Biological and Clinical Insight from Analysis of the Tumor B-Cell Receptor Structure and Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. IG Status Defines Two CLL Subsets with Different Origin and Clinical Behavior
3. The Clinical and Biological Significance of IGHV3-21-Associated Characteristics in CLL: IG Structure or Epigenetic Signature?
4. Surface IgM Dynamics Indicate Chronic Antigen Engagement in CLL
5. IG Selection in CLL
6. Surface Ig Engagement Occurs at Tissue Sites in CLL
7. CLL at the Edge between Anergy and Survival
8. Microenvironmental Influences on sIgM Expression and Function
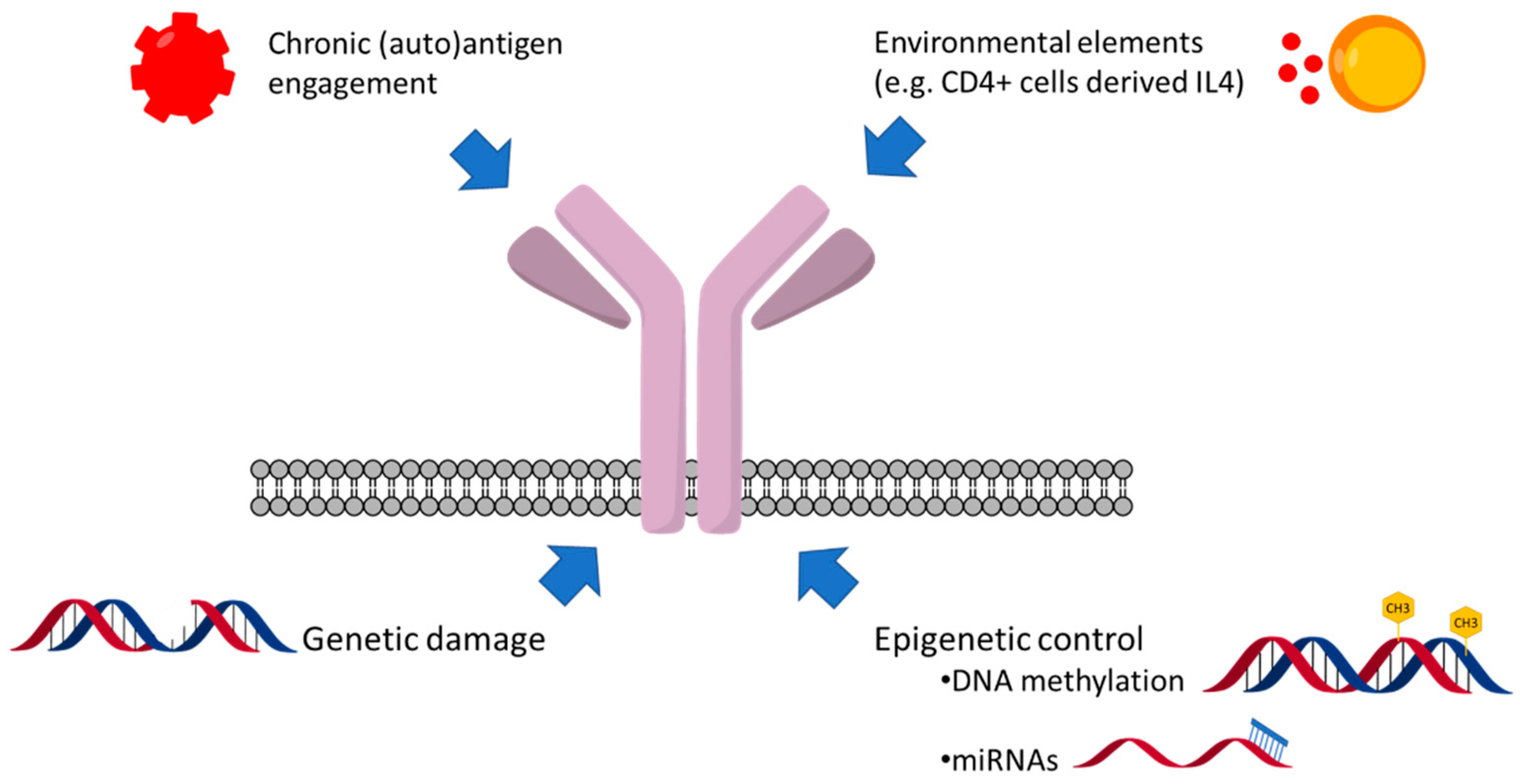
9. Genetic and Epigenetic Factors Affecting sIgM Expression and Function
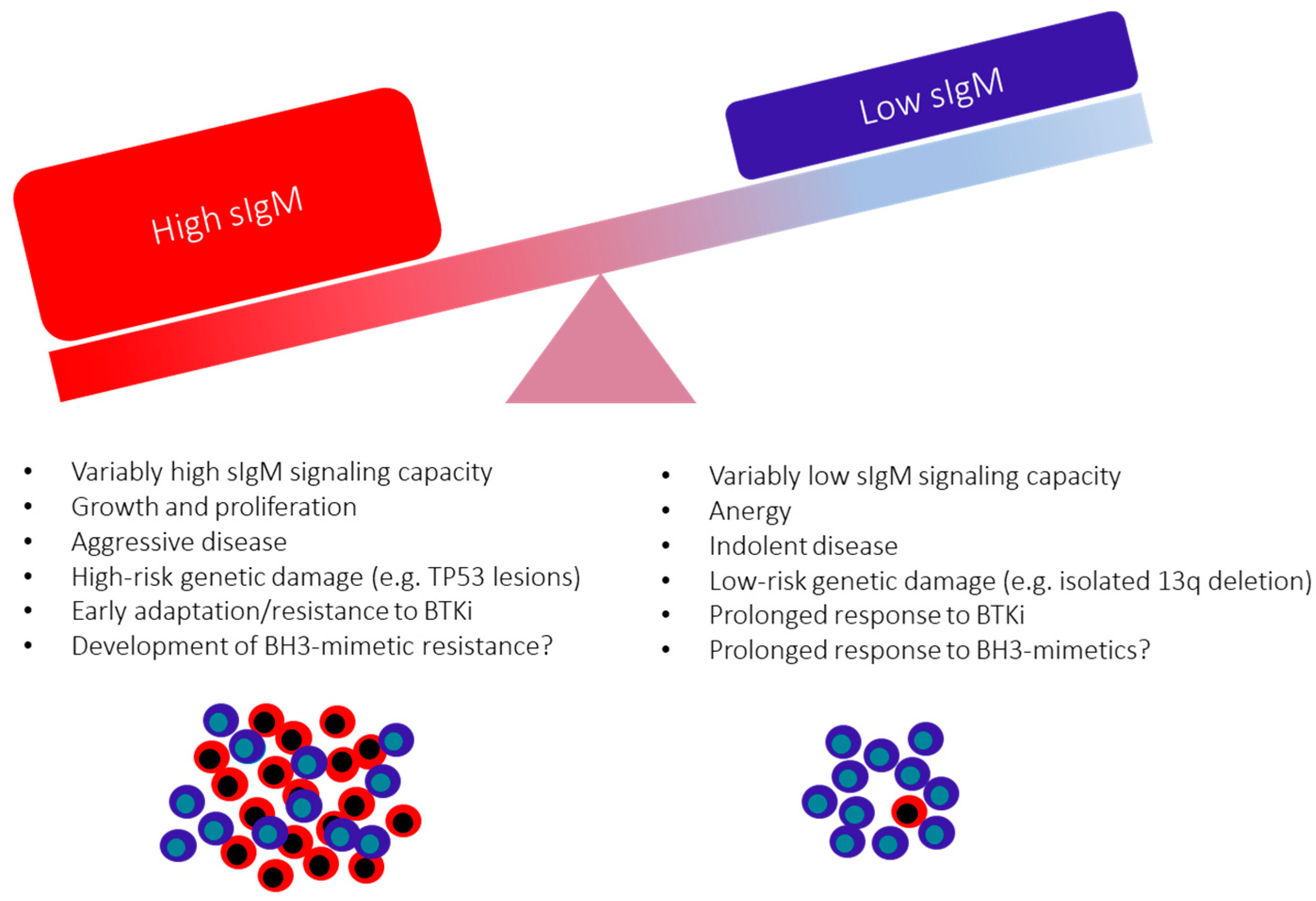
10. The Consequences of the Variable sIgM Expression Levels and Function on CLL Progression
11. Surface IgM Levels and Function May Identify Responses to BCR Inhibitors in Patients with CLL
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternynck, T.; Dighiero, G.; Follezou, J.; Binet, J.L. Comparison of normal and CLL lymphocyte surface Ig determinants using peroxidase-labeled antibodies. I. Detection and quantitation of light chain determinants. Blood 1974, 43, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messmer, B.T.; Messmer, D.; Allen, S.L.; Kolitz, J.E.; Kudalkar, P.; Cesar, D.; Murphy, E.J.; Koduru, P.; Ferrarini, M.; Zupo, S.; et al. In vivo measurements document the dynamic cellular kinetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calissano, C.; Damle, R.N.; Hayes, G.; Murphy, E.J.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Moreno, C.; Sison, C.; Kaufman, M.S.; Kolitz, J.E.; Allen, S.L.; et al. In vivo intraclonal and interclonal kinetic heterogeneity in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2009, 114, 4832–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, D.A.; Tausch, E.; Taylor-Weiner, A.N.; Stewart, C.; Reiter, J.; Bahlo, J.; Kluth, S.; Bozic, I.; Lawrence, M.S.; Böttcher, S.; et al. Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 2015, 526, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Monti, S.; Ciardullo, C.; Deambrogi, C.; Khiabanian, H.; Serra, R.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Integrated mutational and cytogenetic analysis identifies new prognostic subgroups in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.A.; Hernandez, A.M.; Shibata, D.; Cortopassi, G.A. BCL2 translocation frequency rises with age in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8910–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Mermel, C.; Robinson, J.T.; Garraway, L.A.; Golub, T.R.; Meyerson, M.; Gabriel, S.B.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature 2014, 505, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti, C.; Vogelstein, B. Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained by the number of stem cell divisions. Science 2015, 347, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, C.; Scarfò, L.; Pecciarini, L.; Cottini, F.; Dagklis, A.; Janus, A.; Talarico, A.; Scielzo, C.; Sala, C.; Toniolo, D.; et al. General population low-count CLL-like MBL persists over time without clinical progression, although carrying the same cytogenetic abnormalities of CLL. Blood 2011, 118, 6618–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berek, C.; Griffiths, G.; Milstein, C. Molecular events during maturation of the immune response to oxazolone. Nature 1985, 316, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Fagarasan, S.; Yamada, S.; Shinkai, Y.; Honjo, T. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 2000, 102, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Sahota, S.S.; Ottensmeier, C.H.; Zhu, D.; Forconi, F.; Hamblin, T.J. The occurrence and significance of V gene mutations in B cell—Derived human malignancy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2001, 83, 81–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, R.N.; Wasil, T.; Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Buchbinder, A.; Budman, D.; Dittmar, K.; Kolitz, J.; et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, M.; Sellmann, L.; Bloehdorn, J.; Wein, F.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Dürig, J.; Küppers, R. Cellular origin and pathophysiology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2183–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathangelidis, A.; Darzentas, N.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Brochet, X.; Murray, F.; Yan, X.-J.; Davis, Z.; Van Gastel-Mol, E.J.; Tresoldi, C.; Chu, C.C.; et al. Stereotyped B-cell receptors in one-third of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A molecular classification with implications for targeted therapies. Blood 2012, 119, 4467–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forconi, F.; Potter, K.N.; Wheatley, I.; Darzentas, N.; Sozzi, E.