Negative Relationship between Post-Treatment Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Dose-Dense Dose-Intense NeoAdjuvant Chemotherapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
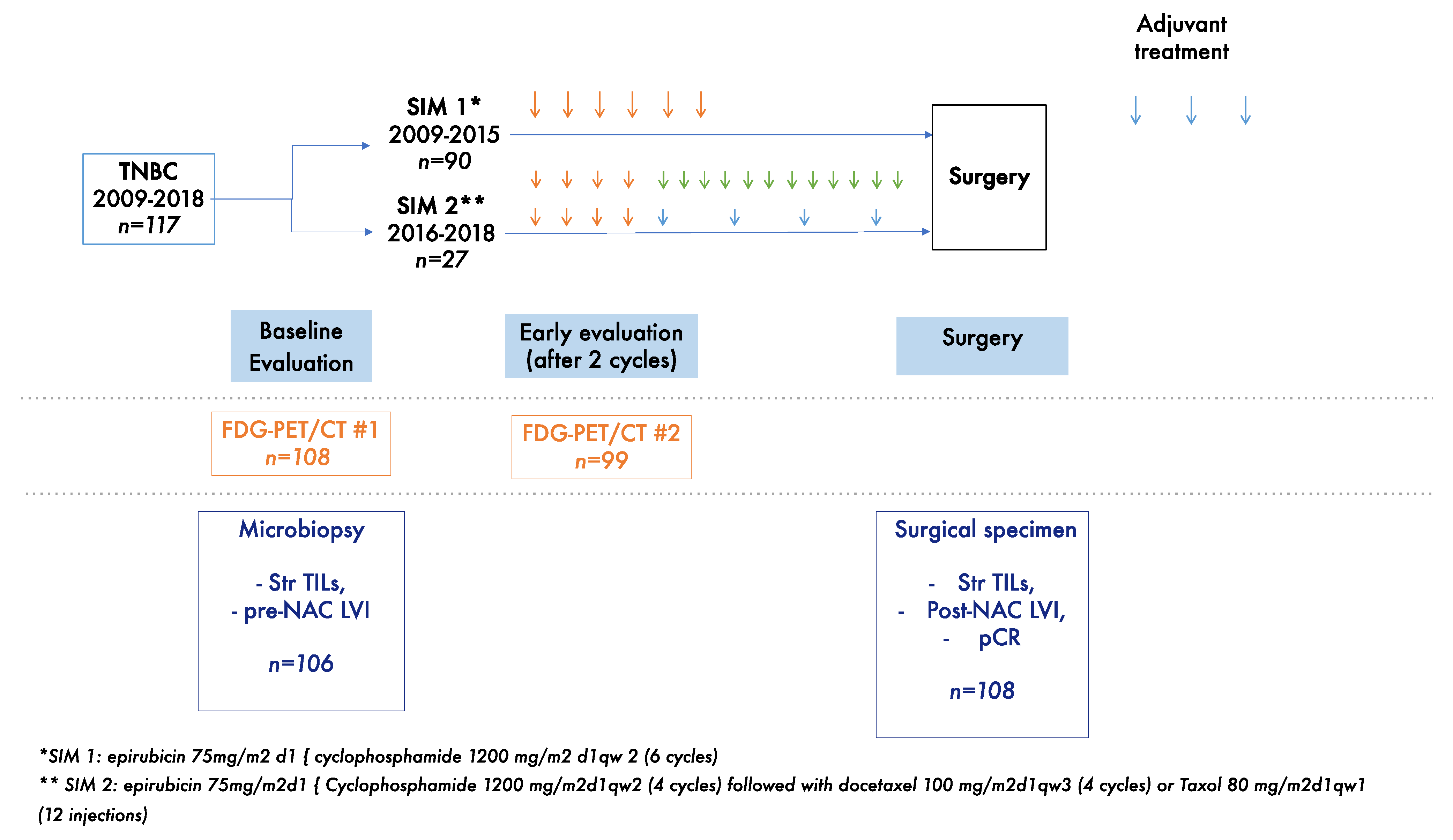
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. BC Diagnosis and Tumor Samples
2.3. BC Treatment
2.4. 18FDG-PET/CT Imaging and Measurement of the Metabolic Response
2.5. Pathological Review
2.6. Study Endpoints
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients and Tumors
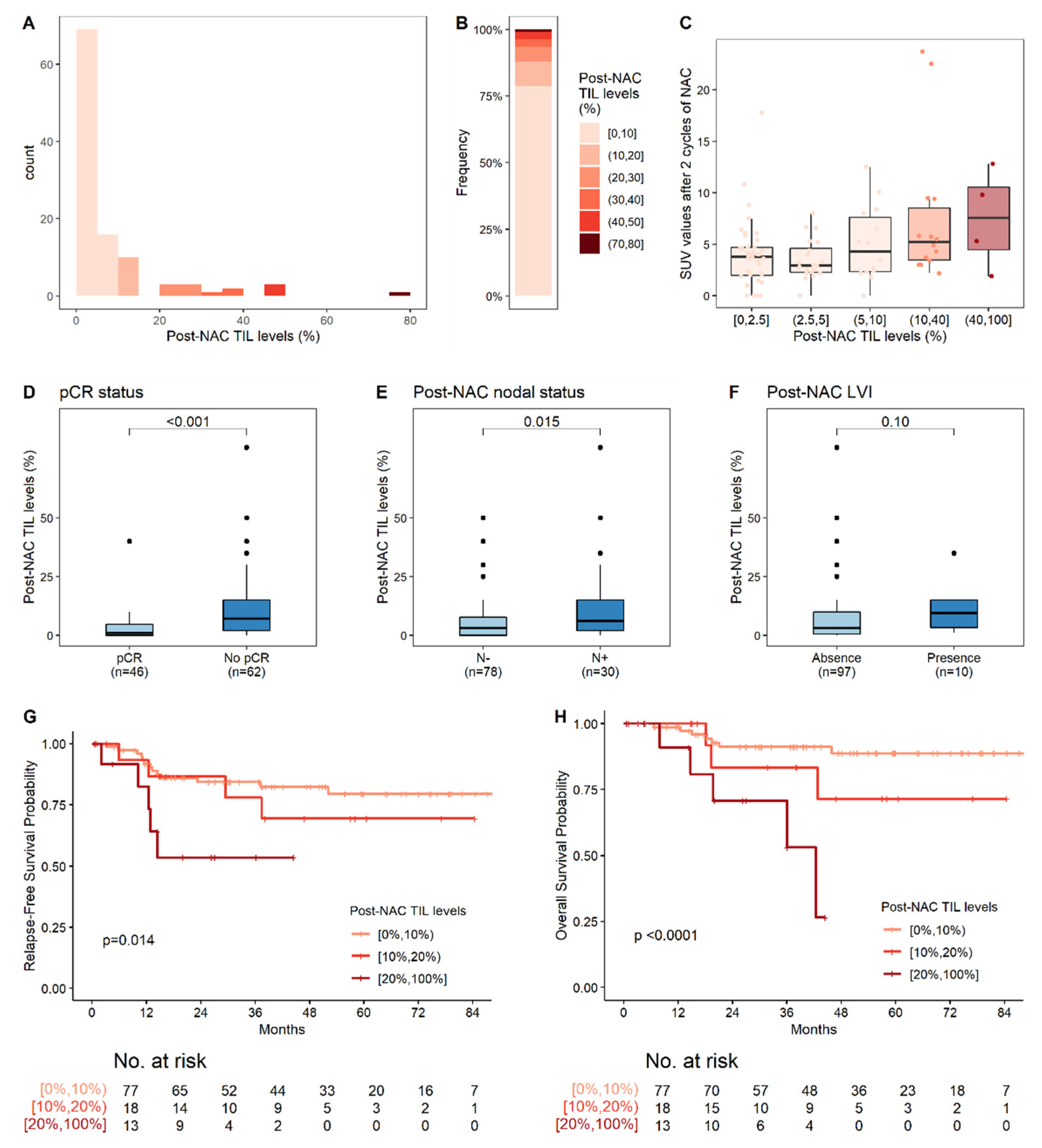
3.2. Metabolic on-Treatment Evaluation and Change in TIL Levels on NAC
3.3. Response to Treatment and Post-NAC Tumor Characteristics
3.4. Survival Analyses
3.4.1. Relapse-Free Survival
3.4.2. Overall Survival (OS)
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ismail-Khan, R.; Bui, M.M. A Review of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Control 2010, 17, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, N.U.; Vanderplas, A.; Hughes, M.E.; Theriault, R.L.; Edge, S.B.; Wong, Y.-N.; Blayney, D.W.; Niland, J.C.; Winer, E.P.; Weeks, J.C. Clinicopathologic Features, Patterns of Recurrence, and Survival among Women with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cancer 2012, 118, 5463–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denkert, C.; von Minckwitz, G.; Brase, J.C.; Sinn, B.V.; Gade, S.; Kronenwett, R.; Pfitzner, B.M.; Salat, C.; Loi, S.; Schmitt, W.D.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with or without Carboplatin in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive and Triple-Negative Primary Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieci, M.V.; Mathieu, M.C.; Guarneri, V.; Conte, P.; Delaloge, S.; Andre, F.; Goubar, A. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Two Phase III Randomized Adjuvant Breast Cancer Trials. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, C.A.; Mittendorf, E.; Casavilca, S.; Wu, Y.; Castillo, M.; Arboleda, P.; Nunez, T.; Guerra, H.; Barrionuevo, C.; Dolores-Cerna, K.; et al. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 7, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkert, C.; von Minckwitz, G.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Lederer, B.; Heppner, B.I.; Weber, K.E.; Budczies, J.; Huober, J.; Klauschen, F.; Furlanetto, J.; et al. Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Prognosis in Different Subtypes of Breast Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of 3771 Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieci, M.V.; Criscitiello, C.; Goubar, A.; Viale, G.; Conte, P.; Guarneri, V.; Ficarra, G.; Mathieu, M.C.; Delaloge, S.; Curigliano, G.; et al. Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes on Residual Disease after Primary Chemotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.W.; Jung, H.; Hyeon, J.; Park, Y.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Im, Y.-H.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Yu, J.-H.; et al. A Nomogram to Predict Pathologic Complete Response (PCR) and the Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) for Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Breast Cancer Patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 173, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luen, S.J.; Salgado, R.; Dieci, M.V.; Vingiani, A.; Curigliano, G.; Gould, R.E.; Castaneda, C.; D’Alfonso, T.; Sanchez, J.; Cheng, E.; et al. Prognostic Implications of Residual Disease Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Residual Cancer Burden in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamy, A.-S.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Sabaila, A.; Laas, E.; Bonsang-Kitzis, H.; Laurent, C.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Cottu, P.; Lerebours, F.; Rouzier, R.; et al. Stromal Lymphocyte Infiltration after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Is Associated with Aggressive Residual Disease and Lower Disease-Free Survival in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelekanou, V.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, D.E.; Altan, M.; Wasserman, B.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, C.; Wimberly, H.; Brown, J.; Lannin, D.; Pusztai, L.; Rimm, D.L. Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer and Its Clinical Significance. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamy, A.-S.; Bonsang-Kitzis, H.; Croze, D.D.; Laas, E.; Darrigues, L.; Topciu, L.; Menet, E.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Lerebours, F.; Pierga, J.-Y.; et al. Interaction between Molecular Subtypes and Stromal Immune Infiltration before and after Treatment in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6731–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groheux, D. Now Is the Time to Use 18 F-FDG PET/CT to Optimize Neoadjuvant Treatment in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer! J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coudert, B.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Mouret-Reynier, M.-A.; Kerrou, K.; Ferrero, J.-M.; Petit, T.; Kerbrat, P.; Dupré, P.