Intratumoral Immunotherapy and Tumor Ablation: A Local Approach with Broad Potential
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
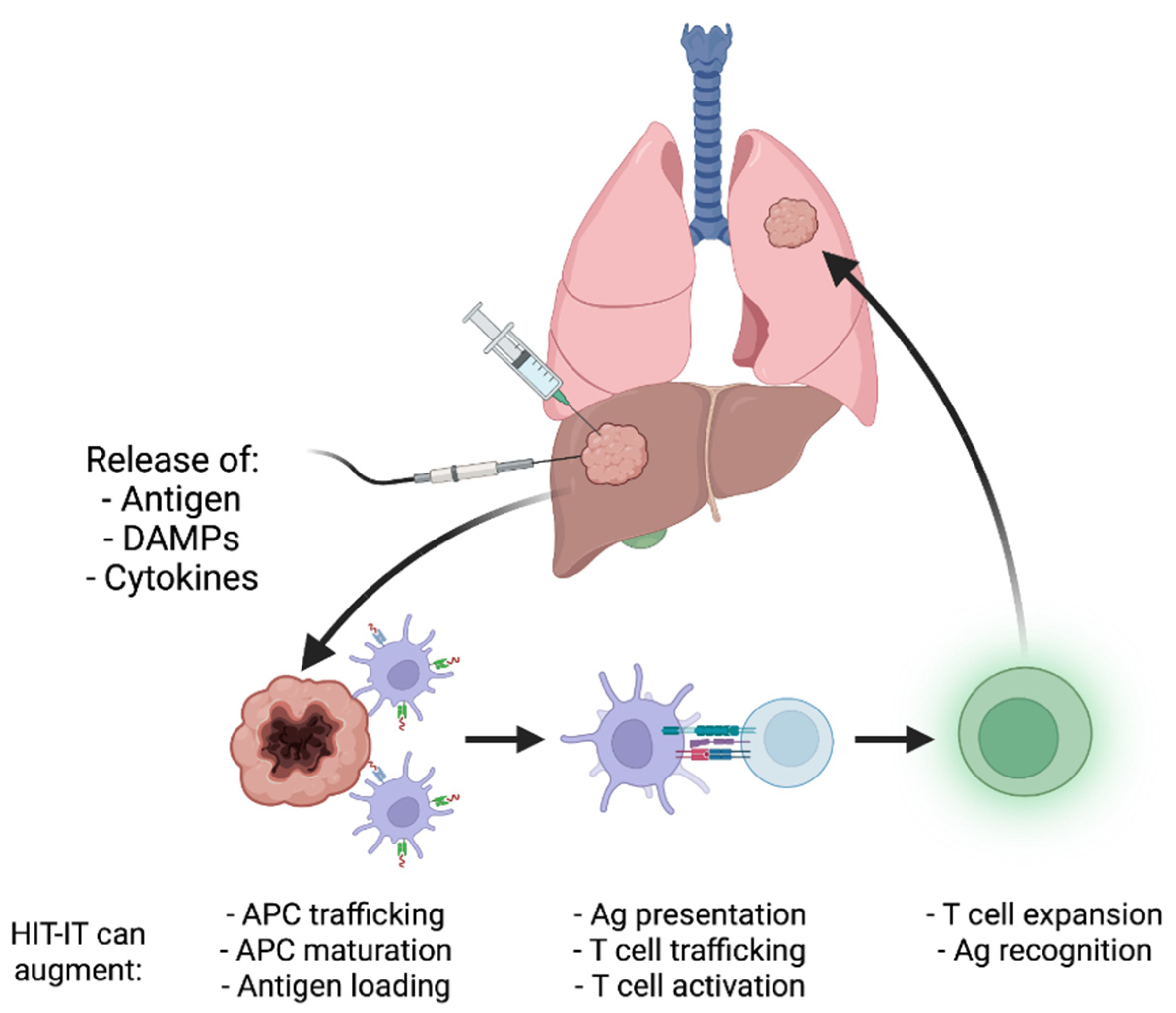
1. Introduction
2. Therapeutic Strategies for Combination HIT-IT and Tumor Ablation
2.1. Virus-Based Therapies
2.2. Cell-Based Therapies
2.3. Pattern Recognition Receptor (PRR) Agonists
2.4. Biomaterials
2.5. Cytokines
3. Opportunities and Challenges
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Olza, M.O.; Rodrigo, B.N.; Zimmermann, S.; Coukos, G. Turning up the heat on non-immunoreactive tumours: Opportunities for clinical development. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e419–e430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, M.A.; Tinari, N.; Rullán, A.J.; Sánchez-Paulete, A.R.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Melero, I. Intratumoral Delivery of Immunotherapy—Act Locally, Think Globally. J. Immunol. 2016, 198, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.X.; Haebe, S.; Lee, A.S.; Westphalen, C.B.; Norton, J.A.; Jiang, W.; Levy, R. Intratumoral Immunotherapy for Early-stage Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marabelle, A.; Tselikas, L.; de Baere, T.; Houot, R. Intratumoral immunotherapy: Using the tumor as the remedy. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, xii33–xii43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, J.; Le Naour, J.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G.; Pol, J.G. Trial watch: Intratumoral immunotherapy. OncoImmunology 2021, 10, 1984677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, O.; Ismail, R.; Puzanov, I. Intratumoral Immunotherapy—Update 2019. Oncologist 2019, 25, e423–e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.S.; Hecht, J.R.; Chan, E. Talimogene laherparepvec: Review of its mechanism of action and clinical efficacy and safety. Immunotherapy 2019, 11, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slovak, R.; Ludwig, J.M.; Gettinger, S.N.; Herbst, R.S.; Kim, H.S. Immuno-thermal ablations—Boosting the anticancer immune response. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brok, M.H.M.G.M.D.; Sutmuller, R.P.M.; Van Der Voort, R.; Bennink, E.J.; Figdor, C.; Ruers, T.J.M.; Adema, G.J. In Situ Tumor Ablation Creates an Antigen Source for the Generation of Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4024–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greten, T.F.; Mauda-Havakuk, M.; Heinrich, B.; Korangy, F.; Wood, B. Combined locoregional-immunotherapy for liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmer, F.E.; Geboers, B.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Schouten, E.A.; Dijkstra, M.; de Vries, J.J.; Tol, M.P.V.D.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Scheffer, H.J.; Meijerink, M.R. Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Percutaneous Management Using Ablation, Brachytherapy, Intra-arterial Chemotherapy, and Intra-tumoral Immunotherapy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestrini, M.T.; Ingham, E.S.; Mahakian, L.M.; Kheirolomoom, A.; Liu, Y.; Fite, B.Z.; Tam, S.M.; Tucci, S.T.; Watson, K.D.; Wong, A.W.; et al. Priming is key to effective incorporation of image-guided thermal ablation into immunotherapy protocols. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e90521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.; Hayat, T.; Hamm, J.; Healey, M.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Martin, R.C. A phase 1b trial of concurrent immunotherapy and irreversible electroporation in the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Surgery 2020, 168, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, A.; Chesney, J.; Long, G.V.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Dummer, R.; Puzanov, I.; Hoeller, C.; Gajewski, T.F.; Gutzmer, R.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. 1037O MASTERKEY-265: A phase III, randomized, placebo (Pbo)-controlled study of talimogene laherparepvec (T) plus pembrolizumab (P) for unresectable stage IIIB–IVM1c melanoma (MEL). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S868–S869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, J.; Xie, F.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Combining NanoKnife with M1 oncolytic virus enhances anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 502, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Tateishi, R.; Iwai, M.; Koike, K.; Todo, T. Neoadjuvant Use of Oncolytic Herpes Virus G47Δ Enhances the Antitumor Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 18, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Levine, B.L.; Zhang, P.J.; Davis, M.M.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Kulikovskaya, I.; Brennan, A.L.; Liu, X.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Intratumoral Injections of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zerbini, A.; Pilli, M.; Fagnoni, F.; Pelosi, G.; Pizzi, M.G.; Schivazappa, S.; Laccabue, D.; Cavallo, C.; Schianchi, C.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Increased Immunostimulatory Activity Conferred to Antigen-presenting Cells by Exposure to Antigen Extract from Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlenkin, A.; Goldberger, O.; Tirosh, B.; Paz, A.; Volovitz, I.; Bar-Haim, E.; Lee, S.-H.; Vadai, E.; Tzehoval, E.; Eisenbach, L. Combined Dendritic Cell Cryotherapy of Tumor Induces Systemic Antimetastatic Immunity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4955–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brossart, P. The Role of Antigen Spreading in the Efficacy of Immunotherapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4442–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, M.; Kudo-Saito, C.; Hasegawa, G.; Yano, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Yaguchi, M.; Toda, M.; Azuma, I.; Iwai, T.; Kawakami, Y. Enhancement of Immunologic Tumor Regression by Intratumoral Administration of Dendritic Cells in Combination with Cryoablative Tumor Pretreatment and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Cell Wall Skeleton Stimulation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7465–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, H.; Mizukoshi, E.; Iida, N.; Terashima, T.; Kitahara, M.; Marukawa, Y.; Kitamura, K.; Nakamoto, Y.; Hiroishi, K.; Imawari, M.; et al. In vivo immunological antitumor effect of OK-432-stimulated dendritic cell transfer after radiofrequency ablation. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitahara, M.; Mizukoshi, E.; Terashima, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Horii, R.; Iida, N.; Arai, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Safety and Long-Term Outcome of Intratumoral Injection of OK432-Stimulated Dendritic Cells for Hepatocellular Carcinomas After Radiofrequency Ablation. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, W.; Pan, H.; Ma, G.; Shi, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, W.; Wang, S. Microwave ablation combined with OK-432 induces Th1-type response and specific antitumor immunity in a murine model of breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Niu, L.; Xu, K. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation combined with allogeneic natural killer cell immunotherapy for patients with unresectable (stage III/IV) pancreatic cancer: A promising treatment. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaggar, M.; Lin, M.; Mesmar, A.; Liang, S.; Qaid, A.; Xu, K.; Chen, J.; Niu, L.; Yin, Z. Allogenic Natural Killer Cell Immunotherapy Combined with Irreversible Electroporation for Stage IV Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Survival Outcome. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, C.; Bertholet, S.; Philpott, D.J.; De Gregorio, E. Unleashing the potential of NOD- and Toll-like agonists as vaccine adjuvants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12294–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luchner, M.; Reinke, S.; Milicic, A. TLR Agonists as Vaccine Adjuvants Targeting Cancer and Infectious Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, B.; Di Fazio, P.; Michl, P.; Neureiter, D.; Kemmerling, R.; Hahn, E.G.; Strobel, D.; Gress, T.; Schuppan, D.; Wissniowski, T.T. Additive antitumour response to the rabbit VX2 hepatoma by combined radio frequency ablation and toll like receptor 9 stimulation. Gut 2014, 65, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brok, M.H.D.; Sutmuller, R.P.; Nierkens, S.; Bennink, E.J.; Toonen, L.W.; Figdor, C.G.; Ruers, T.J.; Adema, G.J. Synergy between In situ Cryoablation and TLR9 Stimulation Results in a Highly Effective In vivo Dendritic Cell Vaccine. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7285–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, J.S.S.; Ray, P.; Hayashi, T.; Whisenant, T.C.; Vicente, D.; Carson, D.A.; Miller, A.M.; Schoenberger, S.P.; White, R.R. Irreversible Electroporation Combined with Checkpoint Blockade and TLR7 Stimulation Induces Antitumor Immunity in a Murine Pancreatic Cancer Model. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczanowska, S.; Joseph, A.M.; Davila, E. TLR agonists: Our bestfrenemyin cancer immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flood, B.A.; Higgs, E.; Li, S.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. STING pathway agonism as a cancer therapeutic. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 290, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, L.; Glickman, L.H.; McWhirter, S.M.; Kanne, D.B.; Sivick, K.E.; Katibah, G.E.; Woo, S.-R.; Lemmens, E.; Banda, T.; Leong, J.J.; et al. Direct Activation of STING in the Tumor Microenvironment Leads to Potent and Systemic Tumor Regression and Immunity. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ager, C.R.; Reilley, M.J.; Nicholas, C.; Bartkowiak, T.; Jaiswal, A.; Curran, M.A. Intratumoral STING Activation with T-cell Checkpoint Modulation Generates Systemic Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, E.-J.; Yang, H.; Chon, H.J.; Yang, D.; Ryu, W.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, D.K.; Kim, C.; Park, W. Combination of Irreversible Electroporation and STING Agonist for Effective Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasarte-Cia, A.; Lozano, T.; Cano, D.; Martín-Otal, C.; Navarro, F.; Gorraiz, M.; Casares, N.; Vivas, I.; Lasarte, J.J. Intratumoral STING Agonist Injection Combined with Irreversible Electroporation Delays Tumor Growth in a Model of Hepatocarcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8852233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Gong, N.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Dou, J.; Huang, J.; Zhu, K.; Liang, P.; Liang, X.-J.; et al. Mannose-Derived Carbon Dots Amplify Microwave Ablation-Induced Antitumor Immune Responses by Capturing and Transferring “Danger Signals” to Dendritic Cells. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2920–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, W.; Kwak, K.; Choi, H.; Kim, D.-H. Electric Pulse Responsive Magnetic Nanoclusters Loaded with Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitor for Synergistic Immuno-Ablation Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 54415–54425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tan, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q. Injectable Immunotherapeutic Thermogel for Enhanced Immunotherapy Post Tumor Radiofrequency Ablation. Small 2021, 17, 2104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Tumor-killing nanoreactors fueled by tumor debris can enhance radiofrequency ablation therapy and boost antitumor immune responses. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbelik, M.; Hode, T.; Lam, S.; Chen, W. Novel Immune Stimulant Amplifies Direct Tumoricidal Effect of Cancer Ablation Therapies and Their Systemic Antitumor Immune Efficacy. Cells 2021, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shen, S.; Peng, B.; Tao, J. Intratumoural GM-CSF microspheres and CTLA-4 blockade enhance the antitumour immunity induced by thermal ablation in a subcutaneous murine hepatoma model. Int. J. Hyperth. 2009, 25, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemdani, K.; Mignet, N.; Boudy, V.; Seguin, J.; Oujagir, E.; Bawa, O.; Peschaud, F.; Emile, J.