Quantitative Spatial Characterization of Lymph Node Tumor for N Stage Improvement of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
3.2. Prognostic LN Spatial Factors
3.3. Combined Prognostic Index
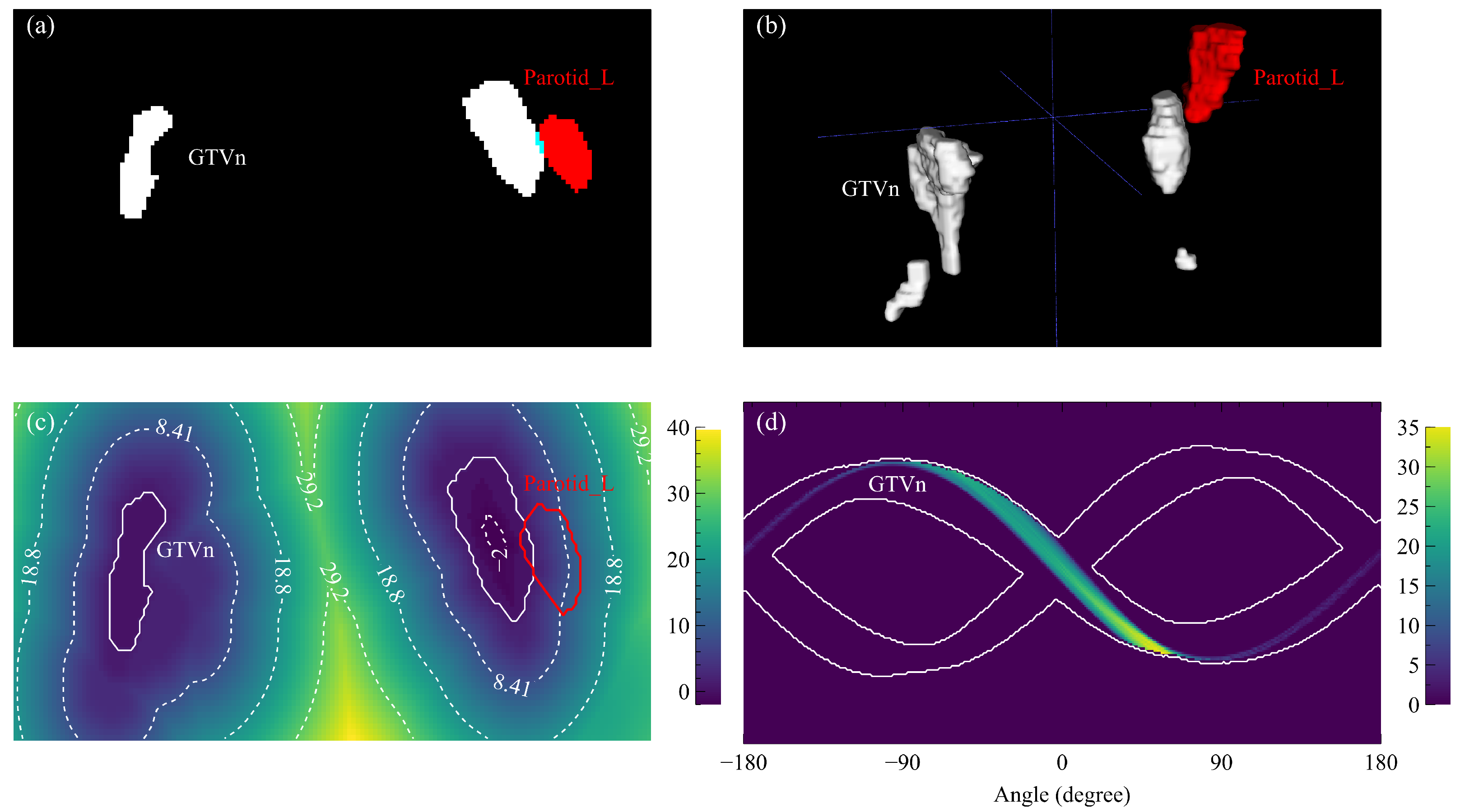
3.4. Representative Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, M.L.; Wee, J.T.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, A.T. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2016, 387, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.X.; Li, J.; Shen, G.P.; Zou, X.; Xu, J.J.; Jiang, R.; You, R.; Hua, Y.J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy prolongs the survival of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma compared with conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy: A 10-year experience with a large cohort and long follow-up. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.W.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, L.L.; Hung, W.M.; Chan, C.C.; Sze, H.C.; Chan, O.S.; Chang, A.T.; Yeung, R.M. Evolution of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer–success and setback in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Su, S.; Chen, C.; Han, F.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, W.; Deng, X.; Huang, S.; Lin, C.; Lu, T. Long-term outcomes of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for 868 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An analysis of survival and treatment toxicities. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, Q. Pattern and prognosis of distant metastases in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A large-population retrospective analysis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6147–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireci, F.; Dispenza, F.; Lorusso, F.; Immordino, A.; Immordino, P.; Gallina, S.; Peretti, G.; Canevari, F. Tumours of Nasal Septum: A Retrospective Study of 32 Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, M.K.; Teo, P.M.; Chau, R.M.; Cheung, K.; Choi, P.H.; Kwan, W.; Leung, S.; Zee, B.; Chan, A.T. Treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intensity-modulated radiotherapy: The Hong Kong experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 60, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, T.; Fan, L.; Jin, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Patterns and prognostic value of lymph node metastasis on distant metastasis and survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end results study, 2006–2015. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 4094395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egner, J.R. AJCC cancer staging manual. JAMA 2010, 304, 1726–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ou, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Shen, C.; Ding, J.; Hu, C. Quantitative metastatic lymph node regions on magnetic resonance imaging are superior to AJCC N classification for the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2018, 2018, 9172585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiang, C.L.; Guo, Q.; Ng, W.T.; Lin, S.; Ma, T.S.W.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, T.; Choi, H.C.W. Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Nasopharyngeal Cancer and Implication for TNM Staging by UICC: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 703995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zong, J.; Guo, Q.; Qiu, S.; Zheng, W.; Lin, S.; Pan, J. Prognostic effect of parotid area lymph node metastases after preliminary diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A propensity score matching study. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, W.F.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Ma, J. Prognosis and staging of parotid lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An analysis in 10,126 patients. Oral Oncol. 2019, 95, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Liang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cui, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, M. Prognostic value of retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis laterality in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and a proposed modification to the UICC/AJCC N staging system. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 140, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.Y.; King, A.D.; Poon, D.M.; Mo, F.K.; Hui, E.P.; Tong, M.; Ahuja, A.T.; Ma, B.B.; Chan, A.T. Extranodal extension is a criterion for poor outcome in patients with metastatic nodes from cancer of the nasopharynx. Oral Oncol. 2019, 88, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Huang, S.H.; O’Sullivan, B.; Fang, Y.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S. Prognostic value of radiologic extranodal extension and its potential role in future N classification for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2019, 99, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, S.; Lydiatt, W.; Shah, J.P.; Colevas, A.D.; Lee, A.W.; O’Sullivan, B.; Guo, R.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Unambiguous advanced radiologic extranodal extension determined by MRI predicts worse outcomes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Potential improvement for future editions of N category systems. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 157, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liang, S.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, F.; Zhou, J.; Dong, A.; Chen, M.; Xie, C.; Li, H. Prognostic significance of quantitative metastatic lymph node burden on magnetic resonance imaging in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study of 1224 patients from two centers. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 151, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, X.L.; Luo, W.; Lee, A.W.; Wee, J.T.S.; Lee, N.; Zhou, G.Q.; Tang, L.L.; Tao, C.J.; Guo, R.; et al. Recommendation for a contouring method and atlas of organs at risk in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients receiving intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Qin, A.; Chen, M.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Miao, J.; Gu, H.; Zhao, C.; Deng, X.; et al. Magnetic resonance-based synthetic computed tomography images generated using generative adversarial networks for nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy treatment planning. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 150, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Liao, W.; Chen, J.; Song, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, N.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S. Efficient semi-supervised gross target volume of nasopharyngeal carcinoma segmentation via uncertainty rectified pyramid consistency. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazhdan, M.; Simari, P.; McNutt, T.; Wu, B.; Jacques, R.; Chuang, M.; Taylor, R. A Shape Relationship Descriptor for Radiation Therapy Planning. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2009, London, UK, 20–24 September 2009; Yang, G.Z., Hawkes, D., Rueckert, D., Noble, A., Taylor, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Ricchetti, F.; Sanguineti, G.; Kazhdan, M.; Simari, P.; Chuang, M.; Taylor, R.; Jacques, R.; McNutt, T. Patient geometry-driven information retrieval for IMRT treatment plan quality control. Med Phys. 2009, 36, 5497–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, C.; Qi, R.; Raghavan, V. A linear time algorithm for computing exact Euclidean distance transforms of binary images in arbitrary dimensions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowekamp, B.; Chen, D.; Ibáñez, L.; Blezek, D. The Design of SimpleITK. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidson-Pilon, C. lifelines: Survival analysis in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Tang, L.; Zong, J.; Lin, A.; Lu, T.; Cui, N.; Cui, C.; Li, L. Retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Prognostic value and staging categories. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.L.; Guo, R.; Zhou, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Lin, A.H.; Mai, H.; Shao, J.; Li, L.; Ma, J. Prognostic value and staging classification of retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Xie, C.M.; Wu, Y.P.; Cui, C.Y.; Huang, Z.L.; Lu, C.Y.; Wu, P.H. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with retropharyngeal lymph node metastases: A minimum axial diameter of 6 mm is a more accurate prognostic predictor than 5 mm. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, J.; He, X.; Zhu, C. Evaluation of contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the detection of retropharyngeal lymph node metastases in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.; Mao, Y.P.; Tang, L.L.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. The evolution of nasopharyngeal carcinoma staging. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.; Ng, W.T.; Pan, J.J.; Poh, S.S.; Ahn, Y.C.; AlHussain, H.; Corry, J.; Grau, C.; Grégoire, V.; Harrington, K.J.; et al. International guideline for the delineation of the clinical target volumes (CTV) for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Dou, Q.; Jin, Y.M.; Zhou, G.Q.; Tang, Y.Q.; Chen, W.L.; Su, B.A.; Liu, F.; Tao, C.J.; Jiang, N.; et al. Deep Learning for Automated Contouring of Primary Tumor Volumes by MRI for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Radiology 2019, 291, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzano, G.; Perri, F.; Maglitto, F.; Togo, G.; De Fazio, G.R.; Apolito, M.; Calabria, F.; Laface, C.; Vaira, L.A.; Committeri, U.; et al. Pre-Treatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios as Predictors of Occult Cervical Metastasis in Clinically Negative Neck Supraglottic and Glottic Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, V.; Barone, S.; Troise, S.; Laface, C.; Bonavolontà, P.; Pacella, D.; Salzano, G.; Iaconetta, G.; Califano, L.; Dell’Aversana Orabona, G. The Combination of Inflammatory Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicator in Salivary Gland Malignancy. Cancers 2022, 14, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Discovery Cohort | Validation Cohort | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Mean | 53.39 | 52.16 | 0.249 | |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 41 | 70 | 0.667 | |
| Male | 153 | 214 | ||
| N stage | ||||
| N1 | 62 | 17 | 0.035 | |
| N2 | 93 | 228 | ||
| N3 | 39 | 39 | ||
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| CCRT | 33 | 178 | 0.330 | |
| CCRT + ACT | 78 | 61 | ||
| CCRT + ICT | 83 | 43 | ||
| WHO histology | ||||
| Type 2 | 27 | 74 | 0.142 | |
| Type 3 | 167 | 210 | ||
| Covariant | HR (95CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| OVH | 0.63 (0.48–0.83) | <0.001 |
| POV | 3.35 (1.40–7.99) | 0.006 |
