which could suggest a post-germinal center origin of both contingents in some cases.
4.3. cHL/Marginal Zone Composite Lymphomas
Patients are classically old males without a history of lymphoma and presenting polyadenopathy but without B symptoms. At presentation, the Ann Arbor stage is classically III/IV. Both contingents are usually separated, with a cHL-MC contingent expressing p53 and often CD15, LMP-1, and EBER, while the marginal zone lymphoma contingent does not. The rate of relapse/death slightly decreased when patients were treated with small/diffuse B-cell lymphoma-like chemotherapy.
No common clonal origin has been identified between both contingents. However, the molecular data available are very limited with only one case reported without IgH rearrangement or somatic hypermutations [6]. In addition, the cellular origins are different as cHL pass through the germinal center while marginal and splenic marginal zone lymphomas pass outside the germinal center [127]. However, an activation of the NF-KB pathway is implicated in the lymphomagenesis of both neoplasms [128,129,130].
4.4. cHL/NLPHL Composite Lymphomas
This entity seems to be the less frequent of all composite lymphomas. Whether the presentation is simultaneous or sequential, the association of cHL and NLPHL is described especially in young males [108]. In one case, a familial history of cHL was reported [106]. Indeed, although the pathophysiology between cHL and NLPHL is different [17], it has been suggested that there is a greater risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma in case of familial history of the same pathology [131], with a predominantly male predisposition [132] and a cumulative risk of Hodgkin lymphoma in first-degree relatives of 0.6% [133]. Recently, familial syndromes with Hodgkin lymphomas have been reported including germinal homozygote CD27 deficiency [134], DICER1 syndrome [36,135,136], association with the human leucocyte antigen (HLA) abnormalities [137], KLHDC8B translocation [138], NPAT germinal mutation [139], homologous germinal variant of ACAN [140], and familial KDR mutations [141]. However, the presence of certain homologous variants in healthy patients supports the necessity but the insufficiency of these genetic defects alone to cause the disease, with a potential role of environmental factors [134]. The exact lymphomagenesis of this neoplasm is unknown. However, based on the data available, we propose a model of lymphomagenesis in Figure 5.
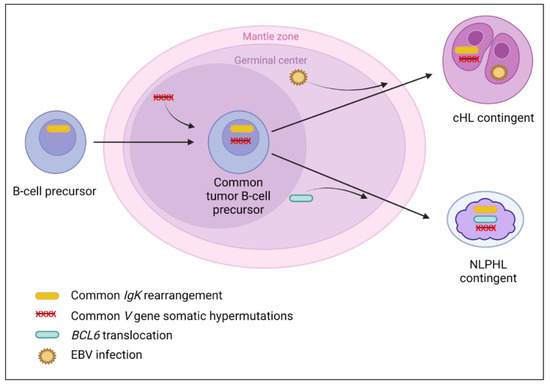
Figure 5.
Suggested lymphomagenesis model for classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL)/nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) composite lymphomas. Both contingents of these lymphomas come from the germinal center [123]. The presence of similar clonal rearrangements of IgK only with polyclonal IgH rearrangements [106], or identical V gene somatic hypermutations [107] between both contingents, suggest that the lymphomagenesis of this entity takes place in the germinal center, or after this step. Indeed, the V gene somatic hypermutations, arising in the germinal center [123], could interfere with the detection of similar IgH rearrangements by avoiding the hybridization of PCR primers on the variable regions. Then, after the germinal center step, additional molecular abnormalities could occur to form both contingents with specific molecular alterations. These abnormalities could be (i) the BCL6 translocation, which is the hallmark of NLPHL, leading to the BCL6 overexpression reported in two cases, without BCL6 expression in the cHL contingent [106,107]; and/or (ii) EBV infection in cHL, absent in the NLPHL contingent [106]. However, few molecular data are available for this composite lymphoma, which complicates lymphomagenesis understanding.
4.5. cHL/DLBCL Composite Lymphomas
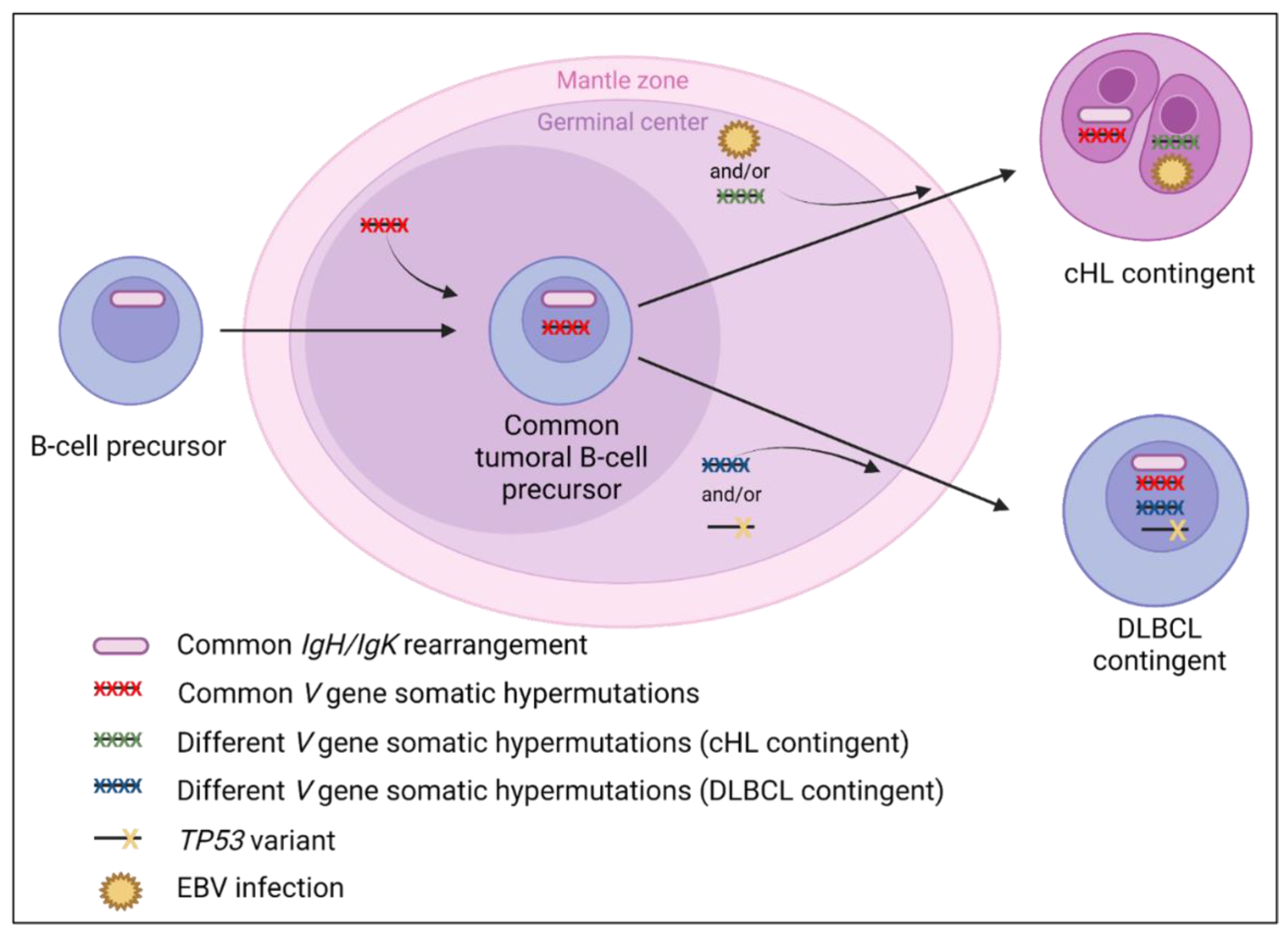
Patients are classically old or middle-aged, without history of lymphoma at presentation, and with polyadenopathy but without B symptoms. Both contingents are usually separated, with a cHL contingent of NS-type and less frequently MC-type. Hodgkin cells often express CD15 and p53 (without TP53 mutation reported in the cHL contingent). These lymphomas have been reported with a better prognosis than those with a sequential presentation [16,142]. The rate of relapse/death slightly decreased when patients were treated with small/diffuse B-cell lymphoma-like chemotherapy. Based on the data available, we suggest a model of lymphomagenesis in Figure 6.
