Dietary EPA+DHA Mitigate Hepatic Toxicity and Modify the Oxylipin Profile in an Animal Model of Colorectal Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
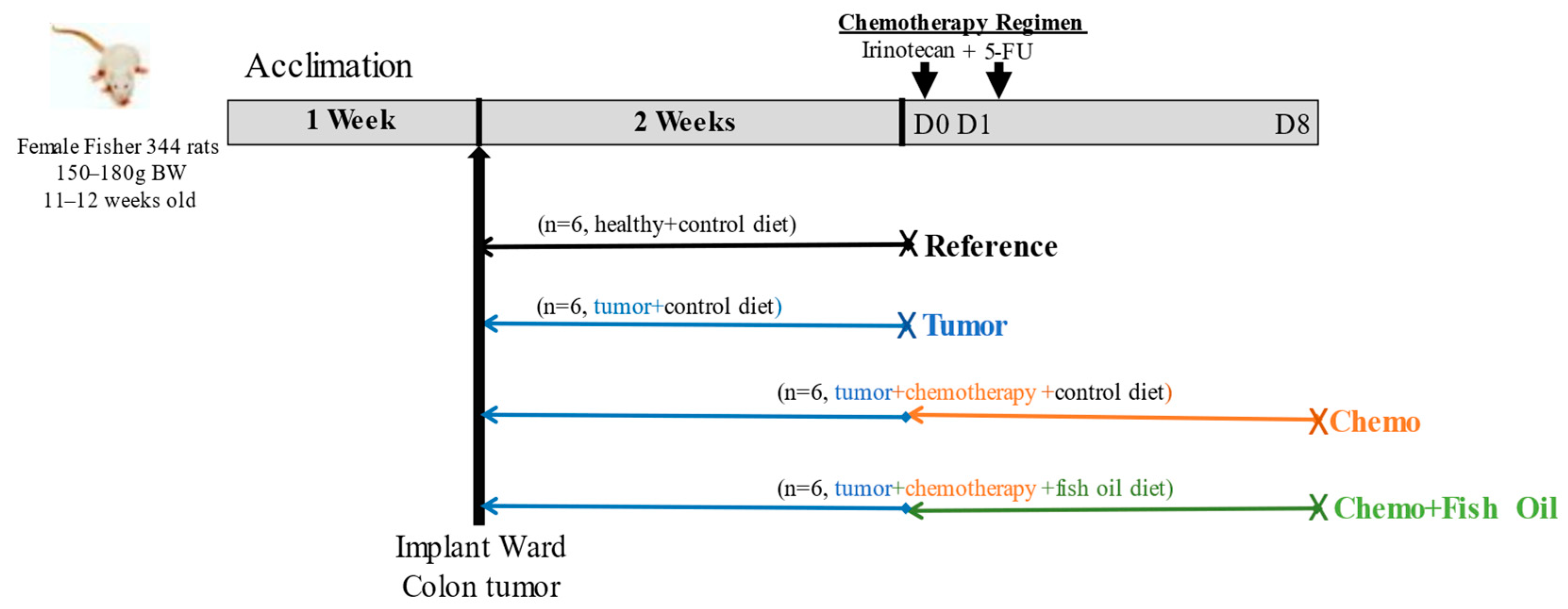
2.1. Animal Handling and Experimental Design
2.2. Assessment of Oxidative Stress, Lipid Peroxidation, and Fibrosis Markers from Liver Tissue
2.3. Oxylipin Analysis
2.4. Phospholipid (PL) Fatty Acid Analysis
2.5. Determination of Cytokines
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Findings
3.2. Effects of Tumor, Chemotherapy, and Dietary Fish Oil on Liver Toxicity Markers
3.3. Oxylipin and PL Fatty Acid Distribution
3.4. Effects of Tumor, Chemotherapy, and Fish Oil on Liver Oxylipins
3.5. Effects of Tumor, Chemotherapy, and Dietary Fish Oil on Liver Cytokines and Chemokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colorectal Cancer Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/colorectal/statistics (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Cancer Stat Facts: Colorectal Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Kow, A.W.C. Hepatic metastasis from colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 1274–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Govindarajan, A.; Ito, H.; Fong, Y. Surgical treatment of hepatic colorectal metastasis: Evolving role in the setting of improving systemic therapies and ablative treatments in the 21st century. Cancer J. 2010, 16, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauthey, J.N.; Choti, M.A.; Helton, W.S. AHPBA/SSO/SSAT Consensus Conference on hepatic colorectal metastases: Rationale and overview of the conference. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 13, 1259–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, F.G.; Ritter, J.; Goodwin, J.W.; Linehan, D.C.; Hawkins, W.G.; Strasberg, S.M. Effect of steatohepatitis associated with irinotecan or oxaliplatin pretreatment on resectability of hepatic colorectal metastases. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2005, 200, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauthey, J.N.; Pawlik, T.M.; Ribero, D.; Wu, T.T.; Zorzi, D.; Hoff, P.M.; Xiong, H.Q.; Eng, C.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; et al. Chemotherapy regimen predicts steatohepatitis and an increase in 90-day mortality after surgery for hepatic colorectal metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, L.; Larrey, D. Chemotherapy-associated steatohepatitis. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbs, M.; Leng, S.; Devassy, J.G.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Advances in our Understanding of Oxylipins Derived from Dietary PUFAs. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christie, W.W.; Harwood, J.L. Oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids to produce lipid mediators. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, S.P.; Love, K.; Winter, T.; Gauthier, J.; Taylor, C.G.; Blydt-Hansen, T.; Zahradka, P.; Aukema, H.M. Dietary linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid differentially affect renal oxylipins and phospholipid fatty acids in diet-induced obese rats. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lone, A.M.; Tasken, K. Pro-inflammatory and immunoregulatory roles of eicosanoids in T cells. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, N.O.; Martins, J.O.; Landgraf, R.G.; Jancar, S. Emerging roles for eicosanoids in renal diseases. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.M.; Kleczko, E.K.; Nemenoff, R.A. Eicosanoids in Cancer: New Roles in Immunoregulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 595498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, D.R.; Liu, H.; Ghosh Dastidar, S.; Warner, J.B.; Prodhan, M.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Feldstein, A.E.; Gao, B.; Prough, R.A.; et al. Ethanol and unsaturated dietary fat induce unique patterns of hepatic omega-6 and omega-3 PUFA oxylipins in a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, S.; Johnson, C.D.; Hennebelle, M.; Holtmann, T.; Taha, A.Y.; Kirpich, I.A.; Eguchi, A.; Ramsden, C.E.; Papouchado, B.G.; McClain, C.J.; et al. Oxidized linoleic acid metabolites induce liver mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and NLRP3 activation in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, M.L.; Lorenzetti, F. Role of eicosanoids in liver repair, regeneration and cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeger, A.L.; Cipollina, C.; Cole, M.P.; Woodcock, S.R.; Bonacci, G.; Rudolph, T.K.; Rudolph, V.; Freeman, B.A.; Schopfer, F.J. Cyclooxygenase-2 generates anti-inflammatory mediators from omega-3 fatty acids. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, E.A.; Norris, P.C. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serhan, C.N. Treating inflammation and infection in the 21st century: New hints from decoding resolution mediators and mechanisms. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ávila-Román, J.; Talero, E.; de Los Reyes, C.; García-Mauriño, S.; Motilva, V. Microalgae-derived oxylipins decrease inflammatory mediators by regulating the subcellular location of NFκB and PPAR-γ. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, S.D.; Rodway, L.A.; Winter, T.; Taylor, C.G.; Zahradka, P.; Aukema, H.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of α-linolenic acid in M1-like macrophages are associated with enhanced production of oxylipins from α-linolenic and linoleic acid. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosviel, R.; Joumard-Cubizolles, L.; Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G.; Bayle, D.; Copin, C.; Hennuyer, N.; Duplan, I.; Staels, B.; Zanoni, G.; Porta, A.; et al. DHA-derived oxylipins, neuroprostanes and protectins, differentially and dose-dependently modulate the inflammatory response in human macrophages: Putative mechanisms through PPAR activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 103, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzioris, E.; Cleland, L.G.; Gibson, R.A.; Neumann, M.A.; Demasi, M.; James, M.J. Biochemical effects of a diet containing foods enriched with n-3 fatty acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, S.; Winter, T.; Aukema, H.M. Dietary ALA, EPA and DHA have distinct effects on oxylipin profiles in female and male rat kidney, liver and serum. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devassy, J.G.; Yamaguchi, T.; Monirujjaman, M.; Gabbs, M.; Ravandi, A.; Zhou, J.; Aukema, H.M. Distinct effects of dietary flax compared to fish oil, soy protein compared to casein, and sex on the renal oxylipin profile in models of polycystic kidney disease. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2017, 123, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorden, D.L.; Myers, D.S.; Ivanova, P.T.; Fahy, E.; Maurya, M.R.; Gupta, S.; Min, J.; Spann, N.J.; McDonald, J.G.; Kelly, S.L.; et al. Biomarkers of NAFLD progression: A lipidomics approach to an epidemic. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Lopez, R.; Tamimi, T.A.; Yerian, L.; Chung, Y.M.; Berk, M.; Zhang, R.; McIntyre, T.M.; Hazen, S.L. Mass spectrometric profiling of oxidized lipid products in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3046–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loomba, R.; Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.; Dennis, E.A. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites as novel lipidomic biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciejewska, D.; Ossowski, P.; Drozd, A.; Ryterska, K.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Banaszczak, M.; Kaczorowska, M.; Sabinicz, A.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Stachowska, E. Metabolites of arachidonic acid and linoleic acid in early stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A pilot study. Subscr. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015, 121, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, P.; Wiest, M.M.; Cheung, O.; Mirshahi, F.; Sargeant, C.; Min, H.K.; Contos, M.