| N stage | 2.26 (1.46–3.49) | <0.001 |
| Survival Endpoint | Training Cohort | Validation Cohort | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prognostic Index (95CI) | N Stage (95CI) | p-Value | Prognostic Index (95CI) | N Stage (95CI) | p-Value | |
| DFS | 0.72 (0.65–0.79) | 0.65 (0.57–0.73) | 0.020 | 0.60 (0.54–0.67) | 0.57 (0.52–0.62) | 0.086 |
| OS | 0.75 (0.63–0.84) | 0.72 (0.64–0.80) | 0.245 | 0.60 (0.48–0.71) | 0.58 (0.50–0.67) | 0.395 |
| RFS | 0.72 (0.62–0.82) | 0.64 (0.54–0.73) | 0.020 | 0.60 (0.52–0.69) | 0.53 (0.47–0.60) | 0.019 |
| DMFS | 0.72 (0.63–0.81) | 0.65 (0.54–0.76) | 0.062 | 0.57 (0.47–0.67) | 0.57 (0.50–0.65) | 0.536 |
| Survival Endpoint | Proposed Risk Stratification | N Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | HR | p-Value | 3y SR | Group | HR | p-Value | 3y SR | |
| Discovery cohort | ||||||||
| DFS | G1 | — | — | 89.6% | N1 | — | — | 87.9% |
| G2 | 4.49 | 0.007 | 74.6% | N2 | 1.83 | 0.139 | 72.6% | |
| G3 | 9.07 | <0.001 | 52.1% | N3 | 5.19 | <0.001 | 45.6% | |
| OS | G1 | — | — | 97.3% | N1 | — | — | 100.0% |
| G2 | 7.66 | 0.055 | 92.7% | N2 | 3.33 | 0.115 | 89.4% | |
| G3 | 13.98 | 0.011 | 79.7% | N3 | 11.62 | 0.002 | 72.6% | |
| RFS | G1 | — | — | 89.6% | N1 | — | — | 93.0% |
| G2 | 2.23 | 0.181 | 85.3% | N2 | 2.64 | 0.079 | 79.5% | |
| G3 | 4.76 | 0.005 | 72.2% | N3 | 4.59 | 0.014 | 74.9% | |
| DMFS | G1 | — | — | 94.0% | N1 | — | — | 92.2% |
| G2 | 4.11 | 0.074 | 86.8% | N2 | 1.52 | 0.428 | 84.5% | |
| G3 | 10.41 | 0.002 | 66.5% | N3 | 4.51 | 0.006 | 59.8% | |
| Validation cohort | r | |||||||
| DFS | G1 | — | — | 81.2% | N1 | — | — | 76.5% |
| G2 | 1.71 | 0.021 | 67.2% | N2 | 0.77 | 0.518 | 77.8% | |
| G3 | 4.02 | <0.001 | 45.5% | N3 | 1.82 | 0.171 | 52.7% | |
| OS | G1 | — | — | 95.2% | N1 | — | — | 87.8% |
| G2 | 1.36 | 0.384 | 93.5% | N2 | 1.56 | 0.548 | 95.3% | |
| G3 | 2.28 | 0.076 | 85.9% | N3 | 2.57 | 0.223 | 89.0% | |
| RFS | G1 | — | — | 88.7% | N1 | — | — | 87.8% |
| G2 | 1.46 | 0.219 | 82.9% | N2 | 0.84 | 0.736 | 85.9% | |
| G3 | 3.69 | 0.001 | 62.7% | N3 | 1.20 | 0.764 | 78.2% | |
| DMFS | G1 | — | — | 89.3% | N1 | — | — | 82.4% |
| G2 | 1.72 | 0.101 | 82.0% | N2 | 0.55 | 0.271 | 88.7% | |
| G3 | 2.93 | 0.014 | 76.2% | N3 | 1.88 | 0.276 | 73.5% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Teng, X.; Lam, S.; Sun, J.; Cheung, A.L.-Y.; Ng, S.C.-Y.; Lee, F.K.-H.; Au, K.-H.; Yip, C.W.-Y.; Lee, V.H.-F.; et al. Quantitative Spatial Characterization of Lymph Node Tumor for N Stage Improvement of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010230
Zhang J, Teng X, Lam S, Sun J, Cheung AL-Y, Ng SC-Y, Lee FK-H, Au K-H, Yip CW-Y, Lee VH-F, et al. Quantitative Spatial Characterization of Lymph Node Tumor for N Stage Improvement of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010230
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiang, Xinzhi Teng, Saikit Lam, Jiachen Sun, Andy Lai-Yin Cheung, Sherry Chor-Yi Ng, Francis Kar-Ho Lee, Kwok-Hung Au, Celia Wai-Yi Yip, Victor Ho-Fun Lee, and et al. 2023. "Quantitative Spatial Characterization of Lymph Node Tumor for N Stage Improvement of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients" Cancers 15, no. 1: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010230
APA StyleZhang, J., Teng, X., Lam, S., Sun, J., Cheung, A. L.-Y., Ng, S. C.-Y., Lee, F. K.-H., Au, K.-H., Yip, C. W.-Y., Lee, V. H.-F., Lin, Z., Liang, Y., Yang, R., Han, Y., Zhang, Y., Kong, F.-M., & Cai, J. (2023). Quantitative Spatial Characterization of Lymph Node Tumor for N Stage Improvement of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancers, 15(1), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010230