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Mockridge, C.I.; Packham, G.; Stevenson, F.K. The normal IGHV1-69–derived B-cell repertoire contains stereotypic patterns characteristic of unmutated CLL. Blood 2010, 115, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, R.N.; Ghiotto, F.; Valetto, A.; Albesiano, E.; Fais, F.; Yan, X.J.; Sison, C.P.; Allen, S.L.; Kolitz, J.; Schulman, P.; et al. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells express a surface membrane phenotype of activated, antigen-experienced B lymphocytes. Blood 2002, 99, 4087–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.; et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.I.; Tam, C.S.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Lerner, S.; Coombes, K.; Schlette, E.; Ferrajoli, A.; Barron, L.L.; et al. Relevance of the immunoglobulin VH somatic mutation status in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) or related chemoimmunotherapy regimens. Blood 2009, 113, 3168–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Terzi-di-Bergamo, L.; De Paoli, L.; Cerri, M.; Ghilardi, G.; Chiarenza, A.; Bulian, P.; Visco, C.; Mauro, F.R.; Morabito, F.; et al. Molecular prediction of durable remission after first-line fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-κB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coller, H.A.; Grandori, C.; Tamayo, P.; Colbert, T.; Lander, E.S.; Eisenman, R.N.; Golub, T.R. Expression analysis with oligo-nucleotide microarrays reveals that MYC regulates genes involved in growth, cell cycle, signaling, and adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3260–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulis, M.; Heath, S.; Bibikova, M.; Queirós, A.C.; Navarro, A.; Clot, G.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Castellano, G.; Brun-Heath, I.; Pinyol, M.; et al. Epigenomic analysis detects widespread gene-body DNA hypomethylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulis, M.; Merkel, A.; Heath, S.; Queiros, A.; Schuyler, R.P.; Castellano, G.; Beekman, R.; Raineri, E.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Clot, G.; et al. Whole-genome fingerprint of the DNA methylome during human B cell differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, C.C.; Seifert, M.; Assenov, Y.; Gu, L.; Przekopowitz, M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Wang, Q.; Imbusch, C.D.; Serva, A.; Koser, S.D.; et al. DNA methylation dynamics during B cell maturation underlie a continuum of disease phenotypes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiros, A.; Villamor, N.; Clot, G.; Martineztrillos, A.; Kulis, M.; Navarro, A.; Penas, E.M.M.; Jayne, S.; Majid, A.; Richter, J.; et al. A B-cell epigenetic signature defines three biologic subgroups of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with clinical impact. Leukemia 2014, 29, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathangelidis, A.; Chatzidimitriou, A.; Gemenetzi, K.; Giudicelli, V.; Karypidou, M.; Plevova, K.; Davis, Z.; Yan, X.-J.; Jeromin, S.; Schneider, C.; et al. Higher-order connections between stereotyped subsets: Implications for improved patient classification in CLL. Blood 2021, 137, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsélius, M.; Kröber, A.; Murray, F.; Thunberg, U.; Tobin, G.; Bühler, A.; Kienle, D.; Albesiano, E.; Maffei, R.; Dao-Ung, L.-P.; et al. Strikingly homologous immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and poor outcome in VH3-21-using chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients independent of geographic origin and mutational status. Blood 2006, 107, 2889–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, G.; Thunberg, U.; Johnson, A.; Eriksson, I.; Söderberg, O.; Karlsson, K.; Merup, M.; Juliusson, G.; Vilpo, J.; Enblad, G.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemias utilizing the VH3-21 gene display highly restricted Vlambda2-14 gene use and homologous CDR3s: Implicating recognition of a common antigen epitope. Blood 2003, 101, 4952–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, G.; Thunberg, U.; Johnson, A.; Thörn, I.; Söderberg, O.; Hultdin, M.; Botling, J.; Enblad, G.; Sällström, J.; Sundström, C.; et al. Rosenquist, Somatically mutated Ig V(H)3-21 genes characterize a new subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 2262–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomben, R.; Bo, M.D.; Capello, D.; Benedetti, D.; Marconi, D.; Zucchetto, A.; Forconi, F.; Maffei, R.; Ghia, E.M.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of IGHV3-21–expressing B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An Italian multicenter study. Blood 2006, 109, 2989–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Bomben, R.; Rasi, S.; Bo, M.D.; Bruscaggin, A.; Rossi, F.M.; Monti, S.; Degan, M.; Ciardullo, C.; et al. Association between molecular lesions and specific B-cell receptor subsets in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4902–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, E.M.; Jain, S.; Widhopf, G.F.