Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Technical Approaches of Gene-Expression Profiling
| First Author(s) | Year | GEP Method | No. of Cases | No. of Genes | No. of Genes in BLYM-777 | Clusters | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alizadeh, Elsen, et al. [7] | 2000 | Microarrays | 47 | 2984 | N.A. | COO | COO classified DLBCL into GCB or ABC with prognostic impact, possible benefit from different treatment options |
| Rosenwald, et al. [8] | 2002 | Microarrays | 240 | 100 | N.A. | GEP subgroups | COO classification into GCB and non-GCB (ABC and type 3), molecular predictor of survival after treatment |
| Monti, Savage, et al. [9] | 2005 | Microarrays | 176 | 2118 | 97 | Consensus clustering | Three identified DLBCL clusters; oxidative phosphorylation, BCR/proliferation or host response, no relation with survival |
| Lenz, et al. [10] | 2008 | Microarrays | 414 | 382 | 60 | Stromal signatures | Consensus clustering identified two stromal signatures predictive for survival and one GCB cluster |
| Alizadeh, Gentles, et al. [6] | 2011 | RT-qPCR | 787 | 2 | 2 | LMO2 and TNFRSF9 | Two survival-correlated biomarkers and associated with TME |
| Scott, et al. [11] | 2014 | NanoString | 119 | 20 | 20 | COO | Validation of COO classification into GCB or ABC, reflecting survival, possible benefit from different treatment options |
| Carey, et al. [12] | 2015 | NanoString | 55 | 200 | 33 | MYC high- and low-risk clusterss | Classification and stratification of MYC-driven, aggressive BCL |
| Dybkær, Bøgsted, et al. [13] | 2015 | Microarrays | 1139 | 223 | 37 | B-cell associated gene signature (BAGS) | Further discrimination of COO in centrocytes, centroblasts, plasmablasts, or memory B cells, with survival outcomes |
| Ciavarella, Vegliante, Fabbri, et al. [14] | 2018 | Publicly available GEP-data and NanoString | 482 | 45 | 45 | TME clusters | TME classification presenting high prevalence of myofibroblasts, dendritic cells, or CD4 T cells related to survival outcomes |
| Michaelsen, et al. [15] | 2018 | NanoString | 1058 | 128 | 53 | BAGS2Clinic(expanded BAGS) | Intensified BAGS classification in centrocytes, centroblasts, plasmablasts, or memory B cells, predictive for survival |
| Davies, et al. [16] | 2019 | Illumina HiSeq sequencing | 1076 | N.A. | N.A. | COO | Molecular characterization for prospective stratification, randomization and analysis of DLBCL subgroups |
| Ennishi, et al. [17] | 2019 | RNA-seq | 157 | 104 | 43 | DHITsig | Defined GEP signature high-grade B-cell lymphoma double or triple hit with BCL2 translocation |
| Staiger, Altenbuchinger, Ziepert, et al. [18] | 2020 | NanoString | 466 | 145 | 17 | Lymphoma-associated macrophage interaction signature (LAMIS) | Signature indicating the presence of macrophages and associated with poor survival |
| Tripodo, Zanardi, Ianelli, Mazzara, et al. [19] | 2020 | NanoString | 551 | 87 | 52 | Spatial dark- versus light-zone microenvironment signature | Distinguishing COO GCB subtype into dark or light zone with prognostic significance |
| Kotlov, et al. [20] | 2021 | Publicly available GEP-data | 4580 | 203 | 144 | Functional gene signatures and TME clusters | Four TME specific categories associated with survival and with opportunities for novel targeted treatment |
| Steen, et al. [21] | 2021 | Bulk/single-cell RNA sequencing | 1584 | 20380 | 192 | Cell states and ecotypes of the TME | Discrimination into cell types and cell states within the TME, correlated with survival, and facilitating development of new targeted treatment strategies |
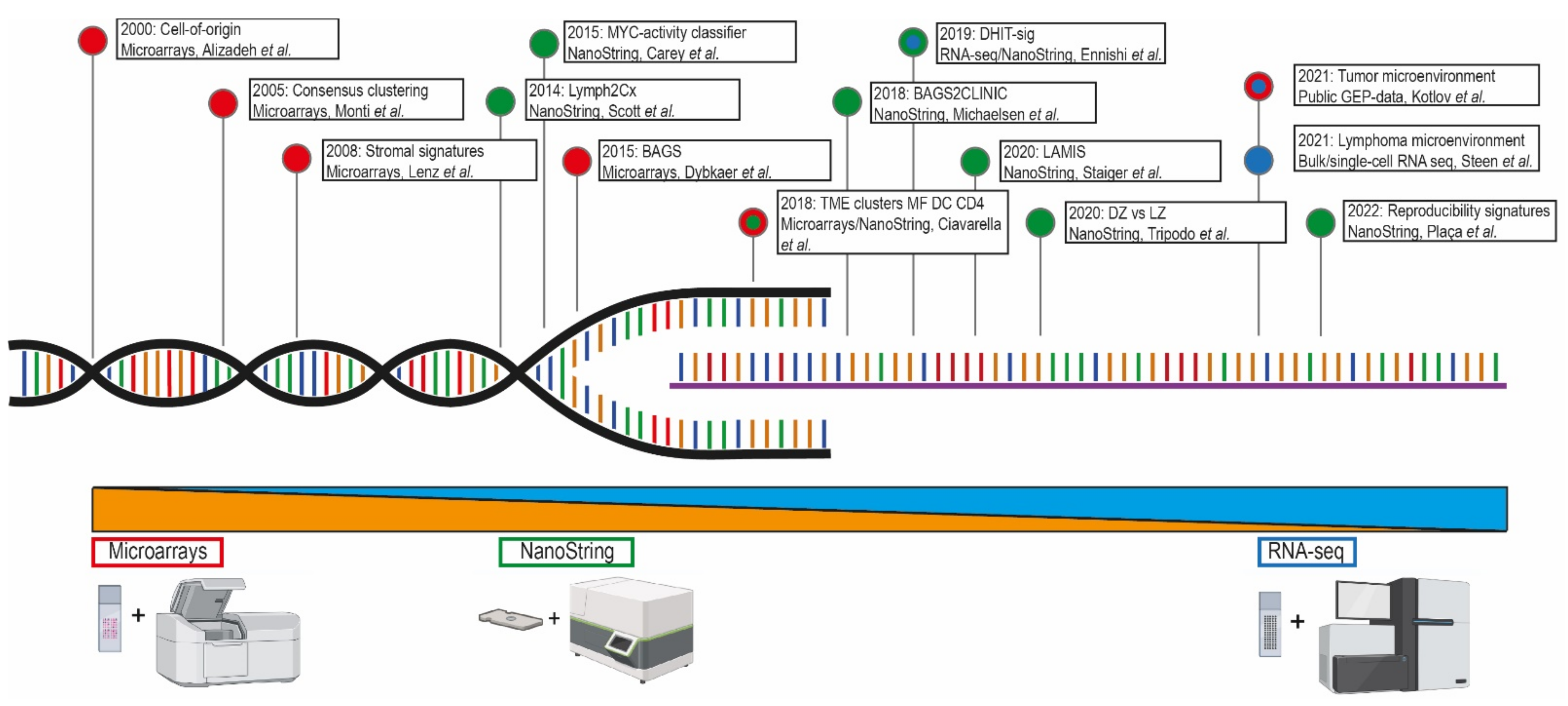
3. The Arrival of Gene-Expression Profiling
4. Integrating Gene-Expression Profiling and Mutational Profiles
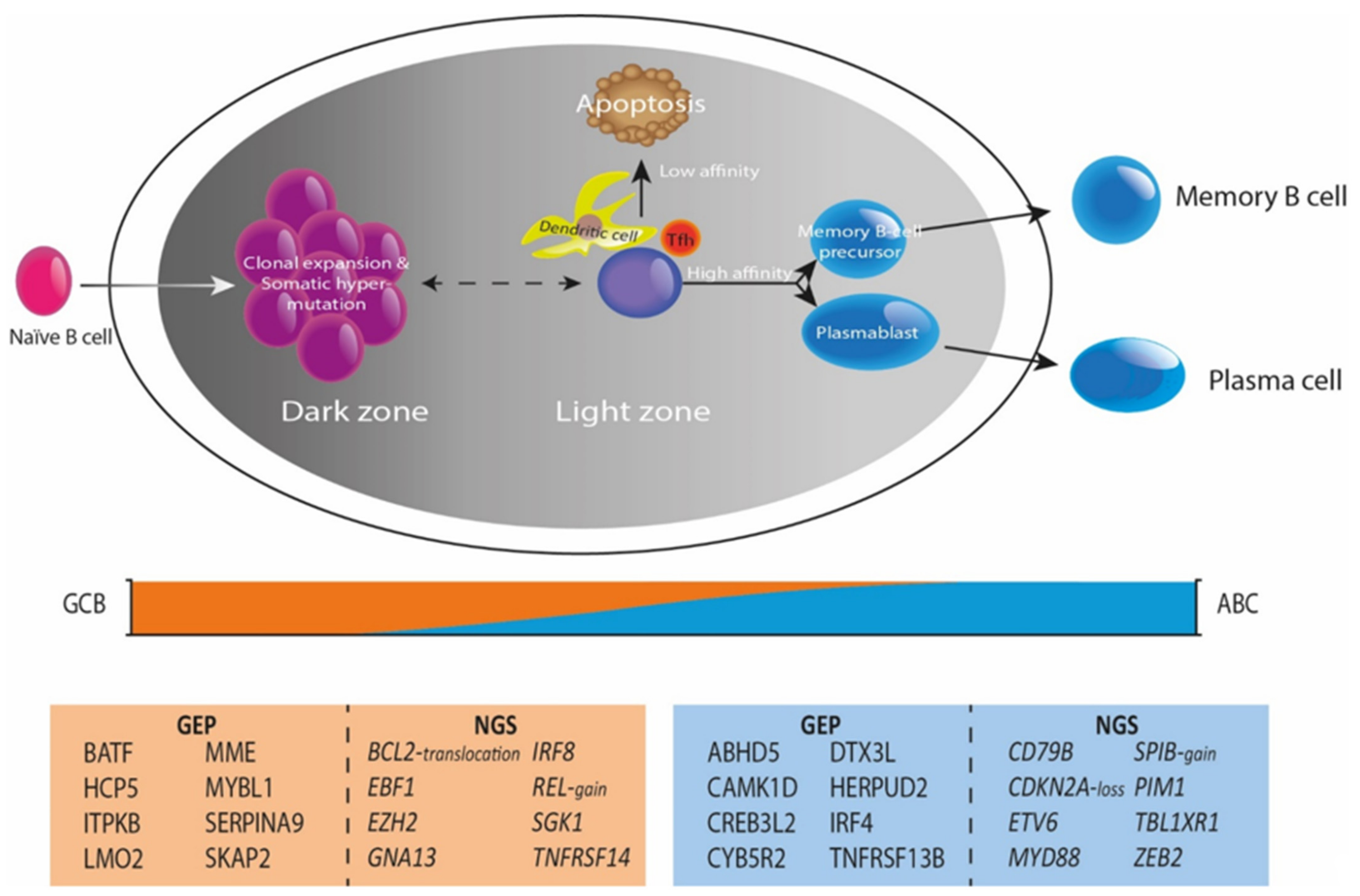
5. The Tumor Microenvironment as Defined by Gene-Expression Profiling
6. Clinical Impact and Future Perspectives of Gene-Expression Profiling Studies
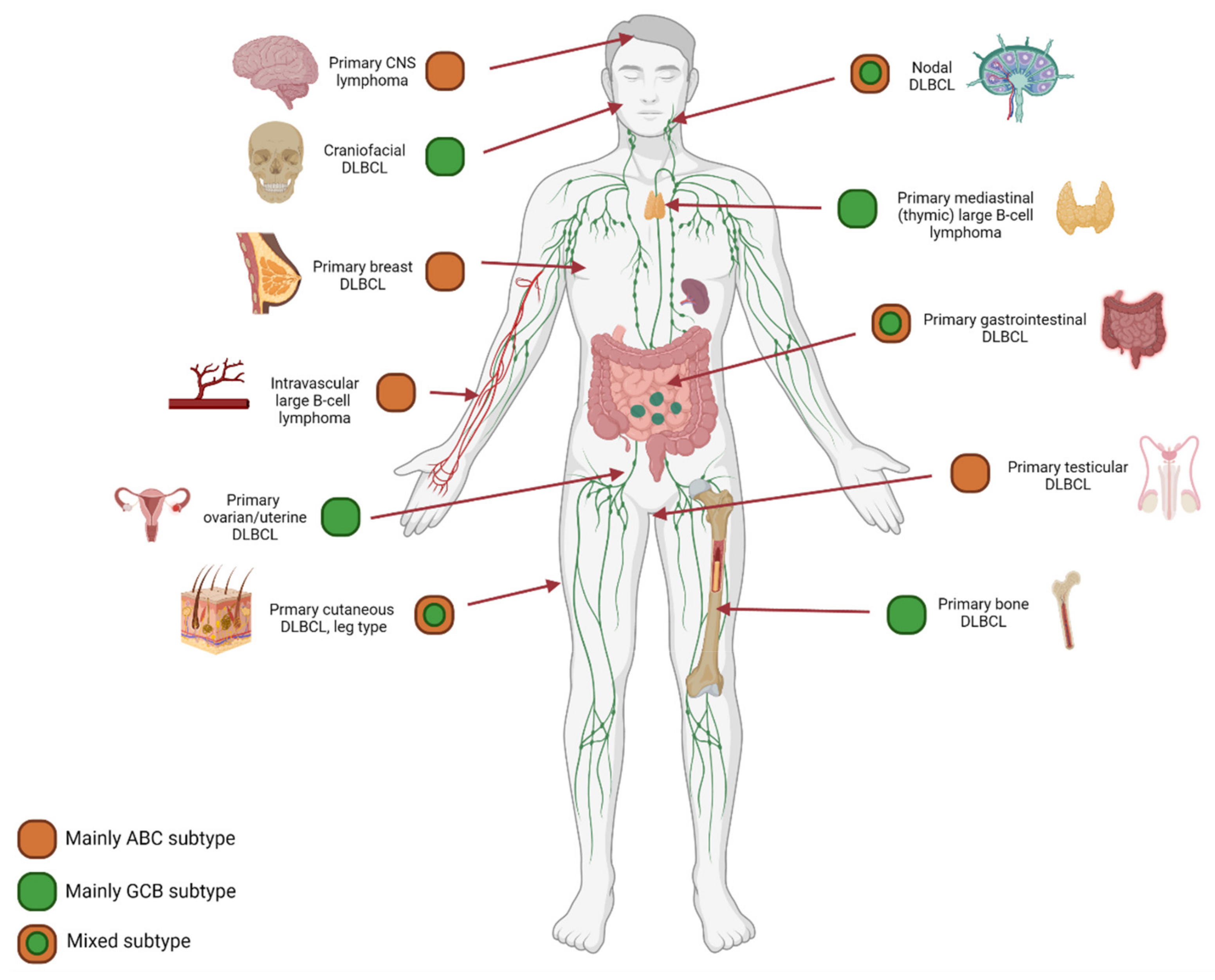
7. Anatomical Localization and Age Matter
8. A Proposal for a Consortium Gene-Expression Profiling Panel: BLYM-777
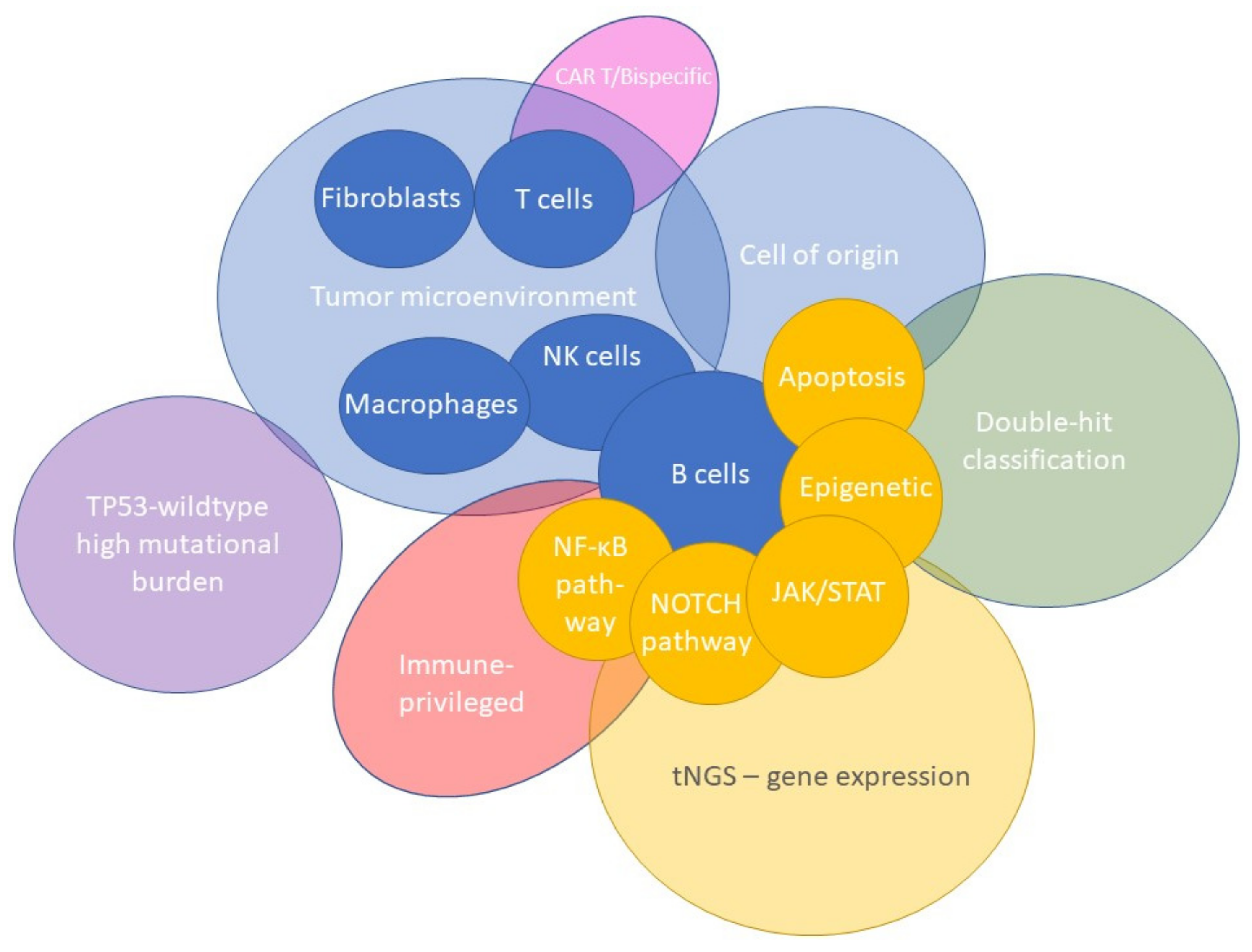
9. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ACTA2 | CKAP4 | HIST1H2BC | MPST | SBK1 |
| ACTB | CLCN1 | HLA-A | MRC1 | SCNN1D |
| ACTG1 | CLCN2 | HLA-B | MRC2 | SCOTIN |
| ACTG2 | CLU | HLA-C | MRPL15 | SAMD13 |
| ACTL7A | COL12A1 | HLA-DMA | MRPL3 | SELPLG |