-F.; Bachelot, T.; Gabelle, P.; et al. Use of [(18)F]-FDG PET to Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Trastuzumab and Docetaxel in Patients with HER2-Positive Breast Cancer, and Addition of Bevacizumab to Neoadjuvant Trastuzumab and Docetaxel in [(18)F]-FDG PET-Predicted Non-Responders (AVATAXHER): An Open-Label, Randomised Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Increasing the Dose Intensity of Chemotherapy by More Frequent Administration or Sequential Scheduling: A Patient-Level Meta-Analysis of 37,298 Women with Early Breast Cancer in 26 Randomised Trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giacchetti, S.; Porcher, R.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Hamy, A.-S.; de Roquancourt, A.; Cuvier, C.; Cottu, P.-H.; Bertheau, P.; Albiter, M.; Bouhidel, F.; et al. Long-Term Survival of Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancers with a Dose-Intense Cyclophosphamide/Anthracycline Neoadjuvant Regimen. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coates, A.S.; Winer, E.P.; Goldhirsch, A.; Gelber, R.D.; Gnant, M.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.-J. Panel Members Tailoring Therapies—Improving the Management of Early Breast Cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann-Che, J.; André, F.; Desmedt, C.; Mazouni, C.; Giacchetti, S.; Turpin, E.; Espié, M.; Plassa, L.-F.; Marty, M.; Bertheau, P.; et al. Cyclophosphamide Dose Intensification May Circumvent Anthracycline Resistance of P53 Mutant Breast Cancers. Oncologist 2010, 15, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groheux, D.; Biard, L.; Giacchetti, S.; Teixeira, L.; Hindié, E.; Cuvier, C.; Vercellino, L.; Merlet, P.; de Roquancourt, A.; de Cremoux, P.; et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT for the Early Evaluation of Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Influence of the Chemotherapy Regimen. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. The Evaluation of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Breast Cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieci, M.V.; Radosevic-Robin, N.; Fineberg, S.; van den Eynden, G.; Ternes, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Pruneri, G.; D’Alfonso, T.M.; Demaria, S.; Castaneda, C.; et al. Update on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Breast Cancer, Including Recommendations to Assess TILs in Residual Disease after Neoadjuvant Therapy and in Carcinoma in Situ: A Report of the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group on Breast Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological Complete Response and Long-Term Clinical Benefit in Breast Cancer: The CTNeoBC Pooled Analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, I.R.; Royston, P.; Wood, A.M. Multiple Imputation Using Chained Equations: Issues and Guidance for Practice. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Gray, R.J.; Demaria, S.; Goldstein, L.; Perez, E.A.; Shulman, L.N.; Martino, S.; Wang, M.; Jones, V.E.; Saphner, T.J.; et al. Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers from Two Phase III Randomized Adjuvant Breast Cancer Trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Drubay, D.; Adams, S.; Pruneri, G.; Francis, P.A.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Joensuu, H.; Dieci, M.V.; Badve, S.; Demaria, S.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Prognosis: A Pooled Individual Patient Analysis of Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Piette, F.; Salgado, R.; Viale, G.; Van Eenoo, F.; Rouas, G.; Francis, P.; Crown, J.P.A.; Hitre, E.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in a Phase III Randomized Adjuvant Breast Cancer Trial in Node-Positive Breast Cancer Comparing the Addition of Docetaxel to Doxorubicin with Doxorubicin-Based Chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.R.; Dariush, A.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.; Abraham, J.E.; Iddawela, M.; Vallier, A.-L.; Hiller, L.; Dunn, J.A.; Bowden, S.J.; et al. Computational Pathology of Pre-Treatment Biopsies Identifies Lymphocyte Density as a Predictor of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.R.; Dariush, A.; Thomas, J.; Provenzano, E.; Dunn, J.; Hiller, L.; Vallier, A.-L.; Abraham, J.; Piper, T.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; et al. Lymphocyte Density Determined by Computational Pathology Validated as a Predictor of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer: Secondary Analysis of the ARTemis Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1832–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noske, A.; Möbus, V.; Weber, K.; Schmatloch, S.; Weichert, W.; Köhne, C.-H.; Solbach, C.; Ingold Heppner, B.; Steiger, K.; Müller, V.; et al. Relevance of Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes, PD-1 and PD-L1 in Patients with High-Risk, Nodal-Metastasised Breast Cancer of the German Adjuvant Intergroup Node-Positive Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 114, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values | n = 117 | Statistics * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-NAC parameters | |||
| Age | 117 | 49.37 (23.69; 72) | |
| Pregnancies | 0 | 33 | 28.2% |
| 1–3 | 66 | 56.4% | |
| >3 | 18 | 15.4% | |
| Menopausal status | premenopausal | 68 | 58.1% |
| postmenopausal | 49 | 41.9% | |