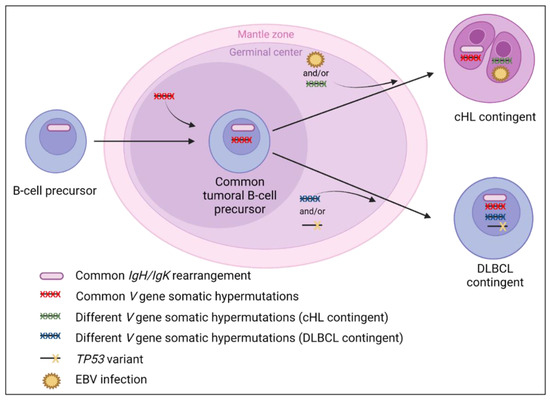
Figure 6.
Suggested lymphomagenesis of classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL)/diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) composite lymphomas. Similar clonal IgH/IgK rearrangements between both contingents are reported and support the common clonal origin. Moreover, the presence of common and distinct V gene somatic hypermutations [6,13] support that the tumor precursor could originate from the germinal center. Schmitz et al. have hypothesized that a TP53 variant, identified only in the DLBCL contingent, could contribute to its formation. In contrast, EBV infection is more prevalent in the Hodgkin cells than in the DLBCL contingent (Table 3), which could contribute to the genesis of the cHL contingent in some cases of composite lymphomas, as suggested by Zettl et al. [76]. However, for EBV-negative cHL cases, further molecular studies are needed to explain the lymphomagenesis more precisely.
Recently, Singh et al. have reported a series of six cHL/DLBCL and DLBCL/cHL sequential lymphomas, and identified identical variants in both contingents (including TNFAIP3, XPO1, TP53, and B2M), reinforcing the clonal relationship between these lymphomas and the concept of plasticity occurring within mature B-cells [143].
4.6. Composite cHL/T-Cell Lymphomas
Patients are classically old or middle-aged, without history of lymphoma at presentation, and present polyadenopathy with or without B symptoms. The cHL contingent is more frequently an MC-type. Hodgkin cells often express p53 and CD15. In the T-cell lymphoma contingent, the less expressed T-cell markers are CD7 and then CD4. In contrast, CD2 and CD3 were always reported as positive on neoplastic T-cells.
To date, there is no molecular evidence of a clonal relationship between both contingents of these composite lymphomas, because, in most cases, the molecular studies were performed on the whole sample without individualization of the two contingents. In addition, no shared B or T rearrangements were observed in the only two cases for which the contingents were individualized [60,110]. However, despite the classic B-cell origin of cHL [127], some authors have identified a T-cell origin of certain cHL, with a clonal rearrangement of TCR-γ [144] or TCR-β [145] in Hodgkin cells. Additionally, common clonal rearrangements of the TCR-encoding gene seem to occur between both contingents of cHL/T-cell sequential lymphomas [112,146], but the histopathological differential diagnosis between cHL and T-cell lymphomas is sometimes difficult in practice. Moreover, cHL have been reported in association with other cutaneous T-cell neoplasms, such as mycosis fungoid or lymphomatoid papulosis [22,112,146], with or without TCR rearrangements, but these neoplasms were excluded in the present review because the pathophysiology is probably different.
Distinguishing between peripheral T-cell lymphoma with Hodgkin-like cells and LR-type cHL or cHL/T-cell composite lymphoma could be very misleading in practice [147,148]. Moreover, the diagnosis of T-cell lymphoma with Hodgkin-like cells is probably more frequent than that of cHL/T-cell composite lymphoma. These Hodgkin-like cells could be EBV positive or EBV negative (especially in T-cell lymphomas of TFH origin), and their presence is commonly interpreted as a consequence of the patient’s immunosuppression [147,148]. The presence of aggregates or sheets of atypical T-cells with clear cytoplasm, expressing CD10 and CXCL13, must alert the pathologist of a potential diagnosis of T-cell lymphoma rather than cHL. Indeed, other TFH-associated markers such as BCL6, PD1, ICOS, are less useful as they are also commonly observed in the microenvironment of cHL [147,148]. Other criteria such as (i) the absence of fibrosis/sclerosis and polymorphic background; (ii) the presence of Hodgkin-like cells distributed in a background of neoplastic TFH-cells without distinct areas of cHL; (iii) the absence of the single layer of rosetting T-cells surrounding the Hodgkin-like cells, replaced by a large aggregate of T cells; and (iv) a more preserved B-cell program of the Hodgkin-like cells with diffuse and intense expression of B-cell markers, also support the diagnosis of T-cell lymphoma with Hodgkin-like cells rather than that of cHL [147,148].
