High Output Heart Failure in Multiple Myeloma: Pathogenetic Considerations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
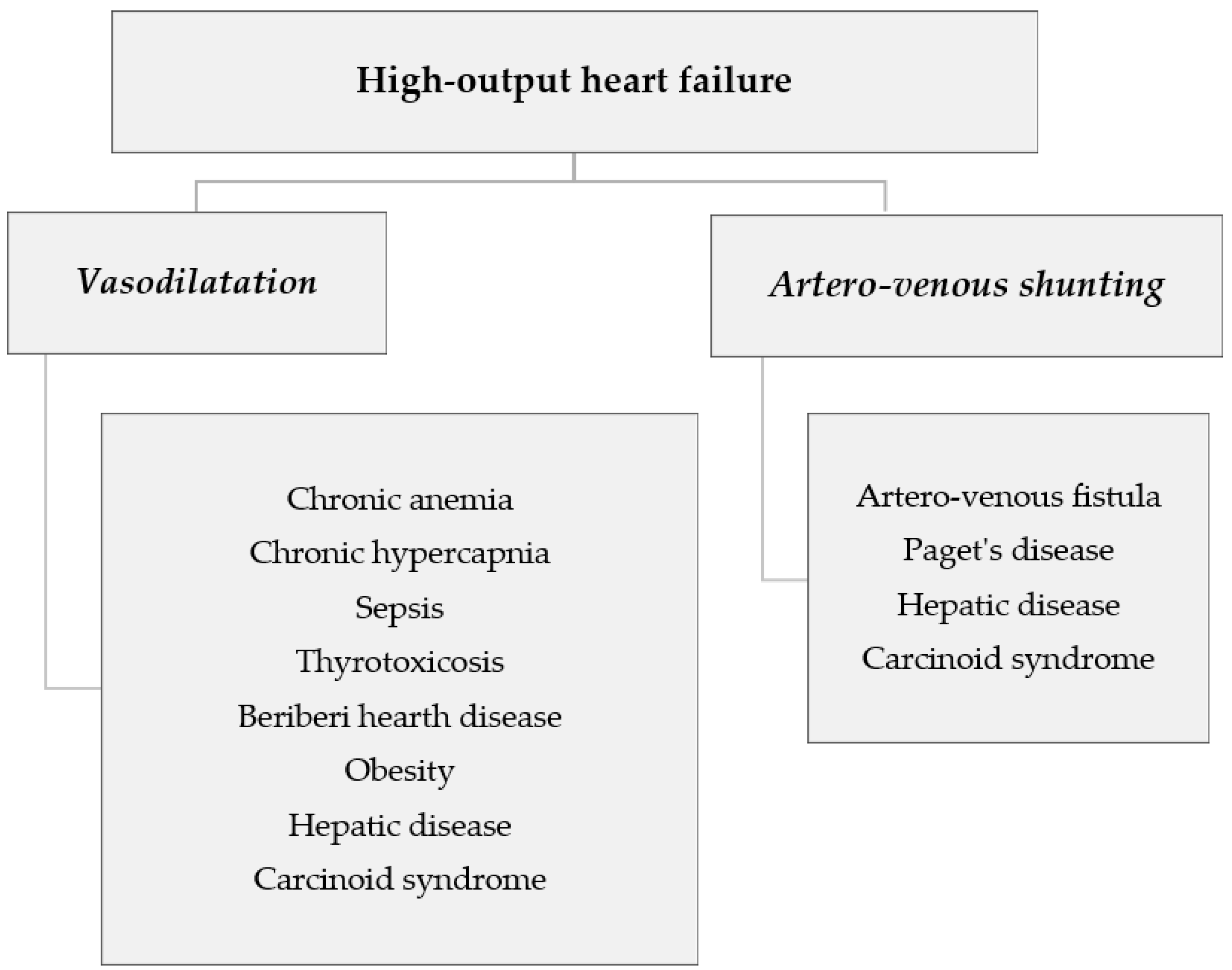
1. Introduction
2. Methods
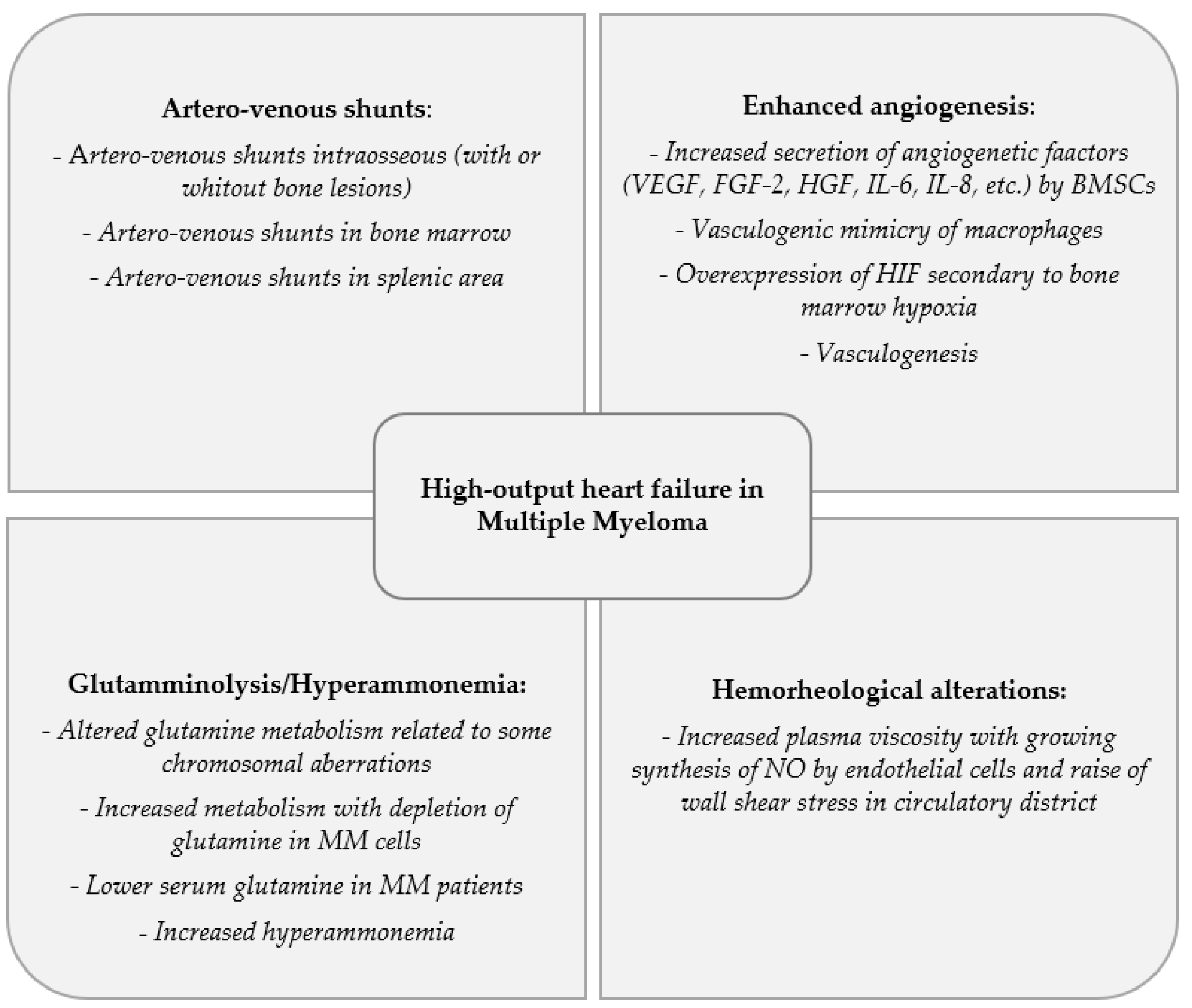
3. Artero-Venous Shunts
4. Enhanced Angiogenesis
5. Glutamminolysis and Hyperammonemia
6. Hemorheological Alterations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, I.S.; Florea, V.G. High output cardiac failure. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2001, 3, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.A.; Dubrey, S.W. High output heart failure. QJM 2009, 102, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, S. High-Output Cardiac Failure. In Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, Y.N.V.; Melenovsky, V.; Redfield, M.M.; Nishimura, R.A.; Borlaug, B.A. High-Output Heart Failure: A 15-Year Experience. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, C.; Driessen, C.; Szabo, Z.; Mateos, M.-V. Management of cardiovascular risk in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, S.; Carlisi, M.; Sarocchi, M.; Napolitano, M.; Siragusa, S. Cardio-oncology in multiple myeloma: Is it time for a specific focus? Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1764–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McBride, W.; Jackman, J.D.; Gammon, R.S.; Willerson, J.T. High-output cardiac failure in patients with multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosisnski, D.J.; Roush, K.; Fraker, T.D.; Grubb, B.P. High cardiac output state in patients with multiple myeloma: Case report and review of the literature. Clin. Cardiol. 1994, 17, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.; Jackman, J.D.; Grayburn, P.A. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of a high cardiac output state in patients with multiple myeloma. Am. J. Med. 1990, 89, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.; Portero, J.A.; Borrego, D.; Barez, A.; San Miguel, J.F. High cardiac output in myeloma patients. Its prevalence and clinical characteristics. The Castile-Leon Cooperative Group for the Study of Monoclonal Gammapathies. Med. Clin. 1997, 108, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Inanir, S.; Haznedar, R.; Atavci, S.; Unlü, M. Arteriovenous shunting in patients with multiple myeloma and high-output failure. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Leporrier, M. High-Output Cardiac Failure in Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1419–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, E.S.; Goddard, B.A.; Markby, D.; Webber, C.E. The spleen as an arteriovenous shunt. Lancet 1969, 1, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.R.; Sobral, K.M.; Culler, H.F.; Campanelli Freitas Couto, S.; Pereira, J.; Rocha, V.; Martinez, G.A.; de Padua Covas Lage, L.A. Acquired hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis as initial manifestation of multiple myeloma. A case report and literature review. Medicine 2020, 99, e22299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gau, Y.-C.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yeh, T.-J. Case report of coexistence of myeloproliferative neoplasms and multiple myeloma. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzalewski, J.; Fisher, M.; Rambaran, R.; Lopez, R. Splenic rupture secondary to amyloid light-chain (AL) amyloidosis associated with multiple myeloma. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2019, 3, rjz021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamir, R.; Lewin, R.F.; Inbal, A.; Heller, I.; Theodor, E. High-output cardiac failure as a presenting symptom of plasma cell leukemia. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1985, 21, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoui, D.; Gallet, B.; Genet, P.; Mbungani, B.; Al Jijakli, A.; Arakelyan, N.; Mesbah, L.; Sutton, L. High-output cardiac failure revealing primary plasma cell leukemia. Case Rep. Hematol. 2013, 2013, 504612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, N.; Colla, S.; Rizzoli, V. Angiogenic switch in multiple myeloma. Hematology 2004, 9, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Vacca, A. Importance of the bone marrow microenvironment in inducing the angiogenic response in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4257–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, K.; Yamashita, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Kimura, T.; Kita, T.; Ichinohe, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Sasada, M.; Uchiyama, T. Analysis of serum angiogenic factors in young multiple myeloma patient with high-output cardiac failure. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ria, R.; Reale, A.; De Luisi, A.; Ferrucci, A.; Moschetta, M.; Vacca, A. Bone marrow angiogenesis and progression in multiple myeloma. Am. J. Blood Res. 2011, 1, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, N.; Storti, P.; Bolzoni, M.; Dalla Palma, B.; Bonomini, S. Angiogenesis and multiple myeloma. Cancer Microenviron. 2011, 4, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Luisi, A.; Binetti, L.; Ria, R.; Ruggieri, S.; Berardi, S.; Catacchio, I.; Racanelli, V.; Pavone, V.; Rossini, B.; Vacca, A.; et al. Erythropoietin is involved in the angiogenic potential of bone marrow macrophages in multiple myeloma. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, A.; Ria, R.; Reale, A.; Ribatti, D. Angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2014, 99, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Vacca, A. Role of endothelial cells and fibroblasts in multiple myeloma angiogenic switch. Cancer Treat. Res. 2016, 169, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Vacca, A. New insights in anti-angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Crivellato, E.; Roccaro, A.M.; Vacca, A. The history of the angiogenic switch concept. Leukemia 2007, 21, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, N.; Lee, H.; Moon, S.Y.; Sohn, J.Y.; Hwang, S.M.; Yoon, O.J.; Youn, H.S.; Eom, H.S.; Kong, S.Y. Adverse prognostic impact of bone marrow microvessel density in multiple myeloma. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Vacca, A. Mast cells and angiogenesis in human plasma cell malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vacca, A.; Ribatti, D. Bone marrow angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2005, 20, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Mesa, R.A.; Fonseca, R.; Schroeder, G.; Plevak, M.F.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Lust, J.A.; Witzig, T.E.; Gertz, M.A.; et al. Bone marrow angiogenesis in 400 patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, multiple myeloma, and primary amyloidosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2210–2216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akob, C.; Sterz, J.; Zavrski, I.; Heider, U.; Kleeberg, L.; Fleissner, C.; Kaiser, M.; Sezer, O. Angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Witzig, T.E.; Timm, M.; Haug, J.; Wellik, L.; Kimlinger, T.K.; Greipp, P.R.; Rajkumar, S.V. Bone marrow angiogenic ability and expression of angiogenic cytokines in myeloma: Evidence favoring loss of marrow angiogenesis inhibitory activity with disease progression. Blood 2004, 104, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribatti, D.; Vacca, A. The role of monocytes-macrophages in vasculogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1535–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otjacques, E.; Binsfeld, M.; Noel, A.; Beguin, Y.; Cataldo, D.; Caers, J. Biological aspects of angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 94, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsi, E.; Perrone, G.; Terragna, C.; Martello, M.; Dico, A.F.; Solaini, G.; Baracca, A.; Sgarbi, G.; Pasquinelli, G.; Valente, S.; et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsi, E.; Terragna, C.; Brioli, A.; Tacchetti, P.; Martello, M.; Cavo, M. Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in multiple myeloma. Transl. Res. 2015, 165, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.; Tiwary, B.N. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and multiple myeloma. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 706–715. [Google Scholar]
- Testa, U.; Saulle, E.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Endothelial progenitor cells in hematological malignancies. Stem Cell Investig. 2016, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitsiades, N.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Poulaki, V.; Chauhan, D.; Richardson, P.G.; Hideshima, T.; Munshi, N.C.; Treon, S.P.; Anderson, K.C. Apoptotic signaling induced by immunomodulatory thalidomide analogs in human multiple myeloma cells: Therapeutic implications. Blood 2002, 99, 4525–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Payvandi, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.-H.; Hariri, R.J.; Man, H.-W.; Chen, R.S.; Muller, G.W.; Hughes, C.C.W.; Stirling, D.I.; et al. The anti-cancer drug lenalidomide inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis via multiple inhibitory effects on endothelial cell function in normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 77, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.H.; Liu, N.; Klimek, V.; Hassoun, H.; Mazumder, A.; Nimer, S.D.; Jagannath, S.; Dhodapkar, M.V. Enhancement of ligand-dependent activation of human natural killer T cells by lenalidomide: Therapeutic implications. Blood 2006, 108, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bloedjes, T.A.; de Wilde, G.; Guikema, J.E.J. Metabolic effects of recurrent genetic aberrations in multiple myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.S.; Hsu, H.W.; Lin, K.D.; Yang, T.J. Amino acid metabolism of myeloma in culture. J. Cell Sci. 1976, 21, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercille, S.; Massie, B. Induction of apoptosis in nutrient-deprived cultures of hybridoma and myeloma cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 44, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchades-Carrasco, L.; Lecumberri, R.; Martínez-López, J.; Lahuerta, J.-J.; Mateos, M.-V.; Prosper, F.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Pineda-Lucerna, A. Multiple myeloma patients have a specific serum metabolomic profile that changes after achieving complete remission. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4770–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wise, D.R.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Mancuso, A.; Sayed, N.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Pfeiffer, H.K.; Nissim, I.; Daikhin, E.; Yudkoff, M.; McMahon, S.B.; et al. Myc regulates a transcriptional program that stimulates mitochondrial glutaminolysis and leads to glutamine addiction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18782–18787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, P.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Chang, T.C.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kita, K.; Ochi, T.; Zeller, K.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Mendell, J.T.; et al. C-Myc suppression of MiR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.Y.; Lovén, J.; Rahl, P.B.; Paranal, R.M.; Burge, C.B.; Bradner, J.E.