Treatment of Classic Hairy Cell Leukemia: Targeting Minimal Residual Disease beyond Cladribine
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Purine Analogues
3. Minimal Residual Disease
4. Chemotherapy Combined with Anti-CD20 Antibodies
5. Moxetumumab Pasudotox
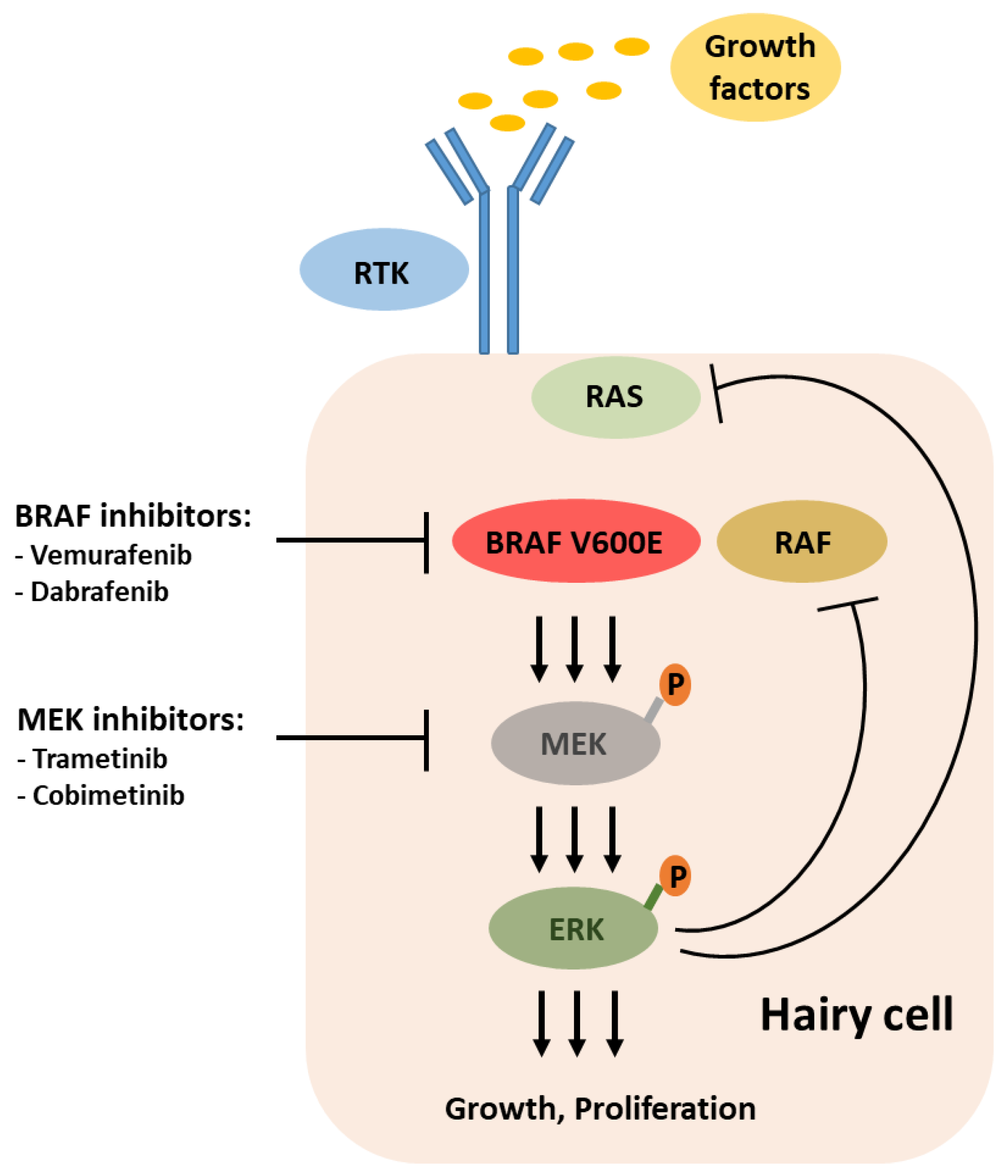
6. Targeting BRAF and MEK
7. Targeting Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase
8. Targeting B Cell Lymphoma 2
9. Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered (CAR) T-Cell Therapy
10. The Remaining Role of Interferon-α in HCL
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms
| HCL | classic hairy cell leukemia |
| Pas | purine analogues |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| ORR | overall response rate |
| CR | complete remission |
| PR | partial remission |
| MRD | minimal residual disease |
| Moxe | moxetumumab pasudotox |
| BTK | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase |
| CAR | chimeric antigen receptor-engineered |
References
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouroncle, B.A.; Wiseman, B.K.; Doan, C.A. Leukemic reticuloendotheliosis. Blood 1958, 13, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quesada, J.R.; Reuben, J.; Manning, J.T.; Hersh, E.M.; Gutterman, J.U. Alpha interferon for induction of remission in hairy-cell leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saven, A.; Burian, C.; Koziol, J.A.; Piro, L.D. Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with Hairy Cell Leukemia After Cladribine Treatment. Blood 1998, 92, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinmohamed, A.G.; Posthuma, E.F.M.; Visser, O.; Kater, A.P.; Raymakers, R.A.P.; Doorduijn, J.K. Relative survival reaches a plateau in hairy cell leukemia: A population-based analysis in The Netherlands. Blood 2018, 131, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, M.; Dearden, C.E.; Catovsky, D. Long-term follow-up after purine analogue therapy in hairy cell leukaemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2015, 28, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Getta, B.M.; Woo, K.M.; Devlin, S.; Park, J.H.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Saven, A.; Rai, K.; Tallman, M.S. Treatment outcomes and secondary cancer incidence in young patients with hairy cell leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiacci, E.; Trifonov, V.; Schiavoni, G.; Holmes, A.; Kern, W.; Martelli, M.P.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; Pacini, R.; Wells, V.A.; et al. BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiacci, E.; Park, J.H.; De Carolis, L.; Chung, S.S.; Broccoli, A.; Scott, S.; Zaja, F.; Devlin, S.; Pulsoni, A.; Chung, Y.R.; et al. Targeting Mutant BRAF in Relapsed or Refractory Hairy-Cell Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Dearden, C.; Zinzani, P.L.; Delgado, J.; Karlin, L.; Robak, T.; Gladstone, D.E.; le Coutre, P.; Dietrich, S.; Gotic, M.; et al. Moxetumomab pasudotox in relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Moreau, P.; Hutchings, M.; Gazzah, A.; Blay, J.-Y.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Stein, A.; Dietrich, S.; de Jonge, M.J.A.; Willenbacher, W.; et al. Treatment with Combination of Dabrafenib and Trametinib in Patients with Recurrent/Refractory BRAF V600E-Mutated Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL). Blood 2018, 132, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, E.; De Carolis, L.; Simonetti, E.; Capponi, M.; Ambrosetti, A.; Lucia, E.; Antolino, A.; Pulsoni, A.; Ferrari, S.; Zinzani, P.L.; et al. Vemurafenib plus Rituximab in Refractory or Relapsed Hairy-Cell Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1810–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.A.; Andritsos, L.A.; Wei, L.; McLaughlin, E.M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Anghelina, M.; Blachly, J.S.; Call, T.; Chihara, D.; Dauki, A.; et al. Phase 2 study of ibrutinib in classic and variant hairy cell leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 3473–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saven, A.; Piro, L.D. 2-Chlorodeoxyadenosine: A newer purine analog active in the treatment of indolent lymphoid malignancies. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenhäusern, R.; Schmitz, S.F.; Solenthaler, M.; Heim, D.; Meyer-Monard, S.; Hess, U.; Leoncini, L.; Bargetzi, M.; Rufener, B.; Tobler, A. Randomized trial of daily versus weekly administration of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in patients with hairy cell leukemia: A multicenter phase III trial (SAKK 32/98). Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, T.; Jamroziak, K.; Gora-Tybor, J.; Blonski, J.Z.; Kasznicki, M.; Dwilewicz-Trojaczek, J.; Wiater, E.; Zdunczyk, A.; Dybowicz, J.; Dmoszynska, A.; et al. Cladribine in a weekly versus daily schedule for untreated active hairy cell leukemia: Final report from the Polish Adult Leukemia Group (PALG) of a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial. Blood 2007, 109, 3672–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benz, R.; Arn, K.; Andres, M.; Pabst, T.; Baumann, M.; Novak, U.; Hitz, F.; Hess, U.; Zenhaeusern, R.; Chalandon, Y.; et al. Prospective long-term follow-up after first-line subcutaneous cladribine in hairy cell leukemia: A SAKK trial. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, E.H.; Bouroncle, B.A.; Grever, M.R. Low-dose deoxycoformycin in the treatment of hairy cell leukemia. Blood 1986, 68, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grever, M.R. How I treat hairy cell leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broccoli, A.; Argnani, L.; Nanni, L.; Terragna, C.; Sabattini, E.; Gabrielli, G.; Stefoni, V.; Pellegrini, C.; Casadei, B.; Morigi, A.; et al. The treatment of hairy cell leukemia with a focus on long lasting responses to cladribine: A 30-year experience. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.D.; Burian, C.; Waalen, J.; Saven, A. Clinical characteristics and long-term outcome of young hairy cell leukemia patients treated with cladribine: A single-institution series. Blood 2014, 123, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grever, M.R.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Andritsos, L.A.; Banerji, V.; Barrientos, J.; Blachly, J.S.; Call, T.G.; Catovsky, D.; Dearden, C.; Demeter, J.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with classic hairy cell leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigal, D.S.; Sharpe, R.; Burian, C.; Saven, A. Very long-term eradication of minimal residual disease in patients with hairy cell leukemia after a single course of cladribine. Blood 2010, 115, 1893–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López Rubio, M.; Da Silva, C.; Loscertales, J.; Seri, C.; Baltasar, P.; Colado, E.; Pérez Fernández, I.; Osma, M.; Gomis, F.; González, M.; et al. Hairy cell leukemia treated initially with purine analogs: A retrospective study of 107 patients from the Spanish Cooperative Group on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (GELLC). Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousou, T.; Friedberg, J. Rituximab in indolent lymphomas. Semin. Hematol. 2010, 47, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M.; Matutes, E.; Farahat, N.; Morilla, R.; Catovsky, D. Levels of expression of CD19 and CD20 in chronic B cell leukaemias. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 51, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauria, F.; Lenoci, M.; Annino, L.; Raspadori, D.; Marotta, G.; Bocchia, M.; Forconi, F.; Gentili, S.; La Manda, M.; Marconcini, S.; et al. Efficacy of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (Mabthera) in patients with progressed hairy cell leukemia. Haematologica 2001, 86, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.A.; O’Brien, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Faderl, S.; Keating, M.J.; Giles, F.J.; Cortes, J.; Kantarjian, H.M. Rituximab in relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia. Blood 2003, 102, 