| ADA | COL1A1 | HLA-DMB | MRPL33 | SEMA7A |
| ADHFE1 | COL1A2 | HLA-DPA1 | MRPS34 | SEP15 |
| AEBP1 | COL3A1 | HLA-DPB1 | MS4A1 | SERPINA1 |
| AEN | COL4A1 | HLA-DQA1 | MSH3 | SERPINA9 |
| AFMID | COL4A2 | HLA-DQB1 | MSR1 | SERPING1 |
| AGER | COL5A2 | HLA-DRA | MUC16 | SGK1 |
| AGR2 | COL6A3 | HLA-DRB1 | MXRA5 | SGPP2 |
| AHCY | COMMD8 | HLA-E | MYBBP1A | SH2D1A |
| AHR | COX7A2L | HMG20A | MYBL1 | SH2D1B |
| AICDA | CPD | HNRNPLL | MYBL2 | SH2D3C |
| AKAP1 | CPNE3 | HPDL | MYC | SH3PXD2A |
| AKAP5 | CPT1A | HRK | MYD88 | SHARPIN |
| AKR1D1 | CREB1 | HS3ST3A1 | NBR1 | SHISA8 |
| ALCAM | CREB3L2 | HSPBL2 | NCAM1 | SIGLEC9 |
| ALDH3B1 | CREBBP | HTR1A | NCR1 | SIK1 |
| ALOX5 | CSF1 | ICAM1 | NCR3 | SIPA1L3 |
| AMT | CSF1R | ICOS | NDUFB1 | SKAP2 |
| ANAPC16 | CTHRC1 | IDH1 | NEMF | SLAMF1 |
| ANGPT1 | CTLA4 | IDO1 | NFAM1 | SLAMF8 |
| ANGPT2 | CTNNA1 | IFITM1 | NFATC2 | SLC12A8 |
| ANO9 | CTNNB1 | IFNA16 | NFKB1 | SLC16A9 |
| ANTXR2 | CTPS1 | IFNAR1 | NFKB2 | SLC25A27 |
| AP1B1 | CTSB | IFNG | NFKBIE | SLC29A3 |
| APLP2 | CTSK | IGHM | NKG7 | SLC2A3 |
| APOL6 | CTSZ | IGLL3 | NME1 | SLC41A1 |
| APRIL | CX3CL1 | IGLL5 | NOD2 | SLFN5 |
| ARG1 | CX3CR1 | IGSF10 | NOLC1 | SMAD1 |
| ARHGAP17 | CXCL10 | IGSF6 | NOTCH3 | SMARCA5 |
| ARID1B | CXCL11 | IK | NPFF | SMIM14 |
| ARSI | CXCL12 | IKZF2 | NPFFR2 | SNHG19 |
| ASB13 | CXCL13 | IKZF4 | NR4A2 | SOCS1 |
| ASNSD1 | CXCL5 | IL10 | NRF1 | SOD1 |
| ASPH | CXCL8 | IL15 | NRN1L | SP3 |
| ATM | CXCL9 | IL16 | NSA2 | SPARC |
| ATP5D | CXCR2 | IL18BP | NSUN2 | SPEN |
| ATRAID | CXCR3 | IL1R1 | NSUN5 | SPI1 |
| AURKA | CXCR4 | IL2 | NTRK1 | SPIB |
| AURKB | CXCR5 | IL21 | OAZ1 | SPP1 |
| B2M | CYB5R2 | IL21R | OPA1 | SRM |
| BATF | DAB2 | IL22 | OR13A1 | SSBP3 |
| BATF3 | DBI | IL2RA | OR4D5 | STAM |
| BAX | DBP | IL2RB | OSBPL10 | STAP1 |
| BBC3 | DDX11 | IL4 | OSMR | STAT1 |
| BCAS4 | DDX21 | IL4I1 | OTULIN | STAT2 |
| BCL10 | DDX6 | IL6 | OXTR | STAT3 |
| BCL11B | DHRS2 | IL6R | P2RY12 | STAT6 |
| BCL2 | DHX33 | IL6ST | P2RY14 | STAU1 |
| BCL2A1 | DKK3 | IL7R | PABPC3 | STC2 |
| BCL2L1 | DNAJB12 | INHBA | PAICS | SULF1 |
| BCL2L12 | DPP8 | INPP5D | PALLD | SYBU |
| BCL6 | DPYSL3 | INSM2 | PAPSS2 | SYNE1 |
| BCL7A | DTX1 | IQCD | PARP1 | TADA2B |
| BCLAF1 | DTX3L | IRF1 | PARP3 | TAP1 |
| BGLAP | DUSP2 | IRF2BP2 | PATL2 | TAP2 |
| BGN | DUSP4 | IRF4 | PAX5 | TBL1XR1 |
| BID | DUSP5 | IRG1 | PAX8-AS1 | TBP |
| BIRC2 | E2F1 | IRS2 | PCDH9 | TBX21 |
| BIRC3 | EARS2 | ISY1 | PCLAF | TCIRG1 |
| BLK | EBER1 | ITGA6 | PCNP | TCL1A |
| BRAF | EBER2 | ITGB2 | PCOLCE | TCP10 |
| BSG | EBF1 | ITGB8 | PDCD1 | TEDC2 |
| BST1 | EBI3 | ITK | PDCD10 | TEK |
| BTBD3 | EBNA1BP2 | ITM2A | PDCD1LG2 | TESPA1 |
| BTC | EEPD1 | ITPKB | PDE5A | TET2 |
| BTG1 | EGFR | ITPR2 | PDGFC | TGFBI |
| BTG2 | EGR1 | JAK1 | PDGFRB | THBS2 |
| BUB1 | EGR3 | JAK2 | PDPN | THPO |
| C10orf128 | ELL2 | JAK3 | PDXDC1 | TIGIT |
| C14orf70 | EMCN | JAKMIP1 | PECAM1 | TIM3 |
| C16orf54 | EOMES | JAML | PEG10 | TIMP1 |
| C17orf56 | EP300 | JCHAIN | PERP | TIMP2 |
| C19orf24 | EPHA4 | KCNA4 | PGF | TIMP3 |
| C2 | ERCC2 | KCNH4 | PHB2 | TINAGL1 |
| C3AR1 | ERN1 | KCNU1 | PHF23 | TJP1 |
| C3orf22 | ESCO2 | KDR | PIK3CA | TLR8 |
| C3orf37 | ETFA | KI67 | PILRA | TMEM119 |
| CA9 | ETS1 | KIAA1128 | PIM1 | TMEM127 |
| CABP2 | ETV6 | KIAA1462 | PIM2 | TMEM135 |
| CACNA1I | EZH2 | KIF14 | PKA | TMEM140 |
| CACNA2D2 | EZR | KIR2DL4 | PLCG2 | TMEM175 |
| CADM4 | F8A3 | KIT | PLCH2 | TMEM202 |
| CALR | FABP5 | KLF2 | PLD3 | TMEM219 |
| CAMK1D | FADD | KLHL14 | PLK1 | TMEM224 |
| CAPS | FAM108C1 | KLHL6 | PLOD2 | TMEM30A |
| CARD10 | FAM117B | KLRC2 | PMP22 | TMEM47 |
| CARD11 | FAM13AOS | KLRF1 | PMPCB | TMEM97 |
| CARD14 | FAM153A | KLRK1 | PMS2P2 | TMSB4X |
| CARD9 | FAM216A | KMT2D | PMS2P9 | TNF |
| CASP10 | FAM26F | KRAS | POLD2 | TNFAIP3 |
| CASP8 | FAS | KRT73 | POLH | TNFRSF10B |
| CBLB | FASLG | LAG3 | POLR1B | TNFRSF13B |
| CCDC154 | FASN | LAMB1 | POSTN | TNFRSF13C |
| CCDC50 | FAT4 | LAMP1 | POTEC | TNFRSF14 |
| CCDC6 | FBL | LDHB | POU6F1 | TNFRSF17 |
| CCL20 | FBLN2 | LGALS7 | PPAT | TNFRSF18 |
| CCL4 | FBLN7 | LGALS9 | PPP1R3B | TNFRSF1A |
| CCL5 | FBXW7 | LIMD1 | PPRC1 | TNFRSF1B |
| CCNB1 | FCER1G | LINC01215 | PRDM1 | TNFRSF4 |
| CCND1 | FCGR1B | LMO2 | PRDX5 | TNFRSF9 |
| CCND2 | FCRL5 | LOC100128071 | PRKCH | TNFSF13B |
| CCND3 | FDCSP | LOC100128682 | PRKCQ | TNFSF8 |
