Second-Harmonic Generation Imaging Reveals Changes in Breast Tumor Collagen Induced by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
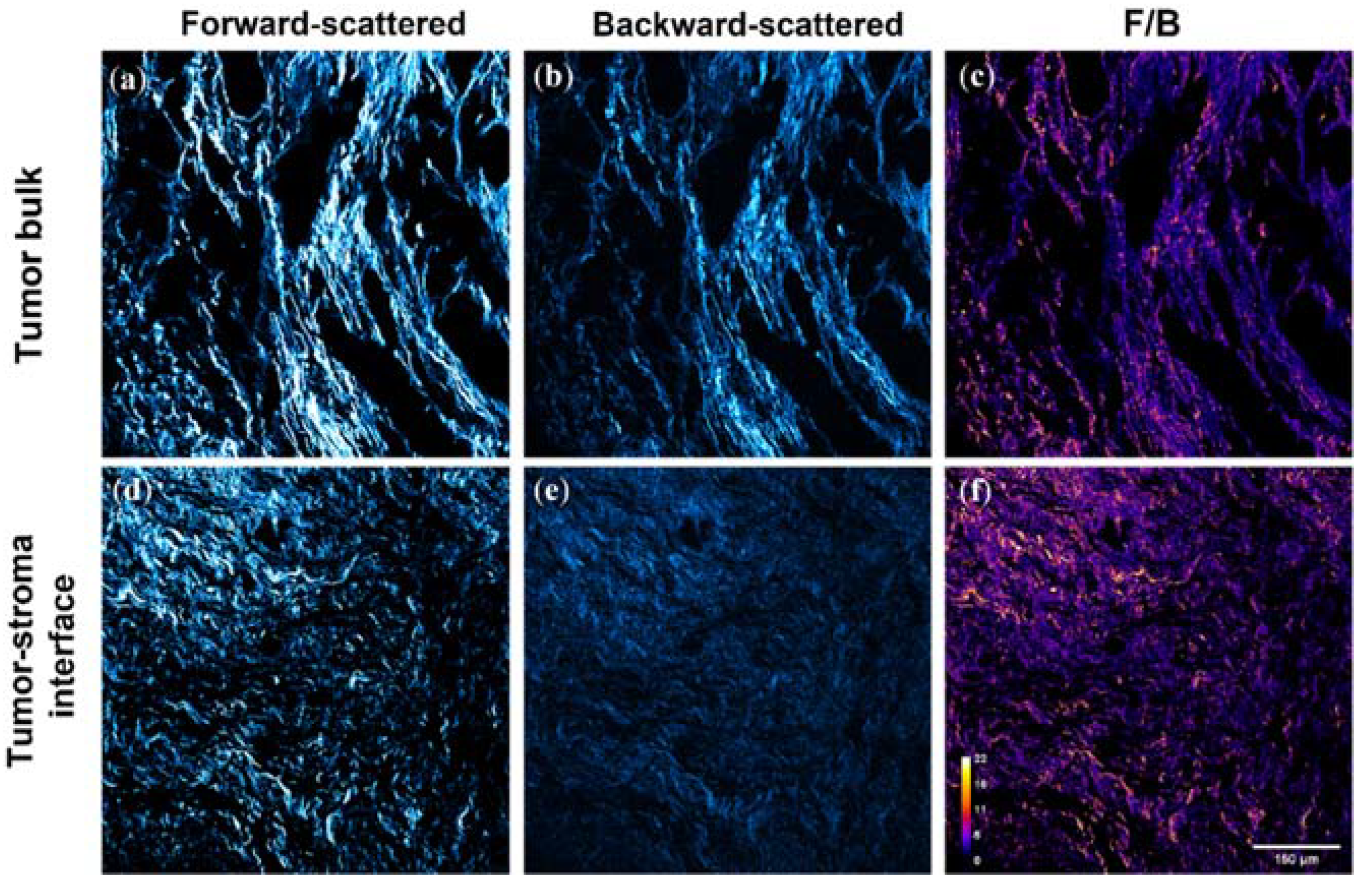
2.2. Imaging
2.3. Image Analysis: F/B with User-Defined Thresholds
2.4. Image Analysis: F/B with Adaptive Thresholds
2.5. F/B Calibration
2.6. Image Analysis: Collagen Fiber Organization
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
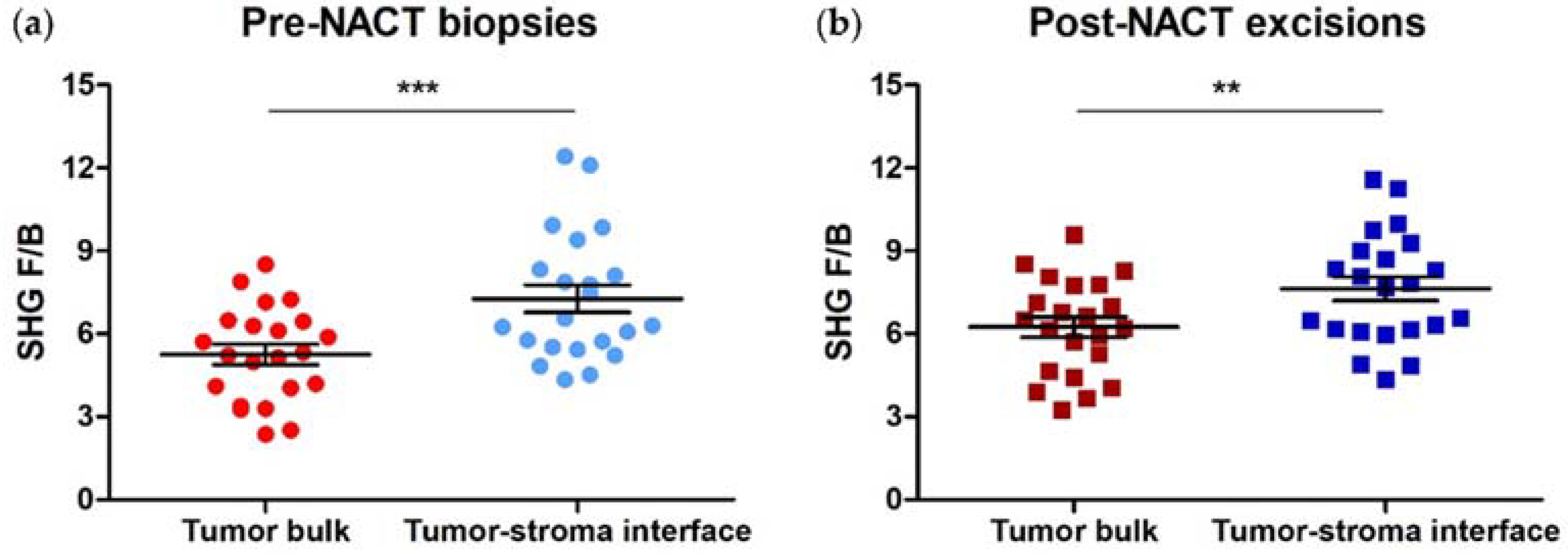
3.1. SHG F/B from the Tumor Bulk Differs from the Tumor-Stroma Interface in HER2+ Tumors
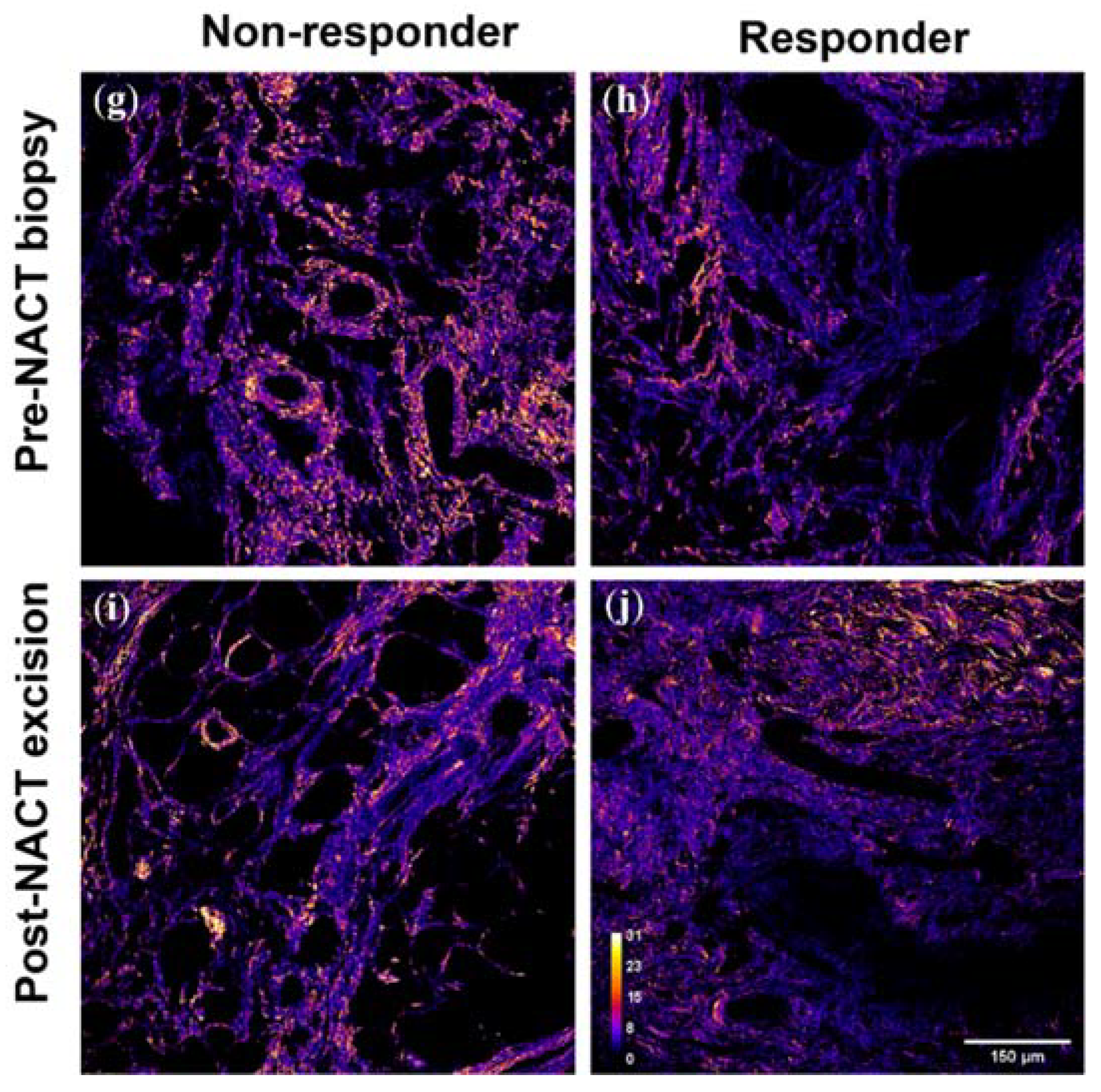
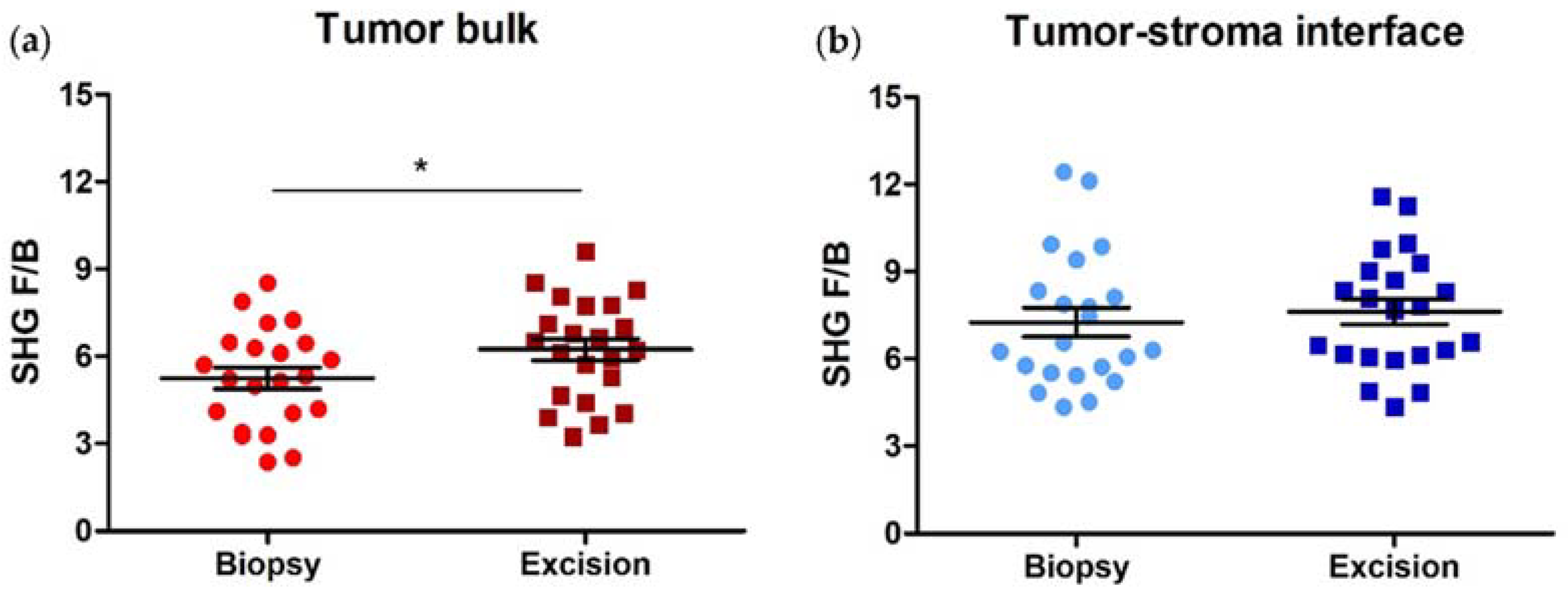
3.2. SHG F/B increases with NACT in the Tumor Bulk but Not the Tumor-Stroma Interface of HER2+ Tumors
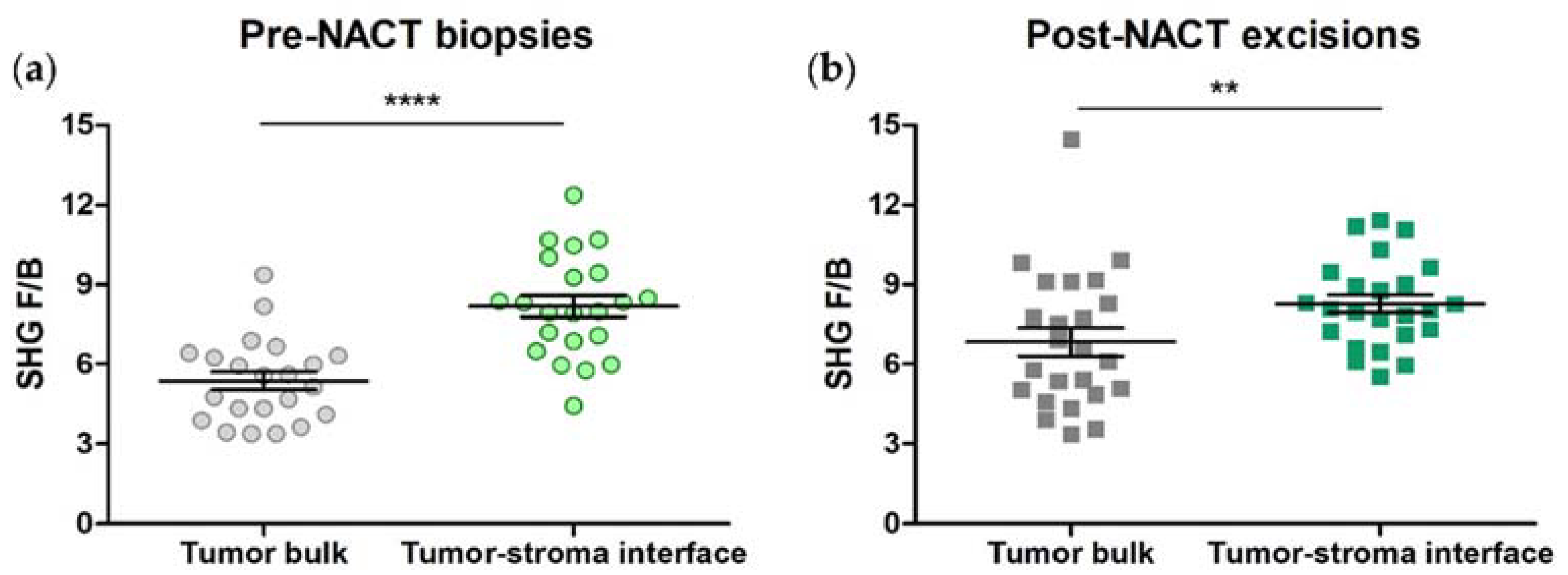
3.3. SHG F/B from Tumor Bulk Differs from Tumor-Stroma Interface in TNBCs
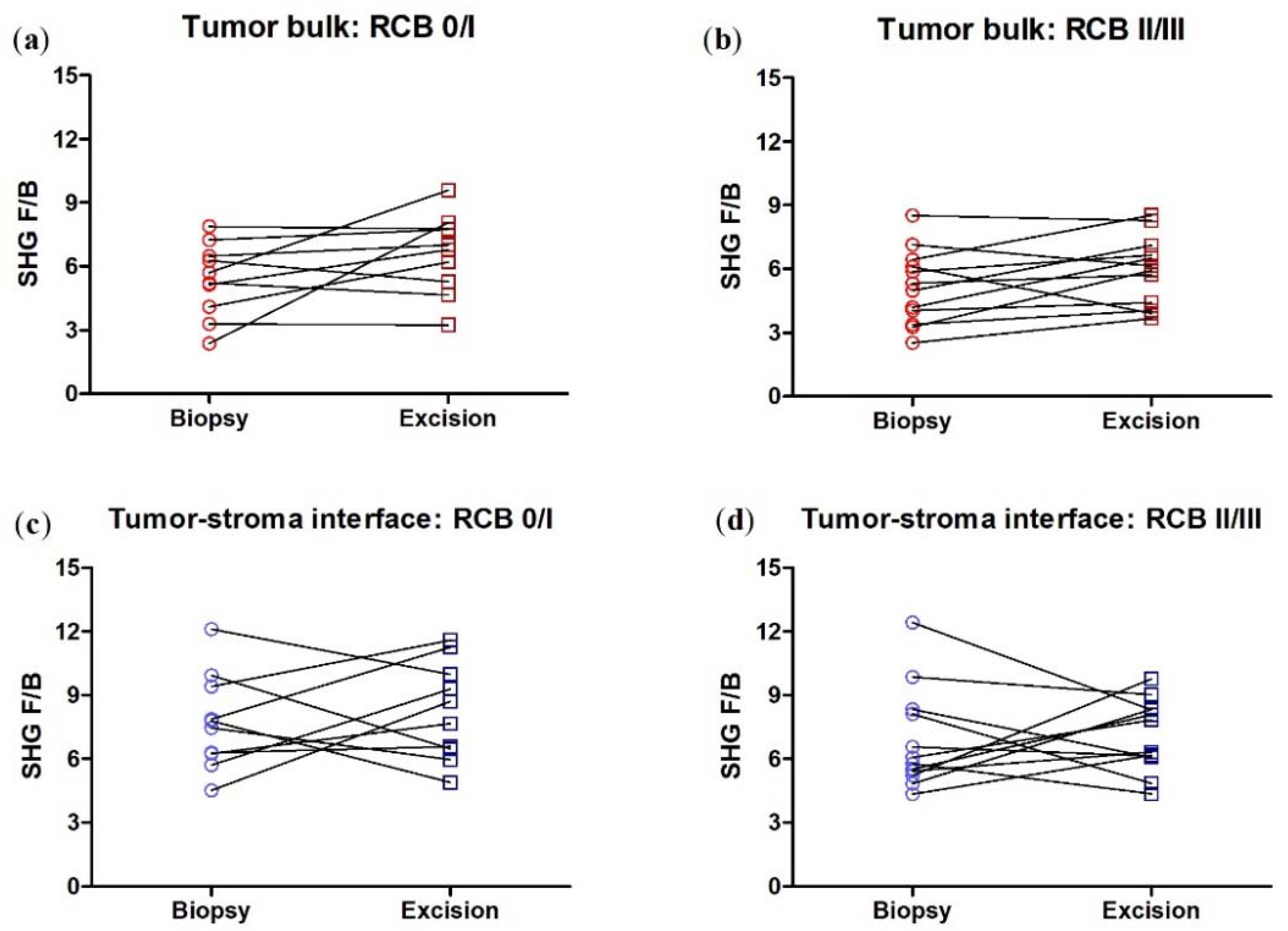
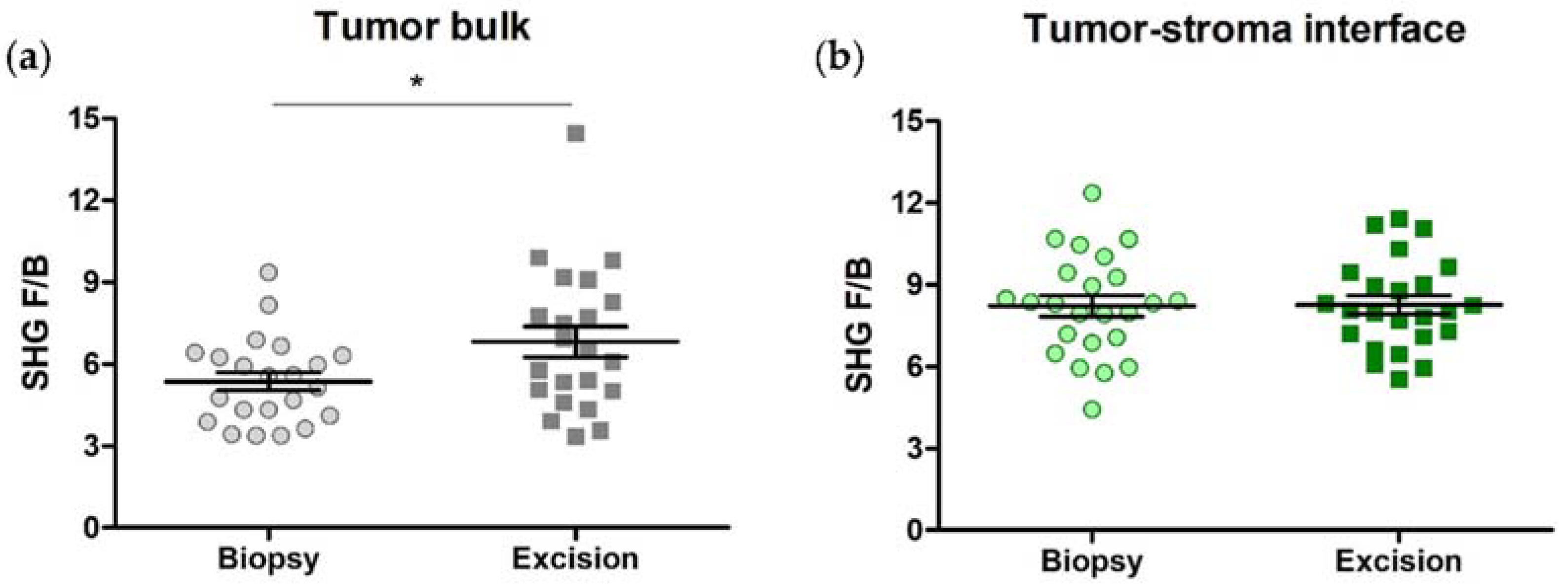
3.4. SHG F/B Increases with NACT in the Tumor Bulk but Not the Tumor-Stroma Interface of TNBCs
3.5. SHG F/B Generated Using Adaptive Thresholding
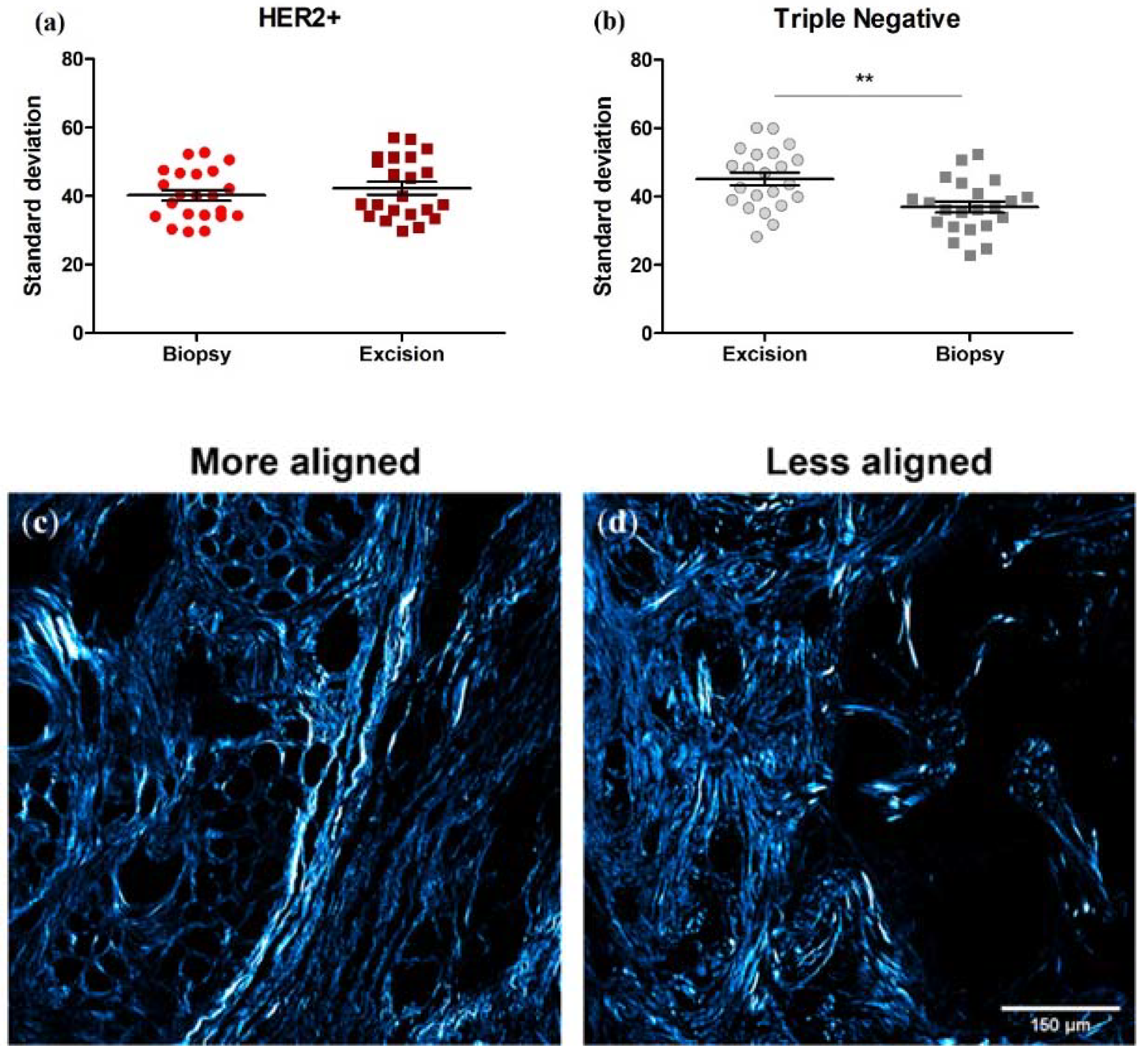
3.6. Collagen Fiber Organization Changes with NACT Administration in TNBC, but Not HER2+ Tumors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SEER. Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Yee, D.; DeMichele, A.M.; Yau, C.; Isaacs, C.; Symmans, W.F.; Albain, K.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Krings, G.; Wei, S.; Harada, S.; et al. Association of Event-Free and Distant Recurrence-Free Survival With Individual-Level Pathologic Complete Response in Neoadjuvant Treatment of Stages 2 and 3 Breast Cancer: Three-Year Follow-up Analysis for the I-SPY2 Adaptively Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, K.R.; Quintana, M.; Foster, M.; Olinger, M.; McGlothlin, A.; Berry, S.M.; Boileau, J.F.; Brezden-Masley, C.; Chia, S.; Dent, S.; et al. Association of Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer With Long-Term Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, T.; Efird, J.T.; Prasad, S.; Jindal, C.; Walker, P.R. The survival benefit of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and pCR among patients with advanced stage triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112712–112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, L.M.; Fell, G.; Arfe, A.; Sharma, C.; Greenup, R.; Reynolds, K.L.; Smith, B.L.; Alexander, B.; Moy, B.; Isakoff, S.J.; et al. Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Survival: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, T.J.; Charehbili, A.; Smit, V.T.; ten Dijke, P.; Kranenbarg, E.M.; van de Velde, C.J.; Nortier, J.W.; Tollenaar, R.A.; Mesker, W.E.; Kroep, J.R. Disorganised stroma determined on pre-treatment breast cancer biopsies is associated with poor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Results from the NEOZOTAC trial. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Long-term outcomes for neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer: Meta-analysis of individual patient data from ten randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelmuter, V.M.; Tashireva, L.A.; Savelieva, O.E.; Denisov, E.V.; Kaigorodova, E.V.; Zavyalova, M.V.; Cherdyntseva, N.V. Mechanisms behind prometastatic changes induced by neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the breast cancer microenvironment. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 11, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk-Draper, L.; Hall, K.; Griggs, C.; Rajput, S.; Kohio, P.; DeNardo, D.; Ran, S. Paclitaxel therapy promotes breast cancer metastasis in a TLR4-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5421–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, L.D.; Flister, M.J.; Chihade, D.; Desai, N.; Trieu, V.; Ran, S. Synergy of nab-paclitaxel and bevacizumab in eradicating large orthotopic breast tumors and preexisting metastases. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenen, L.G.; Houthuijzen, J.M.; Cirkel, G.A.; Roodhart, J.M.; Shaked, Y.; Voest, E.E. Treatment-induced host-mediated mechanisms reducing the efficacy of antitumor therapies. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyckoff, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Lin, E.Y.; Li, J.F.; Goswami, S.; Stanley, E.R.; Segall, J.E.; Pollard, J.W.; Condeelis, J. Direct visualization of macrophage-assisted tumor cell intravasation in mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2649–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harney, A.S.; Arwert, E.N.; Entenberg, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P.; Qian, B.Z.; Oktay, M.H.; Pollard, J.W.; Jones, J.G.; Condeelis, J.S. Real-Time Imaging Reveals Local, Transient Vascular Permeability, and Tumor Cell Intravasation Stimulated by TIE2hi Macrophage-Derived VEGFA. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.D.; Sica, G.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Rohan, T.E.; Gertler, F.B.; Condeelis, J.S.; Jones, J.G. Tumor microenvironment of metastasis in human breast carcinoma: A potential prognostic marker linked to hematogenous dissemination. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, G.S.; Pastoriza, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Harney, A.S.; Entenberg, D.; Pignatelli, J.; Sharma, V.P.; Xue, E.A.; Cheng, E.; D’Alfonso, T.M.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy induces breast cancer metastasis through a TMEM-mediated mechanism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Jalgaonkar, S.P.; Middleton, J.D.; Hai, T. Stress-inducible gene Atf3 in the noncancer host cells contributes to chemotherapy-exacerbated breast cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7159–E7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.L.; Bissell, M.J. The tumor microenvironment is a dominant force in multidrug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2012, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, T.J.; van de Velde, C.J.; van Pelt, G.W.; Kroep, J.R.; Julien, J.P.; Smit, V.T.; Tollenaar, R.A.; Mesker, W.E. Prognostic significance of the tumor-stroma ratio: Validation study in node-negative premenopausal breast cancer patients from the EORTC perioperative chemotherapy (POP) trial (10854). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, M.W.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Riching, K.M.; Pehlke, C.A.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Provenzano, P.P.; Friedl, A.; Keely, P.J. Aligned collagen is a prognostic signature for survival in human breast carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Campbell, J.M.; Inman, D.R.; White, J.G.; Keely, P.J. Collagen reorganization at the tumor-stromal interface facilitates local invasion. BMC Med. 