3906–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, H.; Lundholm, L. Rituximab, a chimaeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of hairy cell leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 115, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravandi, F.; O’Brien, S.; Jorgensen, J.; Pierce, S.; Faderl, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Koller, C.; Challagundla, P.; York, S.; Brandt, M.; et al. Phase 2 study of cladribine followed by rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 3818–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravandi, F. Chemoimmunotherapy for hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2015, 28, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, K.U.; Sommerlad, W.D.; Boehrer, S.; Schneider, B.; Seipelt, G.; Rummel, M.J.; Hoelzer, D.; Mitrou, P.S.; Weidmann, E. Anti-CD20 antibody (IDEC-C2B8, rituximab) enhances efficacy of cytotoxic drugs on neoplastic lymphocytes in vitro: Role of cytokines, complement, and caspases. Haematologica 2002, 87, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Albertioni, F.; Lindemalm, S.; Reichelova, V.; Pettersson, B.; Eriksson, S.; Juliusson, G.; Liliemark, J. Pharmacokinetics of cladribine in plasma and its 5′-monophosphate and 5′-triphosphate in leukemic cells of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Chihara, D.; Arons, E.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yuan, C.M.; Wang, H.W.; Zhou, H.; Raffeld, M.; Xi, L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Feurtado, J.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of First-Line Cladribine with Concurrent or Delayed Rituximab in Patients with Hairy Cell Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, M.J.; Gregory, S.A. Bendamustine’s emerging role in the management of lymphoid malignancies. Semin. Hematol. 2011, 48 (Suppl. S1), S24–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ujjani, C.; Cheson, B.D. Bendamustine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2010, 10, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burotto, M.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Arons, E.; Zhou, H.; Wilson, W.; Kreitman, R.J. Bendamustine and rituximab in relapsed and refractory hairy cell leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6313–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robbins, D.H.; Margulies, I.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Kreitman, R.J. Hairy cell leukemia, a B-cell neoplasm that is particularly sensitive to the cytotoxic effect of anti-Tac(Fv)-PE38 (LMB-2). Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Pastan, I. Targeting Pseudomonas exotoxin to hematologic malignancies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1995, 6, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, R.F.; Kreitman, R.J.; Chen, T.; Yeung, P.; Herbst, R.; Fox, J.A.; Pastan, I. CAT-8015: A second-generation pseudomonas exotoxin A-based immunotherapy targeting CD22-expressing hematologic malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Tallman, M.S.; Robak, T.; Coutre, S.; Wilson, W.H.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Lechleider, R.; Pastan, I. Phase I trial of anti-CD22 recombinant immunotoxin moxetumomab pasudotox (CAT-8015 or HA22) in patients with hairy cell leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Dearden, C.; Zinzani, P.L.; Delgado, J.; Robak, T.; le Coutre, P.D.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Troussard, X.; Roboz, G.J.; Karlin, L.; et al. Moxetumomab pasudotox in heavily pre-treated patients with relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL): Long-term follow-up from the pivotal trial. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitman, R.J. Hairy cell leukemia: Present and future directions. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2869–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Tallman, M.S.; Robak, T.; Coutre, S.; Wilson, W.H.