| CCNE1 | FEM1C | LOC100131225 | PRMT1 | TOX |
| CCR6 | FGD5 | LOC100131354 | PRNP | TP53 |
| CCR8 | FGFBP2 | LOC100287094 | PSAT1 | TPO |
| CD11C | FIBP | LOC100287259 | PSEN1 | TPT1 |
| CD160 | FLJ37307 | LOC100287308 | PSIMCT.1 | TRAC |
| CD163 | FLJ37786 | LOC100288639 | PSMA2 | TRAF1 |
| CD19 | FLT1 | LOC100288728 | PSMA5 | TRAF2 |
| CD2 | FN1 | LOC100289566 | PSMA6 | TRAP1 |
| CD20 | FNDC1 | LOC196415 | PSMB10 | TRAT1 |
| CD22 | FNDC3B | LOC284889 | PSMB9 | TRBC1 |
| CD226 | FOXJ3 | LOC391358 | PSMD14 | TRIAL-R1 |
| CD24 | FOXP1 | LOC401433 | PSMD3 | TRIM21 |
| CD244 | FOXP3 | LOC440311 | PTEN | TRIM56 |
| CD274 | FSTL1 | LOC729535 | PTGES2 | TRRAP |
| CD276 | FYB | LRP12 | PTPN11 | TSKU |
| CD28 | FYN | LRP1B | PTPN13 | TSPAN9 |
| CD300LF | GABRB1 | LRP8 | PTPRC | TTC8 |
| CD37 | GAMT | LSM1 | PTTG1IP | UBA1 |
| CD39 | GATA2 | LTB | QRSL1 | UBASH3A |
| CD3D | GATA3 | LTBR | R3HDM1 | UBE2D2 |
| CD3E | GATAD2B | LUM | RAB27A | UBXN4 |
| CD3G | GBP1 | LY6E | RAB29 | UBXN7 |
| CD4 | GBP5 | LY75 | RAB33A | UCHL3 |
| CD40 | GDF2 | LYAR | RAB3GAP2 | UCK2 |
| CD40LG | GEMIN4 | MAF | RAB7A | VASP |
| CD44 | GIT2 | MAFB | RABEPK | VCAM1 |
| CD47 | GLRX | MAG | RAD54L | VEGFA |
| CD58 | GNA13 | MALT1 | RAG2 | VEGFB |
| CD6 | GNAI2 | MAML3 | RANBP1 | VEGFC |
| CD68 | GNG12 | MAP2 | RASA1 | VISTA |
| CD70 | GNLY | MAP2K2 | RASGRF1 | VPS24 |
| CD79A | GOT2 | MAP4K1 | RASL11A | VRK3 |
| CD79B | GPNMB | MARCKSL1 | RBL2 | VTN |
| CD80 | GPR124 | MCL1 | RBPJL | VWF |
| CD81 | GPR137B | MCM2 | REL | WAC |
| CD83 | GPRIN3 | MCM6 | RELA | WASH2P |
| CD84 | GRHPR | MDFIC | RELB | WASL |
| CD8A | GRIN3A | MDM2 | RFC3 | WDR3 |
| CDC25A | GRN | MED23 | RFFL | WDR55 |
| CDCA7L | GSK3B | MEF2B | RGCC | XBP1 |
| CDH23 | GUK1 | MEX3C | RNF130 | XRCC3 |
| CDH5 | GZMB | MFAP2 | RNF213 | XRCC5 |
| CDK2 | GZMH | MFGE8 | ROCK1 | ZBTB4 |
| CDK4 | HDAC1 | MIF | RPLP0 | ZEB2 |
| CDK5R1 | HERPUD2 | MIR155HG | RRS1 | ZFAND4 |
| CDKN2A | HIF1A | MME | RUBCNL | ZNF22 |
| CDKN2B | HIST1H1C | MMP14 | RUNX3 | ZNF438 |
| CETN3 | HIST1H1D | MMP2 | S100A11 | |
| CFLAR | HIST1H1E | MMP9 | S100Z | |
| CIITA | HIST1H2AC | MPEG1 | S1PR2 |
References
- Ernst, M.; Oeser, A.; Besiroglu, B.; Caro-Valenzuela, J.; Abd El Aziz, M.; Monsef, I.; Borchmann, P.; Estcourt, L.J.; Skoetz, N.; Goldkuhle, M. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for people with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 9, Cd013365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K. Treatment of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2016, 56, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.B.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppa, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Gentles, A.J.; Alencar, A.J.; Liu, C.L.; Kohrt, H.E.; Houot, R.; Goldstein, M.J.; Zhao, S.; Natkunam, Y.; Advani, R.H.; et al. Prediction of survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on the expression of 2 genes reflecting tumor and microenvironment. Blood 2011, 118, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; Campo, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Smeland, E.B.; Giltnane, J.M.; et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.; Savage, K.J.; Kutok, J.L.; Feuerhake, F.; Kurtin, P.; Mihm, M.; Wu, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Neuberg, D.; Aguiar, R.C.; et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.W.; Wright, G.W.; Williams, P.M.; Lih, C.J.; Walsh, W.; Jaffe, E.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 2014, 123, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, C.D.; Gusenleitner, D.; Chapuy, B.; Kovach, A.E.; Kluk, M.J.; Sun, H.H.; Crossland, R.E.; Bacon, C.M.; Rand, V.; Dal Cin, P.; et al. Molecular classification of MYC-driven B-cell lymphomas by targeted gene expression profiling of fixed biopsy specimens. J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dybkaer, K.; Bogsted, M.; Falgreen, S.; Bodker, J.S.; Kjeldsen, M.K.; Schmitz, A.; Bilgrau, A.E.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Bergkvist, K.S.