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Fuchs, M.; Zhou, H.; et al. The plasma lipidomic signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Pan, X.; Luo, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Bestman, P.L.; Luo, M. Association of Inflammatory Cytokines with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.S.; Qin, H.L.; Wang, T.; Li, H.T.; Li, H.; Xia, S.H.; Xiang, X.H. Global publication trends and research hotspots of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review. Springerplus 2015, 4, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monirujjaman, M.; Pant, A.; Nelson, R.; Bathe, O.; Jacobs, R.; Mazurak, V.C. Alterations in hepatic fatty acids reveal depletion of total polyunsaturated fatty acids following irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil treatment in an animal model of colorectal cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2021, 174, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Sawyer, M.B.; Field, C.J.; Dieleman, L.A.; Baracos, V.E. Nutritional modulation of antitumor efficacy and diarrhea toxicity related to irinotecan chemotherapy in rats bearing the ward colon tumor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7146–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Rustum, Y.M. Synergistic antitumor activity of irinotecan in combination with 5-fluorouracil in rats bearing advanced colorectal cancer: Role of drug sequence and dose. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3717–3721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almasud, A.A.; Giles, K.H.; Miklavcic, J.J.; Martins, K.; Baracos, V.E.; Putman, C.T.; Guan, L.L.; Mazurak, V.C. Fish oil mitigates myosteatosis and improves chemotherapy efficacy in a preclinical model of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition slows disease progression and improves the altered renal lipid mediator profile in the Pkd2WS25/− mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monirujjaman, M.; Devassy, J.G.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sidhu, N.; Kugita, M.; Gabbs, M.; Nagao, S.; Zhou, J.; Ravandi, A.; Aukema, H.M. Distinct oxylipin alterations in diverse models of cystic kidney diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, A.L.; Waytt, V.; Winter, T.; Leng, S.; Duhamel, T.A.; Aukema, H.M. Oxylipin profiles and levels vary by skeletal muscle type, dietary fat and sex in young rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, H.M.; Winter, T.; Ravandi, A.; Dalvi, S.; Miller, D.W.; Hatch, G.M. Generation of Bioactive Oxylipins from Exogenously Added Arachidonic, Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acid in Primary Human Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells. Lipids 2016, 51, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deems, R.; Buczynski, M.W.; Bowers-Gentry, R.; Harkewicz, R.; Dennis, E.A. Detection and quantitation of eicosanoids via high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 432, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.M.; Murphy, R.C. Electrospray mass spectrometric analysis of 5-hydroperoxy and 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids generated by lipid peroxidation of red blood cell ghost phospholipids. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 9, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, D.; Laurent, A.; Pawlik, T.M.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Vauthey, J.N.; Abdalla, E.K. Chemotherapy-associated hepatotoxicity and surgery for colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Surg. 2007, 94, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris-Stiff, G.; Tan, Y.M.; Vauthey, J.N. Hepatic complications following preoperative chemotherapy with oxaliplatin or irinotecan for hepatic colorectal metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 34, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, Y.; Bentrem, D.J. CASH (Chemotherapy-Associated Steatohepatitis) costs. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwe, G.; Knitter, S.; Pesthy, S.; Beierle, A.S.; Bahra, M.; Schmelzle, M.; Schmuck, R.B.; Lohneis, P.; Raschzok, N.; Öllinger, R.; et al. Hepatotoxicity following systemic therapy for colorectal liver metastases and the impact of chemotherapy-associated liver injury on outcomes after curative liver resection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 1668–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.C.; Choi, J.E.; Kang, H.S.; Han, S.I. Ursodeoxycholic acid switches oxaliplatin-induced necrosis to apoptosis by inhibiting reactive oxygen species production and activating p53-caspase 8 pathway in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, J.S.; Navarro, V.J.; Rossi, S. Review article: Drug-induced liver injury—Its pathophysiology and evolving diagnostic tools. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; Lima-Júnior, R.C.; Aragão, K.S.; Medeiros, R.P.; Marques-Neto, R.D.; de Sá Grassi, L.; Leite, L.L.; Nunes, L.G.; de Mesquita Neto, J.W.; de Castro Brito, G.A.; et al. Chemotherapy-associated steatohepatitis induced by irinotecan: A novel animal model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, J.; Mahli, A.; Freese, K.; Schiergens, T.S.; Kuecuekoktay, F.S.; Teufel, A.; Thasler, W.E.; Müller, M.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hellerbrand, C. Analysis of molecular mechanisms of 5-fluorouracil-induced steatosis and inflammation in vitro and in mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13059–13072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, X.P.; Jiang, H.L. Arachidonic acid attenuates brain damage in a rat model of ischemia/reperfusion by inhibiting inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, Z.; Bond, N.J.; Ashmore, T.; Sanders, F.; Ament, Z.; Wang, X.; Murray, A.J.; Bellafante, E.; Virtue, S.; Vidal-Puig, A.; et al. Lipid zonation and phospholipid remodeling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patrono, C.; Rocca, B. Measurement of Thromboxane Biosynthesis in Health and Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patrono, C.; Ciabattoni, G.; Pugliese, F.; Pierucci, A.; Blair, I.A.; FitzGerald, G.A. Estimated rate of thromboxane secretion into the circulation of normal humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Needleman, P.; Moncada, S.; Bunting, S.; Vane, J.R.; Hamberg, M.; Samuelsson, B. Identification of an enzyme in platelet microsomes which generates thromboxane A2 from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Nature 1976, 261, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwendijk, R.J.; Zijlstra, F.J.; Wilson, J.H.; Bonta, I.L.; Vincent, J.E. Raised plasma thromboxane B2 levels in alcoholic liver disease. Prostaglandins Leukot. Med. 1983, 10, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davì, G.; Ferro, D.; Basili, S.; Iuliano, L.; Camastra, C.; Giammarresi, C.; Santarone, S.; Rocca, B.; Landolfi, R.; Ciabattoni, G.; et al. Increased thromboxane metabolites excretion in liver cirrhosis. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 79, 747–751. [Google Scholar]
- Baratta, F.D.; Pastori, D.; Delben, M.; Carnevale, R.; Novo, M.; Labbadia, G.; Angelico, F.; Violi, F. Enhanced urinary excretion of thromboxane B2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Implication for antiplatelet treatment. Atherosclerosis 2018, 275, e65–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, F.; Del Ben, M.; Pastori, D.; Bartimoccia, S.; Cammisotto, V.; Cocomello, N.; Colantoni, A.; Pani, A.; Nocella, C.; Carnevale, R.; et al. The platelets behaviour in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A potential role for antiplatelets drugs? Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, ehaa946.3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanji, A.A.; Khwaja, S.; Rahemtulla, A.; Miao, L.; Zhao, S.; Tahan, S.R. Thromboxane inhibitors attenuate pathological changes in alcoholic liver disease in the rat. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K.; Frydas, I.; Younes, A.; Di Emidio, P.; Ronconi, G.; Toniato, E. IL-1 induces throboxane-A2 (TxA2) in COVID-19 causing inflammation and micro-thrombi: Inhibitory effect of the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra). J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Shimazawa, T.; Yakuo, I.; Aoki, M.; Koda, A.; Kasahara, M. The role of thromboxane A2 [TxA2] in liver injury in mice. Prostaglandins 1989, 38, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomishima, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Matsunaga, N.; Nagatome, M.; Furusho, H.; Irikura, M.; Ohdo, S.; Irie, T. Ozagrel hydrochloride, a selective thromboxane A(2) synthase inhibitor, alleviates liver injury induced by acetaminophen overdose in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanji, A.A.; Liong, E.C.; Xiao, J.; Tipoe, G.L. Thromboxane inhibitors attenuate inflammatory and fibrotic changes in rat liver despite continued ethanol administrations. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ćavar, I.; Kelava, T.; Pravdić, D.; Čulo, F. Anti-thromboxane B2 antibodies protect against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J. Xenobiot. 2011, 1, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Morgan, M.T.; Fiedler, T.L.; Djukovic, D.; Hoffman, N.G.; Raftery, D.; Marrazzo, J.M.; Fredricks, D.N. Metabolic signatures of bacterial vaginosis. mBio 2015, 14, e00204-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilaseca, J.; Salas, A.; Guarner, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Malagelada, J.R. Participation of thromboxane and other eicosanoid synthesis in the course of experimental inflammatory colitis. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Yan, G.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ye, D.; Li, Y. Anti-versus pro-inflammatory metabololipidome upon cupping treatment. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.D.; Clish, C.B.; Schmidt, B.; Gronert, K.; Serhan, C.N. Lipid mediator class switching during acute inflammation: Signals in resolution. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 27, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Arita, M.; Arai, H.; Nakanishi, H.; Taguchi, R.; Miyasho, T.; Takamiya, R.; Asano, K.; Ishizaka, A.; et al. The anti-inflammatory and proresolving mediator resolvin E1 protects mice from bacterial pneumonia and acute lung injury. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devassy, J.G.; Leng, S.; Gabbs, M.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Oxylipins in Neuroinflammation and Management of Alzheimer Disease. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arita, M.; Ohira, T.; Sun, Y.P.; Elangovan, S.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin E1 selectively interacts with leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and ChemR23 to regulate inflammation. J. Immunol. 2007, 17, 3912–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freire, M.O.; Van Dyke, T.E. Natural resolution of inflammation. Periodontology 2000, 63, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Hjorth, E.; Cortés-Toro, V.; Eyjolfsdottir, H.; Graff, C.; Nennesmo, I.; Palmblad, J.; Eriksdotter, M.; Sambamurti, K.; et al. Resolution of inflammation is altered in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serhan, C.N.; Yang, R.; Martinod, K.; Kasuga, K.; Pillai, P.S.; Porter, T.F.; Oh, S.F.; Spite, M. Maresins: Novel macrophage mediators with potent antiinflammatory and proresolving actions. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heshmati, J.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Maroufizadeh, S.; Akbari, A.; Yavari, M.; Amirinejad, A.; Maleki-Hajiagha, A.; Sepidarkish, M. Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation and oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 149, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, Y.; Malnick, S. Liver injury induced by anticancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Int. J. Hepatol. 2013, 2013, 815105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, D.; Kefi, K.; Barbe, U.; Bausero, P.; Visioli, F. Polyunsaturated fatty acids as antioxidants. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Rocha, J.É.; Mendes Furtado, M.; Mello Neto, R.S.; da Silva Mendes, A.V.; Brito, A.; Sena de Almeida, J.; Rodrigues Queiroz, E.I.; de Sousa França, J.V.; Silva Primo, M.G.; Cunha Sales, A.; et al. Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Liver Damage in Hypercholesterolemic Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.J.; Thayne, K.A.; Harris, M.; Shaikh, S.R.; Darden, T.M.; Lark, D.S.; Williams, J.M.; Chitwood, W.R.; Kypson, A.P.; Rodriguez, E. Do fish oil omega-3 fatty acids enhance antioxidant capacity and mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in human atrial myocardium via PPARγ activation? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kutzner, L.; Esselun, C.; Franke, N.; Schoenfeld, K.; Eckert, G.P.; Schebb, N.H. Effect of dietary EPA and DHA on murine blood and liver fatty acid profile and liver oxylipin pattern depending on high and low dietary n6-PUFA. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9177–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburg, K.; Esser, D.