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Gribben, J.G.; Brown, J.R.; Rai, K.R.; Byrd, J.C.; et al. Use of IGHV3-21 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with high-risk disease and reflects antigen-driven, post-germinal center leukemogenic selection. Blood 2008, 111, 5101–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baliakas, P.; Agathangelidis, A.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Sutton, L.-A.; Minga, E.; Tsanousa, A.; Scarfo, L.; Davis, Z.; Yan, X.-J.; Shanafelt, T.; et al. Not all IGHV3-21 chronic lymphocytic leukemias are equal: Prognostic considerations. Blood 2015, 125, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeu, F.; Royo, R.; Clot, G.; Duran-Ferrer, M.; Navarro, A.; Martín, S.; Lu, J.; Zenz, T.; Baumann, T.; Jares, P.; et al. IGLV3-21R110 identifies an aggressive biological subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with intermediate epigenetics. Blood 2021, 137, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avola, S.; Drennan, I.; Tracy, I.; Henderson, L.; Chiecchio, M.; Larrayoz, M.; Rose-Zerilli, J.; Strefford, C.; Plass, P.W.; Johnson, A.J.; et al. Surface IgM expression and function are associated with clinical behavior, genetic abnormalities, and DNA methylation in CLL. Blood 2016, 128, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F.; Kipps, T.J. Exploring the pathways to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanham, S.; Hamblin, T.; Oscier, D.; Ibbotson, R.; Stevenson, F.; Packham, G. Differential signaling via surface IgM is associated with VH gene mutational status and CD38 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2003, 101, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ian Mockridge, C.; Potter, K.N.; Wheatley, I.; Neville, L.A.; Packham, G.; Stevenson, F.K. Reversible anergy of sIgM-mediated signaling in the two subsets of CLL defined by VH-gene mutational status. Blood 2007, 109, 4424–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.N.; Wormald, M.R.; Suter, D.M.; Radcliffe, C.M.; Harvey, D.J.; Dwek, R.A.; Rudd, P.M.; Sim, R.B. Human serum IgM glycosylation: Identification of glycoforms that can bind to mannan-binding lectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29080–29087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.N.; Wormald, M.R.; Sim, R.B.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A. The Impact of Glycosylation on the Biological Function and Structure of Human Immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysov, S.; Potter, K.N.; Mockridge, C.I.; Coelho, V.; Wheatley, I.; Packham, G.; Stevenson, F.K. Surface IgM of CLL cells displays unusual glycans indicative of engagement of antigen in vivo. Blood 2010, 115, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhren-von Minden, M.; Ubelhart, R.; Schneider, D.; Wossning, T.; Bach, M.P.; Buchner, M.; Hofmann, D.; Surova, E.; Follo, M.; Kohler, F.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling. Nature 2012, 489, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, M.; Müller, F.; Frick, M.; Wehr, C.; Simon, F.; Leistler, B.; Veelken, H.; Mertelsmann, R.; Trepel, M. CLL B-cell receptors can recognize themselves: Alternative epitopes and structural clues for autostimulatory mechanisms in CLL. Blood 2013, 121, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minici, C.; Gounari, M.; Übelhart, R.; Scarfo, L.; Minden, M.D.-V.; Schneider, D.; Tasdogan, A.; Alkhatib, A.; Agathangelidis, A.; Ntoufa, S.; et al. Distinct homotypic B-cell receptor interactions shape the outcome of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, V.; Krysov, S.; Steele, A.; Hidalgo, M.S.; Johnson, P.; Chana, P.S.; Packham, G.; Stevenson, F.; Forconi, F. Identification in CLL of circulating intraclonal subgroups with varying B-cell receptor expression and function. Blood 2013, 122, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Duffy, S.F.; Carson, D.A.; Kipps, T.J. Evidence for somatic selection of natural autoantibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widhopf, G.F.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Toy, T.L.; Gribben, J.G.; Wierda, W.G.; Kipps, T.J. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells of more than 1% of patients express virtually identical immunoglobulins. Blood 2004, 104, 2499–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemenetzi, K.; Psomopoulos, F.; Carriles, A.A.; Gounari, M.; Minici, C.; Plevova, K.; Sutton, L.A.; Tsagiopoulou, M.; Baliakas, P.; Pasentsis, K.; et al. Chatzidimitriou, Higher-order immunoglobulin repertoire restrictions in CLL: The illustrative case of stereo-typed subsets 2 and 169. Blood 2021, 137, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipps, T.J.; Tomhave, E.; Pratt, L.F.; Duffy, S.; Chen, P.P.; Carson, D.A. Developmentally restricted immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene expressed at high frequency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5913–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomben, R.; Bo, M.D.; Capello, D.; Forconi, F.; Maffei, R.; Laurenti, L.; Rossi, D.; del Principe, M.I.; Zucchetto, A.