2006, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natal, R.A.; Vassallo, J.; Paiva, G.R.; Pelegati, V.B.; Barbosa, G.O.; Mendonca, G.R.; Bondarik, C.; Derchain, S.F.; Carvalho, H.F.; Lima, C.S.; et al. Collagen analysis by second-harmonic generation microscopy predicts outcome of luminal breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2018, 40, 1010428318770953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bera, K.; Toro, P.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, C.; Feldman, M.; Ganesan, S.; Goldstein, L.J.; Davidson, N.E.; et al. Collagen fiber orientation disorder from H&E images is prognostic for early stage breast cancer: Clinical trial validation. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.M.; Zipfel, W.R.; Webb, W.W. Interpreting second-harmonic generation images of collagen I fibrils. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Burke, R.M.; Zettel, M.L.; Tang, P.; Brown, E.B. Second harmonic properties of tumor collagen: Determining the structural relationship between reactive stroma and healthy stroma. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacomb, R.; Nadiarnykh, O.; Townsend, S.S.; Campagnola, P.J. Phase Matching considerations in Second Harmonic Generation from tissues: Effects on emission directionality, conversion efficiency and observed morphology. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Nadiarynkh, O.; Plotnikov, S.; Campagnola, P.J. Second harmonic generation microscopy for quantitative analysis of collagen fibrillar structure. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiarnykh, O.; LaComb, R.B.; Brewer, M.A.; Campagnola, P.J. Alterations of the extracellular matrix in ovarian cancer studied by Second Harmonic Generation imaging microscopy. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilbury, K.; Campagnola, P.J. Applications of second-harmonic generation imaging microscopy in ovarian and breast cancer. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.; Tang, P.; Brown, E. Second harmonic generation reveals matrix alterations during breast tumor progression. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 31106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottmann, R.M.; Sharp, J.; Owens, K.; Salzman, P.; Xiao, G.Q.; Phipps, R.P.; Sime, P.J.; Brown, E.B.; Perry, S.W. Second harmonic generation microscopy reveals altered collagen microstructure in usual interstitial pneumonia versus healthy lung. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desa, D.E.; Strawderman, R.L.; Wu, W.; Hill, R.L.; Smid, M.; Martens, J.W.M.; Turner, B.M.; Brown, E.B. Intratumoral heterogeneity of second-harmonic generation scattering from tumor collagen and its effects on metastatic risk prediction. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, K.; Smid, M.; Dawes, R.P.; Timmermans, M.A.; Salzman, P.; van Deurzen, C.H.; Beer, D.G.; Foekens, J.A.; Brown, E. Using second harmonic generation to predict patient outcome in solid tumors. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmans, W.F.; Peintinger, F.; Hatzis, C.; Rajan, R.; Kuerer, H.; Valero, V.; Assad, L.; Poniecka, A.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symmans, W.F.; Wei, C.; Gould, R.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Walls, A.; Bousamra, A.; Ramineni, M.; Sinn, B.; et al. Long-Term Prognostic Risk After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Associated With Residual Cancer Burden and Breast Cancer Subtype. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Residual Cancer Burden Calculator. Available online: http://www3.mdanderson.org/app/medcalc/index.cfm?pagename=jsconvert3 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Monaghan, M.G.; Kroll, S.; Brucker, S.Y.; Schenke-Layland, K. Enabling Multiphoton and Second Harmonic Generation Imaging in Paraffin-Embedded and Histologically Stained Sections. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristu, R.; Stanciu, S.G.; Dumitru, A.; Paun, B.; Floroiu, I.; Costache, M.; Stanciu, G.A. Influence of hematoxylin and eosin staining on the quantitative analysis of second harmonic generation imaging of fixed tissue sections. Biomed Opt. Express 2021, 12, 5829–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.; Roth, G. Adaptive Thresholding using the Integral Image. J. Graph. Tools 2007, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacomb, R.; Nadiarnykh, O.; Campagnola, P.J. Quantitative second harmonic generation imaging of the diseased state osteogenesis imperfecta: Experiment and simulation. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 4504–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.A.; Dawes, R.P.; Cheema, M.K.; Van Hove, A.; Benoit, D.S.; Perry, S.W.; Brown, E. Second-harmonic generation scattering directionality predicts tumor cell motility in collagen gels. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 051024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, J.; Sun, M.; Gkousioudi, A.; Pilvar, A.; Roblyer, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zaman, M.H. Compressive Remodeling Alters Fluid Transport Properties of Collagen Networks—Implications for Tumor Growth. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, S.P.; Starchenko, A.; McGregor, A.L.; Reinhart-King, C.A. Leading malignant cells initiate collective epithelial cell invasion in a three-dimensional heterotypic tumor spheroid model. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2013, 30, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, H.E.; Bird, D.; Lang, G.; Erler, J.T. Tumor-secreted LOXL2 activates fibroblasts through FAK signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, Z.; Qiu, L.; Kang, D.; Zhan, Z.; Tu, H.; Chen, J. Label-free multiphoton imaging to assess neoadjuvant therapy responses in breast carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, F.; Jarrar, A.M.; Pai, R.K.; Hitomi, M.; Lathia, J.; Mace, A.; Gantt, G.A., Jr.; Sukhdeo, K.; DeVecchio, J.; Vasanji, A.; et al. Chemotherapy activates cancer-associated fibroblasts to maintain colorectal cancer-initiating cells by IL-17A. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2851–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, M.; Ben-Chetrit, N.; Zhuravlev, A.; Afik, R.; Bassat, E.; Solomonov, I.; Yarden, Y.; Sagi, I. Tumor Cell Invasion Can Be Blocked by Modulators of Collagen Fibril Alignment That Control Assembly of the Extracellular Matrix. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4249–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannasch, K.; Wegwitz, F.; Lenfert, E.; Maenz, C.; Deppert, W.; Alves, F. Chemotherapy of WAP-T mouse mammary carcinomas aggravates tumor phenotype and enhances tumor cell dissemination. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukina, M.M.; Dudenkova, V.V.; Shimolina, L.E.; Snopova, L.B.; Zagaynova, E.V.; Shirmanova, M.V. In vivo metabolic and SHG imaging for monitoring of tumor response to chemotherapy. Cytom. A 2019, 95, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.J.; Cook, R.S.; Lee, J.H.; Arteaga, C.L.; Skala, M.C. Collagen density and alignment in responsive and resistant trastuzumab-treated breast cancer xenografts. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 26004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Jin, Q.; Dai, Y. Human breast cancer decellularized scaffolds promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions and stemness of breast cancer cells in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9447–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattet, L.; Jung, H.Y.; Matsumoto, M.W.; Aubol, B.E.; Kumar, A.; Adams, J.A.; Chen, A.C.; Sah, R.L.; Engler, A.J.; Pasquale, E.B.; et al. Matrix Rigidity Controls Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity and Tumor Metastasis via a Mechanoresponsive EPHA2/LYN Complex. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 302–316.e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanker, A.B.; Estrada, M.V.; Bianchini, G.; Moore, P.D.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, F.; Koch, J.P.; Gianni, L.; Tyson, D.R.; Sanchez, V.; et al. Extracellular Matrix/Integrin Signaling Promotes Resistance to Combined Inhibition of HER2 and PI3K in HER2(+) Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3280–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.L.; Wu, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chai, C.Y.; Hou, M.F.; Chang, S.J.; Tsai, H.P.; Hung, W.C.; Pan, M.R.; Luo, C.W. beta1 Integrin as a Prognostic and Predictive Marker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoudjit, F.; Vuori, K. Integrin signaling inhibits paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 4995–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chod, J.; Zavadova, E.; Halaska, M.J.; Strnad, P.; Fucikova, T.; Rob, L. Preoperative transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) plasma levels in operable breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2008, 29, 613–616. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, M.F.; Georgoudaki, A.M.; Lambut, L.; Johansson, J.; Tabor, V.; Hagikura, K.; Jin, Y.; Jansson, M.; Alexander, J.S.; Nelson, C.M.; et al. TGF-beta1-induced EMT promotes targeted migration of breast cancer cells through the lymphatic system by the activation of CCR7/CCL21-mediated chemotaxis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampieri, S.; Manning, C.; Hooper, S.; Jones, L.; Hill, C.S.; Sahai, E. Localized and reversible TGFbeta signalling switches breast cancer cells from cohesive to single cell motility. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2009, 11, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, S.; Diop-Frimpong, B.; Chen, W.; Goel, S.; Naxerova, K.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Boucher, Y.; Jain, R.K.; Xu, L. TGF-beta blockade improves the distribution and efficacy of therapeutics in breast carcinoma by normalizing the tumor stroma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16618–16623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desa, D.E.; Wu, W.; Brown, R.M.; Brown, E.B., IV; Hill, R.L.; Turner, B.M.; Brown, E.B., III. Second-Harmonic Generation Imaging Reveals Changes in Breast Tumor Collagen Induced by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040857
Desa DE, Wu W, Brown RM, Brown EB IV, Hill RL, Turner BM, Brown EB III. Second-Harmonic Generation Imaging Reveals Changes in Breast Tumor Collagen Induced by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers. 2022; 14(4):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040857
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesa, Danielle E., Wencheng Wu, Robert M. Brown, Edward B. Brown, IV, Robert L. Hill, Bradley M. Turner, and Edward B. Brown, III. 2022. "Second-Harmonic Generation Imaging Reveals Changes in Breast Tumor Collagen Induced by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy" Cancers 14, no. 4: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040857
APA StyleDesa, D. E., Wu, W., Brown, R. M., Brown, E. B., IV, Hill, R. L., Turner, B. M., & Brown, E. B., III. (2022). Second-Harmonic Generation Imaging Reveals Changes in Breast Tumor Collagen Induced by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers, 14(4), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040857