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Müller, M.; van Duynhoven, J.; van Golde, J.; van Dijk, S.J.; Afman, L.A.; Jacobs, D.M. Postprandial fatty acid specific changes in circulating oxylipins in lean and obese men after high-fat challenge tests. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, A.H.; Pedersen, T.L.; Fillaus, K.; Larson, M.K.; Shearer, G.C.; Newman, J.W. Basal omega-3 fatty acid status affects fatty acid and oxylipin responses to high-dose n3-HUFA in healthy volunteers. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 5, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieves, D.; Moreno, J.J. Effect of arachidonic and eicosapentaenoic acid metabolism on RAW 264.7 macrophage proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 208, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes-Cal, T.; Mattos, R.T.; Medeiros, N.I.; Pinto, B.F.; Belchior-Bezerra, M.; Roque-Souza, B.; Dutra, W.O.; Ferrari, T.; Vidigal, P.; Faria, L.C.; et al. Crosstalk Between Plasma Cytokines, Inflammation, and Liver Damage as a New Strategy to Monitoring NAFLD Progression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaa, F.A.; Abdel-Wahhab, K.G. Physiological potential of cytokines and liver damages. Hepatoma Res. 2016, 2, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederreiter, L.; Tilg, H. Cytokines and fatty liver diseases. Liver Res. 2018, 2, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gayyar, M.M.; Shams, M.E.; Barakat, E.A. Fish oil improves lipid metabolism and ameliorates inflammation in patients with metabolic syndrome: Impact of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocsan, I.C.; Milaciu, M.V.; Pop, R.M.; Vesa, S.C.; Ciumarnean, L.; Matei, D.M.; Buzoianu, A.D. Cytokines Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4297206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Balakrishnan, V. Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 26, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stojsavljević, S.; Gomerčić Palčić, M.; Virović Jukić, L.; Smirčić Duvnjak, L.; Duvnjak, M. Adipokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18070–18091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C. Intracellular survival pathways in the liver. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Anderson, J.E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Paradoxical association between body mass index and mortality in men with CKD not yet on dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, M.H.; Baranova, A.; Collantes, R.; Ranard, B.; Stepanova, M.; Bennett, C.; Fang, Y.; Elariny, H.; Goodman, Z.; Chandhoke, V.; et al. Adipokines and cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieckowska, A.; Papouchado, B.G.; Li, Z.; Lopez, R.; Zein, N.N.; Feldstein, A.E. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, A.; Schlauch, K.; Elariny, H.; Jarrar, M.; Bennett, C.; Nugent, C.; Gowder, S.J.; Younoszai, Z.; Collantes, R.; Chandhoke, V.; et al. Gene expression patterns in hepatic tissue and visceral adipose tissue of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emshaty, H.M.; Nasif, W.A.; Mohamed, I.E. Serum Cytokine of IL-10 and IL-12 in Chronic Liver Disease: The Immune and Inflammatory Response. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 707254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Den Boer, M.A.; Voshol, P.J.; Schröder-van der Elst, J.P.; Korsheninnikova, E.; Ouwens, D.M.; Kuipers, F.; Havekes, L.M.; Romijn, J.A. Endogenous interleukin-10 protects against hepatic steatosis but does not improve insulin sensitivity during high-fat feeding in mice. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4553–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsia, C.Y.; Huo, T.I.; Chiang, S.Y.; Lu, M.F.; Sun, C.L.; Wu, J.C.; Lee, P.C.; Chi, C.W.; Lui, W.Y.; Lee, S.D. Evaluation of interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and human hepatocyte growth factor 9as tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 33, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H. The role of cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Wei, W.; Li, X. Effects of fish oil supplementation on inflammatory markers in chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2012, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez-Ramirez, V.; Macias-Islas, M.A.; Ortiz, G.G.; Pacheco-Moises, F.; Torres-Sanchez, E.D.; Sorto-Gomez, T.E.; Cruz-Ramos, J.A.; Orozco-Aviña, G.; Celis de la Rosa, A.J. Efficacy of fish oil on serum of TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 oxidative stress markers in multiple sclerosis treated with interferon beta-1b. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 709493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jose, P.J.; Griffiths-Johnson, D.A.; Collins, P.D.; Walsh, D.T.; Moqbel, R.; Totty, N.F.; Truong, O.; Hsuan, J.J.; Williams, T.J. Eotaxin: A potent eosinophil chemoattractant cytokine detected in a guinea pig model of allergic airways inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tacke, F.; Trautwein, C.; Yagmur, E.; Hellerbrand, C.; Wiest, R.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Up-regulated eotaxin plasma levels in chronic liver disease patients indicate hepatic inflammation, advanced fibrosis and adverse clinical course. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Thissen, U.; Keshtkar, S.; Accart, B.; Stienstra, R.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Roskams, T.; Kersten, S.; Müller, M. Adipose tissue dysfunction signals progression of hepatic steatosis towards nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in C57BL/6 mice. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sindhu, S.; Akhter, N.; Shenouda, S.; Wilson, A.; Ahmad, R. Plasma fetuin-A/α2-HS-glycoprotein correlates negatively with inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and activation biomarkers in individuals with type-2 diabetes. BMC Immunol. 2016, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarantino, G.; Costantini, S.; Finelli, C.; Capone, F.; Guerriero, E.; La Sala, N.; Gioia, S.; Castello, G. Carotid intima-media thickness is predicted by combined eotaxin levels and severity of hepatic steatosis at ultrasonography in obese patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Le Roy, H.; Sawyer, M.B.; Field, C.F.; Dieleman, L.A.; Baracos, V.E. Single and combined supplementation of glutamine and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on host tolerance and tumour response to 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxy-camptothecin (CPT-11)/5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in rats bearing Ward colon tumour. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willenberg, I.A.I.; Ostermann, A.I.; Schebb, N.H. Targeted metabolomics of the arachidonic acid cascade: Current state and challenges of LC-MS analysis of oxylipins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostermann, A.I.; Willenberg, I.; Schebb, N.H. Comparison of sample preparation methods for the quantitative analysis of eicosanoids and other oxylipins in plasma by means of LC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, M.; Martín-Venegas, R.; Moreno, J.J. Differential cell growth/apoptosis behavior of 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid enantiomers in a colorectal cancer cell line. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G664–G671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monirujjaman, M.; Bathe, O.F.; Mazurak, V.C. Dietary EPA+DHA Mitigate Hepatic Toxicity and Modify the Oxylipin Profile in an Animal Model of Colorectal Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225703
Monirujjaman M, Bathe OF, Mazurak VC. Dietary EPA+DHA Mitigate Hepatic Toxicity and Modify the Oxylipin Profile in an Animal Model of Colorectal Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy. Cancers. 2022; 14(22):5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225703
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonirujjaman, Md, Oliver F. Bathe, and Vera C. Mazurak. 2022. "Dietary EPA+DHA Mitigate Hepatic Toxicity and Modify the Oxylipin Profile in an Animal Model of Colorectal Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy" Cancers 14, no. 22: 5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225703
APA StyleMonirujjaman, M., Bathe, O. F., & Mazurak, V. C. (2022). Dietary EPA+DHA Mitigate Hepatic Toxicity and Modify the Oxylipin Profile in an Animal Model of Colorectal Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy. Cancers, 14(22), 5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225703







