Downregulation and Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer Features
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culturing
2.2. Patients and Tumor Specimens
2.3. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Cohort of PTC
2.4. Sanger Sequencing
2.5. RNA Interference (RNAi) Transfection
2.6. Gene Expression by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.7. Cellular Invasion Assays
2.8. Cell Proliferation Analyses
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Zebrafish Husbandry and Injection Experiments
2.11. Pyrosequencing for DNA Methylation Analyses
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
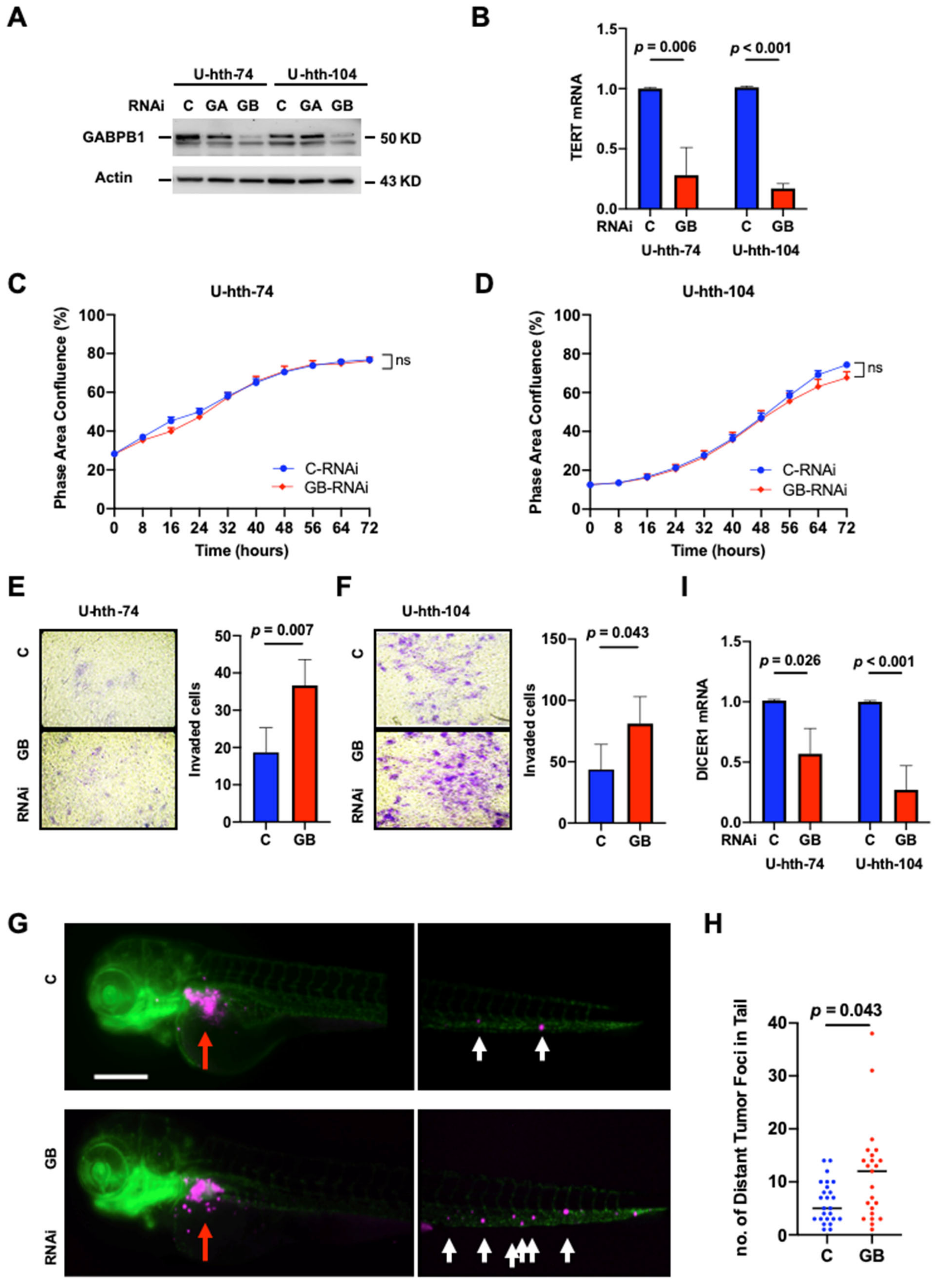
3.1. Reduced TERT Expression Coupled with Enhanced Invasion in GABPB1-Depleted TC Cells
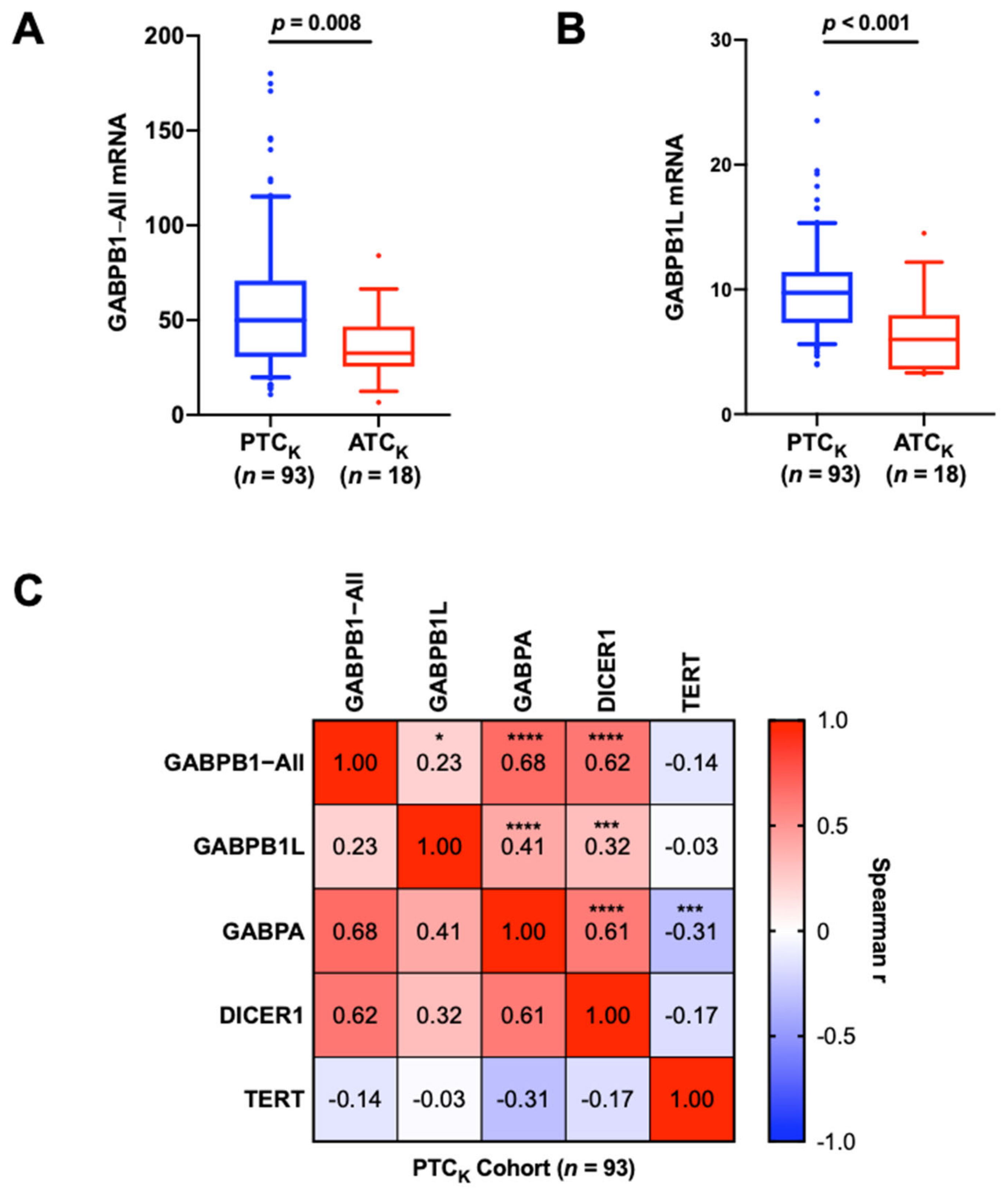
3.2. The Association between Low GABPB1 Expression and Aggressiveness in TC
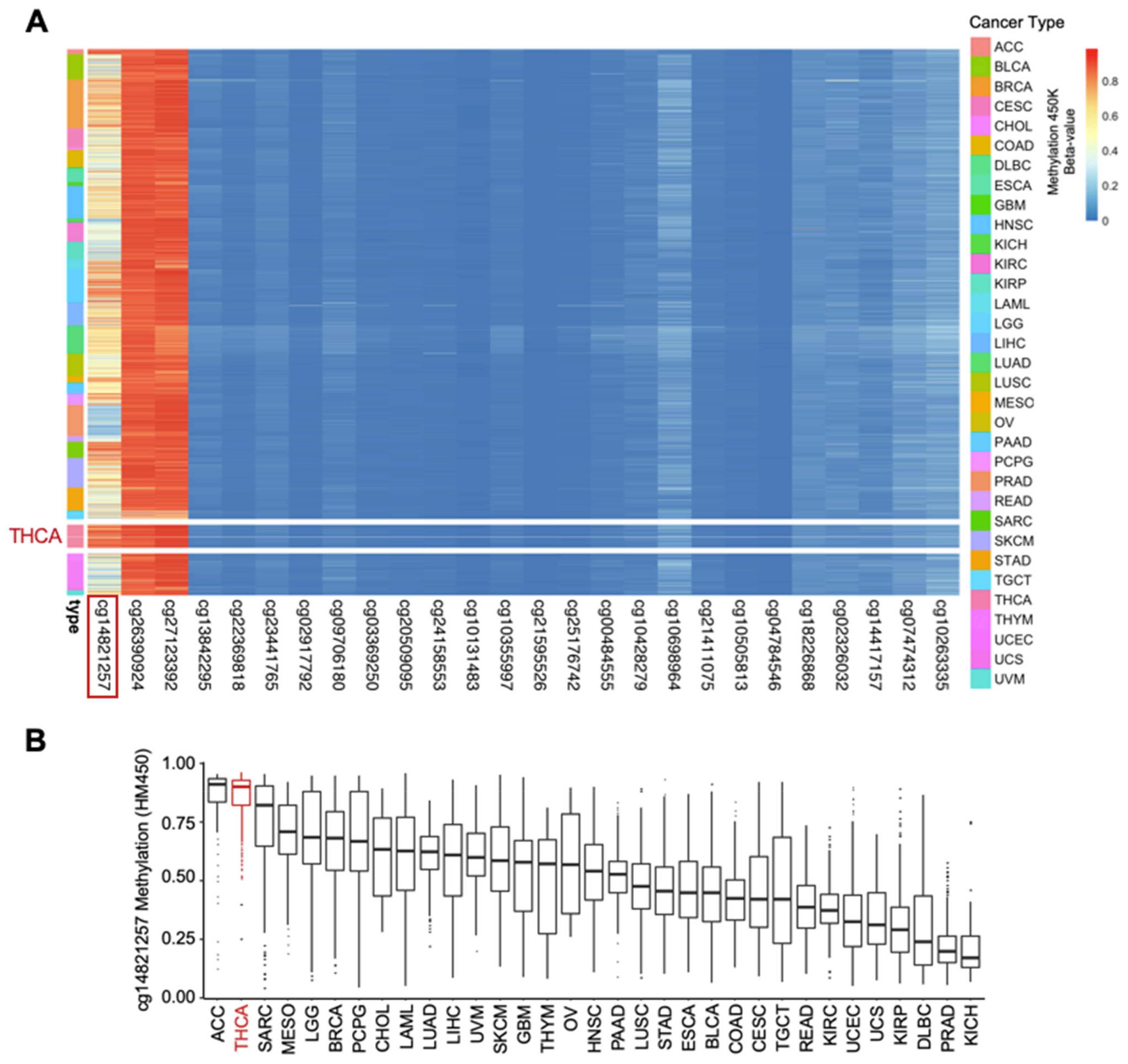
3.3. The Methylation Landscape of the GABPB1 Locus across TCGA Pan-Cancer
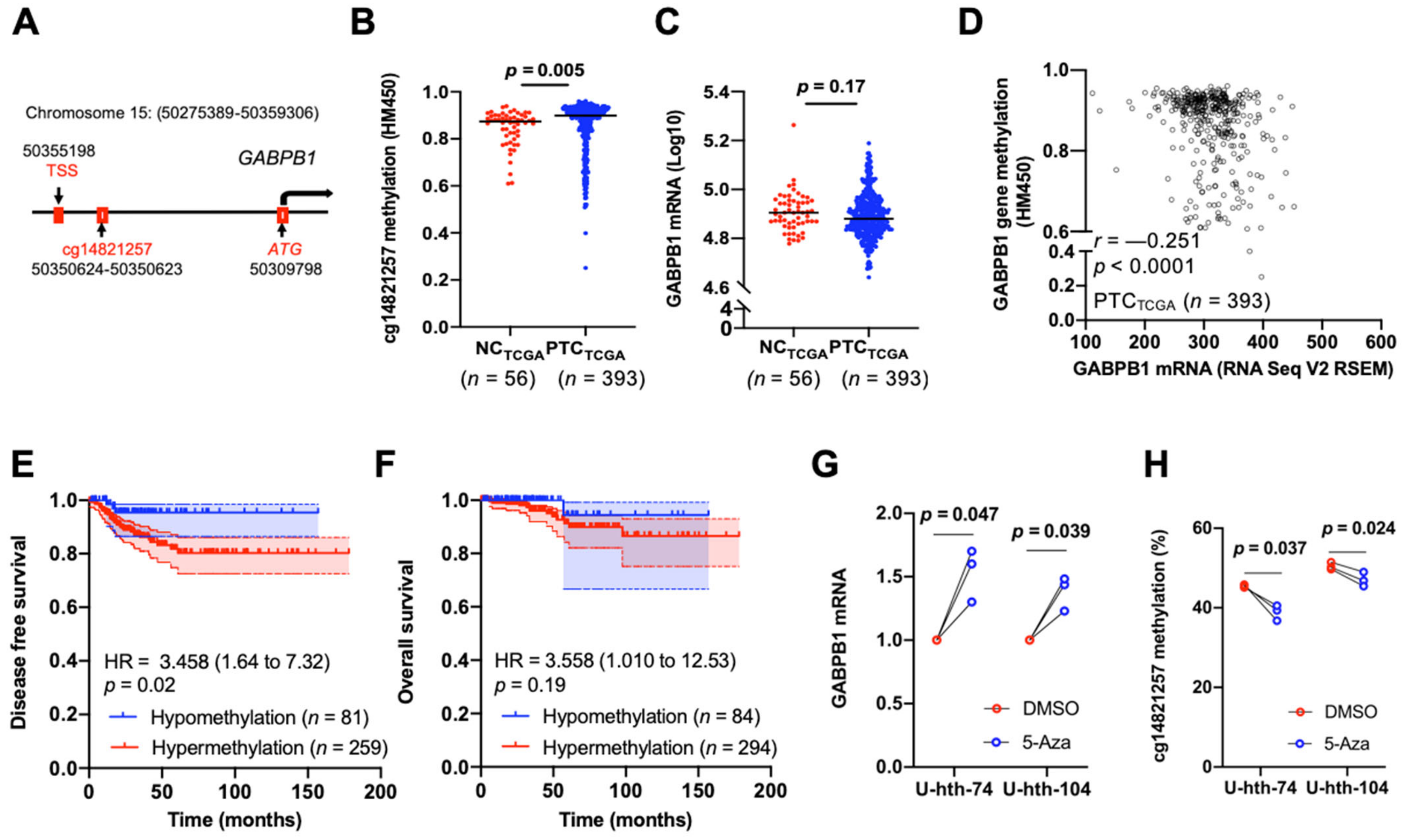
3.4. Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Promoter Resulted in GABPB1 Downregulation and Was Associated with Shorter Disease-Free Survival
3.5. Association of GABPB1 Expression with Clinico-Pathological Variables in TC Tumors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Telomeres and telomerase, Three decades of progress. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Larsson, C.; Xu, D. Mechanisms underlying the activation of TERT transcription and telomerase activity in human cancer, Old actors and new players. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6172–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jafri, M.A.; Ansari, S.A.; Alqahtani, M.H.; Shay, J.W. Roles of telomeres and telomerase in cancer, and advances in telomerase-targeted therapies. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, J.C.; Cech, T.R. Human telomerase, Biogenesis, trafficking, recruitment, and activation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer, The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardes de Jesus, B.; Blasco, M.A. Telomerase at the intersection of cancer and aging. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Tang, W.J.; Shi, J.B.; Liu, M.M.; Liu, X.H. Therapeutic strategies for targeting telomerase in cancer. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 532–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.W.; Hodis, E.; Xu, M.J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Chin, L.; Garraway, L.A. Highly recurrent TERT promoter mutations in human melanoma. Science 2013, 339, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horn, S.; Figl, A.; Rachakonda, P.S.; Fischer, C.; Sucker, A.; Gast, A.; Kadel, S.; Moll, I.; Nagore, E.; Hemminki, K.; et al. TERT promoter mutations in familial and sporadic melanoma. Science 2013, 339, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, R.J.A.; Rube, H.T.; Kreig, A.; Mancini, A.; Fouse, S.D.; Nagarajan, R.P.; Choi, S.; Hong, C.; He, D.; Pekmezci, M.; et al. The transcription factor GABP selectively binds and activates the mutant TERT promoter in cancer. Science 2015, 348, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Dai, M.; Xu, D. TERT promoter mutations and GABP transcription factors in carcinogenesis, More foes than friends. Cancer Lett. 2020, 493, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosmarin, A.G.; Resendes, K.K.; Yang, Z.F.; McMillan, J.N.; Fleming, S.L. GA-binding protein transcription factor, A review of GABP as an integrator of intracellular signaling and protein-protein interactions. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2004, 32, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, A.; Xavier-Magalhaes, A.; Woods, W.S.; Nguyen, K.T.; Amen, A.M.; Hayes, J.L.; Fellmann, C.; Gapinske, M.; McKinney, A.M.; Hong, C.; et al. Disruption of the beta1L Isoform of GABP Reverses Glioblastoma Replicative Immortality in a TERT Promoter Mutation-Dependent Manner. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 513–528.e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Jing, X.; Colgan, J.D.; Zhao, D.M.; Xue, H.H. Targeting tetramer-forming GABPβ isoforms impairs self-renewal of hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stern, J.L.; Theodorescu, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Cech, T.R. Mutation of the TERT promoter, switch to active chromatin, and monoallelic TERT expression in multiple cancers. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, T.; Xu, D. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations in thyroid carcinomas, Implications in precision oncology-a narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Murugan, A.K.; Zhu, G.; Zeiger, M.A.; Pai, S.; Bishop, J. BRAF V600E and TERT promoter mutations cooperatively identify the most aggressive papillary thyroid cancer with highest recurrence. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2718–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo, M.; da Rocha, A.G.; Vinagre, J.; Sobrinho-Simoes, M.; Soares, P. Coexistence of TERT promoter and BRAF mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma, Added value in patient prognosis? J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, N.; Cao, J.; Sofiadis, A.; Dinets, A.; Zedenius, J.; Larsson, C.; Xu, D. The age- and shorter telomere-dependent TERT promoter mutation in follicular thyroid cell-derived carcinomas. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4978–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landa, I.; Ganly, I.; Chan, T.A.; Mitsutake, N.; Matsuse, M.; Ibrahimpasic, T.; Ghossein, R.A.; Fagin, J.A. Frequent somatic TERT promoter mutations in thyroid cancer, Higher prevalence in advanced forms of the disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1562–E1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Xing, M. TERT promoter mutations in thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R143–R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Fuchs, T.; Dogan, S.; Landa, I.; Katabi, N.; Fagin, J.A.; Tuttle, R.M.; Sherman, E.; Gill, A.J.; Ghossein, R. Dissecting Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma, A Comprehensive Clinical, Histologic, Immunophenotypic, and Molecular Study of 360 Cases. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Xiu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, D. DNA Methylation Age Drift Is Associated with Poor Outcomes and De-Differentiation in Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, G.; Xing, M. Regulation of mutant TERT by BRAF V600E/MAP kinase pathway through FOS/GABP in human cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Tan, J.; Shen, X.; Jiang, K.; Wang, C.; Zhu, G.; Xing, M. Therapeutic targeting of FOS in mutant TERT cancers through removing TERT suppression of apoptosis via regulating survivin and TRAIL-R2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022779118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, Y.C.; Ahn, S.H.; Ryu, J.; Chen, Y.; Williams, M.D.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Gagea, M.; Schweppe, R.E.; Haugen, B.R.; Lai, S.Y.; et al. Development and characterization of six new human papillary thyroid carcinoma cell lines. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E243–E252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Mu, N.; Wang, N.; Straat, K.; Sofiadis, A.; Guo, Y.; Stenman, A.; Li, K.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, L.; et al. GABPA inhibits invasion/metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma by regulating DICER1 expression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.V. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10, Chapter 2; pp. 65–91. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.C.; Jafari, N.; Kibbe, W.A.; Hou, L.; Lin, S.M. Comparison of Beta-value and M-value methods for quantifying methylation levels by microarray analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, M.Q.; Gazdar, A.F. DNA methylation data analysis and its application to cancer research. Epigenomics 2013, 5, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittbrodt, J.N.; Liebel, U.; Gehrig, J. Generation of orientation tools for automated zebrafish screening assays using desktop 3D printing. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulsson, J.O.; Wang, N.; Gao, J.; Stenman, A.; Zedenius, J.; Mu, N.; Lui, W.O.; Larsson, C.; Juhlin, C.C. GABPA-dependent down-regulation of DICER1 in follicular thyroid tumours. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.S.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, H.H.; Jung, G.; Oh, A.R.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, S.W.; Lee, K.E.; Seo, J.S.; et al. Interaction of BRAF-induced ETS factors with mutant TERT promoter in papillary thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 2019, 26, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, M.; Lim, G.; Zhu, Y.; Åberg, H.; Kurdyukov, S.; Clifton-Bligh, R. ETS Factor ETV5 Activates the Mutant Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Promoter in Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, K.; Dai, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Sun, C.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, G.; Liu, C.; et al. GABPA is a master regulator of luminal identity and restrains aggressive diseases in bladder cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1862–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter (n = Informative) | Observations | GABPB1−All mRNA | GABPB1L mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (n = 93) | r = −0.258, p = 0.013 | r = −0.171, p = 0.101 | |
| Median (min–max) yrs | 51 (15–97) | ||
| Sex (n = 93) | p = 0.751 | p = 0.262 | |
| Female/Male | n = 67/n = 26 | ||
| Tumor size (n = 88) | r = −0.183, p = 0.089 | r = −0.109, p = 0.313 | |
| Median (min–max) cm | 2.5 (0.3–12) | ||
| Lymph node metastasis (n = 93) | p = 0.114 | p = 0.627 | |
| Yes | n = 49 | ||
| No | n = 44 | ||
| Distant metastasis (n = 93) | p = 0.176 | p = 0.973 | |
| Yes | n = 12 | ||
| No | n = 81 | ||
| BRAF V600E (n = 93) | p = 0.119 | p = 0.454 | |
| Mutation | n = 70 | ||
| Wild-type | n = 23 | ||
| TERT promoter mutation (n = 93) | p = 0.007 | p = 0.154 | |
| Mutation | n = 29 | ||