-F.; Capron, C.; Malafosse, R. Local immunomodulation combined to radiofrequency ablation results in a complete cure of local and distant colorectal carcinoma. OncoImmunology 2018, 8, 1550342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, B.; Peng, B. Effects of intratumoral injection of immunoactivator after microwave ablation on antitumor immunity in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 15, 1914–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Kmieciak, M.; Graham, L.; Morales, J.K.; Bear, H.D.; Manjili, M.H. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of breast tumors combined with intralesional administration of IL-7 and IL-15 augments anti-tumor immune responses and inhibits tumor development and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 114, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, E.E.; Yamane, B.H.; Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Lum, H.D.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Mahvi, D.M.; Gillies, S.D.; Sondel, P.M. Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with KS-IL2 Immunocytokine (EMD 273066) Results in an Enhanced Antitumor Effect against Murine Colon Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4875–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, T.; Inou, Y.; Iwai, M.; Tateishi, R.; Koike, K.; Todo, T. Enhancement of the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation by neoadjuvant oncolytic virus therapy via antitumor immunity and the booster effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, S.R.; Nave, H.; Korangy, F.; Schlote, K.; Pabst, R.; Jaffee, E.; Manns, M.P.; Greten, T.F. Apoptotic, but not necrotic, tumor cell vaccines induce a potent immune responsein vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 103, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, H.J.; Stam, A.G.; Geboers, B.; Vroomen, L.G.; Ruarus, A.; De Bruijn, B.; Tol, M.P.V.D.; Kazemier, G.; Meijerink, M.R.; De Gruijl, T.D. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer transiently alleviates immune suppression and creates a window for antitumor T cell activation. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, 1652532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulvik, B.E.; Rozenblum, N.; Gourevich, S.; Ahmed, M.; Andriyanov, A.V.; Galun, E.; Goldberg, S.N. Irreversible Electroporation versus Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparison of Local and Systemic Effects in a Small-Animal Model. Radiology 2016, 280, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandit, H.; Hong, Y.K.; Li, Y.; Rostas, J.; Pulliam, Z.; Li, S.P.; Martin, R.C.G. Evaluating the Regulatory Immunomodulation Effect of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.S.; Liu, Z.; Bartlett, D.L. Oncolytic Immunotherapy: Dying the Right Way is a Key to Eliciting Potent Antitumor Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vivas, I.; Iribarren, K.; Lozano, T.; Cano, D.; Lasarte-Cia, A.; Chocarro, S.; Gorraiz, M.; Sarobe, P.; Hervás-Stubbs, S.; Bilbao, J.I.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of Irreversible Electroporation in Combination with Poly-ICLC Adjuvant in Preclinical Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, C.R.; Field, D.H.; Kim, A.Y. Current State of Combination of Locoregional Therapies with Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1740–1744.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geboers, B.; Timmer, F.; Ruarus, A.; Pouw, J.; Schouten, E.; Bakker, J.; Puijk, R.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Dijkstra, M.; Tol, M.V.D.; et al. Irreversible Electroporation and Nivolumab Combined with Intratumoral Administration of a Toll-Like Receptor Ligand, as a Means of In Vivo Vaccination for Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PANFIRE-III). A Phase-I Study Protocol. Cancers 2021, 13, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champiat, S.; Tselikas, L.; Farhane, S.; Raoult, T.; Texier, M.; Lanoy, E.; Massard, C.; Robert, C.; Ammari, S.; De Baère, T.; et al. Intratumoral Immunotherapy: From Trial Design to Clinical Practice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 27, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Andtbacka, R.; Harrington, K.; Melero, I.; Leidner, R.; de Baere, T.; Robert, C.; Ascierto, P.A.; Baurain, J.