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; FitzGerald, D.J.; Santiago, L.; Gao, G.; Lanasa, M.C.; et al. Minimal residual hairy cell leukemia eradication with moxetumomab pasudotox: Phase 1 results and long-term follow-up. Blood 2018, 131, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, S.; Glimm, H.; Andrulis, M.; von Kalle, C.; Ho, A.D.; Zenz, T. BRAF inhibition in refractory hairy-cell leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2038–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Puzanov, I.; Kim, K.B.; Ribas, A.; McArthur, G.A.; Sosman, J.A.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Lee, R.J.; Grippo, J.F.; Nolop, K.; et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, S.; Pircher, A.; Endris, V.; Peyrade, F.; Wendtner, C.M.; Follows, G.A.; Hullein, J.; Jethwa, A.; Ellert, E.; Walther, T.; et al. BRAF inhibition in hairy cell leukemia with low-dose vemurafenib. Blood 2016, 127, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebers, N.; Roider, T.; Bohn, J.P.; Haberbosch, I.; Pircher, A.; Ferstl, B.; Ebnöther, M.; Wendtner, C.M.; Dearden, C.; Follows, G.A.; et al. BRAF inhibitor treatment in classic hairy cell leukemia: A long-term follow-up study of patients treated outside clinical trials. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1454–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, J.P.; Pircher, A.; Wanner, D.; Vill, D.; Foeger, B.; Wolf, D.; Steurer, M. Low-dose vemurafenib in hairy cell leukemia patients with active infection. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, E180–E182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Hugo, W.; Kong, X.; Hong, A.; Koya, R.C.; Moriceau, G.; Chodon, T.; Guo, R.; Johnson, D.B.; Dahlman, K.B.; et al. Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkin, J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Dréno, B.; Atkinson, V.; Liszkay, G.; Maio, M.; Mandalà, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Turke, A.B.; Coffee, E.M.; Nishino, M.; Cogdill, A.P.; Brown, R.D.; Della Pelle, P.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Hung, K.E.; et al. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to RAF inhibition with vemurafenib. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caeser, R.; Collord, G.; Yao, W.Q.; Chen, Z.; Vassiliou, G.S.; Beer, P.A.; Du, M.Q.; Scott, M.A.; Follows, G.A.; Hodson, D.J. Targeting MEK in vemurafenib-resistant hairy cell leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, B.H.; Getta, B.; Dietrich, S.; Taylor, J.; Won, H.; Bogenberger, J.M.; Scott, S.; Kim, E.; Chung, Y.R.; Chung, S.S.; et al. Genomic analysis of hairy cell leukemia identifies novel recurrent genetic alterations. Blood 2017, 130, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettirossi, V.; Santi, A.; Imperi, E.; Russo, G.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; Schiavoni, G.; Fortini, E.; Spanhol-Rosseto, A.; Sportoletti, P.; et al. BRAF inhibitors reverse the unique molecular signature and phenotype of hairy cell leukemia and exert potent antileukemic activity. Blood 2015, 125, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Shukla, M.; Salcedo, J.M.; Vemuri, S.; Kinoshita, J.C.; Smith, M.D.; Winer, E.S.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Tallman, M.S. First Line Chemo-Free Therapy with the BRAF Inhibitor Vemurafenib Combined with Obinutuzumab Is Effective in Patients with Hcl. Blood 2019, 134, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, R.W.; Yuvaraj, S.; Kil, L.P. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cell malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Cymbalista, F.; Buske, C.; Hillmen, P.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyling, M.; Campo, E.; Hermine, O.; Jerkeman, M.; Le Gouill, S.; Rule, S.; Shpilberg, O.; Walewski, J.; Ladetto, M. Newly diagnosed and relapsed mantle cell lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv62–iv71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Leblond, V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Kimby, E.; Staber, P.; Kersten, M.J.; Tedeschi, A.; Buske, C. Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivina, M.; Kreitman, R.J.; Arons, E.; Ravandi, F.; Burger, J.A. The bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) blocks hairy cell leukaemia survival, proliferation and B cell receptor signalling: A new therapeutic approach. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereertbrugghen, A.; Colado, A.; Gargiulo, E.; Bezares, R.F.; Fernández Grecco, H.; Cordini, G.; Custidiano, M.d.R.; François, J.-H.; Berchem, G.; Borge, M.; et al. In Vitro Sensitivity to Venetoclax and Microenvironment Protection in Hairy Cell Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Advances in chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savani, M.; Oluwole, O.; Dholaria, B. New targets for CAR T therapy in hematologic malignancies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2021, 34, 101277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, J.P.; Gastl, G.; Steurer, M. Long-term treatment of hairy cell leukemia with interferon-α: Still a viable therapeutic option. Memo 2016, 9, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feld, J.J.; Kandel, C.; Biondi, M.J.; Kozak, R.A.; Zahoor, M.A.; Lemieux, C.; Borgia, S.M.; Boggild, A.K.; Powis, J.; McCready, J.; et al. Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of outpatients with COVID-19: A phase 2, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troussard, X.; Maître, E.; Cornet, E. Hairy cell leukemia 2022: Update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Phase | Drugs | Disease Status | Patients | ORR (%) | CR (%) | MRD Free (%) | PFS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ravandi et al. [30] | II | 2-CdA + R | Untreated Relapsed | 59 14 | 100 100 | 100 100 | 76 64 | 95 (5-year) 100 (5-year) |
| Chihara et al. [34] | II | 2-CdA + R vs. delayed | Relapsed | 68 | 100 | 100 vs. 88 | 97 vs. 24 | 94 vs. 12 |
| Burotto et al. [37] | II | Benda + R | Relapsed | 12 | 100 | 50 vs. 67 | 67 vs. 100 | 31 months for patients in CR |
| Trial | Phase | Drugs | Disease Status | Patients | ORR (%) | CR (%) | MRD Free (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kreitman et al. [41] | I | Moxe (5–40 µg/kg) Moxe (50 µg/kg) | Relapsed Relapsed | 16 33 | 86 88 | 57 64 | n.a. 33 |
| Kreitman et al. [10,42] | III | Moxe (40 µg/kg) | Relapsed | 80 | 75 | 41 | 34 |
| NCT03805932 | I | Moxe (40 µg/kg) + R | Relapsed | 20 | ongoing | ongoing | ongoing |
| Trial | Phase | Drugs | Disease Status | Patients | ORR (%) | CR (%) | MRD Free (%) | 1-Year PFS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiacci et al. [9] | II | Vem | Relapsed | 54 | 100 | 38 | 0 | 73 |
| Tiacci et al. [12] | II | Vem + R | Relapsed | 30 | 100 | 87 | 65 | 78 (3-year) |
| Kreitman et al. [11] | II | Dabra + Tram | Relapsed | 43 | 78 | 49 | 15 | 98 |
| Park et al. [56] | I | Vem + Obi | Untreated | 9 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 9.7 months PFS |
| Trial | Phase | Drugs | Disease Status | Patients | ORR (%) | CR (%) | MRD Free (%) | 3-Year PFS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rogers et al. [13] | II | Ibrutinib | Relapsed | 37 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bohn, J.-P.; Dietrich, S. Treatment of Classic Hairy Cell Leukemia: Targeting Minimal Residual Disease beyond Cladribine. Cancers 2022, 14, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040956
Bohn J-P, Dietrich S. Treatment of Classic Hairy Cell Leukemia: Targeting Minimal Residual Disease beyond Cladribine. Cancers. 2022; 14(4):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040956
Chicago/Turabian StyleBohn, Jan-Paul, and Sascha Dietrich. 2022. "Treatment of Classic Hairy Cell Leukemia: Targeting Minimal Residual Disease beyond Cladribine" Cancers 14, no. 4: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040956
APA StyleBohn, J.-P., & Dietrich, S. (2022). Treatment of Classic Hairy Cell Leukemia: Targeting Minimal Residual Disease beyond Cladribine. Cancers, 14(4), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040956