| C228T/C250T | n = 24/n = 5 | ||
| Wild-type | n = 64 | ||
| TERT mRNA (n = 93) | r = −0.137, p = 0.191 | r = −0.024, p = 0.818 | |
| Median (min–max) | 0.01 (0.00–12.3) | ||
| GABPA mRNA (n = 93) | r = 0.676, p < 0.001 | r = 0.410, p < 0.001 | |
| Median (min–max) | 6.8 (0.2–15.9) | ||
| DICER1 mRNA (n = 93) | r = 0.624, p < 0.001 | r = 0.321, p = 0.002 | |
| Median (min–max) | 19.8 (1.3–124.6) | ||
| Overall survival (n = 93) | * HR = 0.998, p = 0.674 | * HR = 0.930, p = 0.191 | |
| Dead | n = 32 | 95% CI = 0.998–1.008 | 95% CI = 0.835–1.037 |
| Alive | n = 61 | ||
| Follow-up: median (min–max) yrs | 14.8 (0.2–26.5) | ||
| Disease-free survival (n = 93) | * HR = 0.994, p = 0.314 | * HR = 0.952, p = 0.391 | |
| Relapsed/progression | n = 26 | 95% CI = 0.982–1.006 | 95% CI = 0.850–1.066 |
| No evidence of disease | n = 67 | ||
| Follow-up: median (min–max) yrs | 13.5 (0.1–26.5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, X.; Mu, N.; Yuan, X.; Wang, N.; Juhlin, C.C.; Strååt, K.; Larsson, C.; Neo, S.Y.; Xu, D. Downregulation and Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer Features. Cancers 2022, 14, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061385
Xing X, Mu N, Yuan X, Wang N, Juhlin CC, Strååt K, Larsson C, Neo SY, Xu D. Downregulation and Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer Features. Cancers. 2022; 14(6):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061385
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Xiangling, Ninni Mu, Xiaotian Yuan, Na Wang, C. Christofer Juhlin, Klas Strååt, Catharina Larsson, Shi Yong Neo, and Dawei Xu. 2022. "Downregulation and Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer Features" Cancers 14, no. 6: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061385
APA StyleXing, X., Mu, N., Yuan, X., Wang, N., Juhlin, C. C., Strååt, K., Larsson, C., Neo, S. Y., & Xu, D. (2022). Downregulation and Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer Features. Cancers, 14(6), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061385