4.7. Limits and Conclusions
This review has some limits. First, the clinical data available are very limited, since most articles are unique cases that do not report the patient’s follow-up and/or treatments. In addition, patient management often differs between studies, even within the same type of composite lymphoma, complicating their comparison and the establishment of treatment guidelines. As a result, the clinical conclusions from these studies are less robust. This is particularly true for laboratory data or the extension assessment, for which data were often missing. However, in the absence of prospective studies, retrospective data remain the only way to understand these rare lymphomas. Another limitation relates to the methodological biases of the review: (i) the non-exhaustive nature of the PubMed database; (ii) the initial selection of articles made by only one reviewer (A.T.); and (iii) the article selection which was dependent on the keywords used. However, to reduce some of these biases, an exhaustive study of the bibliography/references of each article included in this review was also carried out, in order to search for articles that would not have been found using the keywords previously cited. In addition, a cross-check of all the articles finally included was performed independently by a second reviewer (A.T.-G.). Moreover, the objective of this review was not to exhaustively describe all clinical, histopathological, and molecular data reported for composite lymphomas, but to estimate the frequency of the variables available in medical-scientific articles in English for composite lymphomas, and to better understand the cellular plasticity occurring in cHL (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6).
5. Conclusions
To conclude, cHL appears to be endowed with a greater plasticity spectrum than previously thought, explaining its association with multiple T and B lymphoid neoplasms, or even myeloid disorders [149]. The lymphomagenesis of composite lymphomas is complex and probably multifactorial, combining genetic, infectious, and environmental factors.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers14225695/s1, Text S1: Classification of treatments; Figure S1: Flow diagram; Table S1: PRISMA 2020 checklist; Table S2: Clinical and laboratory data of cHL/follicular composite lymphomas; Table S3: Histopathological and molecular data of cHL/follicular composite lymphomas; Table S4: Clinical and laboratory data of cHL/mantle cell composite lymphomas; Table S5: Histopathological and molecular data of cHL/mantle cell composite lymphomas); Table S6: Clinical and laboratory data of cHL/marginal zone composite lymphomas; Table S7: Histopathological and molecular data of cHL/marginal zone composite lymphomas; Table S8: Clinical and laboratory data of cHL/diffuse large B-cells composite lymphomas; Table S9: Histopathological and molecular data of cHL/diffuse large B-cells composite lymphomas; Table S10: Clinical and laboratory data of cHL/NLPHL composite lymphomas; Table S11: Histopathological and molecular data of cHL/NLPHL composite lymphomas; Table S12: Clinical and laboratory data of cHL/T-cell composite lymphomas; Table S13: Histopathological and molecular data of cHL/T-cell composite lymphomas. Ref. [150] has been cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Data collection from the literature, A.T.; writing of the first draft, A.T. and A.T.-G.; proofreading and critical revision, M.D., J.F., H.G., L.J., G.A., C.L. and C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Garance Tondeur, Jimmy Perrot and Mathilde Bardou from the Centre de Pathologie et de Biologie Moléculaire de Lyon-Sud, Hospices Civils de Lyon. The authors also thank Véréna Landel (Direction de la Recherche en Santé, Hospices Civils de Lyon, Lyon, France) for help in manuscript preparation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, H.; Hendrickson, R.; Dorfman, R.F. Composite lymphoma. Cancer 1977, 40, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Zarate-Osorno, A.; Kingma, D.W.; Raffeld, M.; Medeiros, L.J. The interrelationship between Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Ann. Oncol. 1994, 5, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, A.M.; Taniguchi, H.; Nomoto, J.; Makita, S.; Kitahara, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Munakata, W.; Suzuki, T.; Maruyama, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Clinicopathological features of classical Hodgkin lymphoma in patients ≥ 40 years old, with special reference to composite cases. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custer, R. Pitfalls in the diagnosis of lymphoma and leukemia from the pathologist’s point of view. In Proceedings of the Second National Cancer Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 3–5 March 1952; American Cancer Society: New York, NY, USA, 1954; pp. 554–557. [Google Scholar]
- Küppers, R.; Dührsen, U.; Hansmann, M.L. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of composite lymphomas. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Renné, C.; Rosenquist, R.; Tinguely, M.; Distler, V.; Menestrina, F.; Lestani, M.; Stankovic, T.; Austen, B.; Bräuninger, A.; et al. Insights into the multistep transformation process of lymphomas: IgH-associated translocations and tumor suppressor gene mutations in clonally related composite Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, N.; Ohshima, K.; Abe, M.; Osamura, Y. Demonstration of chimeric DNA of bcl-2 and immunoglobulin heavy chain in follicular lymphoma and subsequent Hodgkin lymphoma from the same patient. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2007, 47, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.; Crescenzi, B.; Schneider, M.; Ascani, S.; Hartmann, S.; Hansmann, M.L.; Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Küppers, R. Subclonal evolution of a classical Hodgkin lymphoma from a germinal center B-cell-derived mantle cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinguely, M.; Rosenquist, R.; Sundström, C.; Amini, R.M.; Küppers, R.; Hansmann, M.L.; Bräuninger, A. Analysis of a clonally related mantle cell and Hodgkin lymphoma indicates Epstein-Barr virus infection of a Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cell precursor in a germinal center. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trecourt, A.; Mauduit, C.; Szablewski, V.; Fontaine, J.; Balme, B.; Donzel, M.; Laurent, C.; Sesques, P.; Ghesquières, H.; Bachy, E.; et al. Plasticity of Mature B Cells Between Follicular and Classic Hodgkin Lymphomas: A Series of 22 Cases Expanding the Spectrum of Transdifferentiation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuninger, A.; Hansmann, M.L.; Strickler, J.G.; Dummer, R.; Burg, G.; Rajewsky, K.; Küppers, R. Identification of common germinal-center B-cell precursors in two patients with both Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küppers, R.; Sousa, A.B.; Baur, A.S.; Strickler, J.G.; Rajewsky, K.; Hansmann, M.L. Common germinal-center B-cell origin of the malignant cells in two composite lymphomas, involving classical Hodgkin’s disease and either follicular lymphoma or B-CLL. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenquist, R.; Menestrina, F.; Lestani, M.; Küppers, R.; Hansmann, M.L.; Bräuninger, A. Indications for peripheral light-chain revision and somatic hypermutation without a functional B-cell receptor in precursors of a composite diffuse large B-cell and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Lab. Invest. 