| Family history | 0 | 82 | 71.3% |
| 1 | 21 | 18.3% | |
| ≥2 | 12 | 10.4% | |
| Clinical tumor stage | T1 | 3 | 2.5% |
| T2 | 52 | 44.00% | |
| T3 | 62 | 53% | |
| Clinical nodal status | N− | 56 | 47.9% |
| N+ | 61 | 52.1% | |
| Tumor grade | 2 | 19 | 16.2% |
| 3 | 98 | 83.8% | |
| p53 (FASAY) | Mutated | 77 | 85.6% |
| Wild type | 13 | 14.4% | |
| LVI | Absence | 91 | 83.5% |
| Presence | 18 | 16.5% | |
| SUV | 108 | 11.95 (2.7; 31.4) | |
| TIL levels | 106 | 15 (0; 80) | |
| Chemotherapy regimen | SIM-1 | 90 | 76.9% |
| SIM-2 | 27 | 23.1% | |
| Post-NAC parameters | |||
| pCR | No pCR | 68 | 58.1% |
| pCR | 49 | 41.9% | |
| Nodal involvment | ypN− | 83 | 71.5% |
| ypN+ | 33 | 28.4% | |
| LVI | Absence | 106 | 91.4% |
| Presence | 10 | 8.6% | |
| SUV at 2 courses | 99 | 3.8 (0; 23.7) | |
| TIL levels | 108 | 3 (0; 80) | |
| Variation Pre/Post-NAC parameters | |||
| SUV relative variation | 100 | −68.77 (−100; 0) | |
| TILs absolute variation | <0 | 69 | 69% |
| Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Levels | Coefficient | IC 95% | p-Value | Coefficient | IC 95% | p-Value |
| Pre-NAC parameters | |||||||
| Age | −0.01 | (−0.03; 0.0097) | 0.31 | ||||
| Age (class) | <45 | ||||||
| ≥45 | −0.089 | (−0.59; 0.41) | 0.726 | ||||
| Pregnancies | 0 | ||||||
| 1–3 | 0.17 | (−0.36; 0.7) | 0.534 | ||||
| >3 | 0.0098 | (−0.71; 0.73) | 0.978 | ||||
| Menopausal status | premenopausal | ||||||
| postmenopausal | −0.13 | (−0.59; 0.34) | 0.595 | ||||
| Family history | 0 | ||||||
| 1 | 0.15 | (−0.45; 0.75) | 0.63 | ||||
| ≥2 | 0.53 | (−0.21; 1.3) | 0.16 | ||||
| Clinical tumor stage | T1–T2 | ||||||
| T3 | 0.45 | (−0.000091; 0.9) | 0.05 | ||||
| Clinical nodal status | N− | ||||||
| N+ | 0.16 | (−0.3; 0.61) | 0.5 | ||||
| Tumor grade | 2 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.06 | (−0.56; 0.68) | 0.847 | ||||
| LVI | Absence | ||||||
| Presence | 0.11 | (−0.54; 0.75) | 0.74 | ||||
| SUV | −0.026 | (−0.065; 0.014) | 0.20 | ||||
| TIL levels | −0.0027 | (−0.014; 0.0083) | 0.63 | ||||
| Chemotherapy regimen | SIM-1 | ||||||
| SIM-2 | 0.43 | (−0.12; 0.98) | 0.127 | ||||
| Post-NAC parameters | |||||||
| pCR | No pCR | ||||||
| pCR | −1.1 | (−1.5; −0.69) | <0.001 *** | −0.89 | (−1.4; −0.38) | 0.0008 *** | |
| Nodal involvment | ypN− | ||||||
| ypN+ | 0.62 | (0.12; 1.1) | 0.015 * | ||||
| LVI | Absence | ||||||
| Presence | 0.65 | (−0.13; 1.4) | 0.10 | ||||
| SUV at 2 cures | 0.072 | (0.012; 0.13) | 0.020 * | ||||
| Variation Pre/Post-NAC parameters | |||||||
| SUV relative variation | 0.017 | (0.0083; 0.025) | 0.0002 *** | 0.0075 | (−0.0026; 0.018) | 0.14 | |
| SUV relative variation (class) | <−70% | ||||||