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Molecular and clinical features of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with stereotyped B cell receptors: Results from an Italian multicentre study. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezinschek, H.P.; Foster, S.J.; Brezinschek, R.I.; Dörner, T.; Domiati-Saad, R.; Lipsky, P.E. Analysis of the human VH gene repertoire. Differential effects of selection and somatic hypermutation on human peripheral CD5(+)/IgM+ and CD5(-)/IgM+ B cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2488–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhopf, G.F.; Kipps, T.J. Normal B cells express 51p1-encoded Ig heavy chains that are distinct from those expressed by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.A.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Kipps, T.J. Ig VH1 genes expressed in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia exhibit distinctive molecular features. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Bagnara, D.; Reverberi, D.; Matis, S.; Cardillo, M.; Massara, R.; Mastracci, L.; Ravetti, J.L.; Agnelli, L.; Neri, A.; et al. Tracing CLL-biased stereotyped immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in normal B cell subsets using a high-throughput immunogenetic approach. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddur, M.S.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Dimitrov, J.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Bayry, J.; Kaveri, S.V. Natural Antibodies: From First-Line Defense Against Pathogens to Perpetual Immune Homeostasis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 58, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Catera, R.; Zhang, L.; Didier, S.; Agagnina, B.M.; Damle, R.N.; Kaufman, M.S.; Kolitz, J.E.; Allen, S.; Rai, K.R.; et al. Many chronic lymphocytic leukemia antibodies recognize apoptotic cells with exposed nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA: Implications for patient outcome and cell of origin. Blood 2010, 115, 3907–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Catera, R.; Hatzi, K.; Yan, X.-J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.B.; Fales, H.M.; Allen, S.L.; Kolitz, J.E.; Rai, K.R.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia antibodies with a common stereotypic rearrangement recognize nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA. Blood 2008, 112, 5122–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, X.; Widhopf, G.F., II; Amir, S.; Hartvigsen, K.; Hansen, L.F.; Woelkers, D.; Tsimikas, S.; Binder, C.J.; Kipps, T.J.; Witztum, J.L. IGHV1-69-encoded antibodies expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia react with malondialde-hyde-acetaldehyde adduct, an immunodominant oxidation-specific epitope. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhrinder, A.L.; Hellqvist, E.; Sidorova, E.; Söderberg, A.; Baxendale, H.; Dahle, C.; Willander, K.; Tobin, G.; Bäckman, E.; Söderberg, O.; et al. A new perspective: Molecular motifs on oxidized LDL, apoptotic cells, and bacteria are targets for chronic lymphocytic leukemia antibodies. Blood 2008, 111, 3838–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Kipps, T.J. CXCR4: A key receptor in the crosstalk between tumor cells and their microenvironment. Blood 2006, 107, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.J.; Tsukada, N.; Burger, M.; Zvaifler, N.J.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Kipps, T.J. Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 2000, 96, 2655–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.J.; Burger, M.; Kipps, T.J. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express functional CXCR4 chemokine receptors that mediate spontaneous migration beneath bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 1999, 94, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drennan, S.; Chiodin, G.; D’Avola, A.; Tracy, I.; Johnson, P.W.; Trentin, L.; Steele, A.J.; Packham, G.; Stevenson, F.; Forconi, F. Ibrutinib Therapy Releases Leukemic Surface IgM from Antigen Drive in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 25, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, M.F.M.; Kuil, A.; Geest, C.R.; Eldering, E.; Chang, B.Y.; Buggy, J.J.; Pals, S.T.; Spaargaren, M. The clinically active BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 targets B-cell receptor– and chemokine-controlled adhesion and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 2590–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponader, S.; Chen, S.-S.; Buggy, J.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Gandhi, V.