Early T-Cell Precursor ALL and Beyond: Immature and Ambiguous Lineage T-ALL Subsets
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Grey Zone of Immature Leukemias
1.2. Immature T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL)
2. ETP-ALL
2.1. Historical Perspective of Immune Markers and Gene Expression Profiles (GEPs)
2.2. Diagnosis
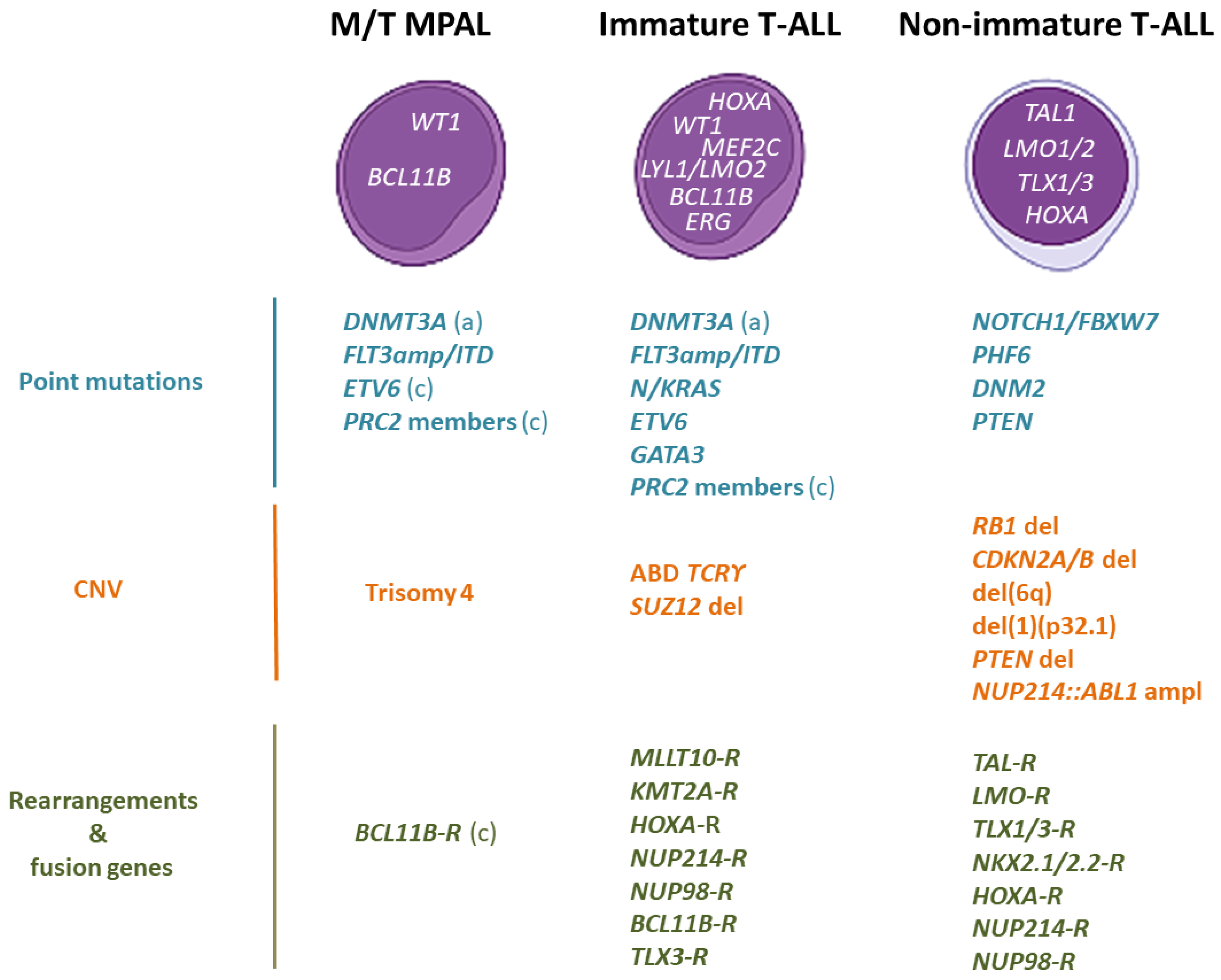
2.3. Genomic Characterization
2.3.1. Genomic Alterations That Cause HOXA Overexpression
| HOXA [10,30,47] | KMT2A [46,52] | MLLT10 [30,46,52] | NUP214 [10,46,52] | NUP98 [46] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mir181::HOXA | KMT2A::MLLT4 | PICALM::MLLT10 | SET::NUP214 | NUP98::RAP1GDS1 |
| TRB@::-HOXA | KMT2A::AFDN | DDX3X::MLLT10 | SQSTM1::NUP214 | NUP98::PSIP1 |
| CDK6::HOXA | KMT2A::ELL | HNRNPH1::MLLT10 | NUP98::DDX10 | |
| TRG@::HOXA | KMT2A::ENL | NAP1L1::-MLLT10 | NUP98::VRK1 | |
| TRAD@::HOXA | KMT2A::CBL | CAPS2::MLLT10 | NUP98::LNP1 | |
| KMT2A::MLLT1 | XPO1::MLLT10 | NUP98::CCDC28A | ||
| KMT2A::MLLT10 | ||||
| KMT2A::CT45A4 | ||||
| KMT2A::MLLT6 |
2.3.2. The BCL11B-a Entity
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Treatment
2.5.1. Frontline Treatment
FLAG-IDA as a Frontline Treatment
2.5.2. Cell-Immunotherapy: Allo-SCT
2.5.3. New Chemotherapy: Nelarabine
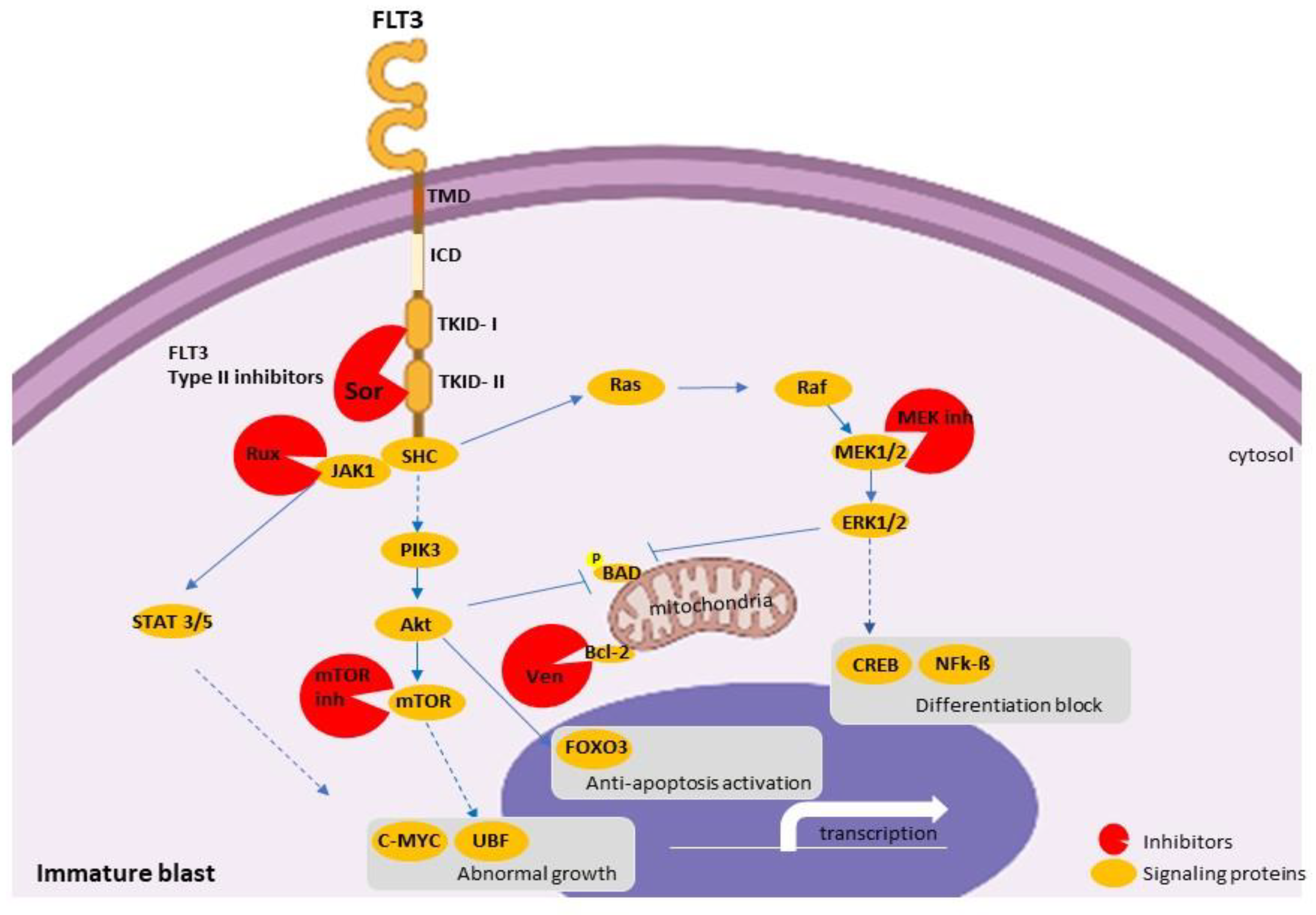
2.5.4. Target Therapy
Venetoclax: Monotherapy or in Combination
Ruxolitinib
FLT3 Inhibitors
3. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.-T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.G.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Proposals for the Classification of the Acute Leukaemias French-American-British (FAB) Co-operative Group. Br. J. Haematol. 1976, 33, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paietta, E. Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. Leukemia 1995, 9, 2147–2148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Catovsky, D.; Matutes, E. The classification of acute leukaemia. Leukemia 1992, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.-T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.G.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Proposal for the recognition of minimally differentiated acute myeloid leukaemia (AML-MO). Br. J. Haematol. 1991, 78, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpeshkar, V.; Bentley, D.J. Adrenergic-Β2 receptor polymorphism and athletic performance. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 55, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, T.B.; Gu, Z.; Iacobucci, I.; Dickerson, K.; Choi, J.K.; Xu, B.; Payne-Turner, D.; Yoshihara, H.; Loh, M.L.; Horan, J.; et al. The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia. Nature 2018, 562, 373–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lindern, M.; Breems, D.; Van Baal, S.; Adriaansen, H.; Grosveld, G. Characterization of the translocation breakpoint sequences of two DEK-CAN fusion genes present in t(6;9) acute myeloid leukemia and a SET-CAN fusion gene found in a case of acute undifferentiated leukemia. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 1992, 5, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, C.; Dastugue, N.; Cances-Lauwers, V.; Mozziconacci, M.J.; Prebet, T.; Vey, N.; Pigneux, A.; Lippert, E.; Visanica, S.; Legrand, F.; et al. PICALM-MLLT10 acute myeloid leukemia: A French cohort of 18 patients. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofrini, V.; Di Giacomo, D.; Mecucci, C. Nucleoporin genes in human diseases. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giacomo, D.; La Starza, R.; Gorello, P.; Pellanera, F.; Kalender Atak, Z.; De Keersmaecker, K.; Pierini, V.; Harrison, C.J.; Arniani, S.; Moretti, M.; et al. 14q32 rearrangements deregulating BCL11B mark a distinct subgroup of T-lymphoid and myeloid immature acute leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardelli, V.; Arniani, S.; Pierini, V.; Di Giacomo, D.; Pierini, T.; Gorello, P.; Mecucci, C.; La Starza, R. T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Biomarkers and their clinical usefulness. Genes 2021, 12, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.H.; Campana, D. New definition of remission in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2000, 14, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marks, D.I.; Rowntree, C. Management of adults with T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winter, S.S.; Dunsmore, K.P.; Devidas, M.; Wood, B.L.; Esiashvili, N.; Chen, Z.; Eisenberg, N.; Briegel, N.; Hayashi, R.J.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; et al. Improved survival for children and young adults with t-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results from the children’s oncology Group AALL0434 methotrexate randomization. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, K.; Jacobs, M.; Stock, W.; Wynne, J. New Approaches to Treating Challenging Subtypes of ALL in AYA Patients. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2020, 15, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnafi, V.; Bond, J.; Graux, C.; Lhermitte, L.; Lara, D.; Cluzeau, T.; Leguay, T.; Cieslak, A.; Trinquand, A.; Pastoret, C.; et al. Early response–based therapy stratification improves survival in adult early thymic precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A Group for research on adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, M.H.; Johnson, J.R.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Nelarabine (Arranon®) for the Treatment of T-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma. Oncologist 2008, 13, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchia, G.; Pastore, D.; Carluccio, P.; Liso, A.; Mestice, A.; Rizzi, R.; Ciuffreda, L.; Pietrantuono, G.; Liso, V. FLAG-IDA in the treatment of refractory/relapsed adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2005, 84, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Kowalczyk, J.; Schmitt, C.; Bielorai, B.; Russo, M.W.; Woessner, M.; Ranganathan, S.; Leverger, G. Safety and efficacy of nelarabine in children and young adults with relapsed or refractory T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia or T-lineage lymphoblastic lymphoma: Results of a phase 4 study. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garand, R.; Voisin, S.; Papin, S.; Praloran, V.; Lenormand, B.; Favre, M.; Philip, P.; Bernier, M.; Vanhaecke, D.; Falkenrodt, A.; et al. Characteristics of pro-T ALL subgroups: Comparison with late T-ALL. Leukemia 1993, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Coustan-Smith, E.; Mullighan, C.G.; Onciu, M.; Behm, F.G.; Raimondi, S.C.; Pei, D.; Cheng, C.; Su, X.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Basso, G.; et al. Early T-cell precursor leukaemia: A subtype of very high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inukai, T.; Kiyokawa, N.; Campana, D.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Kikuchi, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Koh, K.; Manabe, A.; Kumagai, M.; et al. Clinical significance of early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Results of the Tokyo Children’s Cancer Study Group Study L99-15. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Wang, X.; Tang, J.; Xue, H.; Chen, J.; Pan, C.; Jiang, H.; Shen, S. Early T-cell precursor leukemia: A subtype of high risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Med. China 2012, 6, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Lamb, A.V.; O’Brien, S.; Ravandi, F.; Konopleva, M.; Jabbour, E.; Zuo, Z.; Jorgensen, J.; Lin, P.; Pierce, S.; et al. Early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ETP-ALL/LBL) in adolescents and adults: A high-risk subtype. Blood 2016, 127, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genescà, E.; Morgades, M.; Montesinos, P.; Barba, P.; Gil, C.; Guàrdia, R.; Moreno, M.J.; Martínez-Carballeira, D.; García-Cadenas, I.; Vives, S.; et al. Unique clinico-biological, genetic and prognostic features of adult early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, E294–E297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, A.A.; Neuberg, D.S.; Staunton, J.; Loh, M.L.; Huard, C.; Raimondi, S.C.; Behm, F.G.; Pui, C.H.; Downing, J.R.; Gilliland, D.G.; et al. Gene expression signatures define novel oncogenic pathways in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soulier, J.; Clappier, E.; Cayuela, J.M.; Regnault, A.; García-Peydró, M.; Dombret, H.; Baruchel, A.; Toribio, M.L.; Sigaux, F. HOXA genes are included in genetic and biologic networks defining human acute T-cell leukemia (T-ALL). Blood 2005, 106, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Neuberg, D.S.; Zhang, J.; Grebliunaite, R.; Sanda, T.; Protopopov, A.; Tosello, V.; Kutok, J.; Larson, R.S.; et al. Absence of biallelic TCRγ deletion predicts early treatment failure in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3816–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuurbier, L.; Gutierrez, A.; Mullighan, C.G.; Canté-Barrett, K.; Gevaert, A.O.; De Rooi, J.; Li, Y.; Smits, W.K.; Buijs-Gladdines, J.G.C.A.M.; Sonneveld, E.; et al. Immature MEF2C-dysregulated T-cell leukemia patients have an early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia gene signature and typically have non-rearranged t-cell receptors. Haematologica 2014, 99, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Holmfeldt, L.; Wu, G.; Heatley, S.L.; Payne-Turner, D.; Easton, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Rusch, M.; et al. The genetic basis of early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2012, 481, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Easton, J.; Shao, Y.; Maciaszek, J.; Wang, Z.; Wilkinson, M.R.; McCastlain, K.; Edmonson, M.; Pounds, S.B.; Shi, L.; et al. The genomic landscape of pediatric and young adult T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morita, K.; Jain, N.; Kantarjian, H.; Takahashi, K.; Fang, H.; Konopleva, M.; El Hussein, S.; Wang, F.; Short, N.J.; Maiti, A.; et al. Outcome of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: Focus on near-ETP phenotype and differential impact of nelarabine. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, C.; Schwab, C.; Broux, M.; Geerdens, E.; Degryse, S.; Demeyer, S.; Lahortiga, I.; Elliott, A.; Chilton, L.; La Starza, R.; et al. Targeted sequencing identifies associations between IL7R-JAK mutations and epigenetic modulators in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genescà, E.; Lazarenkov, A.; Morgades, M.; Berbis, G.; Ruíz-Xivillé, N.; Gómez-Marzo, P.; Ribera, J.M.; Juncà, J.; González-Pérez, A.; Mercadal, S.; et al. Frequency and clinical impact of CDKN2A/ARF/CDKN2B gene deletions as assessed by in-depth genetic analyses in adult T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlierberghe, P.; Ambesi-Impiombato, A.; De Keersmaecker, K.; Hadler, M.; Paietta, E.; Tallman, M.S.; Rowe, J.M.; Forne, C.; Rue, M.; Ferrando, A.A. Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Heesch, S.; Schlee, C.; Schwartz, S.; Gökbuget, N.; Hoelzer, D.; Konstandin, N.P.; Ksienzyk, B.; Vosberg, S.; Graf, A.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in adult ETP-ALL reveals a high rate of DNMT3A mutations. Blood 2013, 121, 4749–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, V.; Haferlach, C.; Weissmann, S.; Roller, A.; Schindela, S.; Poetzinger, F.; Stadler, K.; Bellos, F.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; et al. The molecular profile of adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Mutations in RUNX1 and DNMT3A are associated with poor prognosis in T-ALL. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2013, 52, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gil, C.; Morgades, M.; Fuster-Tormo, F.; García-Chica, J.; Montesinos, P.; Torrent, A.; Diaz-Beyá, M.; Coll, R.; Ribera, J.; Zhao, R.; et al. Genomic Data Improves Prognostic Stratification in Adult T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Enrolled in Measurable Residual Disease-Oriented Trials. Blood 2021, 138, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiede, C.; Steudel, C.; Mohr, B.; Schaich, M.; Schäkel, U.; Platzbecker, U.; Wermke, M.; Bornhäuser, M.; Ritter, M.; Neubauer, A.; et al. Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: Association with FAB subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis. Blood 2002, 99, 4326–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kiyoi, H.; Nakano, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Kodera, Y.; Miyawaki, S.; Asou, N.; Kuriyama, K.; Yagasaki, F.; Shimazaki, C.; et al. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood 2001, 97, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, M.; Coskun, E.; Fransecky, L.; Mochmann, L.H.; Bartram, I.; Farhadi Sartangi, N.; Heesch, S.; Gökbuget, N.; Schwartz, S.; Brandts, C.; et al. FLT3 Mutations in Early T-Cell Precursor ALL Characterize a Stem Cell Like Leukemia and Imply the Clinical Use of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homminga, I.; Pieters, R.; Langerak, A.W.; de Rooi, J.J.; Stubbs, A.; Verstegen, M.; Vuerhard, M.; Buijs-Gladdines, J.; Kooi, C.; Klous, P.; et al. Integrated Transcript and Genome Analyses Reveal NKX2-1 and MEF2C as Potential Oncogenes in T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, E.; Neumann, M.; Schlee, C.; Liebertz, F.; Heesch, S.; Goekbuget, N.; Hoelzer, D.; Baldus, C.D. MicroRNA profiling reveals aberrant microRNA expression in adult ETP-ALL and functional studies implicate a role for miR-222 in acute leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belver, L.; Ferrando, A. The genetics and mechanisms of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.; Marchand, T.; Touzart, A.; Cieslak, A.; Trinquand, A.; Sutton, L.; Radford-Weiss, I.; Lhermitte, L.; Spicuglia, S.; Dombret, H.; et al. An early thymic precursor phenotype predicts outcome exclusively in HOXA-overexpressing adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A group for research in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia study. Haematologica 2016, 101, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, M.L.; Li, J.F.; Li, B.S.; Peng, L.J.; Dai, Y.T.; Cui, B.W.; Yan, T.Q.; Zhang, W.N.; et al. Identification of fusion genes and characterization of transcriptome features in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 115, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Starza, R.; Pierini, V.; Pierini, T.; Nofrini, V.; Matteucci, C.; Arniani, S.; Moretti, M.; Lema Fernandez, A.G.; Pellanera, F.; Di Giacomo, D.; et al. Design of a