| ≥−70% | 0.83 | (0.37; 1.3) | 0.0005 *** | ||||
| Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Levels | HR | (95% CI) | p-Value | HR | (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Pre-NAC parameters | |||||||
| Age (class) | <45 | 1 | |||||
| ≥45 | 0.67 | (0.29; 1.5) | 0.34 | ||||
| Pregnancies | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1–3 | 0.69 | (0.29; 1.6) | 0.41 | ||||
| >3 | 0.65 | (0.18; 2.4) | 0.52 | ||||
| Menopausal status | premenopausal | 1 | |||||
| postmenopausal | 0.57 | (0.24; 1.4) | 0.21 | ||||
| Family history | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 1 | (0.34; 3) | 0.98 | ||||
| ≥2 | 1.5 | (0.44; 5.2) | 0.50 | ||||
| Clinical tumor stage | T1-T2 | 1 | |||||
| T3 | 1.2 | (0.52; 2.6) | 0.71 | ||||
| Clinical nodal status | N− | 1 | |||||
| N+ | 1.9 | (0.82; 4.5) | 0.13 | ||||
| Tumor grade | 2 | 1 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | (0.53; 29.3) | 0.18 | ||||
| LVI | Absence | 1 | |||||
| Presence | 3.1 | (1.3; 7.5) | 0.010 * | ||||
| TIL levels (continuous) a | 0.99 | (0.97; 1) | 0.43 | ||||
| Post-NAC parameters | |||||||
| pCR | No pCR | 1 | |||||
| pCR | 0.39 | (0.16; 0.99) | 0.047 * | ||||
| Nodal involvment | ypN− | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ypN+ | 3.3 | (1.5; 7.3) | 0.004 ** | 2.2 | (0.91; 5.2) | 0.080 | |
| LVI | Absence | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Presence | 4.6 | (1.8; 11.6) | 0.001 ** | 3.1 | (1.2; 8.3) | 0.020 * | |
| TIL levels (continuous) b | 1.5 | (1.2; 2) | 0.002 ** | 1.4 | (1.1; 1.9) | 0.014 * | |
| Variation Pre/Post-NAC parameters | |||||||
| SUV relative variation c | 0.11 | ||||||
| SUV relative variation (class) | <−70% | 1 | |||||
| ≥−70% | 1.3 | (0.55; 2.9) | 0.59 | ||||
| TILs absolute variation | <0 | 1 | |||||
| ≥0 | 1.9 | (0.81; 4.5) | 0.14 | ||||
| Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Levels | HR | (95% CI) | p-Value | HR | (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Pre-NAC parameters | |||||||
| Age (class) | <45 | 1 | |||||
| ≥45 | 0.9 | (0.34; 2.4) | 0.84 | ||||
| Pregnancies | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1–3 | 1.3 | (0.45; 3.7) | 0.63 | ||||
| >3 | 0.81 | (0.16; 4.2) | 0.80 | ||||
| Menopausal status | premenopausal | 1 | |||||
| postmenopausal | 0.46 | (0.16; 1.3) | 0.14 | ||||
| Family history | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 0.58 | (0.13; 2.6) | 0.47 | ||||
| ≥2 | 1 | (0.23; 4.4) | 1 | ||||
| Clinical tumor stage | T1-T2 | 1 | |||||
| T3 | 0.91 | (0.36; 2.3) | 0.85 | ||||
| Clinical nodal status | N− | 1 | |||||
| N+ | 1.4 | (0.54; 3.6) | 0.50 | ||||
| LVI | Absence | 1 | |||||