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; O’Brien, S.; Chiorazzi, N.; Burger, J.A. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2012, 119, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Montserrat, E. Coming full circle: 70 years of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell redistribution, from glucocorticoids to inhibitors of B-cell receptor signaling. Blood 2013, 121, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodarz, D.; Garg, N.; Komarova, N.L.; Benjamini, O.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Kantarjian, H.; James, D.; O’Brien, S.; Burger, J.A. Kinetics of CLL cells in tissues and blood during therapy with the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib. Blood 2014, 123, 4132–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, G.; Krysov, S.; Allen, A.; Savelyeva, N.; Steele, A.J.; Forconi, F.; Stevenson, F.K. The outcome of B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Proliferation or anergy. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodnow, C.; Crosbie, J.; Adelstein, S.; Lavoie, T.B.; Smith-Gill, S.J.; Brink, R.A.; Pritchard-Briscoe, H.; Wotherspoon, J.S.; Loblay, R.H.; Raphael, K.; et al. Altered immunoglobulin expression and functional silencing of self-reactive B lymphocytes in transgenic mice. Nature 1988, 334, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarkoni, Y.; Getahun, A.; Cambier, J.C. Molecular underpinning of B-cell anergy. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambier, J.C.; Gauld, S.B.; Merrell, K.T.; Vilen, B.J. B-cell anergy: From transgenic models to naturally occurring anergic B cells? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, A.; Glenn, M.; Slupsky, J.R.; Packham, G.; Kalakonda, N. Variable induction of PRDM1 and differentiation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with anergy. Blood 2014, 123, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollonio, B.; Scielzo, C.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; Hacken, E.T.; Scarfo, L.; Ranghetti, P.; Stevenson, F.; Packham, G.; Ghia, P.; Muzio, M.; et al. Targeting B-cell anergy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 3879–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, M.; Apollonio, B.; Scielzo, C.; Frenquelli, M.; Vandoni, I.; Boussiotis, V.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Ghia, P. Constitutive ac-tivation of distinct BCR-signaling pathways in a subset of CLL patients: A molecular signature of anergy. Blood 2008, 112, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaizo Moore, V.; Brown, J.R.; Certo, M.; Love, T.M.; Novina, C.D.; Letai, A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia requires BCL2 to sequester prodeath BIM, explaining sensitivity to BCL2 antagonist ABT-737. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drennan, S.; D’Avola, A.; Gao, Y.; Weigel, C.; Chrysostomou, E.; Steele, A.J.; Zenz, T.; Plass, C.; Johnson, P.; Williams, A.P.; et al. IL-10 production by CLL cells is enhanced in the anergic IGHV mutated subset and associates with reduced DNA methylation of the IL10 locus. Leukemia 2016, 31, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, G.A.; Calin, M.; Fabbri, M.V.; Iorio, M.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, S.E.; Wojcik, R.I.; Aqeilan, S.; Zupo, M.; Dono, L.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Nonlinear partial differential equations and applications: Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.; Ferracin, M.; Cimmino, A.; Di Leva, G.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Iorio, M.; Visone, R.; Sever, N.I.; Fabbri, M.; et al. A MicroRNA Signature Associated with Prognosis and Progression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, S.J. Chromosomal translocations in lymphoid malignancies reveal novel proto-oncogenes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1992, 10, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.S.; Seymour, J.F.; Roberts, A.W. Progress in BCL2 inhibition for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Johnson, A.J.; Lee, A.M.; Gorgün, G.; Le Dieu, R.; Blum, W.; Byrd, J.C.; Gribben, J.G. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia T cells show impaired immunological synapse formation that can be reversed with an immunomodulating drug. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Clear, A.J.; Fatah, R.; Gribben, J.G. Multiple inhibitory ligands induce impaired T-cell immunologic synapse function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia that can be blocked with lenalidomide: Establishing a reversible immune evasion mechanism in human cancer. Blood 2012, 120, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forconi, F.; Moss, P. Perturbation of the normal immune system in patients with CLL. Blood 2015, 126, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.S.; Benet, Z.L.; Grigorova, I.L. Signals 1, 2 and B cell fate or: Where, when and for how long? Immunol. Rev. 2020, 296, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, P.; Buggins, A.G.S.; Richards, J.; Wotherspoon, A.; Salisbury, J.; Mufti, G.J.; Hamblin, T.J.; Devereux, S. CD38 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by the tumor microenvironment. Blood 2008, 111, 5173–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granziero, L.; Ghia, P.; Circosta, P.; Gottardi, D.; Strola, G.; Geuna, M.; Montagna, L.; Piccoli, P.; Chilosi, M.