TIA1 Loss Exacerbates Fatty Liver Disease but Exerts a Dual Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.1.1. Animal Housing
2.1.2. AAV8 Injection
2.1.3. Computed Tomography (CT)
2.1.4. Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet
2.1.5. Serum Analysis
2.2. In Vitro Cultures
2.2.1. siRNA Transfection
2.2.2. Plasmid Transfection
2.2.3. Treatments
2.2.4. Primary Hepatocytes Isolation
2.3. Cellular Assays
2.3.1. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3.2. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.3.3. TUNEL Assay
2.3.4. Migration and Invasion Assays
2.4. Real Time PCR
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Immunostainings
2.6.1. Preparation of Histological Slides
2.6.2. Human Tissue Microarray Immunohistochemistry
2.6.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.6.4. Immunofluorescence
2.6.5. Bodipy Staining
2.7. Translatomics Analysis
2.7.1. Polysome Profiling
2.7.2. RNA Sequencing
2.8. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. TIA1 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Hepatic Cancer Cells and Is a Relevant Component of Sorafenib-Induced Stress Granules
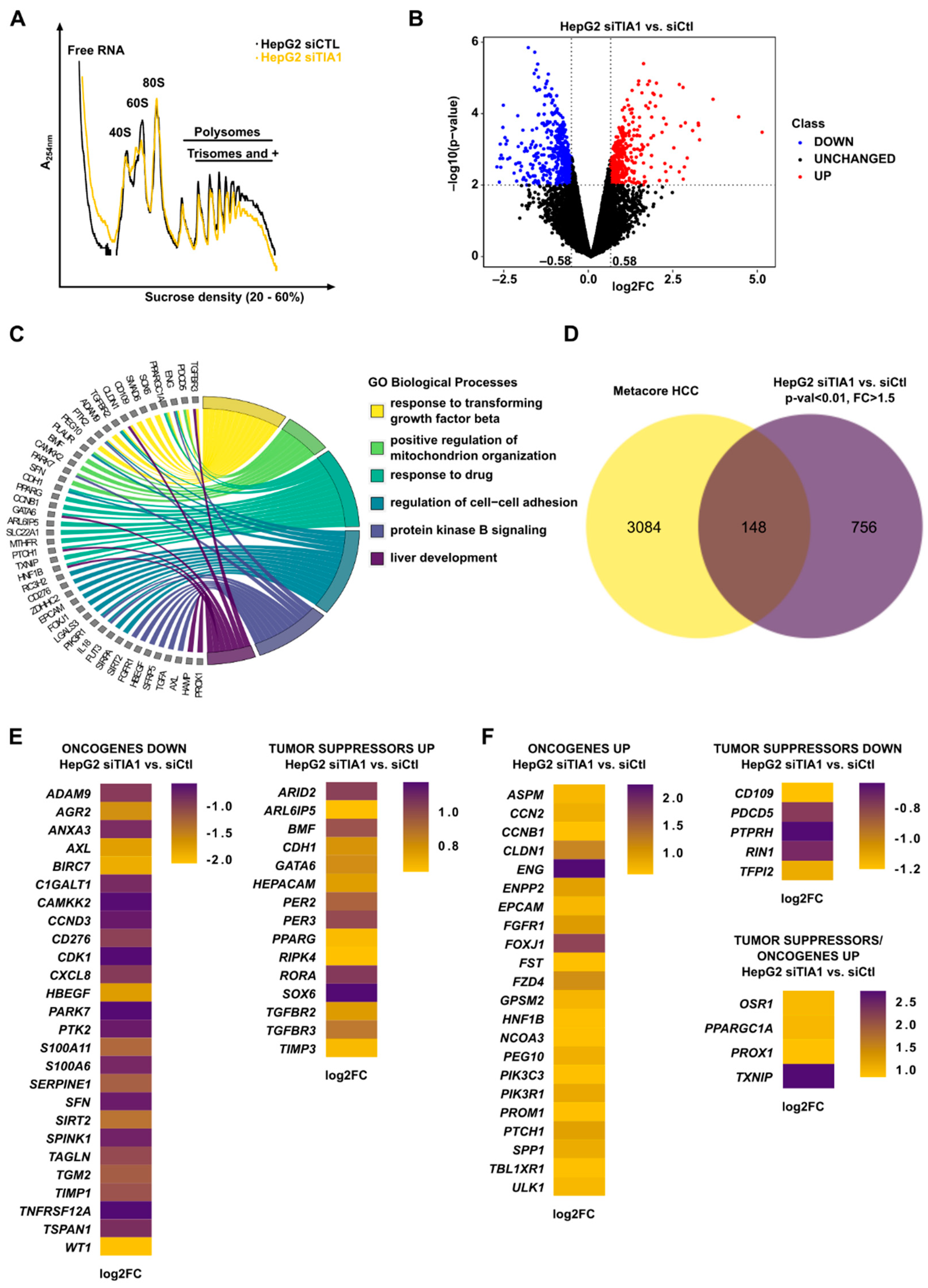
3.2. TIA1 Loss Alters the Translation of HCC-Related Genes
3.3. TIA1 Loss Promotes Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis
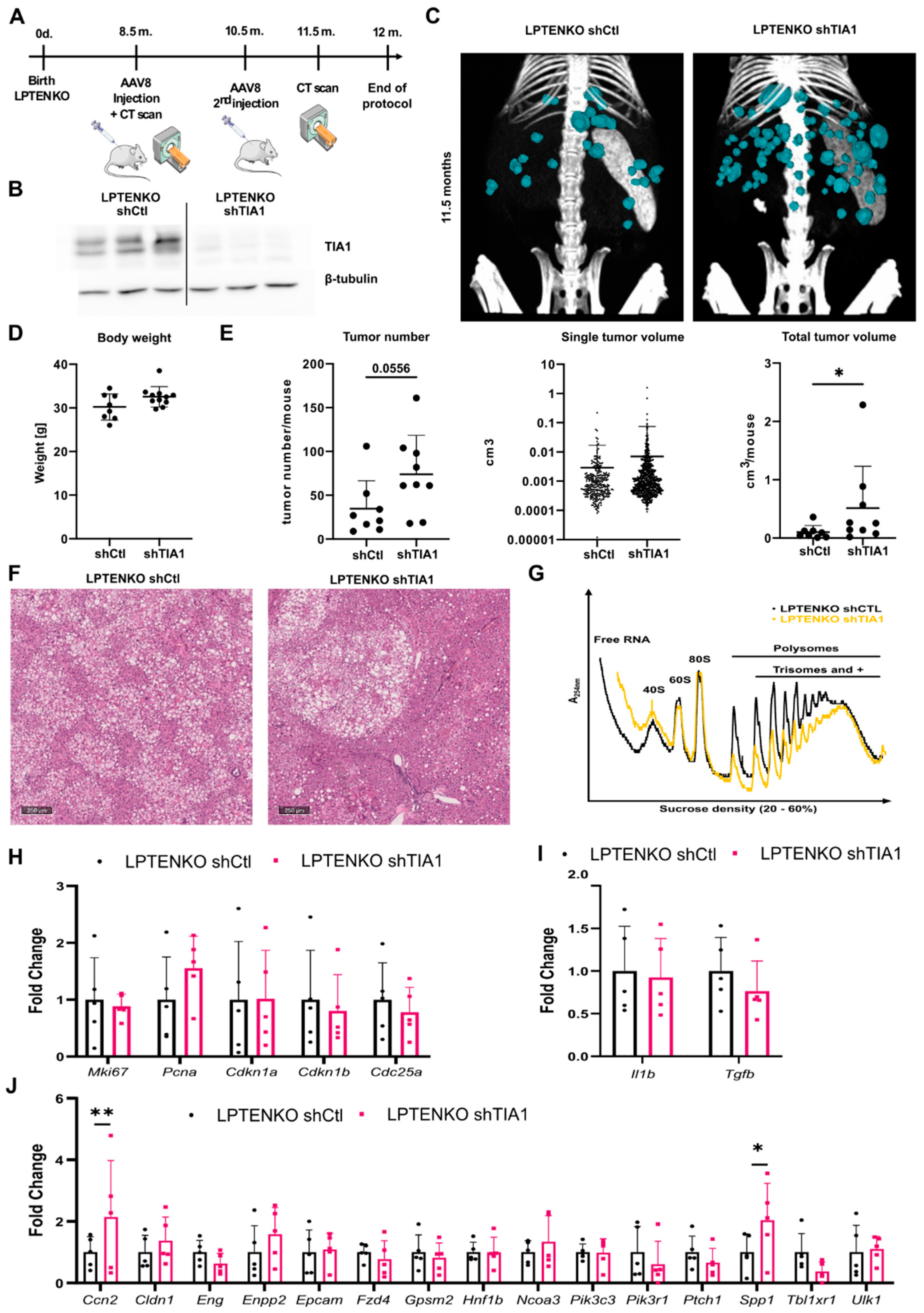
3.4. TIA1 Loss Promotes Hepatic Tumor Burden in Mice
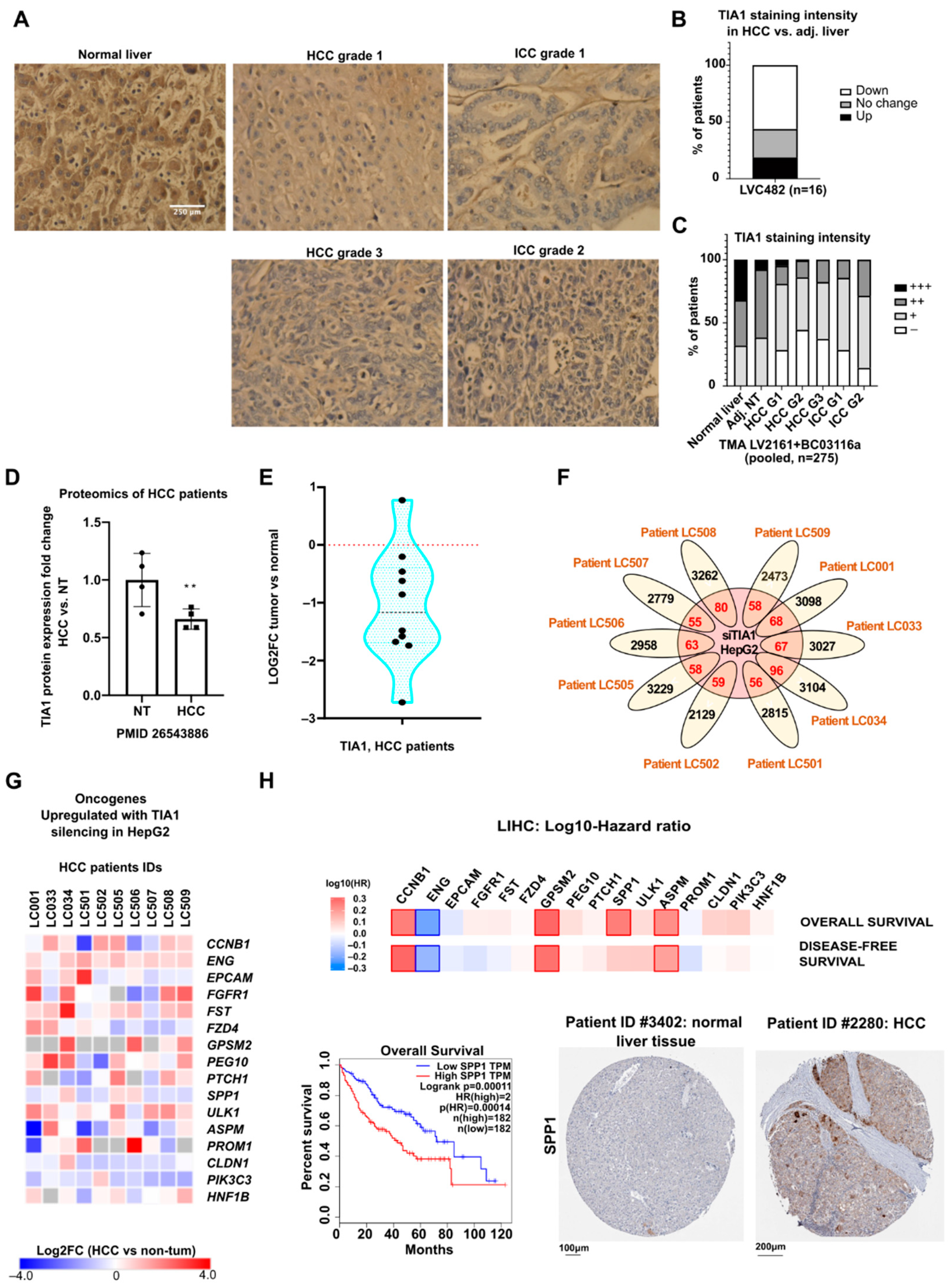
3.5. TIA1 Protein Expression Is Downregulated in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. 1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Tabas, I.; Pajvani, U.B. Mechanisms of fibrosis development in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S. The mutational landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2015, 21, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobolewski, C.; Abegg, D.; Berthou, F.; Dolicka, D.; Calo, N.; Sempoux, C.; Fournier, M.; Maeder, C.; Ay, A.S.; Clavien, P.A.; et al. S100A11/ANXA2 belongs to a tumour suppressor/oncogene network deregulated early with steatosis and involved in inflammation and hepatocellular carcinoma development. Gut 2020, 69, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zong, C.; Jiang, M.; Hu, H.; Cheng, X.; Ni, J.; Yi, X.; Jiang, B.; Tian, F.; Chang, M.W.; et al. Hepatic HuR modulates lipid homeostasis in response to high-fat diet. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolicka, D.; Sobolewski, C.; Correia de Sousa, M.; Gjorgjieva, M.; Foti, M. mRNA Post-transcriptional regulation by au-rich element-binding proteins in liver inflammation and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreau, C.; Paillard, L.; Osborne, H.B. AU-rich elements and associated factors: Are there unifying principles? Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 7138–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Chantada, M.; Fernandez-Ramos, D.; Embade, N.; Martinez-Lopez, N.; Varela-Rey, M.; Woodhoo, A.; Luka, Z.; Wagner, C.; Anglim, P.P.; Finnell, R.H.; et al. HuR/methyl-HuR and AUF1 regulate the MAT expressed during liver proliferation, differentiation, and carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramaniam, K.; Ooi, L.L.; Hui, K.M. Transcriptional down-regulation of IGFBP-3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells is mediated by the binding of TIA-1 to its AT-rich element in the 3′-untranslated region. Cancer Lett. 2010, 297, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia de Sousa, M.; Calo, N.; Sobolewski, C.; Gjorgjieva, M.; Clement, S.; Maeder, C.; Dolicka, D.; Fournier, M.; Vinet, L.; Montet, X.; et al. Mir-21 suppression promotes mouse hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.; Cho, M.R.; Li, W.; Yacono, P.W.; Chen, S.; Gilks, N.; Golan, D.E.; Anderson, P. Dynamic shuttling of TIA-1 accompanies the recruitment of mRNA to mammalian stress granules. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, K.; Fukuda, H.; Imajoh-Ohmi, S.; Saito, H.; Takekawa, M. Formation of stress granules inhibits apoptosis by suppressing stress-responsive MAPK pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, D.A.; Balch, G.C.; Kedersha, N.; Anderson, P.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Prescott, S.M. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by the translational silencer TIA-1. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, F.; Cheng, R.; Chen, X.; Cui, S.; Gu, Y.; Sun, W.; You, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. miR-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamada, J.; Shoda, K.; Masuda, K.; Fujita, Y.; Naruto, T.; Kohmoto, T.; Miyakami, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Kudo, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; et al. Tumor-promoting function and prognostic significance of the RNA-binding protein T-cell intracellular antigen-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17111–17128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adjibade, P.; St-Sauveur, V.G.; Quevillon Huberdeau, M.; Fournier, M.J.; Savard, A.; Coudert, L.; Khandjian, E.W.; Mazroui, R. Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, induces formation of stress granules in hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 43927–43943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, R.; Marion, M.J.; Furio, L.; Trepo, C.; Petit, M.A. Origin and characterization of a human bipotent liver progenitor cell line. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, C.; Garzia, A.; Mazzola, M.; Gerstberger, S.; Molina, H.; Tuschl, T. The TIA1 RNA-binding protein family regulates EIF2AK2-mediated stress response and cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyrou, M.; Bourgoin, L.; Poher, A.L.; Altirriba, J.; Maeder, C.; Caillon, A.; Fournier, M.; Montet, X.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Foti, M. Hepatic PTEN deficiency improves muscle insulin sensitivity and decreases adiposity in mice. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dieudonne, F.X.; O’Connor, P.B.; Gubler-Jaquier, P.; Yasrebi, H.; Conne, B.; Nikolaev, S.; Antonarakis, S.; Baranov, P.V.; Curran, J. The effect of heterogeneous Transcription Start Sites (TSS) on the translatome: Implications for the mammalian cellular phenotype. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seimetz, J.; Arif, W.; Bangru, S.; Hernaez, M.; Kalsotra, A. Cell-type specific polysome profiling from mammalian tissues. Methods 2019, 155, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibraim, I.C.; Parise, M.T.D.; Parise, D.; Sfeir, M.Z.T.; de Paula Castro, T.L.; Wattam, A.R.; Ghosh, P.; Barh, D.; Souza, E.M.; Goes-Neto, A.; et al. Transcriptome profile of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in response to iron limitation. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Della Bella, E.; Buetti-Dinh, A.; Licandro, G.; Ahmad, P.; Basoli, V.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J. Dexamethasone Induces Changes in osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells via SOX9 and PPARG, but not RUNX2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjorgjieva, M.; Sobolewski, C.; Ay, A.S.; Abegg, D.; Correia de Sousa, M.; Portius, D.; Berthou, F.; Fournier, M.; Maeder, C.; Rantakari, P.; et al. Genetic ablation of miR-22 fosters diet-induced obesity and NAFLD development. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Gao, R.; Yang, R.; Bi, J.; Hou, J. In silico identification of EP400 and TIA1 as critical transcription factors involved in human hepatocellular carcinoma relapse. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, J.R.; Matheny, T.; Jain, S.; Abrisch, R.; Parker, R. Distinct stages in stress granule assembly and disassembly. Elife 2016, 5, e18413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piecyk, M.; Wax, S.; Beck, A.R.; Kedersha, N.; Gupta, M.; Maritim, B.; Chen, S.; Gueydan, C.; Kruys, V.; Streuli, M.; et al. TIA-1 is a translational silencer that selectively regulates the expression of TNF-alpha. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4154–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Munoz, M.D.; Kiselev, V.Y.; Le Novere, N.; Curk, T.; Ule, J.; Turner, M. Tia1 dependent regulation of mRNA subcellular location and translation controls p53 expression in B cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeBlang, C.J.; Medalla, M.; Nicoletti, N.W.; Hays, E.C.; Zhao, J.; Shattuck, J.; Cruz, A.L.; Wolozin, B.; Luebke, J.I. Reduction of the RNA binding protein TIA1 exacerbates neuroinflammation in tauopathy. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pihlajamaki, J.; Boes, T.; Kim, E.Y.; Dearie, F.; Kim, B.W.; Schroeder, J.; Mun, E.; Nasser, I.; Park, P.J.; Bianco, A.C.; et al. Thyroid hormone-related regulation of gene expression in human fatty liver. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3521–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heck, M.V.; Azizov, M.; Stehning, T.; Walter, M.; Kedersha, N.; Auburger, G. Dysregulated expression of lipid storage and membrane dynamics factors in Tia1 knockout mouse nervous tissue. Neurogenetics 2014, 15, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horie, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kataoka, E.; Sasaki, T.; Hamada, K.; Sasaki, J.; Mizuno, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Kishimoto, H.; Iizuka, M.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific Pten deficiency results in steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chi, M.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Zeng, J.; Lin, M.; Han, X.; et al. Dataset for the quantitative proteomics analysis of the primary hepatocellular carcinoma with single and multiple lesions. Data Brief 2015, 5, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Yang, X. Survey of the translation shifts in hepatocellular carcinoma with ribosome profiling. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4141–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Lin, B.; Yao, D.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, R.; Yu, S. miR-487a promotes progression of gastric cancer by targeting TIA1. Biochimie 2018, 154, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.M.; Xiao, S.; Lei, X.; Yang, H.; Fang, F.; Yang, L.Y. miRNA-487a promotes proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, Z.J.; Heinrich, B.; Greten, T.F. Mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma: An overview and highlights for immunotherapy research. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Schrooders, Y.; Hauser, D.; van Herwijnen, M.; Albrecht, W.; Ter Braak, B.; Brecklinghaus, T.; Castell, J.V.; Elenschneider, L.; Escher, S.; et al. Comparing in vitro human liver models to in vivo human liver using RNA-Seq. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolicka, D.; Sobolewski, C.; Gjorgjieva, M.; Correia de Sousa, M.; Berthou, F.; De Vito, C.; Colin, D.J.; Bejuy, O.; Fournier, M.; Maeder, C.; et al. Tristetraprolin promotes hepatic inflammation and tumor initiation but restrains cancer progression to malignancy. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 597–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Goldin, R.D. Mouse models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis research. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2006, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forch, P.; Puig, O.; Kedersha, N.; Martinez, C.; Granneman, S.; Seraphin, B.; Anderson, P.; Valcarcel, J. The apoptosis-promoting factor TIA-1 is a regulator of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, J.M.; Majos, N.; Bonnal, S.; Martinez, C.; Castelo, R.; Guigo, R.; Bilbao, D.; Valcarcel, J. Regulation of Fas alternative splicing by antagonistic effects of TIA-1 and PTB on exon definition. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlinden, A.; Liang, L.; Mukudai, Y.; Imamura, T.; Sandell, L.J. Nuclear protein TIA-1 regulates COL2A1 alternative splicing and interacts with precursor mRNA and genomic DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24444–24454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilli, T.M.; Mello, K.D.; Ferreira, L.B.; Matos, A.R.; Accioly, M.T.; Faria, P.A.; Bellahcene, A.; Castronovo, V.; Gimba, E.R. Both osteopontin-c and osteopontin-b splicing isoforms exert pro-tumorigenic roles in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2012, 72, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhoo, A.; Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta, M.; Beraza, N.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J.L.; Embade, N.; Fernandez-Ramos, D.; Martinez-Lopez, N.; Gutierrez-De Juan, V.; Arteta, B.; Caballeria, J.; et al. Human antigen R contributes to hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.T.; Berasain, C.; Bhatia, S.; Rivera, K.; Liu, B.; Rigo, F.; Pappin, D.J.; Spector, D.L. PHAROH lncRNA regulates Myc translation in hepatocellular carcinoma via sequestering TIAR. Elife 2021, 10, e68263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilks, N.; Kedersha, N.; Ayodele, M.; Shen, L.; Stoecklin, G.; Dember, L.M.; Anderson, P. Stress granule assembly is mediated by prion-like aggregation of TIA-1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 5383–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mi, H.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mills, C.; Albou, L.P.; Mushayamaha, T.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 16: A revised family classification, tree-based classification tool, enhancer regions and extensive API. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D394–D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, J.; Zhao, E.Y.; Grewal, J.; Jones, M.R.; Jones, S.J.M. CancerMine: A literature-mined resource for drivers, oncogenes and tumor suppressors in cancer. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Villanueva, A.; Mallona, I.; Peinado, M.A. Wanderer, an interactive viewer to explore DNA methylation and gene expression data in human cancer. Epigenet. Chromatin 2015, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. OncomiR: An online resource for exploring pan-cancer microRNA dysregulation. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, G.; Yang, Y.T.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, B.; Xie, D.; Lu, Z.J.; Wang, P. POSTAR2: Deciphering the post-transcriptional regulatory logics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D203–D211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pujato, M.; Kieken, F.; Skiles, A.A.; Tapinos, N.; Fiser, A. Prediction of DNA binding motifs from 3D models of transcription factors; identifying TLX3 regulated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 13500–13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naboulsi, W.; Megger, D.A.; Bracht, T.; Kohl, M.; Turewicz, M.; Eisenacher, M.; Voss, D.M.; Schlaak, J.F.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Weber, F.; et al. Quantitative Tissue Proteomics Analysis Reveals Versican as Potential Biomarker for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolicka, D.; Zahoran, S.; Correia de Sousa, M.; Gjorgjieva, M.; Sempoux, C.; Fournier, M.; Maeder, C.; Collart, M.A.; Foti, M.; Sobolewski, C. TIA1 Loss Exacerbates Fatty Liver Disease but Exerts a Dual Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071704
Dolicka D, Zahoran S, Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Sempoux C, Fournier M, Maeder C, Collart MA, Foti M, Sobolewski C. TIA1 Loss Exacerbates Fatty Liver Disease but Exerts a Dual Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers. 2022; 14(7):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071704
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolicka, Dobrochna, Szabolcs Zahoran, Marta Correia de Sousa, Monika Gjorgjieva, Christine Sempoux, Margot Fournier, Christine Maeder, Martine A. Collart, Michelangelo Foti, and Cyril Sobolewski. 2022. "TIA1 Loss Exacerbates Fatty Liver Disease but Exerts a Dual Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis" Cancers 14, no. 7: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071704
APA StyleDolicka, D., Zahoran, S., Correia de Sousa, M., Gjorgjieva, M., Sempoux, C., Fournier, M., Maeder, C., Collart, M. A., Foti, M., & Sobolewski, C. (2022). TIA1 Loss Exacerbates Fatty Liver Disease but Exerts a Dual Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers, 14(7), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071704