2004, 84, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.L.; Medeiros, L.J.; Jaffe, E.S. Composite lymphoma. A clinicopathologic analysis of nine patients with Hodgkin’s disease and B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 96, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumala, S.; Esposito, M.; Fuchs, A. An unusual variant of composite lymphoma: A short case report and review of the literature. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aussedat, G.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Stamatoullas, A.; Molina, T.; Safar, V.; Laurent, C.; Michot, J.M.; Hirsch, P.; Nicolas-Virelizier, E.; Lamure, S.; et al. Composite and sequential lymphoma between classical Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal lymphoma/diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, a clinico-pathological series of 25 cases. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weniger, M.A.; Küppers, R. Molecular biology of Hodgkin lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.K.; Sheikh, Z.A.; Al-Shama’a, M.H.; John, B.; Alawi, A.M.; Junaid, T.A. A case of composite classical and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma with progression to diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Diagnostic difficulty in fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2017, 45, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C.; Griem, M.L.; Grozea, P.N.; Freel, R.J.; Variakojis, D. Mycosis fungoides and Hodgkin’s disease occurring in the same patient: Report of three cases. Cancer 1979, 44, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, D.; Green, J.A.; White, M. Mycosis fungoides associated with nodular sclerosing Hodgkin’s disease: A case report. Cancer 1980, 46, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, K.A.; Schinella, R.; Schwartz, M.; Ramsey, D.; Weintraub, A.H.; Silber, R.; Amorosi, E.L. Simultaneous occurrence of mycosis fungoides and Hodgkin disease: Clinical and histologic correlations in three cases with ultrastructural studies in two. Am. J. Hematol. 1983, 14, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Chung, H.C.; Lim, H.Y.; Kim, D.L.; Koh, E.H.; Kim, J.H.; Roh, J.K.; Chun, S.I.; Yang, W.I.; Kim, G.E. Coexisting mycosis fungoides and Hodgkin’s disease as a composite lymphoma: A case report. Yonsei. Med. J. 1991, 32, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bee, C.S.; Blaise, Y.P.; Dunphy, C.H. Composite lymphoma of Hodgkin lymphoma and mycosis fungoides: Previously undescribed in the same extracutaneous site. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 42, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Nong, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Cutaneous composite lymphoma of mycosis fungoides and Hodgkin lymphoma: Response to sequential therapy. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willenbrock, K.; Ichinohasama, R.; Kadin, M.E.; Miura, I.; Terui, T.; Meguro, K.; Fukuhara, O.; DeCoteau, J.F.; Hansmann, M.L. T-cell variant of classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma with nodal and cutaneous manifestations demonstrated by single-cell polymerase chain reaction. Lab. Invest. 2002, 82, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhoff, M.; Hummel, M.; Assaf, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Treudler, R.; Geilen, C.C.; Stein, H.; Orfanos, C.E. Cutaneous T cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma of the B cell type within a single lymph node: Composite lymphoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 57, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delabie, J.; Greiner, T.C.; Chan, W.C.; Weisenburger, D.D. Concurrent lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin’s disease and T-cell lymphoma. A report of three cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, S.; Hidaka, E.; Katsuyama, T. Clonal identity of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s disease and T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1124–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Trenn, G.; Wu, G.; Abou-Elella, A.; Reis, H.E.; Chan, W.C. The clonal relationship between nodular sclerosis Hodgkin’s disease with a clonal Reed-Sternberg cell population and a subsequent B-cell small noncleaved cell lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Dargent, J.L.; Lespagnard, L.; Meiers, I.; Bradstreet, C.; Heimann, P.; De Wolf-Peeters, C. Composite follicular lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin’s disease. Virchows. Arch. 2005, 447, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J.P.; Quinn, F.; Dowling, A.; Walker, J.; Hayes, T.; Bird, B.; Flavin, R. Composite t(14;18)-Negative Follicular Lymphoma and Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma. Case. Rep. Hematol. 2018, 2018, 4312594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esper, A.; Alhoulaiby, S.; Zuhri-Yafi, R.; Alshehabi, Z. Composite lymphoma of T-cell rich, histiocyte-rich diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: A case report. J. Med. Case. Rep. 2021, 15, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, S.; Webber, S.; Ahuja, S.; Jaffe, R. Hodgkin-like posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in children: Does it differ from posttransplant Hodgkin lymphoma? Pediat. Dev. Pathol. 2004, 7, 348–360. [Google Scholar]
- Karube, K.; Takatori, M.; Kohno, K.; Tomoyose, T.; Ohshiro, K.; Nakazato, I. Co-occurrence of EBV-positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma and B-cell lymphomas of different clonal origins: A case report and literature review. Pathol. Int. 2020, 70, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, F.; Kowsari, F.; Darakhshandeh, A.; Adibi, P. Composite lymphoma in a patient with ulcerative colitis: A case report. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem. Cell. Res. 2014, 8, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.S.; Ben-Ezra, J.; Burke, J.S.; Sheibani, K.; Rappaport, H. Reed-Sternberg-like cells in low-grade lymphomas are transformed neoplastic cells of B-cell lineage. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1993, 99, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerl, M.G.; Bentley, G.; Bellan, C.; Leoncini, L.; Ehmann, W.C.; Palutke, M. Lacunar and reed-sternberg-like cells in follicular lymphomas are clonally related to the centrocytic and centroblastic cells as demonstrated by laser capture microdissection. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 122, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, D.; Matsuishi, E.; Akashi, M.; Shibaki, M.; Hirano, T.; Ide, M.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Tsukiji, H.; Gondo, H. Hodgkin-like peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) with preserved Hodgkin-like lesions at autopsy: A case report with an interesting clinical course. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, G.; Berkowitz, J.; Morris, J.C.; Janik, J.E.; Raffeld, M.A.; Pittaluga, S. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with Epstein-Barr virus-positive Hodgkin-like cells. Human. Pathol. 2011, 42, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBrun, D.P.; Ngan, B.Y.; Weiss, L.M.; Huie, P.; Warnke, R.A.; Cleary, M.L. The bcl-2 oncogene in Hodgkin’s disease arising in the setting of follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 1994, 83, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedobitek, G.; Baumann, I.; Brabletz, T.; Lisner, R.; Winkelmann, C.; Helm, G.; Kirchner, T. Hodgkin’s disease and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: Composite lymphoma with evidence of Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Pathol. 2000, 191, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, H.; Jaffe, E.S.; Shin, S.