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Transcriptional amplification in tumor cells with elevated C-Myc. Cell 2012, 151, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Matsuno, F.; Yoshida, M.; Hata, H.; Okazaki, K.; Takatsuki, K. Human myeloma cell line (KHM-4) established from a patient with multiple myeloma associated with hyperammonemia. Intern. Med. 1992, 31, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caminal, L.; Castellanos, E.; Mateos, V.; Astudillo, A.; Moreno, C.; Diéguez, M.A. Hyperammonaemic encephalopathy as the presenting feature of IgD multiple myeloma. J. Intern. Med. 1993, 233, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Hata, H.; Sonoki, T.; Matsuno, F.; Kuribayashi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Nagasaki, A.; Murata, H.; Fujiyama, S.; Takatsuki, K. Serum amino acid disturbance in multiple myeloma with hyperammonemia. Int. J. Hematol. 1995, 61, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, Y.; Imanaka, F.; Hayashi, Y.; Morioka, S. A patient with ammonia-producing multiple myeloma showing hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Leukemia 1996, 10, 918–919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, G.; Peccatori, F.; Ullrich, B.; Ghielmini, M.; Roggero, E.; Goldhirsch, A. Clinical manifestation of severe hyperammonemia in patients with multiple myeloma. Ann. Oncol. 1997, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuribayashi, N.; Matsuzaki, H.; Hata, H.; Yoshida, M.; Sonoki, T.; Nagasaki, A.; Kimura, T.; Okamoto, K.; Kurose, M.; Tsuda, H.; et al. Multiple myeloma associated with serum amino acid disturbance and high output cardiac failure. Am. J. Hematol. 1998, 57, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.R.; Keller, K. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 1998, 57, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Retortillo, J.A.; Marco, F.; Amutio, E.; Conde, E.; Iriondo, A.; Zubizarreta, A. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in multiple myeloma. Haematologica 1998, 83, 956–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, T.; Yamada, O.; Sakaguchi, H.; Ichiki, T.; Kouguchi, K.; Wada, H.; Hata, H.; Yawata, Y.; Ueki, A. In vitro excess ammonia production in human myeloma cell lines. Leukemia 1998, 12, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, L.; Wang, C.; Levitt, L. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1674–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holahan, J.R. Hyperammonemia: Elevated ammonia levels in multiple myeloma. Am. J. Med. 2004, 116, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.; Shetty, N.; Jaiswal, S.; Mehta, B.C. Hyperammonemia: An unusual presenting feature of multiple myeloma. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2005, 59, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furer, V.; Heyd, J. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in multiple myeloma. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2007, 9, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talamo, G.; Cavallo, F.; Zangari, M.; Barlogie, B.; Lee, C.-K.; Pineda-Roman, M.; Kiwan, E.; Krishna, S.; Tricot, G. Hyperammonemia and encephalopathy in patients with multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2007, 82, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Palom, X.; Sarrá, J.; Gasch, O.; Isern, V.; Fernández de Sevilla, A.; Pujol, R. Multiple myeloma and hyperammonemic encephalopathy: Review of 27 cases. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2008, 8, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikewaki, J.; Ogata, M.; Imamura, T.; Kohno, K.; Nakayama, T.; Kadota, J.