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. Survivin is expressed on CD40 stimulation and interfaces proliferation and apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 2777–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, E.M.; Pepper, A.; Mele, S.; Folarin, N.; Townsend, W.; Cuthill, K.; Phillips, E.H.; Patten, P.E.M.; Devereux, S. In vitro and in vivo evidence for uncoupling of B-cell receptor internalization and signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 103, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.M.A.; Blunt, M.D.; Dobson, R.; Yeomans, A.; Thirdborough, S.; Larrayoz, M.; Smith, L.D.; Linley, A.; Strefford, P.J.C.; Davies, A.; et al. IL-4 enhances expression and function of surface IgM in CLL cells. Blood 2016, 127, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Chiorazzi, N.; Rothstein, T.L. IL-4 rescues surface IgM expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Ghia, E.M.; Choi, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Widhopf, G.F.; Messer, K.; et al. Cirmtuzumab blocks Wnt5a/ROR1 stimulation of NF-kappaB to repress autocrine STAT3 activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M.D.; Koehrer, S.; Dobson, R.C.; Larrayoz, M.; Wilmore, S.; Hayman, A.; Parnell, J.; Smith, L.D.; Davies, A.; Johnson, P.W.; et al. The Dual Syk/JAK Inhibitor Cerdulatinib Antagonizes B-cell Receptor and Microenvironmental Signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 23, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, D.; Tissino, E.; Pozzo, F.; Bittolo, T.; Caldana, C.; Perini, C.; Martorelli, D.; Bravin, V.; D’Agaro, T.; Rossi, F.M.; et al. NOTCH1 mutations are associated with high CD49d expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Link between the NOTCH1 and the NF-kappaB pathways. Leukemia 2018, 32, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Fabbri, G.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Forconi, F.; Marasca, R.; Laurenti, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cerri, M.; et al. Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Benner, A.; Leupolt, E.; Kröber, A.; Bullinger, L.; Döhner, K.; Bentz, M.; Lichter, P. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulian, P.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Fegan, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Cro, L.M.; Nückel, H.; Baldini, L.; Kurtova, A.V.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.A.; et al. CD49d Is the Strongest Flow Cytometry–Based Predictor of Overall Survival in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruga, F.; Bracciamà, V.; Vitale, N.; Vaisitti, T.; Gizzi, K.; Yeomans, A.; Coscia, M.; D’Arena, G.; Gaidano, G.; Allan, J.N.; et al. Bidirectional linkage between the B-cell receptor and NOTCH1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and in Richter’s syndrome: Therapeutic implications. Leukemia 2019, 34, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, E.; Lemm, S.; Wilmore, B.E.; Cavell, B.; Valle-Argos, S.; Krysov, M.S.; Hidalgo, E.; Leonard, A.E.; Willis, F.; Forconi, F.K.; et al. PEITC-mediated inhibition of mRNA translation is associated with both inhibition of mTORC1 and increased eIF2alpha phosphorylation in established cell lines and primary human leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74807–74819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeomans, A.; Thirdborough, S.M.; Valle-Argos, B.; Linley, A.; Krysov, S.; Hidalgo, M.S.; Leonard, E.; Ishfaq, M.; Wagner, S.D.; Willis, A.E.; et al. Engagement of the B-cell receptor of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells drives global and MYC-specific mRNA translation. Blood 2016, 127, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmore, S.; Rogers-Broadway, K.-R.; Taylor, J.; Lemm, E.; Fell, R.; Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F.; Steele, A.J.; Coldwell, M.; Packham, G.; et al. Targeted inhibition of eIF4A suppresses B-cell receptor-induced translation and expression of MYC and MCL1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6337–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Yeomans, A.M.; Packham, G. Targeted inhibition of mRNA translation initiation factors as a novel therapeutic strategy for mature B-cell neoplasms. Explor. Target. Anti-Tumor Ther. 2020, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mraz, M.; Kipps, T.J. MicroRNAs and B cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.; Liu, C.-G.; Sevignani, C.; Ferracin, M.; Felli, N.