| Presence | 2.3 | (0.8; 6.4) | 0.12 | ||||
| TIL levels (continuous) | 1 | (0.99; 1) | 0.45 | ||||
| Post-NAC parameters | |||||||
| Nodal involvment | ypN− | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ypN+ | 2.6 | (0.94; 7.4) | 0.066 | 2.2 | (0.76; 6.4) | 0.15 | |
| LVI | Absence | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Presence | 3.6 | (1.3; 9.5) | 0.012 * | 3.4 | (1.2; 9.3) | 0.020 * | |
| TIL levels (continuous) a | 1.6 | (1.1; 2.1) | 0.005 ** | 1.6 | (1.1; 2.1) | 0.005 ** | |
| Variation Pre/Post-NAC parameters | |||||||
| SUV relative variation | 0.99 | (0.97; 1) | 0.17 | ||||
| SUV relative variation (class) | <−70% | 1 | |||||
| ≥−70% | 0.65 | (0.22; 1.9) | 0.44 | ||||
| TILs absolute variation | <0 | 1 | |||||
| ≥0 | 1.8 | (0.67; 4.9) | 0.24 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giacchetti, S.; Faucheux, L.; Gardair, C.; Cuvier, C.; de Roquancourt, A.; Campedel, L.; Groheux, D.; de Bazelaire, C.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Miquel, C.; et al. Negative Relationship between Post-Treatment Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Dose-Dense Dose-Intense NeoAdjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051331
Giacchetti S, Faucheux L, Gardair C, Cuvier C, de Roquancourt A, Campedel L, Groheux D, de Bazelaire C, Lehmann-Che J, Miquel C, et al. Negative Relationship between Post-Treatment Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Dose-Dense Dose-Intense NeoAdjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers. 2022; 14(5):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051331
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiacchetti, Sylvie, Lilith Faucheux, Charlotte Gardair, Caroline Cuvier, Anne de Roquancourt, Luca Campedel, David Groheux, Cedric de Bazelaire, Jacqueline Lehmann-Che, Catherine Miquel, and et al. 2022. "Negative Relationship between Post-Treatment Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Dose-Dense Dose-Intense NeoAdjuvant Chemotherapy" Cancers 14, no. 5: 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051331
APA StyleGiacchetti, S., Faucheux, L., Gardair, C., Cuvier, C., de Roquancourt, A., Campedel, L., Groheux, D., de Bazelaire, C., Lehmann-Che, J., Miquel, C., Cahen Doidy, L., Amellou, M., Madelaine, I., Reyal, F., Someil, L., Hocini, H., Hennequin, C., Teixeira, L., Espié, M., ... Hamy, A.-S. (2022). Negative Relationship between Post-Treatment Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Dose-Dense Dose-Intense NeoAdjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers, 14(5), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051331