-I. Development of hyperammonemic encephalopathy in patients with multiple myeloma may be associated with the appearance of peripheral blood myeloma cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bénet, B.; Alexandra, J.-F.; Andriu, V.; Sedel, F.; Ajzenberg, N.; Papo, T. Multiple myeloma presenting as hyperammonemic encephalopathy. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 1620–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.; Reagan, J.L.; Castillo, J.J. Multiple myeloma-induced hyperammonemic encephalopathy: An entity associated with high in-patients mortality. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Song, J.-N.; Chen, X.-Z.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Sun, Y. Analysis of clinical prognosis in patients with non-hepatic hyperammonemia. Medicine 2021, 100, e24157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.K.; Granner, D.K.; Mayes, P.A.; Rodwell, V.W. Harper’s Biochemistry; McGraw-Hill: Milan, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, H.A.; Veech, R.L. Regulation of the redox state of pyridine nucleotids in rat liver. In Pyridine Nucleotide Dependent Dehydrogenases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1970; pp. 413–434. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, A. Glutamine Synthetase of Mammals. In The Enzymes; Boyer, P.D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 10, pp. 699–754. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Hemmens, B. Biosynthesis and action of nitric oxide in mammalian cells. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 22, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovamees, O.; Shemykin, A.; Eriksson, M.; Angelin, B.; Pernow, J. Arginase inhibition improves endothelial function in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia irrespective of their cholesterol levels. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 279, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, A.; Kovamees, O.; Checa, A.; Wheelock, C.E.; von Heijne, M.; Alvarsson, M.; Pernow, J. Arginase inhibition improves endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus despite intensive glucose-lowering therapy. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaan, H.C. Hyperviscosity in plasma cell dyscrasias. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2013, 55, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uggla, B.; Nilsson, T.K. Whole blood viscosity in plasma cell dyscrasia. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 537–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, G.; Merceron, S.; Zafrani, L.; Canet, E.; Lemiale, V.; Kouatchet, A.; Azoulay, E. Hyperviscosity syndrome. Rev. Med. Interne. 2015, 36, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caimi, G.; Carlisi, M.; Montana, M.; Gallà, E.; Lo Presti, R.; Hopps, E.; Siragusa, S. Erythrocyte deformability and hemorheological profile in multiple myeloma. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2018, 68, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimi, G.; Hopps, E.; Carlisi, M.; Montana, M.; Gallà, E.; Lo Presti, R.; Siragusa, S. Hemorheological parameters in Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS). Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2018, 68, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caimi, G.; Lo Presti, R.; Carlisi, M. Reflections on the unexpected laboratory finding of hemorheological alterations observed in some hematological disorders. Microvasc. Res. 2021, 136, 104171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisi, M.; Mancuso, S.; Lo Presti, R.; Siragusa, S.; Caimi, G. Comparison between whole blood viscosity measured and calculated in subjects with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and in patients with multiple myeloma: Re-evaluation of our survey. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popel, A.S.; Johnson, P.C. Microcirculation and hemorheology. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gori, T.; Forconi, S. Endothelium and hemorheology. In Handbook of Hemorheology and Hemodynamics; Baskurt, O.K., Hardeman, M.R., Rampling, M.W., Meiselman, H.J., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Forconi, S.; Wild, P.; Munzel, T.; Gori, T. Endothelium and hyperviscosity. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2011, 49, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forconi, S.; Gori, T. Endothelium and hemorheology. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2013, 53, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.G.; Acero, C.; Nance, P.R.; Cabrales, P.; Frangos, J.A.; Buerk, D.G.; Intaglietta, M. Elevated plasma viscosity in extreme hemodilution increases perivascular nitric oxide concentration and microvascular perfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H1730–H1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrales, P.; Martini, J.; Intaglietta, M.; Tsai, A.G. Blood viscosity maintains microvascular conditions during normovolemic anemia independent of blood oxygen-carrying capacity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H581–H590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katritsis, D.; Kaiktsis, L.; Chaniotis, A.; Pantos, J.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Marmarelis, V. Wall shear stress: Theoretical considerations and methods of measurement. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 49, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, K.; Intaglietta, M.; Tartakovsky, D.M. Non-Newtonian flow of blood in arterioles: Consequences of wall shear stress measurements. Microcirculation 2014, 21, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.-S.; Chien, S. Shear stress-initiated signaling and its regulation of endothelial function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzarski, J.S.; Scott, E.W.; McFetridge, P.S. Adaptation of endothelial cells to physiologically-modeled, variable shear stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, J.-I.; Berk, B.C. Novel mechanisms of endothelial mechanotransduction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balligand, J.L.; Feron, O.; Dessy, C. eNOS activation by physical forces: From short-term regulation of contraction to chronic remodeling of cardiovascular tissues. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 481–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Laughin, J.G.; Rangamani, P.; Tartakovsky, D.M. Shear-induced nitric oxide production by endothelial cells. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carlisi, M.; Mancuso, S.; Lo Presti, R.; Siragusa, S.; Caimi, G. High Output Heart Failure in Multiple Myeloma: Pathogenetic Considerations. Cancers 2022, 14, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030610
Carlisi M, Mancuso S, Lo Presti R, Siragusa S, Caimi G. High Output Heart Failure in Multiple Myeloma: Pathogenetic Considerations. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030610
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarlisi, Melania, Salvatrice Mancuso, Rosalia Lo Presti, Sergio Siragusa, and Gregorio Caimi. 2022. "High Output Heart Failure in Multiple Myeloma: Pathogenetic Considerations" Cancers 14, no. 3: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030610
APA StyleCarlisi, M., Mancuso, S., Lo Presti, R., Siragusa, S., & Caimi, G. (2022). High Output Heart Failure in Multiple Myeloma: Pathogenetic Considerations. Cancers, 14(3), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030610