Comprehensive Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization Assay for Genetic Classification of T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauwelier, B.; Cavé, H.; Gervais, C.; Lessard, M.; Barin, C.; Perot, C.; Van den Akker, J.; Mugneret, F.; Charrin, C.; Pagès, M.P.; et al. Clinical, cytogenetic and molecular characteristics of 14 T-ALL patients carrying the TCRβ-HOXA rearrangement: A study of the Groupe Francophone de Cytogénétique Hématologique. Leukemia 2007, 21, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Noir, S.; Abdelali, R.B.; Lelorch, M.; Bergeron, J.; Sungalee, S.; Payet-Bornet, D.; Villarèse, P.; Petit, A.; Callens, C.; Lhermitte, L.; et al. Extensive molecular mapping of TCRα/δ- and TCRβ-involved Chromosomal translocations reveals distinct mechanisms of oncogene activation in T-ALL. Blood 2012, 120, 3298–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Abdelali, R.; Asnafi, V.; Petit, A.; Micol, J.B.; Callens, C.; Villarese, P.; Delabesse, E.; Reman, O.; Lepretre, S.; Cahn, J.Y.; et al. The prognosis of CALM-AF10-positive adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias depends on the stage of maturation arrest. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matlawska-Wasowska, K.; Kang, H.; Devidas, M.; Wen, J.; Harvey, R.C.; Nickl, C.K.; Ness, S.A.; Rusch, M.; Li, Y.; Onozawa, M.; et al. MLL rearrangements impact outcome in HOXA-deregulated T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1909–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steimlé, T.; Dourthe, M.E.; Alcantara, M.; Touzart, A.; Simonin, M.; Mondesir, J.; Lhermitte, L.; Bond, J.; Graux, C.; Grardel, N.; et al. Clinico-biological features of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with fusion proteins. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefiori, L.E.; Bendig, S.; Gu, Z.; Chen, X.; Pölönen, P.; Ma, X.; Murison, A.; Zeng, A.; Garcia-Prat, L.; Dickerson, K.; et al. Enhancer hijacking drives oncogenic bcl11b expression in lineage-ambiguous stem cell leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2846–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lux, S.; Blätte, T.J.; Gillissen, B.; Richter, A.; Cocciardi, S.; Skambraks, S.; Schwarz, K.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Döhner, H.; Döhner, K.; et al. Deregulated expression of circular RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.H.; Pei, D.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Onciu, M.; Campana, D.; Kun, L.E.; Jeha, S.; et al. Long-term results of st jude total therapy studies 11, 12, 13a, 13b, and 14 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrick, K.; Wade, R.; Goulden, N.; Mitchell, C.; Moorman, A.V.; Rowntree, C.; Jenkinson, S.; Hough, R.; Vora, A. Outcome for children and young people with Early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated on a contemporary protocol, UKALL 2003. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombret, H.; Cluzeau, T.; Huguet, F.; Boissel, N. Pediatric-like therapy for adults with ALL. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2014, 9, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, D.M.; Sayed, H.A.R.; Raslan, H.N.; Ali, A.M.; Zahran, A.; Al-Hayek, R.; Daama, S.A.; Al-Saber, A. Outcome and Clinical Significance of Immunophenotypic Markers Expressed in Different Treatment Protocols of Pediatric Patients with T-ALL in Developing Countries. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataller, A.; Garrote, M.; Oliver-Caldés, A.; López-Guerra, M.; Colomer, D.; Aymerich, M.; Camós, M.; Vega-García, N.; Díaz-Beyá, M.; Esteve, J. Early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukaemia: Response to FLAG-IDA and high-dose cytarabine with sorafenib after initial refractoriness. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conter, V.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Buldini, B.; Parasole, R.; Locatelli, F.; Colombini, A.; Rizzari, C.; Putti, M.C.; Barisone, E.; Nigro, L.L.; et al. Early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children treated in AIEOP centres with AIEOP-BFM protocols: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e80–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, J.E.; Saliba, R.M.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Ledesma, C.; Gaballa, S.; Poon, M.; Maziarz, R.T.; Champlin, R.E.; Hosing, C.; Kebriaei, P. Multi-center analysis of the effect of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia subtype and minimal residual disease on allogeneic stem cell transplantation outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzer, D.; Thiel, E.; Arnold, R.; Beck, J.; Beelen, D.W.; Bornhäuser, M.; Bunjes, D.; Ditz, D.; Dührsen, U.; Finke, J.; et al. Successful Subtype Oriented Treatment Strategies in Adult T-All; Results of 744 Patients Treated in Three Consecutive GMALL Studies. Blood 2009, 114, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebel, S.; Marks, D.I.; Boissel, N.; Baron, F.; Chiaretti, S.; Ciceri, F.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Doubek, M.; Esteve, J.; Fielding, A.; et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission: A position statement of the European Working Group for Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (EWALL) and the Acute Leuke. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Advani, A.S.; Hanna, R. The treatment of adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, E.; Dufour, C.; Mohty, M.; Kröger, N. (Eds.) The EBMT Handbook: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; p. 702. ISBN 9783030022785. [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmore, K.P.; Devidas, M.; Linda, S.B.; Borowitz, M.J.; Winick, N.; Hunger, S.P.; Carroll, W.L.; Camitta, B.M. Pilot study of nelarabine in combination with intensive chemotherapy in high-risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunsmore, K.P.; Winter, S.S.; Devidas, M.; Wood, B.L.; Esiashvili, N.; Chen, Z.; Eisenberg, N.; Briegel, N.; Hayashi, R.J.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; et al. Children’s oncology group AALL0434: A phase III randomized clinical trial testing nelarabine in newly diagnosed t-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3282–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Thomas, D.; O’Brien, S.; Kadia, T.; Burger, J.; Borthakur, G.; Daver, N.; Jabbour, E.; et al. The combination of hyper-CVAD plus nelarabine as frontline therapy in adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-lymphoblastic lymphoma: MD Anderson Cancer Center experience. Leukemia 2014, 28, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, Y.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Faderl, S.; Jabbour, E.; Jain, N.; Thomas, D.; Kadia, T.; Borthakur, G.; Khoury, J.D.; Burger, J.; et al. Hyper-CVAD plus nelarabine in newly diagnosed adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcade, E.; Leguay, T.; Vey, N.; Baruchel, A.; Delaunay, J.; Robin, M.; Socié, G.; Dombret, H.; Peffault de Latour, R.; Raffoux, E. Nelarabine for T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapsing after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Opportunity to Improve Survival. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candoni, A.; Lazzarotto, D.; Ferrara, F.; Curti, A.; Lussana, F.; Papayannidis, C.; Del Principe, M.I.; Bonifacio, M.; Mosna, F.; Delia, M.; et al. Nelarabine as salvage therapy and bridge to allogeneic stem cell transplant in 118 adult patients with relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. A CAMPUS ALL study. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirs, S.; Matthijssens, F.; Goossens, S.; Van De Walle, I.; Ruggero, K.; De Bock, C.E.; Degryse, S.; Canté-Barrett, K.; Briot, D.; Clappier, E.; et al. ABT-199 mediated inhibition of BCL-2 as a novel therapeutic strategy in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Chonghaile, T.; Roderick, J.E.; Glenfield, C.; Ryan, J.; Sallan, S.E.; Silverman, L.B.; Loh, M.L.; Hunger, S.P.; Wood, B.; DeAngelo, D.J.; et al. Maturation stage of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia determines BCL-2 versus BCL-XL dependence and sensitivity to ABT-199. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bose, P.; Gandhi, V.; Konopleva, M. Pathways and mechanisms of venetoclax resistance. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, S.K.; Smith, M.L.; Hessler, P.; Rapp, L.R.; Idler, K.B.; Park, C.H.; Leverson, J.D.; Lam, L.T. Potential mechanisms of resistance to venetoclax and strategies to circumvent it. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Vachhani, P.; Bachiashvili, K.; Jamy, O. Venetoclax with chemotherapy in relapse/refractory early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 2292–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Carpentier, G.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E. Recent Advances in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadfar, N.; Li, Y.; May, W.S.; Adams, C.B. Venetoclax and decitabine for treatment of relapsed T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A case report and review of literature. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2021, 14, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappone, E.; Cencini, E.; Defina, M.; Sicuranza, A.; Gozzetti, A.; Ciofini, S.; Raspadori, D.; Mecacci, B.; Bocchia, M. Venetoclax in association with decitabine as effective bridge to transplant in a case of relapsed early T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2000–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, D.; Kelly, G.L.; Lessene, G.; Wei, A.H.; Roberts, A.W.; Strasser, A. BH3-Mimetic Drugs: Blazing the Trail for New Cancer Medicines. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caenepeel, S.; Brown, S.P.; Belmontes, B.; Moody, G.; Keegan, K.S.; Chui, D.; Whittington, D.A.; Huang, X.; Poppe, L.; Cheng, A.C.; et al. AMG 176, a selective MCL1 inhibitor, is effective in hematologic cancer models alone and in combination with established therapies. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1582–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moujalled, D.M.; Pomilio, G.; Ghiurau, C.; Ivey, A.; Salmon, J.; Rijal, S.; Macraild, S.; Zhang, L.; Teh, T.C.; Tiong, I.S.; et al. Combining BH3-mimetics to target both BCL-2 and MCL1 has potent activity in pre-clinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsey, H.E.; Fischer, M.A.; Lee, T.; Gorska, A.E.; Arrate, M.P.; Fuller, L.; Boyd, K.L.; Strickland, S.A.; Sensintaffar, J.; Hogdal, L.J.; et al. A novel MCL1 inhibitor combined with venetoclax rescues venetoclax-resistant acute myelogenous Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1566–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teh, T.C.; Nguyen, N.Y.; Moujalled, D.M.; Segal, D.; Pomilio, G.; Rijal, S.; Jabbour, A.; Cummins, K.; Lackovic, K.; Blombery, P.; et al. Enhancing venetoclax activity in acute myeloid leukemia by co-targeting MCL1. Leukemia 2018, 32, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Starza, R.; Cambò, B.; Pierini, A.; Bornhauser, B.; Montanaro, A.