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Weiss, L.M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with Reed-Sternberg-like cells and possible transformation to Hodgkin’s disease. Mediation by Epstein-Barr virus. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, I.; Herndier, B.G.; Glassberg, A.B.; Hamill, T.R. A case of composite Hodgkin’s disease and chronic lymphocytic leukemia in bone marrow. Lack of Epstein-Barr virus. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1996, 120, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanzler, H.; Küppers, R.; Helmes, S.; Wacker, H.H.; Chott, A.; Hansmann, M.L.; Rajewsky, K. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg-like cells in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia represent the outgrowth of single germinal-center B-cell-derived clones: Potential precursors of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 2000, 95, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, M.J.; Kaleem, Z.; Bolger, M.J.; Swanson, P.E.; Zutter, M.M. Composite prolymphocytoid and hodgkin transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, A.; Maggio, E.; Rust, R.; Kooistra, K.; Diepstra, A.; Poppema, S. Clonal relation in a case of CLL, ALCL, and Hodgkin composite lymphoma. Blood 2002, 100, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, M.S.; Ledakis, P.; Novinski, D.; Fu, K.; Hutchins, M.; Frankforter, S.; Mleczko, K.; Sanger, W.G.; Chan, W.C. An unusual case of composite lymphoma involving chronic lymphocytic leukemia follicular lymphoma and Hodgkin disease. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2004, 45, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leval, L.; Vivario, M.; De Prijck, B.; Zhou, Y.; Boniver, J.; Harris, N.L.; Isaacson, P.; Du, M.Q. Distinct clonal origin in two cases of Hodgkin’s lymphoma variant of Richter’s syndrome associated With EBV infection. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, M.; Dobrea, C.; Badea, D.; Genunche-Dumitrescu, A.; Mitruţ, P.; Duţă, D. The composite lymphoma: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia-classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2010, 51, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Rathnam, K.; Karpurmath, S.; Cyriac, S.; Gnana, S.T.; Sundersingh, S. Composite Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A rare case. J. Cancer. Res. Ther. 2011, 7, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelis, F.V.; Kourti, G.; Skertsou, M.; Karmiris, T.; Rontogianni, D.P.; Harhalakis, N. Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia into composite diffuse large B-cell and Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2012, 53, 2302–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, M.; Ehsani, M.; Moosavian, M.; Khooeei, A. Primary composite lymphoma of the lung: A case report. Tanaffos 2014, 13, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, M.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Nishio, T.; Abe, M.; Kuroda, M.; Saito, S.; Sakurai, K. Composite lymphoma arising in the parotid gland: A case report. Auris. Nasus. Larynx. 2004, 31, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, J.A.; Nair, R.A.; Sukumaran, R.; Nair, S.G. Composite lymphomas: Experience from a tertiary cancer center in Kerala, South India. Indian. J. Cancer 2017, 54, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, S.; Larson, D.P.; Shi, M.; He, R.; Dave, B.J.; Greiner, T.C.; Fu, K.; McPhail, E.D.; Ketterling, R.P.; et al. Composite Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma and Follicular Lymphoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 22 Cases With Review of 27 Additional Cases in the Literature. Am. J. Surg. Path. 2022, 46, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linck, D.; Lentini, G.; Tiemann, M.; Fauser, A.A.; Parwaresch, R.; Basara, N. Sequential application of chemotherapy and monoclonal CD 20 antibody: Successful treatment of advanced composite-lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2005, 46, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Zarate-Osorno, A.; Medeiros, L.J. The interrelationship of Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas-lessons learned from composite and sequential malignancies. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 1992, 9, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Hansmann, M.L.; Fellbaum, C.; Hui, P.K.; Lennert, K. Morphological and immunohistochemical investigation of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma combined with Hodgkin’s disease. Histopathology 1989, 15, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demurtas, A.; Aliberti, S.; Bonello, L.; Di Celle, P.F.; Cavaliere, C.; Barreca, A.; Novero, D.; Stacchini, A. Usefulness of multiparametric flow cytometry in detecting composite lymphoma: Study of 17 cases in a 12-year period. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 135, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Ichikawa, A.; Miyoshi, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Kimura, Y.; Nino, D.; Ohshima, K. High frequency of t(14;18) in Hodgkin’s lymphoma associated with follicular lymphoma. Pathol. Int. 2012, 62, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Griffin, G.K.; Yenamandra, A.; Wheeler, F.C.; Ligon, A.H.; Nandedka, M.A.; Shaheen, S.P.; Mosse, C.A.; Kim, A.S. Transformation of follicular lymphoma into classical Hodgkin lymphoma showing t(14;18). Hematopathology 2016, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.N.; Jeon, M.J.; Yu, E.S.; Kim, D.S.; Choi, C.W.; Ko, Y.H. Composite follicular lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2022, 56, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, A.; Ureshino, H.; Ando, T.; Kizuka, H.; Kusaba, K.; Sano, H.; Itamura, H.; Kubota, Y.; Kojima, K.; Ohshima, K.; et al. Three coexisting lymphomas in a single patient: Composite lymphoma derived from a common germinal center B-cell precursor and unrelated discordant lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 107, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzella, M.; Brogna, B.; Romano, A.; Torelli, F.; Esposito, G.; Petrillo, M.; Romano, F.M.; Di Martino, N.; Reginelli, A.; Grassi, R. Detecting a rare composite small bowel lymphoma by Magnetic Resonance Imaging coincidentally: A case report with radiological, surgical and histopathological features. Int. J. Surg. Case. Rep. 2018, 46, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, D.W.; Medeiros, L.J.; Barletta, J.; Raffeld, M.; Mann, R.B.; Ambinder, R.F.; Jaffe, E.S. Epstein-Barr virus is infrequently identified in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas associated with Hodgkin’s disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1994, 18, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caleo, A.; Sánchez-Aguilera, A.; Rodríguez, S.; Dotor, A.M.; Beltrán, L.; de Larrinoa, A.F.; Menárguez, F.J.; Piris, M.A.; García, J.F. Composite Hodgkin lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma: Two clonally unrelated tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giua, R.; Fontana, D.; Deda, G.; Bianchi, A.; Rabitti, C.; Antonelli Incalzi, R. Composite mantle-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma in a very old adult. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.J.; Banerjee, S.S.; Cook, Y.; Houghton, J.B.; Menasce, L.P. Composite mantle-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Histopathology 2006, 48, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, R.; Miyagawa-Hayashino, A.; Shishido-Hara, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Omatsu, I.; Morinaga, Y.; Shimura, Y.; Kuroda, J.; Imura, T.; Itoh, K.; et al. Mantle cell lymphoma with EBV-positive Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg-like cells in a patient after autologous PBSCT: Phenotypically distinct but genetically related tumors. Pathol. Int. 2021, 71, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, S.; Uppal, G.; Wang, Z.X.; Gong, J.Z. Mantle Cell Lymphoma With Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells: Review With Illustrative Case. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2019, 27, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.; Quinn, F.; Illyes, G.; Walker, J.; Castriciano, G.; O’Sullivan, P.; Grant, C.; Vandenberghe, E.; Bird, B.; Flavin, R. Composite Blastoid Variant of Mantle Cell Lymphoma and Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 25, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, V.; Bisaria, D.; Tangri, R. Composite lymphoma comprising mantle cell lymphoma and Epstein-Barr virus positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma: A rare case. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2019, 62, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, K.; Nagayama, R.; Yonekawa, N.; Nihei, T.; Sando, N.; Yatabe, Y.; Mori, N. Concurrent gastric MALT and Hodgkin lymphoma: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 20, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Kalla, H.; Balasubramanian, M.; Brodsky, I.; Gladstone, D.; Hou, J.S. Classical Hodgkin lymphoma concurrently evolving in a patient with marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the spleen. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2008, 12, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zettl, A.; Rüdiger, T.; Marx, A.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Ott, G. Composite marginal zone B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A clinicopathological study of 12 cases. Histopathology 2005, 46, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahy, H.; Hawley, I.; Beard, J. Composite splenic marginal zone lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma—An unusual combination. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2007, 29, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, K.; Shinonaga, M.; Nagayama, R.; Kashimura, H.; Yonekawa, N.; Tatebe, S.; Kuraoka, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Mori, N. Coexistence of primary pulmonary Hodgkin lymphoma and gastric MALT lymphoma associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection: A case report. Pathol. Int. 2010, 60, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, E.K.; Neuhauser, T.S.; Thompson, L.D. Hodgkin-like transformation of a marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the larynx. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2002, 6, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aguilera, N.S.; Howard, L.N.; Brissette, M.D.; Abbondanzo, S.L. Hodgkin’s disease and an extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma in the small intestine: An unusual composite lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 1996, 9, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Auditeau, C.; Lambotte, O.; Feriel, J.; Lazure, T.; Turhan, A.; Aumont, C. A composite lymphoma combining a Hodgkin lymphoma and a marginal zone lymphoma transformed into a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Case. Rep. 2018, 6, 2341–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladari, E.; Dimopoulou, G.; Margellou, E.; Paraskevas, A.; Kafetzis, G.; Rontogianni, D.; Vadiaka, M. Coexistence of Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma; Composite Lymphoma [CL] in a Patient Presenting with Waxing and Waning Lymphadenopathy. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.H.; Pittaluga, S.; Nicolae, A.; Camphausen, K.; Shovlin, M.; Steinberg, S.M.; Roschewski, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Dunleavy, K. A prospective study of mediastinal gray-zone lymphoma. Blood 2014, 124, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, C.; Lazzi, S.; Zazzi, M.; Lalinga, A.V.; Palummo, N.; Galieni, P.; Marafioti, T.; Tonini, T.; Cinti, C.; Leoncini, L.; et al. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement analysis in composite hodgkin disease and large B-cell lymphoma: Evidence for receptor revision of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes in Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells? Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2002, 11, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, E.X.; Flamholz, R.B.; Lowery-Nordberg, M.; Veillon, D.M.; Behm, W.; Heldmann, M.; Cotelingam, J.D. Pathology case of the month. A mediastinal mass. Malignant lymphoma, composite (nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). J. La. State. Med. Soc. 2004, 156, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traverse-Glehen, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Gaulard, P.; Sorbara, L.; Alonso, M.A.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma: The missing link between classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma and mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; de Jong, D.; de Mascarel, A.; Hsi, E.D.; Kluin, P.; Natkunam, Y.; Parrens, M.; Pileri, S.; Ott, G. Gray zones around diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Conclusions based on the workshop of the XIV meeting of the European Association for Hematopathology and the Society of Hematopathology in Bordeaux, France. J. Hematop. 2009, 2, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oschlies, I.; Burkhardt, B.; Salaverria, I.; Rosenwald, A.; d’Amore, E.S.; Szczepanowski, M.; Koch, K.; Hansmann, M.L.; Stein, H.; Möller, P.; et al. Clinical, pathological and genetic features of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphomas and mediastinal gray zone lymphomas in children. Haematologica 2011, 96, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, F.C.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Wei, L.; Hanson, J.C.; Killian, J.K.; Sun, H.W.; Adams, L.G.; Hewitt, S.M.; Wilson, W.H.; Pittaluga, S.; et al. Methylation profiling of mediastinal gray zone lymphoma reveals a distinctive signature with elements shared by classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2011, 96, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Kong, L.; Qu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L. Composite lymphoma in the anterior mediastinum: A case report and review of the literature. Diagn. Pathol. 2011, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, H.W.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.L.; Lu, J.Y. Composite diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the stomach: Case report and literature review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6304–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Hadid, T.; Ibrar, W.; Sano, D.; Al-Katib, A. Composite Lymphoma: Opposite Ends of Spectrum Meet. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goyal, G.; Nguyen, A.H.; Kendric, K.; Caponetti, G.C. Composite lymphoma with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma components: A case report and review of the literature. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, A.D.; Burkhart, H.M.; Manduch, M.; Feldman, A.L.; Inwards, D.J.; Connolly, H.M. Composite hodgkin and non-hodgkin lymphoma of the mitral and aortic valves. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2010, 23, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, T.T.; Cousar, J.B.; Mangum, M.; Williams, M.E.; Lee, J.T.; Greer, J.P.; Collins, R.D. Monomorphic lymphomas arising in patients with Hodgkin’s disease. Correlation of morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular genetic findings in 12 cases. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 136, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guarner, J.; del Rio, C.; Hendrix, L.; Unger, E.R. Composite Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. In-situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer 1990, 66, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wilczynski, S.P.; Chang, K.L.; Weiss, L.M. Composite recurrent hodgkin lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: One clone, two faces. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 126, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R. Composite lymphoma of cervical lymph nodes with classical Hodgkin lymphoma and diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A case report and literature review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3651–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerl, K.; Girardet, C.; Borisch, B. A common B-cell precursor in composite lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwein, T.; Lackner, H.; Ebetsberger-Dachs, G.; Beham-Schmid, C.; Zach, K.; Tamesberger, M.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; Lüftinger, R.; Dworzak, M.; Mann, G.; et al. Management of children and adolescents with gray zone lymphoma: A case series. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, 28206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagaki, T.; Sugaya, M.; Minatani, Y.; Fujita, H.; Hangaishi, A.; Kurokawa, M.; Takazawa, Y.; Tamaki, K. Mycosis fungoides with recurrent Hodgkin’s lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2009, 89, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulli, M.; Rosso, R.; Kindl, S.; Boveri, E.; Sirchi, M.; De Medici, A.; Invernizzi, R.; Magrini, U. Nodular sclerosing Hodgkin’s disease and large cell lymphoma. Immunophenotypic characterization of a composite case. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1992, 421, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.Y.; Leung, A.Y.; Lau, W.H.; Loong, F.; So, J.C.; Tse, E.; Kwong, Y.L. Synchronous Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly and Epstein-Barr virus-positive classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Histopathology 2011, 59, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hell, K.; Hansmann, M.L.; Pringle, J.H.; Lauder, I.; Fischer, R. Combination of Hodgkin’s disease and diffuse large cell lymphoma: An in situ hybridization study for immunoglobulin light chain messenger RNA. Histopathology 1995, 27, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, D.S.; Fareed, S.; Alkuwari, E.; El-Omri, H.; Al-Sabbagh, A.; Gameel, A.; Yassin, M. Concomitant Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma of Lymph Node and cMYC-Positive Burkitt Leukemia/Lymphoma of the Bone Marrow Presented Concurrently at the Time of Presentation: A Rare Combination of Discordant Lymphomas. Clin. Med. Insights Blood Disord. 2016, 9, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Eberle, F.C.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Rahma, O.; Wilson, W.H.; Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. Coexisting and clonally identical classic hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte predominant hodgkin lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanowski, M.; Masqué-Soler, N.; Oschlies, I.; Schmidt, W.; Lück, A.; Klapper, W. Composite lymphoma of nodular lymphocyte-predominant and classical Hodgkin lymphoma-Epstein-Barr virus association suggests divergent pathogenesis despite clonal relatedness. Human. Pathol. 2013, 44, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, A.B.; Dorfman, R.F.; Warnke, R.A. Coexistence of nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin’s disease and Hodgkin’s disease of the usual type. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1993, 17, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, A.; Miyoshi, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Arakawa, F.; Kawano, R.; Muta, H.; Sugita, Y.; Akashi, K.; Ohshima, K. Composite lymphoma of peripheral T-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma, mixed cellularity type; pathological and molecular analysis. Pathol. Int. 2017, 67, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualco, G.; Chioato, L.; Van Den Berg, A.; Weiss, L.M.; Bacchi, C.E. Composite lymphoma: EBV-positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A case report. App. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2009, 17, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.; Holmes, H.; Katabi, N.; Newman, J.; Domiatti-Saad, R.; Stone, M.; Netto, G. Composite lymphocyte-rich Hodgkin lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma associated with Epstein-Barr virus: A case report and review of the literature. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2006, 130, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Weng, A.P.; Freedman, A.S. Hodgkin disease associated with T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas: Case reports and review of the literature. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 121, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodarska, I.; Delabie, J.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Mecucci, C.; Stul, M.; Verhoef, G.; Cassiman, J.J.; Van den Berghe, H. T-cell lymphoma developing in Hodgkin’s disease: Evidence for two clones. J. Pathol. 1993, 170, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, L. Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review. Open Med. 2020, 15, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niino, D.; My Hanh, L.T.; Miura, S.; Nakashima, M.; Iwanaga, M. Incidence Patterns of Sequential or Composite Lymphoma: A Population-Based Cancer Registry Study. Tohoku. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 254, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassidakis, G.Z.; Medeiros, L.J.; Viviani, S.; Bonfante, V.; Nadali, G.P.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Mesina, O.; Herling, M.; Angelopoulou, M.K.; Giardini, R.; et al. CD20 expression in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin’s disease: Associations with presenting features and clinical outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Kang, S.Y.; He, X.H.; Zhou, S.Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.L.; Zhang, C.G.; Yang, S.; Gui, L.; Shi, Y.K. Clinical features and prognosis of CD20-positive classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 96, 2224–2228. [Google Scholar]