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma classification system that associates normal B-cell subset phenotypes with prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciavarella, S.; Vegliante, M.C.; Fabbri, M.; De Summa, S.; Melle, F.; Motta, G.; De Iuliis, V.; Opinto, G.; Enjuanes, A.; Rega, S.; et al. Dissection of DLBCL microenvironment provides a gene expression-based predictor of survival applicable to formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaelsen, T.Y.; Richter, J.; Brondum, R.F.; Klapper, W.; Johnsen, H.E.; Albertsen, M.; Dybkaer, K.; Bogsted, M. A B-cell-associated gene signature classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by NanoString technology. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Cummin, T.E.; Barrans, S.; Maishman, T.; Mamot, C.; Novak, U.; Caddy, J.; Stanton, L.; Kazmi-Stokes, S.; McMillan, A.; et al. Gene-expression profiling of bortezomib added to standard chemoimmunotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (REMoDL-B): An open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, A.M.; Altenbuchinger, M.; Ziepert, M.; Kohler, C.; Horn, H.; Huttner, M.; Huttl, K.S.; Glehr, G.; Klapper, W.; Szczepanowski, M.; et al. A novel lymphoma-associated macrophage interaction signature (LAMIS) provides robust risk prognostication in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma clinical trial cohorts of the DSHNHL. Leukemia 2020, 34, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodo, C.; Zanardi, F.; Iannelli, F.; Mazzara, S.; Vegliante, M.; Morello, G.; Di Napoli, A.; Mangogna, A.; Facchetti, F.; Sangaletti, S.; et al. A Spatially Resolved Dark- versus Light-Zone Microenvironment Signature Subdivides Germinal Center-Related Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas. iScience 2020, 23, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlov, N.; Bagaev, A.; Revuelta, M.V.; Phillip, J.M.; Cacciapuoti, M.T.; Antysheva, Z.; Svekolkin, V.; Tikhonova, E.; Miheecheva, N.; Kuzkina, N.; et al. Clinical and Biological Subtypes of B-cell Lymphoma Revealed by Microenvironmental Signatures. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1468–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, C.B.; Luca, B.A.; Esfahani, M.S.; Azizi, A.; Sworder, B.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Kurtz, D.M.; Liu, C.L.; Khameneh, F.; Advani, R.H.; et al. The landscape of tumor cell states and ecosystems in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1422–1437.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narrandes, S.; Xu, W. Gene Expression Detection Assay for Cancer Clinical Use. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2249–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, R.; Michal, J.J.; Zhang, S.; Dodson, M.V.; Zhang, Z.; Harland, R.M. Whole transcriptome analysis with sequencing: Methods, challenges and potential solutions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3425–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.N.; Fu, K.; Greiner, T.; Smith, L.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Braziel, R.; Campo, E.; et al. The stromal cell marker SPARC predicts for survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 135, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keane, C.; Gill, D.; Vari, F.; Cross, D.; Griffiths, L.; Gandhi, M. CD4+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic and independent of R-IPI in patients with DLBCL receiving R-CHOP chemo-immunotherapy. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdou, A.G.; Asaad, N.; Kandil, M.; Shabaan, M.; Shams, A. Significance of stromal-1 and stromal-2 signatures and biologic prognostic model in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Nagel, I.; Siebert, R.; Roschke, A.V.; Sanger, W.; Wright, G.W.; Dave, S.S.; Tan, B.; Zhao, H.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. Aberrant immunoglobulin class switch recombination and switch translocations in activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roider, T.; Seufert, J.; Uvarovskii, A.; Frauhammer, F.; Bordas, M.; Abedpour, N.; Stolarczyk, M.; Mallm, J.P.; Herbst, S.A.; Bruch, P.M.; et al. Dissecting intratumour heterogeneity of nodal B-cell lymphomas at the transcriptional, genetic and drug-response levels. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaça, J.R.; Diepstra, A.; Los, T.; Mendeville, M.; Seitz, A.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Zijlstra, J.; Lam, K.; da Silva, W.A., Jr.; Ylstra, B.; et al. Reproducibility of Gene Expression Signatures in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Burggraaff, C.N.; Nijland, M.; Bakunina, K.; Mous, R.