-F.; Imperiale, M.; et al. Starting the fight in the tumor: Expert recommendations for the development of human intratumoral immunotherapy (HIT-IT). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Fine, G.C.; Adema, G.J.; Ahmed, M.; Chapiro, J.; Brok, M.D.; Duran, R.; Hunt, S.J.; Johnson, D.T.; Ricke, J.; et al. Immunotherapy and the Interventional Oncologist: Challenges and Opportunities—A Society of Interventional Oncology White Paper. Radiology 2019, 292, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldmacher, G.V.; Khilnani, A.D.; Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Luke, J.J.; Hodi, F.S.; Marabelle, A.; Harrington, K.; Perrone, A.; Tse, A.; Madoff, D.C.; et al. Response Criteria for Intratumoral Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors: itRECIST. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category of IT Immunotherapy | Agent | Ablation Technique | Species Studied | Tumor Type | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based therapies | DCs | RFA | Mouse | Urothelial | Dromi |
| DCs | Cryo | Mouse | Lung/Melanoma | Machlenkin | |
| DCs | Phototherapy | Mouse | Colon/Melanoma | Saji | |
| DCs + BCG | Cryo | Mouse | Colon | Udagawa | |
| OK432-stimulated DCs | RFA | Human | Hepatocellular | Kitahara | |
| OK432-stimulated DCs | RFA | Mouse | Colon | Nakagawa | |
| NK cells | IRE | Human | Hepatocellular | Alnaggar | |
| NK cells | IRE | Human | Pancreas | Lin | |
| NK cells | IRE | Human | Pancreas | Lin | |
| Pattern recognition receptor agonists | TLR3 agonist (Poly-ICLC) | IRE | Mouse/Rabbit | Hepatocellular | Vivas |
| TLR7 agonist (1V270) | IRE | Mouse | Pancreas | Narayanan | |
| TLR9 agonist (CpG-ODN) | Cryo | Mouse | Melanoma | den Brok | |
| TLR9 agonist (IMO-2125) | IRE | Human | Pancreas | Geboers | |
| TLR9 agonist (CpG B) | RFA | Rabbit | Hepatocellular | Behm | |
| STING agonist (c-di-GMP) | IRE | Mouse | Melanoma/Hepatocellular | Lasarte-Cia | |
| STING agonist (RR-CDA) | IRE | Mouse | Lung | Go | |
| Oncolytic viruses | Human Adenovirus Type 5 (rhAd5) | RFA | Human | Hepatocellular | Xie |
| Human HSV Type 1 (G47d) | RFA | Mouse | Neuroblastoma | Yamada | |
| Human HSV Type 1 (G47d) | RFA | Mouse | Hepatocellular | Yamada | |
| Alphavirus M1 | IRE | Mouse | Pancreas | Sun | |
| Biomaterials | IDOi-loaded nanoclusters | IRE | Mouse | Prostate | Yu |
| Carbon dots | MWA | Mouse | Hepatocellular | Zhou | |
| N-dihydrogalactochitosan (IP-001) | MWA | Mouse/Human | Various | Korbelik | |
| HLCaP nanoreactors | RFA | Mouse | Breast/Colon/HCC/Melanoma | Yang | |
| Thermogel + ROCK inhibitor | RFA | Mouse | Melanoma | Chen | |
| Cytokines | GM-CSF-BCG hydrogel | RFA | Mouse | Colon | Lemdani |
| GM-CSF microspheres | MWA | Mouse | Hepatocellular | Chen | |
| IL-2 microspheres | MWA | Mouse | Hepatocellular | Wu | |
| KS-IL2 | RFA | Mouse | Colon | Johnson | |
| IL-7/IL-15 | RFA | Mouse | Breast | Habibi | |
| Others | DC stimulant (OK432) | MWA | Mouse | Breast | Li |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senders, Z.J.; Martin, R.C.G., II. Intratumoral Immunotherapy and Tumor Ablation: A Local Approach with Broad Potential. Cancers 2022, 14, 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071754
Senders ZJ, Martin RCG II. Intratumoral Immunotherapy and Tumor Ablation: A Local Approach with Broad Potential. Cancers. 2022; 14(7):1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071754
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenders, Zachary J., and Robert C. G. Martin, II. 2022. "Intratumoral Immunotherapy and Tumor Ablation: A Local Approach with Broad Potential" Cancers 14, no. 7: 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071754
APA StyleSenders, Z. J., & Martin, R. C. G., II. (2022). Intratumoral Immunotherapy and Tumor Ablation: A Local Approach with Broad Potential. Cancers, 14(7), 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071754