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Mecucci, C.; Roti, G. Venetoclax and Bortezomib in Relapsed/Refractory Early T-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Dolai, S.; Delgado-Martin, C.; Vincent, T.; Robbins, A.; Selvanathan, A.; Ryan, T.; Hall, J.; Wood, A.C.; Tasian, S.K.; et al. Efficacy of JAK/STAT pathway inhibition in murine xenograft models of early T-cell precursor (ETP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lhermitte, L.; Ben Abdelali, R.; Villarèse, P.; Bedjaoui, N.; Guillemot, V.; Trinquand, A.; Libura, M.; Bedin, A.S.; Petit, A.; Dombret, H.; et al. Receptor kinase profiles identify a rationale for multitarget kinase inhibition in immature T-ALL. Leukemia 2013, 27, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravandi, F.; Aribi, A.; O’Brien, S.; Faderl, S.; Jones, D.; Ferrajoli, A.; Huang, X.; York, S.; Pierce, S.; Wierda, W.; et al. Phase II study of alemtuzumab in combination with pentostatin in patients with T-cell neoplasms. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5425–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratz, K.W.; Cortes, J.; Roboz, G.J.; Rao, N.; Arowojolu, O.; Stine, A.; Shiotsu, Y.; Shudo, A.; Akinaga, S.; Small, D.; et al. A pharmacodynamic study of the FLT3 inhibitor KW-2449 yields insight into the basis for clinical response. Blood 2009, 113, 3938–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
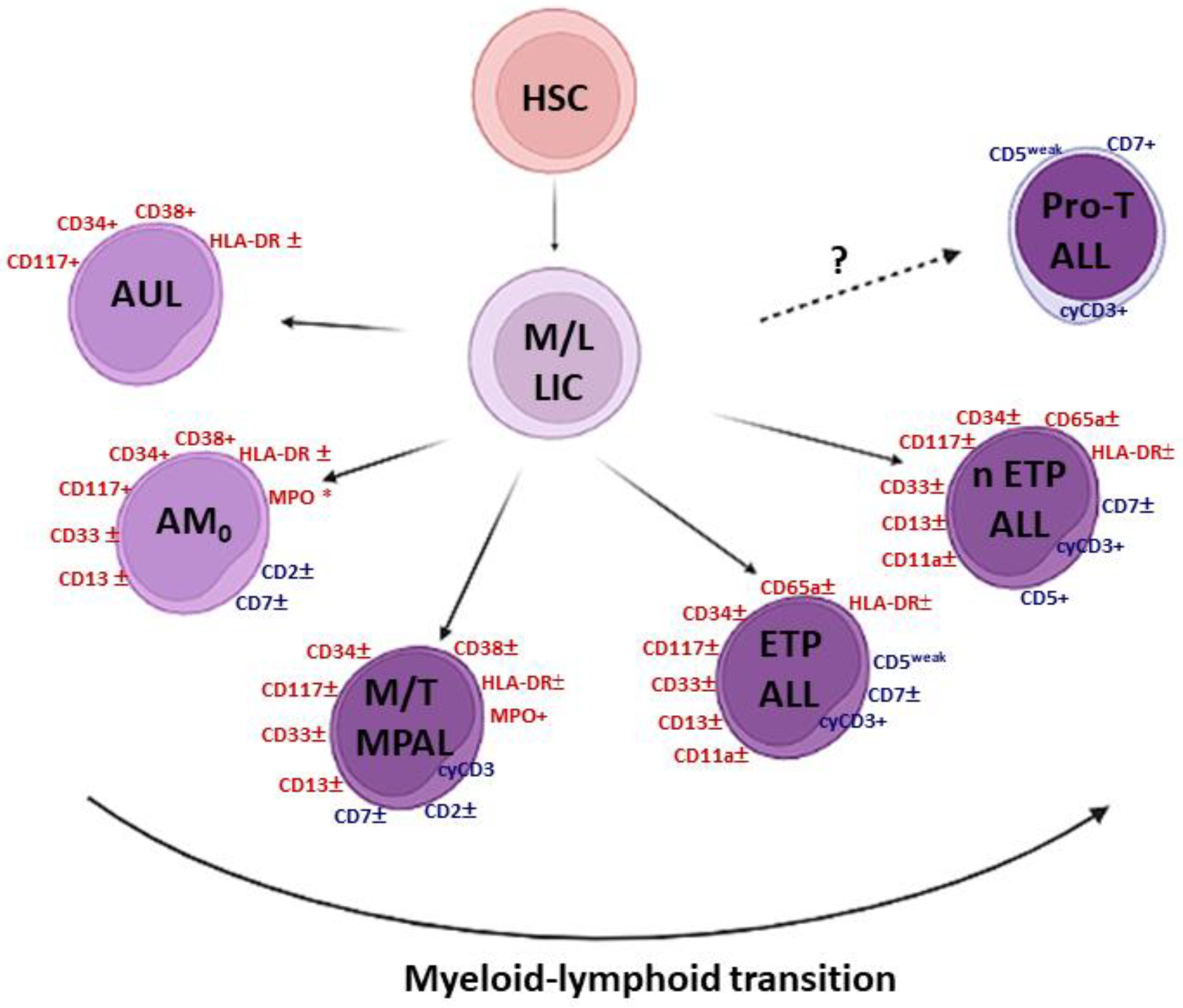
| CD3 * | MPO | CD19 | Stem Cells | Other Myeloids | Other Lymphoids | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUL | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| AML with minimal differentiation | − | − | − | CD117+, CD38+ | HLA-DR± CD33±, CD13± | CD7±, CD2± |
| T/M, MPAL, NOS | + | + | - | +/− | +/− | CD7±, CD2± |
| cCD3 | sCD3 | CD7 | CD1a | TdT | CD2 | CD5 | CD4/CD8 | Stem Cell/Myeloid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETP-ALL | + | − | + | − | ± | − | ± | −/− | +/− or −/+ or +/+ |
| Near-ETP-ALL | + | − | + | − | ± | − | + | −/− | +/− or −/+ or +/+ |
| Pro-T ALL | + | − | + | − | ± or + | − | − | −/− | − |
| Pre-T | + | ± | + | − | ± or + | + | + | −/− or +/+ | − |
| Cortical | + | ± | + | + | ± | + | + | ±/± | − |
| Mature | + | + | + | − | ± or − | + | + | +/− or −/+ | − |
| Molecular Mechanism [9,53] | Type of Alteration [9,53] |
|---|---|
| Chromosomal rearrangement | Fusion transcript |
| t(2;14)(22.3;q32.2) | ZEB2::BCL11B |
| Chromosomal rearrangement | Enhancer hijacking |
| t(3;14)(p24.3;q32.2) | SATB1::BCL11B |
| t(6;14)(q25.3;q32.2) ins(6;14)(q25.3;q32q32) | ARID1::BCL11B |
| t(7;14)(q22.1;q32.2) | CDK6::BCL11B |
| t(8;14)(q24.2;q32.2) | CCDC26::BCL11B |
| t(12;14)(p13.2;q32.2) | ETV6::BCL11B |
| t(14;21)(q32.2;q22.1) | RUNX1::BCL11B |
| Focal amplification | New enhancer |
| 14q32 non-coding sequence | BETA_BCL11B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Genescà, E.; la Starza, R. Early T-Cell Precursor ALL and Beyond: Immature and Ambiguous Lineage T-ALL Subsets. Cancers 2022, 14, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081873
Genescà E, la Starza R. Early T-Cell Precursor ALL and Beyond: Immature and Ambiguous Lineage T-ALL Subsets. Cancers. 2022; 14(8):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081873
Chicago/Turabian StyleGenescà, Eulàlia, and Roberta la Starza. 2022. "Early T-Cell Precursor ALL and Beyond: Immature and Ambiguous Lineage T-ALL Subsets" Cancers 14, no. 8: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081873