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Dierickx, D.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Vermaat, J.S.P.; Marijt, E.A.F.; et al. Treatment of patients with MYC rearrangement positive large B-cell lymphoma with R-CHOP plus lenalidomide: Results of a multicenter HOVON phase II trial. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Polak, P.; Kryukov, G.V.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Carter, S.L.; Stewart, C.; Mermel, C.H.; Roberts, S.A.; et al. Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature 2013, 499, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küppers, R.; Rajewsky, K.; Hansmann, M.L. Diffuse large cell lymphomas are derived from mature B cells carrying V region genes with a high load of somatic mutation and evidence of selection for antibody expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Børresen-Dale, A.L.; et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trabucco, S.E.; Sokol, E.S.; Maund, S.L.; Moore, J.A.; Frampton, G.M.; Albacker, L.A.; Oestergaard, M.Z.; Venstrom, J.; Sehn, L.H.; Bolen, C.R. Prediction and characterization of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell-of-origin subtypes using targeted sequencing. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 4171–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, K.; Enjuanes, A.; Dlouhy, I.; Jares, P.; Martin-Garcia, D.; Nadeu, F.; Ordonez, G.R.; Rovira, J.; Clot, G.; Royo, C.; et al. Integrating genomic alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies new relevant pathways and potential therapeutic targets. Leukemia 2018, 32, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Schmitz, R. Molecular Subgroups of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Biology and Implications for Clinical Practice. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Guan, Y.Q.; Shen, K.F.; Zhang, M.L.; Cai, H.D.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Cao, Y.; et al. Novel bioinformatic classification system for genetic signatures identification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Alarcon Tomas, A.; Fein, J.A.; Flynn, J.R.; Markovits, E.; Mayer, S.; Olaide Afuye, A.; Alperovich, A.; Anagnostou, T.; Besser, M.J.; et al. Impact of TP53 Genomic Alterations in Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With CD19-Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 40, jco2102143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcelis, L.; Antoranz, A.; Delsupehe, A.M.; Biesemans, P.; Ferreiro, J.F.; Debackere, K.; Vandenberghe, P.; Verhoef, G.; Gheysens, O.; Cattoretti, G.; et al. In-depth characterization of the tumor microenvironment in central nervous system lymphoma reveals implications for immune-checkpoint therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, C.; Vari, F.; Hertzberg, M.; Cao, K.A.; Green, M.R.; Han, E.; Seymour, J.F.; Hicks, R.J.; Gill, D.; Crooks, P.; et al. Ratios of T-cell immune effectors and checkpoint molecules as prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A population-based study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e445–e455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, H.P.; Ezell, S.A.; Schweighofer, K.J.; Cheung, L.W.K.; Hsieh, S.; Apatira, M.; Sirisawad, M.; Eckert, K.; Hsu, S.J.; Chen, C.T.; et al. Combination of Ibrutinib and ABT-199 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Follicular Lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Chiappella, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Scott, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Jurczak, W.; Özcan, M.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Jin, J.; et al. ROBUST: A Phase III Study of Lenalidomide Plus R-CHOP Versus Placebo Plus R-CHOP in Previously Untreated Patients With ABC-Type Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Sehn, L.H.; Johnson, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Patti, C.; Belada, D.; Samoilova, O.; Suh, C.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Ibrutinib and Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone in Non-Germinal Center B-Cell Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Sonneveld, P.; Schuster, M.W.; Irwin, D.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Facon, T.; Harousseau, J.L.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Lonial, S.