- Benharroch, D.; Nalbandyan, K.; Lazarev, I. CD20 Over-Expression in Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg Cells of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: The Neglected Quest. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelgasim, K.A.; Shammari, R.A.; Alshieban, S.; Alahmari, B.; Alzahrani, M.; Alhejazi, A.; Alaskar, A.; Damlaj, M. Impact of cluster of differentiation 20 expression and rituximab therapy in classical Hodgkin lymphoma: Real world experience. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2021, 15, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.H. A practical approach to the understanding and diagnosis of lymphoma: An assessment of the WHO classification based on immunoarchitecture and immuno-ontogenic principles. Pathology 2009, 41, 305–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kridel, R.; Mottok, A.; Farinha, P.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Ennishi, D.; Zheng, Y.; Chavez, E.A.; Shulha, H.P.; Tan, K.; Chan, F.C.; et al. Cell of origin of transformed follicular lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano, L.; Balagué, O.; Dlouhy, I.; Rovira, J.; Karube, K.; Pinyol, M.; Rivas-Delgado, A.; Costa, D.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; González-Farre, B.; et al. Clinicobiological features and prognostic impact of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma component in the outcome of patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.L.; Arber, D.A.; Pittaluga, S.; Martinez, A.; Burke, J.S.; Raffeld, M.; Camos, M.; Warnke, R.; Jaffe, E.S. Clonally related follicular lymphomas and histiocytic/dendritic cell sarcomas: Evidence for transdifferentiation of the follicular lymphoma clone. Blood 2008, 111, 5433–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Yoshida, T.; Masuda, Y.; Kimura, N. Lymph nodes in incipient adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with Hodgkin’s disease-like histologic features. Cancer 1991, 67, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Fend, F.; Moguel, L.R.; Spilove, L.; Beaty, M.W.; Kingma, D.W.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma with Reed-Sternberg-like cells of B-cell phenotype and genotype associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus latent genes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küppers, R. Mechanisms of B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, K.; Jarrett, R.F. The molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma. Histopathology 2011, 58, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, V.; Rossi, D. Molecular pathogenesis of splenic and nodal marginal zone lymphoma. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2017, 30, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzel, M.; Baseggio, L.; Fontaine, J.; Pesce, F.; Ghesquières, H.; Bachy, E.; Verney, A.; Traverse-Glehen, A. New Insights into the Biology and Diagnosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 3430–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, S.; Pukkala, E.; Vahteristo, P.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Franssila, K.; Aaltonen, L.A. High familial risk in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiernik, P.H.; Wickramasinghe, D.; Dutcher, J.P. Families with both Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma in their pedigrees. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 13, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kharazmi, E.; Fallah, M.; Pukkala, E.; Olsen, J.H.; Tryggvadottir, L.; Sundquist, K.; Tretli, S.; Hemminki, K. Risk of familial classical Hodgkin lymphoma by relationship, histology, age, and sex: A joint study from five Nordic countries. Blood 2015, 126, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, D.; Güzelçiçek, A.; Öz, Ö.; Erdem, A.Y.; Haliloğlu, Y.; Witzel, M.; Klein, C.; Ünal, E. The Mutation of CD27 Deficiency Presented With Familial Hodgkin Lymphoma and a Review of the Literature. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 44, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlen, M.; Hönscheid, A.; Schemme, J.; Merz, H.; Mauz-Körholz, C.; Borkhardt, A.; Troeger, A. Hodgkin lymphoma as a novel presentation of familial DICER1 syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandapalli, O.R.; Paramasivam, N.; Giangiobbe, S.; Kumar, A.; Benisch, W.; Engert, A.; Witzens-Harig, M.; Schlesner, M.; Hemminki, K.; Försti, A. Whole genome sequencing reveals DICER1 as a candidate predisposing gene in familial Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 143, 2076–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harty, L.C.; Lin, A.Y.; Goldstein, A.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Carrington, M.; Tucker, M.A.; Modi, W.S. HLA-DR, HLA-DQ, and TAP genes in familial Hodgkin disease. Blood 2002, 99, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salipante, S.J.; Mealiffe, M.E.; Wechsler, J.; Krem, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Namkoong, S.; Bhagat, G.; Kirchhoff, T.; Offit, K.; Lynch, H.; et al. Mutations in a gene encoding a midbody kelch protein in familial and sporadic classical Hodgkin lymphoma lead to binucleated cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14920–14925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, S.; Aavikko, M.; Aittomäki, K.; Launonen, V.; Lehtonen, R.; Franssila, K.; Lehtonen, H.J.; Kaasinen, E.; Broderick, P.; Tarkkanen, J.; et al. Exome sequencing reveals germline NPAT mutation as a candidate risk factor for Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristolainen, H.; Kilpivaara, O.; Kamper, P.; Taskinen, M.; Saarinen, S.; Leppä, S.; d’Amore, F.; Aaltonen, L.A. Identification of homozygous deletion in ACAN and other candidate variants in familial classical Hodgkin lymphoma by exome sequencing. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunno, M.; McMaster, M.L.; Boland, J.; Bass, S.; Zhang, X.; Burdett, L.; Hicks, B.; Ravichandran, S.; Luke, B.T.; Yeager, M.; et al. Whole exome sequencing in families at high risk for Hodgkin lymphoma: Identification of a predisposing mutation in the KDR gene. Haematologica 2016, 101, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Dai, X. Survival among patients with composite and sequential lymphoma between primary mediastinal lymphoma/diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma: A population-based study. Leuk. Res. 2021, 111, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Lezama, L.S.; Kurzer, J.; Oak, J.; Schultz, L.M.; Walkush, A.; Cheng, T.C.; Chen, E.H.; May, W.A.; Chang, C.; et al. Targeted Mutational Profiling Reveals Clonal Relationships in Metachronous Occurrence of Classic Hodgkin and Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, V.; Hummel, M.; Marafioti, T.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Assaf, C.; Stein, H. Detection of clonal T-cell receptor gamma-chain gene rearrangements in Reed-Sternberg cells of classic Hodgkin disease. Blood 2000, 95, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müschen, M.; Rajewsky, K.; Bräuninger, A.; Baur, A.S.; Oudejans, J.J.; Roers, A.; Hansmann, M.L.; Küppers, R. Rare occurrence of classical Hodgkin’s disease as a T cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.H.; Morton, C.C.; Miller-Cassman, R.; Balk, S.P.; Kadin, M.E. Hodgkin’s disease, lymphomatoid papulosis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma derived from a common T-cell clone. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroch, J.; Copie-Bergman, C.; de Leval, L.; Plonquet, A.; Martin-Garcia, N.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Molinier-Frenkel, V.; Belhadj, K.; Haioun, C.; Audouin, J.; et al. Follicular peripheral T-cell lymphoma expands the spectrum of classical Hodgkin lymphoma mimics. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Venkataraman, G.; Vijnovich-Baron, A.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas of follicular T-helper cell derivation with Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells of B-cell lineage: Both EBV-positive and EBV-negative variants exist. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefliger, S.; Bihl, M.; Krasniqi, F.; Tzankov, A. PET-positive bone lesion due to Langerhans cell histiocytosis after BEACOPP therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma: How anamnesis, histopathological accuracy, and molecular analysis could resolve a clinical dilemma. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).