Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Impair Glioblastoma Cell Motility and Proliferation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Western Blot
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Limiting Dilution Assay
2.5. Cell Treatments
2.6. Immunofluorescence of Cultured Cells
2.7. GBM Cell Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.8. Gene Expression Profiling and Data Analysis
2.9. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time (RT) PCR
2.10. Migration/Motility Assays
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HDI TSA and SAHA Suppress TCF4 Levels and Affect GBM Cell Stemness
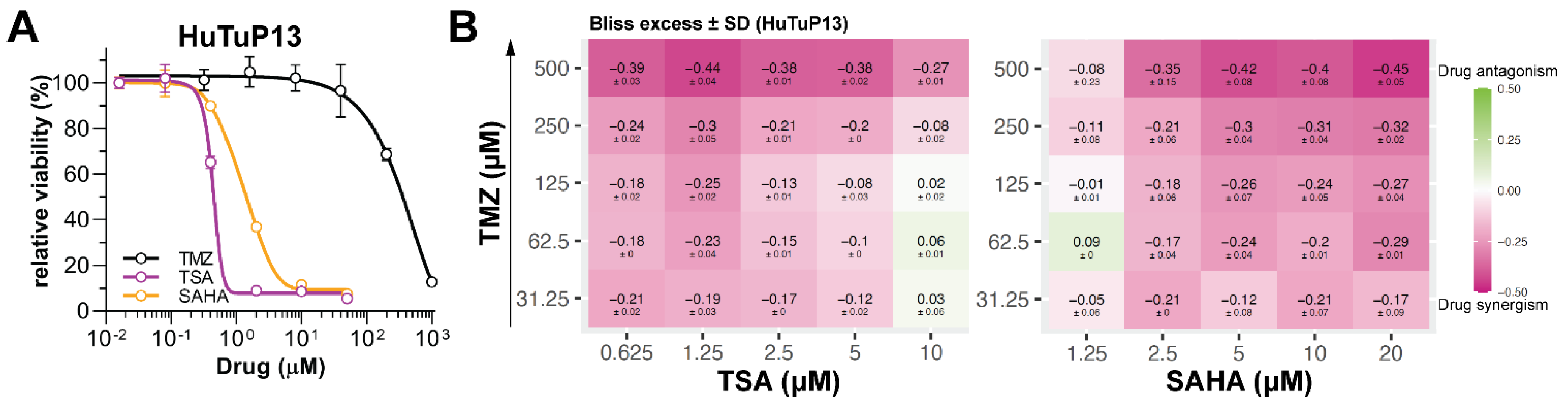
3.2. HDI Treatment Impairs GBM Cell Proliferation and Synergize with TMZ
3.3. TSA and SAHA Suppress HIF-1α and Wnt Signaling Activation
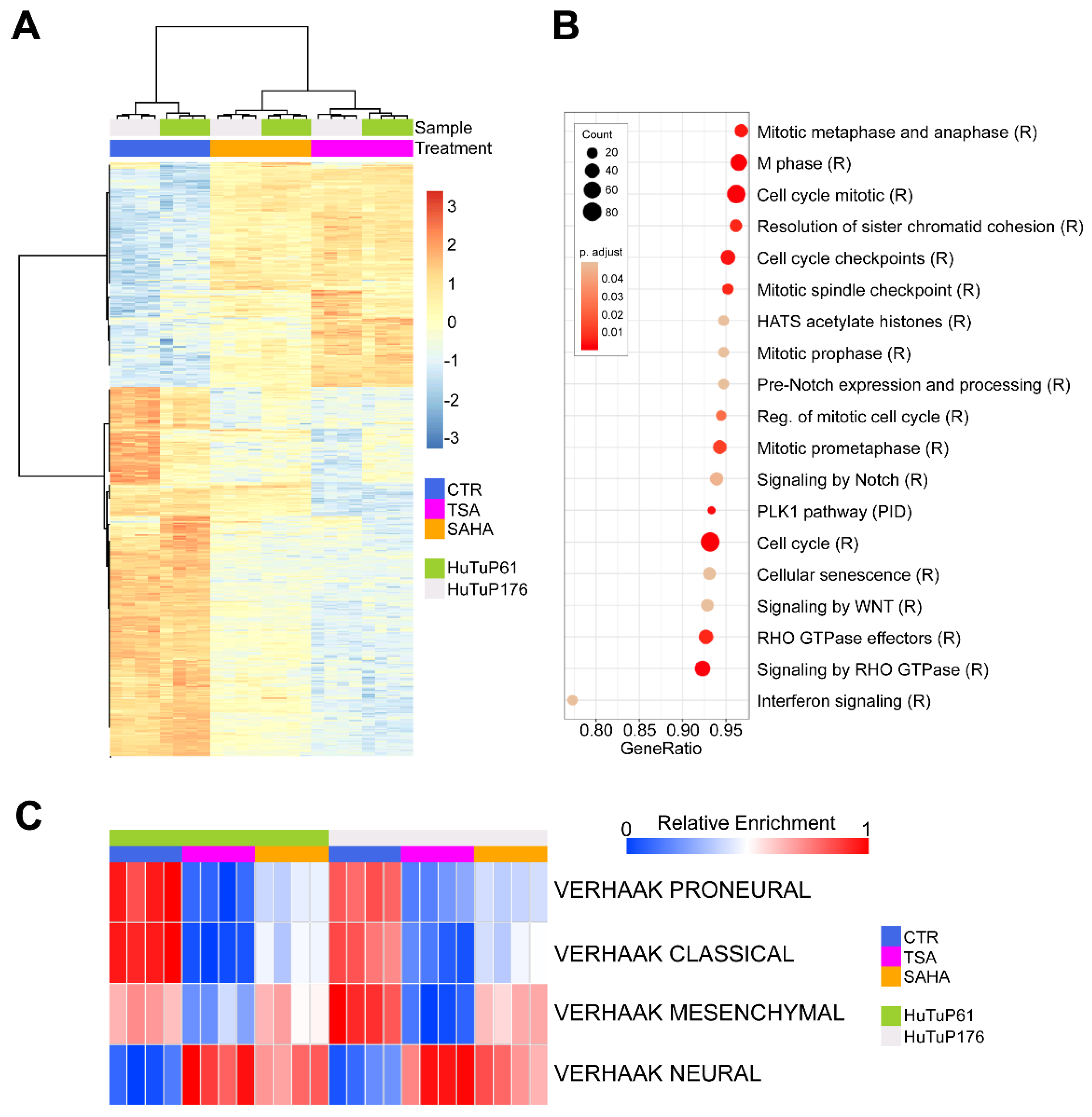
3.4. Gene Expression Profiling Reveals an HDI-Induced Modulation of Cell Cycle and Cell Migration-Associated Transcriptional Programs
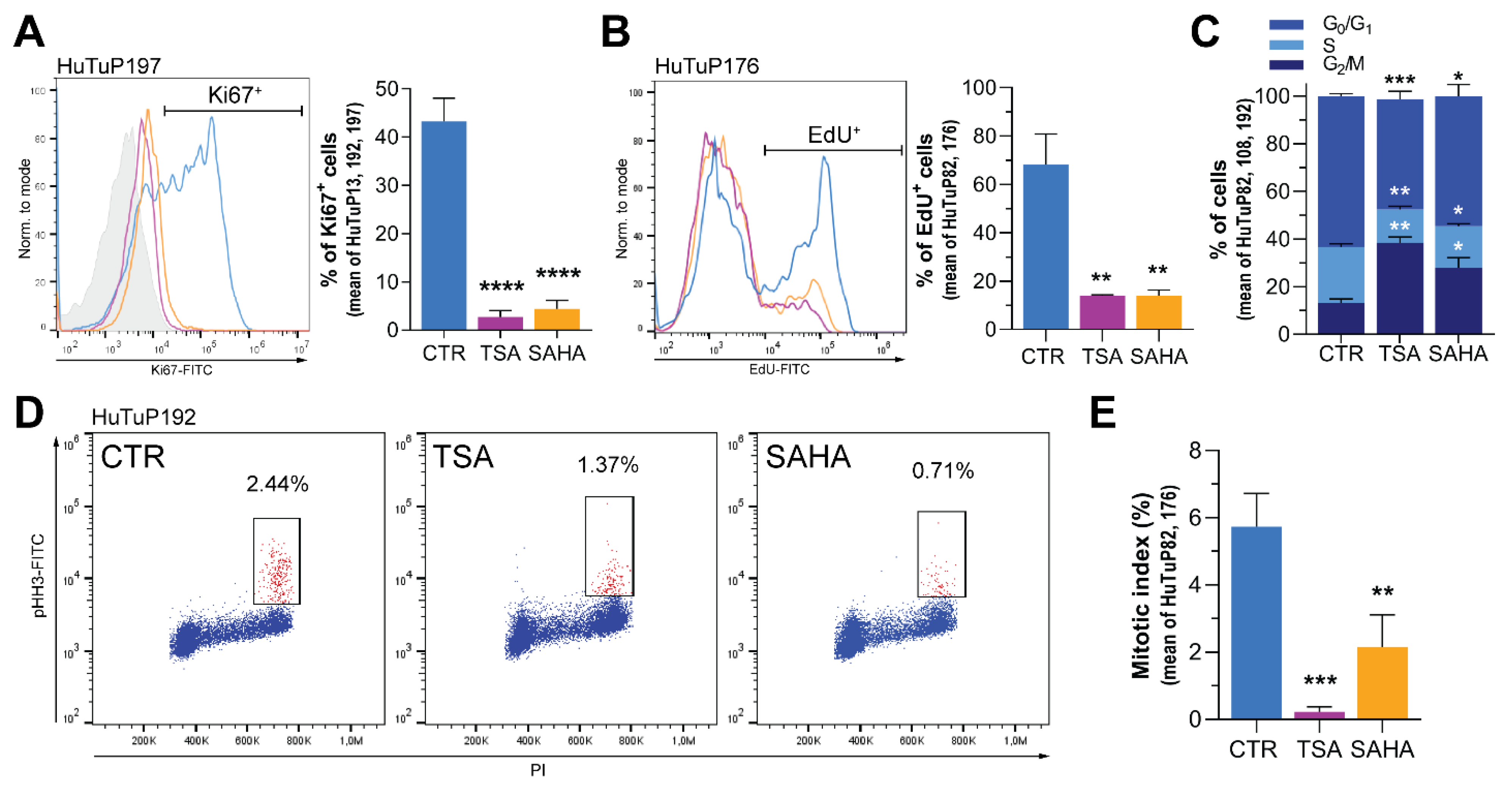
3.5. HDI Inhibit GBM Cell Proliferation by Acting at the G2/M Cell Cycle Checkpoint
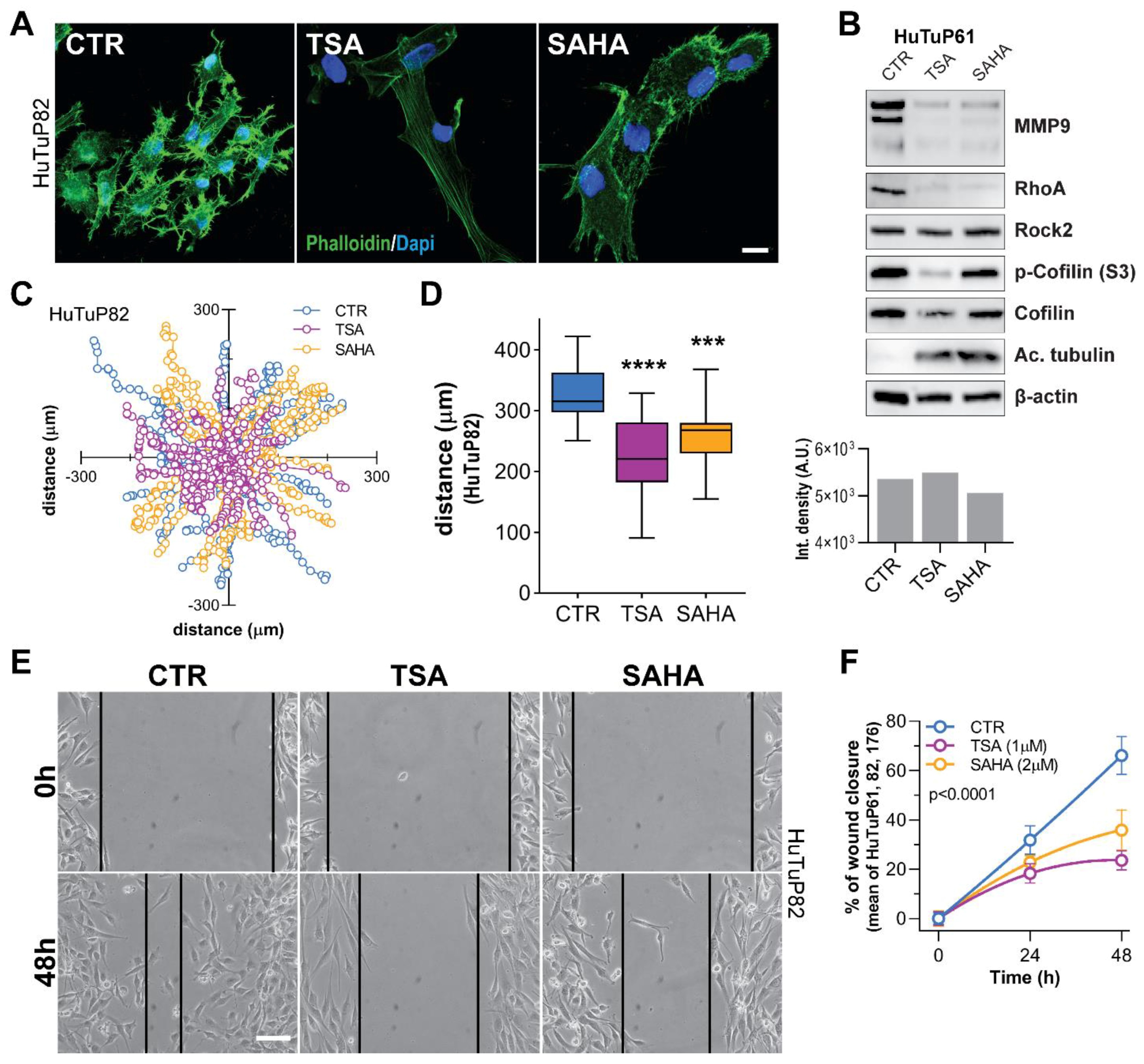
3.6. TSA and SAHA Inhibit GBM Cell Motility by Affecting RhoA and Interferon-Dependent Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marenco-Hillembrand, L.; Wijesekera, O.; Suarez-Meade, P.; Mampre, D.; Jackson, C.; Peterson, J.; Trifiletti, D.; Hammack, J.; Ortiz, K.; Lesser, E.; et al. Trends in glioblastoma: Outcomes over time and type of intervention: A systematic evidence based analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampazzo, E.; Della Puppa, A.; Frasson, C.; Battilana, G.; Bianco, S.; Scienza, R.; Basso, G.; Persano, L. Phenotypic and functional characterization of Glioblastoma cancer stem cells identified through 5-aminolevulinic acid-assisted surgery [corrected]. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 116, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Valentim, C.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pistollato, F.; Abbadi, S.; Rampazzo, E.; Persano, L.; Della Puppa, A.; Frasson, C.; Sarto, E.; Scienza, R.; D’Avella, D.; Basso, G. Intratumoral hypoxic gradient drives stem cells distribution and MGMT expression in glioblastoma. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boso, D.; Rampazzo, E.; Zanon, C.; Bresolin, S.; Maule, F.; Porcu, E.; Cani, A.; Della Puppa, A.; Trentin, L.; Basso, G.; et al. HIF-1alpha/Wnt signaling-dependent control of gene transcription regulates neuronal differentiation of glioblastoma stem cells. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4860–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo, E.; Persano, L.; Pistollato, F.; Moro, E.; Frasson, C.; Porazzi, P.; Della Puppa, A.; Bresolin, S.; Battilana, G.; Indraccolo, S.; et al. Wnt activation promotes neuronal differentiation of glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lien, W.H.; Fuchs, E. Wnt some lose some: Transcriptional governance of stem cells by Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lien, W.H.; Polak, L.; Lin, M.; Lay, K.; Zheng, D.; Fuchs, E. In vivo transcriptional governance of hair follicle stem cells by canonical Wnt regulators. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Matise, M.P. Tcf7l2/Tcf4 Transcriptional Repressor Function Requires HDAC Activity in the Developing Vertebrate CNS. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Jeong, H.S. Histone deacetylase inhibition-mediated neuronal differentiation via the Wnt signaling pathway in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 668, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotze, S.; Coersmeyer, M.; Muller, O.; Sievers, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce attenuation of Wnt signaling and TCF7L2 depletion in colorectal carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidugu, V.K.; Pidugu, H.B.; Wu, M.M.; Liu, C.J.; Lee, T.C. Emerging Functions of Human IFIT Proteins in Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, C.W.; Willey, C.D.; Zhi, D.; Cui, X.; Harris, J.J.; Vaughan, L.K.; Mehta, T.; McCubrey, R.O.; Khodarev, N.N.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; et al. Expression signature of IFN/STAT1 signaling genes predicts poor survival outcome in glioblastoma multiforme in a subtype-specific manner. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Ng, S.S.; Chow, B.K.; Sze, J.; Lu, G.; Poon, W.S.; Kung, H.F.; Lin, M.C. Knockdown of interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1) inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 103, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fensterl, V.; Sen, G.C. The ISG56/IFIT1 gene family. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lo, U.G.; Wu, S.; Wang, B.; Pong, R.C.; Lai, C.H.; Lin, H.; He, D.; Hsieh, J.T.; Wu, K. The roles and mechanism of IFIT5 in bladder cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danish, H.H.; Goyal, S.; Taunk, N.K.; Wu, H.; Moran, M.S.; Haffty, B.G. Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 (IFIT1) as a prognostic marker for local control in T1-2 N0 breast cancer treated with breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy (BCS + RT). Breast J. 2013, 19, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, J.; Bai, C.; Li, Z.; Fan, J.; Ng, I.O.L.; Zhou, W.; Sun, H.; Dong, Q.; et al. Hepatic IFIT3 predicts interferon-alpha therapeutic response in patients of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2017, 66, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, G.S.; Zhang, J.D.; Tang, W.L.; Huang, J.H.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, X.F.; Lin, Z.X. High IFIT1 expression predicts improved clinical outcome, and IFIT1 along with MGMT more accurately predicts prognosis in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 52, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; Pozios, I.; Camaj, P.; Daberitz, T.; Wang, X.; Niess, H.; Seeliger, H.; Popp, F.; Betzler, C.; et al. Elevated interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 (IFIT3) is a poor prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistollato, F.; Persano, L.; Della Puppa, A.; Rampazzo, E.; Basso, G. Isolation and expansion of regionally defined human glioblastoma cells in vitro. Curr. Protoc. Stem Cell Biol. 2011, 3, Unit 3.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, E.A.; Warth, P.T.; Long, P.H. Studies of combinations of antibiotics in vitro and in experimental infections in mice. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952, 90, 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Flobak, A.; Niederdorfer, B.; Nakstad, V.T.; Thommesen, L.; Klinkenberg, G.; Laegreid, A. A high-throughput drug combination screen of targeted small molecule inhibitors in cancer cell lines. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maretto, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Dupont, S.; Braghetta, P.; Broccoli, V.; Hassan, A.B.; Volpin, D.; Bressan, G.M.; Piccolo, S. Mapping Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during mouse development and in colorectal tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persano, L.; Pistollato, F.; Rampazzo, E.; Della Puppa, A.; Abbadi, S.; Frasson, C.; Volpin, F.; Indraccolo, S.; Scienza, R.; Basso, G. BMP2 sensitizes glioblastoma stem-like cells to Temozolomide by affecting HIF-1alpha stability and MGMT expression. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Yan, W.; Gao, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; You, Y. Prevalence and clinicopathologic characteristics of the molecular subtypes in malignant glioma: A multi-institutional analysis of 941 cases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmann-Zwerenz, A.; Leidgens, V.; Feliciello, G.; Klein, C.A.; Hau, P. Tumor Cell Invasion in Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawson, C.D.; Burridge, K. The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPase signalling in cell migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwiatkowska, A.; Didier, S.; Fortin, S.; Chuang, Y.; White, T.; Berens, M.E.; Rushing, E.; Eschbacher, J.; Tran, N.L.; Chan, A.; et al. The small GTPase RhoG mediates glioblastoma cell invasion. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gooijer, M.C.; Guillen Navarro, M.; Bernards, R.; Wurdinger, T.; van Tellingen, O. An Experimenter’s Guide to Glioblastoma Invasion Pathways. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Ashley, D.M.; Lopez, G.Y.; Malinzak, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Khasraw, M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comba, A.; Faisal, S.M.; Varela, M.L.; Hollon, T.; Al-Holou, W.N.; Umemura, Y.; Nunez, F.J.; Motsch, S.; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R. Uncovering Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of High-Grade Gliomas: From Disease Biology to Therapeutic Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 703764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Mamun, A.A.; Alghamdi, B.S.; Tewari, D.; Jeandet, P.; Sarwar, M.S.; Ashraf, G.M. Epigenetics of glioblastoma multiforme: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic approaches. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Shim, J.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, J.H.; Kang, S.G. Transcriptome profiling-based identification of prognostic subtypes and multi-omics signatures of glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, R.; Binda, E.; Orfanelli, U.; Cipelletti, B.; Gritti, A.; De Vitis, S.; Fiocco, R.; Foroni, C.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Clarke, I.D.; Terasaki, M.; Bonn, V.E.; Hawkins, C.; Squire, J.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unruhe-Knauf, B.; Knauer, S.K. Analysis of HDACi-Induced Changes in Chromosomal Passenger Complex Localization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1510, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Overview and perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.; Murphy, B.; Miller, R.; Menon, V.; Banik, N.L.; Giglio, P.; Lindhorst, S.M.; Varma, A.K.; Vandergrift, W.A., 3rd; Patel, S.J.; et al. Mechanisms and clinical significance of histone deacetylase inhibitors: Epigenetic glioblastoma therapy. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 615–625. [Google Scholar]
- Bajbouj, K.; Mawrin, C.; Hartig, R.; Schulze-Luehrmann, J.; Wilisch-Neumann, A.; Roessner, A.; Schneider-Stock, R. P53-dependent antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of trichostatin A (TSA) in glioblastoma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 107, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez Valle, R.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Stummer, W. Established and emerging uses of 5-ALA in the brain: An overview. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, R.G.; Ridley, A.J. Regulating Rho GTPases and their regulators. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K. Signaling mechanisms and functional roles of cofilin phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; He, H.; Niu, H.; Li, Y. Interferon induced transmembrane protein 3 regulates the growth and invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac. Cancer 2017, 8, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidugu, V.K.; Wu, M.M.; Yen, A.H.; Pidugu, H.B.; Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Lee, T.C. IFIT1 and IFIT3 promote oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and contribute to the anti-tumor effect of gefitinib via enhancing p-EGFR recycling. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3232–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. Deciphering the Roles of IFITM1 in Tumors. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, U.G.; Pong, R.C.; Yang, D.; Gandee, L.; Hernandez, E.; Dang, A.; Lin, C.J.; Santoyo, J.; Ma, S.; Sonavane, R.; et al. IFNgamma-Induced IFIT5 Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Prostate Cancer via miRNA Processing. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rampazzo, E.; Manfreda, L.; Bresolin, S.; Cani, A.; Mariotto, E.; Bortolozzi, R.; Della Puppa, A.; Viola, G.; Persano, L. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Impair Glioblastoma Cell Motility and Proliferation. Cancers 2022, 14, 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081897
Rampazzo E, Manfreda L, Bresolin S, Cani A, Mariotto E, Bortolozzi R, Della Puppa A, Viola G, Persano L. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Impair Glioblastoma Cell Motility and Proliferation. Cancers. 2022; 14(8):1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081897
Chicago/Turabian StyleRampazzo, Elena, Lorenzo Manfreda, Silvia Bresolin, Alice Cani, Elena Mariotto, Roberta Bortolozzi, Alessandro Della Puppa, Giampietro Viola, and Luca Persano. 2022. "Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Impair Glioblastoma Cell Motility and Proliferation" Cancers 14, no. 8: 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081897
APA StyleRampazzo, E., Manfreda, L., Bresolin, S., Cani, A., Mariotto, E., Bortolozzi, R., Della Puppa, A., Viola, G., & Persano, L. (2022). Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Impair Glioblastoma Cell Motility and Proliferation. Cancers, 14(8), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14081897