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Bortezomib or high-dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robak, T.; Huang, H.; Jin, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, T.; Samoilova, O.; Pylypenko, H.; Verhoef, G.; Siritanaratkul, N.; Osmanov, E.; et al. Bortezomib-based therapy for newly diagnosed mantle-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, W.H.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Hodkinson, B.; Balasubramanian, S.; Fan, Y.; Vermeulen, J.; Shreeve, M.; Staudt, L.M. Effect of ibrutinib with R-CHOP chemotherapy in genetic subtypes of DLBCL. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1643–1653.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartert, K.T.; Wenzl, K.; Krull, J.E.; Manske, M.; Sarangi, V.; Asmann, Y.; Larson, M.C.; Maurer, M.J.; Slager, S.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Targeting of inflammatory pathways with R2CHOP in high-risk DLBCL. Leukemia 2021, 35, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morschhauser, F.; Feugier, P.; Flinn, I.W.; Gasiorowski, R.; Greil, R.; Illés, Á.; Johnson, N.A.; Larouche, J.F.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Patti, C.; et al. A phase 2 study of venetoclax plus R-CHOP as first-line treatment for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccaro, N.; Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Perrone, T.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine? Cancers 2020, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morin, R.D.; Arthur, S.E.; Hodson, D.J. Molecular profiling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Why so many types of subtypes? Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 196, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfò, I.; Maus, M.V. Current approaches to increase CAR T cell potency in solid tumors: Targeting the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van de Donk, N.; Themeli, M.; Usmani, S.Z. Determinants of response and mechanisms of resistance of CAR T-cell therapy in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Lacey, S.F.; Orlando, E.J.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Gohil, M.; Lundh, S.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Wang, Y.; O’Connor, R.S.; Hwang, W.T.; et al. Determinants of response and resistance to CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viardot, A.; Goebeler, M.E.; Hess, G.; Neumann, S.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Adrian, N.; Zettl, F.; Libicher, M.; Sayehli, C.; Stieglmaier, J.; et al. Phase 2 study of the bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) antibody blinatumomab in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 127, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.; Morschhauser, F.; Iacoboni, G.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Offner, F.C.; Sureda, A.; Salles, G.; Martínez-Lopez, J.; Crump, M.; Thomas, D.N.; et al. Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, X.U.; Montes de Jesus, F.M.; Glaudemans, A.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Jorritsma-Smit, A.; Plattel, W.J.; van Meerten, T.; Diepstra, A.; van den Berg, A.; Kwee, T.C.; et al. Molecular imaging in lymphoma beyond (18)F-FDG-PET: Understanding the biology and its implications for diagnostics and therapy. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e479–e489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijsselsteijn, M.E.; van der Breggen, R.; Farina Sarasqueta, A.; Koning, F.; de Miranda, N. A 40-Marker Panel for High Dimensional Characterization of Cancer Immune Microenvironments by Imaging Mass Cytometry. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, E.W.; Cheng, Y. Mass cytometry: Blessed with the curse of dimensionality. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, D.R.; Baranov, V.I.; Ornatsky, O.I.; Antonov, A.; Kinach, R.; Lou, X.; Pavlov, S.; Vorobiev, S.; Dick, J.E.; Tanner, S.D. Mass cytometry: Technique for real time single cell multitarget immunoassay based on inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6813–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijland, M.; Seitz, A.; Terpstra, M.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Kluin, P.M.; van Meerten, T.; Atayar, Ç.; van Kempen, L.C.; Diepstra, A.; Kok, K.; et al. Mutational Evolution in Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albitar, M.; Zhang, H.; Goy, A.