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Cimmino, A.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11755–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Mraz, M.; Fecteau, J.-F.; Yu, J.; Ghia, E.M.; Zhang, L.; Bao, L.; Rassenti, L.Z.; et al. MicroRNA-155 influences B-cell receptor signaling and associates with aggressive disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, V.; Vojackova, E.; Ondrisova, L.; Kostalova, L.; Sharma, S.; Loja, T.; Pavlasova, G.M.; Zicha, D.; Peskova, M.K.; Krivanek, J.; et al. FoxO1-GAB1 axis regulates homing capacity and tonic AKT activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, M.; Chen, L.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Ghia, E.M.; Li, H.; Jepsen, K.; Smith, E.N.; Messer, K.; Frazer, K.A.; Kipps, T.J. miR-150 influences B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by regulating expression of GAB1 and FOXP1. Blood 2014, 124, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna, K.; Oppelt, J.; Chochola, V.; Musilova, K.; Seda, V.; Pavlasova, G.; Radova, L.; Arigoni, M.; Calogero, R.; Benes, V.; et al. MicroRNA miR-34a downregulates FOXP1 during DNA damage response to limit BCR signalling in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia B cells. Leukemia 2018, 33, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International CLL-IPI Working Group. An international prognostic index for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL-IPI): A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Di Bergamo, L.T.; Langerbeins, P.; Hoechstetter, M.A.; Herling, C.D.; De Paoli, L.; Delgado, J.; Rabe, K.G.; Gentile, M.; Doubek, M.; et al. International prognostic score for asymptomatic early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarello, A.N.; Gentner-Göbel, E.; Minden, M.D.-V.; Tarasenko, T.N.; Nicolò, A.; Ferrer, G.; Vergani, S.; Liu, Y.; Bagnara, D.; Rai, K.R.; et al. B-cell receptor isotypes differentially associate with cell signaling, kinetics, and outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 132, e149308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, J.S.; Märklin, M.; Truckenmüller, F.M.; Hinterleitner, C.; Dörfel, D.; Haap, M.; Kopp, H.; Wirths, S.; Müller, M.R. A novel flow cytometry-based assay to measure compromised B cell receptor signaling as a prognostic factor in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A. Inhibiting B-Cell Receptor Signaling Pathways in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malign. Rep. 2011, 7, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Bojnik, E.; Ruppert, A.S.; Stefanovski, M.R.; Goettl, V.M.; Smucker, K.A.; Smith, L.L.; Dubovsky, J.A.; Towns, W.H.; MacMurray, J.; et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) function is important to the development and expansion of chronic lympho-cytic leukemia (CLL). Blood 2014, 123, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Ibrutinib–Rituximab or Chemoimmunotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Zhong, Y.; Lozanski, A.; Lozanski, G.; Dong, S.; Strattan, E.; Lehman, A.; Zhang, X.; Jones, J.A.; et al. Hypermorphic mutation of phospholipase C, gamma2 acquired in ibrutinib-resistant CLL confers BTK independency upon B-cell receptor activation. Blood 2015, 126, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Furman, R.R.; Liu, T.M.; Ozer, H.G.; Zapatka, M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Xue, L.; Li, D.H.H.; Steggerda, S.M.; Versele, M.; et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Landau, D.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Bozic, I.; Zhang, H.; Sarosiek, K.; Wang, L.; Stewart, C.; Fan, J.; Hoellenriegel, J.; et al. Clonal evolution in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia developing resistance to BTK inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Galanina, N.; Guo, A.; Lee, J.; Kadri, S.; Van Slambrouck, C.; Long, B.; Wang, W.; Ming, M.; Furtado, L.V.; et al. Identification of a structurally novel BTK mutation that drives ibrutinib resistance in CLL. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68833–68841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.M.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Coleman, J.; Jones, D.; et al. BTK(C481S)-Mediated Resistance to Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, S.; Lee, J.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Galanina, N.; Sukhanova, M.; Venkataraman, G.; Sharma, S.; Long, B.; Petras, K.; Theissen, M.; et al. Clonal evolution underlying leukemia progression and Richter transformation in patients with ibrutinib-relapsed CLL. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.-M.; Letestu, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Fleury, C.; Lazarian, G.; Dilhuydy, M.