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Bhagat, G.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Fang, X.; Zhu, F.; Dybkaer, K.; et al. Determining clinical course of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using targeted transcriptome and machine learning algorithms. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, M.K.; Hoang, T.; Law, S.C.; Brosda, S.; O’Rourke, K.; Tobin, J.W.D.; Vari, F.; Murigneux, V.; Fink, L.; Gunawardana, J.; et al. EBV-associated primary CNS lymphoma occurring after immunosuppression is a distinct immunobiological entity. Blood 2021, 137, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groen, R.A.; van Eijk, R.; Boehringer, S.; van Wezel, T.; Raghoo, R.; Ruano, D.; Jansen, P.M.; Briaire-de Bruijn, I.; de Groot, F.A.; Kleiverda, K.; et al. Frequent mutated B2M, EZH2, IRF8, and TNFRSF14 in primary bone diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reflect a GCB phenotype. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3760–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.S.; Somers, S.F.; de Wreede, L.C.; Kraan, W.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Schrader, A.M.R.; Kerver, E.D.; Scheepstra, C.G.; Berenschot, H.; Deenik, W.; et al. MYD88 mutations identify a molecular subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with an unfavorable prognosis. Haematologica 2020, 105, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; Jansen, P.M.; Willemze, R.; Vermeer, M.H.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; Somers, S.F.; Veelken, H.; van Eijk, R.; Kraan, W.; Kersten, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kersten, M.J.; Kraan, W.; Doorduijn, J.; Bromberg, J.; Lam, K.; Kluin, P.M.; van der Holt, B.J.; Spaargaren, M.; Pals, S.T. Diffuse large B cell lymphomas relapsing in the CNS lack oncogenic MYD88 and CD79B mutations. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraan, W.; van Keimpema, M.; Horlings, H.M.; Schilder-Tol, E.J.; Oud, M.E.; Noorduyn, L.A.; Kluin, P.M.; Kersten, M.J.; Spaargaren, M.; Pals, S.T. High prevalence of oncogenic MYD88 and CD79B mutations in primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Willemze, R.; Jansen, P.M.; Quint, K.D.; van Wezel, T.; van Eijk, R.; Ruano, D.; Tensen, C.P.; Hauben, E.; et al. Cell-of-origin classification using the Hans and Lymph2Cx algorithms in primary cutaneous large B-cell lymphomas. Virchows Arch. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Xu, P.P.; Wang, N.; Yi, H.M.; Dong, L.; Fu, D.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Janin, A.; Cheng, S.; et al. Influence of oncogenic mutations and tumor microenvironment alterations on extranodal invasion in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelaria, M.; Oñate-Ocaña, L.F.; Corona-Herrera, J.; Barrera-Carmona, C.; Ponce-Martínez, M.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, O.; Avilés-Salas, A.; Cacho-Díaz, B. Clinical characteristics of primary extranodal versus nodal diffuse large b-cell lymphoma: A retrospective cohort study in a cancer center. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2019, 71, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Mottok, A.; Wright, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Ott, G.; Ramsower, C.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Delabie, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Song, J.Y.; et al. Molecular classification of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma using routinely available tissue specimens. Blood 2018, 132, 2401–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klapper, W.; Kreuz, M.; Kohler, C.W.; Burkhardt, B.; Szczepanowski, M.; Salaverria, I.; Hummel, M.; Loeffler, M.; Pellissery, S.; Woessmann, W.; et al. Patient age at diagnosis is associated with the molecular characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2012, 119, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilenko, D.A.; Shchukina, I.; Artyomov, M.N. Immune ageing at single-cell resolution. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.S.; Pals, S.T.; Younes, A.; Dreyling, M.; Federico, M.; Aurer, I.; Radford, J.; Kersten, M.J.; Eha Lymphoma Group. Precision medicine in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Hitting the target. Haematologica 2015, 100, 989–993. [Google Scholar]
- You, H.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Wei, L.; Nunns, H.; Nagy, M.L.; Bhagat, G.; Fang, X.; Zhu, F.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Genomic complexity is associated with epigenetic regulator mutations and poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1928365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, M.; Alexsson, A.; Sundstrom, C.; Ladenvall, C.; Mansouri, L.; Lindskog, C.; Berglund, M.; Cavelier, L.; Enblad, G.; Hollander, P.; et al. PD-L1 and IDO1 are potential targets for treatment in patients with primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the CNS. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J. Understanding the Mechanisms of Resistance to CAR T-Cell Therapy in Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croci, G.A.; Au-Yeung, R.K.H.; Reinke, S.; Staiger, A.M.; Koch, K.; Oschlies, I.; Richter, J.; Poeschel, V.; Held, G.; Loeffler, M.; et al. SPARC-positive macrophages are the superior prognostic factor in the microenvironment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and independent of MYC rearrangement and double-/triple-hit status. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durek, P.; Nordstrom, K.; Gasparoni, G.; Salhab, A.; Kressler, C.; de Almeida, M.; Bassler, K.; Ulas, T.; Schmidt, F.; Xiong, J.; et al. Epigenomic Profiling of Human CD4(+) T Cells Supports a Linear Differentiation Model and Highlights Molecular Regulators of Memory Development. Immunity 2016, 45, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gennert, D.G.; Lynn, R.C.; Granja, J.M.; Weber, E.W.; Mumbach, M.R.; Zhao, Y.; Duren, Z.; Sotillo, E.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Wong, W.H.; et al. Dynamic chromatin regulatory landscape of human CAR T cell exhaustion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104758118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, J.; Ruella, M.; Houot, R. Born to survive: How cancer cells resist CAR T cell therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leveille, E.; Johnson, N.A. Genetic Events Inhibiting Apoptosis in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfroi, B.; De Grandis, M.; Moreaux, J.; Tabruyn, S.; Mayol, J.F.; Quintero, M.; Righini, C.; Sturm, N.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Huard, B. The microenvironment of DLBCL is characterized by noncanonical macrophages recruited by tumor-derived CCL5. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4338–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chai, J.; Wang, K.; Jia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, K.; Zhao, D.; Ma, J.; et al. Tumor Immune Microenvironment Components and Checkpoint Molecules in Anaplastic Variant of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 638154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Groot, F.A.; de Groen, R.A.L.; van den Berg, A.; Jansen, P.M.; Lam, K.H.; Mutsaers, P.G.N.J.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Stevens, W.B.C.; Plaça, J.R.; et al. Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081857
de Groot FA, de Groen RAL, van den Berg A, Jansen PM, Lam KH, Mutsaers PGNJ, van Noesel CJM, Chamuleau MED, Stevens WBC, Plaça JR, et al. Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach. Cancers. 2022; 14(8):1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081857
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Groot, Fleur A., Ruben A. L. de Groen, Anke van den Berg, Patty M. Jansen, King H. Lam, Pim G. N. J. Mutsaers, Carel J. M. van Noesel, Martine E. D. Chamuleau, Wendy B. C. Stevens, Jessica R. Plaça, and et al. 2022. "Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach" Cancers 14, no. 8: 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081857
APA Stylede Groot, F. A., de Groen, R. A. L., van den Berg, A., Jansen, P. M., Lam, K. H., Mutsaers, P. G. N. J., van Noesel, C. J. M., Chamuleau, M. E. D., Stevens, W. B. C., Plaça, J. R., Mous, R., Kersten, M. J., van der Poel, M. M. W., Tousseyn, T., Woei-a-Jin, F. J. S. H., Diepstra, A., Nijland, M., & Vermaat, J. S. P. (2022). Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach. Cancers, 14(8), 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081857