-S.; Nollet, D.; Guieze, R.; Feugier, P.; et al. Prevalence of BTK and PLCG2 mutations in a real-life CLL cohort still on ibrutinib after 3 years: A FILO group study. Blood 2019, 134, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gángó, A.; Alpar, D.; Galik, B.; Marosvári, D.; Kiss, R.; Fésüs, V.; Aczél, D.; Eyüpoglu, E.; Nagy, N.; Nagy, Á.; et al. Dissection of subclonal evolution by temporal mutation profiling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with ibrutinib. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 146, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlarikova, L.; Petrackova, A.; Papajik, T.; Turcsanyi, P.; Kriegova, E. Resistance-Associated Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients Treated With Novel Agents. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, L.; Sasaki, Y.; Calado, D.P.; Zhang, B.; Paik, J.H.; DePinho, R.A.; Kutok, J.L.; Kearney, J.F.; Otipoby, K.L.; Rajewsky, K. PI3 Kinase Signals BCR-Dependent Mature B Cell Survival. Cell 2009, 139, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodin, G.; Dutton, D.; Martino, E.A.; Drennan, S.; Tracy, I.; Ondrisova, L.; Henderson, I.; D’Avola, A.; Pitsillidou, C.; Mraz, M.; et al. High Surface IgM Levels Associate with Shorter Response Duration and Bypass of the BTK Blockade during Ibrutinib Therapy in CLL Patients. Blood 2019, 134, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Rawstron, A.C.; Brock, K.; Muñoz-Vicente, S.; Yates, F.J.; Bishop, R.; Boucher, R.; Macdonald, D.; Fegan, C.; McCaig, A.; et al. Ibrutinib Plus Venetoclax in Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: The CLARITY Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Keating, M.; Thompson, P.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.; Borthakur, G.; Takahashi, K.; Estrov, Z.; Fowler, N.; Kadia, T.; et al. Ibrutinib and Venetoclax for First-Line Treatment of CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojarczuk, K.; Sasi, B.K.; Gobessi, S.; Innocenti, I.; Pozzato, G.; Laurenti, L.; Efremov, D. BCR signaling inhibitors differ in their ability to overcome Mcl-1–mediated resistance of CLL B cells to ABT-199. Blood 2016, 127, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysov, S.; Dias, S.; Paterson, A.; Mockridge, C.I.; Potter, K.N.; Smith, K.A.; Ashton-Key, M.; Stevenson, F.K.; Packham, G. Surface IgM stimulation induces MEK1/2-dependent MYC expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2012, 119, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, A.; Mockridge, C.I.; Adams, J.E.; Krysov, S.; Potter, K.N.; Duncombe, A.S.; Cook, S.J.; Stevenson, F.K.; Packham, G. Mechanisms and clinical significance of BIM phosphorylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobessi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Longo, P.G.; Carsetti, L.; Berno, V.; Sica, S.; Leone, G.; Efremov, D. Inhibition of constitutive and BCR-induced Syk activation downregulates Mcl-1 and induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leukemia 2008, 23, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NCT Number | Investigation | Comparator(s) | Setting | Status | Main Outcome Measures | Enrollment | Sponsor | Start | Completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05057494 | Acalabrutinib + Venetoclax | Venetoclax + Obinutuzumab | Untreated | Not yet recruiting | PFS; PB and BM uMRD; OS; EFS; ORR; CR rate; QLQ; AE | 750 | Industry | Mar-22 | Sep-28 |
| NCT04965493 | Pirtobrutinib + Venetoclax + Rituximab | Venetoclax + Rituximab | relapsed/refractory | Recruiting | PFS; OS; TTNT; EFS; ORR | 600 | Industry | Sep-21 | Oct-25 |
| NCT04608318 | Ibrutinib + Venetoclax | Venetoclax + Obinutuzumab or Ibrutinib | Untreated | Recruiting | PFS; PB and BM uMRD; ORR; CR; AE | 897 | Academic | Mar-21 | Mar-27 |
| NCT03836261 | Acalabrutinib + Venetoclax ± Obinutuzumab | FCR or BR | Untreated | Recruiting | PFS | 780 | Industry | Feb-19 | Jan-27 |
| NCT03737981 | Ibrutinib + Venetoclax + Obinutuzumab | Ibrutinib + Obinutuzumab | untreated, elderly | Recruiting | PFS; BM MRD; CR rate; OS; AE | 454 | Academic | Jan-19 | Jun-27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forconi, F.; Lanham, S.A.; Chiodin, G. Biological and Clinical Insight from Analysis of the Tumor B-Cell Receptor Structure and Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030663
Forconi F, Lanham SA, Chiodin G. Biological and Clinical Insight from Analysis of the Tumor B-Cell Receptor Structure and Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030663
Chicago/Turabian StyleForconi, Francesco, Stuart A. Lanham, and Giorgia Chiodin. 2022. "Biological and Clinical Insight from Analysis of the Tumor B-Cell Receptor Structure and Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Cancers 14, no. 3: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030663
APA StyleForconi, F., Lanham, S. A., & Chiodin, G. (2022). Biological and Clinical Insight from Analysis of the Tumor B-Cell Receptor Structure and Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers, 14(3), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030663







